Mouse disease in humans symptoms. Mouse fever, symptoms in men. Is there a cure for mouse fever?
Mouse fever is an acute viral pathology. It is spread by rodents. The scientific name of the disease is hemorrhagic fever with renal syndrome (HFRS). The infection is characterized by severe manifestations of the excretory organs and blood vessels. Initial signs illnesses can resemble flu symptoms. Often the patient does not attach importance to them, and the visit to the doctor is postponed. Meanwhile, the pathology progresses, and the virus infects the kidneys. Delayed treatment can lead to severe complications and even to death.
The causative agent of the disease and ways of spread
Pathogen mouse fever is hantavirus. It is quite resistant to cold, but quickly dies at temperatures above +50 degrees. In Russia, there are 2 types of this infection:
- East Virus. It is found in the regions of the Far East and is spread by mice - Manchurian voles. Causes the most severe and dangerous forms diseases with a mortality rate of up to 20%.
- Western virus. Observed in the European part of Russia. He's being smashed native species mice are red and Fever caused by this type of infection is milder. It leads to death in only 5% of cases, usually with untimely or insufficient treatment.
Hantavirus passes from mice to humans in the following ways:
- Through dust and air. The virus enters the body by inhalation of dry rodent excrement in the form of dust.
- Through food. If the food is contaminated with particles of mouse feces, then the infection enters the body through the stomach.
- Through skin contact. You can become infected by coming into contact with objects contaminated with rodent secretions. Sometimes infection occurs through the bite of an animal.
It is important to remember that this disease is never transmitted from a sick person to a healthy one. A patient with mouse fever does not pose any danger to others. You can only get infected from animals.
After an illness, a person develops a strong immunity. It is impossible to re-infect this disease.
Mouse fever in men is much more common. Women suffer from this disease quite rarely. This is due to the fact that infection often occurs during agricultural work, in which predominantly men are employed. The incidence usually increases in autumn and winter.
However, this does not mean that you can get this disease only by living in the village. If mice live in a city apartment, then there are quite a few high risk infections.

Infection often occurs during the collection of mushrooms and berries in the forests where voles live, or during work on garden plots. Infection of children is noted in the summer, during the holiday season in pioneer camps and in summer cottages.
Stages of the disease
To understand the symptoms and treatment of mouse fever, you need to understand how the virus spreads throughout the body. The infectious agent enters the body through the respiratory tract, stomach or skin lesions. If a person works well the immune system, then it quickly destroys the virus. But when the body is weakened, the infection begins to multiply, and a disease occurs. Pathology has several stages:
- incubation period. It can last different times- from 1 week to 1.5 months. But on average, the latent period lasts 12-14 days. At this time, the virus multiplies in the body.
- feverish period. The infection enters the bloodstream and causes intoxication of the body. This stage does not last long, about 2-3 days.
- period of oliguria. The virus is starting to hit vascular walls which causes bleeding. The pathogen leaves the body with urine. This leads to damage to the vessels of the kidneys. This is the most severe stage of the pathology, which lasts from 3 to 9-11 days of the disease.
- period of polyuria. This stage of the disease is the beginning of recovery. Symptoms of mouse fever gradually disappear from 11 to 30 days of illness.
- Full recovery. This period lasts from 1 to 3 years.
It should be noted that the recovery of the body after past infection takes a long period. The consequences of infection can affect the functioning of the body for several months and even years after the disappearance of acute symptoms.
Mouse fever in women is milder than in men. The manifestations of the disease are not so pronounced. However, asymptomatic and erased pathology is not observed.
Incubation and febrile period
During incubation period the patient does not feel any change in well-being. Then the first signs of mouse fever appear:
- The patient's temperature rises sharply (up to +39.5 ... +40 degrees). The febrile stage of pathology begins. The fever lasts for about 6 days. At the same time, more high performance temperatures are recorded in the morning and afternoon. By evening, the fever is somewhat reduced.
- There are phenomena of intoxication: aching joints, thirst, loss of appetite, general malaise.
- The patient suffers from severe headaches, which are aggravated by bright light and eye movement.
- The skin of the patient becomes hot, a plaque is noticeable on the tongue.
- Patients have redness of the face, neck and eyes. Doctors call this symptom the "hood symptom." The face looks swollen.
