Amorphous crystals in the urine. Amorphous phosphates in the urine in large quantities - what does this mean? How is the treatment carried out
The main indicators of metabolism in the body displays a urine test. It displays those metabolic products that are no longer useful to a person. You can track which substances and in what quantity are excreted or retained in the body. And if deviations from the norm of certain indicators are observed in the urine, it can be assumed that there is pathological processes in the body.
Reasons for crystallization
General information about crystalluria
It is impossible to dissolve the amount of calcium, phosphate and oxalate present in 24-hour urine in 1-2 liters of water, so it must be concluded that there are substances that inhibit crystallization. This inhibitory role seems to be due to sialic acid residues, so urine is a supersaturated solution in equilibrium. The formation of crystals may be due.The most common cause is a decrease in dilution, but an increase in elimination can also be the cause of a decrease in supersaturation capacity. This decrease may be the result of inhibitor reduction, neutralization of inhibitors by electrolyte concentration, or the like, from a change in pH to the presence of crystals that have a promoter effect on the formation of another.
- Increasing concentrations above the supersaturation capacity.
- Some crystals have a promoter effect.
- A case of urate to calcium oxalate is known.
One of the indicators of deviations is the presence of amorphous phosphates in urine. These are structureless salts that do not transform into crystals and are excreted in the urine as a precipitate. Despite the fact that formations do not have a typical structure, sometimes they can form calculi, which becomes a prerequisite for urolithiasis. If amorphous phosphates in the urine are temporary, their appearance can be associated with nutritional habits. But sometimes such a phenomenon may indicate the presence of diseases. Therefore, if phosphates are found in the urine, it is necessary to find out the reasons for their appearance.
We are what we eat
Amorphous crystals are often identified using pH. Thus, if the urine is alkaline, then amorphous phosphates are identified, while if it is acidic, amorphous urates are identified. This practice is a bit risky as amorphous phosphates and triple phosphates are possible at slightly acidic pH.
Causes of appearance in children
Certain clinical situations that may explain stone formation are also likely to favor crystal formation. An increase in calciuria can cause the formation of crystals, usually calcium oxalates. The causes of hypercalciuria are.
The process of formation of salts in urine

Phosphorus is present in the tissues of our body. Most (about 85%) of it is in the bones and teeth. Phosphates are salts that are formed as a result of the reaction of phosphoric acid with alkalis. They enter our body with food.
Related video
This situation is often found in myeloproliferative diseases such as multiple myelomas. A number of cases of overabsorption bone tissue can be called primary hyperparathyroidism. a combination of the previous reasons.
- Increasing the proportion of diet consumed.
- Increasing the proportion of diet consumed leads to an increase in calcium content.
- Loss of calcium by the kidney causes a drop in calcium.
- Cristuria is mainly formed from oxalate.
Phosphorus needs calcium to perform its function in the body. In symbiosis, they provide the synthesis of protein and enzymes, regulate the process of muscle contraction. The content of phosphorus in the body should normally be half the content of calcium. If the concentration of phosphates begins to rise, this leads to calcium leaching from the bones.
In most cases, the presence of these crystals does not clinical significance. According to Conyers, only 10-15% of the oxalate in urine comes directly from the diet. Most oxalates in the urine are formed by metabolism. Apparently, even mild hyperoxaluria after a decrease in urine volume is the most significant factor in recurrent calcium oxalate lysase.
In some cases, the crystallization of calcium oxalates is massive and catastrophic. A typical example is ethylene glycol poisoning, in which case oxalate crystals can be found in tissues. toxic syndrome affects organs such as the liver, kidneys and brain and is accompanied by metabolic acidosis. Naturally, oxalate crystals are important and unique in that they are rich in aggregates of oval oxalates called microlites.
The concentration of its salts in the urine depends on the amount of phosphorus. Phosphate compounds are retained in the proximal tubules of the kidneys. About 12% of phosphates pass through the filters and are excreted in the urine.
