What does herpetic stomatitis look like in children. Herpetic stomatitis in a child: acute and chronic form. Latent period or mild form
One of the most common infectious inflammation affecting the oral mucosa in children is herpetic stomatitis. Almost all parents have to deal with this disease in their baby, and the most important thing is to take up treatment in time to prevent the transition of acute herpes stomatitis in a child into a chronic phase.
Acute herpetic stomatitis in children is caused by the herpes virus, which affects the oral mucosa and provokes a syndrome of general intoxication. The most vulnerable group of children in the face of the disease are children aged from one to three years, for whom infection with herpes is actually the first contact with this pathogen.
Acute herpetic stomatitis in children is caused by the herpes virus.
The child's body at this age is especially susceptible to many infectious diseases, including the herpes virus, which is associated with a number of objective reasons. First, it is about specific features the structure of the body of such a small child, which is complemented by the loss of the immunity inherited transplacentally from the mother.
It is worth adding to this the fact that the baby’s own cellular immunity is not yet able to produce enough antibodies to fight viruses, which creates a favorable basis for pathogenic invasion.
Important! If a child during the first year of life was forced to artificial feeding He is also at risk.
In addition to the acute form, herpetic stomatitis can also be chronic, giving relapses from time to time. Having been ill with this disease, most babies acquire immunity to it and simply become carriers of the virus, but treatment should be taken very seriously: those whose disease has become chronic may subsequently suffer from diseases of the central nervous system or internal organs.
Causes

The main source of infection of the child with herpetic stomatitis are other children - sick or carriers.
The main source of infection of a child with herpetic stomatitis are other children - sick or carriers, since this virus is very contagious. The route of transmission can be contact or airborne. In the first case, the pathogen is transmitted through contact healthy child with an infected person or his things, toys, personal hygiene items.
In the second case, the transmission of herpes occurs after a sick baby coughs or sneezes next to a healthy one, but, one way or another, the infected child must be isolated until he is fully recovered. Unfortunately, non-compliance with this principle leads to a consistently high level of the epidemiological situation in relation to herpes, and most often a child becomes infected with it in kindergarten or polyclinic with a large congestion of children.
There are a number of factors that suppress the resistance of the child's body and increase the risk of the disease:
- hypothermia or overheating;
- prolonged exposure to solar radiation;
- avitaminosis;
- long courses of antibiotics (or immunosuppressants);
- ARVI diseases;
- stress.

The virus that enters the body first of all begins to actively multiply, infecting the epithelium and submandibular lymph nodes.
The virus that enters the body first of all begins to actively multiply, infecting the epithelium and submandibular lymph nodes, after which it enters the internal organs with the bloodstream. There is a sharp increase in its activity, which is reflected on the skin and mucous membranes in the form of symptoms typical of herpes.
Note! In case of an unfavorable development of events, the virus, having a neuroinvasive nature, can permanently gain a foothold in the body, hitting nervous system and causing the child to have meningitis or encephalitis.
Clinical picture
Usually, children suffer from herpetic stomatitis easily or relatively hard, although there are also complicated cases. Distinctive feature of this disease is the presence of a prodromal period - the time between the incubation period and the course of stomatitis itself. The virus can develop asymptomatically in the body of a child for up to two weeks, after which the first warning signs diseases: sleep and appetite disorders, capriciousness or restlessness.
Most parents, if they attach importance to this, then look for the cause in more simple and everyday factors, thereby losing precious time, during which it would already be possible to begin treatment of herpes stomatitis in children. Following the described symptoms, more severe manifestations are added:
- nausea (up to vomiting);
- refusal of food;
- noticeable swelling of the lymph nodes in the neck.

Usually, children suffer from herpetic stomatitis easily or relatively hard, although there are also complicated cases.
At the end of the prodromal period, the disease reaches its peak of development, causing characteristic herpetic eruptions both on the oral mucosa and on the lips (sometimes cheeks). Initially, this rash looks like small vesicular vesicles with thin walls and cloudy liquid inside. Having burst, they form erosive defects (or aphthae, more characteristic of aphthous stomatitis), which are small whitish ulcers that are very painful - especially when eating.
Inevitably, fever also occurs, accompanied by a high temperature of up to 40 degrees, as well as typical catarrhal symptoms such as a runny nose and cough. Sometimes conjunctivitis and are added to them, during which the gums swell and turn red (including bleeding).
The vesicular stage of stomatitis lasts about three to five days, and the erosions and ulcers after them heal on their own, leaving no traces. A complication of the disease with another infection can lead to suppuration of ulcers on the skin or in the mouth, which makes healing much more difficult.
Additional Information. With proper treatment and strong immunity, the child will cope with herpetic stomatitis in a week, otherwise recovery will have to wait two to three weeks.
Treatment

The most revealing will be blood and saliva tests, as well as a smear.
Before starting treatment herpetic stomatitis in children, you must first make a correct diagnosis, on which the set of necessary therapeutic measures will depend. Apart from visual inspection and interviewing parents, the doctor will need to conduct a series of tests to confirm the diagnosis. The most revealing will be blood and saliva tests, as well as a smear made in the oral cavity - they will distinguish this type of stomatitis from its other varieties, as well as from diseases like scarlet fever, diphtheria, herpetic sore throat and other infectious diseases.
In severe cases, the baby may need hospitalization, but usually everything is limited to providing proper home care based on several important principles:
- bed rest;
- plentiful drink;
- isolation from healthy children.
With regard to drug treatment, it is determined by the severity and variety of symptoms. To reduce the temperature, the doctor may recommend Paracetamol or Ibuprofen, to combat the herpes virus are effective on early stages diseases will be Acyclovir or Interferon. Puffiness is best eliminated with antihistamine drugs like Suprastin, Clemastine or Cetirizine, and to strengthen general health need to use immunocorrectors.

Puffiness is best eliminated with antihistamines.
Of course, you will need the organization and local treatment carried out by the dentist (or), which will consist in treating the oral mucosa with special antiseptic and antiviral drugs. If necessary, the use of local anesthetics and rinsing of the mouth is also allowed. herbal infusions. The areas of the mucous membrane affected by erosion will need to be removed, for which the child will be prescribed proteases that eliminate necrotic plaque.
The subsequent healing of the epithelium will be faster if the baby takes vitamin complexes and vegetable oils. Finally, physiotherapeutic measures such as ultraviolet radiation or infrared radiation, which have decongestant and vasodilating effects, will also be useful.
Prevention

The best prevention is to strengthen the immune system.
The main thing that parents need to remember is to avoid infecting the baby with a virus. herpes simplex impossible, since its prevalence is too high, even if for the most part the source of the disease is simply the carriers of the infection. For this reason, strengthening the general immunity of the child comes to the fore, for which doctors recommend resorting to regular exercise and hardening. It will not be superfluous to avoid the child being in enclosed spaces among a large number of people who can potentially transmit the virus (this is especially true in spring and autumn).
In general, with acute herpetic stomatitis in a child, the prognosis is favorable if the treatment was started on time and the disease did not worsen. secondary infection. The recovery process usually takes about 10-15 days, after which the baby receives immunity to this pathogen.
Parents must understand that they are responsible not only for their child, but also for those children with whom he contacts in nurseries. educational institutions, therefore, they are obliged to notify the other parents if their baby is sick. This will prevent the general spread of the infection and will make it possible to start treatment for other children in time.
Reading time: 10 minutes
Your child began to act up and eat poorly, and a rash in the form of small bubbles appeared in the mouth? There is a high probability that this viral infection, which causes not only inflammatory processes in the oral cavity, but also general intoxication organism. Herpetic stomatitis in children is a common disease that requires timely diagnosis, proper complex treatment.
What it is
Herpetic stomatitis is infection oral cavity, which occurs when the child's body first comes into contact with the herpes simplex virus of the first type. This infection develops in children with weakened or unformed cellular and specific immunity, therefore it is more common between the ages of six months and three years.

