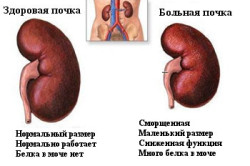
Renal indicators in the blood. Analysis of urine in acute inflammation of the kidneys. Why do kidney blood counts rise?
Analysis of kidney samples is carried out to diagnose kidney pathologies. They are blood tests. With the help of kidney tests, it became possible to detect pathological changes kidney function and problems such as muscle diseases, diseases of the joints, glands endocrine system, monitoring the dynamics of the disease or the results of the therapy used.
Most kidney ailments will require the delivery of biomaterial.
general information
A kidney test is ordered when blood levels need to be established:
- keratin;
- urea;
- uric acid.
An increase in the norm indicates deviations, since the kidneys with impaired functions are unable to remove these substances from the body in sufficient volume. With such a biochemical blood test, it becomes possible to assess the level of healthy renal functioning. If deviations are found, this indicates chronic course diseases.
Indications for kidney tests
Appoint this species analysis to assess renal performance in case of suspected diseases such as:
- pyelonephritis;
- glomerulonephritis;
- renal failure (including acute and chronic forms this disease)
- cyst in the kidneys;
- amyloidosis.
Systematic increase in pressure, pain in the lumbar region, regular headaches, unstable body temperature, swelling of the face - symptoms that may serve as a reason for the appointment of a kidney test. If the family has previously been found renal pathologies, this is one of the indicators that at the first symptoms it is necessary to conduct a kidney test for a comprehensive blood test.
What does the analysis show?
If the excretion of a substance such as carotene from the body is impaired, this indicates the presence of inflammatory process in the acute phase of its development. Keratin is the substance that has importance for a complete energy metabolism at the cellular level. After being released from muscle cells, this substance is transported to the kidneys, and then excreted from the body along with urine. In the case of a pathological lesion of the kidney, the function of removing keratin by it is markedly reduced, and elevated level is one of the main indicators of impaired renal function.
A comprehensive analysis during renal tests includes the detection of the level of urea in the blood. This substance arises in the process of protein cleavage. The amount of urea directly indicates the quality of the excretory renal function.
The level of uric acid changes when kidney failure accompanies the presence of any disease. Normally, uric acid is completely excreted from the body with urine. Occurs in the process of splitting nuclides. Even the slightest presence of uric acid indicates disorders in the body.
How to take an analysis?
If an analysis in the form of a kidney test is prescribed, it is necessary to carry out necessary training. This is necessary in order to eliminate the risk of obtaining incorrect data and, as a result, incorrect setting diagnosis. Factors affecting the result of the study are excluded by the following actions:
- medication is stopped 2 weeks before the kidney test;
- a few days before the test, you must adhere to light diet: fatty and fried foods are excluded from consumption;
- the day before the kidney test, you should refrain from smoking and drinking drinks that include alcohol;
- for 12 hours you can not load yourself with physical stress;
- the time after eating before the analysis should be about 12 hours;
- Before donating blood, you need to lie down for about 20 minutes.
Biochemical analysis takes from 24 to 36 hours. Normal data will differ in men, women, children under 15 years old, newborn babies up to 28 days from birth, infants up to 1 year old. the main objective analysis - timely detection pathology of the kidneys, as a result of which the healthy excretion of processed metabolic products from the body is disrupted.
 The results of tests for kidney health are analyzed by the doctor, according to the established standards.
The results of tests for kidney health are analyzed by the doctor, according to the established standards. Deciphering the results
Biochemical studies of a renal blood sample give a range of quantitative values that appear to be in the range of normal healthy results. When there is a decoding of the complex for the study of renal samples, this includes comparative analysis sample data with average reference values, separately for each age categories patients.
Norm of indicators
To indicate the average range of normal values of kidney samples, an international quantitative unit is defined - micromoles per liter with the abbreviation µmol / l. Normal performance urea levels for men range from 2.8 to 8.1 µmol/l, creatinine levels - from 44 to 110 µmol/l, uric acid - from 210 to 420 µmol/l.
