The prothrombin test according to the quick was lowered. We understand what is prothrombin by quick? Preparation for the delivery of the analysis
Prothrombin is a complex protein produced in the liver. According to its quantity, a conclusion is made about the coagulation system of the blood. In order for the result of the analysis to be informative, blood on an empty stomach, better in the morning between eight and eleven o'clock.
Before blood sampling, at least eight and no more than fourteen hours should elapse after the last meal. During this time, you can only drink water. The day before the analysis, you need to limit fried and fatty foods, do not take alcohol, it is necessary to exclude severe physical exercise. Within half an hour before the test, psycho-emotional and physical stress. It is impossible for half an hour before blood sampling.
Blood sampling should be carried out before the start of the reception. medicines and not earlier than one to two weeks after them. If their reception cannot be canceled, in the direction for the study, the doctor must indicate which drugs the patient is taking and in what doses.
High level fibrinogen indicates acute inflammatory processes and about tissue death, it may be associated with increased risk hypertension, heart attack, stroke, diabetes and even cancer. Increased fibrinogen causes inflammatory damage to the walls of the arteries in the body, prepares the ground for atherosclerotic plaque and the formation of a blood clot. A blood clot that blocks one of the arteries of the brain can cause a stroke, and thrombosis coronary artery provokes the development of myocardial infarction.
Too low fibrinogen levels can cause heavy bleeding that are hard to stop. As a rule, it is the result of a donor, large blood loss, while using drugs. A decrease in its concentration is also observed in congenital hypofibrinogenemia and afibrinogenemia, secondary disorders of fibrinogen formation in the liver, as well as in coagulopathy of various origins. For normal formation clot, the minimum required plasma fibrinogen level should be 0.5 g/l.
During pregnancy, the membranes of the embryo are formed. The cells of the shell of the embryo, that is, the cells of the chorion, synthesize the hormone into the blood of a woman - chorionic gonadotropin human (hCG). All studies for diagnosing pregnancy are built on the definition of this hormone.

You will need
- - direction of the gynecologist.
Instruction
To diagnose pregnancy, a blood test is performed for human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG or hCG).
A blood test for hCG is carried out in specialized laboratories in the direction of a gynecologist.
Prothrombin, prothrombin index and time: norms in the blood, decoding of analyzes
Typically, doing hospital treatment, each patient the next morning before breakfast takes mandatory tests from a finger ( general analysis blood, sugar and prothrombin). These laboratory tests are referred to as the main indicative studies, since they are the ones that “draw” big picture the patient's condition. The rest (biochemical, including coagulation) tests can be prescribed on the day of admission, if the problem in the patient's body is clearly defined, or if, during the examination and treatment, the goal is to thoroughly study the functional abilities of the patient's organs and systems and monitor the effectiveness of therapy .
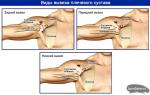
The unique medium moving through the blood vessels, according to its characteristics, is classified as connective tissue. Being in a liquid state and possessing fluidity, which prevents gluing shaped elements, blood, however, is able to quickly clot when the vascular wall is damaged. She has such an opportunity thanks to the blood coagulation system and its factor, one of which is prothrombin . It should be noted that all factors without violating the integrity vascular walls are in an inactive state. Activation of factors and formation of blood clots inside circulatory system without any reason threatens with serious complications for the body.
What is prothrombin?

stages of blood clotting
Prothrombin or factor II (FII) of the prothrombin complex is a protein (glycoprotein), a plasma factor of the coagulation system, which belongs to alpha2-globulins and is synthesized by hepatocytes (liver cells). It is important to note that prothrombin production it will be noticeably difficult if the amount of vitamin K in the body for some reason decreases, which the synthesis so needs this factor. If everything is normal in the body, then prothrombin does not show any activity, remaining as a precursor of thrombin, an enzyme that causes polymerization and the formation of a clot (thrombus), if necessary.
In circulating blood, plasma factors, being in the form of an inactive form of a profactor (prothrombin → thrombin), always remain in relatively constant concentrations, activation occurs under the influence of coagulation factor XII ( internal system hemostasis) and in contact of blood with damaged tissues(external hemostasis system).
The norm of prothrombin in the blood in healthy people is 0.10 - 0.15 g / l (1.4 - 2.1 μmol / l).
Importance of the prothrombin complex
The lack of this factor can be both congenital and educated in the process of life. Congenital prothrombin deficiency is not so common, that is, it refers to a rare pathology. Low prothrombin from birth is due to a mutation of recessive genes located on chromosome 11.
With hypoproteinemia of any origin, as a rule, the level of this protein is also reduced. Diseased liver (hepatocytes are the site of formation of the main factors of the prothrombin complex) and K-avitaminosis (vitamin K is involved in the synthesis of FII and other factors that are called K-dependent) give sharp drop the concentration of this indicator.
Decreased levels of prothrombin lead to the fact that it takes more time for blood to clot. To determine how the coagulation system works depending on the level of prothrombin, coagulation tests are used in clinical laboratory diagnostics, which allow you to have an idea of the state of the entire prothrombin complex:
- PTI (prothrombin index, in percent);
- PO (prothrombin ratio, inverse PTI value, in percent);
- PTT (prothrombin time, in seconds);
- Prothrombin according to Quick (more sensitive analysis than PTI and PTT, as a percentage);
- INR (international normalized ratio, in percent).
Excessive activity of prothrombin without any need is also fraught with various troubles, and, at times, a disaster for the body. Increased clotting, the formation of clots that can close a vital blood vessel, can result in dangerous situation up to and including death.
Orientation tests and full analysis
The study of blood coagulation, as a rule, begins with indicative methods that make it possible to detect an anomaly of coagulation (prothrombin) without revealing its essence. Then, based on the results of the analysis of the coagulation ability of the blood, other (already specific) methods are prescribed (PTT, INR, APTT and other indicators of the hemostasiogram).

