Withdrawal syndrome symptoms treatment. Signs and treatment of withdrawal syndrome. Vomiting and gagging
Withdrawal syndrome is a pathopsychological symptom complex that develops when refusing to use a psychotropic substance, which has varying degrees severity and causing psychophysical discomfort. When the patient abruptly stops using alcohol or drugs, his state of health deteriorates significantly and rapidly. This the substance is built into the biochemical reactions occurring in the body and becomes vital. If it ceases to flow in a certain amount, an abstinence syndrome develops, and a strong desire is formed to take it again.
Withdrawal is common with alcoholism, somewhat less common with drug addiction, and extremely rare with certain medications – narcotic analgesics, sleeping pills and psychotropic drugs.
Clinical manifestations alcohol withdrawal similar to the usual, but different irresistible craving to alcohol and a longer period of malaise.
The reason for withdrawal is the continuous use of alcohol for a long time, after which its entry into the body abruptly stops. The lack of psychoactive substances leads to the development of withdrawal not only among alcoholics, but also among drug addicts and smokers.
Pathology is manifested by hyperhidrosis, palpitations, hand tremors, incoordination of movements, insomnia, depressed mood, irritability. A sick person becomes disabled, aggressive, psychotic. Except neurological symptoms his body temperature rises, his appetite is disturbed, there are signs of dyspepsia. Patients feel bad without alcohol. To improve your psycho-emotional state, they need to constantly increase the dose of alcohol. Withdrawal can lead to seizures and even death.
Women and young people in most susceptible to alcoholism. Alcohol dependence in them is formed in the first year of alcohol abuse. With absence adequate therapy the transition of the syndrome to dementia or delirium is possible.
With drug addiction, withdrawal is a "withdrawal" that occurs in the absence of the next dose of the drug. A similar condition develops in drug addicts 8 to 12 hours after withdrawal. The peak of symptoms occurs 2-3 days after the last dose.
Etiology and pathogenesis

The main cause of alcohol withdrawal syndrome is the accumulation of ethanol decay products in the liver and intestines and severe poisoning of the body with these toxic substances. People who rarely use alcoholic drinks, special enzymes are produced that neutralize these toxins.
The breakdown of ethanol occurs in two ways:
- with the participation of alcohol dehydrogenase in liver hepatocytes,
- using catalase or microsomal ethanol-oxidizing system of the liver.
As a result of a number of biochemical transformations, acetaldehyde is formed - the strongest toxin that can cause acute intoxication organism. Alcoholics do not have these enzymes. Increased content ethanol in the blood slows down the work of enzymatic systems, they do not have time to convert acetaldehyde. Over time, the production of these enzymes is disrupted and their formation is blocked.
 Acetaldehyde affects the metabolism of the neurotransmitter dopamine in the body. Alcohol abuse leads to dopamine deficiency. Ethanol itself begins to interact with the receptors of neurons, making up for the lack of dopamine. Sober patients lack stimulation of these receptors. In the future, with the progression of the pathology, the cessation of alcohol intake leads to insufficient compensation, disintegration and hyperproduction of dopamine. Its excess contributes to the appearance of autonomic reactions, which become the main symptoms of withdrawal. These include: superficial and restless sleep, irritability, hypertension. A threefold increase in dopamine in the blood leads to the development of alcoholic delirium.
Acetaldehyde affects the metabolism of the neurotransmitter dopamine in the body. Alcohol abuse leads to dopamine deficiency. Ethanol itself begins to interact with the receptors of neurons, making up for the lack of dopamine. Sober patients lack stimulation of these receptors. In the future, with the progression of the pathology, the cessation of alcohol intake leads to insufficient compensation, disintegration and hyperproduction of dopamine. Its excess contributes to the appearance of autonomic reactions, which become the main symptoms of withdrawal. These include: superficial and restless sleep, irritability, hypertension. A threefold increase in dopamine in the blood leads to the development of alcoholic delirium.
The pathogenic effect of acetaldehyde is also associated with cell and tissue hypoxia, metabolic disorders, and dystrophy of internal organs. These processes give rise to somatic symptoms ailment. Toxic Substances with the blood flow are carried throughout the body and have their pathogenic effect on the work of internal organs. Without alcohol, the cells of the body can no longer function normally. Developing physical addiction, which becomes the main cause of abstinence. The patient's body gets used to the constant functioning in the mode alcohol poisoning. When there is not enough ethanol, the metabolism, brain and nervous system are disturbed.
Symptoms

