Why did the muscles cramp during the first time. Cramping: why it appears, what happens, how to get rid of it. Why are seizures dangerous?
Physical exercise is good for the health of the body. Then why sometimes so unexpectedly and painfully reduces muscles after a workout? Why, instead of pleasant fatigue, a person may experience convulsive muscle contractions? And this applies not only to professional athletes, but also amateurs.
During training, the main systems of the body work intensively, but the skeletal muscles experience the most serious load. It consists of individual muscle fibers, each of which has its own innervation. The signal to contract comes to the muscle from the motor center of the brain through a chain of neurons.
Sometimes such contractions are regulated by humoral mechanisms - the release of special substances into the blood that provoke sudden strong paroxysmal movements. This phenomenon is called neurohumoral regulation and occupies one of the main places among the causes of the development of convulsive contractions.
The body receives energy for movement from the breakdown of carbohydrates and fats. However, the resources of each organism are individual. One can do two or three workouts a day, the other gets tired after an hour and the muscles “refuse to train”.
In both cases, involuntary contractions of the muscle fiber are possible, blocking its movements and often accompanied by pain. This is a spasm - evidence of muscle strain, a kind of signal to reduce the load. It can occur directly during the exercise or after some time after its termination.
What muscles are affected?
Theoretically, any muscle can develop a spasm. In practice, this most often occurs in the following muscles:
- Calf (located in the back of the lower legs);
- Quadruple (occupies the front of the thighs);
- Thoracic (close the chest);
- Semimembranosus and semitendinosus (back of the thighs).
It is possible that it can reduce the trapezius and sternocleidomastoid muscles of the neck and fibers of the hands. Rare, but possible muscle spasms of the feet.
Speaking of skeletal muscles, many people forget that the smooth muscles of internal organs, such as the intestinal wall, blood vessels, and the bronchial tree, are also subject to convulsions. Severe physical activity can provoke sudden contractions of such muscles and the corresponding clinical picture.

About risk factors
Post-workout cramps cannot be managed. However, it is necessary to try to understand what provokes their appearance. In the first place should be put disproportionate physical activity. As a result, an overvoltage signal enters the brain, and it gives a command for functional blocking. The muscle is so strongly strained that its movement is almost impossible. It seems to a person that something holds his muscles and does not allow him to make free movements.
The second factor is violations of the water-salt balance. During exercise, the body intensively evaporates moisture, which lowers its physical endurance. In addition, along with sweat, electrolytes (substances that can conduct electricity) leave the body. The most important of them are chlorine, magnesium, calcium, sodium, potassium. Thanks to such components, electrical impulses are formed in the body, stimulating the work of the heart muscle, respiratory and nervous systems.

The third is associated with a decrease in muscle mass, for example, due to age, prolonged lack of exercise, a change in sport, past illnesses, dietary restrictions, changes in living conditions.
This factor is directly related to impaired blood supply to the muscles, insufficient saturation of them with oxygen and essential nutrients. If the tissues are deficient in blood supply, they have a disturbed metabolism, and, consequently, the ability to convulsions.
The following risks cannot be completely excluded: hypothermia, previous long-term use of medications, the presence of chronic diseases, experiencing stressful situations, severe allergic reactions, smoking and alcohol.
What to do in this case?
If during training the muscle “stopped” in an unpleasant way, you need to give it rest and endure the time. Usually, the cramp gradually releases, returning the muscle fiber to its original state. This will take up to a minute (in extreme cases - no more than 5). However, there are several tricks that will help make it softer.

- It is necessary to stop moving, it is convenient to become or sit down to maintain balance (if it concerns the muscles of the legs);
- With superficial light movements, stroke the spasmodic muscle, slightly stretching it to the sides.
If after a minute the cramp has not released the muscle, it is recommended to cool it with ice or apply a special rubberized bandage.
The significance of this phenomenon should not be underestimated. Most likely, the body gives a signal that it is not ready for such loads, or the organization of the lesson was carried out incorrectly. It is worth thinking about the functional redistribution of physical activity and alternating it with sufficient rest.
How to prevent?
What to do so that the nervous system does not interfere with sports? Make a regimen of your classes, taking into account age, muscle fitness, lifestyle, regularity and duration of classes, types of exercises, the presence of bad habits and the state of health of the body at a particular moment.
Exercise should not exhaust the body and exhaust all available resources. It is necessary to give an intermediate rest, in which to drink water and restore breathing. To prevent stagnation of blood and lymph in the muscles, it is optimal to alternate flexion and extension movements with stretching.

