Ultrasound adrenal preparation. What shows and how to prepare for ultrasound of the adrenal glands. Dimensions of healthy adrenal glands in children
Ultrasound of the adrenal glands is a fairly well-known procedure in which the doctor can find out the size of these organs and their structure. The adrenal glands are paired organs, like the kidneys. This suggests that the doctor often prescribes jointly with the adrenal glands in order to surely identify the pathology if the patient has it. Ultrasound of the kidneys and adrenal glands is prescribed if the patient cannot accurately determine the area. And also, ultrasound of the kidneys and adrenal glands is performed in the treatment of an already identified disease in order to control and exclude the transition of the disease to another organ, for example, if it is an inflammatory process.
Paragangliomas may be solitary or multiple, and they may have greater malignant potential. Paragangliomas can also be found in the neck, mediastinum, and wall Bladder. The central necrosis may be so extensive as to mimic a cyst. Calcification is uncommon; if present, it may have a pattern with eggshell. After intravenous administration iodinated contrast medium, pheochromocytomas exhibit heterogeneous enhancement, a pattern indistinguishable from adrenal malignancy.
Ultrasound of the adrenal glands is most often used in order for the doctor to evaluate such factors:
How are the organs of the adrenal glands located?
- clarity of the contours of these paired organs;
- sizes of organs;
- tracking the structure of organs (the presence of violations in the structure);
- the presence of foreign entities.
For ultrasound of the adrenal glands, there are such indications:
- the patient's skin color may change (the acquisition of a dark shade in some areas);
- uncontrolled weight gain, if there are no objective reasons for this;
- males may experience problems with potency;
- excessive hairiness on the body of a woman;
- useless attempts of women to get pregnant, which end in vain;
Stretch marks may appear on the body for no apparent reason.
Correlation with biochemical function is required to establish a correct diagnosis. Some concern has been raised about the use of intravenous contrast in patients with pheochromocytoma. Plasma catecholamine levels can be elevated by intravenous injection iodinated contrast medium, but symptomatic increase blood pressure usually does not occur. Only if the patient has had hypertensive episodes and there is no adequate pharmacological adrenergic blockade should contrast be avoided.
How to Prepare for an Adrenal Ultrasound
Before the procedure of ultrasound of the adrenal glands, it is necessary special training. It is the preparation of the patient for ultrasound of the adrenal glands that can affect the success of the procedure and its final results.
The lower the weight of the patient, the more opportunities to see the picture of the organs
Contrast is particularly useful for identifying extra-adrenal lesions. Radionuclide metaidobenzylguanidine scintigraphy may be useful in documenting whether a retroperitoneal mass is in fact a paraganglioma. They are easy to spot as they are several centimeters in diameter.
Permanent enhancement after intravenous gadolinium is typical. Since lipid is not detected in the pheochromocytoma, there is no signal reduction on reverse phase images. Biopsy of a mass suspected to be a pheochromocytoma is not recommended, especially if adequate control of hypertension has not been achieved, as several episodes of severe hemorrhage and even death have occurred following cranial biopsy. However, this is an expensive test that takes up to 72 hours to complete and is not widely available.
However, a person will not be able to reduce weight so rapidly, but he can make sure that there is no fat in his stomach and intestines. large cluster gases. To do this, a few days before the procedure, it is better to stick to a diet and eat boiled food, excluding fried and smoked foods, as well as the use of carbonated and alcoholic beverages. Food of animal origin is recommended to be completely excluded for several days, but what you can eat is pasta, cereals, vegetables. As a liquid, you can use non-carbonated water and juices (exclusively natural). Sweets are also not recommended for use before an ultrasound of the adrenal glands.
Preparing for an adrenal ultrasound in the afternoon should include a morning without breakfast. And in order to better prepare for the procedure, by the evening of the day before it, you can take a laxative to reduce intestinal fullness and reduce the level of gas present.
Contraindications and accuracy of the method
In addition, it does not provide sufficient anatomical detail for surgical planning. The presence of hypertension in this group of patients does not always indicate persistence or recurrence of the disease. Other causes of hypertension should be evaluated, such as kidney changes due to chronic disease.
What can be determined during ultrasound diagnostics?
Intolerable adrenal tumors are clinically silent until they become very large, although they may experience pain if they bleed. At present, most of these masses are discovered incidentally in studies carried out for other reasons. Most incidental adrenal masses are benign and do not have clinical significance especially in patients with unknown malignancy. In two large series, only 7% and 9% of loose adrenal masses were subsequently found to be malignant.