- At very high temperature meningitis-like symptoms may occur: severe headache with vomiting, tension neck muscles, disorders of consciousness. This is due to the reaction of the central nervous system for intoxication.
- IN severe cases blood pressure drops sharply and a state of shock occurs.

It should be noted that the same manifestations are observed in many other pathologies. Symptoms of mouse fever in adults in the initial period resemble severe influenza, meningitis and many other diseases that occur with high fever and intoxication of the body. specific features this infection (hemorrhage, kidney damage) is not yet. Put accurate diagnosis this stage is often difficult.
Symptoms of mouse fever in children during this period are similar. But in a child, the disease is more severe. It begins acutely, without warning. Already on initial stage pain in the lower back due to kidney damage. Children become lethargic, drowsy, constantly lying in bed.
Oliguria
At this stage, develop specific symptoms mouse fever. The temperature gradually drops, but the patient's condition does not improve, but becomes even more severe.
There are signs of kidney damage, which manifest themselves in lumbar pain different intensity. This is often accompanied by bloating and abdominal discomfort. abdominal cavity. A sharp decrease in the amount of urine produced (oliguria), even with sufficient use liquids. Because of this, the patient develops edema. In the analysis of urine, the amount of protein increases.

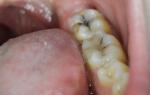
Another manifestation of the disease are hemorrhages and bleeding (hemorrhagic syndrome). The skin is covered with small red dots. There are hemorrhages in eyeballs. One of the symptoms of mouse fever in women is uterine bleeding. Reddish impurities can be found in urine and feces. Hemorrhages from the nose and intestines are noted. In the photo below you can see hemorrhagic rashes with this disease.

Patients have severe nausea. Sometimes patients vomit even from a sip of water. There are jumps in blood pressure. Frequent complaints of abdominal pain and diarrhea.
Hemorrhages in the brain may occur. At the same time, signs of damage to the central nervous system occur: confusion, delirium, hallucinations, fainting.
Polyuria
During this period, patients feel better. Hemorrhages gradually resolve. The excretory function of the kidneys is being improved. At this stage of the disease, patients dramatically increase the amount of urine (up to 10 liters per day). This is called polyuria. Approximately 1 month after the onset of the disease, urination returns to normal.
convalescence period
Recovery of the body after the disease takes a long period (1-3 years). Are celebrated residual effects in the form of weakness fatigue. After illness, many patients experience slight dysfunction of the nervous and hormonal system, which manifests itself in hypersensitivity limbs, thirst, sweating. One of residual symptoms mouse fever in men during the recovery period may be impotence.
Can be kept for 3-6 months discomfort and heaviness in the lower back, nocturnal urge to urinate, thirst, increased diuresis.
Possible Complications
The disease can lead to serious complications. They usually develop at the oligouric stage. TO dangerous consequences fevers include:
- Uremia. Because of sharp decline amount of urine is poisoning the body with decay products. There is vomiting bad smell from the patient's skin, inhibited state. Urination may disappear completely. Often this condition ends in a coma with a fatal outcome.
- Cardiovascular insufficiency. The complication occurs at the initial stage due to intoxication of the body or during the period of oliguria due to hemorrhage in the adrenal glands. The patient has a sharp drop in blood pressure, while there is a strong tachycardia.
- Damage or complete break renal capsule with hemorrhages. In this case, there are severe unbearable pain in the lower back.
- Hemorrhage in the pituitary gland. It is characterized by the development of drowsiness, and then a coma.
- Accession bacterial infection. Against the background of hemorrhagic fever, pneumonia or pyelonephritis may occur.
Diagnostic methods
Diagnosis and treatment of mouse fever are carried out in a hospital setting. If this disease is suspected, the patient is hospitalized in the infectious or therapeutic department of the hospital.
The following types of examinations are prescribed:
- general blood and urine tests;
- Ultrasound of the kidneys;
- test for antibodies to the virus.

Only linked immunosorbent assay for antibodies. The results of other studies speak about the disease only indirectly. IN general analysis blood levels are usually elevated ESR indicators and leukocytes, and in the urine a reduced density and an increase in protein are detected. Ultrasound of the kidneys shows swelling and changes in the parenchyma.