With a fixed load on one muscle, metabolic processes of the breakdown of purine bases begin to occur in it with the formation of uric acid. Competent stretching does not allow such a component to accumulate in one place and evenly distributes it over the entire area of \u200b\u200bthe muscle. This also explains the beneficial effects of massages and rubbing.
While exercising, you can not limit your body in the intake of nutrients, water, vitamins and minerals. The diet should be balanced and contain all the necessary elements.
Many resort to sports exercises in order to lose weight. They are malnourished and exhaust the body with nutritional deficiencies. No matter how much a person wants to lose weight, intense exercise will not help achieve results. On the contrary, by depleting his biological resources, a person becomes weaker, he often has unreasonable convulsive muscle contractions. If, having taken the necessary measures to stabilize the process, convulsions continue to recur periodically, you should consult a doctor and find out their causes.
Overstrain of muscle tissue with a painful and unpleasant feeling after a workout is familiar to absolutely every person involved in both amateur and professional sports. The causes of seizures, when the muscles begin to reduce, can be very different. An agonizing sensation most often appears during active training. It can be in two forms - light and heavy.

The following muscles are most susceptible to overexertion:
- Semimembranosus, biceps, semitendinosus. They form the back of the thigh.
- Calf. Located on the back of the leg.
- Four-headed. It is not located on the front side of the thigh.
- Breast. Located along the entire chest.
In addition, cramps quite often reduce the muscles in the arms and even on the feet.
Who is at risk?

Athletes and all people who are physically active are most often subject to muscle overstrain. Spasms can begin not only during direct training, but much later. Sometimes convulsions occur after 4-6 hours after direct employment.
The elderly are also at risk. The main reason for this is the age-related decrease in muscle mass, which occurs after 40 years, as well as a sharp decrease in physical activity.
In young children, control over muscle tissue is poorly developed, so convulsions can occur at any time. In pregnant women, in 30% of cases, muscle tissue is also reduced. This condition occurs due to a sharp fluctuation in weight in the direction of increasing mass.
Causes of muscle contraction

Seizures can occur due to:
- strong overvoltage, which increases against the background of high temperatures, when a large amount of microelements is excreted from the body along with sweat;
- some chronic diseases;
- hypothermia;
- taking certain medications;
- abuse of alcoholic beverages and smoking;
- overweight;
- nervous diseases.
Often, the cause of cramps can be sprains of the tendons, as well as an excessively high load on the muscles.
Muscle fatigue and neuromuscular control

Most people associate post-workout muscle pain with tissue growth, which is a misnomer. Unpleasant painful sensations are a reaction of the body that signals a person about excessively high loads or microscopic damage.
To avoid this, muscle tissues need to adapt, that is, to establish a neuromuscular connection when information about active physical activity is stored in memory. It is much easier for a person to return to good shape and not suffer from overexertion when he used to play sports. Prepared muscles become more resilient, stronger, grow faster in volume.
Neuromuscular control is an essential tool in the prevention of seizures for those who have taken breaks from training for any reason. This will allow you to recover three to four times faster when you return to the gym after suffering an injury and so on.
Dehydration or electrolyte deficiency
Training provokes increased sweating, which leads to the loss of salts and moisture. Sodium, calcium, magnesium, potassium ions are excreted from the body. This condition often causes dehydration and spasmodic attacks.
Against the background of water imbalance disrupts the exchange of electrolytes. It should be understood that this can happen not only because of training, but also because of the lack of clean drinking water drunk during the day. To avoid problems, it is necessary to maintain a normal water-salt balance.
Other reasons

Convulsions are most often mild, but sometimes they indicate hidden diseases. If spasms occur frequently, you should make an appointment with your doctor.
Muscle strain may be associated with:
- diseases of the musculoskeletal system, including osteochondrosis;
- circulatory disorders;
- problems of the nervous system;
- metabolic disorders;
- thyroid diseases;
- varicose veins;
- beriberi.
Some medications can also lead to muscle tension.
Seizure symptoms
Cramps cannot be ignored, but the degree of contraction can vary from a slight tingling to excruciating severe pain. A spasmodic attack makes the muscles unnaturally hard and tight. In some cases, there is twitching under the skin. The duration of seizures varies. They can last a few seconds and even a quarter of an hour, be regular, and pain persist for several days.