The norm for women and children is slightly different: urea - 2-6.5 µmol / l, creatinine - 44-104, uric acid - 140-350. In children under 15 years of age: urea - 1.8-5.1 µmol / l, creatinine - 27-88, uric acid - 140-340. Infants up to 28 days: urea - 1.8-5.1 µmol / l, creatinine - 12-48, uric acid - 143-340. Infants under the age of 1 year: urea - 1.4-5.4, creatinine - 21-55, uric acid - 120-340.
What to do if the kidney blood counts are elevated? This question will be answered by a qualified nephrologist. To be healthy, a person needs to periodically visit the clinic, take tests, and the doctor must study all the results of the data obtained in order to notice any negative changes in time and immediately respond to them.
Why do kidney blood counts increase?
A lot of information can be provided by blood data, and if kidney indicators are elevated, it is possible to evaluate the functioning of this organ using a set of tests.
It is the biochemical data of the blood that can tell whether the kidneys cope with their purpose to cleanse the body of toxins. In most cases, kidney tests are taken with liver tests.
Appointed in the first place in the event that:
- There are kidney diseases so that you can control their functions and notice deviations in time. First of all, this applies to those patients who are on medical records with chronic pyelonephritis, diabetes, glomerulonephritis, high blood pressure.
- There are hereditary pathologies associated with kidney disease.
- All signs of kidney disease are noted, which include swelling, lumbar and headaches, high blood pressure.
- Were appointed potent drugs negatively affecting this organ;
- Pregnancy, during which the kidneys are overworked and can become inflamed.
What kidney blood counts may be elevated?
In renal indicators, there are 3 main groups of data. These are test data for creatinine, uric acid and urea. It is by their indicators that they determine how the kidney works.
All 3 components are metabolic products, and with the help of the kidney they are excreted from the body on time, unless, of course, the kidney is healthy, but if this organ is weak, the concentration of these substances immediately increases significantly, then it can be determined that a person has kidney failure. Especially by the level of creatinine, this diagnosis can be made and the work of the kidneys can be diagnosed.
Creatinine is the end product of the metabolic breakdown of creatine phosphate. This is the kind of connection that is needed to give energy to the muscles in time when they contract.
Creatinine must be produced constantly, having a stable concentration, it is entirely volume dependent muscle mass. That is why men tend to have higher amounts than women.
As age increases, the concentration of a substance in the blood also increases. And when reading the analysis, this factor is taken into account. This is due to muscle atrophy.
Creatinine is excreted along with the urine, there should be no reabsorption, and if there are no pathologies, it passes through the filtration in the renal glomeruli and is removed as unnecessary waste material. If blood counts indicate that creatinine is high, it means that kidney filtration is impaired.
What diseases cause elevated kidney values?
An increase in the concentration of this substance may indicate that there is a possibility of such diseases:
- Pyelonephritis in chronic stage, urolithiasis, renal artery stenosis.
- Diseases that arose after taking medications that have destructive action on the kidneys, for example, diuretics, penicillins and many others.
- Gigantism and acromegaly, that is, diseases associated with the endocrine system.
- Muscle damage. Occurs most often from physical influences when falling, severe bruises, necrosis.
- Kidney failure caused by bleeding and dehydration.
Creatinine rises when there is a strong exercise stress. First of all we are talking about athletes and bodybuilders. If included in the diet a large number of meat or products large quantity protein, this substance will be in the body more than normal. Or a person decided to starve, and the body began to use its resource - protein, and its increased decay provoked an increase in creatinine.
The need to check creatinine arises if you need to examine the work of the kidneys or check if the skeletal muscles are in order. blood for laboratory research must be submitted in the morning. The unit of measurement for blood concentration is micromoles per litre.
If creatinine is elevated, you can feel it by:
- pain in the lower back;
- urine, it can be produced too actively, more than 2 liters per day, or almost not excreted at all, and it contains protein and red blood cells;
- increased pressure;
- severe swelling;
- convulsions;
- shortness of breath
- constant fatigue;
- anemia.