Symptoms of alcohol withdrawal syndrome are divided into two large groups:
- Early clinical signs appear almost immediately after alcohol withdrawal and quickly disappear after drinking. Patients lose their rest, are excited and quickly irritated, refuse to eat. They develop tachycardia, hyperhidrosis, hypertension, dyspepsia, diarrhea, and muscular hypotension. Jumps in blood pressure are harbingers of a stroke. The same symptoms occur with abrupt refusal from smoking.
- Late symptoms appear 2-3 days after stopping alcohol intake. In patients, the psyche is disturbed: delusions, illusions, hallucinations, epileptic seizures appear. The face turns pale, the pulse quickens, fever and chills occur. Dreams are accompanied by nightmares. Formed paranoid disorder personality. Late symptoms often overlaps with earlier ones. Clinical signs may occur suddenly even in patients who feel well.
The severity of the withdrawal syndrome:
- 1 degree develops with short binges lasting 2-3 days. Patients are dominated by signs of asthenia of the body and vegetative symptoms: tachycardia, shortness of breath, dry mouth, weakness, impaired concentration.
- Grade 2 develops with binges lasting up to 10 days. Psychoneurological and somatic signs, caused by damage to internal organs, join the previous symptoms. In patients, the whites of the eyes and skin turn red, fluctuate arterial pressure, gait is disturbed, eyelids and hands tremble, speech becomes incoherent, the head is heavy.
- Grade 3 is observed with prolonged binges and is manifested by mental disorders: the inability to maintain eye contact, anxiety, guilt, superficial drowsiness with nightmares, longing, rejection of others, irritability, aggression. It is possible to develop complications that can result in death.
There are several clinical options for the course of pathology:
- Neurovegetative variant - insomnia, weakness, anorexia, tachycardia, fluctuations blood pressure, swelling of the face, hyperhidrosis, thirst.
- Brain variant - pre-syncope, hypersensitivity to sound and light, epileptic seizures, migraine pain.
- Somatic variant - jaundice, sclera injection, flatulence, stool disorder, epigastric pain, cardialgia, salivation.
- Psychopathic option - anxiety, fear, illusions, turning into hallucinations, phobias, psychoses.
Alcohol withdrawal is characterized by unproductive thought processes, lack of a sense of humor, depressed mood, constant desire drink up. Patients can deceive loved ones, run away from home, steal money. Withdrawal syndrome is often manifested by panic and fear. Patients are afraid for their lives, suffocate with fear and often call a doctor.

Withdrawal in drug addiction develops gradually . The four phases of the syndrome smoothly replace each other. The first phase is characterized by emotional overstrain, mydriasis, profuse lacrimation, rhinitis, loss of appetite. During the second phase, fever and chills replace each other, weakness becomes more pronounced, patients suffer from hyperhidrosis, frequent sneezing and yawning. In the third phase, all signs intensify, convulsions appear in almost all muscle groups, the patient becomes angry and dissatisfied. The fourth phase is the predominance of dyspepsia, abdominal pain, false calls for defecation. Patients lack normal sleep, the mood becomes depressed, aggressive.
Complications
Unpleasant consequences of withdrawal syndrome:
- exacerbation peptic ulcer, diabetes, kidney failure,
- hallucinatory syndrome,
- insomnia,
- loss of human form
- cerebral edema,
- gastrointestinal bleeding
- acute coronary insufficiency,
- sclerosis of cerebral vessels,
- severe psychosis,
- liver failure,
- ischemic or hemorrhagic stroke of the brain,
- alcoholic coma,
- inflammatory diseases of the myocardium, leading to dystrophic processes,
- pneumonia,
- dementia,
- epileptic seizures
- memory loss,
- death.
Alcoholic delirium is an extreme degree of withdrawal, characterized by a serious condition of patients and often ending in death. Delirium is manifested by hallucinosis, delusions, agitation, insomnia, disorientation in time, distortion of thoughts, memory impairment, depression, panic, thoughts of suicide.
Diagnostics
The sooner medical care is provided to the patient, the sooner therapeutic effect. To begin treatment, specialists need to make a diagnosis. To do this, you should establish the presence of cravings for alcohol, study the symptoms of withdrawal, its duration, the amount of alcohol consumed. When examining a patient, it is necessary to pay attention to his physical condition and the main symptoms - tachycardia, tremor, neurological status, dyspeptic symptoms, and discoordination of movements.

Laboratory diagnostics:
- increased liver enzymes in the blood: alcohol dehydrogenase, aldehyderogenase,
- hyperlipidemia, hypertriglyceridemia, hypercholesterolemia,
- anemia, macrocytosis, neutropenia,
- decrease in the number of platelets in the blood,
- level up uric acid in blood,
- decrease in vital trace elements in blood serum,
- increased activity of AST and ALT,
- increased IgA and IgM in the blood,
- enzyme immunoassay - detection of autoantibodies to glutamate receptors.
Instrumental diagnostic methods:
- radionuclide hepatography and scanography,
- radiography or endoscopy of the gastrointestinal tract,
- Ultrasound of the abdominal organs,
- CT scan of the liver, spleen, skull,
- liver biopsy,
- electrocardiography and echocardiography.
Treatment
Withdrawal syndrome treatment for alcoholism is carried out in a narcological dispensary or a specialized private clinic. Treatment of mild forms is allowed at home or outpatient settings under the supervision of a physician.
Indications for hospitalization:
- cachexia,
- body dehydration,
- fever,
- hallucinosis,
- epileptic seizures
- the presence of psychosomatic pathology,
- disturbances of consciousness.

To relieve alcohol withdrawal in a hospital, patients are prescribed:
- Tranquilizers - Oxazepam, Lorazepam, Phenazepam.
- Adrenoblockers - "Atenolol", "Timolol".
- Calcium antagonists - Nifedipine, Cordaflex.
- Vitamins of group B - injections of "Thiamin", "Riboflavin".
- Dehydration therapy - intravenous administration colloid and crystalloid solutions, saline, glucose, diuretics.
- Enterobrents - " Activated carbon”, “Polysorb”.
- Antipsychotics - "Aminazin", "Tizertsin".
- Antidepressants - "Triptizol", "Flunisan", "Imipramine".
- Anticonvulsants - "Carbamazepine", "Finlepsin".
- Nootropics - Piracetam, Vinpocetine, Cerebrolysin.
- Hepatoprotectors to protect the liver - Essentiale Forte, Phosphogliv, Karsil.
- Funds that improve the functioning of the heart - "Panangin", "Asparkam".
- Antispasmodics - "No-shpa", "Spazmalgon".
- Diuretics - "Furosemide", "Veroshpiron".
Psychotherapy is widely used in the treatment of withdrawal symptoms. The psychotherapist asks the patient about his feelings and experiences. During the sessions, coding for alcoholism is carried out.

