Pro in the analysis of urine is the norm. Urobilinogen in the urine: the norm and what does the increase mean. How is urobilinogen formed?
Today, urinalysis is the norm, the delivery of which is required for almost any disease. Deciphering such an analysis allows the doctor to diagnose the pathology. The fact is that urine is responsible for excretion a large number toxins, due to which it is possible to diagnose renal, cardiovascular diseases or an immune problem. Sometimes the decoding of the analysis shows that urobilinogen in the urine is elevated. Not everyone knows what this means.
The analyzer takes approximately 80 seconds to read the strip. The calibration procedure takes less than two minutes. In the quick reference guide or user guide. Urinalysis includes a semi-quantitative measure of both biochemical components and shape elements such as cells and casts. During different states hydration and normal kidney physiology, these components will present variable concentrations in the urine, making it impossible to identify a set of control intervals.
The results should be interpreted together with the urine concentration. In this way, any artifact or change due to urine discoloration is minimized. Moderate and important changes urine color, and the results should be analyzed in terms of these changes.
Urobilin in urine is a bile pigment derived from bilirubin. It is this compound that explains the color of human urine. Compared to bilirubin, urobilinogen in urine is normal condition is present. However, if its level is elevated, it becomes a signal of pathology.
The formation of urobilinogen is carried out in the intestine, for this, bilirubin is used, which is there along with bile. The synthesis of enzymes and microorganisms carries out the procedure of oxidation and absorption into the blood. After that, ubg is sent to the kidneys and is excreted in the urine.
What are possible consequences? What should I do? The isolated presence of urobilinogen in the urine, without other analytical changes in the blood, is usually an incidental finding that disappears when the analytes are repeated later. Theoretically, the presence high performance may be the result of an exaggerated destruction of red blood cells, which can cause a large contribution of hemoglobin-bilirubin, which is the precursor of urobilinogen. This type of problem usually causes jaundice and anemia.
These two changes would be easily detected by analytical and physical examination. Other circumstances that could lead to its increase in the blood were important infections and insufficiency of liver function. Both of them are also easily detected earlier.
The ubg norm that urine should show healthy person, ranging from 5 to 10 mg/l. When the indicator is increased or decreased, we can talk about disorders in the body associated with the metabolism of pigments.
When urobilinogen rises in the urine, doctors diagnose urobilinuria. The rate of the indicator most often changes with problems with the liver and intestines. When the uro in the urinalysis does not correspond to normal values, the doctor may suspect:
Therefore, it is unlikely that he could be held responsible for the analytical changes. Thus, if everything else is correct, the analysis should be repeated in a couple of weeks and, depending on the results, it will be seen whether the study should be expanded. A urinalysis is a test done at your doctor's office that explains various aspects your health. Once the urine sample is collected, a urinalysis is done, the test is compared with the various components of the urine against an average or normal temperature.
Reading urine tests takes a bit of work, but once understood, the test can be very revealing. Collect one to two ounces of urine in the morning to get the most accurate urine reading possible. Dip only one test strip into the urine and wait a minute for the chemical reaction, and make a stripe to change the colors.
- viral hepatitis;
- hepatic cirrhosis;
- neoplasms in the liver, including malignant ones;
- congestion in the liver tissue;
- acute infection.
However, it is worth emphasizing that when urobilinogen in the urine is elevated, but the decoding of other components of the problems did not reveal, it is too early to talk about the disease. Sometimes the norm can be violated due to some features of physiology, combined with an additional renal load.
Observe the smell of the urine to detect the presence of ketones, which indicates a strange fruity smell. Consider urine coloration: dark colored urine indicates dehydration, while light colored urine may indicate hydration. Check and compare chemistry with test strips using the color chart and dipstick to assess pH levels, specific gravity, nitrate levels, protein levels, ketone presence, glucose, blood and hemoglobin levels.
Document information directly on the color bar indicator versus conventional levels. Normal specific gravity levels are between 1, 0 and 1, pH levels should be between 4.8 and 7. A good test for protein, glucose and ketone should be negative.
Sometimes the indicators are increased due to the fact that the urinary system demonstrates high efficiency. However, lack of fluid can cause dark color urine. There are cases when the decoding of the analysis indicates the complete absence of urobilinogen. This certainly indicates an internal problem, as it means that there is no bilirubin in the intestine.
Look for positive nitrate levels in urine; a healthy urine sample should be free of nitrate. If bilirubin is elevated, a condition of anemia, liver problems, or hepatitis can occur. Observe white blood cell levels and make sure they are in the 0 to 10 range, if the test is high and outside the normal range, the sample may reveal a kidney infection.