To reduce the substance in the blood, those drugs are usually prescribed that can restore the processes of protein breakdown. If the increase is not so strong, organ pathologies are not observed, it is necessary to improve nutrition by discussing the problem with a nutritionist. Attention needs to be paid drinking regime and properly calculated physical activity.
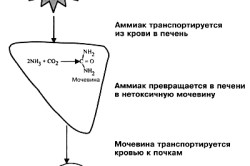
Urea - a low molecular weight compound - begins to rise from a meat diet or during fasting, with kidney failure and from the same states as in high level creatinine. But they have a significant difference: the increased presence of urea indicates long-term pathological processes, and not about acute.
Urea appears when it goes to the liver required process neutralization of ammonia, and is filtered from the blood in the glomeruli. Its amount in plasma depends entirely on the speed:
- own synthesis;
- glomerular filtration;
- renal perfusion.
It does not have great toxicity, but along with it there are guanidine derivatives, as well as potassium ions, they pose a threat in terms of toxicity. When urea is elevated, tissues begin to suffer:
- central nervous system;
- subcutaneous tissue;
- parechymatous organs;
- myocardium.
A large amount of urea is accompanied by intoxication. The reasons for its increase are as follows:
- catabolic states;
- a lot of protein that enters the body;
- stomach bleeding when proteins and amino acids are absorbed;
- dehydration.
Uric acid and cystatin C. If the blood counts indicate an increase in uric acid, most likely the person has a disease such as:
- leukemia;
- gout;
- renal failure, chronic form;
- changes in the thyroid gland;
- poisoning;
- alcoholism.
Indicators can also increase after taking certain medications. Recently, cystatin C has been used in the analysis. It reacts to changes in the body even earlier than creatinine, it is so sensitive. Its best quality lies in the fact that it is used for research in cases where patients have a disease of the liver, since in many diseases of the liver, those cells that should synthesize creatinine die.
According to studies, 18-20% of the total population suffer from chronic pyelonephritis. Women get sick 5-6 times more often than men. Chronic glomerulonephritis and chronic pyelonephritis are the main causes.
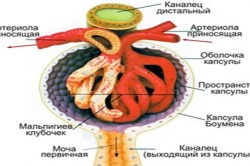
Glomerulonephritis is acute or chronic inflammation renal glomeruli. As you know, the renal glomeruli consist of a capillary network surrounded by a special capsule. The blood flowing through the capillaries of the glomerulus is filtered into the cavity of the capsule - thus primary urine is formed.
Pyelonephritis- this is an inflammation of the intermediate tissue, vessels and system of tubules of the kidneys, including the intrarenal pathways for excretion of urine (calyx and pelvis). AT renal tubules urine formed during blood filtration at the level of the renal glomeruli (primary urine) is reabsorbed (reabsorption). More than 90% of the volume of primary urine is reabsorbed. Thus, water returns to the body, mineral salts, nutrients. Secondary urine is formed in the terminal sections of the collecting ducts, where various substances and it acquires its own peculiarities.
In addition to the function of excretion of urine, they also perform other important functions: they participate in water-volitional and mineral metabolism, regulate the volume of circulating blood and arterial pressure, stimulate hematopoiesis through a special hormone - erythropoietin, are involved in the activation of vitamin D.
Methods for diagnosing glomerulonephritis
The first step in the diagnosis of glomerulonephritis is the collection of an anamnesis (interrogation of the patient) and a clinical examination (general examination) of the patient.
The questioning of the patient is aimed at clarifying the patient's complaints - the symptoms of the disease. Symptoms of the disease depend on the stage and form of the disease. At acute glomerulonephritis patients complain of an increase in body temperature, general weakness and malaise. More specific symptoms indicating kidney damage are: the appearance of edema, darkening of urine (urine becomes cloudy, the color of "meat slops"), pain in the lumbar region, a decrease in the total amount of urine. As a rule, acute glomerulonephritis develops as a result of a sore throat, pneumonia or erysipelas skin. It is known that the pathogenesis of the disease is involved hemolytic streptococcus group B, causing angina. As a result of sensitization of the body in relation to the antigens of streptococcus and deposition in the capillaries of the glomeruli of immune complexes develops aseptic inflammation glomeruli. Glomerular capillaries become clogged with blood clots, and the capillary membrane becomes permeable to blood cells (erythrocytes enter the urine). This explains the development common symptom glomerulonephritis. Pain in lumbar region in glomerulonephritis are caused by stretching of the capsule of the inflamed kidneys.