Withdrawal treatment for drug addiction is carried out only in the hospital and consists in the appointment of psychotropic drugs:
- Detoxification therapy - "Naloxone".
- Anxiolytics - Grandaxin, Relanium.
- Preparations from NSAID groups- Ibuprofen, Nurofen.
- Substitution therapy - "Methadone", "Buprenorphine".
To get rid of alcohol withdrawal on your own, you need to take "Activated Charcoal" at the rate of 1 tablet per 10 kg of a person's weight. During the day, you should drink as much mineralized water as possible to restore electrolyte balance and reduce intoxication. Help relieve anxiety and fear sedatives- "Novopassit", "Finebut", "Corvalol".
Alternative treatment of abstinence is the use of herbal remedies. Their daily use reduces dependence on alcoholism. The most common folk remedies:
- a decoction of unpeeled oats,
- juice from carrots, apples, beets, lemon,
- hypericum decoction,
- infusion of bay leaves,
- thyme infusion,
- infusion from a mixture of herbs - wormwood, thyme, centaury,
- infusion herbal collection from motherwort, elecampane, milk thistle,
- tea with chamomile or rose hips.
Phytotherapy normalizes the psycho-emotional state and eliminates physical discomfort.
Withdrawal mild syndrome severity has a favorable prognosis and resolves without treatment in 10 days, and with treatment in 5 days. Unfavorable prognosis characteristic of severe abstinence with a predominance psychopathological symptoms. If the patient continues to drink, withdrawal worsens. The causes of death at an extreme degree of pathology are: acute coronary insufficiency, severe intoxication of the body, pancreatic necrosis, cirrhosis of the liver.
Video: about withdrawal symptoms in alcoholism
Today, people know a lot about how harmful alcohol is, what severe consequences for health can cause its systematic use. One of the dangers that a person who decides to stop drinking can face is withdrawal symptoms. alcohol syndrome. Many people often hear about such a thing as alcohol withdrawal syndrome, but few people can correctly explain what is meant by this term. In the meantime, people who are prone to alcohol abuse, at least once in their lives, may encounter this unpleasant syndrome, especially if they suddenly decide to stop drinking.
What it is
It is important for people suffering from alcoholism, as well as their relatives, to understand what withdrawal symptoms are. It is usually understood as a state of severe intoxication that has developed against the background of regular consumption of products containing ethanol.
Withdrawal syndrome, the signs of which are manifested by a set of physiological and psychological disorders, is considered classical in its course and occurs most often.
Symptoms of withdrawal syndrome are usually well expressed, therefore diagnostic search presents no difficulty. In some cases, this condition can pose a significant threat to the life and health of a person, and then he without fail urgent medical assistance is needed. Relief of the condition of a sick person usually occurs if he takes another dose of alcohol, but it must be understood that the pathology from such methods of "treatment" only gets worse.
It is believed that alcohol withdrawal syndrome is a consequence of the depletion of the resources of the whole organism in general and the liver in particular. This means that the body can no longer fight the toxic effects of ethanol, its active transformation into acetaldehyde, which is a strong poison for the human body, begins.
Pathogenesis
To better understand what withdrawal syndrome is in chronic alcoholism, it is necessary to understand the mechanisms by which this develops. pathological condition. Normally, ethanol, having entered the human body, undergoes splitting in two main ways: either with the help of alcohol dehydrogenase, or with the help of catalase - special enzymes that ensure the neutralization of this toxin. During the transformations, acetaldehyde is also formed, which is very harmful to the body and is responsible for the development hangover syndrome.

If a person is healthy and does not drink alcohol too regularly, then the main load on the breakdown of ethanol falls on alcohol dehydrogenase, due to which a smaller amount of acetaldehyde is formed. However, the amount of this enzyme is gradually depleted, and in the presence of chronic alcoholism, catalase and other additional mechanisms for neutralizing the harmful substance come into play.
As a result, there is more acetaldehyde, and the damage done to the body is expressed more and more.
Another important mechanism involved in withdrawal symptoms is a violation of dopamine synthesis. If on early stages the development of addiction to this mediator is not enough, and it is replaced by alcohol, then late stages, if the use of alcoholic beverages stops abruptly, dopamine begins to be produced, on the contrary, too much.

The withdrawal syndrome, the symptoms of which are directly related to the amount of dopamine, is felt by a person the more acutely, the more it becomes in the body after refusing to take alcoholic beverages.
If the level of the mediator rises three or more times, then doctors are already talking about full-fledged delirium tremens.
Withdrawal syndrome in alcoholics can last for quite a long time. If the hangover disappears in a few hours, then in order to get rid of intoxication, the body needs more time and effort. Sometimes it takes up to several days.
Classification
Alcohol withdrawal syndrome is usually divided into three main stages, which depend on the severity of the symptoms, the duration of the attack. These include:
- Stage I is accompanied by the transition of chronic alcoholism from the first stage to the second, usually not very pronounced and develops after binges that last for several days. It is easiest to provide medical assistance during this period to the patient, since the dependence has not yet been fully formed. Usually accompanied by sleep disturbances, increased heart rate, sweating.
- Stage II usually accompanies binges lasting up to 10 days inclusive. It is characterized by a worsening of the symptoms that occur in the first stage, the addition of neurological symptoms.
- Stage III develops if the binge lasted more than 10 days. Accompanied by the development of not only neurological syndromes, but also varied.
The manifestation may lie in attacks of aggression, the appearance of guilt, sleep disturbances, etc.