Depending on the nature infectious process allocate acute and chronic recurrent types of herpetic stomatitis in children. A child who has had an acute illness may become an asymptomatic virus carrier or have a chronic form of this infection. To understand in more detail the features of the course, as well as the treatment of herpetic stomatitis in childhood, watch the video with the professor of the department therapeutic dentistry S.Yu. Stakhova.
Causes and symptoms of herpetic stomatitis
Herpes simplex virus type 1 (HSV-1) - the causative agent of the disease, enters the child's body mainly through the skin, mucous membranes upon contact with a sick person or virus carrier, by household or airborne droplets. After entering the body, it begins to function inside the cells, actively multiply, using the resources and components of the cells. The activation of the manifestations of symptoms is associated with intensive reproduction of the virus, which is manifested by a mild, moderate or severe form of the disease.

Clinical manifestations of herpetic stomatitis in children occur if there are factors that reduce resistance:
- weakened immunity;
- abrupt change temperature regime, overheating or hypothermia;
- injuries of the oral cavity, lips;
- non-compliance with sanitary and hygienic rules;
- stress, nervous strain.

Mild symptoms:
- the child becomes lethargic, capricious, there is a slight increase in temperature;
- redness, swelling of the oral mucosa, inflammation of the gums;
- swollen lymph nodes;
- not a large number of painful vesicles, sores in the mouth.
In a state of moderate severity, it is noted:
- temperature rise to 38-39 degrees;
- weakness, nausea, chills, headache;
- an increase in the submandibular, cervical lymph nodes;
- inflammation and swelling of the gums, oral mucosa;
- the appearance of a rash in the form of bubbles on the mucous membranes of the mouth, tongue, cheeks, lips, skin around the mouth.

The severe form of the disease is characterized by:
- high critical temperature body;
- severe general condition, signs of severe intoxication;
- severe headache, muscle pain;
- nausea, vomiting;
- lowering blood pressure, heart rhythm disturbance;
- lymphadenitis of the cervical, submandibular lymph nodes;
- multiple painful rashes in the form of vesicles, erosions that spread to the area around the mouth, wings of the nose, eyelids, conjunctiva of the eyes.
Bubbles, characteristic of stomatitis, appear in a group, tend to merge. After the herpetic vesicle bursts, a focus of painful erosion is formed. If there are no complications, then scars at the site of the affected areas of the skin do not form. Such damage to the mucous membranes and skin is typical only for this disease, therefore it is important diagnostic sign. In the photo you can see a rash typical of herpetic stomatitis.

Diagnosis of the disease is based on the analysis of symptoms, clinical manifestations, as well as cytological examination scrapings of the contents of the bubble or erosion. The duration of the active phase of the disease depends on general condition child, timeliness medical measures and severity of the disease. With a mild form of herpetic stomatitis, treatment takes up to 7 days, with an average form - several weeks, and a severe form requires immediate hospitalization. The duration of the child's symptomatic period will depend on the effectiveness of treatment measures.
Treatment of herpetic stomatitis in children
Doctors recommend that at the first signs of a disease in a child, immediately contact a specialist. You will probably need to consult a pediatrician, dentist, neurologist, and in severe cases, hospitalization. The earlier assigned effective therapy, the easier the course of the disease will be and the less the risk of developing severe complications.

Herpetic stomatitis in children is treated comprehensively, in several areas:
- antiviral therapy. It is aimed at neutralizing the causative agent of infection, carried out with the help of drugs in the form of tablets, ointments for local application.
- Anti-inflammatory and antihistamines. Assign to relieve the symptoms of intoxication, reduce body temperature.
- Increasing the body's resistance and strengthening the immune system with the help of vitamin and mineral complexes, immunostimulating drugs.
- To accelerate healing, relieve inflammation and pain, gels, ointments with an analgesic effect, as well as drugs with keratoplastic properties are prescribed.
How and what to treat
In case of herpetic stomatitis in children, drug therapy is prescribed by the attending physician, taking into account the severity of the disease, condition, age of the child. Parents are advised to:
- provide the baby with a plentiful drink with a comfortable temperature, a balanced diet;
- avoid food that can injure the affected areas;
- it is advisable to feed the baby 3-4 times a day, and in between do not give additional food, so that the time interval necessary for the effects of drugs is observed;
- follow the rules of hygiene and oral care to avoid adherence bacterial infection;
- provide a sick baby with separate dishes, toys;
- treat the affected areas several times a day in accordance with the doctor's recommendations;
- do not self-medicate with the help of information from forums on the Internet and consult a doctor at the first sign of illness.

Treatment of the oral cavity in a child with herpetic stomatitis:
- Rinsing. Toddlers do not know how to rinse their mouths on their own, so the mouth is irrigated by gently tilting their heads over the basin. Older children can rinse their mouths with herbal decoctions, saline solution or medicines that have been prescribed by a pediatrician.
- Treatment of areas of the mucous membranes of the mouth and skin affected by stomatitis. After rinsing, it is recommended to treat healthy and damaged areas with antiviral, analgesic or wound healing agents. This is done with a cotton swab. It is necessary to carefully lubricate the affected areas, trying to do it carefully so that the child does not hurt.
- Gadgets. Applications and lotions for stomatitis can be done if herpetic crusts form, and also to prolong the action medicinal product. Procedures with herbal remedies, analgesic drugs help relieve pain, inflammation. At the healing stage, it is recommended to use sea buckthorn oil, rosehip oil, oil solutions vitamins A and E to speed up healing.
During the period of the disease, it is necessary to follow the appointments, the rules for caring for a sick child, because the herpes simplex virus is highly contagious and can actively spread. With herpetic stomatitis, drugs are prescribed various forms release, pharmaceutical action. The sooner treatment is started, the more likely it is that the disease will pass without complications and in a mild form, so it is important to contact a pediatrician or dentist in a timely manner. We provide you with an overview of pharmaceuticals recommended by experts.
Review of pharmaceutical preparations

Holisal
- Ingredients: active substances choline salicylate and citaclonium chloride, auxiliary components.
- Action: anti-inflammatory, analgesic, antiviral and antifungal.
- Application: in case of herpetic stomatitis, children after 1 year are prescribed topically 2-3 times a day. It is recommended to squeeze 0.5 cm strips of gel onto a clean finger, gently apply with light massaging movements to the area of the child's oral cavity affected by stomatitis. As an analgesic, it is used before meals, as an antimicrobial and anti-inflammatory agent - after breakfast, before bedtime.
- Price: from 260 rubles (10 g)

Viferon
- Compound: active substance interferon alpha-2b human recombinant.
- Action: antiviral and immunomodulatory.
- Application: at the first signs of stomatitis, a strip of gel 0.5 cm is squeezed onto a spatula or cotton swab, applied to a pre-dried surface 4-5 times a day for 6-7 days.
- Price: from 130 rubles (12 g)
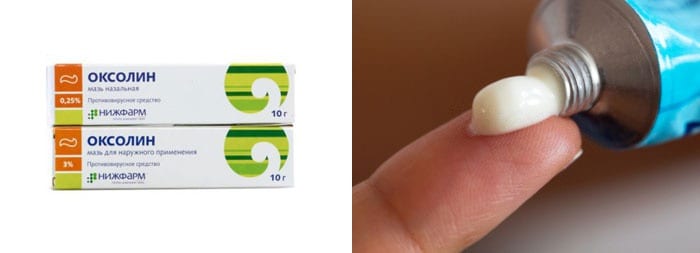
Oxolinic ointment 0.25%
- Ingredients: active substance oxolin.
- Action: antiviral.
- Application: for herpetic stomatitis, it is recommended only for children over 2 years old. Apply with a cotton swab or bandage 3-4 times a day on the affected areas of the oral cavity, lips for a week.
- Price: from 20 rubles (10 g)

Acyclovir
- Action: antiviral.
- Application: for the treatment of herpetic stomatitis, children over 2 years old are prescribed 1 tablet 4-5 times a day, under 2 years old - half the dose. The cream is applied to the skin 5 times a day for 5-10 days.
- Price: tablets 200 mg No. 20 - from 40 rubles, cream 5% 2 g - from 50.