Reasons for the increase in performance
Excess amorphous phosphate in the urine healthy person associated with alkalization of the body, which can be caused by dietary habits:
The presence of oxalate casts is very important as they include sediment where the urine is diluted. Conyers reports other substances that can lead to oxalosis. Some of these substances are used as a substitute for glucose in the parenteral diet.
Hyperuricosuria and calcium oxalate
Other causes of hyperoxaluria. Primary hyperoxaluria, pyridoxine deficiency, increased intestinal oxalate absorption. Decreased fat absorption leads to an increase in fatty acids in the gut, which then compete with oxalate for unabsorbed calcium. Calcium in the intestine limits the absorption of oxalate. . Hyperuricosuria is most commonly associated with a purine-rich diet, overproduction of purines occurs in some cases, and in hyperuricosuria, a urine pH above 5.5 favors the formation of urate crystals. that pH 5.5 promotes crystal formation uric acid.
- reduction in the diet of animal proteins;
- abuse of dairy products, fish, seafood, canned food;
- frequent use of carbonated drinks, coffee, alkaline mineral waters.
Find out how to prepare for and how the procedure is performed.
What are Tripel Phosphates?
Oxalate crystals are often found in sediment simultaneously with amorphous urates. Apparently, urate crystals promote the crystallization of calcium oxalate. Probable Cause- competition between them for adsorption on lithoinhibiting macromolecules. Citrate reduces saturation to calcium salts due to its chelating properties. In addition, the formation of a soluble calcium complex seems to play an inhibitory role in the formation of crystals. Therefore, we can expect an increase in the formation of crystals or even calcium stones in cases of hypocitratura.
The page is written about the rules for using Madder dye tablets for the treatment of kidneys.
Except malnutrition, the causes of amorphous phosphates in the urine may be pathological conditions:
- phosphate poisoning;
- congenital anomalies of the renal tubules;
- renal phosphate diabetes;
- hyperparateriosis;
- renal tubular acidosis;
- hyperfunction of the parathyroid glands;
- dehydration caused by frequent vomiting, diarrhea;
Symptoms

Hypocitraturia is found in conditions such as. renal tubular acidosis, chronic diarrhea, excessive consumption of animal protein. Several bacteria that infect the urinary tree reduce the concentration of citrate. Between 66 and 75% of the uric acid removed passes through the urine. The amount to be eliminated depends largely on the diet.
Crystallization with uric acid may be caused by a decrease in urine volume. combined with an acidic pH or an overproduction of uric acid. Most cases of uric acid crystalluria are of no clinical significance and represent a punctual situation. Some conditions, such as chronic diarrhea, can lead to the formation of uric acid stones by lowering urine volume and urine pH. A few patients with uric acid stones also have calcium stones.
If a small amount of amorphous phosphorus salts is present in the urine, then general condition a person may not be affected. Especially if the cause of their appearance was malnutrition.
But if phosphates in the urine appeared against the background of diseases, then sooner or later they will manifest themselves with other symptoms. If phosphaturia is present long time, then it is noted that an extraneous sediment appears in it.
Uric acid stones are common in gout, myeloproliferative syndromes, glycogenoses, and neoplasms. Cystine crystals are found only in patients with genetic disease, which affects the metabolism of essential amino acids called cystinuria. A small proportion of patients with cystinuria make calculations. This formation is highly dependent on the pH of the urine. Cystine is less soluble at pH 5.0 compared to pH 7.4.
Phosphaturia as a symptom
Urinary infection with organisms that hydrolyze urea leads to the formation of ammonia and alkalinization of the urine. The resulting ammonia promotes the formation of magnesium ammonia phosphates, also called triple phosphates, and alkalization promotes the formation of amorphous phosphates. The presence of triple phosphate is almost always accompanied by amorphous phosphates. The presence of struvite stones is a sign of an active or previous infection urinary tract.
The presence of salts in the body may indicate:
- pain in the lumbar region, which becomes more intense when bending, turning;
- sometimes there may be colic in the abdomen, nausea, flatulence.