Differences from a hangover
Hangover and alcohol withdrawal syndromes are often confused by patients with each other. People tend to mistakenly believe that these are two terms for the same concept, but this is fundamentally wrong. The fact is that a hangover is a reaction of the body that can occur in any person who consumes ethanol inside. At the same time, he does not have to be a drunken alcoholic, he can generally try drinks of this type for the first time in his life. It is usually possible to cope with this condition without additional medical help.
Symptoms of alcohol withdrawal syndrome may resemble a hangover, but this condition is not characteristic of people who drink alcohol rarely or for the first time in their lives.
The set of symptoms that manifest themselves during the development of this pathology is characteristic of drunken alcoholics who are used to drinking in large quantities without caring about their own health and life. It occurs if a person abruptly switches to abstinence from ethanol after prolonged use. It is also important to remember that the removal of withdrawal symptoms often requires the intervention of professionals, which cannot be said about.

Symptoms
Symptoms of withdrawal syndrome largely depend on what individual characteristics body, how long and in what quantities a person is applied to the bottle. The main complaints of patients will be as follows:
- an excessive desire to drink again in order to improve one's own condition, at least for a while;
- asthenia, feeling of lack of strength;
- insufficient staining skin;
- against the background of dizziness or without it;
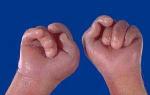
- tremor (trembling) not only of the hands, but of the whole body;
- attacks of tachycardia or arrhythmias, which may be accompanied by sweating, loss of consciousness;
- change mental state in the form of increased aggressiveness, loss of the ability to find compromises, etc.
Many of these symptoms resemble a hangover, but are usually much more pronounced. .
The classic type of withdrawal syndrome is delirium tremens.
In this state, the patient is a danger to others, alcohol withdrawal treatment is required in a psychiatric hospital.

Methods of therapy
Many are wondering what type of medical care is relevant for the development of such a condition in a patient prone to alcoholism. It all depends on how severe the symptoms are and how dangerous the person is to others. If just pills can help a patient with a hangover, then it is better to trust the treatment of withdrawal symptoms in alcoholism to professionals.
If an abstinence syndrome has developed with alcoholism, home treatment can be started with the use of medications such as Alcoseltzer or Medichronal. These drugs can effectively alleviate the patient's condition, especially if they are provided as additional conditions tranquility, plentiful drink and healthy sleep.
Treatment at home becomes impossible when alcoholism is chronic.
In this case, classic drugs for a hangover will not have an effect, hospitalization is recommended. In a hospital setting, doctors will administer saline preparations to the patient, which can cope with intoxication. For example, glucose solution, Reopoliglyukin, vitamins of group B or vitamin C in large dosages can be used.

How to alleviate the patient's condition if he is irritated, dangerous to others? For this, drugs such as Relanium, Amitriptyline, Sonopax are used in a hospital setting. Treatment of withdrawal symptoms in the form of delirium tremens is not carried out at home, it is possible only in a hospital setting!
If alcohol withdrawal syndrome has developed, treatment will not help get rid of alcoholism.
The health worker usually puts special emphasis on this. However, therapy is still able to help: thanks to it, the body is cleansed, cravings for alcoholic beverages may slightly decrease. An important element of treatment is such a tool as conversations with a psychotherapist. It is considered important to try to remind a person that the complete abolition of alcohol will positively affect his life, insure against new hospitalizations.
What is the danger
Treatment of alcohol withdrawal syndrome should be carried out by professionals.
You can not ignore this pathological condition, hoping that it will pass on its own.
It is important to remember that against the background of abstinence. Develop various violations ranging from bouts of irritability to episodes of memory loss. Sometimes violations in it are so irreversible that no medicine can improve the situation. Because of this syndrome, not only nervous system but also cardiovascular. The risk of diseases such as heart attacks, strokes, arrhythmic seizures increases greatly.

