Torsion dystonia symptoms. Pathogenesis of torsion dystonia. Clinic and symptoms of the disease
Torsion dystonia (lat. torsio, torsionis rotation, twisting; Greek dys- + tomos tension; synonyms: torsion, deforming muscle, progressive torsion spasm)
chronic progressive, which is based on the extrapyramidal system. characteristic feature Etc. is a changing, uneven distribution of muscle tone in certain parts of the body, accompanied by a kind of hyperkinesia, often with rotational movements. is rare. Men are more often ill. In the etiology of Etc., the hereditary factor is of primary importance. inheritance is different. In some families, it is inherited in an autosomal dominant manner, in others, which is more common, in an autosomal recessive manner. T. d., inherited according to the first type, was traced for 2-3 generations, and in individual families - for 4-5 generations. With autosomal recessive inheritance, cases of consanguinity of parents were noted. The pathogenesis has not been established. Primary metabolic was not identified. It is assumed that dysfunction of the dopaminergic systems of the brain is important in the pathogenesis. Pathological anatomical examination reveals rough degenerative changes in the cerebral cortex and more pronounced in the basal nuclei, the red nucleus, Lewis, substantia nigra, and the cerebellar dentate nucleus. clinical picture. As a rule, the first signs of T. appear at the age of 5-20 years. The course of the disease is usually slowly progressive. T. D., inherited in an autosomal recessive manner, often begins earlier and is more severe than in patients with an autosomal dominant type of inheritance. The first signs of the disease are involuntary in one, often lower, limb. At the same time, patients experience a feeling of awkwardness in gait. gradually spread, they arise and intensify when trying to change the position of the body, do anything, while standing, walking, emotional arousal. Other diseases of the extrapyramidal system that occur with torsion-dystonic syndromes differ from T. d. in that they do not progress, they undergo reverse development (to one degree or another) with a decrease in the frequency and severity of hyperkinesis. In their clinical picture, along with hyperkinesis, there are other symptoms of brain damage that are not observed with torsion dystonia. Treatment conservative and operational. Assign cyclodol, artan, norakin, dinezin, tropacin, small doses of L-DOPA in combination with tranquilizers (elenium, seduxen, etc.), group B; conduct courses therapeutic gymnastics, . In the later stages of T., with deformities of the joints and muscle contractures, orthopedic operations are sometimes performed. Stereotactic operations are indicated in cases where the disease progresses rapidly and deprives the patient of the ability to work and the possibility of self-care. The duration of the illness and severe course in the later stages are not contraindications to surgical intervention. Stereotactic operations on the basal nuclei of the brain (see Functional neurosurgery) consist in the destruction of one or two subcortical structures, which leads to a break in the pathological chain through which impulses circulate, causing hyperkinesis and impaired muscle tone. After stereotactic operations, hyperkinesis and muscle rigidity in most cases decrease or disappear. Forecast adverse. IN late stage patients often die from intercurrent diseases. Prevention. The family of a patient with T. should be under the supervision of a medical genetic consultation (see Medical genetic counseling) .
Parents of a child sick with Etc. are advised to refrain from further childbearing. Biographical: Diseases nervous system, ed. P.V. Melnychuk, vol. 2, p. 115. M., 1982; Gusev E.I., Grechko V.G., and Burd G.S. .
Nervous diseases. With. 618, M., 1988.
1. Small medical encyclopedia. - M.: Medical Encyclopedia. 1991-96 2. First health care. - M.: Bolshaya Russian Encyclopedia. 1994 3. encyclopedic Dictionary medical terms. - M.: Soviet Encyclopedia. - 1982-1984.