In some forms progressive malignancy glomerulonephritis leads to the rapid establishment of acute renal failure. Kidney failure is characterized complete cessation urination, increased edema, signs of intoxication of the body.
When examining a patient with acute glomerulonephritis, pay attention to the presence of edema (especially in the face). Various symptoms may also be present. streptococcal infection skin or tonsils (erysipelas, tonsillitis, etc.). When tapping the lumbar region, there is pain in the region of the kidneys. most often increased, the pulse is accelerated.
The correct and careful collection of anamnestic data, and the clinical examination of the patient, in most cases, make it possible to establish provisional diagnosis glomerulonephritis.
For a more accurate diagnosis of the disease, laboratory diagnostic methods.
General blood analysis- allows you to identify signs of inflammation: leukocytosis (an increase in the number of leukocytes), an increase in the erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR), an increase in the concentration of protein C.
Blood chemistry- establishes an increase in the concentration of urea (normal concentration up to 15 mmol / l, or 90 mg / 100 ml) and blood creatinine (normal concentration 15.25-76.25 μmol / l or 0.2-1.0 mg / 100 ml) . In some cases, studies are carried out to determine the antibodies of antistreptolysin O (ASLO) - indicating the bacterial (streptococcal) nature of glomerulonephritis.
Analysis of urine- determines increased content protein in the urine (normally, there is no protein in the urine) and the presence of a large number of erythrocytes - hematuria (normally, the number of erythrocytes in the urine does not exceed 1000 per 1 ml).
Kidney biopsy allows you to determine the morphological type of glomerulonephritis. A characteristic picture for glomerulonephritis is the proliferation of mesangial cells and the detection of deposition of immune complexes on the basement membrane of the glomerular capillaries.
Instrumental Methods research, such as ultrasound diagnostics, help to establish an increase in the size of the kidneys, which, however, is a low specific sign.
In chronic glomerulonephritis, the clinical picture of the disease is more blurred. In the first place are signs of progressive renal failure. Diagnostics chronic glomerulonephritis presupposes the exclusion of all other possible causes renal failure (chronic pyelonephritis, urolithiasis, nephropathy in diabetes or arterial hypertension etc.). For clarification, carry out histological analysis kidney tissues. A specific lesion of the glomerular apparatus indicates glomerulonephritis.
Methods for diagnosing pyelonephritis
Unlike glomerulonephritis, pyelonephritis disrupts the process of urine excretion. This happens due to damage to the excretory tubules of the kidneys. Inflammation in pyelonephritis is caused by direct reproduction of microorganisms in the tissues of the kidneys. Most often, the infection enters the kidneys from the lower urinary system: bladder and ureters.
Pyelonephritis is in many ways similar to those of glomerulonephritis
At acute pyelonephritis patients complain of a strong fever (39-40 °), chills, weakness, pain in muscles and joints. Pain in the lumbar region is characteristic symptom. Unlike glomerulonephritis, which always affects both kidneys, pyelonephritis often occurs unilaterally. Sometimes the symptoms of pyelonephritis occur after suffering renal colic. This indicates an established obstruction (blockage) of the urinary excretion pathways. Factors provoking pyelonephritis are hypothermia, physical and mental overload, poor nutrition.
The severity of symptoms depends on the form clinical development pyelonephritis. Sharp forms proceed with pronounced clinical manifestations, whereas in chronic pyelonephritis, symptoms may be practically absent. Chronic pyelonephritis is one of the most common causes of kidney failure. With the onset of chronic renal failure, the main symptom is an increase in the amount of urine excreted. This happens due to the fact that the kidneys lose the ability to concentrate urine at the level of the collecting ducts.
