Treatment regimen for polycystic ovaries to get pregnant. Is it possible to get pregnant with polycystic ovaries and how to cure PCOS so that this becomes possible? The main methods of treating the disease
Despite the fact that PCOS can be an obstacle to pregnancy, many women manage to successfully conceive and give birth to a healthy baby with PCOS. In some cases, pregnancy occurs on its own, and sometimes in order to become pregnant, a woman needs to undergo a course of medication or even undergo ovarian surgery.
I have PCOS and want to get pregnant. What to do?
Not all women with PCOS need treatment to get pregnant. If you have regular periods, then you may be able to get pregnant on your own, without medical intervention. Usually, in this case, the doctor gives 1 year for conception. At this time, it is recommended to lead and use, which will help you understand on which days the conception of a child is most likely. If pregnancy has not occurred within a year, you need to be treated.
If you have irregular periods, or have not been able to conceive a child within a year, then the doctor prescribes treatment. It is necessary to prepare for the fact that the long-awaited pregnancy may not occur immediately after the start of treatment, but after another 6-12 months.
Why was I prescribed birth control pills if I want to get pregnant?
Birth control pills are the drug of choice (that is, "first aid") in the treatment of polycystic ovaries. Of course, while taking these pills, you will not be able to get pregnant, but after the end of the course of treatment (which lasts from 3 to 6 months), the chances of pregnancy increase significantly. This paradox is due to the fact that hormonal birth control helps to regulate the menstrual cycle, and after the end of the pill, a woman usually ovulates.
Most often, with polycystic ovaries, contraceptive pills with an anti-androgenic effect are prescribed:, etc.
The choice of the drug is carried out by the attending physician in each case. Do not self-medicate.What is ovulation stimulation?
If you have irregular periods with PCOS and are not ovulating (this can be checked with an ovarian ultrasound or ovulation tests), your gynecologist may recommend ovulation induction.
Ovulation induction is a course of treatment during which you take certain hormones in the form of pills or injections on certain days of your menstrual cycle. Thanks to these hormones, the follicle matures in the ovaries, which, bursting in the middle of the menstrual cycle, releases the egg. This process is called ovulation. It is on the day of ovulation that a woman can become pregnant.
What tests should be done before ovulation stimulation?
In order for ovulation stimulation to be effective and still lead to pregnancy, it is necessary that your husband has high-quality sperm, and you have passable fallopian tubes. Otherwise, all treatment will be in vain.
Before inducing ovulation, your husband should have a semen analysis (spermogram) and you should have a (tubal patency test). If everything is in order with these tests, then you can begin to stimulate ovulation.
What medications are used to stimulate ovulation?
To stimulate ovulation in polycystic ovaries (and some other diseases), medications containing hormones are used: Clomiphene (analogues: Clostilbegit, Clomid, etc.), chorionic gonadotropin (hCG, analogues: Pregnil, Horagon, etc.) and, sometimes, Duphaston. Each of these drugs must be taken on certain days of the menstrual cycle, which are specified by your gynecologist.
The most common ovulation stimulation scheme is as follows:
1 stepClomiphene (Klostilbegit, Clomid, etc.) Drink from the 5th to the 9th day of the menstrual cycle. |
2 stepUltrasound of the ovaries and uterus to follow the growth of the follicle and endometrium from the 11-12th day of the menstrual cycle. When the follicle reaches the desired size (more than 18 mm), they proceed to the next stage. Usually, this is the 15-16th day of the cycle. |
3 stepChorionic gonadotropin An injection that is given intramuscularly to rupture the follicle and release the egg. Ovulation occurs 24-36 hours after the injection. |
4 stepSexual intercourse on the day of the hCG injection and the next day. |
5 stepFrom the 16th day of the cycle, drink Progesterone (Dufaston, Utrozhestan, etc.) to maintain the corpus luteum (which helps maintain pregnancy). Usually within 10-12-14 days. On the 17-18th day, a second ultrasound to find out if ovulation has occurred. |
The ovulation stimulation scheme above is approximate and may be modified by your gynecologist depending on the length of the menstrual cycle and ultrasound data.
What if ovulation induction didn't work?
If, as a result of stimulation, the follicles did not reach the desired size and ovulation did not occur, then in the next cycle your gynecologist will increase the dose of Clomiphene. In each new cycle, the doctor will increase the dose of Clomiphene until the follicles grow to the desired size, or until the dose of the drug reaches 200 mg. A further increase in the dose is pointless, since the ovaries are probably resistant (immune) to this drug. But this problem is also solvable. If Clomiphene does not help, then in the first half of the next cycle you will be prescribed a drug from another group, which also stimulates the growth of follicles. This is a menopausal gonadotropin (Menopur, Menogon, Gonal, etc.)
The introduction of the drug begins on the 2nd-3rd day of the menstrual cycle and regularly (every few days) monitor the growth of follicles using ultrasound. When one of the follicles reaches the desired size, ovulation stimulation continues in the usual way, starting from step 3.
Are there any side effects of ovulation stimulation?
Like any other drug effect on the body, ovulation stimulation is associated with some risks. That is why ovulation stimulation should be carried out only under the supervision of a gynecologist, who will be able to notice in time if something goes wrong.