Zovirax
- Compound: active substance acyclovir.
- Action: antiviral.
- Application: for herpetic stomatitis, children over 2 years old are prescribed one tablet (200 mg) 4 times a day or two tablets 2 times a day, children under 2 years old receive a half dose. Intravenous injections are used at a dosage of 10 mg / kg with an interval of 8 hours. Cream for external use is applied to the affected areas 4-5 times a day at the first symptoms of the disease.
- Price: tablets 200 mg No. 25 - from 780 rubles, cream 5% 5 g - from 185 rubles.

Immunal
- Ingredients: active ingredient - plant extract echinacea purpurea.
- Action: stimulator of nonspecific immunity, increases resistance to infectious diseases, has an antiviral effect.
- Application: children from 6 to 12 years old are recommended to take 1.5 ml of the solution with a small amount of liquid 3 times a day or 1 tablet 2-3 times a day for 10 days.
- Price: tablets No. 20 - from 210 rubles, drops of 50 ml - from 220 rubles.

Oil solutions A and E
- Ingredients: vitamins A (retinol), E (tocopherol).
- Action: keratoplastic, accelerate the regeneration and epithelialization of tissues.
- Application: local. The areas affected by herpetic stomatitis are lubricated with an oily solution of vitamins A or E several times a day for 5-7 days.
- Price: vitamin E 25% oil solution - from 120 rubles (100 ml), vitamin A - from 2 rubles per 1 ampoule (10 ml).
Folk remedies
Vegetable oils, decoctions in the form of lotions, applications, rinses relieve swelling of the mucous membrane and inflammation, pain, promote healing and regeneration. But folk remedies treatment of herpetic stomatitis cannot be an alternative to antiviral therapy. Before taking herbal remedies or using traditional medicine methods, consult your doctor. Here are a few recipes that experts recommend using along with others. therapeutic activities in the treatment of this disease.

Decoction of chamomile. It has anti-inflammatory and analgesic action. To prepare a decoction 4 tbsp. chamomile flowers are poured with 1.5 liters of water and boiled for 5-10 minutes. After 45-60 minutes, filter. Doctors recommend using it for herpetic stomatitis several times a day for rinsing or irrigating damaged areas of the skin, mucous membranes. oral cavity.
A decoction of calendula flowers. Calendula relieves swelling and inflammation. To prepare a decoction 1 tbsp. flowers pour 1 cup boiling water, cover with a lid. Withstand 10 minutes on low heat and filter after 45-60 minutes. it remedy is intended for rinsing and irrigation of the oral cavity, and can also be used for applications on areas with herpetic vesicles, erosions.
Kalanchoe juice and pulp of aloe leaves. Kalanchoe juice has powerful anti-inflammatory and bactericidal properties, and in case of herpetic stomatitis it is also used as an analgesic. The pulp of aloe leaves relieves inflammation, prevents the attachment of a bacterial infection and promotes tissue regeneration. The funds are applied to the foci of the disease in the form of applications several times a day for 15-20 minutes.
Vegetable oils of wild rose and sea buckthorn. They contain unsaturated fatty acid, complexes of vitamins and microelements. These natural oils relieve pain, inflammation, irritation and promote regeneration and healing. The keratoplastic effect of sea buckthorn and wild rose is especially important, therefore, at the stage of recovery, it is recommended to lubricate herpetic erosions or apply in the form of applications to the affected areas 1-2 times a day.
Solution chicken protein and water. Crude protein is mixed with 0.5 l boiled water, mix thoroughly and use for rinsing. Helps with a deficiency of lysozyme in the saliva of a sick child and has analgesic action. Use several times a day as a rinse after meals.
Water-soda solution. Add a dessert spoon of baking soda to a glass of boiled water and mix thoroughly. The remedy is relevant at the first signs of herpetic stomatitis in a child, when there is swelling and redness of the oral mucosa. It is recommended to rinse the mouth with it 3-4 times a day or irrigate the inflamed areas with this liquid.

Prevention of herpetic stomatitis in children
Preventive measures are to avoid contact of the child with patients and virus carriers in active phase diseases. Also, doctors recommend observing the rules of oral hygiene and, if there are traumatic factors, eliminate them in a timely manner. Good nutrition and increased body resistance can minimize the risks of complications.
If your child has been ill with herpetic stomatitis, he becomes a virus carrier, so relapses are not ruled out. To avoid the transition of the disease into a chronic form, it is important to adhere to the general principles of prevention and take measures to correct immunity.