As for the prothrombin test, it is very important integral part and can be presented in various forms. The lack of factors of the prothrombin complex (II, V, VII, X) is determined mainly in the analysis of PTT according to Quick, which primarily reveals a violation external education thromboplastin. However, it is also possible to study these indicators separately according to the principle of replacement samples.
Meanwhile, it is impossible to ignore the indicators of the coagulation ability of blood in women during the planning or onset of pregnancy, because this allows you to calculate the possible risks during childbirth. Bearing in mind these indicators during pregnancy, it is possible to foresee and prevent bleeding (if the PTV is prolonged) or the development of thrombosis and premature detachment of the placenta, if the blood shows a particularly high tendency to clot. During the very period of childbirth, the prothrombin time is somewhat shortened compared to the norm, and the prothrombin index is increased. In women during pregnancy and childbirth, the study of the coagulation function of the blood is not enough only with indicators of the prothrombin complex. With the aim of having complete picture functional ability of the hemostasis system, expectant mothers are assigned a maximum of coagulogram indicators.
prothrombin time

Prothrombin time, as a laboratory test, enables clinicians to quickly evaluate not only the external hemostasis system, but the entire cascade of blood coagulation reactions.
In emergency situations for the body (injuries with tissue damage, heavy bleeding, necrosis and other pathological conditions), a glycoprotein enters the blood, a membrane protein - tissue thromboplastin, which indicates the inclusion of a backup (external) hemostasis system.
Tissue (cellular) thromboplastin, called tissue factor (TF), interacting with coagulation factors (FVII) circulating in the bloodstream, successively includes other plasma thromboplastic factors in the process. This means that the hemocoagulation system is activated and the first phase of coagulation begins - the transformation of inactive prothrombin into active thrombin. Thrombin causes the enzymatic conversion of fibrinogen into fibrin, under its influence factors (V, VIII, IX, XIII) are activated, it destroys platelets, which causes (together with Ca ++) a viscous metamorphosis of platelets, contributing to the release of platelet factors.
The norm of PTT in adults ranges from 11-15 seconds (in newborns up to 3-4 days of life - 12-18, in premature babies - 15-20). In newborn full-term infants from 4-5 days of life, the prothrombin time corresponds to that of an adult.
This indicator increased (clotting time lengthens) in the following pathological conditions:
- Diseases of the liver, because there is a synthesis of prothrombin;
- Lack of vitamin K, the participation of which is necessary for the synthesis of K-dependent factors (including prothrombin);
- Increasing the level blocking thrombin and other factors of the hemocoagulation system;
- Increasing the fibrinolytic ability of the blood (dissolution of clots);
- pancreatic cancer;
- Separate hematological pathology (myeloid metaplasia);
- GrBN ( hemorrhagic disease newborns);
- High level of erythrocytes in the blood (above 6.0 x 10 12 / l);
As biological material for the study of prothrombin time, the one-stage method according to Quick (as the analysis is called) is whole blood taken with an anticoagulant (sodium citrate).
PTT, Quick test or thromboplastin time is an indicator of the external factor II activation system, where prothrombin time depends on the concentration of fibrinogen in the blood plasma, factors V, VII, X. The PTT norm (Quick test) is determined thromboplastin activity and is 12-20 seconds.
Prothrombin according to Quick
The definition of "prothrombin according to Quick" means the concentration of factors of the prothrombin complex as a percentage of the norm. This method are currently considered among the most significant methods for studying prothrombin.
The test allows you to identify the activity of the factors of the prothrombin complex of the patient's blood when compared with the known PTT of "normal" plasma. This method is undoubtedly more informative than the calculation of PTI. Quick prothrombin determines FII in a patient based on a calibration graph ( dependence of PTT on the total, total, activity of all participants in the reaction - factors of the prothrombin complex of diluted "healthy" plasma).
Normal prothrombin values according to Quick vary more widely than PTI, and normally range from 75 to 140%. In women, the upper limits of normal are usually lower. The results of the analysis may depend on the age of the patient, the treatment that he takes (anticoagulants), the sensitivity of the reacting substances.

Prothrombin according to Quick is primarily reduced during treatment with indirect anticoagulants.(INR at the same time - increases), therefore, when monitoring anticoagulant therapy, this fact should be borne in mind first of all and, taking into account it, the patient's blood test should be carried out in one way and in one CDL. Otherwise, you can get inadequate results that adversely affect the further course of anticoagulant therapy, if it is carried out at the time of the study.
The values of prothrombin according to Quick and PTI (prothrombin index) often give the same results in the zone normal indicators. As for the zone of low values, here the results differ markedly, for example, you can get the following test answers: PTI - about 60%, and prothrombin according to Quick - 30%)
Prothrombin index

The prothrombin index (PTI) is the ratio between the clotting time of "healthy" plasma (control) and the clotting time of the blood of a sick person. The result is calculated as a percentage (PTT of normal plasma: PTT of the patient's plasma x 100%), the norm is from 90 to 105%. The inverse ratio (blood clotting time of the patient: the clotting time of "healthy" plasma), expressed as a percentage, is called the prothrombin ratio (PO).
A low prothrombin index and prolongation of the PTT give rise to many pathological conditions:
- Congenital deficiency of some blood coagulation factors (II, V, VII, X);
- Damage to hepatocytes during a chronic pathological process localized in the hepatic parenchyma;
- Syndrome of disseminated intravascular coagulation;
- hemorrhagic syndrome due to low content plasma fibrinogen (fibrinogenopenia);
- Violation of fibrinogen polymerization (dysfibrinogenemia);
- Vitamin K deficiency;
- Carrying out anticoagulant therapy;
- The use of clotting factor inhibitors, such as heparin, which inhibits the conversion of prothrombin to thrombin.