Usually, spasmodic attacks do not require any special therapy, but require a certain sequence of actions to help eliminate the spasm:
- Cessation of the movement that provoked the spasm.
- Slow massaging and stretching the muscle.
- Relaxation and rest in a few minutes.
- Cooling with ice or applying an elastic bandage.
When these manipulations do not relieve painful contractions, you should contact a specialist who will accurately diagnose and give instructions for further action.
Prevention of muscle spasms
The best remedy for cramps is a good stretch, so warm-up and cool-down is a must. This reduces the likelihood of muscle convergence by 80%. In addition, massage helps a lot.
Muscle rubbing should be carried out with the use of oils, which not only make the process more enjoyable, but also contribute to the replenishment of microelements in the muscles. It is recommended to apply something warm to the problem area after the massage.
Rubbing the hands and feet is aimed at massaging the points that connect the body. Along with massage, warm baths are useful, as water also gives a slight massage effect. It is good to take water procedures with herbs, because aromatherapy allows you to relax well.
Diet food
If you suffer from abdominal cramps, you should drink a glass of warm milk at night. The menu should include more foods containing calcium and magnesium. They strengthen connective tissues. Phyto-tea gives a good effect. Herbal decoctions are useful not only for the muscles, but also have a calming effect on the nervous system.
Various salty snacks, convenience foods, sweet, fried and too fatty foods should be excluded from the diet. It contains a minimum of valuable and nutrients and negatively affects the metabolism in the body, that is, it is not useful.
Find out why muscles cramp and how to get rid of this painful and unwanted phenomenon.
Many of you have experienced the feeling when the muscles live their own lives and begin to voluntarily contract on their own, and very often this happens when you are just relaxing, and even worse at night during.
This phenomenon has long been studied by sports medicine specialists, but despite the rather tangible progress in solving this problem, unfortunately, muscle cramps have not been fully studied.
CAUSES IN MUSCLE CRAMPS
Despite the fact that muscle cramps occur during rest, it can often occur during exercise, for several reasons:
During a heavy physical exercise, the muscle that takes on the main load gives off all the strength and energy earlier than the load has ended on it. She has exhausted all her reserves, as a result of which her contractile and nervous abilities are temporarily disturbed. There is only one way out to stop the load on the muscles, then there will be no sense, and the pain will increase.
- muscle wasting, as a result of too intense training and an unbalanced diet. It turns out that the muscles are not completely, they are deficient in important substances and, having not received a proper rest, the muscle fibers, experiencing another load, fail and, as it were, turn on a protective mechanism in the form of convulsions, refusing to work further.
-
deficiency in the body of magnesium-potassium-sodium. These trace elements are consumed by the body and the greater the physical activity, the greater their loss. Without sufficient use of them, the muscles begin to give up in their work and then do not be surprised why the muscles cramp, besides this, it will not be superfluous to take B vitamins.
- calcium deficiency. Another cause of convulsions is considered to be a lack of calcium, a low concentration of which reduces neuromuscular excitability, in addition, calcium is important for strength, its deficiency can be compensated by increasing dairy products or in emergency cases by buying special preparations, for example - Calcemin.