One of the most dangerous side effects of ovulation stimulation is ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome. With hyperstimulation in the ovaries, a large number of follicles ripen at once, which leads to an increase in the size of the ovaries, the appearance of pain and discomfort in the lower abdomen, as well as the accumulation of fluid in the abdominal cavity. Excessive enlargement of the ovaries can lead to their rupture. In order to detect hyperstimulation syndrome in time and prevent serious complications, women undergoing a course of ovulation stimulation should regularly undergo ultrasound examination of the ovaries on the days specified by the gynecologist.
What is Metformin (Siofor)?
Your gynecologist may recommend Metformin (Siofor) as your fertility treatment for PCOS. By itself, Metformin is not a drug for the treatment of infertility, but it has been observed that in women with polycystic ovaries, while taking this medication, menstruation becomes regular, ovulation occurs and pregnancy becomes possible.
Metformin is mainly used in the treatment of diabetes mellitus. But even if you do not have diabetes, this drug can have a beneficial effect on the course of polycystic ovaries.
Among other things, there is evidence that taking Metformin before ovulation induction reduces the risk of ovarian resistance to Clomiphene.
The effect of Metformin on the chance of getting pregnant with PCOS is not yet fully understood, and some doctors recommend taking this drug only if the woman has shown signs of insulin resistance (increased fasting blood glucose). Other doctors prescribe Metformin regardless of blood glucose levels. Time will tell who is right, but in the meantime, more and more data is being published on the effectiveness of Metformin in the treatment of infertility in polycystic ovaries.
There are several studies that have shown the feasibility of taking Metformin not only when planning a pregnancy, but also in the first trimester of a pregnancy that has already begun. It is noted that Metformin reduces the risk of miscarriage in polycystic ovaries. However, the effects of Metformin on the fetus are not yet fully understood, so you should consult with your healthcare provider before you start taking Metformin.
What is laparoscopy for polycystic ovaries?
Laparoscopy is an operation performed under general anesthesia. A distinctive feature of laparoscopy is that the surgeon does not make large incisions on the abdomen and therefore you will not have a memory of this operation in the form of a large scar. All manipulations of the surgeon are carried out through small punctures on the skin of the abdomen with thin instruments.
The very next day after laparoscopy, you will be able to walk, and 1-2 days after the operation, you will be discharged from hospitals.
How can laparoscopy for PCOS help me get pregnant?
One of the methods of treating infertility in polycystic ovaries is the procedure of "drilling" the ovaries. Drilling is performed during laparoscopy and is the removal of sections of the thickened ovarian capsule. Thanks to this procedure, 2 goals are achieved at once: firstly, ovulation becomes possible through the holes in the capsule, and secondly, the level of male sex hormones in the blood decreases (since it is in the capsule that their enhanced synthesis occurs).
How long after laparoscopy can I get pregnant?
As a rule, already in the next menstrual cycle after laparoscopy, you have every chance of becoming pregnant. According to statistics from the American Society for Reproductive Surgery, more than half of women who undergo ovarian drilling become pregnant within a year of the operation, and most have their regular menstrual cycles restored.
Does PCOS increase the risk of miscarriage?
Women with PCOS have a slightly higher risk of miscarriage than women without PCOS. The most likely cause of miscarriage in PCOS is a hormonal imbalance that persists throughout pregnancy.
It is also noted that pregnant women with polycystic disease have a slightly higher risk of developing (diabetes mellitus during pregnancy), increased blood pressure and.
Women who become pregnant on the background of polycystic ovaries require more careful monitoring by a doctor.
Many women perceive the diagnosis of "polycystic ovaries" as a sentence, believing that they will not be able to have children. The probability of pregnancy is low, since a change in the structure of ovarian tissues greatly complicates the processes in it that precede fertilization. However, it is possible to increase the chances of conceiving and having a healthy baby. This requires serious treatment. The sooner it is possible to detect signs of the disease and consult a doctor, the more favorable the prognosis. The best thing is to get rid of the pathology in advance, even when planning conception.
Content:
Is it possible to get pregnant with polycystic
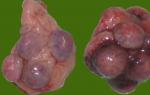
Polycystic ovaries is a pathology caused by hormonal failure in the body. There is a significant increase in the size of the organ and the sealing of its wall due to the formation of many small cysts filled with fluid in it. Characteristic signs of polycystic disease are menstrual disorders and the absence of ovulation.
Hormonal failure worsens, as estrogen production decreases. The level of testosterone from which they are produced increases. This leads to the appearance in a woman of changes in appearance according to the male type. In addition, in 85% of cases with polycystic ovaries, pregnancy and its normal course are impossible.
There are several reasons that dramatically reduce the likelihood of conception:
- Mature follicles cannot go beyond the ovary.
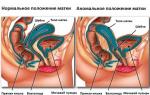
- Even if the egg manages to leave it, it cannot get into the fallopian tube, the entrance to which is blocked by the ovary that has increased several times.
- Due to a decrease in the production of female sex hormones, the normal maturation of the endometrium of the uterus becomes impossible. The fertilized egg is not kept in it and dies, and the woman does not have menstruation.
However, in 15% of cases at an early stage of the disease, a woman can still become pregnant even without treatment, if she has regular enough menstruation, ovulation occurs at least occasionally. In this case, the development of the fetus outside the uterus is sometimes observed. If a woman does not have periods, then she will be able to become pregnant only after special treatment.
Treatment during pregnancy planning
The goal of treatment is to suppress the production of male hormones in the ovaries with the help of antiandrogenic drugs, to restore the ratio of female sex hormones. In this way, it is possible to regulate the menstrual cycle. To stimulate ovulation, drugs based on progesterone are used.