Treatment Methods
Treatment of the disease is carried out for at least 4 weeks. Within 2-4 weeks, the patient must comply with bed rest. The patient is prescribed a sparing diet with a restriction of coarse food and a predominance of fresh and lean food. It is necessary to ensure that the patient consumes enough liquids.
The treatment of the disease is following methods:
- A specific immunoglobulin is administered against hemorrhagic fever with renal syndrome. This the only way treatment that affects the cause of the pathology. All other therapy is symptomatic.
- Patients are given droppers with infusion solutions. This method of treatment helps to reduce intoxication and cause some increase in diuresis. Use solutions of glucose with insulin, "Prednisolone", "Lasix", as well as saline. If urination does not increase, then "Kurantil", "Eufillin", "Dopamine" are prescribed intravenously.
- For cupping pain syndrome apply "Analgin", "Ketorol", "Ibuprofen", "Baralgin", "Spazgan".
- To reduce the temperature, drugs with paracetamol are prescribed.
- Antibiotics in this disease are ineffective, since the pathology is not caused by bacteria, but by a virus. Prescribe drugs "Ingavirin", "Amiksin", "Lavomax", "Jodantipirin", "Virazole". They are able to fight viral infection.
- Anti-inflammatory drugs are used: Piroxicam, Aspirin.
- Used to boost immunity restorative means: vitamins C, K and group B.
- Nausea and vomiting are stopped with drugs "Cerukal" and "Ceruglan".
- In severe kidney damage, hemodialysis is performed ("artificial kidney").

The patient is discharged from the hospital not earlier than 3-4 weeks of illness. For a year after recovery, you must follow a diet and avoid physical activity. Kidney function is fully restored only 2-3 years after the disease. Within 1-3 years, the patient must regularly visit the attending physician and undergo all necessary examinations.
Prevention measures
There is currently no vaccine for mouse fever. In natural foci during the outbreak of the disease, it is recommended to take with preventive purpose antiviral drug "Jodantipyrin".
Also, to prevent infection, deratization (destruction of rodents) is carried out. It is necessary to avoid contact with mice, keep food away from them and thoroughly wash vegetables and fruits. Food must be submitted heat treatment because the virus dies at high temperature. When carrying out work in places where rodents accumulate, it is useful to use a gauze bandage on the face, this will protect against inhalation of contaminated dust.
Many people dislike mice and rats, and girls are often just terribly afraid of them. And doctors say that there are real reasons to stay away from rodents. After all, they can endure a lot of the most various diseases some of which are deadly. These ailments include mouse fever, which is also known as hemorrhagic fever with renal syndrome. It's pretty unpleasant disease, which can lead to the development various complications. Let's clarify in a little more detail what mouse fever is, whether it is transmitted from person to person or not, let's talk.
Mouse fever is an acute viral natural focal disease. Its development is accompanied by the appearance of fever, general intoxication and some kind of kidney damage. With absence adequate therapy The disease can hit the kidneys hard and even cause death.
Is mouse fever transmitted from person to person?
The causative agent of mouse fever is carried by rodents - field mice, rats, as well as the bats. The bank vole is considered the main vector.
The disease is not transmitted from person to person, it is impossible.
Infection occurs mainly by airborne dust. In this case, the person inhales the contaminated dust.
There is also evidence that mouse fever is transmitted to humans by the alimentary route, when water or food is infected with the secretions of infected rodents, or fever passes to humans with an infection that enters the body with dirty hands.
Residents are particularly susceptible to the disease. countryside as well as tourists.
How to suspect the development of mouse fever?
At the initial stage of development, mouse fever does not make itself felt at all. The duration of the incubation period can vary from seven to forty-six days. Usually the disease develops in three weeks.
At the initial stage of mouse fever, the patient's temperature rises to almost forty degrees. Chills are possible. Also, the disease leads to severe headaches. The patient is worried severe dryness in the mouth and general weakness. On examination, reddening of the skin is noticeable, a hemorrhagic rash may appear. Some patients complain of visual impairment, namely the appearance of the so-called "grid" and "fog" before the eyes.