See what "torsion dystonia" is in other dictionaries:
torsion dystonia- Progressive brain disease, probably NZH; manifests itself in the form of rotational hyperkinesis; cases of inheritance both in an autosomal recessive and in an autosomal dominant manner have been noted. [Arefiev V.A., Lisovenko L.A. English… … Technical Translator's Handbook
Torsionic distonia torsion dystonia. Progressive brain disease, probably NZH; manifests itself in the form of rotational hyperkinesis; cases of inheritance both in an autosomal recessive and in an autosomal dominant manner have been noted. ... ... Molecular biology and genetics. Dictionary. Big Medical Dictionary
Dystonia torsion hereditary Synonym: Ziehen-Oppenheim disease. Hereditary disease, manifested by torsion spasm (see) in children aged 5–15 years ( early forms) or in adults ( later forms). Patients rarely live to 40-45 years. characteristic muscular dystonia By… …
- (dystonia torsionica symptomatica) torsion dystonia syndrome, which occurs secondarily in some diseases of the nervous system (hepatocerebral dystrophy, epidemic encephalitis, etc.) ... Big Medical Dictionary
Dystonia torsion symptomatic- Manifestations of recurrent hyperkinesis by the type of torsion dystonia (see) in other diseases of the extrapyramidal system (epidemic encephalitis, hepatocerebral dystrophy, etc.) ... Encyclopedic Dictionary of Psychology and Pedagogy
Dystonia torsion- (disbasia lordosica progressiva) - a hereditary (with a recessive and dominant type of genetic transmission) chronic progressive disease, characterized by peculiar changes in muscle tone, slow tonic ... ... Encyclopedic Dictionary of Psychology and Pedagogy
- (Greek hyper + kinēsis movement) involuntary movements caused by contraction of the muscles of the face, trunk, limbs, less often the larynx, soft palate, tongue, external muscles of the eyes. Develop with infectious lesions senior researcher (epidemic encephalitis, ... ... Medical Encyclopedia
Torsion dystonia affects an average of 3 people for every 100,000 of the population.
Usually, the first symptoms of the disease occur in young age: up to 20 or even up to 15 years, and in further disease progresses, at times interrupted by remissions and aggravated with renewed vigor.
Torsion dystonia can be either a side effect of other diseases (brain cancer, encephalitis, cerebral palsy, etc.), or an independent hereditary disease. In the first case, the disease is called symptomatic. torsion dystonia, and in the second - family.
Generalized torsion dystonia is a disease that is characterized by impaired muscle tone and associated movement disorders.
The disease got its name from the word torsion, which means "twisting".
This is due to the characteristic spasms of the muscles of the body, which lead to the twisting of the body around its longitudinal axis. Such a spasm is also called torsion, or rotational.
The term "generalized" means "general", "covering the whole organism". The disease received this name because the spasm affects not one muscle or part of the body, but the entire torso, both limb belts and the neck.
Causes
Dystonia occurs due to damage to the neurons of the dentate nucleus of the cerebellum and subcortical formations forebrain. Corresponding parts of the brain may be affected oncological diseases or infections.
Familial torsion dystonia is a group of hereditary diseases. They are inherited autosomal (regardless of gender), and can be either dominant or recessive.
Torsion dystonia - symptoms
 Torsion dystonia is characterized by prolonged tonic contractions of the muscles of the head, trunk, neck, shoulder and pelvic girdle, athetosis (involuntary movements) of the fingers.
Torsion dystonia is characterized by prolonged tonic contractions of the muscles of the head, trunk, neck, shoulder and pelvic girdle, athetosis (involuntary movements) of the fingers.
The amplitude and number of involuntary muscle contractions remain variable.
It varies greatly depending on the physical and emotional state patient, as well as his posture.
Modern medical science identifies individual forms of torsion dystonia:
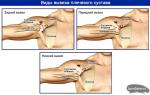
- Rigid form. Its symptoms: an uneven change in muscle tone, as a result of which the body twists sharply around the longitudinal axis or sharply leans to one side. Pathological postures are fixed. The head also turns to the side.
- Diaponically-hyperkinetic form. This form is characterized by the fact that hyperkinesis begins with the limbs. This is followed by involuntary contractions of the muscles of the neck, which leads to torticollis, and over time causes hypertrophy of the muscles of this part of the body.
According to localization, in addition to generalized torsion dystonia, there is also a local one, which is characterized by the fact that it affects only a certain part of the body, for example, limbs and / or neck.
Diagnosis of symptoms
Torsion dystonia must be distinguished from diseases whose symptoms can be very similar.

These include hepatocerebral dystrophy, in which there are changes in the psyche and disorders of copper metabolism, Hertington's chorea, which is also characterized by a violation mental activity, and hysteria, in which there are hyperkinesis, but for hysterical hyperkinesis, the participation of the muscles of the body is uncharacteristic. It is also possible to confuse family torsion dystonia with a secondary one.
The criteria for making such a diagnosis are the appearance of hyperkinesis, which persist for a long time and intensify with emotional experiences, but disappear during sleep.
It is important that there are no symptoms characteristic of mental and psychological abnormalities, which can also cause convulsions and hyperkinesis.
For the final diagnosis, electromyography, electroencephalography (study electrical activity in muscles and brain respectively), and magnetic resonance imaging of the central nervous system.
For the correct diagnosis, the anamnesis often plays a decisive role, i.e., information from the patient himself or his relatives.
How to treat torsion dystonia?
Used to treat torsion dystonia various methods, from therapeutic gymnastics to surgical intervention in brain structures.
- Physiotherapy. With torsion dystonia, it is important to teach the patient to relax the muscles and stop hyperkinesis (pathological involuntary movements), as well as to normalize breathing and improve support in order to avoid accidents associated with the patient's fall. For this, various forms of massage are used, aimed at relaxation. autogenic training and weight training exercises.
- Medical treatment. Apply medicinal substances that affect the functioning of the nervous system: neuroleptics, anticholinergics, glucocorticoids, anticonvulsants and B vitamins.
- Electrical stimulation of subcortical formations. This technique is the most modern and progressive. Electrodes are implanted into the affected areas of the brain, which act with weak impulses. electric current to those centers that are responsible for pathological impulses. The activity of the affected area is suppressed due to these impulses. The disadvantage of such operations is their complexity, as well as the inaccessibility and high cost resulting from it. The most difficult thing is to find the affected areas that have to be affected.
- Surgical intervention. Operations are performed aimed at destroying the structures responsible for pathological impulses. As in the case of electrical stimulation, the physician needs to accurately determine the location of the pathological zone. To do this, you have to use stereotaxic guidance.
If a person has symptoms of a disorder in the work of the nervous, cardiovascular and digestive systems, but the diagnosis of the disease is not detected, then doctors given state commonly referred to as autonomic dysfunction syndrome. You can find out from this link detailed information about this symptom complex.
Forecast and prevention
The prognosis for hereditary torsion dystonia is unfavorable. The disease will slowly progress over many years.In the absence of treatment, by about forty years, intercurrent diseases develop, which lead to death.
If torsion dystonia is a consequence of another disease (eg, brain cancer), then the prognosis depends on the course of this disease.
If in the family the child has symptoms of torsion dystonia, in the future, childbearing should be abandoned. Also, for prevention, you should use vitamins of group B.
There are foods that contain large quantities B vitamins, especially B1 and B6, necessary for normal operation nervous system. These are beans walnuts, buckwheat, corn, beef, cabbage, eggs.
Thus, torsion dystonia is a disease in which the muscles of the trunk, neck and limbs involuntarily contract, twisting the body around its axis. The cause of the disease is a violation in the work of certain parts of the brain. The prognosis in the absence of treatment is unfavorable. To treat the disease, a complex of measures is used, including exercises, taking medications and surgical intervention.
Torsion dystonia (from Latin torsio - “rotation, twisting”; from Greek dys tonos - “tension”) is a chronic progressive disease of the brain, in which the extrapyramidal system is mainly affected. It is characterized by a changing, uniform distribution of muscle tone in individual parts of the body with accompanying characteristic hyperkinesias, often with rotational movements. This rare disease characteristic mainly of men.
Symptoms of the development of torsion dystonia
Usually the first signs of the disease appear at the age of 5-20 years. The disease is slowly progressive, rarely stationary. Torsion dystonia, which is inherited in an autosomal recessive manner, often occurs earlier and is more severe than in patients with an autosomal dominant pattern of inheritance.
- The first symptoms of torsion dystonia include involuntary movements in one, often lower, limb.
- At the same time, patients experience a feeling of discomfort during gait.
- Gradually, hyperkinesis spreads, which appear and intensify when trying to change the position of the body, make any movement, while standing, walking, emotional arousal.
In connection with different localization hyperkinesis secrete
local
and a generalized form of torsion dystonia.
Symptoms of different forms of torsion dystonia
With a local form, hyperkinesis of the muscles of the limbs and neck is formed. In the limbs (in each separately), various, sometimes fanciful involuntary movements may appear:
athetoid,
hemiballic,
myoclonic,
choreic,
tick-like,
tonic spasms
and shaking.
With symptoms of local torsion dystonia, rotational movements are observed along the longitudinal axis of the limbs. In the proximal parts of the extremities, hyperkinesis is more pronounced than in the distal ones. There are times when muscle hyperkinesis right hand may be characterized by the clinical picture of the syndrome of writing spasm.
At the same time, in initial stage diseases spasms appear mainly only when writing. Then the spasms slowly spread to other muscles of the hand that are not involved in the act of writing. Due to hyperkinesis of muscles appear sharp turns heads back, forward, to the sides. At the onset of the disease, tonic spasms neck muscles may be similar to spasmodic torticollis syndrome. Then there are other involuntary movements that are not characteristic of spastic torticollis.
The local form of torsion dystonia is much more common than the generalized form. It passes into a generalized form gradually and in different dates from the onset of the disease and is manifested by the occurrence of hyperkinesis of the muscles of the body. Gradually they become more and more pronounced. Due to hyperkinesis of the long muscles of the back, the configuration of the spine changes, its curvature, hyperextension in the lumbar and lower thoracic with severe lordosis and kyphoscoliosis. Sometimes there are corkscrew-like movements of the body. Increased hyperkinesis of the muscles of the limbs, neck, and sometimes there are spasms of the facial muscles. There may be a speech disorder. During pauses between hyperkinesis, muscle tone is increased, decreased, and sometimes normal.
With symptoms of generalized torsion dystonia, a short-term freezing of the patient in abnormal postures is often noted. The gait is characterized by pretentiousness, swaying (“gait of a camel”). Self-care of the patient is difficult, but patients adapt to movement disorders, they are able to temporarily reduce or eliminate the resulting hyperkinesis and perform complex movements, such as running, jumping, dancing. When the patient lies, as well as at rest and with distraction, hyperkinesis stops, during sleep they do not appear. Patients do not develop paresis, coordinating, sensory and pelvic disorders. Tendon reflexes are preserved, pathological reflexes are not caused. There are no intellectual-mnestic disorders. With an unfavorable course in the late stages of torsion dystonia, the development of joint deformities, muscle contractures of the trunk and extrapyramidal rigidity of the muscles of the trunk, limbs, face, tongue, and pharynx are possible, which is accompanied by violations of chewing, swallowing and breathing.
Diagnosis of torsion dystonia
The diagnosis is made on the basis of clinical data. Basically, it is not in doubt if there are cases of torsion dystonia in the family. In cases of dispute, one should differential diagnosis with torsion-dystonic syndromes, especially manifested by the chronic form of epidemic encephalitis and hepato-cerebral dystrophy.
Differential diagnostic value in epidemic encephalitis is acute development diseases, sleep disturbance, diplopia, convergence insufficiency, gaze convulsions, autonomic disorders and in the most advanced stages, Parkinson's symptoms. The difference between torsion dystonia and hepato-cerebral dystrophy is the Kaiser-Fleischer ring (deposition of a copper-containing greenish-brown pigment on the periphery of the cornea of the eyes), a defect in the exchange of copper with low content ceruloplasmin in the blood, cirrhosis of the liver.
Other diseases of the extrapyramidal system, which have torsion-dystonic syndromes, differ from torsion dystonia in that they do not increase, they undergo reverse development (to one degree or another) with a decrease in the frequency and severity of hyperkinesis. In their clinical picture, hyperkinesis is accompanied by other symptoms of brain damage that are not characteristic of torsion dystonia.
How to treat torsion dystonia?
Treatment of the disease is conservative and surgical. They take Cyclodol, Artan, Norakin, Dinezin, Tropatsin, small doses of a-DOPA in combination with tranquilizers (Elenium, Seduxen), B vitamins; conduct courses of therapeutic gymnastics, hydrotherapy. In the later stages of torsion dystonia, with joint defects and muscle contractures, orthopedic surgeries are sometimes used. With torsion-dystonic syndromes, therapy is aimed at the underlying disease, according to indications, symptomatic agents are prescribed.
Surgical removal of torsion dystonia
Surgical treatment (stereotactic operations) is used in cases where the disease progresses and deprives the patient of the ability to work and the possibility of self-care. Surgery is contraindicated for cachexia, serious illnesses internal organs, blood diseases. The long duration and severity of torsion dystonia in the later stages are not contraindications.
Stereotactic operations on the basal ganglia of the brain are based on the destruction of one or two subcortical structures, which leads to a break in the pathological chain along which impulses circulate, causing hyperkinesis and defects in muscle tone. Previously, for this purpose, the medial segment of the pale ball was destroyed, which gave positive effect in approximately half of the patients.
In the 1960s surgical treatment diseases began to produce by thalamotomy the destruction of the ventral nucleus of the thalamus, to which the paths connecting the necessary links of the extrapyramidal system converge. Now, in order to increase the effectiveness of treatment, a combined destruction of the ventrolateral nucleus of the thalamus and the subthalamic region is carried out, due to which more than 80% of patients experience a stable and significant improvement in their condition.
With a local form of torsion dystonia, the destruction of the basal nuclei of the brain is carried out on the side opposite to that side of the body on which there are violations of muscle tone and hyperkinesis. With a generalized form of torsion dystonia, two operations are usually performed with an interval between them of about 6–8 months. The first operation, as a rule, is performed on the side opposite to the more affected limbs. If the lesion is expressed equally on both sides, then the first operation is performed on the left to restore, first of all, the functions of the right hand.
With severe hyperkinesis, the operation is performed under anesthesia, less often (in milder cases) local anesthesia is used.
Prognosis of treatment and prevention of torsion dystonia
The prognosis is unfavorable. In the late stage, patients often die from intercurrent diseases. After stereopathic surgery, hyperkinesis and muscle rigidity generally decrease or disappear.
As a result, patients can walk and serve themselves, perform many necessary actions. According to E. N. Kandel, in 66% of patients for many years after surgery, the result remained good or was assessed as a significant improvement.
Prevention of torsion dystonia
The patient's family should be under the supervision of a medical genetic consultation. Parents of a child with torsion dystonia are advised to refuse further childbearing.
Causes of torsion dystonia
The first manifestations of the disease were described by M. V. Schwalbe in 1907. Over the years, he observed a family that had 5 patients in two generations, ill, in his opinion, hysterical neurosis, but in fact - torsion dystonia. In 1911 G. Oppenheim proved that torsion dystonia is an organic disease of the brain caused by damage to the subcortical nodes, and that attributing it to hysteria is erroneous. long time the question of the nosological affiliation of the disease remained controversial. Some scientists believed that it was an independent hereditary disease.
Others not only did not attach importance to heredity in the etiology of torsion dystonia, but were also sure that there were only torsion-dystonic syndromes in violations of the extrapyramidal system of various etiologies: infectious and toxic encephalitis, traumatic brain injury, vascular diseases brain, birth trauma and etc.
It is now established and generally accepted that torsion dystonia is an independent nosological form, in the formation of which the hereditary factor plays the main role. Inheritance is different. In some families, the disease is inherited in an autosomal dominant manner, in others, which happens more often, in an autosomal recessive manner. Torsion dystonia, inherited in the first case, is observed for 2–3 generations, and in other families for 4–5 generations. With an autosomal recessive type of inheritance, there were cases of consanguinity of parents. Sporadic cases of the disease have been reported.
Pathogenesis of torsion dystonia
The pathogenesis of the disease is not known. No primary metabolic disorder was identified. It is possible that disturbances in the content of catecholamines, mainly dopamine, are involved in the pathogenesis. The pathophysiological essence of torsion dystonia is characterized by a violation of the subcortical regulation of muscle tone. Pathological and anatomical examination reveals mild degenerative changes in the cerebral cortex and more pronounced ones in the basal nuclei, the red nucleus, the Lewis body (nucleus subthalamicus), the black substance (substantia nigra), and the dentate nucleus of the cerebellum.
Torsion dystonia, or Tsien-Oppenheim disease (distonia lordotica progressivas, dystonia musculorum deformans) is a kind of muscle dystonia with a constant change in convulsions.
Symptoms of torsion dystonia
The main symptom of the disease is dystonia of voluntary muscles, leading to the development of peculiar, constantly changing convulsive attitudes. Spiral rotation with curvature of the spine is characteristic. The cramps are associated with walking. At rest, patients relatively well maintain the position of their body. Despite the extreme ugliness of gait, patients are able to move independently for a long time. Lordosis and scoliosis of the spine disappear when lying down. In a dream, hyperkinesis completely disappears. As with parkinsonism, "paradoxical kinesias" are sometimes observed in patients with torsion dystonia. Thus, some patients with gross gait disturbance can dance freely or move backwards without difficulty or pushing a wheelchair in front of them. IN muscular system ascertain various combinations of hypotension and hypertension. In some cases, there is a greater selectivity of the lesion: torsion dystonia covers a relatively small muscle group, and therefore only torticollis or a persistent cramp develops in the form of forced pronation of the hand. The muscles of the face are not involved in convulsions. Speech persists for a very long time. Pyramidal symptoms and sensory disturbances are usually absent. The psyche is not changed. Often choreic convulsions, athetoid convulsions, myoclonus, tics join torsion dystonia. A combination of torsion dystonia with trembling is much less common. Changes in the liver, enlargement of the spleen is not observed. The Kaiser-Fleischer ring is missing. Gradually, imperceptibly starting in childhood(the maximum incidence occurs at 10-13 years), the disease further progresses non-stop. Patients die from cachexia and respiratory or urogenic infections.
pathological anatomy
Not yet fully elucidated. In a few cases, autopsy revealed histopathological changes of a degenerative nature in the striatum.
Diagnosis of torsion dystonia
It is necessary to differentiate the primary form of torsion dystonia from symptomatic. Among the causes of the latter, epidemic encephalitis and hepatolenticular degeneration most often appear. The originality of convulsions in torsion dystonia, their exacerbation during emotional stress often causes unfounded assumptions about hysteria. Meanwhile, participation of the trunk and proximal parts of the extremities is uncharacteristic for hysterical hyperkinesis.
Torsion dystonia manifests itself in the form of familial or sporadic cases. Dominant inheritance with low gene penetrance is assumed.
Incomparably more often than the developed forms of torsion dystonia, its local variant is found - spastic torticollis (torticollis spastica). This syndrome is based on tonic or clinical spasms of the cervical muscles. Depending on which muscles are involved, the patient's head is either only turned to the side, or at the same time tilted to the shoulder, or, finally, thrown back (retrocollis). Many patients complain of neck pain. Spasms often depend on the position of the body, disappearing in horizontal position and sharply intensifying when walking. There may be hypertrophy of the muscles involved in hyperkinesis (for example, m. sternocleidomastoideus). Passive movement of the head to the normal position sometimes succeeds completely freely, but in other cases it encounters significant resistance from the contracted muscles. In most patients, a very peculiar phenomenon is found: the patient's finger, placed on the cheek, stops hyperkinesis for as long as this symbolic pressure of the finger is maintained.
In the pathogenesis of spastic torticollis, dysfunction of the higher vestibular centers, apparently, should play a significant role, since it is the labyrinth and the cervical reflexes associated with it that play the leading role in the correct position of the head.
Along with organic causes(torsion dystonia, past encephalitis, hepatolenticular degeneration) spastic torticollis occasionally has a hysterical basis. Unlike spastic torticollis, congenital torticollis is caused by a stationary shortening of m. sternocleidomastoideus, or an anomaly of the cervical vertebrae. Finally, one must also keep in mind Grisel's disease, in which torticollis is in the nature of an analgesic contracture in response to subluxation of the atlanto-epistropheal joint. The disease is observed in childhood and is due to the spread of inflammation from the nasopharynx to the joints of the upper cervical vertebrae.
Treatment of torsion dystonia
The condition of patients can sometimes be alleviated by the appointment of drugs of the atropine series and sedatives. IN Lately there have been reports of pronounced effect L-DOPA. The appointment of this drug for the first time in the history of conservative treatment of torsion dystonia made it possible to achieve a sharp decrease in tonic spasms, as a result of which bedridden patients are able to move freely and serve themselves. Widely used in torsion dystonia is stereotaxic intervention on the basal ganglia. Termination of hyperkinesis in spastic torticollis can be obtained by crossing 3-4 pairs of cervical roots and accessory nerves.
The article was prepared and edited by: surgeonPatients often end up in the hospital with motor activity. This condition is caused by poor muscle tone and is characterized as torsion dystonia. The disease is manifested by spasms, in which muscle tissues bodies are compressed, deformed. This condition can cover the entire body.
Torsion dystonia is a neurological disorder, causing problems with muscle tone, uncontrolled contractions in which the patient assumes abnormal postures. This disease is rare, but it is highly complex. Deforming muscular dystonia causes pain, requires the attention of doctors.

Only 3 patients out of 100 experience such a disease in their youth. Over time, the disorder progresses, symptoms and stages change. The eyelids close arbitrarily, the muscles on the face contract, the speech function and the swallowing reflex are disturbed.
Forms of the disorder are determined by the affected area:
- Local. There is a fragmentary lesion of muscle tissue.
- Segment. Spasms spread near the located muscles.
- Generalized forms of the disease. Muscle tissues on the back, in the pelvis, arms, and body are affected.
- Arise severe pain when the disorder is localized in a certain place.

The strength of the symptoms that occur is determined by the site of muscle damage. Often, one after another, the forms spread to each other, and an increasing part of the muscle tissue is affected. In such a state, the patient seems to break or twist.
Causes
The disease has two forms of occurrence: hereditary, symptomatic. Symptomatic is characterized by such provoking factors: oncology, tick bites and development, cerebral palsy, post-traumatic complications.
More detailed studies of this disease have not been conducted. More obvious reasons medicine does not consider the occurrence of such disorders. Scientists accurately distinguish several forms of this disease, the appearance of which is caused by several factors.

An autosomal dominant form of the disease appears in adulthood, the symptoms are not too difficult to bear. Torsion dystonia appears on the basis of diabetes, difficult childbirth, poor heredity, CNS pathologies, vascular problems, intoxication, toxoplasmosis, cerebral palsy, etc. the hereditary variety of the disease is less often diagnosed, manifestations in such a situation occur in 2-3 generations in this genus or in a situation where the parent of the children is too closely related.
Symptoms
In most situations, the disorder is acute. The complication of symptoms and the appearance of complications occurs in as soon as possible. Chronic form appears in a small number of patients. IN early age torsion dystonia manifests itself as follows: convulsions periodically appear, gait changes, spastic torticollis occurs.