A high prothrombin index (shortening of the PTT) is noted in the following cases:
- Formation of blood clots in blood vessels that block the blood flow as a result of various pathological conditions of the hemostasis system (thrombosis);
- Consumption coagulopathy (DIC);
- Excessive activation of the anticoagulant system, over-education plasmin (hyperfibrinolysis), which leads first to bleeding, and then (with depletion of plasminogen) to thrombosis;
- Liver diseases;
- Increases in factor VII activity (traumatic tissue injury, necrosis);
- Inclusion defense mechanisms in women during childbirth.
Thus, prolongation of the PTT will decrease the prothrombin index and indicate a possible hypocoagulation(low blood clotting, tendency to bleed). And, conversely, a reduction in clotting time (PTT) increases the values of the prothrombin index and indicates the presence of signs, that is, increased blood clotting (the risk of developing thromboembolic conditions).
Unity and struggle of opposites
Violation in the hemostasis system leads to the development of coagulopathy, where the pathology that exhibits a tendency to thrombosis is usually denoted by the term, and diseases that are accompanied by increased bleeding are called "hemorrhagic diathesis". Violation of blood coagulation abilities may be hereditary or result from conditions formed in the course of life (diseases of the hepatic parenchyma, K-avitaminosis, the use of anticoagulants in medicinal purposes, activation of the fibrinolytic system).

The development of the syndrome of impaired hemocoagulation is due to the loss (or decrease) in the ability of liver cells to biosynthesis of coagulation factors. Moreover, it should be noted that the factors of the systems of coagulation, anticoagulation and fibrinolysis do not exist in isolation, a violation of the activity of any one link leads to pathological conditions of other components. For example:
- A disorder in the biosynthesis of the protein we are considering - prothrombin, will certainly lead to a violation of the production of other factors (VII, IX, X) and a deficiency of all components of the prothrombin complex, which will subsequently result in a decrease in FV activity, an increase in the concentration of fibrin monomers, a decrease in FXIII activity and an increase in the ability of fibrin to lysis.
- Violation of fibrinogen metabolism will cause a change in the structural structure of the profibrin layer of blood vessels, opening the way for the movement of erythrocytes through the vascular walls.
The combination of seemingly absolutely opposite properties of the above systems (provided that they normal functioning) provides a liquid state of blood, freely moving through all the blood vessels of the body, and its coagulation, if there is a need to patch the gap formed as a result of tissue damage.
Research can be expanded...
If the described methods are not fully informative, studies of the hemostasis system can be expanded, for example, by studying individual functions and quantitative values of platelet and plasma factors. The prothrombin test provides a basis for the search various violations hemocoagulation, prompting the direction of further research. For this purpose, they resort to determining other parameters of the hemostasiogram:
- Indicator of the transition of fibrinogen to fibrin (thrombin time);
- impaired blood clotting;
- liver disease;
- antiphospholipid syndrome - increased thrombus formation due to autoimmune causes;
- blood cancer;
- pathologies in which the production of vitamin K is impaired (blockage biliary tract, poor digestibility of food in the intestines, etc.).
- lack of vitamin K;
- the initial stage of DIC;
- liver pathologies;
- taking drugs from the group of anticoagulants - Tromboass, Agregal, Warfarin, Heparin and others;
- hemorrhagic diathesis of newborns;
- inflammation and blockage of the biliary tract;
- Zollinger-Ellison syndrome;
- malabsorption of fats in the intestine;
- deficiency of coagulation factors - prothrombin, AC-globulin, proconvertin and Stuart-Prauer factor.
- pregnancy;
- DIC;
- high levels of antithrombin-III and other anticoagulants produced by the body;
- deviation from the norm of hematocrit - the ratio of the volume of blood cells to the volume of plasma.
- DIC syndrome;
- cholestasis and other diseases that reduce the activity of vitamin K;
- diseases that disrupt the functioning of fibrin;
- hereditary and acquired pathologies leading to a deficiency of coagulation factors (, liver disease, nephrotic syndrome).
- antibiotics;
- diuretics;
- aspirin;
- indirect anticoagulants;
- anabolics;
- Methotrexate;
- laxatives;
- nicotinic acid;
- Heparin and other clotting inhibitors.
- pregnancy and the period after childbirth;
- vein thrombosis;
- penetration of thromboplastin into the vessels due to tissue damage;
- high blood viscosity (polycythemia).
- The norm of the prothrombin index for women carrying a child is 80-100%. At its high values, in order to avoid thrombosis and other complications, drugs are indicated that reduce increased activity clotting.
- Low PI, on the contrary, carries the risk of bleeding. Normal value prothrombin time for pregnant women - 11-18 sec. During pregnancy, any deviation from the norm in the coagulogram is a reason for a thorough examination and, in most cases, hospitalization.
- Laboratory analysis for prothrombin allows you to assess the quality of the coagulation mechanism.
- Antiphospholipid syndrome in pregnant women (it is manifested by miscarriages, missed pregnancy, placental insufficiency and other obstetric complications);
- Pathology of the liver;
- Atherosclerosis, varicose veins;
- Imbalance of vitamin K in the body;
- The presence of autoimmune diseases;
- Long-term use of anticoagulants of indirect action.
- Heart valve defects;
- Chronic atrial fibrillation and taking "Warfarin" against its background;
- Treatment venous thrombosis and prevention of deep vessel thrombosis after surgery;
- Mitral and aortic valve implantation;
- Treatment of thromboembolism in the pulmonary artery.
- The prothrombin index is calculated taking into account the sensitivity of thromboplastin to blood coagulation factors.