Video: How to recognize stomatitis in a child-Doctor Komarovsky
We offer you to watch the recording of the program “School of Doctor Komarovsky”, dedicated to the topic stomatitis. A well-known pediatrician will teach you to recognize the signs of the disease and give you recommendations for treatment.
Herpetic stomatitis in children is not such a simple disease as it might seem at first glance. In terms of severity, herpetic stomatitis in a child is divided into mild, moderate and severe. For Get well soon and comfortable treatment this disease, it is necessary to understand the causes of damage to the oral mucosa, and to make sure that the disease is correctly diagnosed.
Herpetic stomatitis in children is primarily severe and dangerous, especially in infancy. This is an extremely thorough infectious disease, in which, in addition to severe damage to the entire mucous membrane in the oral cavity, it can directly excite characteristic symptoms limiting joint intoxication human body, serious malfunctions of the immune and nervous systems.
Herpes in the mouth, which is a common pathogen somatic disease, long time doesn't let you know. Most of the infection infection usually occurs at a fairly early infancy.
Activation of herpes stomatitis in a child usually occurs with a significant deficiency of immunity. The virus begins to multiply successfully, in connection with this, the body temperature increases significantly, acute inflammation in the area of the mucous membranes of the oral cavity, painful, bleeding ulcers form on the surface, the increase in submandibular lymph nodes is constantly increasing.
The most significant causes of herpetic stomatitis are usually:
- previous infectious diseases;
- antibiotic treatment;
- a significant decrease in immunity;
- acute lack of vitamins, lack of macronutrients and microelements in the child's body;
- very close contact with infected herpes stomatitis;
- actual problems of the immune status;
- severe injuries and purely mechanical serious damage to the oral mucosa;
- irrational baby food;
- insufficient intake of water and any other liquid, resulting in complete drying of the oral mucosa;
- bad, improper care behind the child's mouth.
If the mother has a herpes infection, then the newborn baby can become infected with the virus during childbirth. In young children, stimulation of the virus actively promotes frequent illnesses.
Herpes stomatitis in children is a contagious disease and the ability to be transmitted increases significantly with periodic exacerbation. Herpes without difficulty, repeatedly transferred to absolutely healthy areas of one's own body.
Symptoms
A gradual underlying onset is the most significant characteristic of herpetic aphthous stomatitis in children. The incubation stage of the further formation of the disease is usually modified in the range from 2 days to 21 days. Let's look at the symptoms of herpetic stomatitis by severity.
Easy degree:
- transient inflammation of the gums, at the same time their redness and swelling;
- a relatively small increase in body temperature;
- a small number of rather painful ulcers;
- lymph nodes are enlarged.
Average degree:
- rather high increase in body temperature;
- persistent presence of significant inflammatory changes on the mucous membrane in the area of the oral cavity;
- immense headache, general lethargy, vomiting, nausea;
- rashes in the form of bubbles, usually located on the gums, on the tongue, in the area inner surface cheeks and around the mouth.
Severe degree:
- a sharp violation of the general well-being of the child;
- significantly, to critical levels, the baby's body temperature increases;
- suddenly there are powerful headaches and muscle pains;
- vomiting and nausea inevitably begin;
- cervical and submandibular lymph nodes increase;
- the rash becomes very much, it begins to spread actively around the perioral region, on the eyelids and on the conjunctiva.
By characteristic features, the course of herpetic stomatitis in children is clearly divided into two forms:
- Acute - usually occurs suddenly, actively formed, somatic signs of herpes stomatitis are clearly expressed.
- Chronic - recurrent form of herpetic stomatitis can last for many years and periodically worsen with a long absence of the necessary treatment.
What does herpetic stomatitis look like in a child
In the photo below you can see different localization herpetic stomatitis, which is also called herpetic gingivostomatitis.
Duration of herpetic stomatitis
The average duration of herpetic stomatitis in children is from several days to three weeks. It all depends on the complexity of the degree of the disease:
- with a mild degree of the disease, the symptoms begin to disappear after three to four days;
- with an average degree, the disease can last up to two weeks;
- with a severe degree of the disease, treatment can be delayed for several weeks. AT this case the child needs to without fail hospitalize.
Of course, the duration of the disease may directly depend on proper treatment and on how timely it was started. Therefore, if herpetic stomatitis is detected in children, treatment should be started as early as possible.
Diagnostics
Based on a visual examination of the patient, analyzing the main causes of the disease, examining the symptoms of the disease, examining tests, experienced specialist can easily make the correct diagnosis of herpetic stomatitis in children.
Based on the surveys correct setting diagnosis includes:
- cytological examination of scrapings from the infected area of the oral cavity;
- polymerase study chain reaction;
- examination of immunofluorescent reaction;
- virological examination;
- for the projective identification of this virus, immune serum can be widely used.
Infection with herpetic stomatitis must be differentiated from fungal, drug-induced, and also allergic stomatitis; from herpetic sore throat; specific infectious diseases such as scarlet fever, chickenpox, diphtheria, measles; erythema multiforme exudative migratory.
Treatment
At the first signs of the disease, you should immediately contact the pediatric clinic for a pediatrician. Given the severity of the disease, it is possible that the attending physician will refer you for a consultation and examination to a dentist and a neuropathologist. Perhaps hospitalization will be scheduled.
Treatment of herpetic stomatitis in children is carried out in a complex manner, in such areas as:
- Antiviral drug therapy. It is aimed at the complete neutralization of the established causative agent of an infectious disease. It is actively implemented with the help of drugs in the form of tablets, injections and ointments for topical use.
- Anti-inflammatory and antihistamine drugs. It is advisable to be prescribed to relieve signs of intoxication, as well as to reduce body temperature.
- A significant increase in the growth of the resistance of the human body and the strengthening of innate immunity. With the help of immunostimulating medications and vitamin and mineral preparations.
- For maximum speed of final removal inflammatory process, healing and pain reduction, specialized gels, analgesic ointments, keratoplastic drugs are usually prescribed.
During herpetic aphthous stomatitis in a child, drug therapy is determined and prescribed only by the attending physician, taking into account the form of the disease, the age and condition of the baby. In addition, the treatment of herpes stomatitis in children may differ from the treatment in adults and possible individual characteristics. Therefore, it is better to seek help from a specialist.
The standard of treatment for herpetic stomatitis is that the attending physician consistently prescribes medications diversified different forms serial production of pharmaceutical exposure.
Preparations for the treatment of childhood herpetic stomatitis
An overview of pharmaceuticals that the child may be treated with, following the advice of qualified professionals:
- Paracetamol and Ibuprofen - to lower body temperature and for pain relief;
- Mebhydrolin and Clemastin, as well as Hifenadin - antihistamines for the complete removal of edema;
- Acyclovir and Interferon - systemic therapy aimed at eliminating the actions of factors that cause herpetic stomatitis in children;
- Thymus extracts, lysozyme and gamma globulin injections are prescribed for the purpose of immunocorrection;
- Vitamins C, B-12, fish fat- tonic, high-calorie drugs for recurrent herpes stomatitis in children.
From the initial stage of infection with herpetic stomatitis in children, it is necessary to adhere to the prescriptions of the treatment plan for a sick child, due to the fact that the virus has a rather high contagiousness, therefore it can easily spread actively and vigorously.
- effectively treat the affected area of the oral cavity in accordance with the recommendations of the attending physician;
- provide a sick child with individual household items and toys;
- strictly adhere to the rules of personal hygiene and oral care, in order to avoid adding a bacterial infection;
- it is mandatory to adhere to the diet and taking medications;
- consistently provide the child with a balanced diet and plenty of fluids;
- It is not recommended to use heating agents.
Oral treatment
- Treatment of the oral cavity can be done by rinsing decoctions from medicinal herbs, water-salt solution, medications prescribed by the attending physician.
- Toddlers who are not yet able to independently engage in rinsing their mouths should carefully irrigate the oral cavity by tilting the child's head over a large container.
- After rinsing the mucous membrane affected by herpetic stomatitis, it is necessary to treat both damaged and healthy areas with antiviral or analgesic, as well as wound healing drugs. This is usually done with a cotton swab. It is necessary to carefully, very carefully, painlessly smear the affected points.
- In the formation of herpetic crusts and to prolong action medications, it is necessary to make lotions and applications. Processes of treatments with analgesic drugs or herbal remedies relieve pain and inflammation.
- And also at the stage of healing, it is strongly recommended to additionally use sea buckthorn oil, oil solutions of vitamins A and E, to significantly accelerate healing.
Summing up, it is worth noting that herpetic stomatitis lends itself very well to complex treatment. Especially if treatment is started on time. Do not forget about the treatment of wounds not only by rinsing, but also by lotions and applications. Well, for pharmacological treatment, we strongly do not recommend going to the pharmacy and choosing medicines on your own or trusting the opinion of a pharmacy employee, it is better to show the child to the doctor.
From this article you will learn:
- what does stomatitis look like in children: a photo in the mouth,
- symptoms and treatment
- children's stomatitis how to quickly cure at home.
The article was written by a dentist with more than 19 years of experience.
Stomatitis in children is of 3 main types -
1)
acute herpetic stomatitis,
2)
chronic recurrent herpetic stomatitis,
3)
chronic aphthous stomatitis.
Depending on what form stomatitis develops in children, the symptoms and treatment will be very different, because. depending on the cause of stomatitis (herpes virus, bacteria, allergies, immune pathology), completely different drugs are prescribed. Therefore, if you decide to cure stomatitis in a child at home, carefully read the symptoms of different forms of stomatitis in order to choose the right type of treatment.
Forms of stomatitis of moderate severity (especially those not accompanied by severe symptoms of intoxication and dehydration) can be successfully treated independently with topical agents in the oral cavity. But for treatment severe cases not only the intervention of a doctor may be required, but also possibly systemic drug therapy and even hospitalization.
1. Herpetic stomatitis in children: symptoms and treatment
herpetic viral stomatitis in children has 2 forms of the disease. Firstly, there is acute herpetic stomatitis, which develops during primary infection with the herpes virus (i.e., the very first case of the disease). This acute form of stomatitis is typical only for very young children, and most often occurs in a child aged 9 to 28 months.
Herpetic stomatitis in newborns/infants is rare. This is due to the fact that at this age in the child's blood there are still quite a lot of antibodies specific to the herpes virus, obtained during pregnancy with the mother's blood. Therefore, it rarely occurs in children younger than 3 months. The second form of the disease is chronic recurrent herpetic stomatitis (i.e., all repeated cases).
a) Acute herpetic stomatitis -
As we said above, the primary case of herpetic stomatitis develops in children most often between the ages of 9 and 28 months. This is due to the fact that at this age, antibodies specific to the herpes virus, obtained from the mother, gradually disappear in the child. Important point here lies in the fact that if the primary case of the disease develops against the background of still enough high content antibodies to the herpes virus received from the mother - the symptoms of stomatitis will be very weak.
That is why primary herpetic stomatitis in 90% of children proceeds almost imperceptibly, and many parents generally take such symptoms as teething symptoms. However, when primary herpetic stomatitis in children develops against the background of already sufficient low content in the blood of maternal antibodies to the herpes virus - the disease is acute (with severe symptoms of intoxication).
Herpetic stomatitis in children: symptoms
the duration of clinical manifestations is usually 10-14 days. At the beginning, weakness, malaise, headache, muscle pain appear, which is associated with intoxication of the body. The temperature (depending on the severity of the disease) by the end of the first or second day can be from 37.5 to 41 degrees. Regional lymph nodes (especially submandibular) are enlarged, painful.
Stomatitis in children: photo in the mouth
Please note that when stomatitis is formed on the tongue of a child, herpetic eruptions / ulcers can be not only on visible surfaces (for example, on the back and tip of the tongue), but also on the sides, as well as on bottom surface tongue (Fig. 6).
Painting in the mouth
–
the mucous membrane of the oral cavity becomes bright red, edematous. During the first 1-2 days from the onset of prodromal symptoms (malaise, fever, etc.), rashes of small bubbles appear on the mucous membrane of the lips, cheeks, tongue, palatine arches (Fig. 1) - approximately the size of a millet grain. Bubbles are usually arranged in groups. The vesicles are first filled with transparent contents, but then it becomes cloudy, and after about 2 days the vesicles burst with the formation of bright red ulcers.
The resulting ulcers very quickly become covered with a whitish or yellowish fibrinous coating (Fig. 2-6). In parallel with this, children often have a total reddening of the gums, which resembles the symptoms of acute gingivitis (Fig. 7-9), and this condition is called herpetic gingivostomatitis. In addition, very often herpetic gingivitis is combined with herpetic eruptions on the skin around the mouth and the red border of the lips.
Photo of gingivitis associated with herpetic stomatitis -
Important : in many cases, ulcers can be very painful. Pain increases sharply when the surface of the ulcer comes into contact with water or food while eating. That is why many children refuse to drink, which leads to the development of dehydration. Against the background of dehydration, the symptoms of intoxication become even stronger, which may require urgent hospitalization. Therefore, one of the most important aspects of treating stomatitis in children is to prevent the development of dehydration.
b) Chronic herpetic stomatitis -
After undergoing primary herpetic infection The virus remains in the body for life. Herpes viruses persist for life nerve ganglia, and when various adverse factors influence the body, the virus is activated. Periodic relapses are usually due to the following reasons –
- hypothermia, SARS,
- avitaminosis, stressful situations, allergy,
- exacerbation chronic diseases(tonsillitis, sinusitis ...),
- taking corticosteroids,
- trauma to the oral mucosa and the red border of the lips,
- foci of dental infection (tartar, dental caries, gingivitis),
- mouth breathing (it causes dryness of the lips and oral mucosa, and as a result - the appearance of cracks).
Symptoms, picture in the oral cavity
–
chronic recurrent form of herpetic stomatitis in the oral cavity manifests itself in the same way as the acute form (see clinic and photo above). The difference is that the general condition, as a rule, does not suffer, i.e. symptoms of intoxication are usually minimal or absent. At the same time, regional lymph nodes are usually enlarged and painful on palpation. Further in the article we will describe in detail - how to treat stomatitis in children at home.
Herpetic stomatitis in children: treatment
How to treat stomatitis in a child (of herpetic origin) will depend on the severity of the clinical manifestations. With a mild form of the disease, there will be enough drugs for topical application + be sure to avoid dehydration in the child. But at severe course herpetic stomatitis, first of all, the use of tableted antiviral drugs (such as) + again control of dehydration will be shown.
It is very important that parents do not treat their child with antiviral drugs in absolutely every case of herpetic stomatitis, because. there is a direct relationship: the more often and longer the courses of antiviral therapy with Acyclovir are, the faster the herpes virus will develop resistance to the drug, and it will cease to be effective. Usually, resistance develops after 4-5 courses of antiviral therapy with acyclovir, and primarily in immunocompromised children.
Treatment of mild/moderate stomatitis -
Removal of symptoms of intoxication –
in prodromal period diseases, i.e. even before the formation of herpetic vesicles on the mucous membrane of the oral cavity, there is usually an increase in temperature, lack of appetite, malaise, and muscle and headache may appear. Often parents mistake this for teething symptoms. With such symptoms, the child can be given a drug with ibuprofen (for example, children's Nurofen).
But keep in mind that taking antipyretic drugs is not advisable at low temperatures, because. this reduces the body's production of its own interferons and prevents the formation of full-fledged immunity against viruses and bacteria. Usually, antipyretics are prescribed to children if their body temperature is not less than 37.8–38.0 degrees.
Local treatment of herpetic eruptions –
after the opening of the herpetic vesicles, painful ulcers form in their place, and therefore, because of the pain, the child may refuse to drink and eat. If this is observed, then it will be very important to avoid the development of dehydration in the child, because. it will promote sharp deterioration general condition (even with a fairly slight severity of lesions of the mucous membrane with herpetic eruptions). To cope with this will allow the application of either an anesthetic anti-inflammatory gel or special film-forming protective agents to the surface of the ulcers.
Below you will find a comprehensive list of effective drugs that are used local treatment herpetic stomatitis. With moderate severity of the disease, such treatment will be sufficient without resorting to systemic tablet antiviral therapy.
1) Antiseptic rinses -
2) Anesthetic anti-inflammatory gel -
If the surface of the ulcers is very painful and the child refuses to eat, drink, brush his teeth, it is necessary to use an anesthetizing agent for ulcers. The best choice is Holisal topical gel, which can be used from 0 years old (there are no age restrictions). This gel has not only analgesic, but also a pronounced anti-inflammatory effect.
But sprays and gels based on lidocaine (for example, Kamistad) will not be in this case good choice, because Lidocaine will mix with saliva, gradually numbing the entire mouth. In a young child, this can cause numbness of the tongue, and as a result, a violation of swallowing and choking with saliva.
3) Protective film-forming agents -
For a long time, it is possible to protect the surface of ulcers from the action of irritants not only with the help of an anesthetic gel, but also special means, which, when applied, form a thin protective film on the surface of the ulcer. Such a film will not only reduce soreness and inflammation, but also accelerate the subsequent epithelialization of ulcers. These drugs include preparations based on bismuth subsalicylate.
Typically, drugs with this component are used in the treatment of gastric ulcer and duodenum. Preparations of this series for herpetic stomatitis can be used in the form of a suspension for application to the surface of ulcers in the oral cavity, or in the form chewable tablets. As a result of the application, an insoluble protective film is formed on the surface of the ulcers, which will reduce pain and inflammation.
The protective gel Gerpenox (from the manufacturer Roks) can also be attributed to film-forming agents. This medicine contains hydroxyethyl cellulose and Chelate Organic Germanium Guanine Complex. These components also create a protective film on the surface of the ulcers, which protects the ulcers from irritants and thereby reduces pain, and secondly, it will accelerate the healing of the damaged mucous membrane by about 1 day.
4) Preparations of the Viferon line -
5) Oral hygiene with stomatitis -
Because ulcerations can be very painful - brushing your teeth can be painful, but this does not mean that hygiene should be abandoned. The accumulation of a large amount of bacterial plaque on the teeth and tongue can lead to the development bacterial complications such as ulcerative necrotic gingivostomatitis. To reduce pain when brushing your teeth, you need to use toothbrush with soft bristles.
If the child does not yet have teeth, the treatment is carried out using a gauze swab dipped in an antiseptic solution. At the end of the article, you will also find information on children's toothpastes, which are best used to prevent the occurrence of new cases of stomatitis.
Treatment of stomatitis SEVERE -
Next, we will tell you how to treat stomatitis in children in the mouth (caused by the herpes virus) if the child develops severe clinical manifestations. It is still critical to prevent dehydration, which can develop due to a child's refusal to drink water, and it is also necessary to control elevated temperature and other symptoms of intoxication. Used in parallel local preparations(Miramistin, as well as Cholisal - for pain relief of ulcers).
1) Systemic antiviral therapy –
However, if severe herpetic stomatitis occurs, in children, the main treatment should be carried out with already tableted antiviral drugs (such as Acyclovir, Valaciclovir, Famciclovir). The peculiarity of their use is that they will be effective only when taken in the first 72 hours of the disease. Moreover, the later you start taking it, the less the effect will be. That's why top scores therapy is achieved at the start of admission in the first 12 hours after the onset of herpetic eruptions.
- The drug "Acyclovir" () -
it is the main antiviral drug for children, which is quite well tolerated and has little side effects. For children from 2 years of age and adults, the effective dosage will be the same - 400 mg 5 times a day (5 days in total). Often in the instructions you can find information that the base dosage is 200 mg, and not 400 mg 5 times a day. This dosage is not effective, and here's why ...Randomized clinical researches() showed that oral acyclovir (200 mg 5 times a day, for 5 days) had practically no effect on the duration pain syndrome, nor for the time of healing of herpetic ulcers. At the same time, it was the dosage of 400 mg according to the above scheme that led to a more rapid decrease in pain and healing of ulcers. As for children under 2 years old, at this age the dosage simply decreases exactly 2 times.
Important : the use of acyclovir may be ineffective in immunocompromised children, because. in this case, the herpes virus can develop resistance to acyclovir. Therefore, in children with weakened immune systems, many experts recommend the use of antiviral drugs only in extreme cases, and focus on local therapy + immunostimulating drugs that will stimulate the body to produce its own interferons.
Remember that the herpes virus quickly develops resistance to acyclovir, and not only the state of immunity affects, but also the frequency / duration of antiviral therapy. Those. the more often you take acyclovir, the faster it will lose its effectiveness. However, if an acute primary (with severe symptoms intoxication) stomatitis in infants - treatment should begin with the immediate intake of antiviral drugs, such as Acyclovir.
2) Immunostimulating agents -
As we said above, drugs in this group can be considered as an alternative to antiviral drugs, in case of resistance to them in the herpes virus, or if the child has weakened immunity. Such drugs should not be prescribed to your children on their own, because. the introduction of a non-specialist into the immune system can only harm and further only worsen the situation. Therefore, drugs of this series should be prescribed only by a doctor.
How to treat stomatitis in children against the background of weakened immunity - for this, the drug Cycloferon, which is an inducer of the production of its own interferon in the body, can help you. This drug can be prescribed to children from 4 years of age. The drug is taken 1 time per day (half an hour before meals, drinking plenty of water). Single dose for children 4-6 years old - 150 mg each,
in children 7-11 years old - 300-450 mg, in adults and children over 12 years old - 450-600 mg.
Although this medicine is over-the-counter, before taking it, it is advisable to consult with an immunologist and pediatrician about the strategy for treating herpetic stomatitis in your child and choose best option. Remember that when we artificially force the body to produce increased amount interferons - gradually he stops doing this at all without additional artificial stimulation. Therefore, everywhere you need to maintain a balance and consult with specialists.
Important : herpes on the red border of the lips or herpetic stomatitis - in children, the skin around them is often also complicated. This is due to the fact that the child first licks his fingers, and then touches his eyes with infected hands. What to do with it - read the link above.
2. Chronic aphthous stomatitis in children -
The aphthous form of stomatitis is manifested by the formation of one or more solitary ulcers on the oral mucosa. Typical localization of ulcers is the mucous membrane of the cheeks and inside lips, soft sky, the surface of the tonsils and palatine arches, as well as the lower and lateral surfaces of the tongue. Less commonly, ulcers can occur on the back of the tongue, the red border of the lips, or the mucosa of the gums.
Unlike herpetic stomatitis, with aphthous stomatitis, the general condition practically does not suffer, but a slight temperature and an increase in the submandibular lymph nodes may still be present. In addition, with aphthous stomatitis, most often only 1 ulcer (or no more than 2-3) is formed - usually 0.5 to 1.0 cm in diameter. In rare cases, ulcers can reach 2-3 cm in diameter.
Aphthous stomatitis in a child: photo
If you look closely at the photo above, you will notice that the surface of the ulcers is always covered with a gray or yellowish necrotic coating. In addition, along the perimeter of the ulcer is always surrounded by a bright red rim of inflamed mucous membrane. Ulcers up to 0.5 cm in diameter usually heal in 6-8 days, about 1 cm in diameter in about 10-14 days without scarring.
But larger ulcers with a diameter of 2-3 cm will heal much longer - up to 6 weeks, and healing most often occurs with the formation of a scar on the mucous membrane. It should also be noted that almost always ulcers are sharply painful when touched, and therefore children may refuse to drink, eat, and brush their teeth with a toothbrush.
Causes of aphthous stomatitis -
The causes of this form of stomatitis have not been fully studied, however, it has been established that the following factors can trigger the development of aphthous stomatitis -
- allergy to the components of oral hygiene products (especially often - to sodium lauryl sulfate),
- food allergens,
- some pathogenic bacteria
- biting the mucous membrane of the cheeks and lips,
- mucosal injury with a sharp edge of a filling or during an anesthetic injection,
- large amounts of nitrates in drinking water and foods.
In addition, there are many conditions of the body that can also cause aphthous stomatitis or increase the risk of its development. Especially often this happens against the background of the pathology of the gastrointestinal tract, the immune system, blood diseases, etc.
How to distinguish between herpetic and aphthous stomatitis -
- Herpetic stomatitis in a child is manifested by the formation of many small vesicles, which then burst with the formation of numerous small aphthae (although they can then merge with the formation of one extensive ulceration). With aphthous stomatitis, aphthae are worn single character, and usually they are much larger - most often from 5 to 10 mm.
- With herpetic stomatitis, as a rule, there is redness and swelling of the marginal gums around all teeth, which looks like acute gingivitis (Fig. 7-9). With aphthous stomatitis, symptoms of acute gingivitis are never observed.