When examining a patient, as well as with glomerulonephritis, attention is paid to the presence of edema, the most characteristic of chronic pyelonephritis turning into renal failure, but this is only the primary diagnosis.
Laboratory methods research with pyelonephritis, it is possible to highlight some specific changes characteristic of this disease.
Blood analysis detects signs of inflammation (leukocytosis, increase in ESR). Big diagnostic value has a comparative analysis of three blood samples taken from the capillaries of the finger and the lumbar region (both sides). The increase in the number of leukocytes is more pronounced in a blood sample taken from the lumbar region on the side of the lesion.
Analysis of urine characterized by severe leukocyturia (an increase in the number of leukocytes in the urine). Leukocyturia serves important criterion for differential diagnosis between glomerulonephritis and pyelonephritis. With glomerulonephritis, the number of leukocytes in the urine increases slightly, while with pyelonephritis, it reaches a significant level. Normally, the content of leukocytes in the urine should not exceed 4000 per 1 ml. urine. Comprehensive urinalysis - Nechiporenko test, determines the content of leukocytes, erythrocytes, cylinders in the urine.
For a more detailed diagnosis, ultrasound diagnostics kidneys (ultrasound). With pyelonephritis, the kidneys are enlarged in size, their mobility during breathing is reduced. Thickening of the walls of the calyx and pelvis is noted. Often ultrasound procedure allows you to determine one of the most common causes pyelonephritis - urolithiasis. CT scan is more informative method than ultrasound. This research method is used in complex diagnostics complications of pyelonephritis - kidney abscess, kidney carbuncle, etc.
Violation of the concentrating function of the kidneys and the dynamics of urine excretion are tested using samples of Zimnitsky. The essence of the method is to collect the entire amount of urine excreted in 24 hours under normal water conditions. Urine is collected every three hours. At the end of the day, all 8 samples are analyzed to determine the relative density of urine. For impaired renal function in pyelonephritis or renal failure, a decrease in the concentrating ability of the kidneys is characteristic - hypostenuria, that is relative density urine is less than the relative density of blood plasma (a sign of insufficient absorption of water in the collecting ducts). The normal relative density of urine (isostenuria) is approximately 1008-1010 g/l.
Also, in addition to the relative density of urine, the Zimnitsky test allows you to determine the rhythm of urine excretion (determination of daytime and nighttime diuresis). Normal daily diuresis is 60-80% of the total amount of urine. With kidney disease, this ratio is violated.
Excretory urography – method of radiographic research functional state kidneys. Excretion of the radiopaque substance through the kidneys makes it possible to judge functional activity kidneys and the patency of the urinary tract. The method is very informative in renal failure or in the presence of obstruction urinary tract.
Bibliography:
- Alekseev V.G. Diagnosis and treatment of internal diseases Kidney disease, M: Medicine, 1996
- Whitworth J.A Guide to Nephrology, M.: Medicine, 2000
- Shulutko B.I. Inflammatory diseases kidneys: Pyelonephritis and other tubulo-interstitial diseases SPb., 1996
Blood biochemistry includes the study of the main parameters that reflect the state of various organs of the body, for example, the work and condition of the kidneys, liver, muscles, pancreas, hematopoietic system. By performing a biochemical blood test, you can see the presence or absence of an active inflammatory process, the features of the general metabolism, the suffering of certain organs, etc.
What parameters of a biochemical blood test are most often examined in diseases of the organs?
Fat metabolism: cholesterol and its fractions, triglycerides, lipoproteins. Atherogenic index - the ratio of "bad" and "good" cholesterol. State fat metabolism most often investigated in the deposition of cholesterol in blood vessels- atherosclerosis. Go to pages about diagnostic tests vessels of the brain, arteries and veins of the extremities, heart.
Mineral exchange : K - potassium, Mg - magnesium, Na - sodium, Cl - chlorine, P - phosphorus, Ca - calcium - these elements can be increased or decreased when various diseases (endocrine disorders, disorders of general metabolism, with hypertension, kidney disease, dehydration, etc.). The data of these studies must necessarily be evaluated by a doctor and correlated with the general clinical picture.