HOW TO REMOVE A CRAMP
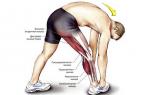
1. Get a massage. If a cramp caught you at the most inopportune moment, try to straighten the sore muscle and massage it, but it will be painful, unpleasant, but if you don’t, then prolong your torment much longer.
2. Straighten the muscle. A cramp can grab anywhere, but most often it grabs the calf muscles, toes and leg muscles in general, to do this, straighten your leg and pull the toe towards you, while kneading the diseased area, if you have a needle at hand, lightly prick the diseased area.
3. Take your medications. Also, if convulsions have been repeated repeatedly, to prevent and suppress the cause of muscle cramps, they use medications - Asparkam and Panangin, the course of which lasts from 2 to 4 weeks.
4. Use ZMA. Based on reason number 3, you can use a sports supplement consisting of magnesium - zinc - vitamin B6 or buy these trace elements separately at a pharmacy.
5. Consult a doctor. In the case when convulsions have sharply negative consequences - severe swelling, swelling of the muscles, consult a doctor immediately.
Live healthy and without pain, I hope the advice from the BOMBA BODY website will benefit you, good luck!
- Muscle cramps are involuntary and intense muscle contractions without a period of relaxation.
- Almost everyone has experienced a seizure at least once in their life.
- There are different types of seizures and different causes for them.
- Many different medications can cause muscle cramps.
- In most cases, a muscle cramp can be stopped by relaxing (stretching) the muscle.
- Muscle cramps can often be prevented through measures such as a nutritious diet with sufficient micronutrients and adequate fluid intake.
This is an involuntary and violent contraction of the muscle, without a period of relaxation of the muscle. When muscles that can be controlled voluntarily, such as the muscles of the arms or legs, are used, they alternately contract and relax as certain movements are made in the limbs. The muscles that support the head, neck, and torso work in sync and maintain the position of the body. A muscle (or even a few muscle fibers) can be involuntarily in a state of spasm. If the spasm is strong and persistent, then this leads to the appearance of convulsions. Muscle cramps are often visualized or palpated in the region of the muscle involved.
They can last from a few seconds to a quarter of an hour, and sometimes longer. It is also not uncommon for the seizures to recur until the muscle relaxes. The spasmodic contractions may involve part of a muscle, the entire muscle, or several muscles that usually contract simultaneously when performing movements, such as flexing several fingers. In some cases, cramps can be simultaneously in the antagonist muscles responsible for movements in opposite directions. Muscle cramps are widespread. Almost all people (about 95% of people according to some studies) have experienced seizures at some point in their lives. Muscle cramps are common in adults and become more common with age, but cramps can still occur in children. In any muscle (skeletal) in which voluntary movements are performed, there may be cramps. Cramps of the limbs, legs and feet, and especially the calf muscle, are very common.
Types and causes of muscle cramps
Skeletal muscle cramps can be divided into four main types. These include "true" seizures, tetanic seizures, contractures, and dystonic seizures. Seizures are classified according to the causes of the seizures and the muscle groups they affect.
Types of muscle cramps
 True convulsions. True cramps involve part or all of a muscle or group of muscles that normally function together, such as the muscles involved in flexing several adjacent fingers. Most researchers agree that true cramps are caused by increased excitability of nerves that stimulate muscle contractions. They are overwhelmingly the most common type of skeletal muscle cramps. True seizures can occur in a variety of circumstances.
True convulsions. True cramps involve part or all of a muscle or group of muscles that normally function together, such as the muscles involved in flexing several adjacent fingers. Most researchers agree that true cramps are caused by increased excitability of nerves that stimulate muscle contractions. They are overwhelmingly the most common type of skeletal muscle cramps. True seizures can occur in a variety of circumstances.
Injuries: Persistent muscle spasms may occur as a defense mechanism after an injury such as a broken bone. In this case, as a rule, spasm allows you to minimize movement and stabilize the area of injury. Injury to just the muscle can also lead to muscle spasm.
Vigorous activity: true cramps are usually associated with active muscle loading and muscle fatigue (when playing sports or during unusual activities). Such convulsions can occur both during the activity and after, sometimes many hours later. In addition, muscle fatigue from sitting or lying down for a long period of time in an awkward position or any repetitive movement can also cause cramps. Older people are more at risk of seizures during vigorous or strenuous physical activity.
Rest spasms: Seizures at rest are very common, especially in the elderly, but can occur at any age, including childhood. Rest spasms often occur at night. Night cramps, while not life threatening, can be painful, disrupt sleep, and may recur frequently (i.e., many times a night and/or many nights a week). The actual cause of nighttime cramps is unknown. Sometimes these cramps are initiated by a movement that contracts the muscles. An example would be stretching the foot in bed, which shortens the calf muscle, where cramps are most common.
Dehydration: Sports and other vigorous physical activity can lead to excessive fluid loss through sweat. With this type of dehydration, the likelihood of true seizures increases. These cramps most often occur in warm weather and may be an early sign of heat stroke. Chronic dehydration due to diuretics and poor fluid intake can similarly lead to seizures, especially in the elderly. Sodium deficiency has also been associated with seizures.
Redistribution of fluids in the body: True convulsions can also be noted in conditions where there is an unusual distribution of fluid in the body. An example is cirrhosis of the liver, in which there is an accumulation of fluid in the abdominal cavity (ascites). Similarly, seizures are a relatively common complication of the rapid changes in body fluids that occur during dialysis for kidney failure.