Look at the slide that contains part of the urine with a microscope. The presence of parasitic life forms may indicate viral infection. If you read the urinalysis results directly from the report, you will find that the information is listed in a specific order. The first point of the report indicates the color of the urine. The next item on the report is called "Specific Gravity" which indicates the concentration of ions in the urine sample, results greater than 1.03 may indicate the presence of ketoacidosis or protein in the urine.
Childhood problems
When we are talking about the analysis of the child, the norm here differs from the amount shown by the adult. In particular, the norm for a child is no more than 2 mg / l. When the decoding of the analysis says that the indicator is increased, most often we are talking about the presence of pathology.
Decoding in such cases should be carried out by a specialist, since in a child an increase in such an indicator may indicate serious illness. For example, not just traces, but a clear presence in the urine more of this component are a symptom of cholelithiasis, hepatitis, liver cirrhosis, severe colitis, anemia, and infectious lesions organism.
Glucose levels, ketones, and proteins are shown negative or positive on the urinalysis report. The preferred conclusion is negative because positive result in any of the latter areas is of concern. High levels of ketones can indicate diabetes, excessive alcohol consumption, or malnutrition. High glucose is also indicative of diabetes, but white blood cell levels also suggest excessive consumption of sugary foods or drinks, stress, and the presence of fever.
Excess protein can indicate kidney disease. The report shows the exact pH levels found near the corresponding reference range, if the pH level is between numbers in the reference range, the reading is normal. Nitrate levels are observed positive or negative on the urinalysis report.

To understand why exactly the indicator is increased, it is necessary to understand the physiology of infants. Often in newborns, the decoding of the analysis may show an increase due to the period of adaptation to the external environment.
Often, babies develop jaundice of a physiological nature. It is connected with the fact that fetal hemoglobin breaks down.
The presence of blood in the urine may indicate poisoning or damage to the kidneys. We will find out what is uribilinogen in urine, when values are considered normal, and when we can talk about high or low urobilinogen and the reasons for these changes. It is mainly excreted with stools, part is reabsorbed by the liver, and only in small quantities passes in the urine.
High urobilinogen: when urine values are higher than normal
In-Depth Study: Bilirubin Metabolism and Neurobilinogen Formation. The urobilinogen present in the urine is dosed with a test called the Ehrlich reaction. This test consists in the reaction of urine collected within 24 hours with a special Ehrlich-based reagent. Generally, as can be seen from short review about metabolic process bilirubin mentioned above, the amount of urobilinogen found in the form of urobilin in the urine is very low.
As a result, the destruction of erythrocytes occurs, which leads to the formation of urobilinogen in a larger amount than necessary. Such physiological jaundice is a temporary phenomenon, therefore, often the decoding of such an analysis will contain the mark "norm".
Data for pregnant women
When it comes to pregnancy, such an indicator as urobilinogen can increase. During pregnancy, most girls are characterized normal rate. However, urine often becomes darker in color.
Reasons: reason for high levels
Thus, urolithinogen is high in the urine when the Ehrlich test results are found to have a urobilinogen concentration of over 2 milligrams per deciliter. The concentration of urobilinogen in the urine can increase significantly for two reasons or because it is produced in excess due to a deficiency of red blood cells or for damaged liver cells that can no longer remove it in an appropriate amount from the circus it enters through the vein door.
Possible reasons high concentration urobilinogen in urine. emolytic anemia. A set of diseases that cause a decrease in the concentration of hemoglobin in the blood below physiological values for excessive destruction of red blood cells. Hence, excessive production of urobilinogen.
During pregnancy, this figure rises due to violations in the liver. The cause of this disorder may be genetics or a disease, including hepatitis. Very often, an indicator of urobilinogen, the amount of which is too high, during pregnancy becomes the result of fluid loss. Because of this, its concentration in the urine increases, and the decoding of the analysis gives out pathology.
Physical injuries that cause large hematomas. A hematoma is a blood clot that accumulates in a cavity to rupture blood vessels as a result of a serious injury. A set of diseases that cause deterioration of liver cells. Under these conditions, they cannot remove the urobilinogen that reaches it through the vein and this is repeated in the systemic circuit and then filtered out of the kidneys and released in the urine.