As the patient matures, the disorder progresses to acute form, attacks appear unexpectedly. Consider the symptoms: the appearance of primary generalized spasms, the adoption forced postures, involuntary gestures.

Under the influence of the following factors, the condition of patients is aggravated: stress, physical and intellectual overload, bad habits, drinks containing caffeine and other stimulants.
After rest or sleep, the symptoms decrease. Medicines prescribed by the therapist help to improve the condition.
Diagnostics
When identifying signs characteristic of torsion dystonia, patients will have to contact neurologists. The doctor conducts a survey, examines the patient. Much attention must be paid muscle tone against the background of maintaining their intensity and the absence of problems caused by hypersensitivity.
The diagnostic tasks include distinguishing torsion dystonia from others. neurological disorders. The following diagnostic methods help people with this:

- Electroneuromyography allows you to determine the change in the activity of muscles and nerve pathways.
- An MRI is done to look for damage to the head.
- X-ray allows you to find out the condition of the bones, indirectly reveal the presence of certain diseases.
- reveals the degree of brain activity.
Based on these results, the specialist determines correct diagnosis. The course of therapy is determined taking into account the complexity of the disease and provoking factors.
Treatment
Therapy of torsion dystonia occurs with medication and surgically. Patients will also have to undergo exercise therapy. Conservative treatment implies the use of such medicines: neuroleptics, tranquilizers, adrenoblockers, anticonvulsants.
Surgery is performed if the pills do not help. The exception is the presence in patients of complex diseases in the organs or blood. In the later stages, these pathologies are not included in the list of contraindications.
Complex forms of the disease show a disappointing prognosis because often such patients die from intercurrent pathologies. After surgery muscular dystrophy and hyperkinesis worsens or disappears completely.
With timely and proper treatment, patients partially recover, begin to walk, perform simple actions, they no longer need to be closely looked after. In 70% of patients after surgery, patients improve. When secondary torsion dystonia appears, surgery brings good results, hyperkinesis and spasms are weakened.

Medical or surgical treatment, regardless of the results, for the period of rehabilitation should be accompanied by the use of drugs that the doctor prescribes. Relatives of such patients should be under medical supervision. Parents whose baby is sick with torsion dystonia are advised to refuse subsequent births.
Electrical stimulation of subcortical structures
Electrical stimulation of food structures - new technique, implying that electrodes are implanted in the place responsible for the painful impulse, generating electrical discharges. Such signals suppress the activity of the inflamed area of the brain.
Surgical intervention is also carried out using the technique of stereotaxic guidance. After identifying the coordinates of the location of the target structure, the doctor conducts a prompt access for intraoperative x-ray examination, fixes the electrodes in the subcortical areas.

The neurostimulator that generates impulses is made in the form of a small device that is implanted in the subcutaneous fat in the area under the collarbone. After surgery, electrical discharges are transmitted to the patient's brain. A person can independently control the functioning of the neurostimulator, taking into account well-being.
At surgical treatment destructive stereotaxic procedures are carried out aimed at deforming brain structures in which painful impulses arise. Initially, a stereotaxic frame is fixed on the patient's head. Then it is carried out.

After that, with the help of special calculations using a tomogram and stereotaxic landmarks, the coordinates of the target structure are determined. The doctor accesses the necessary section of the central nervous system and cuts off problem areas of the brain using various methods.
Forecast
The idiopathic form of the disease develops slowly. The outcome can be determined by the time of its manifestation. early manifestation symptoms causes a complex development and generalization of the disease with a significant degree of disability of the patient. Death patients due to intercurrent infection.
Surgical intervention helps to significantly improve the prognosis. In most cases, regression or a complete absence of hyperkinesis and rigidity occurs after surgery. Patients can take care of themselves for a long time after the operation, move without outside help, and perform some simple tasks. secondary form torsion dystonia ends favorably. IN similar situations there is a regression of spasms and hyperkinesis.