Low Blood Electrolytes (Calcium, Magnesium): Low blood levels of calcium or magnesium directly increase the excitability of nerve endings that innervate muscles. This may be a predisposing factor for the spontaneous true seizures that many older people experience, and these seizures are also common in pregnant women. Low levels of calcium and magnesium are common in pregnant women, especially if these minerals are not getting enough from the diet. Seizures occur in any circumstance that reduces the availability of calcium or magnesium in body fluids, such as diuretics, hyperventilation, excessive vomiting, lack of calcium and/or magnesium in the diet, insufficient absorption of calcium due to vitamin D deficiency, decreased parathyroid function.
Low potassium levels: Low blood potassium levels sometimes cause muscle cramps, although muscle weakness is more common with hypokalemia.
Tetany
With tetany, all the nerve cells in the body are activated, which then stimulate muscle contraction. In this type, convulsive contractions occur throughout the body. The name tetany comes from the spasms that occur when tetanus toxin affects the nerves. However, this name for this type of cramp is now widely used to refer to muscle cramps in other conditions, such as low blood levels of calcium and magnesium. Low levels of calcium and magnesium increase the activity of the nervous tissue non-specifically, which can lead to the appearance of tetanic seizures. Often these seizures are accompanied by signs of hyperactivity of other nerve functions in addition to muscle hyperstimulation. For example, low blood calcium not only causes muscle spasm in the hands and wrists, but it can also cause numbness and tingling sensations around the mouth and other areas of the body.
Sometimes, tetanic convulsions indistinguishable from true seizures. Additional changes in sensation or other nerve function may not be noticeable, as the pain of a cramp may mask other symptoms.
contractures
Contractures occur when muscles cannot relax for an even longer period than with the main types of muscle cramps. Constant spasms are caused by the depletion of adenosine triphosphate (ATP), the energy intracellular substrate of the cell. This prevents relaxation of the muscle fibers. The nerves are inactive in this type of muscle cramp.
Contracture can be the result of genetic inheritance (eg, McArdle disease, which is a defect in the breakdown of glycogen to sugar in muscle cells) or acquired conditions (eg, hyperthyroid myopathy, which is a muscle disease associated with an overactive thyroid gland). Convulsions of the type of contractures are rare.
Dystonic spasms
The last category of seizures are dystonic seizures, in which muscles not involved in the intended movement are affected and contracted. Muscles that are involved in this type of cramp include antagonistic muscles that usually work in the opposite direction of the intended movement, and/or others that enhance the movement. Some dystonic spasms usually affect small muscle groups (eyelids, cheeks, neck, larynx, etc.). The arms and hands may be affected during repetitive movements such as pissing (writer's cramp), playing a musical instrument. These activities can also lead to true cramps due to muscle fatigue. Dystonic seizures are not as common as true seizures.
Other types of seizures
Some spasms are caused by a number of nervous and muscular diseases. For example, these are diseases such as amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (Lou Gehrig's disease), accompanied by muscle weakness and atrophy; radiculopathy in degenerative diseases of the spine (hernia, disc protrusion, osteophytes), when root compression is accompanied by pain, impaired sensitivity and sometimes convulsions. Seizures can also occur with peripheral nerve damage, such as diabetic neuropathy.
Crumpy. This type of cramps, as a rule, describes cramps in the calf muscle, and associate their appearance with muscle strain and the presence of degenerative changes in the spine (osteochondrosis of the lumbar spine, lumbar ischialgia). In addition, cramps are possible with disorders of the vascular circulation in the lower extremities (with obliterating endarteritis or post-thrombophlebitic syndrome). Also, various biochemical disorders in the triceps muscle of the leg can be the cause of cramps.
Many medicines can cause seizures. Strong diuretics such as furosemide or vigorous fluid removal from the body, even with less potent diuretics, can induce seizures as dehydration and sodium loss occur. At the same time, diuretics often cause loss of potassium, calcium and magnesium, which can also cause seizures.
Medications such as donepezil (Aricept, which is used to treat Alzheimer's disease) and neostigmine (Prostigmine, used for myasthenia gravis) and asraloxifene (Evista) used to prevent osteoporosis in postmenopausal women can be a cause of seizures. Tolcapone (Tasmar), which is used to treat Parkinson's disease, has been shown to cause muscle cramps in at least 10% of patients. True convulsions have been reported with nifedipine and the drugs Terbutaline (Brethine) and albuterol (Proventil, Ventolin). Some medicines used to lower cholesterol, such as lovastatin (Mevacor), can also cause seizures.
Seizures are sometimes noted in dependent individuals during the cessation of sedatives.
A lack of certain vitamins can also lead directly or indirectly to muscle cramps. These include deficiencies in thiamine (B1), pantothenic acid (B5), and pyridoxine (B6). The exact role of deficiency of these vitamins in causing seizures is unknown.
Poor circulation in the legs leads to a lack of oxygen in the muscle tissue and can cause severe muscle pain (intermittent claudication) that occurs when walking. It usually occurs in the calf muscles. But the pain in vascular disorders in such cases is not caused by the muscle cramp itself. This pain may be more related to the buildup of lactic acid and other chemicals in muscle tissue. Cramps in the calf muscles can also be associated with a violation of the outflow of blood in varicose veins and, as a rule, cramps in the calf muscles occur at night.
Symptoms and diagnosis of muscle cramps
Characteristically, the spasm is often quite painful. As a rule, the patient has to stop activities and urgently take measures to relieve seizures; the person is unable to use the affected muscle during the seizure. Severe cramps may be accompanied by soreness and swelling, which can sometimes persist for up to several days after the cramp has subsided. At the time of the cramp, the affected muscles will bulge, feel hard and tender to the touch.
Diagnosis of seizures usually does not present difficulties, but finding out the reasons may require both a careful collection of the medical history and instrumental and laboratory methods of examination.
Treatment
 Most cramps can be interrupted by stretching the muscle. For many leg and foot cramps, this stretch can often be achieved by standing up and walking. With cramps in the calf muscles, it is possible to bend the ankle with the help of the hand, while lying in bed with the leg extended straight. For writing spasm, pressing the hand against the wall with the fingers down will stretch the flexors of the fingers.