- The analysis results card in any laboratory will contain Quick prothrombin. The norm is in the range of 78% - 142%. The indicator may slightly exceed the average value, but at the same time it should be within normal percentages.
- However, any pathology of prothrombin factors needs to be controlled or even treated.
- An imbalance of vitamin K, which interferes with the proper synthesis of prothrombin in the liver, where it is normally formed;
- Chronic liver diseases and disorders of its work, which also prevent normal synthesis prothrombin;
- Congenital anomalies: lack of factor II, V, VII, X blood clotting;
- The presence of a heparin inhibitor in the coagulation mechanism;
- Nephrotic syndrome, amyloidosis (deposition of a specific pathological protein in the organs);
- Taking antiseptics, laxatives, anabolic agents, hormonal drugs, nicotine and acetylsalicylic acid, quinine, quinidine.
- Thromboembolism (clotting of blood vessels by blood clots);
- Polycythemia (an increase in the number of erythrocytes in the blood, including and in connection with oncological processes);
- cancers: leukemia, cancerous tumors different localization;
- Pre-infarction state of the body;
- Myocardial infarction.
- Vitamin K deficiency - a violation of the synthesis of prothrombin;
- Congenital deficiency of certain factors regulating processes in the blood;
- Pathologies of the liver that prevent the normal synthesis of coagulation factors;
- Lack of fibrinogen in the blood (congenital and acquired);
- Taking drugs that reduce the ability of blood to clot.
- Dysbacteriosis;
- Pathology of the gastrointestinal tract;
- Prothrombin deficiency;
- Hypovitaminosis.
- Varicose veins on the limbs;
- Bleeding and noticeable bruising after minor injuries
- Improper functioning of the liver;
- A long period of no results when trying to conceive;
- Conception through the IVF procedure;
- Multiple pregnancy;
- Delay in the development of the fetus from the norm;
- Drinking alcohol, smoking the expectant mother;
- Long-term treatment with anticoagulants;
- Multiple miscarriages.
- From the 14th to the 20th week, the prothrombin index for INR ranges from 0.55 to 1.1;
- From the 21st to the 28th week, the indicator can decrease to 0.5, but cannot exceed 1.15;
- From the 29th to the 35th week, the result is 0.6 - 1.17;
- From the 36th to the 42nd week, the index is from 0.55 to 1.15.
- newborns - 14-17 s;
- children of the first year of life - 13-15 s;
- children 2-10 years old - 13-18 s;
- adolescents under 16 years old - 11-13 s;
- adults 17-45 years old - 10-15 s;
- after 45 years - 12-14 s.
- International normalized ratio (INR) - the test shows the ratio between the indicators of the patient's prothrombin time and the norms established for a healthy person, taking into account all the individual characteristics and conditions of the body (pregnancy, old age, the presence of chronic diseases).
- Thrombin time - displays the indicator for which fibrinogen is transformed into fibrin.
- Identification of platelet factors - allows you to identify the quantitative composition of all components that are involved in the formation of a blood clot.
- Activated partial thromboplastin time - indicates how quickly activation occurs internal processes triggering the mechanism of blood clotting.
- There are prerequisites for the development oncological diseases blood, as shown by previous blood tests.
- Liver diseases that can affect the ability of the organ to synthesize prothrombins.
- In the presence of increased bleeding gums, scratches and wounds, which is determined visually.
- There is a hormonal failure, against the background of which the efficiency of the circulatory system and hematopoietic organs is reduced.
- Autoimmune diseases that provoke thickening of the blood and an increase in the number of platelets.
- Organ diseases digestive tract, in which there is a lack of vitamin K, which is necessary for the synthesis of prothrombin by liver cells.
- chronic or congenital deficiency vitamin K;
- pathologies of the liver, in which the synthesis of prothrombin cells is slowed down or occurs with defects;
- the use of drugs that promote blood thinning (Aspirin);
- diseases of the digestive tract, in which the absorption of nutrients necessary for the synthesis of prothrombin cells is impossible.
- increased fatigue;
- problems with the digestive tract;
- frequent dysbacteriosis;
- stool disorder;
- pain in the right hypochondrium that occurs after eating fatty foods;
- pain in the left hypochondrium, which most often have a paroxysmal character and depend on the food consumed.
- Prolonged dehydration is when insufficient fluid is taken into the body.
- The presence of problems with the cardiovascular system.
- Increased production of vitamin K and liver diseases that precede it.
- Pathology of the endocrine system.
- Autoimmune diseases.
- The presence of oncological neoplasms.
- Normalization of nutrition and restriction of consumption harmful products that have an increased effect on the pancreas and liver.
- Rejection bad habits and alcohol addiction.
- Active lifestyle with measured physical activity.
An analysis for prothrombin is part of a blood coagulation study - a coagulogram. In addition to the activity of this protein, indicators such as PI (prothrombin index, or PTI) and PT (prothrombin time) are also determined, which allow assessing the rate of clotting. The normal values of prothrombin in women, men and children, as well as the reasons for their deviation from the norm, are described in detail below.
Prothrombin - what is it?
Prothrombin is a high molecular weight protein compound involved in blood coagulation. Its production occurs in the liver in the presence of many substances. In particular, vitamin K, the deficiency of which leads to the synthesis of incorrect prothrombin molecules - they form blood clots that disrupt blood flow and can be fatal.
An analysis of prothrombin is needed to assess blood clotting, and the most accurate and versatile research method is PC - Quick prothrombin. What it is? This test detects the activity of prothrombin in the patient's blood compared to that in a control portion of plasma. This is the ratio of the clotting time of the patient's plasma to the time of this process in the sample.
The analysis is named after the scientist A. Quick, who proposed this method. In the test results, prothrombin according to Quick is expressed as a percentage. In the international nomenclature, it is assigned number II, since it was the second discovered after fibrinogen.
Quick analysis is used not only to assess the activity of blood coagulation elements, but also to study the functioning gastrointestinal tract and liver. The PC test is more versatile than the prothrombin time and prothrombin index tests.
List of indications for the analysis of prothrombin according to Quick:
Reference: Vitamin K is produced by bacteria in the intestine and is actively involved in the formation of prothrombin. The rate of blood clotting is negatively affected by both its lack and excess.
The PC test is necessary to control the hemocoagulation system during the period of use of anticoagulants - Heparin, Warfarin and others. The structure of the blood and its composition also change with the onset of menopause in women (after 45 years), which is a risk factor for the development cancer. Therefore, at this age, it is especially important to regularly take an analysis for prothrombin.
Prothrombin time - what is it?

Depending on the causes of bleeding, blood can begin to clot in two ways - internal or external. The first is activated if the vessels are damaged from the outside - as a result of a bruise, cut, scratch, bite, abrasion. The internal path works when the integrity of the wall blood vessel was broken from the inside - under the influence of toxins, pathogenic microorganisms, antibodies.
Prothrombin time is an indicator that reflects the work of the internal pathway in the hemocoagulation system.
It reflects the effectiveness of the "repair" of vessels that have been damaged by compounds circulating in the bloodstream. In the results of the analysis, the prothrombin time may be referred to as PT, ecombipl RT or RT.
Prothrombin time is increased, compared with the norm, under the following conditions:
The lower the concentration of prothrombin in the blood, the higher the prothrombin time, because the process of blood clotting is slower.
prothrombin time is decreased if the following conditions exist:
Low prothrombin time during the test may be due to long-term storage plasma before the study and violations when taking blood.
 The prothrombin index is an indicator that reflects the rate of start of blood coagulation by inner path. It is calculated on the basis of prothrombin time, so its increase is observed with the same disorders in the body as an increase in PT, as well as a decrease.
The prothrombin index is an indicator that reflects the rate of start of blood coagulation by inner path. It is calculated on the basis of prothrombin time, so its increase is observed with the same disorders in the body as an increase in PT, as well as a decrease.
To determine the PTI, the patient's plasma clotting time is divided by this value in the control sample. Normally, the result should be 95-105%.
The accuracy of the analysis for the prothrombin index depends on the sensitivity of the drugs used in the laboratory. Therefore, it cannot be called universal, in contrast to the Quick prothrombin test.
Elevated prothrombin
If the Quick prothrombin test is elevated and shows high values (up to 150% or more), the reason for this may be:
Elevated prothrombin also appears with prolonged use of drugs:
Prothrombin rate, table
The extreme values of the PC are the numbers below 78 and above 142%. The rates of prothrombin according to Quick are presented in the table.
| Age, years | PK/td> norm limits |
| until 6 | 80-100 |
| 6-12 | 79-102 |
| 12-18 | 78-110 |
| 18-25 | 82-115 |
| 25-45 | 78-135 |
| 45-65 | from 78 to 142 |
Norms of prothrombin in men and women of one age group do not differ. Normal prothrombin time for both sexes is 9-12 sec. The rate of prothrombin in the blood of women who are expecting a baby is slightly higher than normal values.
Low prothrombin
Low prothrombin according to Quick always indicates an excessively rapid formation of blood clots and can be triggered by conditions such as:
The decrease in PC can be explained by such a dependence - the activity of the prothrombin protein is high, the blood coagulates faster compared to the control plasma sample, therefore the Quick prothrombin test is below normal.
Low prothrombin according to Quick can also be caused by taking Mercaptopurine, hormonal contraceptives and other drugs that increase blood density.
prothrombin during pregnancy
Coagulogram - obligatory part tests for pregnant women. The evaluation of this study, including prothrombin tests, allows timely detection of conditions dangerous to the health of the child and the expectant mother.
Prothrombin according to Quick during pregnancy is normally slightly lowered, that is, the activity of the coagulation system increases. This is due to the emergence of a new circle of blood circulation and the preparation of the body for the upcoming birth and possible blood loss.
A very low PC can provoke the development of thrombosis, and its increase in pregnant women can cause severe bleeding during childbirth, including internal bleeding.
Severe bleeding can cause hemolytic shock due to mixing of mother's and baby's blood. This is one of common causes postpartum mortality. To avoid this, in this situation, not only monitor and control the state of the coagulation system, but also introduce immunoglobulins at the 28th week of pregnancy that destroy potentially dangerous antibodies.
Quick page navigation
What it is? Prothrombin is a protein involved in the mechanism of blood clotting, its synthesis occurs in the liver with the participation of vitamin K. Clotting implies the transfer of blood from liquid state into thick.
For comfortable functioning in the body, blood must have a liquid consistency. If the vessels are damaged, the process of coagulation - thickening should occur. The body cannot lose a large volume of blood and clog the vessels with numerous blood clots.
Like any analysis, the prothrombin test is taken on an empty stomach. Patient who cannot perform this condition for health reasons, takes food 4-5 hours before the procedure. Drugs that affect blood clotting should not be taken before taking the test - the results will be far from the truth. If you refuse medicinal product If it doesn't work, tell your doctor if you're taking it.
An analysis of the quality of blood coagulation is necessary when the following diseases and suspicion of their presence:
A prothrombin test can also be prescribed for other diseases to screen for clotting. Under a microscope, the natural mechanism of blood clotting is recreated.
Potassium ions and thromboplastin are added to the recalcified plasma. prothrombin complex has several clotting factors - the analysis allows you to identify a deficiency or surplus of such factors.
Prothrombin time - what is it? (norm)
Prothrombin time is the period of blood clotting from the moment a mixture of potassium and thromboplastin is added to the plasma. Thromboplastin used in laboratories has a certain level of sensitivity to factors II, V, VII and X.
The norm of prothrombin time is from 11 to 16 seconds, but the activity of the substance may differ depending on the sample. Accordingly, draw conclusions by comparing general meaning result in seconds is wrong. Relative evaluation required.
Prothrombin index - what is it? (norm)
The prothrombin index is the ratio of the fixed normal clotting time to individual indicator patient. More precisely, it allows you to determine the prothrombin index analysis by INR (international normalized ratio).
The prothrombin index mathematically corrects the prothrombin time. Individual result in seconds divided by a fixed rate healthy person and multiplied by the sensitivity factor of the taken thromboplastin. The number of the latter is from 1 to 3, it can be found in the universal international classification.
Remember, when determining the prothrombin index: the norm for women and men is the same - from 0.8 to 1.3. But the figure may vary depending on age and health status.
The results of the preoperative study should not go beyond 0.85 - 1.25. An indicator of 3.0 - 4.0 is observed in a patient who has had a myocardial infarction or is suffering from serious cardiovascular diseases.
The norm of the prothrombin index is 2.0 - 3.0 in the case of:
The prothrombin index for INR above 6.0 requires urgent hospitalization of the patient. This coefficient indicates a high risk of internal bleeding in various locations.
The situation is complicated if a person has already observed ulcerative lesions gastrointestinal tract, renal failure, hypertension and blood flow disorders in the brain. In this case, increases potential risk hemorrhagic (associated with bleeding) heart attacks in the organs.
Upon receipt of unsatisfactory results of the analysis according to the INR system, a second study is not required (the result is very sensitive and reliable). Index indicators do not differ depending on the type of laboratory material taken (capillary, deoxygenated blood).
Prothrombin according to Quick - what is it? (low, high and normal)

For several decades now, laboratory conditions calculate prothrombin according to Quick. What it is? This is the percentage of prothrombin activity. The scientist proposed to compare the indicator of the patient's prothrombin time with the indicator of the dependence of this period of time on the number of prothrombin complex factors in the taken plasma. The result is a percentage.
The construction of the dependence allows a very accurate assessment of the coagulation index, but the thromboplastin sensitivity coefficient is not taken into account.
This feature of the test affects the quality of the result in the region of critical values below and above the norm. In standard results and minor deviations from them, the INR index and Quick index are directly proportional.
IN healthy body blood clotting is often increased - hypercoagulability is observed. Such a process is considered the norm until a person has any vascular diseases or chronic tissue damage. Their presence becomes a risk of blood clots.
After the appointment of blood-thinning drugs, regular screening is necessary. In some cases, a depot (a stage of accumulation of a substance) can form in the body from these funds, which will lead to a state of hypocoagulation with increased bleeding.
In addition, in the results of the analysis there may be an opposite process - hypercoagulation (increased coagulation activity). Indicators of insufficient blood density are observed much less frequently than excessive ones.
Elevated prothrombin in men and women
Prothrombin in men and women over 45-50 years of age is often elevated - more than 142% according to Quick. Hypercoagulability can be caused by both the presence of vascular disease and temporal factors. The latter include:
Elevated prothrombin, not due to the above factors, indicates the presence serious illnesses. So, diagnostic search is based on the following nosologies:
Prothrombin in women may be elevated due to long-term use hormonal contraceptives, especially with an increased dosage of the estrogen component (from 30 to 50 mcg in 1 tablet).
If the patient has serious vascular disease, birth control pills need to be cancelled. It is possible to switch to hormonal preparations local exposure (candles, vaginal ring).
Diet does not significantly affect blood clotting. You can reduce the indicator for Quick by a few percent by adding to daily menu"oxidizing" products. Increased score causes malnutrition fermented milk products, red and black berries, citrus fruits, fatty varieties fish and water intake.
Low prothrombin - what does it mean?
Low prothrombin is observed during hypocoagulation. This result indicates the tendency of the body to internal bleeding. The lack of coagulation factors is observed in the following situations:
A low prothrombin rate indicates diseases:
Adjust slightly reduced rate prothrombin can be obtained with foods containing vitamin K. Cabbage, carrots, bananas, apples, pears, spinach and lettuce will be useful.
The reason for the lower results in the diet concerns more men than women. It is the male gender that prefers meat products vegetables. As a result of such addictions, there is a deficiency of vitamins in the body.
prothrombin during pregnancy
Pregnant women are tested for prothrombin index in without fail. During childbirth, a low rate can lead to heavy bleeding, and high - to premature contractions and even miscarriage at a later date.
Therefore, it is very important to evaluate this indicator during gestation, especially if there are various complications both in this pregnancy and in the previous one.
During the gestation period, a blood test for the prothrombin index is taken at least 3 times (once per trimester). If future mother significant deviations are diagnosed, it is necessary to do a clotting test more often. The rate of prothrombin in the blood of women during pregnancy is lower than usual - from 70% to 120%.
Violations in the mechanism of blood clotting in pregnant women are evidenced by:
Since prothrombin according to Quick decreases during pregnancy, the INR index also decreases. Changes are especially noticeable in the second trimester of gestation. Until the 13th week, the coefficient should correspond to the norm: from 0.8 to 1.3. Further, the indicator decreases:
In the case of pregnant women, the INR indexing method is preferred. The indicators are quite low, and the Quick method gives errors at critical values.
Wounds, scratches and surgical operations, which are accompanied by blood loss, would expose a person to mortal danger if the blood could not clot and form blood clots. One of these proteins that prevent huge blood loss is prothrombin. The level of prothrombin in the blood has its own indicators. Exceeding it indicates too a large number of this protein in the blood, which causes the blood to thicken and can lead to blood clots. The lack of prothrombin is no less life-threatening, since during the slightest bleeding a person can lose a large amount of blood. What is the established norm of prothrombin in the blood, and on what indicators does this value depend, we will consider further.
Prothrombin is the protein that rolls up fairly quickly, so extract it from general composition plasma is quite difficult.
In this regard, there are several methods for determining the level of prothrombin, on which the normal indicator depends. The prothrombin index, which is calculated as a percentage, indicates that normally for all people, regardless of age, the indicators should fall within such boundaries as 95-105
%. The only exception are women during pregnancy, for whom the upper limit is somewhat reduced to 98-100%. This process quite natural and is dictated by the need to secure the body during childbirth, when there is a high probability of profuse blood loss.
The prothrombin index, which is calculated as a percentage, indicates that normally for all people, regardless of age, the indicators should fall within such boundaries as 95-105
%. The only exception are women during pregnancy, for whom the upper limit is somewhat reduced to 98-100%. This process quite natural and is dictated by the need to secure the body during childbirth, when there is a high probability of profuse blood loss.
The Quick prothrombin study, which has some differences in the detection process itself, has such limits - 70-120. In older people, the upper limit barely reaches 110, which is also the norm and indicates age-related changes in the body caused by active aging processes. During pregnancy, especially in the third trimester, values up to 110% are acceptable.
An important study that shows how long the blood coagulates without exposure to any anticoagulants is the prothrombin time.It is measured in seconds and for each age interval has its own norms of values:

 Too fast blood clotting about its oversaturation with prothrombins, which leads to its thickening and difficulty in passing through the vessels.
Too fast blood clotting about its oversaturation with prothrombins, which leads to its thickening and difficulty in passing through the vessels.
Ask your question to the doctor of clinical laboratory diagnostics
Anna Poniaeva. Graduated from the Nizhny Novgorod medical academy(2007-2014) and residency in clinical laboratory diagnostics (2014-2016).
In the case when the indicators are very different from the norm, there is a need to additional method research INR - international normalized ratio. This coefficient reflects the rate of coagulation, and also indicates possible problems with health. Normally, acceptable INR values are 0.85-1.15.
In order to understand what values \u200b\u200bare indicated in the analysis, it is necessary to analyze what methods are used to detect prothrombin in the blood. Consider all technologies used in details.
What analyzes are used?
All methods for the determination of prothrombin are based on biological processes blood coagulation that take place in several stages. At mechanical damage vessel receives a signal about the beginning of bleeding. Thrombin factors are released at the site of injury, activating increased viscosity blood, resulting in the formation of a blood clot. This blood clot blocks the leak, after which the integrity of the vessel is gradually restored.
The clotting process can be external factors, and internal ones, the activation of which completely depends on the situation. An analysis for prothrombin can be calculated by several methods that have their own distinctive features.
The most common analyzes that are part of the coagulogram are prothrombin time, prothrombin index, Quick prothrombin.prothrombin time
 Prothrombin time is a numerical indicator, calculated in seconds, which shows how long it takes the blood to clot and transform into a blood clot. Every person has this numerical value will differ, due to the characteristics of the organism. For the study, venous blood is required, which is poured into a test tube with an anticoagulant (most often sodium citrate).
Prothrombin time is a numerical indicator, calculated in seconds, which shows how long it takes the blood to clot and transform into a blood clot. Every person has this numerical value will differ, due to the characteristics of the organism. For the study, venous blood is required, which is poured into a test tube with an anticoagulant (most often sodium citrate).
The vessel is placed in a centrifuge, where all blood elements under the influence of centrifugal force settle to the bottom and are removed. Calcium is injected into the purified blood obtained to neutralize the action of sodium citrate in a ratio of 9:1. Next, a tissue factor (a special reagent that acts as a catalyst for the reaction) is added, after which natural process coagulation.
In the case where there is increased content bilirubin, the analysis is performed using a special apparatus that allows you to count automatically.Prothrombin index
 This indicator is calculated according to the formula, where the value of prothrombin time in a healthy person is taken, divided by the indicator of the studied blood sample, and then multiplied by 100%. The resulting value reflects the activation of blood clotting along the external pathway. This indicator helps to identify liver problems when prothrombin is produced in insufficient quantities, as well as to monitor the effectiveness of anticoagulant treatment.
This indicator is calculated according to the formula, where the value of prothrombin time in a healthy person is taken, divided by the indicator of the studied blood sample, and then multiplied by 100%. The resulting value reflects the activation of blood clotting along the external pathway. This indicator helps to identify liver problems when prothrombin is produced in insufficient quantities, as well as to monitor the effectiveness of anticoagulant treatment.
PTI = normal PV / patient PV *100%
Data for determining this indicator are taken from a previous study of prothrombin time, which uses exclusively venous blood purified by centrifugation.Prothrombin according to Quick
This research method is the most informative and reliable to date. The results obtained as a percentage reflect the activity of the prothrombin complex, which guards blood clotting. Simply put, the resulting numerical value indicates how quickly all the mechanisms of blood coagulation are launched.
Prothrombin in the blood is calculated according to Quick using a formula where it is required to divide the indicator of the temporary activity of the prothrombin protein by the indicators of the control sample. The data obtained can give a more complete picture of the state of blood coagulation.
For analysis, blood from a vein is used, which is cleared of red blood cells.
After that, under the influence of various catalysts and reagents, a study is carried out, the results of which are calculated by the formula.Additional research methods
In the case when the coagulogram has conflicting indicators and there is a need for additional research, resort to such analyzes., How:

Indications for the study
Prothrombin study included in the coagulogram, which is mandatory analysis blood during clinical examination, as well as during pregnancy. Also, this analysis can be prescribed in the following situations:
What can affect the result?
Because quantitative and qualitative composition may vary throughout the day, then to get the most reliable results It is recommended to donate blood in the first hours after waking up. At this time everything is vital important features are just starting to activate, so the percentage of error caused by external factors is reduced.
It is important that blood sampling be carried out on an empty stomach, since at the time of digestion and assimilation of food, a large amount enters the bloodstream. nutrients capable of influencing the rate of blood coagulation. It is necessary to establish nutrition 2-3 days before donating blood, excluding fried and fatty foods, as well as sweets.
Alcohol and any alcoholic beverages should be excluded 4-5 days before blood donation.
Smoking, if it has become a habit, is stopped 12 hours before the analysis, since high concentrations of nicotine and tar in the blood can affect the indicators, giving incorrect results.
If a person is forced to take any medication for permanent basis, then this is reported to the doctor, who gives a referral for an examination. A corresponding note is made in the control sheet, which will allow assessing the real picture of the state of blood coagulation, taking into account the error.
A few days before the analysis, it is recommended to exclude any physical activity that provokes physical overwork. A person should have a good rest and sleep, and also not experience emotional shock or stress.
In the case when the results obtained are below the norm or above the norm, and the blood clotting time has its own deviations, it is recommended to retake the blood in a few days in another laboratory.
Not to be underestimated human factor and characteristics of the laboratory.Decryption
After a blood test has been performed, the patient is given a transcript, which indicates all the data on the state of blood coagulation. It is usually presented in the form of a table divided into several columns. The first column indicates the research methodology and indicator, and the second column indicates the numerical value. The third column contains normal values for various groups of patients, which makes it easier for people who do not have a medical education to perceive the results.
With the received transcript, you must contact the doctor who gave the referral.
He will evaluate the results and decide whether additional studies are needed, or whether the coagulogram data will be enough to make a diagnosis.What values are considered low?
Low levels of the prothrombin index are extremely life-threatening, as it signals slow blood clotting. This, in turn, is fraught with the development of bleeding, which in a healthy person proceeds without consequences and threats to life. Indicators that tend to 80% are considered low. The lower this indicator, the more dangerous the state of human health.
 Some transcripts contain another column that indicates the reasons for deviations from the norm. Low rates can be caused by:
Some transcripts contain another column that indicates the reasons for deviations from the norm. Low rates can be caused by:
External clinical manifestations and symptoms of low rates may be as follows:
A normal finger cut can result in the loss of 100-150 ml of blood, and a deeper abrasion can even cause full-blown life-threatening bleeding.
When low prothrombin reaches critical indicators, that is, the need for hospitalization and complete examination. Otherwise, a person is in mortal danger, and any awkward movement can provoke the development internal bleeding. It is possible to increase the level of prothrombin in the blood in women and in men with the help of blood transfusion, when we are talking about critical situations that threaten a fatal outcome.
Treatment is carried out only after assessing the state of health, as well as after identifying the root cause. Blood transfusion cannot be used permanently.
This is only a necessary measure that supports the life of a person in a critical situation.What values are considered elevated?
No less dangerous are indicators that significantly exceed the maximum allowable norms. A high prothrombin of 110-120% indicates the presence high concentration platelets in the blood, which makes the blood thicker. This, in turn, makes it difficult to pass through the vessels, causing stagnant processes.
by the most dangerous consequence, which can develop with prolonged high rates of blood clotting is the formation of blood clots. Dense blood clots moving along the bloodstream along with blood can settle on the walls of blood vessels, preventing the flow of blood to individual tissues and organs.
The mortal danger is that a blood clot can break off at any moment and, together with the general blood flow, enter the heart, where it will cause it to stop due to valve blockage.An increase in blood viscosity can develop for several reasons:
Certain medications can cause blood to thicken, so it is important to let your doctor know before doing the test.
Experienced laboratory assistants are able to determine the presence high performance blood clotting after a finger prick or blood sampling from a vein.If the blood flows too slowly and you have to apply force to draw it, then there is a high probability of a high prothrombin index. special clinical manifestations this pathology does not have and is often detected during a routine examination or during pregnancy.
It is strictly forbidden to independently take medications that can thin the blood. Especially if there is a suspicion of the progression of thrombophlebitis or thromboembolism. Aspirin-containing medicines that thin the blood artificial way, can provoke a separation of a blood clot from the walls of the vessel and its free movement to the heart, which will lead to inevitable death.
In the case when the obtained indicators differ significantly from normal, it is necessary to retake the analysis after 2-3 days. If the repeated results turn out to be identical, then it will be necessary to produce a series additional research, which can indicate the presence of a specific health problem.
Because if there is thick blood there is a high probability of blood clots, patients will definitely need to consult a phlebologist and a cardiac surgeon, who will be able to assess possible health risks. Treatment is tailored to individual characteristics each patient, after a full examination and identification of the root cause.
Self-medication is strictly prohibited, as it can cause death.Normal level prevention
 Since the quantitative indicator directly depends on the lifestyle of a person, the following recommendations can be considered prevention:
Since the quantitative indicator directly depends on the lifestyle of a person, the following recommendations can be considered prevention:
In order to timely identify the presence of pathologies in the body, it is worth paying attention to how quickly blood coagulates when cut.
If the blood is quite difficult to stop, then you need to pass an appropriate analysis and establish the cause of what is happening.It is strictly forbidden to take any medications that can change the viscosity of the blood. Only a doctor has the right to prescribe this kind of treatment, based on the results of the study.
Thus, the prothrombin rate of which depends on the research method, shows the ability of blood to coagulate and form blood clots. This property is extremely important, as it provides protection during operations or injuries, accompanied by a violation of the integrity of parts of the body.