At further development disease, the temperature remains the same high, if it decreases, the patient's condition worsens. classic symptom this stage becomes painful sensations in the lower back, which may have varying degrees expressiveness. In parallel, vomiting develops, abdominal pain, and bloating are possible. Kidney damage is accompanied by the corresponding symptoms: puffiness of the face, pastosity of the eyelids, oliguria. Pathological processes can lead to the development of bleeding from the nose or gums. Hematemesis is also possible. This stage disease is considered especially dangerous, if the patient is not provided with appropriate medical care, he may die.
With adequate correction, a polyuric period occurs. The patient is no longer worried about vomiting, the severity of pain in the abdomen, as well as in the lower back, decreases somewhat, appetite and sleep normalize. Also, the amount of urine excreted gradually increases. Recovery is coming slowly.
Is there a cure for mouse fever?
If you suspect the development of muscle fever, the patient needs urgent hospitalization. Therapy is carried out exclusively in the infectious diseases department, while patients must adhere to strict bed rest.
To date, there are no specific methods mouse fever therapy. The method of treatment is selected on an individual basis, while doctors take into account the peculiarities of the course of the disease, the stages of its development, the presence of complications and, of course, age indicators.
Patients with murine fever require detoxification therapy. Doctors also take measures to normalize the general condition of the patient, to stabilize water-salt balance, prevention and correction of complications. Of the medicines, antipyretic and anti-inflammatory drugs, analgesics and antiviral compounds are usually used.
Extremely important role plays control over the activity of the kidneys. Doctors monitor the amount of fluid injected and the amount of output. In the event that drug correction does not contribute to recovery normal activities kidneys, carry out extracorporeal hemodialysis.
Patients with mouse fever must adhere to diet food. If the disease proceeds without complications, they are shown nutrition according to diet No. 4, and otherwise - according to treatment table №1.
Possible Complications mouse fever
Given pathological condition can lead to a serious disruption of the kidneys - to the development of azotamic uremia or to rupture of the kidney. Besides pathological processes can cause eclampsia (the occurrence of convulsions that are accompanied by loss of consciousness), cause the development of acute vascular insufficiency, pulmonary edema and focal pneumonia. The resulting complications, in turn, can provoke the development lethal outcome.
Fever from person to person is not transmitted, but there are other ways of defeat. Unfortunately, doctors do not know of effective measures that will help prevent infection with mouse fever. It is important to observe personal hygiene.
- Skin redness
- Headache
- Skin rash
- Nausea
- Elevated temperature
- Vomit
- Eye redness
- Nosebleeds
- Low blood pressure
- Photophobia
- Weak pulse
- Eye hemorrhages
Infections carried by rodents can have very deplorable consequences for humans when they enter the body. One of these infections is mouse fever, the symptoms of which in the initial stage are manifested in the form acute form. Meanwhile, despite the direct relation to this category, the consequences of infection are expressed not only in fever, as the name implies, but also in kidney damage, general and thrombohemorrhagic syndrome. The danger of the disease lies in the fact that if it hits the kidneys with untimely treatment, it can lead to death.
- Virus transmission
- Symptoms and course of the disease
- Treatment
Vole mice and Norwegian rats act as carriers of the virus. At the same time, animals themselves do not get sick, but only carry this virus. It is excreted through the urine and feces of animals. Among the ways of infection, there are several types of them:
- Airborne dust type of infection, in which dust containing excrement with a virus is inhaled;
- Alimentary type of infection, in which food or water contaminated with secretions with the virus is consumed;
- A contact type of infection, in which damaged skin comes into contact with contaminated objects with the virus or directly with rodents infected with it.
There is no transmission of the virus from one person to another.
Mouse fever: symptoms, course of the disease
The duration of the incubation period can be on the order of 7-46 days, but the most frequent period is 21-25 days. Initial period, oliguric (characterized by hemorrhagic and renal manifestations), the polyuric period and the convalescence period are those actual periods of the course of the disease that characterize mouse fever. Symptoms of mouse fever in children appear gradually, while their first manifestations can be seen only on the fifteenth or even twentieth day after the infection has occurred. Among them are the following:
- Temperature rise up to 40°C;
- muscle pain, joint pain;
- Chills;
- Nausea with alternate vomiting;
- Migraines of frequent occurrence;
- visual impairment;
- Severe bleeding gums, as well as bleeding from the nose.