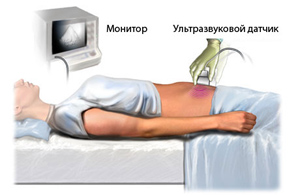
It is noteworthy that this procedure is not well suited for accurate recognition of a tumor in the adrenal glands. To recognize tumors, it is better to use the MRI procedure for the greatest reliability of the result. You can also use CT, which is more accurate than ultrasound of these organs, but requires a special mode and with the presence of contrast medium. This is due to the fact that the organs of the adrenal glands are located deep enough that even the most modern ultrasound technology is not always able to determine the presence of a tumor in these organs with low accuracy.
Although the historical size is considered an important factor, larger tumors more likely malignancy, are an imperfect criterion. Although malignancies were all over 5 cm in one study, and most benign masses are less than 5 cm, there is significant overlap. Most incidental masses larger than 5 cm are still benign in patients with no history of malignancy, and lesions up to 1 cm may be metastases.
What can a sonologist detect with ultrasound
Thus, imaging criteria are required for differentiation. They are most often unilateral, although bilateral adenomas do occur. Calcification may be present. They are smooth, round or oval, with a well-defined edge. Korobkin et al. and Boland et al. confirmed these results.
However, there are a number of conditions that must be observed in order to see the most accurate picture from an ultrasound examination of the adrenal glands:
1. The patient's body weight should be normal (the thinner the patient, the more likely it is to recognize a clear picture). Because the presence of adipose tissue in large quantities closes the visibility of the organs.
2. The absence of operations in the patient's abdomen (the presence of sutures and adhesions is inevitable, which adversely affects the effect of ultrasound and does not provide access to information);
3. Absence of gases in the body. However, even if the patient follows all the preparation rules, there may be excess gases in the body.
Adrenal adenomas, unlike most metastases and other non-adenomas, often contain a large number of intracellular lipid. Korobkin et al. established washout curve values for adenomas. The established formula for this calculation includes the density of the lesion during the pre-contrast, portal, and 15-minute delay phases. Calcified and necrotic nodules are not suitable for this calculation.
The percentage increase in concentration is calculated as follows. In this case, no further evaluation is necessary. If the washout is greater than 60%, the most likely diagnosis is a low lipid adenoma. Again, no further evaluation is necessary. If the washout on elevation is less than 60%, the mass is considered indeterminate. Percutaneous adrenal biopsy is recommended if the patient has a primary neoplasm without any other evidence of metastasis.
As a conclusion, it can be understood that an ultrasound examination of organs such as the adrenal glands is shown only in not too dangerous cases. If there is a suspicion of the presence of tumors, then it is better to choose a different method of research. Eg, CT scan is more effective method in this case, however, not as harmless as ultrasound. CT provides a radiation dose that is not safe method. However, in some cases it is necessary to take such a step when the risk of a small dose of radiation is justified and will help cure a life-threatening disease for the patient. In any case, you should not self-medicate and prescribe procedures for yourself, because the attending physician knows better what his patient needs.
Adrenal metastases are common from a variety of primary malignancies, including cancer. thyroid gland, kidney, stomach, colon, pancreas and esophagus, as well as melanoma. Even in patients with lung cancer, about a third of the adrenal masses are benign. So image features should be used to help make correct diagnosis. Finding a new small adrenal mass on observation is clear evidence of metastasis if baseline showed normal adrenals.
In contact with
May 2, 2017 VrachIT IS IMPORTANT TO KNOW! Alexander Myasnikov in the program "About the Most Important": The only remedy for KIDNEY DISEASES that really helps almost immediately...
One of the most common methods for diagnosing a condition internal organs- ultrasonography. This procedure is carried out in relation to the adrenal glands. However, it cannot be called the most informative. This is due to the peculiarities of the location of this body. Nevertheless, ultrasound of the adrenal glands is often used to obtain primary information about the size of the gland, its structure.
Adrenal metastases can be unilateral or bilateral. When they are small, they are usually fairly well defined, round or oval, and have soft tissue densities. They may have smooth or irregular, lobulated contours. They may show local invasion, a sign of malignancy. Calcification is rare and they may bleed.
Small metastases to the adrenal glands are solid tumors and generally have uniform damping values soft tissue, similar to or higher than those of muscles in non-contrast scans. However, if there is central necrosis, the density is not lower than that of water, because malignant tumors do not produce lipids.
When appointed
Because the adrenal glands are the organ that produces various hormones, then the presence of signs of hormonal imbalance may cause the need for their diagnosis. The first step is an ultrasound. The reason is the symptoms characteristic of hormonal disorders. In some cases, these manifestations develop slowly, in others suddenly and are very pronounced.
After intravenous administration of iodinated contrast agent, there may be uniform enhancement, but enhancement is usually heterogeneous, especially with larger tumors. A thick, knot-enriched rim may also be seen. They may be heterogeneous. Numerous calculations based on signal strength ratios or calculated T2 values have been investigated, but none of these have proven reliable in practice for distinguishing metastases from adenomas.
Because metastases do not produce lipid, there is no signal reduction on reverse phase images. After intravenous administration of gadolinium compounds, metastases show excessive and heterogeneous enhancement that persists for several minutes, the picture of improvement being very different from that of adenoma. Computed tomography is the most cost-effective method for screening and monitoring patients with malignant neoplasms. However, complications can occur and a biopsy is not needed if the imaging results are diagnostic.
Indications
- General weakness for no apparent reason.
- Change in skin color.
- Obesity.
- Infertility in women.
- Stretch marks on the skin.
- Decreased potency in men.
- Cycle failures in women.
- Persistent hypertension, uncontrollable, or pressure spikes.
- Injuries abdominal cavity.
Contraindications and restrictions
There are no absolute contraindications for ultrasound of the adrenal glands, since the radiation exposure during this procedure is minimal. However, doctors do not recommend such an examination during pregnancy, and damage is also a temporary limitation. skin in the sensor area. Adhesions formed after abdominal surgery can become an obstacle, as they scatter ultrasound.
Neoplastic patients often show diffuse enlargement of the adrenals but no mass or contour changes. Biochemical research conducted with this group of patients have demonstrated a number of changes in gland function that have been shown to be consistent with hyperplasia. There is a definite relationship between malignant neoplasms and adrenal hyperplasia; there is a higher prevalence of adrenal hyperplasia in patients with tumors compared to the general population.
Lymphoma sometimes involves the adrenal glands, with common non-Hodgkin's being the most common type. It can be detected on presentation or on observation, with adrenal lymphoma being reported in 1%-4% of patients that follow lymphoma. most often found in association with an area outside the adrenal glands. Primary adrenal lymphoma is rare and is thought to arise from hematopoietic cells in the adrenal gland.
Information in the diagnosis of an organ
What does an ultrasound of the adrenal glands show? If the organ was visualized, then its dimensions can be determined. The norm of the adrenal glands is 1-1.5 cm in length and 0.3-1.6 cm in width for the right, 1.5-2 cm in length and 0.8-1.5 cm in width for the left.
It is also normal that the left and right parts of the body have different sizes, and the left one is not always determined, which is possible in half the cases. If an increase in the size of the adrenal gland is detected, this indicates organ hyperplasia, the presence inflammatory process, hematomas, tumors or cysts.
The method of conducting an ultrasound examination
Adrenal lymphomas are bilateral in one third of cases; if bilateral, the patient may develop Addison's disease. Lesions may be homogeneous, but they are often heterogeneous with low levels weakening even before therapy. Occasionally, a growth pattern may indicate lymphoma, as it is more likely to infiltrate or insinuate around the upper pole of the kidney than to displace it, which would be typical of a carcinoma. There may be hemorrhage and calcification may be found, especially after chemotherapy.

Study preparation
In order for the survey to be successful, you need to prepare for it. Such preparation is due to the peculiarities of the location of the organ, which complicate the ultrasound of the glands. The adrenal glands are located at the very top of the kidneys and are under the diaphragm deep in the space behind the peritoneum. It will not work to carry out a qualitative examination of the organ from the back, because the muscles, ribs and vertebral structures interfere. Therefore, visualization is carried out from the side of the abdomen, through the front wall.
Myelolipoma is an uncommon, benign, non-functioning neoplasm of the adrenal glands found in less than 1% of autopsies. It is composed of varying amounts of adipose and hematopoietic tissue, including myeloid and erythroid cells and megakaryocytes. It affects men and women equally. Although it is a non-functioning tumor, in 10% of cases it is associated with endocrine disorders, including Cushing's syndrome, congenital adrenal hyperplasia, and Conn's syndrome. Most myelolipomas are asymptomatic and have no clinical significance.
However, in this examination, the ultrasound signal passes through several layers of different tissues before reaching the target. These are skin, subcutaneous fat, intestinal loops, retroperitoneal adipose tissue. Such a number of obstacles for ultrasound leads to the fact that it weakens. Therefore, to improve the diagnosis, it is necessary to ensure the maximum possible visualization. It is for this that preparation for the procedure is necessary.
Some become large and cause vague symptoms or pain. Large myelolipomas may bleed, which can cause pain. Sometimes a mass may appear in the retroperitoneal space. Almost all contain a certain density of fat. However, the amount of fat varies widely, from nearly all fat to more than half fat, to just a few tiny foci of fat in a soft tissue mass. Sometimes mass has a fading value between fat and water content because fatty and myeloid elements diffuse.