Addition: Paradoxically, in order to cure a woman of infertility, she is prescribed birth control pills (COCs). Their mechanism of action is that they help to normalize hormonal levels.

Mandatory elements of treatment are the correction of body weight and the elimination of inflammatory diseases of the genital organs. If the treatment is ineffective, the woman fails to become pregnant, then surgical treatment is performed (wedge resection of the ovary or incision with a laser knife). Operations are performed using laparoscopy. It becomes possible for the egg to leave the ovary and move it into the fallopian tube for fertilization. The alternative is IVF.
The time of possible conception after the treatment depends on the individual characteristics of the organism, the stage of the disease and the method of therapy. The likelihood of ovulation after surgery is quite high for six months, then it decreases.
However, full recovery of ovarian function usually occurs no earlier than 3 months after surgery, so if a woman becomes pregnant too early, she may have a miscarriage.
Does pregnancy help get rid of PCOS
Such an opinion is erroneous. First, conception in the presence of the disease occurs quite rarely. And secondly, even if the cause of the disease (hormonal failure) disappears, it will be a temporary phenomenon. After 9 months, problems with hormones will resume, and treatment is indispensable. The disease is far from safe, since, in addition to infertility, a host of other consequences are possible, including cancer.
Signs and diagnosis of polycystic disease in pregnant women
Signs of the onset of the disease are found after the onset of pregnancy. At the same time, ultrasound shows that the ovaries are enlarged, their capsules are thickened, they have separate cavities. You can see that there is an embryo in the uterine cavity.
Other manifestations during this period are difficult to notice. Signs such as weight gain, deterioration of the skin, the appearance of acne, hair loss, do not surprise anyone at this time, they are usually explained by the restructuring of the body characteristic of this period.
One ultrasound is not enough, since changes in the ovaries also occur in the presence of inflammatory processes or tumors. To clarify the diagnosis, it is necessary to do a blood test for hormones (the levels of LH and testosterone are increased, and the concentration of progesterone is lowered). A biochemical analysis for glucose and cholesterol is also carried out.

One of the signs of polycystic disease is a decrease in the body's susceptibility to insulin. At the same time, glucose accumulates in the blood.
What are the complications of polycystic disease in pregnant women?
Hormonal failure that occurs with polycystic ovaries complicates pregnancy and entails the following consequences:
- Early miscarriage.
- Termination of development and death of the fetus (missed pregnancy).
- premature birth.
- Heavy bleeding.
- Late toxicosis (increased blood pressure, the appearance of edema). There is a violation of blood flow in the mother's body, hypoxia occurs in the fetus. The consequence may be the appearance of malformations of physical and mental development in the child. There is a danger to the life of the mother and child.
- Gestational diabetes mellitus, which causes impaired functioning of the respiratory, cardiovascular and nervous systems in the newborn.
There is also a significant increase in body weight, which leads to a deterioration in the general well-being of a woman and the progression of a hormonal disorder.
Is there any treatment for pregnant women?
The use of hormonal drugs adversely affects the development of the fetus and causes complications in the health of the child. Therefore, therapy is carried out only after childbirth.
Throughout the entire period of bearing a child, especially careful monitoring of the patient's condition and the development of the fetus is carried out. Blood pressure and blood sugar are strictly controlled. When gestational diabetes occurs, insulin therapy is performed.
Diet plays an important role. In the normal course of pregnancy, dieting for women is not recommended. With polycystic disease, it becomes necessary to control weight to prevent the progression of the disease. It is required to limit the consumption of sweets and fatty foods. It is necessary to include foods rich in fiber in the diet. Vitamins are prescribed to improve metabolism.
Video: How to increase the chances of conception with polycystic. Possible Complications
Comparison of ovaries. Increase.
Polycystic ovary syndrome is a fairly common hormonal disease that significantly reduces the chances of conception and a healthy pregnancy. Some doctors believe that it is basically impossible to get pregnant with polycystic ovaries, since the body does not produce enough hormones necessary for conceiving and bearing a child. However, with a timely diagnosis and proper treatment, PCOS and pregnancy are not at all mutually exclusive.
Scheme of PCOS. Increase.
Every woman faced with this diagnosis will certainly ask doctors the question: is it possible to get pregnant with polycystic ovaries? Pregnancy with this disease is possible, but rather difficult to achieve and requires great effort, both on the part of the expectant mother and on the part of her attending physician. Why is the chance of getting pregnant with PCOS so low?
PCOS is a hormonal disease caused by a malfunction of the endocrine system. With polycystic in the body of a woman, excessive production of male sex hormones begins against the background of a decrease in the production of female hormones necessary for conception. The lack of the female "beauty hormone" (estrogen) leads to the fact that the ovaries do not receive a signal from the pituitary gland to start the cycle. Follicles do not develop, eggs do not mature, and ovulation does not occur.
 Is it possible to get pregnant with polycystic if ovulation still occurred? It is possible, but there is no 100% guarantee of pregnancy. The lack of estrogen leads to the fact that the endometrium - the upper layer of the uterine cavity, which receives a fertilized egg and helps it to gain a foothold there, is not able to fully perform its functions. In a healthy body, in the first phase of the menstrual cycle (a few days before ovulation), under the influence of estrogen, the endometrial layer increases several times, preparing to receive the embryo. If hormones are not enough or their quantity is unstable, the endometrium is not able to fully fulfill its task, therefore, even in the event of successful ovulation and conception, the egg may not be fixed in the uterus, and the pregnancy will be terminated.