As a result of this, the development of pathologies such as hepatitis, and then cirrhosis, is possible. Treat alcoholic hepatitis modern conditions possible, but cirrhosis of the liver is a disease characterized not only by rapid progression, but also by the absence of effective treatment to this day.
withdrawal syndrome is dangerous state, the therapy of which requires the intervention of professionals.
If you choose the wrong drugs to improve the patient's condition or completely ignore the symptoms, the consequences can be unpredictable. Such a form of withdrawal as delirium tremens is especially dangerous. If you suspect its development, be sure to call an ambulance!
(Visited 3 314 times, 1 visits today)
Often develop psychomotor agitation and delirium, but until the 1950s. remained unclear whether alcohol use, discontinuation, or concomitant psychological disorders. It has now been shown that these complications are due to alcohol withdrawal syndrome, a severe and common condition in both hospitalized and outpatients.
Symptoms of alcohol withdrawal syndrome
This is a condition that develops a few hours or days after the cessation of intensive and prolonged use alcohol and characterized by symptoms that should not be caused by another organic disease. Alcohol withdrawal syndrome is classified according to the time of onset (early or late) and severity (complicated or uncomplicated), although there are no completely suitable and generally accepted criteria for distinguishing these options. In addition, the course of the disease, including the sequence of its stages, can vary significantly in different patients. Some alcoholics do not experience withdrawal symptoms at all after stopping drinking. The severity of the condition is largely determined by subjective factors, so we believe that it cannot be assessed only on the basis of the presence of certain syndromes (for example, delirium tremens).
Early uncomplicated withdrawal syndrome
The disease begins within 6 hours after the cessation of alcohol consumption. Its onset is characterized by vegetative reactions (tachycardia, tremor, arterial hypertension) and psychomotor agitation. These symptoms are unpleasant for the patient, but not dangerous. With these manifestations in most cases, although not always, begin and severe forms alcohol withdrawal syndrome. At this stage, the symptoms are easily eliminated by taking ethanol, which is what most alcoholics do daily.
Alcoholic hallucinosis
Hallucinations occur in approximately 25% of patients with alcohol withdrawal syndrome, and some of them develop alcoholic hallucinosis - a condition manifested by constant hallucinations, mainly tactile or visual. Unlike alcoholic delirium, hallucinosis occurs against the background of clear consciousness.
Withdrawal epileptic seizures
Epileptic seizures are observed in approximately 10% of patients with alcohol withdrawal syndrome, and often they are its first sign. Approximately 40% of patients have single seizures, and 3% develop status epilepticus. Withdrawal seizures are usually generalized tonic-clonic, short-term, with a short postictal period. They may develop in the absence of other signs of alcohol withdrawal. Because of quick recovery and the normal mental state of the patient after a seizure, the severity of seizures is underestimated. But in a third of patients with alcoholic delirium, its development was preceded by single withdrawal seizures.
Alcoholic delirium
Alcoholic delirium (delirium tremens) - the most severe complication alcohol withdrawal syndrome. As a rule, it begins 48-96 hours after the cessation of drinking. Many manifestations of alcoholic delirium - tremor, autonomic disorders (tachycardia and arterial hypertension) and psychomotor agitation - are the same as in early uncomplicated alcohol withdrawal syndrome, although more pronounced. Unlike alcohol withdrawal syndrome, alcoholic delirium, as defined by DSM-IV, there are:
mental disorder with reduced ability to switch or focus attention, confusion, with delirium and psychosis
impairment of cognitive functions (memory loss, disorientation, speech impairment) or perception that cannot be explained by existing or developing dementia.
If early uncomplicated alcohol withdrawal syndrome disappears after 3-5 days, then alcoholic delirium can last up to 2 weeks.
Pathophysiology
At the core clinical manifestations syndrome is a change in mediator transmission with constant alcohol use. Constant stimulation of GABA receptors by ethanol leads to a decrease in the number of these receptors. As a result, even against the background of such a concentration of ethanol in the brain, which normally has sedation, the level of consciousness remains the same and tolerance develops - an additional intake of alcohol is required to achieve euphoria. This, in turn, leads to an additional decrease in the number of GABA receptors. With glutamate NMDA receptors occur reverse processes. As a consequence, the cessation of alcohol consumption leads to a decrease in inhibitory GABAergic effects and an increase in excitatory glutamatergic effects. Clinically, this is manifested by autonomic disorders and psychomotor agitation.
Predisposing factors and prognostic indicators
The risk of alcohol withdrawal syndrome is highest in individuals who have already experienced it or have a family history. One of the most commonly used methods for determining the severity of alcohol withdrawal syndrome is the CIWA-Ar (Clinical Institute With Drawal Assessment for Alcohol-Revised) alcohol withdrawal severity scale.
Many attempts have been made to find biochemical factors that predispose to the development or contribute to a more severe course of the disease. If the patient has an increased concentration of ethanol in the blood, then this syndrome, as a rule, is more severe.
Treatment of alcohol withdrawal syndrome
Treatment of withdrawal seizures
These seizures usually go away spontaneously. If this does not occur, benzodiazepines are the drugs of choice. Phenytoin does not contribute to either the prevention or relief of seizures - apparently, it does not affect the GABAergic and glutamatergic transmission that plays leading role in the occurrence of alcohol withdrawal seizures. On the other hand, phenytoin may be effective in seizures in patients with alcoholism if these seizures occur against the background of a non-alcoholic withdrawal syndrome or have a history.
alcohol withdrawal syndrome
On initial stages patients often take alcohol on their own, which leads to an improvement in the condition. Of those who seek medical help, many have enough outpatient treatment. Others require hospitalization in a poisoning center or regular hospitalization, depending on the severity of the withdrawal syndrome and comorbidities.
Initially, a thorough examination is necessary to identify concomitant somatic and mental disorders or intoxications. If CNS injury or infection is suspected, CT and lumbar puncture are indicated. In case of impaired consciousness or fever, antibiotics are prescribed before the procedure. lumbar puncture. All patients are given thiamine to prevent Wernicke's encephalopathy.
Benzodiazepines are usually helpful in early stages or mild withdrawal symptoms. They can be administered orally, although it is more effective in / in the introduction in increasing doses until the effect is achieved. In / in the introduction of diazepam allows the fastest effect, which reduces the risk of overdose with excessive sedation. Against, maximum effect Lorazepam develops approximately 10-20 minutes after IV administration, so this drug is sometimes erroneously administered again before the first dose has taken effect. If intravenous administration is not possible, midazolam may be prescribed intramuscularly, although in this case it enters the blood more slowly. Due to better pharmacokinetic properties and ease of administration, it is preferable to start treatment with benzodiazepines rather than barbiturates, although there is no significant difference between them in terms of duration of delirium and mortality.
In alcoholic delirium, start with intravenous administration of benzodiazepines in increasing doses until a sedative effect is achieved. The goal of treatment is to reduce arousal while maintaining spontaneous breathing and basic physiological indicators. The mode of administration of diazepam should be chosen so that as the symptoms subside, the concentration in the blood of both diazepam itself and its active metabolite desmethyldiazenam decreases with a corresponding decrease in the sedative effect. Numerous studies have shown that titration of benzodiazepines is best based on symptoms rather than according to any standard regimen.
Resistant alcohol withdrawal syndrome and alcoholic delirium
To achieve and maintain a sedative effect, very high doses of benzodiazepines are sometimes required - up to 2600 mg of diazepam in the first 24 hours of treatment. Such patients should be under constant supervision or in the ICU. tactics depend on various factors, including the possibility of hospitalization in the ICU. In the setting of ICU, we recommend continuing to administer benzodiazepines despite their apparent ineffectiveness. Usually in such cases, with a jet injection of 10 to 100 mg of diazepam, a sedative effect occurs, but it is short-lived. In conventional wards, repeated intravenous diazepam is limited, so it is better to use other drugs - for example, phenobarbital at a dose of up to 130 mg IV in combination with a benzodiazepine. It must be remembered that the effect of phenobarbital begins in about 20-40 minutes, and in order to avoid an overdose, do not rush to repeated injections. Propofol acts quickly, but it is more difficult to choose its dose.
ethanol
There are few reliable data on the use of alcohol or vodka orally and intravenously for the treatment of hospitalized patients. It is better not to use this method, as it is fraught with serious complications, and it is difficult to determine the safe mode of ethanol administration.
Antiadrenergics
In randomized placebo-controlled trials, it was found that blockers and clonidine reduce blood pressure and heart rate. However, these drugs act only symptomatically, so they cannot be recommended as monotherapy.
The article was prepared and edited by: surgeonWithdrawal syndrome in alcoholism is not a simple hangover that occurs after a "good" drink. This is the state when a physical, nervous disorder begins.
Patients are subject to it chronic alcoholism 2 and 3 degrees, when you stop drinking alcohol, reducing the dose. You can get out of this thanks to another.
What is it, symptoms
The symptoms of the condition are different. A hangover is a poisoning of the body with all the ensuing consequences:
- Heaviness in the head, migraine-type pain.
- Unpleasant feeling in the stomach, nausea, vomiting.
- Weakness.
- Trembling of hands.
- Strong thirst.
- Aversion to alcoholic drinks.
This condition lasts for several hours, disappears without a trace. Many recommend in the morning, after libations, to drink a small dose for therapeutic purposes. The opinion is wrong. Alcohol poisoning cannot be treated.
The symptoms of the syndrome are much more severe, over 3-5 days. This is due to the accumulation of toxins in the blood, which are formed as a result of the breakdown of alcohol. Without it, a person can no longer do.
Ethanol becomes a component of the blood, takes part in metabolic processes, the body requires it, causing such conditions:
- Feelings of anxiety, anxiety, fear.
- Drops in blood pressure.
- Problems with coordination, dizziness.
- Nausea, vomiting, diarrhea.
- Aversion to food pale color faces.
- General weakness, hand trembling, fever.
- Confused mind, hallucinations.
Syndrome stages