Phosphaturia during pregnancy
For women in given period this is a common occurrence. Salts in the urine are more often found with toxicosis on early dates pregnancy and at the end of the last trimester. At frequent urges to vomiting and nausea, a woman has to reconsider her diet. Often food becomes the same type, which creates conditions for loss phosphate salts into sediment.
Solids fall into two broad groups; amorphous substances and crystalline substances. Crystals have definite geometric shapes while amorphous substances do not, and crystals have a precise melting point while amorphous substances have a melting point that is in a range of temperatures. In crystallography, we talk about planes, edges, and vertices to describe their shape. Crystals, while retaining their primary form, are of very variable size, but the ratio and angles between facets and edges are constant.
Causes of phosphates in urine
Crystals of the cubic system are called isotropic, but have only one refractive index. Crystals of other systems are anisotropic, i.e. have two or even three refractive indices. Anisotropic substances are classified into two groups; uniaxial crystals and biaxial crystals. Crystals of the tetragonal and hexagonal systems have two refractive indices, while crystals of the orthorhombic, monoclinic, and triclinic systems have three refractive indices. From this double reference, some crystals form typical interfering images such as the Maltese cross.
Phosphaturia in pregnant women can occur when there are violations of the urinary system. The patient needs to contact a nephrologist, do and. It is important to eliminate inflammatory process to prevent the infection from spreading further without affecting the development of the fetus.
On a note! Pregnancy is accompanied by an increase in progesterone levels. The hormone relaxes muscle tissue, which causes urine to stagnate for longer. bladder, salt concentration increases. Women are encouraged to move more, strengthen the muscles of the small pelvis with the help of special exercises.
The following table shows the bifurcation behavior of some of the crystals found in the urine. Another characteristic feature crystals is the partial interpenetration of crystals of the same nature, resulting in the formation of a twin. The twin is described according to an apparent fusion mechanism. Thus, we are talking about the double connection of the twin by the penetration of the cyclic twin, and so on.
Urine is a liquid with a complex composition that affects crystallization. The same substance often crystallizes in different forms depending on the concentration and composition of urine. Known fact is that slow crystallization tends to form a larger and better formed crystal than fast crystallization which produces rather small crystals, often amorphous. The formation of crystals in the urine often leads to truncated shapes, erosions and sometimes more or less spherical.
Amorphous phosphates in the urine of a child

In children, phosphates are detected only in amorphous form. A small number of them are found before the age of five. Some functions of the body are not yet fully formed; when the diet changes, the body may react in a special way.
Dr. Boris Bogov Nephrology Clinic, Medical University- Sofia. Since ancient times, kidney stones have been associated with humans. Kidney stones have been proven in Egyptian mummies. Data about kidney stone disease revealed in the writings of Hippocrates, Galen and Avicenna. The frequency of the disease varies from 17 to 8% of the population in different countries.
According to Bulgaria, about 2% of the population suffers from nephrolithiasis. It occurs among all races, but more often in the Caucasian race. Male ratio: female 2-3: represents the formation of stones in the renal pelvis and calyces, and the true manifestation of the disease is associated with the migration of the urinary tract, causing their obstruction. Concrete is made up of crystals and an organic matrix. According to the composition crystalline substance they are divided into.
At the first detection of amorphous phosphates in the urine, the child's diet should be changed and a second urinalysis should be done after a few days. This will make it possible to determine whether the appearance of salts is related to nutrition or the cause should be sought in pathological changes. Nutrition in children should be balanced, include enough not only vegetable, but also animal proteins, carbohydrates.
How to solve a problem
Chemical composition. According to the content of calcium, kidney stones are divided into: calcium-containing and not containing calcium. They are also organic and inorganic. Depending on the possibility of proof in the usual x-ray examination, congeners are X-ray and X-ray.
Table 1: Types of kidney stones according to chemical composition. The most common are calcium-containing concretes, and the constituents of uric acid, called "urate", make up about 15%. The part of cystine and xanthine is less common.