Is it possible to get pregnant with polycystic if ovulation still occurred? It is possible, but there is no 100% guarantee of pregnancy. The lack of estrogen leads to the fact that the endometrium - the upper layer of the uterine cavity, which receives a fertilized egg and helps it to gain a foothold there, is not able to fully perform its functions. In a healthy body, in the first phase of the menstrual cycle (a few days before ovulation), under the influence of estrogen, the endometrial layer increases several times, preparing to receive the embryo. If hormones are not enough or their quantity is unstable, the endometrium is not able to fully fulfill its task, therefore, even in the event of successful ovulation and conception, the egg may not be fixed in the uterus, and the pregnancy will be terminated.
In a healthy body, after ovulation, the corpus luteum begins to actively produce progesterone, called the “pregnancy hormone”. He is responsible for the preservation of the fertilized egg and the normal development of pregnancy. With polycystic progesterone, progesterone is often produced in insufficient quantities, which also leads to termination of pregnancy in the early stages.
With polycystic ovaries, they change their anatomy, increasing several times in size, which significantly complicates the release of the egg from them, blocking the normal movement to the uterus.
The volume of examination of a woman at the diagnosis of PCOS
| Recommendations | Laboratory diagnostics | |
|---|---|---|
| Biochemical hyperandrogenism | It is one of the diagnostic criteria. | General testosterone. Testosterone is free. Free testosterone index (total testosterone and sex-binding globulin) |
| thyroid pathology | All women are an exception. | Thyrotropic hormone |
| Hyperprolactinemia | All women are an exception. | Prolactin. At elevated values - macroprolactin |
| Congenital dysfunction of the adrenal cortex (deficiency of 21-hydroxylase) | All women are an exception. | 17-hydroxyprogesterone. Early follicular phase at 8:00 am |
| Androgen-producing tumors | An exception in case of a sudden onset, rapid progression of the clinic, data from instrumental methods about education in the area of the adrenal glands or ovaries. | DHEA-S Testosterone total |
| Hypothalamic amenorrhea/primary ovarian failure | Amenorrhea in combination with a clinic characteristic of this pathology. | FSH, LH, estradiol |
| Pregnancy | Amenorrhea associated with signs of pregnancy. | hCG |
| Cushing's syndrome | Amenorrhea, clinic hyperandrogenism, obesity, type 2 diabetes in combination with myopathy, purple striae, easy bruising. | Cartisol in saliva at 23:00. Cortisol in daily urine. Suppression test with 1 mg dexamethasone |
| Acromegaly | Oligomenorrhea, clinic of hyperandrogenism, type 2 diabetes, polycystic ovaries in combination with headaches, hyperhidrosis, visceromegaly, changes in appearance, limbs. | Insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF-1, somatomedin-C) |
How to get pregnant with PCOS
With polycystic ovaries, you can become pregnant after a course of hormone therapy, which is prescribed by your doctor. As a rule, this therapy cannot completely cure polycystic ovaries, but it is enough to get pregnant and bear a child.
 The goal of hormone therapy is to restore the menstrual cycle. To do this, use oral contraceptives prescribed by the attending gynecologist. They are aimed at regulating the cycle and restoring the level of female hormones in the body. The next step is to stimulate ovulation. It is produced with the help of an antiandrogenic drug - clostilbegit. Next, the optimal days for conception are calculated, which are confirmed by ultrasound of the ovaries (the study should show the formation of a dominant follicle). If ovulation and conception have occurred successfully, the first trimester of pregnancy, the woman is under close medical supervision. It is imperative to continue taking hormonal drugs to compensate for the insufficient work of the corpus luteum and increase the level of progesterone.
The goal of hormone therapy is to restore the menstrual cycle. To do this, use oral contraceptives prescribed by the attending gynecologist. They are aimed at regulating the cycle and restoring the level of female hormones in the body. The next step is to stimulate ovulation. It is produced with the help of an antiandrogenic drug - clostilbegit. Next, the optimal days for conception are calculated, which are confirmed by ultrasound of the ovaries (the study should show the formation of a dominant follicle). If ovulation and conception have occurred successfully, the first trimester of pregnancy, the woman is under close medical supervision. It is imperative to continue taking hormonal drugs to compensate for the insufficient work of the corpus luteum and increase the level of progesterone.
Quite often, doctors recommend supplementing hormone therapy with a special diet aimed at weight loss. PCOS can cause excessive fullness, and male sex hormones actively accumulate in body fat, preventing pregnancy. Reducing the fat layer significantly weakens the manifestation of polycystic, increasing the chances of pregnancy.
How to get pregnant with polycystic ovaries if hormone therapy has not given results? If pregnancy has not occurred within a year of starting therapy, doctors may recommend surgery. The need for surgery may arise in advanced and severe cases of polycystic disease. Modern technologies allow for the removal of cysts through small incisions.
The operation helps to defeat polycystic ovaries for a while, usually long enough to become pregnant. According to statistics, after surgery, pregnancy occurs in about 80% of women. However, even in successful cases, surgery is not a panacea. Often the effect of it lasts about a year or a year and a half, after which the disease can resume. You should make every effort to get pregnant in the allotted time and bear the child without complications and problems.