Most cramps can be interrupted by stretching the muscle. For many leg and foot cramps, this stretch can often be achieved by standing up and walking. With cramps in the calf muscles, it is possible to bend the ankle with the help of the hand, while lying in bed with the leg extended straight. For writing spasm, pressing the hand against the wall with the fingers down will stretch the flexors of the fingers.
You can also perform a gentle massage of the muscle, which allows you to relax the spasmodic muscle. If the cramp is associated with fluid loss, as is often the case with strenuous exercise, rehydration and restoration of electrolyte levels is necessary.
Muscle relaxants may be used in the short term in certain situations to allow muscles to relax during injury or other conditions (eg, radiculopathy). These drugs include cyclobenzaprine (Flexeril), orphenadrine (NORFLEX), and baclofen (Lioresal).
In recent years, injections of therapeutic doses of botulinum toxin (Botox) have been successfully used for certain dystonic muscle disorders that are localized to a limited group of muscles. A good response may last several months or more and injections may be repeated.
Seizure treatment that are associated with specific diseases, usually focuses on the treatment of the underlying disease.
In cases where convulsions are severe, frequent, prolonged, difficult to treat or are not associated with an obvious cause, then in such cases both additional examination and more intensive treatment are required.
Prevention of seizures
In order to prevent the possible occurrence of seizures, a good diet with sufficient fluids and electrolytes is necessary, especially during intense physical exertion or during pregnancy.
Night cramps and other rest cramps can often be prevented with regular stretching exercises, especially if performed before bed.
Also a good means of preventing seizures is taking magnesium and calcium supplements, but caution is required when prescribing them in the presence of renal failure. In the presence of hypovitaminosis, it is necessary to take vitamins of group B, vitamin D, E.
If the patient is taking diuretics, then a mandatory intake of potassium supplements is necessary.
Recently, the only drug that is widely used for the prevention, and sometimes for the treatment of seizures, is quinine. Quinine has been used for many years in the treatment of malaria. The action of quinine is due to a decrease in muscle excitability. However, quinine has a number of serious side effects that limit its use to all groups of patients (nausea, vomiting, headaches, heart rhythm disturbances, hearing loss, etc.).
Spasms are called uncontrolled contractions of the muscular apparatus, which are often accompanied by pain. The muscle in a convulsive state becomes dense and hard, its shape may also change, twitching is noted. If the attack is severe, muscle pain often persists for several days. When faced with such inexplicable pain for the first time, a person often experiences fear: what to do so that the pain does not happen again. Some people are familiar with seizures since childhood, someone meets with this ailment in adolescence or even in adulthood, they often bother pregnant women. At any age, it is necessary to get rid of them - because they significantly worsen the quality of life.
Causes
What is the cause of spontaneous seizures? If there are no deviations in terms of health in the body, then this phenomenon can be found in the following cases:
- hypothermia. A common cause of painful muscle contraction, and cramps occur only during the cooling period: bathing in cold water. Such a phenomenon is not a sign of disease, and it does not happen very often.
- prolonged stay in an uncomfortable position. When this happens, the muscle nerve is clamped in the muscle canal. In such a situation, they urgently change the position to a comfortable one, relaxing the muscle group that is "numb" and carry out a light but kneading massage.
- excess caffeine and nicotine. Muscle twitching is characteristic in the case of smokers and lovers of strong coffee and its frequent consumption. This reason is easily corrected - it is enough to quit smoking and replace coffee with tea or other drinks.
Kinds
There are cramps that cover a large part of the body, cramps of the upper limbs and cramps of the legs (calf muscles). Let's take a closer look at each of these types.
Body cramps
The causes of painful contraction of the muscles of the whole body often include serious diseases of a latent nature:
.jpg)
In these cases, it is necessary to consult a specialist - a neurologist. After establishing the cause and adequate treatment of the disease, convulsions usually disappear.
Seizures begin to develop on the basis of the strongest degree of excitation of nerve cells in the brain, which usually accumulates in a certain part of the brain. Such an accumulation is diagnosed using electroencephalography and according to certain manifestations (special sensations before the onset of an attack).
Symptoms
Consider the most common type of seizures of the whole body - the disease of epilepsy. The main manifestation is an epileptic seizure, the clinical symptoms of which are extremely specific: a moment before the onset of an attack, the patient feels a change in the perception of taste, sounds, and aroma. As a rule, one person has the same sensations before each attack, which is used to judge the onset of epilepsy. Immediately, the patient has a strong tension in the muscles of the whole body, after which the muscles of the limbs regularly contract and tremors are felt in the body. The attack may be accompanied by a transient cessation of the breathing process. After a seizure, the patient usually falls asleep and cannot remember what happened to him afterwards.
Treatment
Treatment must be started as early as possible in order to stop the development of the disease and changes in the psyche. After the first manifestation, you need to undergo electroencephalography and, when an accumulation of nerve cells is established, treatment is prescribed, which is carried out for a long time. The drugs are canceled after two or three years of use - only in that case can we say about a complete cure.
Assistance and self-help
It is important to know how to help a person with body convulsions - an attack of epilepsy. The fact is that the patient must always be among people - he will not be able to help himself, which can end rather badly.
Surrounding should put the patient in a "rescue position" - on his side, face down. Then unfasten all tight clothing and allow fresh air to enter.
No need to try to insert anything between the teeth, as well as to do artificial respiration. Just be there until the doctors arrive.
Medical treatment