Each stage is characterized by different symptoms:
- The first (initial) is manifested in a violation of concentration, anxiety, weakness, desire to drink.
- Second (moderate). Clinical picture more pronounced. Added loss of appetite, increased heart rate, breathing. Running look.
- The third is a dangerous mental state with hallucinations, anxiety, insomnia, nightmares.
- Fourth (heavy). The symptoms of withdrawal syndrome are clearly conditioned, requiring medical care. People call it "white fever". Possible death.
Features of withdrawal

IN easy man several hours go without alcoholic beverages, the condition almost does not worsen. It happens at the beginning of the second stage of alcoholism. With a moderate need to drink occurs immediately after sleep, to improve the condition, take a dose of alcohol.
A person can still abstain from alcohol by an effort of will. Occurs in the middle of the second stage of alcoholism with chronic addiction. Expressed is characterized by the fact that it is almost impossible to live without alcohol.
Symptoms persist for several days, without a dose of alcohol they do not pass. This occurs at the end of the second, beginning of the third stage of alcoholism. Severe with all the symptoms can last a very long time. Without appropriate treatment leads to mental disorders, of death.
Stages of alcoholism

Even in ancient times, the great Horace said: "Intoxication is voluntary madness" It is difficult to disagree with this. Current medicine defines four when normal, healthy man turns into a mentally, physically sick, clear signs madness.
First. No strong psychological dependence. A man may abstain from drinking for a while if it cannot be purchased. At the first opportunity, he will find and bite. Company, friends, depression, loneliness, the desire to relax lead to alcoholism.
At this stage, a person can be freed from addiction if he reconsiders his attitude to the world around him, changes his priorities. Complete failure from ethanol, sports, new friends. Life without alcohol can be much more joyful, happier. If you continue to aggravate, there will be persistent addiction.
Second. An obsessive desire haunts constantly. All thoughts are occupied with the search for alcohol. The dose is increased to achieve a "high", while there are no symptoms of poisoning. Concepts about the negative of drunkenness disappear. There is a transition to the next severe form.
Third. Irreparable mental damage is done, physical health. The dose taken is more than allowable norms. Alcohol burns internal organs, fabrics.
First of all, the liver and kidneys suffer. At the alcoholic severe swelling, due to poor functioning of the urinary system, the skin turns yellow, caused by stagnation of bile, pathological changes in the liver.
Mental health has been irreparably damaged. At compulsory treatment"break" occurs. A person commits inadequate, insane acts, becomes violent, insane.

Stage 4 complete indifference to the outside world. The only thought is to drink. All organs and systems practically do not work. Man is lost not only to society, but also to himself. During this period, everything that contains alcohol is used: cologne, glass cleaner, and other alcohol-containing substances.
They are no longer amenable to forced treatment. During the withdrawal from the binge may die. 99% die painful death from cirrhosis, renal failure, heart attacks, cerebral hemorrhages.
It is believed that stages 3 and 4 are a one-way ticket. Such patients are no longer being treated. As Plutarch said: "No body can be so strong that the wine could not damage it." At these stages, immunity is almost destroyed.
Relief of the syndrome
Conclusion from the difficult alcohol intoxication When the body cannot cope with a large dose of ethanol, mental and physical discord begins. The symptoms of poisoning are eliminated medically.
Individually assigned complex therapy. Cupping is not a method of treatment; after it, a consultation with a psychologist is indicated, long recovery, which will depend on the degree of the disease.
How to withdraw