Alternative ways to get pregnant with PCOS
 Eco scheme. Increase.
Eco scheme. Increase. It happens that polycystic ovaries are not amenable to either conservative or surgical treatment, and then the question arises whether it is possible to get pregnant in other ways? If pregnancy does not occur against the background of anovulation within 1.5-2 years, doctors recommend turning to IVF programs - in vitro fertilization. It will also be an excellent solution for those women who have had to completely remove their ovaries due to PCOS.
IVF requires special attention from doctors, as well as proper preparation of the patient, since with polycystic ovaries, an inadequate response of the ovaries to the drugs used during the procedure is possible. Therefore, the first step towards IVF should be a thorough and in-depth examination of the body, aimed at compiling a picture of the individual characteristics of each case. Only after that, the doctor can prescribe the necessary drugs to prepare the body for fertilization.

In order for the IVF procedure for polycystic ovaries to be effective and safe, it is necessary to assess the possibility of complications in advance. The most common complication is ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome, with polycystic disease, the risk of its development reaches 12%. Also, in patients with polycystic ovaries, there is a high risk of developing multiple pregnancies and subsequent reduction of embryos. Careful preliminary analyzes, proper preparation of the patient and careful observation of doctors throughout the procedure will help to avoid complications and achieve the desired result.
According to statistics, the success rate of IVF with a diagnosis of polycystic ovaries is not lower than with other forms of infertility. This procedure allows you to conceive a child even if you cannot get a “native” egg due to a severe form of the disease or after the removal of the ovaries.
Why is PCOS dangerous during pregnancy?
 Polycystic does not completely exclude conception and pregnancy, it is quite possible to conceive with such a diagnosis, however, the entire pregnancy will be accompanied by constant threats and complications for both the child and the pregnant woman. Those women who decide to become pregnant against the background of polycystic disease should be prepared for the possible consequences:
Polycystic does not completely exclude conception and pregnancy, it is quite possible to conceive with such a diagnosis, however, the entire pregnancy will be accompanied by constant threats and complications for both the child and the pregnant woman. Those women who decide to become pregnant against the background of polycystic disease should be prepared for the possible consequences:
- the constant threat of spontaneous abortion (miscarriage), especially in the early stages;
- in most cases - premature birth;
- danger of missed pregnancy;
- persistent hypertension;
- excessive weight gain;
- the onset of diabetes, its rapid development.
All these complications, threats are caused by one reason - the unstable work of the endocrine system, namely, the lack of female hormones. It is hormones that are responsible for whether pregnancy is possible with polycystic ovaries and how easy and safe it will be.
 Therefore, how to get pregnant with polycystic is not the only issue that worries women. No less questions are raised by the preservation of pregnancy against the background of polycystic disease. Due to hormonal deficiency, it is fraught with many complications, primarily spontaneous abortion. Therefore, it is extremely important to follow all the doctor's recommendations and be extra careful in everything, especially in the first few months of pregnancy. If this item is neglected, you may experience a miscarriage or missed pregnancy. Both options will have an extremely negative impact on the health of a woman, further complicating the path to the desired pregnancy.
Therefore, how to get pregnant with polycystic is not the only issue that worries women. No less questions are raised by the preservation of pregnancy against the background of polycystic disease. Due to hormonal deficiency, it is fraught with many complications, primarily spontaneous abortion. Therefore, it is extremely important to follow all the doctor's recommendations and be extra careful in everything, especially in the first few months of pregnancy. If this item is neglected, you may experience a miscarriage or missed pregnancy. Both options will have an extremely negative impact on the health of a woman, further complicating the path to the desired pregnancy.
Polycystic itself causes excessive weight gain, and during pregnancy this process can accelerate several times. Excess weight creates a huge burden on the body, all the forces of which are spent on the preservation and development of the child, so it is necessary to strictly monitor this indicator. A suitable diet and level of physical activity will be prompted by the attending physician. You can’t pick them up on your own, as this can harm the health of mother and baby.
| Major Complications | Screening |
|---|---|
| Complications of pregnancy: 1. Gestational diabetes 2. Hypertensive disorders | There are no official guidelines and recommendations. Measurement of fasting glucose levels during the first trimester. Monitor blood pressure and possibly uterine circulation in the second trimester. |
| Impaired glucose tolerance | 75 g. OGTT (at baseline) in women with PCOS with the following: - BMI > 30 kg/m2 and/or - Waist circumference > 80 cm and/or - Acanthosis and/or - Family history of type 2 diabetes and/or - Gestational diabetes mellitus in history. - Violations of the menstrual cycle and hyperandrogenism. |
| Risk of cardiovascular disease | Women with PCOS at any age are: - Measurement of waist circumference. - Measurement of blood pressure. - Study of the lipid profile. - Analysis of physical activity. - Nutrition analysis. - Survey on the presence of tobacco dependence. |
| endometrial cancer | Ultrasound or biopsy of the endometrium in women with prolonged amenorrhea. At least four progesterone tests for endometrial hyperplasia. |
Conclusions from the article
- a poorly understood and complex disease. All elements of the endocrine system take part in its development, so the treatment should be just as complex. Refusing treatment under the pretext of preventing unwanted pregnancy is not worth it, as this can have serious consequences for health in general. In addition, there are cases when pregnancy occurred even in the absence of treatment, but they, of course, are extremely rare.