Aphthous stomatitis in children: how to treat
If a child has developed aphthous stomatitis, treatment should be aimed at eliminating pain and speedy healing of ulcers, but it is very important to try to determine possible cause diseases in order to prevent the development of new outbreaks. Therefore, immediately after you find aphthae in a child, you must immediately exclude allergenic foods from the diet (honey, strawberries, chocolate, nuts, citrus fruits). The same applies to spicy, spicy, rough foods, highly salty and acidic foods (no tomatoes, pineapple, fruit juices), as well as carbonated drinks.
Check if your child's toothpaste contains sodium lauryl sulfate. If there is, it is urgent to replace it with a paste without this component. Elimination of other local causative factors will already require a visit to the dentist. Because allergic reaction is one of the most common causes development of this form of stomatitis - it makes sense to immediately start taking antihistamine (anti-allergic) drugs for a course of 10 days.
Local treatment in the oral cavity –
Treatment of aphthous stomatitis with mild symptoms and moderate usually enough is carried out with preparations for topical application in the oral cavity, + physiotherapy procedures and a laser are sometimes used.
- Antiseptic rinses
–
they are necessary, because often pathogenic bacteria of the oral cavity are involved in the development of aphthous stomatitis. In very young children, it is optimal to use Miramistin spray for this, and for older children (who are already able to rinse their mouths themselves) - a 0.05% solution of chlorhexidine. The spray can be used either to irrigate oral ulcers or to moisten with it. gauze swab for mucosal treatment. Scheme: 3 times a day, for 10 days.