The diseases that shape this situation can be. sharp or even chronic inflammation leading to the death of hepatocytes after infection with various viral agents. Inflammation of the liver caused various types intoxication: alcohol, fungi, chemicals, drugs, etc. this type of hepatitis also leads to the death of hepatocytes with impaired liver function. A degenerative disease that causes necrosis of liver tissue and consequently progressive loss of organ function. Liver cancer.
- Toxic hepatitis.
- Hepatic cirrhosis.

In such cases, in women during pregnancy, indicators up to 34 mg / l can be found. If the cause of dark urine is not dehydration, diet or intake medicines, then the woman is assigned an additional study.
It should be noted that during pregnancy, in general, permanent basis tests are given. The fact is that during pregnancy, a woman’s body inevitably encounters excessive loads. During pregnancy, you should also pay attention to complete absence urobilinogen, which also indicates pathology.
Reasons for low urobilinogen: low urine of this metabolic residue
Usually, antibiotic therapy responsible for changes in the bacterial flora. A block that prevents the infusion of bile into duodenum through the well. The reasons for the block can be different: calculations, tumors, malformations, pregnancy, etc. the absence of bilirubin does not allow intestinal bacteria produce urobilinogen. Deficiency of glucuronyltransferase prevents the formation of conjugated bilirubin, which will not be released into bile and then converted into eurobilinogen.
- Changes in the intestinal bacterial flora.
- Urobilinogen is produced by bacteria in the colon by bilirubin.
- Cholestasis or obstructive tear.
- enzyme deficiencies.
It is worth noting that the treatment of such a condition is carried out upon the fact of the root cause. That is, if the cause is not of a physiological nature, then it is necessary to conduct a more thorough study, especially for various inflammations.
Human urine contains bile pigments that are excreted in the urine. Contains urobilinogen in the urine. It appears by the regradation of bilirubin with the help of protein. It is colorless, but when excreted as part of the components of urine, it interacts with air and darkens. This is how urobilin appears. That is why urine, which contains this component, after a while becomes dark in color when exposed to air. Urobilin in urine is within allowable rate. Indicators that go beyond the norm indicate a violation of the body or some organ (pancreas, stomach, liver).
To find out if the excess of urobilinogen is due to excessive hemolysis of hemolysis, it is associated with such an analysis of hemorrhoids, i.e. with evaluation of erythrocytes and liver function. Therapy involves identifying the cause that is causing the problem and, if possible, removing it with appropriate pharmacological therapy.
Supervisor: Vincenzo Angerano. Urine values allow control general state health, diagnose some clinical conditions, evaluate the evolution of a current disease, or understand the effectiveness of certain medications. From a sample of 10 milliliters of urine collected in a sterile container, analyzed physical characteristics, chemicals, and urine sediment, but may require microbiological examination and toxicological testing of drugs.
Education process
Urobilinogen is produced from bile bilirubin in the gastrointestinal tract. The intestinal microflora contributes to this. Partially, the newly formed mass turns into stercobilinogen. This component disappears with feces. Another part of this substance is absorbed by the blood. Since, first of all, blood is transported through the liver, therefore, the cells of the organ also receive urobilinogen. And again they modify it into bilirubin. After combining with bile, all the substance is excreted from the body.
Urine is produced by the kidneys, which use this fluid to eliminate metabolic waste products. To explore your health, you can conduct a simple and non-invasive laboratory analysis recommended to everyone, and work once a year.
Reactive strip analysis
Urinalysis is performed in several ways. Visual analyzes study the physical characteristics and are evaluated. Color: Normal values: Pale yellow Clarity: Normal values: Limited Odor Normal values: Normal. Reactive Strips Explore chemical characteristics.
Pure bilirubin is extremely toxic to the body. Protein (albumin), like bilirubin, is also localized in the intestine. After this protein combines with bilirubin, the entire component becomes non-toxic. A mixture of "protein + bilirubin" enters the circulatory system. A number of biochemical processes are carried out, not without the participation of protein. It is with the help of protein that the formation direct bilirubin, and, hence, urobilinogen. But still, some blood runs across the hemorrhoidal anastomoses without filling the liver. Part of the urobilinogen enters the urine. Quantitatively, the urinary fluid contains 4 mg per day, which is considered the norm.
 Increased rates urobilinogen in the urine are possible with toxic liver damage.
Increased rates urobilinogen in the urine are possible with toxic liver damage.
In an adult or child, urine urobilinogen rises if there are some diseases ( hemolytic jaundice, toxic injury liver, inflammatory and chronic processes in the human body). Increased rates are typical for ailments of the gastrointestinal tract, for example, stool retention and food poisoning. bad sign a deficiency (less than the prescribed norm) of urobilinogen is considered. This testifies about the stones in bile ducts, due to which bile does not flow into the intestines. A level of urobilin that is elevated is called urobilinuria.