If phosphates are found repeatedly, this may be a signal of the disease. More often it is rickets, in which there is a deficiency of vitamin D in the body ( daily rate for a child 300-600 IU). Rickets usually occurs in infants and young children. preschool age. In addition to phosphates in the urine, a blood test may contain high concentration calcium and phosphorus.
With rickets in children, the limbs are bent, the bone skeleton is deformed. Muscle tissues lethargic, pale skin.
Indicator level diagnostics
Phosphaturia is diagnosed by a general urine test. Normally, an adult should receive about 1200 mg of phosphates per day. About 800 mg should be excreted in the urine. In the analysis of urine, the level of salts is indicated by the sign "+" in the amount of 1-4. The indicator + or ++ in the sample is the norm. If there are more pluses, this indicates a violation of salt metabolism.
To get more reliable and detailed information about the presence of amorphous phosphates, the dynamics of their concentration, it is recommended to collect daily urine ().
Rules for taking urine for analysis

To obtain reliable result, it is recommended:
- 7 days before the analysis, exclude from the diet foods that promote alkalization of urine (smoked meats, sweets, alcohol).
- Buy in a pharmacy special containers for collecting material.
- If you need to do a general urine test, take the morning average portion of urine on an empty stomach, deliver it to the laboratory within 2 hours.
- If it is intended to collect daily urine, the first portion should be collected at 6 am and filled with a new container every 3 hours.
- Before urinating, be sure to wash yourself without the use of soap so that foreign impurities do not get into the material.
- Store the collected urine in a dark, cool place (not in the refrigerator), the container is carefully sealed.
- On each container you need to indicate the time of the collected portion of urine, the initials of the patient.
General rules and methods of treatment
the main objective medical measures- prevent amorphous phosphates from being converted into stones. To drug treatment are resorted to if pathological causes have become the cause of the increased phosphate content.
In case of violation hormonal background it is necessary to consult an endocrinologist who will prescribe a replacement hormone therapy. Inflammation of the organs of the urinary system is carried out under the supervision of a urologist or nephrologist. If the infection was due to bacterial microflora, a course of antibiotics is prescribed, taking into account the sensitivity of the pathogen.
Learn about the signs and how to relieve pain.
Scroll effective drugs from cystitis and the rules for their use can be seen in the article.
Go to the address and read about the causes of red urine in women and treatment options for associated diseases.
Diet and nutrition rules
The main emphasis in phosphaturia is on the correction of nutrition. Any alkalizing foods are excluded from the diet. To prevent the formation of phosphorus-calcium salts, it is recommended to adhere to treatment table No. 14. For normal operation urinary system and accelerate the excretion of salt residues, you must also adhere to abundant drinking regime(about 2.5 liters per day).
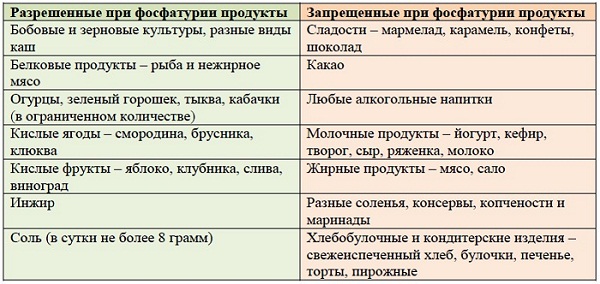
To prevent the appearance of salts in the urine, it is necessary to observe certain rules nutrition and lifestyle:
- do not abuse smoked meats, spicy, sour, salty foods;
- drink enough fluids;
- do not overcool;
- treat urinary tract infections in a timely manner;
- for children, in order to avoid vitamin D deficiency and the development of rickets, it is enough to be exposed to sunlight or use the vitamin in the form of a solution;
- at least 2 times a year, conduct a preventive examination by a urologist, take, do an ultrasound.
Amorphous phosphates in the urine are not necessarily a symptom of disease. Their appearance may be associated with errors in nutrition, physiological changes during pregnancy. To find out the cause of errors in urine indicators, you need to conduct a series additional research. Do not leave the presence of salts in the urine without attention, even if the person does not experience any discomfort. Phosphaturia may hide diseases, the treatment of which should not be delayed.
More details about the causes of the appearance of amorphous phosphates in the urine of a child and how to bring the indicators back to normal will tell children's doctor Komarovsky in the following video:
Amorphous phosphates are structureless salts that are excreted from the body in the urine. The term "amorphous" means that the salts do not have a clear structure and do not combine into crystals. In most cases amorphous salts phosphates do not lead to the formation of kidney stones, but still, such cases occur. The most common causes of the appearance of phosphate salts in the urine are associated with a violation of the diet. Often, phosphates are detected in the urine of children under 5 years of age, which is associated with the immaturity of the metabolic system. Phosphates in the urine during pregnancy are also not a symptom of the disease, but are the result of temporary hormonal changes.
Reasons for the appearance of phosphate salts in the urine:
- children's age up to 5 years;
- pregnancy;
- change in diet;
- vegetarianism;
- the use of foods rich in phosphorus;
excessive high level phosphate in the urine may be a symptom of the disease. Often, in addition to increasing the level of salts in laboratory tests, an adult or a child is also concerned about other manifestations of the disease.
Diseases in which the level of phosphates in the urine increases:
- rickets;
- renal phosphate diabetes;
- hyperparathyroidism;
- cystitis;
The norm of urine analysis does not imply the presence of salts in it. Urine with high content phosphate loses transparency, and becomes cloudy. If the urine stands for a while, phosphorus flakes form in it, which precipitate. When examining urine samples, along with an increased level of phosphates, a violation of the acidity of the urine is often found. The normal acid-base reaction of urine is in the range from 5 to 7 pH. In the presence of amorphous phosphates, the urine loses its acidity, the pH level rises to 7.5.
Usually, elevated level amorphous phosphates is an accidental finding during a routine urinalysis. Phosphate excretion in the urine does not cause any additional symptoms and worries.
Nutrition and amorphous phosphates in urine
 Amorphous phosphate salts precipitate in the urine with a decrease in its acidity. Urine becomes alkaline when there is insufficient consumption of meat and proteins of animal origin. The norm of protein in the diet of an adult is in the range of 1-1.2 grams per kg. For children, the norm of protein in daily diet should be approximately 3-4 grams per kg. Very often, phosphate salts are found in people who follow a vegan diet. Dairy products (kefir, cottage cheese, milk) also cause a decrease in the acidity of urine and the appearance of phosphate salts in it.
Amorphous phosphate salts precipitate in the urine with a decrease in its acidity. Urine becomes alkaline when there is insufficient consumption of meat and proteins of animal origin. The norm of protein in the diet of an adult is in the range of 1-1.2 grams per kg. For children, the norm of protein in daily diet should be approximately 3-4 grams per kg. Very often, phosphate salts are found in people who follow a vegan diet. Dairy products (kefir, cottage cheese, milk) also cause a decrease in the acidity of urine and the appearance of phosphate salts in it.
Excessive consumption of alkaline mineral water rich in phosphates is common cause salt increase in general analysis urine. It is important to remember that mineral water with a high content of various minerals is healing and should be taken in courses. For daily use doctors recommend using a dining room or a medical dining room mineral water. Quantity information minerals in water can always be found on the label.
A diet high in phosphorus and calcium is also a common cause of phosphate deposition in the urinary sediment.
Foods rich in phosphorus and calcium:
- Fish and seafood;
- seaweed;
- cottage cheese;
- eggs;
- oatmeal;
- buckwheat;
- bean products.
Sometimes even eating a moderate amount of foods with great content phosphorus, calcium and phosphate the day before urine collection can affect the analysis.
The reasons for the increase in phosphates in the urine may lie in the disruption of work gastrointestinal tract. At hyperacidity gastric juice the body excretes a large amount of hydrochloric acid, which can also lead to the excretion of excess salts in the urine.