- Laser treatment -
the use of a special medical diode laser with a wavelength of 940 nm, or Nd: YAG laser - almost instantly after a single procedure reduces pain, and also provides much faster healing. For example, laser-treated ulcers measuring 0.5 cm in diameter are completely epithelialized in just 3-4 days (instead of 7-10 days). Usually such treatment is carried out in private medical centers.A weaker alternative to laser is UVR (ultraviolet irradiation of the oral cavity). This method of physiotherapy also helps to accelerate the healing of ulcers in aphthous stomatitis, and the device is in any physiotherapy room for children. dental clinic. You can get a referral to a physiotherapy room from a dentist or pediatrician.
- Epithelial agents –
after the subsidence of pain and inflammation, it is necessary to focus on the early epithelialization of ulcers. This can be done with the help of special tools that accelerate the epithelization of lesions of the oral mucosa, for example, in the form of a gel. It should be noted that this gel also has a moderate analgesic effect.
Treatment of severe aphthous stomatitis -
With severe symptoms, long-term non-healing ulcers, as well as in the case of the regular occurrence of this form of stomatitis, home treatment with topical preparations is no longer enough. It is very important in these conditions to examine the child. Depending on symptoms, a complete blood count may be required to rule out hematological disorders, plasma immunoglobulin and lymphocyte tests, and plasma levels various types antibodies to rule out autoimmune diseases.
Usually, in severe cases of aphthous stomatitis, the following types are used drug therapy –
- a single injection of glucocorticoids at the base of each ulcer,
- systemic glucocorticoid therapy,
- taking immunomodulators.
Prevention of stomatitis in children -
The first is regular oral hygiene. The fact is that the lack of proper hygiene in the oral cavity accumulates a large amount of microbial plaque. Plaque bacteria constantly release acid and toxins. The secreted acid destroys tooth enamel, and toxins affect the oral mucosa, weakening its protective factors (i.e., reduce local immunity in the oral cavity).
As a result, the mucous membrane is more vulnerable to herpes viruses, pathogenic bacteria and other adverse factors. That's why good hygiene- this is the first and most important thing to prevent the development of new cases of stomatitis. You can read more about this in the article:.
The second important aspect is the use of hygiene products with special components such as licorice extract, lysozyme and a whole complex of lactic enzymes (such as lactoperoxidase, glucose oxidase, etc.). Such components increase the local immunity of the oral mucosa, which contributes to the prevention of the development of stomatitis. Such is, for example, the company SPLAT.
In general, we hope that our article on the topic: How to treat stomatitis in children at home turned out to be useful to you, and it became clear to you that frequent repeated cases of stomatitis indicate significant disorders in the child’s body and it’s not enough just to anoint with blue or drink acyclovir . Here, consultations of doctors, analysis of the blood system, immunity, etc. are necessary.
(152
ratings, average: 4,16
out of 5)
Herpes stomatitis in children is one of the most common diseases of the oral cavity. The disease is widespread among all age categories people, but most often they suffer from children from 6 months to 3 years of age.