The first drug that is usually used in the treatment of epilepsy is which is dispensed purely on prescription, as it refers to light narcotic substances. Pharmacological group - barbiturates, has anticonvulsant, hypnotic and sedative effects.
An effective antiepileptic drug - carbamazepine. A very popular drug in the treatment and prevention of seizures of epilepsy, is able to have a strong anticonvulsant effect, stabilizes the mental state of patients. From drugstores it is released only according to recipes.
Hand cramps
This problem affects many people, hand cramps become especially relevant with age. Frequent manifestations of seizures indicate a deviation in health and that a doctor's consultation and treatment is necessary.
Causes
The most common cause of convulsive hand syndrome is a lack of important chemical elements in the body: magnesium, potassium and calcium. These substances ensure the transmission of nerve impulses to muscle fibers. Also, the causes of this disease are:
- fluid deficiency in the body,
- irregular meals,
- stress,
- circulatory disorders,
- long-term use of diuretics, etc.
Treatment
The patient during hand cramps is always conscious, even if the muscle tension is very painful, therefore he can help himself: vigorous stroking with pinching, rubbing the area of stiffness. Of course, you can not refuse outside help - the same will be done by a close person present nearby.
If cramps often grab the same place, you can prevent seizures by regularly massaging the problem area. You can help in the disappearance of symptoms by regularly using vitamin and mineral complexes.
To determine the exact cause and select an individual treatment, a consultation with a neurologist is necessary.
leg cramps
Leg cramps are uncontrolled painful muscle contractions (usually the calf muscles). Many people have experienced this unpleasant sensation, and some are constantly worried about it. What are the reasons that the legs "reduces"?

Treatment
Treatment is to get rid of the cause of seizures. During an attack, a person can help himself by rubbing and massaging the cramp area.
The video discusses the treatment options: