How is a urine test done in a lab? Laboratory study of urine. Analysis according to Nechiporenko
Laboratory research urine allows you to determine not only functional state kidneys (clinical and other urinalysis), but also diseases of other organs, for example Bladder, biliary tract, liver, as well as metabolic disorders. For the study of urine, more concentrated urine is used from the morning portion, which is taken on the first morning after the patient is admitted to the hospital. In the future, urinalysis is done at least once every 7-10 days (during the stay in the hospital). More frequent repeated clinical researches urine is needed during treatment, after surgical interventions, before and after blood transfusion and in cases where urinalysis may reveal pathological disorders other organs and systems. Before taking urine, a woman must be washed, and if she is menstruating, urine should be taken using a catheter. For a general analysis, 150-200 ml of urine is sufficient. Urine is collected in a carefully washed dish or bedpan. From the vessel, it should be poured into a clean glass container for sending to the laboratory. The dishes used for collecting and storing urine should not be washed with alkali solutions in order to avoid distorting the results of the study. Before taking urine for bacteria and fungi (inoculation) or for biological research, it is necessary to wash the genitals with a disinfectant solution (for example, a solution of furacilin or potassium permantanate) and take 15 -20 ml of urine with a sterile catheter into a special container, which is immediately closed. Antiseptic substances are not added to the taken urine. Urine changes its properties under the influence various circumstances: physical work, overheating of the body, the amount of fluid you drink, the characteristics of the food you eat, and even emotional overstrain. To get more accurate results, urine must always be taken in a relatively same conditions- in the morning immediately after waking up. On the dishes with urine sent to the laboratory, an accompanying note should be pasted with the patient's last name, first name and patronymic, the number of the department in which he lies, the number of the ward and the purpose of the study. urine should be stored in a dark and cool place, and it is advisable to examine it no later than 2 hours after collection. Determination of the daily amount of urine. Daily amount of urine healthy person averages about 1500 ml, but it is subject to significant fluctuations. If less than 750 ml or more than 3000 ml of urine is allocated per day, then this indicates the development of a disease of the urinary organs or other organs and systems. Determining the color of urine. The color of urine depends on the presence and concentration of urochrome and other pigments in it. The color of urine can change depending on a number of circumstances: the amount of fluid drunk, various pathological impurities (blood, pus, etc.).
Daytime urine is less concentrated. Light urine occurs with sugar and diabetes insipidus. With jaundice, urine has the color of dark beer. Concentrated dark urine occurs in febrile patients! With the loss of an abundant precipitate of phosphates, the urine acquires a whitish-milky color. The presence of blood in the urine gives it the color of meat slops. This happens when acute inflammation kidney ( acute nephritis). The color of urine can also be affected by the intake of certain drugs. Determination of the transparency of urine. Normally, urine is clear, but it can become cloudy if left in an open container for a long time. The turbidity of normal urine in an open container depends on the precipitation of certain salts. Only sediment microscopy solves the issue of the presence of pathological impurities. Determination of the smell of urine. Freshly excreted urine has a specific, but not intense smell. When standing in an open container for a long time, it decomposes and emits a sharp bad smell ammonia. Ammonia smell urine immediately after urination makes one think that urine decomposes in the bladder due to certain pathological changes in the urinary tract. Determination of the relative density of urine. The density of urine depends on the concentration of dense constituents in it; normally, as already mentioned, the relative density of urine is 1017-1024. It is the higher, the more dense constituent parts in urine and the more intense its color. Determination of urine reaction. In the vast majority of healthy people, the reaction of urine is acidic, which is mainly due to the composition of the food consumed. With the predominance of plant foods, the urine becomes alkaline, and in those who eat mixed or meat we write, the urine is acidic. The reaction of urine is determined using red and blue litmus paper. With an acid reaction of urine, the paper does not change color, and with an alkaline one, it turns blue. Blue litmus paper turns red in an acidic reaction, but does not change color in an alkaline reaction. Protein definition. The presence of protein in the urine is called albuminuria. There are several ways to qualitatively determine the protein in the urine, but the test with sulfosalicylic acid is usually used. Determination of blood in urine. Blood in the urine is determined using a sample with guaiac tincture. 5 ml of boiled urine is poured into a test tube and a few drops of freshly prepared alcohol tincture of guaiac resin and 10% hydrogen peroxide or turpentine are added, after which the mixture is shaken; in the presence of blood, the mixture turns blue. Urinalysis according to Zimnitsky. This test is set to determine the concentration ability of the kidneys. Urine is collected from 9 a.m. to 6 a.m. next day, i.e., during the day. Determination of sugar in urine. The definition of grape sugar is practically important, the presence of which in the urine indicates glucosuria. Several reactions have been proposed for the qualitative determination of sugar in urine. Great importance has a study of urine sediment (Fig. 12). The precipitate is obtained by settling or centrifugation.
Bladder cancer can sometimes be detected earlier. Detecting this early improves your chances of successful treatment. Screening is the use of tests or exams to look for disease in people who do not have symptoms. Currently, no major professional organizations recommend routine screening of the general public for bladder cancer. This is because the screening test has not been shown to reduce the risk of death from bladder cancer in people at intermediate risk.
Tests that may be used to look for bladder cancer
Some doctors may recommend bladder cancer tests for people with very high risk, such as. People who have had bladder cancer, in people who have had certain birth defects of the bladder. People exposed to certain chemical substances at work. . Bladder cancer tests look for various substances or cancer cells in the urine.
When diseases are suspected internal organs or it is necessary to check the condition of the body, usually a urine test is prescribed. What are urine tests, their types and what do they talk about? After all, urine is complex in composition. biological fluid, which contains a variety of inorganic and organic compounds(enzymes, hormones, trace elements, mineral salts etc.). Below are the main types of analyses.
Urinalysis: One way to check for bladder cancer is to check for blood in the urine. This can be done during a urinalysis, which is a simple test to check for blood and other substances in a urine sample. This test is sometimes done during a general health checkup.
Blood in the urine is usually caused by benign conditions such as infections, but can also be the first sign of bladder cancer. A large amount of blood in the urine can be seen if the urine turns pink or red, but to determine small quantities urinalysis is required.
Types of general urine tests in children and adults
The most common is a general urine test. It is prescribed to people of all ages, regardless of the nature and duration of the disease. A simple study can clearly show clinical picture and flow pathological processes in the body. For example, to identify kidney disease, disruption of other systems and organs. During pregnancy, the analysis is given repeatedly, since the load on the kidneys increases during the bearing of the fetus.
A.3 Types of urine samples
Urinary analysis can help find bladder cancer on early stage, but it has not been shown to be useful as a routine screening test. Urinary Cytology: In this test, the doctor uses a microscope to look for cancer cells in urine. Urine cytology finds some types of cancer, but it is not reliable enough to make a good screening test.
Urine tests for tumor markers: Several new tests look for substances in the urine that may indicate bladder cancer. These tests can find bladder cancer early, but they can also miss some. In other cases, the test result may be abnormal even in some people who do not have cancer. During this time, tests are used primarily to look for bladder cancer in people who already have signs or symptoms of cancer, or in people who have had bladder cancer removed to check for cancer recurrence.
Physiochemical properties
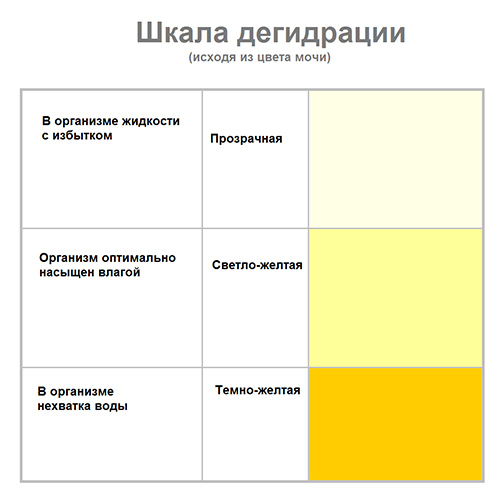 The following indicators determine the type of urine:
The following indicators determine the type of urine:
- Color:
- colorless - after taking diuretics;
- dark - with hepatitis;
- cloudy - in the presence of mucus, bacteria, epithelial cells;
- red - with kidney injuries or tumor diseases.
- Smell. The aroma of fish with a smell, acetone, mice, ammonia indicates the presence of a variety of diseases, such as phenylketonuria, cystitis, fistulas, E. coli.
- Transparency, presence or absence of protein, glucose, nitrites, urobilinogen, bilirubin.
- reaction and relative density.