Ways of infection
Herpes stomatitis - a disease infectious nature, the causative agent of which is the herpes simplex virus of the first type (HSV-1).
The main ways of infection:
- during pregnancy in the womb;
- in the process of natural childbirth;
- airborne droplets, for example, when coughing and sneezing;
- in a household way, for example through objects of daily use.
Once in the body, the pathogen is activated and multiplies in the cells of the epithelium and lymph nodes. This process is accompanied by characteristic symptoms.
Causes of the disease
Herpetic stomatitis in children and relapses are provoked by the following factors:
- weak immunity;
- exacerbation of existing chronic diseases;
- taking antibiotics;
- injuries of the lips and oral cavity;
- exposure to cold and high temperatures;
- poisoning;
- allergy;
- wrong hygiene care behind the oral cavity;
- stress impact;
- lack of vitamins and unbalanced nutrition;
- contact with patients infected with herpes;
- the presence of HSV-1 in the mother's body during pregnancy.
Symptoms

Herpetic stomatitis in its development goes through several successive stages: the incubation period, prodromal, catarrhal, the extinction of the disease and the recovery period. Incubation period in children lasts from 2 days to 3 weeks.
Initial signs of the disease:
- weakness and malaise;
- burning sensation in the mouth;
- active salivation;
- increase in body temperature;
- bad breath from the mouth;
- enlargement of the submandibular lymph nodes.
In infants, the symptoms of the disease are manifested by refusal to suck, refusal to drink, poor sleep, crying, fever, intestinal colic. If appropriate measures are not taken, dehydration may occur.
If measures are not taken at the first signs of the development of the disease, after a few days, painful and itchy rashes will appear on the mucous membrane of the mouth, spreading to the lips, tongue, cheeks and wings of the nose.
Depending on the characteristics of the course, an acute form of herpetic stomatitis and recurrent are distinguished. The first type appears suddenly, develops rapidly and has pronounced symptoms of the disease. In the absence or improper treatment, acute herpes stomatitis becomes chronic.
According to the severity, herpetic stomatitis is divided into mild (3-4 days), moderate (1-2 weeks) and severe form(more than 2 weeks).
Symptoms of a mild form of herpes stomatitis in a child:
- the child is tired and whiny;
- slight increase in temperature;
- inflammation and redness of the gums, swelling of the oral mucosa;
- the appearance of painful vesicles and sores in the oral cavity in a small amount;
- swollen lymph nodes.
signs medium-heavy form diseases:
- rise in body temperature to 39 degrees;
- a noticeable deterioration in the general condition of the child;
- enlarged lymph nodes;
- the appearance of inflammatory foci on the oral mucosa, swelling of the gums;
- bubble rash localized on the mucous membranes of the mouth, gums, tongue, cheeks, lips and perioral region.
The severe form is determined by:
- an increase in body temperature to a maximum value;
- feeling heavy, accompanied by nausea, vomiting and severe headache;
- the presence of symptoms of severe intoxication;
- violation of the rhythm of the heart and blood pressure;
- inflammation of the cervical and submandibular lymph nodes;
- blistering rash in large quantities, accompanied by severe pain and extending to the area around the mouth, conjunctiva, eyelids, wings of the nose.
Herpetic stomatitis in a child is diagnosed by a pediatrician or dentist. The diagnosis is made based on the patient's questioning, general clinical picture, the results of cytological, virological and serological studies.
To determine the causative agent of herpes stomatitis in a child, immunofluorescence (RIF) and polymerase chain reaction (PCR) methods are used. Serological identification of the antibody titer of the virus is carried out using enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) and complement fixation reaction (RCC).