Unfortunately, modern medicine does not know the answer to the question of how to quickly get pregnant with polycystic ovaries. This is an insidious disease that may not cause any inconvenience for many years and be discovered only after several unsuccessful attempts to get pregnant. But early diagnosis significantly increases the chances of successful treatment. But even in this case, the treatment of PCOS requires a lot of time and joint efforts of the woman and her doctor. Read more about the types and methods of treatment in this article! About .
Reading 7 min. Views 2k. Published on 05/19/2018
Polycystic ovaries is a pathological change in the structure of the ovary with the simultaneous formation of many small cysts with liquid internal contents. The organ of the reproductive system itself can also increase, which disrupts its functioning. The main cause of the disease is a hormonal failure, in which the production of male sex hormones is much larger in relation to female ones.
Is it possible to get pregnant with polycystic ovaries, only a doctor can say after a thorough examination, since the answer to the question depends entirely on the degree of organ damage and the characteristics of the neoplasms themselves. In medical practice, pathology is also called polycystic ovarian syndrome (PCOS) or Stein-Leventhal disease. A full restoration of the reproductive system of the female body is possible only after successful treatment under the supervision of a doctor.
Why is it difficult to get pregnant with PCOS
Often, patients learn about the presence of the disease only after an examination prescribed to determine the reasons for the absence of the desired pregnancy.
With polycystic disease, the surface of the ovaries can be covered with multiple hollow tumors with liquid contents, which in turn prevents the full maturation of the follicles and the release of the egg, which is completely ready for fertilization. This leads to a violation of the menstrual cycle and the problematic process of ovulation, which makes pregnancy with polycystic disease almost impossible.
The lack of full and timely treatment can provoke infertility.
There are still chances to become pregnant and successfully bear a fetus with this pathology, but at the same time, under the supervision of a doctor, it is necessary to restore the full functioning of all disturbed systems of the female body. First of all, this concerns the elimination of hormonal dysfunction by dosed intake of special medications. Do not disregard possible problems in the work of the organs of the endocrine system, namely, the thyroid gland and adrenal glands.
The appointment of drugs and the treatment itself is carried out individually in each individual case, since it completely depends on the results of tests and studies, as well as on the degree of damage to the organs of the reproductive system.
What to do?
If there is even the slightest suspicion of a disease, you should seek help from your attending gynecologist, and also be prepared to undergo a series of examinations to refute or, conversely, confirm the diagnosis.
It is important to understand that multiple cysts cannot resolve on their own, so treatment is needed in any case, especially if the patient plans to become pregnant with polycystic disease and give birth to a healthy child.
The treatment procedure depends entirely on:
- the degree of neglect of the pathology (the earlier the disease is detected, the faster and easier it is to get rid of it);
- the patient's age and readiness to clearly follow absolutely all the doctor's recommendations;
- the presence of dangerous comorbidities, such as diabetes or obesity.
In addition to taking medications and possible surgical intervention, doctors strongly recommend that patients establish a healthy lifestyle by changing the diet and abandoning existing bad habits.
What if you don't work?
If you refuse the prescribed treatment or even visit a doctor, PCOS can continue to develop and grow, thereby seriously exacerbating the problem itself. Possible complications include:
- the onset of infertility (the inability not only to bear a child, but also to conceive it);
- profuse uterine bleeding, which seriously undermine the health of the patient and can lead to serious blood loss;
- the possibility of multiple tumors to develop into a malignant formation, which in turn requires more serious and not always successful treatment.
These complications are not an exhaustive list, since hormonal imbalance can lead to a general deterioration in health, the manifestation of excessive sweating, severe headaches and rising blood pressure. That is why the treatment of polycystic ovaries is mandatory, regardless of whether pregnancy is planned in the future.
Treatment Methods
The need to cure polycystic ovaries for the purpose of conception is best entrusted to a competent attending physician. At the same time, even taking any folk remedies should be discussed in advance with a specialist, since self-medication can seriously harm. The choice of a suitable method for treatment is carried out exclusively by the attending physician. This takes into account the stage of development of the disease and specifically the degree of organ damage in polycystic ovaries.
Depending on the patient's health condition, the doctor may recommend:
- lose weight (reduce excess weight and thereby establish normal production of estrogen that accumulates in fatty tissues);
- visit an endocrinologist to normalize blood glucose levels in the presence of diabetes;
- first, conduct hormonal therapy, which will restore the balance, and therefore, establish normal ovulation and the full release of a mature egg for further conception;
- undergo an additional examination to determine the degree of readiness of the reproductive system for the full bearing of the fetus.
Quite often, with scrupulous observance of the basic recommendations of the doctor, patients get pregnant with PCOS and without surgical intervention. If within a year after such therapy, polycystic ovaries and pregnancy are incompatible, the patient is prescribed an appropriate operation.
Conservative treatment
When planning pregnancy and the presence of pathology, treatment is first carried out with certain medications, which are prescribed by the doctor in stages and with mandatory regular examinations. The drugs used can help:
- restore a normal (individual in each individual case) cycle;
- to stimulate the full production of insufficient female hormones by the body and reduce the number of male hormones, due to which there is a complete restoration of hormonal balance;
- normalize the patient's weight;
- improve the functioning of organs and systems involved in the functioning of the reproductive system.
In the process of drug treatment, it is possible to prescribe oral contraceptives, due to which the menstrual cycle is stabilized. The use of the drug Metformin allows you to normalize the level of glucose in the blood.

At the same time, conservative therapy may include a number of special physiotherapeutic methods aimed at restoring the full blood supply to the pelvic organs, taking immunostimulants and mandatory diet therapy.
In total, drug therapy cannot last more than six months. After this period, the medication is canceled and the patient is given the opportunity to try to get pregnant on their own.
Stimulation of ovulation
To become pregnant, the patient can be prescribed oral contraceptives, the substances of which are able to create the necessary conditions for the normal functioning of the ovaries and the full maturation of the egg. Thus, on the day of ovulation (the release of the egg from the follicle), you can become pregnant. In medical practice, this is called the ability to stimulate the ovulatory process. In this case, the dosage and duration of taking the selected drugs is determined solely by the doctor.
Surgery
Surgical intervention is the only true way to treat polycystic ovaries, if within 12 months after the conservative treatment, the woman did not manage to get pregnant, and the reason itself lies precisely in the existing pathology.
As a rule, operations are performed laparoscopically. In this case, it is possible:
- wedge-shaped resections (excision of cysts and affected areas of tissues with a scalpel, with the condition of maximum preservation of healthy tissues and organs);
- decortication, which is carried out using needle-shaped electrodes;
- cauterization, in which the affected areas are excised so that new, completely healthy tissue can form in the incisions made.

With proper preparation for surgery, the risks of complications are minimal and in more than 90% of cases a long-awaited pregnancy still occurs.
Folk methods
The use of traditional medicine recipes cannot be the only or the leading method of therapy, since the pathology itself is hormonal in nature, and uncontrolled intake of infusions and herbal decoctions can seriously harm. Only after consultation with a doctor, patients can use decoctions and infusions prepared on the basis of a red brush, boron uterus, licorice or basil. Permissible dosage, as a rule, is indicated on the packaging of the funds.
Risk of miscarriage
One of the serious dangers when planning a conception while treating a polycystic disease is an increased risk of miscarriage or miscarriage. That is why the entire period of gestation should take place under the regular supervision of a doctor and with the condition of scrupulous implementation of all recommendations and prescriptions. This is especially true of a balanced diet and the avoidance of serious physical exertion.
Today, more and more often you can hear the depressing diagnosis of "Polycystic". The increase in the number of women with this pathology is due to several reasons: improving the quality of diagnostics, a real increase in the incidence, and expanding the concept. Most often, a girl learns about the problem when she has been unsuccessfully planning a pregnancy for some time. Indeed, the symptoms of the disease are ambiguous, and the treatment is ineffective. Is it possible to get pregnant with polycystic ovaries and what should be done for this?
Read in this article
What is the danger of PCOS
The main danger of polycystic disease is that there is no single theory about the causes of its occurrence. Therefore, there is no effective treatment. And polycystic disease ultimately entails a lot of problems for a woman: from a tendency to overweight and menstrual irregularities to infertility and an increased risk of oncological pathology of the genital organs.
Primarily or secondarily, with the onset of puberty, a girl has an imbalance of sex hormones and an incorrect response is formed from the pituitary gland and hypothalamus to them. This can be caused by adrenal hyperplasia and increased secretion of androgens, or directly by problems in the ovaries.
As a result, there is no cyclic production of sex hormones, and this is a prerequisite for the normal maturation of the follicle and ovulation. Soon, a dense sheath of connective tissue forms on the ovaries. Under it, there are many small follicles that once wanted to reach the final stage of their development. The more pronounced polycystic, the more clearly the signs are visible on ultrasound. Sometimes the ovaries can be compared in their structure to honeycombs in bees.
So, the risks of the following diseases are increased significantly in women who have any signs of polycystic ovaries:
- Problems with conception. Women with PCOS often ovulate extremely infrequently, sometimes once a year or not at all. There are also difficulties in the growth of the endometrium and its subsequent rejection.
- Obesity. Both hyperandrogenemia directly and the insulin resistance that occurs with PCOS lead to overweight. Extra pounds complete a vicious circle, increasing the production of estrogens, from which further diseases follow.
- Impaired glucose tolerance, which significantly increases the risk of developing type 2 diabetes.
- Increased likelihood of endometrial and cervical cancer, as well as all kinds of hyperplastic processes (polyps, etc.).
- Also, with polycystic disease, a number of somatic problems gradually appear, such as arterial hypertension and many others.
Symptoms of polycystic
It is possible to distinguish primary polycystic, Stein-Leventhal syndrome, as well as a secondary form of the disease. In the latter case, the pathology is formed in various neuroendocrine conditions - Itsenko-Cushing's disease, adrenogenital syndrome, hyperprolactinemia, etc. The clinical picture of those and others does not have fundamental differences, some one symptom or group always prevails.
With the development of changes against the background of other diseases, one should talk about polycystic ovaries, and not about the syndrome as a whole. Since in practice these concepts are in most cases not distinguished, the frequency of PCOS diagnosis has increased in recent years.
Most often, the symptoms of polycystic disease are detected during puberty. At this point, the girl's menstrual cycle is not completely established until two years after menarche. If the mother and daughter do not pay special attention to this, or the failures are not critical, the pathology is diagnosed when there are problems with conception.
Classic PCOS has a fairly vivid clinical picture, but is much less common. More often you have to deal with the prevalence of some symptoms.