As for adults, mouse fever has symptoms of a similar nature, general form which is presented as follows:
- Temperature around 40°C;
- Severe headaches;
- Increased sensitivity to light exposure, as well as pain in the eye area;
- Vagueness of surrounding objects, a feeling of having a "grid" before the eyes;
- Rare pulse;
- Lowering blood pressure;
- Redness of the skin in the neck, face, eyes;
- Occurrence on the 3rd-4th day of the disease small spots rashes that focus on the sides of the trunk and armpits;
- Eye hemorrhages;
- nosebleeds;
- Nausea and frequent vomiting.
Initial period. Its duration is 1-3 days, it is characterized by a rather acute onset. The temperature, as we have already indicated, reaches about 40 ° C, often accompanied by chills. There is a headache quite strong in its manifestation, the patient's condition is accompanied by dry mouth, general weakness. Examination reveals the presence of signs of hyperemia of the skin (neck, face, upper thoracic regions), a conjunctiva occurs, in some cases a hemorrhagic rash appears.
2-4 - 8-11 days of illness. As in the past period, the disease is characterized elevated temperature, which lasts up to 4-7 days. A decrease in temperature does not lead to an improvement in the general condition, moreover, it may even worsen. Typical manifestations for this period are pain in the lower back with varying degrees their expression. With the onset of pain lumbar vomiting also occurs (6-8 or more times a day), while it is not associated with eating or food. There are also pains in the abdomen, often bloating. characteristic manifestation disease is expressed in kidney damage, which causes puffiness of the face, positive symptom Oliguria, pastosity of the eyelids.
9-13 days. Polyuric period. Vomiting stops, pain in the abdomen and lower back gradually disappears, appetite and sleep return to normal, the daily amount of urine excreted increases. Dry mouth and weakness persist, the recovery period comes gradually, from 20-25 days.
Mouse Fever Treatment
Treatment of this disease occurs in the infectious diseases department at the hospital. For him, the appointment of bed rest for a period of 1-4 weeks is characteristic. Antipyretics, painkillers and antiviral drugs and anti-inflammatory drugs. Additionally assigned infusion therapy, if necessary, glucocorticoids and hemodialysis are used. The development of thrombohemorrhagic syndrome requires the use of anticoagulants. In addition, vitamin therapy and the exclusion of drugs that increase kidney damage are relevant.
To diagnose mouse fever, you should contact an infectious disease specialist; additionally, laboratory methods studies (blood, urine, PCR, coagulogram).
The disease murine fever is a condition in which the whole body experiences general poisoning, it is characterized by a feverish state of the patient and is accompanied dangerous defeat kidneys. Mouse fever is one of the varieties of hemorrhagic fever, on a par with Ebola. This fever aggravates the patient's well-being, as it literally causes blood to boil and coagulate. Fever causes damage to the kidneys, which is why its name is often supplemented with the diagnosis of renal dysfunction syndrome. This disease is extremely dangerous, and when the first symptoms appear, it requires immediate medical intervention. The symptoms by which mouse fever is determined are quite specific and very threatening. Symptoms of the disease appear very suddenly. The body temperature rises sharply to 40 *, the head is literally torn from pain, and a characteristic bloody rash pops up all over the body. Strong pain affects the abdomen and lumbar region, the mucous membrane of the nose and gums begins to bleed heavily. Observed significant reduction the amount of urine excreted, and after the temperature comes to normal level, general well-being Not only is it not getting better, it's getting worse.
The causes of the development of the disease include a virus that is carried with rodents, which can be transmitted by airborne droplets. Exacerbations are more common in summer period, and certain factors are considered the sources of the disease. Firstly, such factors include eating foods that carry the virus. Secondly, the cause may be contact with rodent droppings. Also, the infection can enter the body with hands that are not washed before eating. The main risk group includes people living in rural areas, as well as tourists and owners of summer cottages and rural areas. At the same time, it is necessary to know that a person is a carrier this disease is not.