Treatment
Treatment of herpetic stomatitis in children is prescribed by the attending physician. The rate of cure and the effect depend on when the therapy began, as well as on the state of the child's immunity.
With a mild course of the disease, treatment is carried out on an outpatient basis, in other cases and in children under three years of age, hospitalization is more often required. The child must be shown bed rest and plentiful drink. You can eat warm, grated food that does not irritate the oral cavity. Tableware and personal hygiene items for the patient must be for individual use.
It is necessary to treat herpetic stomatitis comprehensively, while focusing on the period of the disease and the degree of symptoms that appear.
Treatment of herpes stomatitis in an acute form in a child is reduced to pain relief, prevention reinfection, increasing the rate of healing of lesions.
For the treatment of herpes stomatitis in children, apply:
- antiviral drugs;
- antimicrobial agents;
- agents that have wound-healing effects;
- drugs to strengthen the immune system.
Initially, the site of the lesion is treated antiseptic. Rivanol or furatsilin can act as an antiseptic. The use of these funds in the treatment does not cause discomfort in the child. It is necessary to process the lesions every three hours.
For rinsing, agents are used that provide direct action for the herpes virus. With this disease, it is appropriate to use a drug such as Miramistin. Infants who do not know how to rinse their mouths are treated with a bandage dipped in a solution, or a cavity with lesions is sprayed with a special sprayer attached to the medication.
At the end of the treatment of the oral cavity with an antiseptic, antiviral and anesthetic ointments are used. local action such as oxalin ointment 0.5%, bonafton ointment, interferon ointment 50%. For the fastest healing of sores and restoration of the oral mucosa, special ointments and aerosols are used, such as Proposol, Ingalipt or Tandum Verde.
In the absence of the possibility of a quick and timely appeal to a specialist, it is recommended to use ointments with local anesthetic(Cholisal, Kalgel, Dentinox).
An important place in the complex therapy of herpes stomatitis in a child belongs to antiviral drugs. Often used antiviral agents in the form of gel and tablets. Most effective drug considered Acyclovir and funds based on it (Zovirax, Vivorax, Gerperax). Acyclovir has an inhibitory effect on the synthesis of the virus inside cells infected with herpes. The greatest efficiency is observed in the primary disease of herpetic stomatitis at the initial stage.
Also, such drugs as Valaciclovir, Penciclovir, Famciclovir, Panovir have an excellent therapeutic effect.
External use of antiviral drugs is effective for small foci of inflammation. The best treatment It is considered to take the medicine in the form of tablets inside.
In the event that the child's body temperature rises to 38 degrees and above, the use of antipyretic drugs is recommended. Panadol, Efferalgan and Cefekon will help not only lower the temperature, but also anesthetize.
An obligatory component of the complex therapy of herpes stomatitis is the stimulation of the child's immunity. Viferon is considered the most common immunomodulator for children. He also possesses antiviral action and approved for the treatment of children of any age. The composition of Viferon includes interferon, which prevents the reproduction of the virus at any stage of the disease, as well as accelerating and increasing the effectiveness of other drugs. In addition to Viferon, Immudon, Galavit, Immunal, Gepon, Amiksin have immunomodulatory properties.
You need to know that immunomodulators should be used only in acute form. Uncontrolled and unreasonable use of these drugs can adversely affect the formation of the natural immunity of the child.
When using adequate treatment, the primary infection with herpes stomatitis passes quickly. The baby makes a full recovery in 10 days. If timely assistance was not provided on time, the disease can develop a complication, for example, herpetic keratoconjunctivitis.
In any case, it is better to refuse self-medication. How to treat herpes stomatitis in a child and how to treat only a doctor decides.
Treatment with folk remedies
Folk remedies for the treatment of herpetic stomatitis are very popular. These methods cannot replace therapy with antiviral drugs. They act only as an addition to the main complex of treatment. Children are allowed to take such funds only after being prescribed by a doctor.
The most popular ways:
- A decoction of calendula flowers. It is necessary to pour 1 tablespoon of flowers with 1 cup of boiling water. Boil for 10 minutes over low heat, covered. Insist for an hour and strain. The decoction is suitable for rinsing and irrigating the oral cavity, as well as for applications on lesions with blisters and erosions.
- Sea buckthorn oil and rosehip oil. Oils reduce pain, inflammation, reduce irritation and help speedy regeneration and healing. At the stage of recovery, it is recommended to lubricate the affected areas or apply in the form of applications a couple of times a day.
- Decoction of chamomile. Pour 4 tablespoons of chamomile flowers with 1.5 liters of water and boil for 5-10 minutes. After that, insist 1 hour and strain. This decoction is recommended for use in herpetic stomatitis several times a day in the form of irrigation or rinsing of the affected areas of the oral cavity membrane. Chamomile has a healing effect and has an anti-inflammatory and analgesic effect.
- Soda solution. Add 1 dessert spoon of soda to a glass of boiled water and stir vigorously. Effective on initial stage herpetic stomatitis. soda solution rinse the mouth or irrigate the foci of inflammation 3-4 times a day. Babies wipe the mouth with a bandage wrapped around a finger and moistened with this solution. It is worth remembering that soda dries out the mucous.
- Aloe leaf pulp. The plant helps to remove inflammation and prevent the development of a bacterial infection, and also contributes to quick recovery fabrics. It is used in fingering form several times a day. The duration of each procedure is 15-20 minutes.
- Kalanchoe juice. The liquid of this plant is used for pain relief. The method of application is similar to the previous one.
- With herpes stomatitis, you can lubricate the oral mucosa with natural honey. But it should be borne in mind that it is a strong allergic product.
- Oak decoction. Pour 2 tablespoons of chopped oak bark with a glass of boiling water. Infuse the liquid until it cools under a closed lid and filter. Rinse the affected areas with oak decoction every 4 hours. The duration of treatment is 4-5 days.
- Peeled raw potatoes grate on a fine grater, wrap in cheesecloth and apply to areas of the mucous membrane affected by herpes stomatitis.
- Lemon juice. Soak a cotton swab or piece of bandage in freshly squeezed lemon juice and gently wipe the affected area.
- 1 tablet ascorbic acid dissolve in warm water and wipe your mouth.

Herpetic stomatitis in children can be prevented. To do this, you must adhere to the following rules:
- Carriers of the virus should take all measures to protect others (wearing a gauze bandage, do not touch wounds and ulcers with your hands, hand hygiene, do not kiss a child).
- Maintaining the child's immunity.
- Compliance with the rules of oral hygiene.
- Timely treatment of injuries of the oral mucosa and all chronic diseases.
- Doing healthy lifestyle life.
- A complete balanced diet.
- Sports.
- Reception complex vitamins during cold periods.
- Noticed the manifestation of the first signs of herpes stomatitis - immediately consult a doctor.
- To avoid exacerbation of the disease in the future, it is necessary to regularly show the child to the dentist.
- vaccination
Timely identified symptoms and treatment, carried out in an appropriate way, allows you to cure the disease without consequences for the health of the child.