The elimination of the withdrawal syndrome in alcoholism consists in the gentle withdrawal of a person from alcohol addiction, elimination of signs caused by the lack of drinking. On different stages alcoholism withdrawal symptoms will be approximately equal, but the duration varies.
IN severe cases drug treatment, which includes many procedures, is carried out in a hospital under the supervision of a narcologist.
A day later, glucose, sodium chloride with thiamine, riboflavin, biotin, ascorbic acid, antiallergic (telfast, hismanal), blood circulation drugs (cavinton, neurovit) are dripped.
All this helps to remove the toxic effect of alcohol in the blood. Strong diuretic medications are prescribed to remove toxins that are formed during the breakdown of ethanol, reduce swelling.
- Drugs that reduce cravings for intoxicating (crotenal, antabuse).
- Sedatives, hypnotics (gidazepam, clozapine).
- Means for improving the functioning of the liver, cleansing the body (Esentiale, preparations based on milk thistle).
After acute course the second stage begins, where you should continue to take drugs that improve metabolism. To these is added the therapy of organs that have been harmed by copious libations.
Treatment for alcohol dependence includes drugs, disgusting to alcohol, vomiting, increased heartbeat, fear of death. They help relieve cravings for alcohol, get rid of dependence on a psychological level.
Treatment at home

Withdrawal syndrome can be removed independently. It may be in the early stages of alcoholism. They usually use Medichronal, which is dispensed in a pharmacy without a prescription.
After taking it, toxins are quickly eliminated from the body, disappear unpleasant symptoms. You have to take it for three days. For the treatment to be successful, you need a long, full sleep. Are used sedatives, plants.
Pharmaceutical sedatives for herbal basis Gerbion, Novo-passit, Fitosed. You can drink decoctions of valerian, motherwort. With nervousness, increased heart rate, Corvalol, Corvalment, Glycine are used. Alcohol upsets the system, destroys the B vitamins needed for cells.
To speed up the recovery process, it is necessary to take minerals, useful substances And ascorbic acid at a double dose. It is advisable to drink natural juices With high content hers - grapefruit, orange. Eat lemon, kiwi.
Food should be varied, high-calorie. It's good to drink dairy products, which restore the intestinal flora, remove toxins. Yoghurts, fermented baked milk, kefir should be in the diet constantly. Meat soups, cereals, vegetables will help restore strength.
Any type of alcohol to relieve symptoms is prohibited. Its complete cancellation will speed up recovery. Common Mistakes(use beer, vodka to soften the signs) will lead to another binge.
Treatment at home is not always possible. The appearance of severe concomitant diseases, the neglected degree of alcoholism, self therapy may not give results, cause harm. Such patients should undergo rehabilitation in a hospital under the supervision of a specialist.
What is withdrawal syndrome - a serious dangerous condition. Untimely, poor-quality assistance can cause serious consequences:
- Exacerbation of concomitant diseases.
- Alcohol destroys the liver - cirrhosis.
- The state of blood vessels worsens - leads to hemorrhages, cerebral edema, heart attacks.
- Mental disorders - nightmares, visions, fears.
- Delirium (madness). Delirium tremens- inappropriate behavior, anxiety, panic. In this state, a person is dangerous to himself and others.
Alcohol withdrawal syndrome can begin after 1.5-2 years of constant aggravation of alcohol. As the great Charles Darwin said that the abuse of alcohol worse than war. The habit of solving problems with a bottle leads to sad consequences.
A whole complex of psychological and somatoneurological disorders that occur against the background of prolonged alcohol use and abrupt cessation is called withdrawal syndrome.
Causes of withdrawal syndrome
 This syndrome appears for the reason that the human body is simply not able to process the amount of alcohol that has entered it. Moreover, people who consume alcohol constantly already have problems with the liver. As a result, toxic substances gradually accumulate in the body, because of which a person begins to feel bad.
This syndrome appears for the reason that the human body is simply not able to process the amount of alcohol that has entered it. Moreover, people who consume alcohol constantly already have problems with the liver. As a result, toxic substances gradually accumulate in the body, because of which a person begins to feel bad.
As a rule, the withdrawal syndrome occurs approximately seven to ten hours after taking the last glass of alcohol. It can last from several hours to several days. If you take alcohol at this moment, then withdrawal disorders will be stopped. In the event that a person is just starting to drink, then this syndrome can only occur after a large number drunk alcohol. But in an alcoholic with experience, this syndrome occurs after taking any dose.
Withdrawal symptoms
You can consider the withdrawal syndrome in drug addiction and alcoholism. In drug addiction, this syndrome is represented by two groups of symptoms: vegetative (somato-neurological) and psychopathological. Only for various forms addiction these symptoms will be slightly different. This syndrome is characterized by a phase course: as soon as the decline in abstinence begins, the symptoms that manifested themselves in human body last.
1 What is the difference between alcohol withdrawal syndrome and hangover syndrome? Duration. As a rule, the syndrome lasts about three to five days, after which it disappears. True, if the patient does not withstand this period and drinks again, then the syndrome softens somewhat. The reason why this syndrome does not last longer is simple: during this time (if you do not take alcohol), the body recovers and eliminates all hangover effects.
2 Another difference between abstinence and a hangover is that it can end in psychosis, which is called delirium tremens in our people. And in general, withdrawal syndrome differs from a hangover in quality and strength. The person feels a great weakness.
3 If you have withdrawal symptoms mild degree, then there may be no vomiting. But in the severe stage, it is observed severe vomiting, which can also contain the content duodenum(bile) and even blood.
In the event that blood is found in the vomit, then this is very a bad sign. This means that bleeding begins in the stomach, which can turn into a stream at any time. In this case, it is necessary to urgently consult a doctor, as it may be necessary surgical intervention. Where does blood come from in vomit? From varicose veins, as well as bursting veins located in the esophagus and stomach. And varicose veins, in turn, may appear as a result of developing cirrhosis of the liver. In addition, blood can appear from burst blood vessels in the rectum (hemorrhoids). In some situations, intra-intestinal bleeding occurs. In this case, its symptom is black feces.
4 And here headache in alcoholics with withdrawal symptoms is extremely rare. In the event that it manifests itself, then this may be the consequences of old craniocerebral injuries. Or increased intracranial pressure.
5 Another characteristic symptom alcohol withdrawal syndrome is either insomnia or dreaming with nightmares. In addition, deceptions of auditory or visual perception may occur for up to five days. So, for example, a patient may take a coat hanging in the hallway for some person, and in the ticking of a clock, he may hear threats addressed to him. If this state of affairs continues long time, then it will end with delirium tremens. In this case, the patient has hallucinatory images.
The danger of withdrawal symptoms is not only in delirium tremens and bleeding. The fact is that during this period, the patient exacerbates all his chronic diseases, which entail damage to internal organs and the development of new diseases.
Indications for hospitalization with withdrawal symptoms
 In what case is the hospitalization of the patient necessary:
In what case is the hospitalization of the patient necessary:
- if he has a pronounced tremor;
- if he develops hallucinations;
- if a person begins to degrade;
- body temperature rises higher than 38.3 ° C;
- if the patient has epileptic seizures without an indication of epilepsy in his anamnesis;
- if there is a clouding of consciousness;
- if there is a head injury (with loss of consciousness);
- if they appear accompanying illnesses;
- if Wernicke's encephalopathy is manifested;
- if there is respiratory or liver failure;
- if gastrointestinal bleeding opens;
- if severe malnutrition develops;
- if a person is sick with pancreatitis;
- if they appear mental illness(this may be an exacerbation of schizophrenia, the risk of suicide, a severe form of depression);
- if there is a history of alcohol withdrawal syndrome, which is accompanied by delirium, epileptic seizures and psychosis.
Features of withdrawal syndrome in alcoholism
1
 If the syndrome mild stage, then the symptoms develop over a period of six to 48 hours and can last, if this condition is not treated, up to ten to fifteen days;
If the syndrome mild stage, then the symptoms develop over a period of six to 48 hours and can last, if this condition is not treated, up to ten to fifteen days;
2 If a symptom of a severe stage occurs, then the symptoms develop more slowly (from 2 to 5 days) after the moment when last time alcohol was taken;
3 There are cases when the symptoms are not formed sequentially, but appear almost immediately;
It is necessary to know that all these symptoms are aggravated in the evening.
Duration of alcohol withdrawal
If speak about mild form, then in this case, this syndrome can last up to ten days (if it is not treated) and up to five days (with specialized treatment). But in severe form, the prognosis will depend on the volume and type of pathology developing in the human body. The most complex and lengthy are syndromes with alcoholic psychoses. Somatovegetative disorders are milder and not as long.
Alcohol withdrawal treatment
 The very first step, which is used in the treatment of alcohol withdrawal, is aimed at reducing the toxic load on the body, stabilizing its condition, as well as restoring the functions of all systems and organs. The treatment regimen is selected based on the symptoms observed in the patient.
The very first step, which is used in the treatment of alcohol withdrawal, is aimed at reducing the toxic load on the body, stabilizing its condition, as well as restoring the functions of all systems and organs. The treatment regimen is selected based on the symptoms observed in the patient.
In the event that somatic symptoms are pronounced, then it is necessary to use drugs that lead to normal condition internal organs. If pronounced neurological signs, then sedatives are used.
But, despite the huge variety of drugs used, in all cases, B vitamins are necessarily used, primarily thiamine. The fact is that the lack of this particular vitamin plays a very important role in the formation of alcohol withdrawal in a person.
It should be emphasized that people who chronically drink alcohol show signs of polyhypovitaminosis. In this case, it is necessary to assign whole complex vitamins.
How is abstinence syndrome removed in a clinical setting?