Detection methods
It is possible to determine the level of a substance using general analysis urine. In ultra-modern clinics and laboratories, urinalysis is performed on trendy devices. As a result of the UBG analysis, the patient receives a decoding of the units not in ml / dl, but in umol, which is the same thing. I stands for norm. Sometimes the number of 34 µmol / l is indicated in the analyzes, that is, the level of urobilinogen has increased due to certain circumstances. Toxins, poisons, heavy substances that poison the body are capable of causing such an increase. In addition, with liver damage (cirrhosis of the liver) and hepatitis, the level of urobilinogen is also 34 μmol / l. If the patient was given poor-quality or incorrect blood during transfusion, the indicators will also be at the level of 34 µmol / l. That is, elevated level possible not only as a direct reaction of the body to the disease.
Decryption
Norm in adults and children
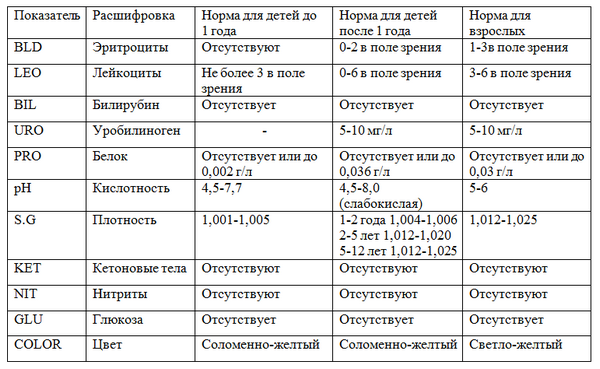 Table of norms for general urine analysis for children and adults.
Table of norms for general urine analysis for children and adults. The norm for women and men is the same - I +. The norm in women and men, if the analysis showed 0.5-2 mg / dl. A level of less than 0.5 mg/dL is considered low. With indicators more than 2 mg / dl - high level substances. But modern analysis on urobilinogen in laboratories gives other values - UBG less than 17 umol/L. This means that the level of urobilinogen is normal. When the analysis indicates 17 umol / L or more, you should consult a doctor and get an appointment for an examination. І+ on the tester shows a light yellow color. The presence in the urine in a small amount is mandatory, but it should not increase. But certain amounts indicate a violation of the norm and are considered a sign of pathology. For children from the age of 1, all data on the analyzes coincide with adults. In a child under the age of 1, at the norm, these substances should not be observed at all.
General analysis determines the urobilinoids in the urine within the acceptable range. Anything above or below the limit is considered a deviation.
Deviations
Reasons for the increase in a child and an adult
 An increase in the indicator indicates a malfunction in the intestines.
An increase in the indicator indicates a malfunction in the intestines. The reason for the increased urobilinogen in the urine may be erythrocytes. Red bodies cause a malfunction in the intestines, in the case of:
Causes of low urobilinogen (less than I) in human urine:
- change in bacterial flora;
- cholestasis of the biliary tract;
- deficiency of enzymes (glucuronyltransferase).
What to do?
 If you change the color and structure of urine, you need to see a doctor.
If you change the color and structure of urine, you need to see a doctor. Sometimes the level of urobilin in the urine is higher than normal - an episodic, isolated case. With diarrhea, there is a load on the kidneys, which is why, when examining urine in a person, traces of urobilinogen in the urine can be observed. But this only indicates that the kidneys are actively working, and not about chronic disease. In people who work in shifts, a weakly positive reaction of urobilin is noted, that is, the indicator rises slightly.
But at constant increase urobilin levels should be consulted with a doctor. He is obliged to appoint a series of examinations to determine the cause of the disease. Further treatment will follow. The doctor will prescribe the patient exercise with minimum load or a visit to the pool. Such physical exercise help to remove unnecessary substances (slags) from the body. A lacto-vegetarian diet is prescribed for the patient. Such dishes help to reconstruct the microflora and start the work of the intestines. You can drink infusions (immortelle, wormwood, tansy). Extracts should be taken warm. full reception food. It is also possible to prescribe medication.
Since the liver starts working from 21:00 to 03:00, doctors recommend going to bed no later than 22:00. In this case, the human body is in a state of calm. You need to wake up no later than 07:00 hours. At home, it is impossible to determine the level of urobilin by 100%. However, the color of urine, which turns from light to dark, should alert.