As a preventive measure for the development of this disease, complete isolation from rodents and the absence of any contact with them and with their vital activity can be considered. As for summer cottages, at the opening of the summer season, it is necessary to thoroughly ventilate the house and clean with potent detergents, bed sheets overwash, and pillows and blankets should be thoroughly fried in the sun. If possible, get rid of long-term storage products (cereals, pasta, flour, sugar, etc.) and, for the future, store food off the floor and preferably in an impermeable sealed container. In addition, household waste must be disposed of in time to avoid the accumulation of flocks of rodents in them.
The consequences of mouse fever are extremely dangerous and fraught with disturbances in the functions of vital organs. If you ignore the symptoms and the disease, and treat the disease yourself, with the help of antipyretic and antispasmodic drugs, the situation can be brought to a rupture of the kidneys, or at least significantly disrupt their work. Kidney failure is dangerous because the removal of excess fluid from the body is difficult, and the blood is not cleansed. The man starts to faint general state the patient becomes critical. The result of the development of the disease may be the appearance of pneumonia (inflammation of the lungs), or dysfunction of cardio-vascular system.
The listed symptoms, characteristic of mouse fever, appear depending on the organism, both in aggregate and separately. If you suspect this disease, you must contact a qualified medical care, in no case wasting time on self-treatment. With a late appeal for help, the outcome of the course of the disease can become unfavorable, and in some cases even fatal. Since mouse fever is an extremely dangerous disease, the treatment of patients is likely to be carried out by the infectious diseases department. With severe kidney damage, there is a need for dialysis (blood transfusion). Mouse fever causes thickening of the blood and the formation of blood clots in the vessels, due to the need to take and topical application anticoagulants.
Chills, a headache that develops into a migraine, nausea and, as a result, vomiting, "aching" pain in the back and joints - that's all obvious symptoms mouse fever in children. But how not to confuse it with a common cold or intestinal disorder?
Mouse fever in children is a rare infection, which occurs after the bite of an infected animal, as well as through direct contact of the child with his feces (urine, feces) and secretions from the mucous membranes (mouth, eyes and nose). Infection usually occurs by inhalation of feces various kinds wild mice or rats, sometimes with a bite. Other infected rodents can also be carriers; they are sources of infection from several months to 2 years. Recently, a case of one of the transmission of a virus of this kind between people was recorded, but it is not common in our country.
The diseases are caused by Hantavirus, which has different strains. The kidneys or lungs are most commonly affected. In Europe and the Middle East, types of this virus that infect the kidneys predominate, resulting in:
- Hemorrhagic fever with renal syndrome(GLPS). Main symptoms: fever, acute kidney failure and hemorrhagic rash on the skin (not always). Mortality is 10%.
- Epidemic Nephropathy (EN) is a type of Puumala virus disease (HFRS) that also affects the kidneys. It is found in various European (mainly Scandinavian) countries and differs more easy flow. Main symptoms: headaches, pain in lumbar region, back, abdomen, fever. Mortality 0.2-0.5%.
Pulmonary syndrome occurs much rarer and commonly found in the Americas. But the mortality rate is very high - up to 76%. Even less common cardiac syndrome.
Therefore, we usually call mouse fever hemorrhagic fever with renal syndrome, which is most common in Eurasia. And it is her symptoms in children that are described in this article.
Depending on the causative agent, the disease can proceed with different severity. In European and Middle Eastern countries, light and medium forms predominate, in the Far East - heavy. Symptoms of mouse fever in children may also differ. Light form can proceed without obvious symptoms, resembling a cold. U is usually worse tolerated.
Symptoms
The first symptoms, as a rule, appear on the 3-10th day after the contact of the child with an infected rodent. Sometimes the symptoms of mouse fever in a child are latent (asymptomatic) in nature, and may appear only 3 weeks after direct contact (statistical medical materials indicate this fact of the manifestation of the first symptoms). Incubation period can be quite long and take from 7 to 45 days. By this time, any tissue damage (bites or scratches), as a rule, is already healing, leaving no trace of itself.
First signs (febrile phase)
The next, after the incubation period, is First stage disease. In its symptoms, it is largely identical to the common viral cold:
- an increase in body temperature to a value of 39-40 degrees, without signs of inflammation respiratory tract;
- the appearance of a headache, while usually the eyes and in the area do not hurt superciliary arches;
- nausea and vomiting;
- nose bleed(due to poor performance blood vessels and drying of the nasal mucosa);
- an increase in the size of the lymph nodes, which are localized close to the bitten wound;
Armpits and groin are the places where swelling is most common The lymph nodes. The small infected patient then develops a fever, chills, and headaches. Sometimes the epidermis in the area of the original wound may flake off. Rashes on the skin do not appear immediately, but if they do, then an itchy rash of a slightly pink hue spreads to different parts of the body.
The general condition of a sick child can be described as "sluggish", weak.
- V oral cavity dryness;
- on skin neck, chest and face can detect the appearance of small rash, but not always;
- the skin in these areas is hyperemic (there is an increased blood flow);
- conjunctivitis develops (damage to the mucous membrane of the eyes), vision deteriorates.
This state of health accompanies the child for three days.
Second phase (hypotensive)
If this phase occurs, then last up to 2 days. Symptoms include tachycardia and hypoxemia (lack of oxygen in the blood), which occurs due to a drop in platelet levels in the blood.
Main period (oligouric stage)
If appropriate treatment is not provided in time and the diagnosis of mouse fever is not made, the third (oliguric) stage of the course of the disease enters its active phase. It can last from 6 to 57 days. The disease becomes more complicated, the state of health worsens, the symptoms are as follows:
- the temperature drops by 0.5-1 degree;
- fever does not go away;
- of the body leads to the fact that the skin becomes dry over the entire area of \u200b\u200bthe child's body.
All the symptoms that appeared at the first stage of the course of the disease are preserved in the child. To the whole "set" of painful sensations is added:
- swelling of the face, eyelids;
- violation of the process of urination - occurs much less frequently.
As soon as the eyelids, eyes and face become swollen, this is the first sign that the kidneys are affected and are no longer able to function properly. The cause of renal syndrome is damage to the vessels of this paired organ as in other parts of the body. Oligouric (third) stage of the course of the disease lasts an average of 10 days.
Diuretic phase
It comes before recovery, but can last from several days to weeks. During it, symptoms of diuresis appear - the child has a very frequent urination, perhaps even several liters per day (depending on age and intensity of the course of the disease).
Rehabilitation stage
With proper and timely treatment, the disease passes into its final phase without serious consequences for good health. This period in medicine is called polyuric stage course of fever and associated with it the following symptoms:
- urination is normalized;
- the general state of health is facilitated (the temperature is no longer so high, vomiting and nausea disappear altogether);
- weakness continues to overcome the child's body.
How to recognize the disease in time
The child's body is individual and can react differently to the stages of the course of mouse fever. Therefore, the symptoms of the manifestation of the disease may also differ.
As soon as an increase in body temperature is recorded, the general condition of the child begins to gradually deteriorate. In children, fever can manifest itself through:
- chills;
- muscle pain;
- pain in the "open" place of the bite;
- rash (manifested in the form of red-purple "plaques", but does not always occur);
- swollen painful joints (articular and muscle pain extremely rare).
After 2-4 days after the onset of fever, a papular rash may appear on the arms and legs. This rash is defined by flat, reddened areas on the skin with small bumps. As a result, one or more joints may swell, becoming red and painful sensation.
Complications and health consequences
Without treatment, the child is at great risk of developing serious infections:
- endocarditis (inflammation of the inner lining of the heart);
- infection of the heart valves;
- pericarditis ( inflammatory disease heart sac - the outer connective tissue membrane of the heart);
- meningitis (inflammation of the membranes of the head and spinal cord);
- mumps ( inflammatory processes parotid gland).
Any tissue or organ of the body is susceptible to infection. Therefore, a focus of infection and pus, called an abscess, can develop in absolutely any part of the body. child's body.
When is it not mouse fever?
In the absence of information and medical knowledge, this disease in children is sometimes confused with a cold or intestinal infection. The fact that this is really not a mouse fever can be assumed if symptoms such as a runny nose, cough are observed. Diarrhea and abdominal discomfort are rarely signs of hantavirus infection, but are more likely only in Scandinavian countries where rodents carry the Puumala virus. But vomiting and nausea are common symptoms of mouse fever in children.
Mouse fever in children - in some cases it can be very serious danger. Correct and timely diagnosis will help to accept necessary measures to reduce the risk of complications. Although there are currently no treatments or vaccines for the virus itself.