The main symptoms of PCOS include the following:
- . In most cases, this is oligomenorrhea, sometimes. With long breaks between menstruation, the discharge may be sufficient, often with clots. This contributes to endometrial hyperplasia and the formation of polyps inside the uterine cavity. If you do not monitor the state of health and do not carry out treatment, then endometrial cancer may subsequently develop. Another option would be the type of opsomenorrhea.
- Violations of ovulation and the menstrual cycle lead to infertility and the need for various types of treatment for the possibility of conception. When plotting the graph, violations are clearly visible. Therefore, almost all women have the question of how to get pregnant with polycystic ovaries.
- Hirsutism of varying severity. It can be either an inconspicuous mustache above the upper lip, or significant hair on the chin, inner thighs, abdomen, mammary glands, etc.
- In 60% of cases, women with PCOS are overweight. This is due to a change in metabolism with a predominance of androgens, which are converted into estrogen in adipose tissue.
- Insulin resistance caused by increased levels of male sex hormones in the blood. Its level in the blood during the study exceeds the normal values by several times. This can eventually lead to diabetes mellitus, although for a long time the impairment of glucose utilization remains unnoticed.
- Imbalance of sex hormones in the blood according to the results of the tests.
- Enlarged and with many small cysts ovaries.
Watch the video about the disease:
Diagnostics
The diagnosis of PCOS is made when three criteria are met. These include:
- violation of the menstrual cycle of a different nature;
- detection of an increase in male sex hormones in the blood;
- enlarged and altered ovaries according to the results of ultrasound examination.
All other tests and examinations are an addition to the main one for prescribing the most optimal treatment and choosing tactics for pregnancy planning.
Related diseases are polycystic ovaries (only according to the results of ultrasound) without significant menstrual irregularities, as well as idiopathic hyperinsulinemia without an increase in the level of androgens in the blood and any other changes. These two conditions are also often interpreted as PCOS, which is not entirely true.
The question of whether it is possible to become pregnant with polycystic ovaries naturally or whether some additional intervention is necessary (laparoscopy, ovulation induction, etc.) can only be answered after a comprehensive examination and analysis of the data obtained.
Treatment
Such operations allow us to solve several problems at once:
- determine if there are other objective reasons that may affect the likelihood of conception;
- check the patency of the fallopian tubes by performing hysterosalpingography;
- if necessary, fibromatous nodes, cysts, etc. can be removed;
- during laparoscopy in case of polycystic disease, a dense albuginea is partially removed, or incisions are made on the ovaries, or their partial resection occurs, which depends on the clinical situation and the severity of the disease.
The likelihood of pregnancy after laparoscopy increases several times. After the operation, you should start planning for the next ovulation, sometimes already 5-7 days after the intervention. Sometimes, in order to increase the chances of conceiving, additional stimulation of ovulation may be carried out.
Actual questions for expectant mothers
All treatment, especially hormonal, should be prescribed by a doctor. Only a specialist can recommend safe and effective treatment regimens.
But no matter how good the doctor is, patients quite often have questions that they do not have time to get answers during the appointment. These include:
- Is pregnancy possible with PCOS without any treatment or induction?
Yes, there is a chance of conception, but sometimes the efforts are stretched for years and even decades. It all depends on the severity of disorders and hormonal changes. But one should not take such risks, because with increasing age, even reproductive technologies do not give such a high result.
- What is the purpose of hormonal birth control if a woman wants to get pregnant?
The fact is that when taking oral contraceptives for 3-4 months (no longer), subsequently, after cancellation, a rebound effect occurs - a sharp increase in pituitary hormones responsible for the growth and maturation of follicles. Often in such situations, healthy girls give birth to twins, triplets. In polycystic, this acts as a natural ovulation induction.
- Where to start the treatment of polycystic if there is a desire to get pregnant?
Of course, you should consult a specialist. This may be a reproductologist, gynecologist-endocrinologist or a regular antenatal clinic doctor. Already before the visit, you can build a graph of basal temperature for 2-3 cycles, make a spermogram for your husband. All further studies will be prescribed by the doctor as needed.
- Is ovulation stimulation dangerous?
Indeed, constant hormonal tremors are not entirely harmless. Therefore, they must be carried out only under the supervision of a specialist. It is reliably known that with frequent stimulation of ovulation and many IVF attempts, the risk of ovarian cancer increases. It also affects the work of all organs of internal secretion (thyroid and pancreas, adrenal glands, etc.). They react to hormonal shocks and mammary glands by increasing the frequency and severity of mastopathy.
- What are the other risks in women with PCOS during pregnancy?
Women with some hormonal disorders, including PCOS, are at risk for miscarriage (higher likelihood of non-developing pregnancy and premature birth), anomalies in labor, pathology in the fetus, infectious complications, the development of gestational diabetes mellitus and preeclampsia of varying degrees, bleeding (placental abruption, etc.) Therefore, they should be under medical supervision at all times.
Polycystic disease is a serious disease, the cause and mechanisms of which have not been fully established. This pathology, in addition to increasing the risk of developing other gynecological problems, reduces the likelihood of independent successful conception and subsequent gestation in women.
They are more likely than others to face infertility problems. Only a specialist after examination can determine the true cause and prescribe the correct treatment (ovulation stimulation, laparoscopy, etc.). But sometimes even they do not give an unambiguous answer whether it is possible to cure polycystic ovaries and get pregnant in a particular situation.
Similar articles
So what effect will the drug have on PCOS? ... How to cure polycystic ovaries, what will help better ... Is it possible to get pregnant with polycystic ovaries: how ...