What does an ultrasound of the adrenal glands show?
Calcification is observed in 30%, often punctured. With hemorrhage, you can see areas with high density. Bilateral myelolipomas occur in about 10%. However, if the mass is almost all of the mature fat, there will be no signal loss with opposite phase images, because the signal loss occurs only with phase cancellation in areas with admixture of fats and water protons. In general, myelolipomas are often heterogeneous because lean areas will have a signal intensity similar to that of hematopoietic bone marrow.
In addition, surplus subcutaneous fat interfere with normal research top scores obtained in thin patients. It is important to ensure as little gas in the intestines as possible.
- Espumizan intake.
- Special diet a few days before the procedure.
- Taking a laxative in the evening on the eve of the day of the ultrasound.
- Dinner on the eve of the procedure should be the last meal.
- Fluid restriction on the day of the ultrasound.
The diet before the ultrasound is observed for three days, it should be light and slag-free. On diet days, it is recommended to take espumizan so that by the time the study is performed, there is no accumulation of gases in the intestines. The diet excludes the use of products that promote gas formation:
- everything fatty and fried;
- meat;
- legumes;
- bakery products;
- strong coffee;
- carbonated drinks;
Ultrasound procedure
Ultrasound examination of the adrenal glands is performed transabdominally, that is, through the anterior abdominal wall. The organ itself is not echogenously visualized, therefore, for examination, you need to find its location. The doctor starts the study on the right, he determines right kidney, inferior vena cava and right side liver, since the right adrenal gland is located between these points.
It is scanned with the patient lying on his back or on his side during deep breath. To study the left side of the organ, the doctor may ask the patient to change position. Left side organ is more accessible for ultrasound through the left hypochondrium.
Scanning is very easy. For him, the patient frees from clothing lower part bodies, the skin on the abdomen in the projection of the adrenal glands is lubricated with a special gel, which provides better ultrasound conductivity. Next, the doctor guides the sensor of the device over the surface of the skin of the abdomen and examines the information received on the screen. The patient does not feel any discomfort during this examination, its duration is no more than 20 minutes. After the end of the procedure, the gel is wiped off with a napkin.
What the results mean
Specialist in ultrasound diagnostics makes records in accordance with the received data. They are the basis for setting preliminary diagnosis endocrinologist.
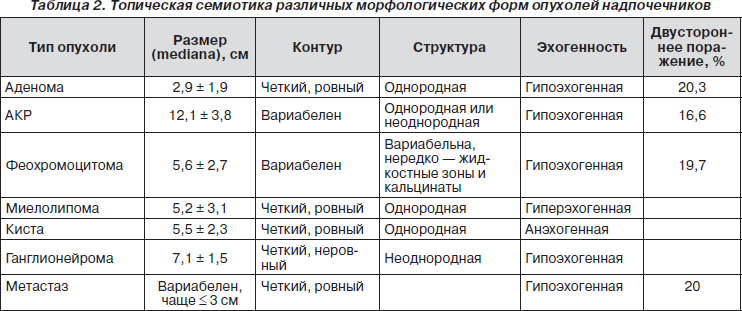
If hyperplasia is detected, then tissue proliferation occurs. Such changes may lead to hormonal disorders. An increase in an organ can be a consequence of its inflammation, injury, or the formation of neoplasms. Any deviation from the norm is a reason for additional surveys. It will take hormonal analysis, computed tomography of the adrenal glands, as well as some other diagnostic procedures that will allow an accurate diagnosis to be made.
Despite the fact that ultrasound of the adrenal glands does not make it possible to obtain full information about the state of this body, it is widely used. The point is that the devices ultrasound research are available in almost all clinics and do this procedure accessible. Plus, it's completely safe. The possibility of making a preliminary diagnosis allows us to assume how serious the deviations are and to prescribe further examinations if necessary. Early detection adrenal dysfunction allows you to get help on time, avoid aggravation of the situation and the development of complications.
How to cure kidneys at home?

Edema face and legs PAIN in the lower back PERMANENT weakness And fast fatiguability, painful urination? If you have these symptoms, then there is a 95% chance of kidney disease.
If you care about your health, then read the opinion of a urologist with 24 years of experience. In his article, he talks about RENON DUO capsules. This is a fast-acting German kidney repair remedy that has been used all over the world for many years. The uniqueness of the drug is:
- Eliminates the cause of pain and brings the kidneys to their original state.
- German capsules eliminate pain already during the first course of use, and help to completely cure the disease.
- Missing side effects and no allergic reactions.