Microscopy of urine sediment
If the secreted liquid has stood for 1-2 hours, a precipitate appears in it. Then they collect with a pipette, centrifuge and study the precipitate from the centrifuge tube under a microscope. Detects the number of leukocytes, erythrocytes, hemoglobin, epithelial cells, cylinders. But sometimes a more detailed examination is required. Therefore, in laboratory practice, there are many types of urine research.
Watching for possible symptoms of bladder cancer
Further research is needed before these or other newer tests are useful as screening tests. Although screening tests are not recommended for people at average risk, bladder cancer can often be detected early because it causes blood in the urine or other urine symptoms. Many of these symptoms often have less serious reasons but it is important that they are checked by a doctor right away so the cause can be found and treated if necessary.
What are the analyses?
According to Nechiporenko
People regardless of age are referred for this urine test. It reveals hidden inflammations in genitourinary system. The technique is based on the determination of erythrocytes, leukocytes, cylinders. The presence of these components in urine will help diagnose pyelonephritis, cystitis, cylindruria, adenoma, and urolithiasis.
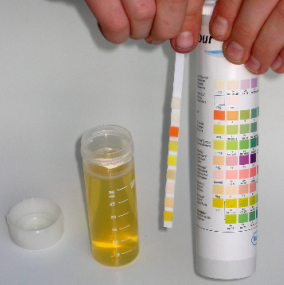
If the symptoms are related to bladder cancer, looking for it early best chance for successful treatment. The test strip exam contains the following analytical parameters. Evidence of hematuria, leukocyturia and proteinuria are direct and early indicators of disorders of the kidneys and urinary tract. The diagnostic sensitivity of the test strips is sufficient to detect clinically significant erythrocyturia and leukocyturia.
Albumin is mainly detected through the protein field. . Urine screening of test strips is done at primary examination patient approximately guiding to rule out kidney disease and urinary tract. In asymptomatic patients, a sediment test strip test precedes and only when a red cell test field, white cell test, or protein sediment analysis is positive are associated. In addition, test strip analysis can provide information on global metabolic diseases such as diabetes and hepatopathy.
According to Zemnitsky

This type of urine test determines the relative density and volume of urine. For this type of analysis, up to 8 containers are required, where urine is collected for a day with a frequency of three hours. A new portion is collected in a separate jar. Differences in indicators from the norm can indicate kidney failure, pyelonephritis, uric acid diathesis, diabetes mellitus, glomerunonephritis.
The test strip is also placed before urine protein analysis. Do you know what preventive research gives most information about health? The answer is a complete blood and urine test. The total research has been reduced from 38 leva. at 18 leva and thyroid gland- from 26 leva. a total of 13 lv. Patients can visit the branch in Burgas or Varna on a convenient day, since an appointment is not required. The only recommendation is that the studies are carried out in the morning, on a fast.
Small to moderate increases can be seen with other autoimmune diseases, such as rheumatoid arthritis, systemic lupus erythematosus, diabetes, etc. in turn, thyroid-stimulating hormone levels are important indicator thyroid function and indicate whether it is normal, increased or decreased. Attention is also paid to a complete analysis of blood and urine, which combines 54 indicators. It includes complete analysis blood with the differentiation of leukocytes into groups, urine analysis and the rate of erythrocyte sedimentation.
A single or daily portion of the biomaterial is used. The technique helps to identify pathologies in the work of the adrenal glands, pancreas, to confirm diabetes at clinical signs, with acute kidney dysfunction, poisoning with substances containing phosphorus. Normally, there is no glucose in urine.
 Normally, protein should be absent in the urine.
Normally, protein should be absent in the urine. In principle, it is absent in urine. Its presence is called proteinuria and may indicate immune pathologies, acute and chronic diseases kidney disease, multiple myeloma, . The protein molecule is large and while the integrity of the kidney tubules is preserved, the protein is again absorbed into the body. Under the influence of infection, they are destroyed, and the protein enters the urine. In most cases, these are albumins.
In addition, carbohydrate, fat, protein metabolism, electrolyte analysis, blood sugar level, good and bad cholesterol, triglycerides, total protein and albumin, calcium, phosphorus, potassium, sodium and chlorides. The absorption test is one of the most basic tests carried out in medical diagnostics. Urine tests can provide valuable information about the condition of the urinary tract as well as other organs.
Recording the results of a urine test is the responsibility of the doctor, but we can judge some basic parameters on our own. For example, red discoloration may indicate porphyria or muscle injury, it is desirable to clear urine, a healthy color and Brown color may indicate poisoning with phenolic compounds. Of course, these are just some examples, and the final interpretation is in the hands of the doctor and also depends on age, gender, drugs taken, etc.
For erythrocytes
Normally, no more than 2 cells in the preparation are absent or detected. Increasing the number of reds blood cells is called hematuria. Erythrocytes found in the urine can be unchanged (i.e. contain hemoglobin) and altered (do not contain hemoglobin, leached). Indicates diseases of the genitourinary system.
What is evaluated during a urinalysis?
It is important to know that a healthy person's urine should be free of bacteria and fungi, as well as excess protein and sugar - the latter often indicates diabetes. Learn how a urine test is done and how your doctor interprets the results. General analysis urine allows you to apply diagnostic light to the entire body through the prism of the kidneys. In addition to evaluation physical properties, the laboratory also analyzes chemical composition piss for a row various substances. What factors are assessed in a general urinalysis and what conclusions can be drawn from it?
For leukocytes
Normal content in men is 0-3 in the field of view, in women - 0-5. Excess of these components is called leukocyturia. Increased number white blood cells indicates inflammation of the kidneys (pyelonephritis) or urinary tract (cystitis, urethritis). Rarely, an increase in leukocytes indicates a disease of tuberculosis, glomerulonephritis. A very large number of leukocytes is called pyuria. it high quantity pus and signals purulent processes in the excretory organs.
physical characteristics collected urine are color, clarity, specific gravity and smell. In the case of taking a sample, it is difficult to estimate its volume - this is done only in the case of daily urine collection. Darkening of urine or discoloration may be side effect medications or may indicate advanced liver or biliary tract disease. The absence of this function may indicate the presence of urinary epithelium, a large number bacteria, mucus or fat in the urine. A change in the specific gravity of the urine may indicate pathology directly derived from the kidneys, the development of diabetes, or simply dehydration or hypopituitarism. Any abnormalities may indicate poorly controlled diabetes or urinary tract infections.
- The color of healthy urine should be straw yellow.
- The urine collected for the test must be clean.
- This may be due to urinating too late in the lab.
- Urine is defined as "characteristic" or "typical", with no impression of esthetics.
For the content of cylinders and epithelial cells
 As a result of urinalysis in a healthy person, the presence of hyaline (protein) cylinders of no more than 1-2 in the preparation is acceptable. Other types should be absent. Exceeding the norm is called cylindruria. The cylinders are composed of protein, epithelial cells, white and red blood cells, and fat. With kidney dysfunction, they accumulate in renal tubules from the inside, creating a semblance of casts. Recognize several types of cylinders: leukocyte, epithelial, granular, waxy, erythrocyte, hyaline. Their presence in the analysis can indicate a variety of kidney diseases. The presence of epithelial cells (renal) is characteristic of damage to the organ against the background of intoxication or an infectious disease.
As a result of urinalysis in a healthy person, the presence of hyaline (protein) cylinders of no more than 1-2 in the preparation is acceptable. Other types should be absent. Exceeding the norm is called cylindruria. The cylinders are composed of protein, epithelial cells, white and red blood cells, and fat. With kidney dysfunction, they accumulate in renal tubules from the inside, creating a semblance of casts. Recognize several types of cylinders: leukocyte, epithelial, granular, waxy, erythrocyte, hyaline. Their presence in the analysis can indicate a variety of kidney diseases. The presence of epithelial cells (renal) is characteristic of damage to the organ against the background of intoxication or an infectious disease.
Requirements for specialists and support staff
Keep in mind that general urine testing will not give you accurate information about the amount of the substance that will be touched, but will tell you only about its presence. To accurately determine the amount and more accurately look at the composition of urine, you should make a daily collection of it.
How to prepare for a general urine test?
The presence of protein in the urine can indicate a number of diseases - from pathology to urinary tract through various metabolic diseases, including abnormalities associated with blood and hematopoietic system. If sugar is present in the urine, this directly indicates that there is too much in the blood. Similar to ketones, their presence may indicate an increase in sugar levels or other metabolic diseases. Bilirubin and urobilinogen are components of the liver and should not be found in the urine. Detection in general study may indicate pathology bile ducts or liver. The presence of nitrites is directly related to bacterial infection urinary tract - urine should be sprayed on existing bacteria. You must start diagnosing diabetes. . A general urinalysis also requires proper preparation.