Definition total protein and protein fractions: they are evaluated in various inflammatory, neoplastic processes, if a disease of the blood system is suspected, autoimmune diseases, damage to the kidneys and other organs. These parameters are rarely evaluated separately, usually they are determined together with other biochemical studies and often, together with ultrasound and X-ray studies, they are correlated with the clinical picture that the doctor sees when examining the patient.
This is not an exhaustive list of biochemical studies; studies are recommended by your doctor. If necessary, we will offer you advice from specialized specialists.
Urinalysis for kidney disease is essential for correct diagnosis and prescription. effective treatment illness. Biochemical research urine allows you to set indicators such as:
- creatinine level;
- the amount of protein.
A general analysis for the presence of bacteria and microscopy of the sediment is necessary to determine diseases of the urinary system. The study of urine according to Nechiporenko establishes the number of cylinders, erythrocytes and leukocytes. It is important to determine the concentration ability of the kidneys using the Zemnitsky analysis. Creatinine daily protein, urea occur in the urine with kidney disease:
- urolithiasis;
- pyelonephritis;
- glomerulonephritis.
Renal and functional tests
 Therapy of diseases of the urinary system is possible only with the determination of the functional ability of the kidneys. The study determines the degree of renal failure in a patient on initial stage its development. In the process of studying the material, parameters such as:
Therapy of diseases of the urinary system is possible only with the determination of the functional ability of the kidneys. The study determines the degree of renal failure in a patient on initial stage its development. In the process of studying the material, parameters such as:
- glomerular filtration;
- creatinine;
- clearance.
The purification coefficient indicates the amount of blood free from the studied substance in the kidney for 1 min.
Creatinine clearance is easy to determine: the secondary adsorption of water in the renal tubules is expressed as a percentage. Normal glomerular filtration of the kidneys is 120-130 ml / min, and readsorption in the tubules urinary organ equal to 98-99%.
In many diseases, the doctor sets the amount of filtration for each of the components of the urinary organ. The received parameters are necessary for functional research with kidney disease.
Determination of urea in urine
 A decrease in the amount of urea occurs when the urinary tubules are damaged, which occurs in the case of the development of renal ailments.
A decrease in the amount of urea occurs when the urinary tubules are damaged, which occurs in the case of the development of renal ailments.
Chemical analysis is carried out in the laboratory. Material is prepared for the study: 40 ml of the patient's urine, porcelain dishes, a burner, nitric acid. The total amount of urea is determined by examining the volume of nitrogen produced. Excretion of the substance in insufficient quantities indicates a decrease in the excretory capacity of the kidneys. The analysis is carried out with a suspicion of a change in renal function, with the activation of protein synthesis in children and pregnant women.
An increase in the level of urea in the blood and its excretion in the urine indicates stable state nitrogen excretion systems through the kidneys. The amount of the compound in urine changes under the influence of pathological and physiological parameters:
- physical activity;
- features of the diet;
- taking medications.
Features of urinalysis for kidney disease
 Nephropathy in pregnant women is accompanied by proteinuria of 5-8 g/l.
Nephropathy in pregnant women is accompanied by proteinuria of 5-8 g/l.
At severe course disease indicators increase to 25-76g / l. The disease is divided into Stage III depending on the amount of protein in the urine. In the 3rd stage of the disease, with proteinuria from 3 g / l, oliguria sets in, and cylinders are present in the urine tests. The borderline state in nephropathy is the amount of protein 0.6 g/l.
Microscopic examination of the sediment reveals granular, waxy, or hyaline casts. The number of erythrocytes is insignificant. Readsorption of the kidneys is carried out in full, and the amount of excreted nitrogen is normal.
With the development of eclampsia in pregnant women, the content of residual nitrogen. In case of appearance diabetic nephropathy urinalysis contains a small amount of squirrel.
Changes in urine tests in glomerulonephritis
Severe kidney damage leads to changes in indicators in general analysis urine. The results of the study indicate the presence of pathological elements:
- cylinders;
- erythrocytes;
- squirrel;
- leukocytes;
- squamous epithelium.
 The presence of protein indicates the progression of the disease: its content reaches 5 g per day, and residual traces of albumin are present in the urine 6 months after the end of the disease.
The presence of protein indicates the progression of the disease: its content reaches 5 g per day, and residual traces of albumin are present in the urine 6 months after the end of the disease.
Erythrocytes in the urine are the main sign of nephritis. Their number varies from 14-5 to 50-60 in the field of view. If single erythrocytes are found, the doctor prescribes the patient a conduction. After microscopy of the sediment, leukocytes, glycine cylinders are examined, indicating a change in the tubules of the kidneys. The diffuse process is accompanied by the absence of bacteria, indicating the cessation infectious inflammation in the urinary tract.
AT initial stage disease total urine is reduced, but its relative density increases. The content of erythrocytes is 5 x 106 / μm per day, they are deformed, which indicates glomerular hematuria.
The normal form of erythrocytes indicates the absence of glomerulonephritis. Immune inflammation is confirmed by an increase in leukocytes, and protein loss exceeds 3 g per day.
Analysis of urine in acute inflammation of the kidneys
With pyelonephritis, the study of urine allows you to determine the type of pathogen and prescribe proper treatment. With the development of pathology in the cortical layer, a large number of leukocytes are present in the anamnesis. An increase in their number is observed in the case of obstructive urinary tract syndrome. Urine color with inflammation renal tissue changes with the progression of the process and against the background of urolithiasis.
Leukocytes increase with the development of tubolointerstitial nephritis: cells of the renal epithelium are found in the urine. In urine, granular casts and their leukocyte counterparts are found, as well as a significant amount of mucus.
With pyelonephritis in children, alkalization of urine occurs. The normal pH of urine is between 4.8 and 7.5. An acute inflammatory process is characterized by a decrease in the density of the material under study. Normally, the relative density value is 1008-1020g/l. The specific gravity of urine in pyelonephritis depends on the amount of dissolved elements and their molecular weight.
The study of urine in urolithiasis according to Nechiporenko and Zemnitsky
With changes in indicators in the general analysis of urine and suspicion of kidney failure, the doctor recommends that the patient additional research biomaterial according to Nechiporenko.
 For analysis, a medium portion of urine is provided to the laboratory. Study 1 ml of material and the number of leukocytes, erythrocytes, cylinders in it.
For analysis, a medium portion of urine is provided to the laboratory. Study 1 ml of material and the number of leukocytes, erythrocytes, cylinders in it.
The norm of erythrocytes is up to 1000 per 1 ml of urine, and leukocytes are contained in the amount of 4000 units per the same volume of urine. Normally, when taking tests according to Nechiporenko, hyaline cylinders are contained in an amount of 20 per 1 ml, and the presence of their other types - pathological condition for the patient's body.
More than 2000 leukocytes per 1 ml is typical for pyelonephritis, urolithiasis, cystitis. An increase in hyaline cylinders is observed with inflammation of the kidneys and acute glomerulonephritis. Granular cylinders appear in the chronic course of the disease, and waxy formations indicate the formation of renal failure in the patient. Epithelial elements arise from the death of the renal tubular mucosa and indicate tubular necrosis or toxic poisoning, accompanied by the death of the renal parenchyma (poisoning with salts of heavy metals).
The collection and study of urine according to Zemnitsky allows you to determine the insufficiency of the urinary organ or its inflammation. The density of several portions of urine, the amount of sodium chloride and urea in each portion are studied. Normally, the relative density ranges from 1.004 to 1.032, and the difference between high and low specific gravity should not be less than 0.007. Slight fluctuations in the density of urine indicate the appearance of an ailment. The filtration clearance is set, which determines the amount of purification of the substance in the glomeruli. O normal operation kidneys indicates the removal of 80% of all fluid taken in the urine within 24 hours. If a reverse suction more than the filtration of urine in the glomeruli, and urine has a large specific gravity, then its amount decreases.
Urine tests prescribed to the patient are highly informative materials that allow the doctor to put correct diagnosis and prescribe treatment.