The concentration of salts in the urine may increase with dehydration. Dehydration accompanies almost everything infectious diseases with an increase in body temperature. Fluid loss can be the result of repeated vomiting or diarrhea. Also, more concentrated urine is excreted after prolonged and intense physical exercise.
Phosphates in urine in children
 In children under the age of 5 years, urine samples very often reveal a small amount of amorphous phosphates. The body of a child at this age is not yet fully mature, and some systems do not function fully. Children's body very sensitive to changes in diet. In case of insufficiency of animal proteins in the daily diet, phosphate salts are detected in the analyzes.
In children under the age of 5 years, urine samples very often reveal a small amount of amorphous phosphates. The body of a child at this age is not yet fully mature, and some systems do not function fully. Children's body very sensitive to changes in diet. In case of insufficiency of animal proteins in the daily diet, phosphate salts are detected in the analyzes.
With a single detection of a small amount of amorphous phosphates, the analysis should be repeated after a few days. Before re-taking the analysis, it is necessary to slightly adjust the diet. The child's diet should be balanced in the content of animals and vegetable proteins as well as carbohydrates. You should not eat a large amount of fish and dairy products a few days before the test.
If the child's diet meets age requirements, and salts in the urine are detected again, then it is worth examining the child more carefully.
Phosphates in the urine of a child can be a symptom of the development of rickets in him. Rickets develops when there is a lack of vitamin D in the body of a child. The norm of vitamin D, which should be supplied with food, is in the range of 300-600 IU. daily diet the child should contain sufficient amounts of vitamin D. In the first months of life, the child receives vitamin D from breast milk, then the deficiency is covered by the introduction of complementary foods.
Most often, the symptoms of rickets appear in infants and early age. A lack of vitamin D leads to a violation of the development of bone and nervous system child. If the child has breastfeeding symptoms of rickets appeared, so it is necessary to carry out additional analysis blood. A blood test for rickets shows the concentration of phosphorus and calcium in the blood.
Causes of rickets in children:
- lack of sunlight;
- vitamin D deficiency in the child's diet;
- malabsorption and metabolism of vitamin;
- frequent use of anticonvulsants;
Depending on the degree of vitamin D deficiency, the symptoms of rickets can be pronounced or more subtle. At infants with rickets sensitive and disturbing dream, older children are very irritable and whiny. Children with rickets sweat more than normal children, have pale skin and flaccid muscles. Deformities develop over time bone skeleton. Children have a flattened back of the head with areas of baldness. Rickets is characterized by curvature of the limbs and the presence of bone seals on the ribs.
Pregnancy and urinary phosphate
 Phosphates in the urine during pregnancy are often detected during routine studies. Analysis with high content phosphate is not evidence of disease or pathological course pregnancy. Phosphates in the urine during pregnancy are formed as a result of hormonal changes that occur in a woman's body during this period. The causes of phosphate deposition in the kidneys lie in the change in the exchange of calcium and phosphorus in the body of a pregnant woman. Vegetarian diet during pregnancy can also cause the formation of salts in the kidneys. Any restricted diet during pregnancy should be discussed with your doctor.
Phosphates in the urine during pregnancy are often detected during routine studies. Analysis with high content phosphate is not evidence of disease or pathological course pregnancy. Phosphates in the urine during pregnancy are formed as a result of hormonal changes that occur in a woman's body during this period. The causes of phosphate deposition in the kidneys lie in the change in the exchange of calcium and phosphorus in the body of a pregnant woman. Vegetarian diet during pregnancy can also cause the formation of salts in the kidneys. Any restricted diet during pregnancy should be discussed with your doctor.
The daily diet of a pregnant woman should contain a sufficient amount of proteins, fats and carbohydrates in the correct proportions. An increase in phosphate salts may be due to a lack of animal proteins and excessive consumption herbal products high in fiber. Also, an increase in phosphate salts develops due to frequent use dairy products.
Usually, the causes of salt loss during pregnancy are not associated with the development of the disease. But, with the repeated detection of a large amount of salts in the test samples, women require a more thorough examination.