The directions that are used in the treatment of withdrawal syndrome are as follows: first of all, it is restored acid-base balance organism, as well as the neurological condition is stabilized. Specialists should select doses in such a way that the patient can fall asleep, but at the same time, after waking up, he does not lose contact. For this, barbiturates, benzodiazepines, antipsychotics can be used.
Also, diuretics are often prescribed (if there is hyperhydration), to maintain the heart - beta1-blockers, as well as potassium and magnesium preparations.
Hospitalization, as a rule, lasts for three to seven days. But this is provided that the patient does not have alcoholic psychoses. In the same case, if psychoses are observed, then the patient should be transferred to a specialized hospital.
How to remove alcohol withdrawal syndrome at home?
 It is not uncommon for situations when they try to cure withdrawal symptoms at home. And in this case, the patient is given droppers with saline or detoxification solutions. In fact, this is fundamentally wrong. After all, most of the time, similar condition the patient has hyperhydration, and additional fluid can provoke the development of complications that are generally not compatible with life.
It is not uncommon for situations when they try to cure withdrawal symptoms at home. And in this case, the patient is given droppers with saline or detoxification solutions. In fact, this is fundamentally wrong. After all, most of the time, similar condition the patient has hyperhydration, and additional fluid can provoke the development of complications that are generally not compatible with life.
To introduce additional fluid (by any means - parenteral or oral) or not, only the doctor can decide. And then only after a thorough examination of the patient and certain studies.
If the symptoms of the syndrome are mild, then in the outpatient clinic the patient is simply observed and given vitamins.