Causes of a large number of red blood cells in the urine. Erythrocytes in urine in women. The reasons why their number in urine may be increased. Elevated red blood cells in the urine in women.
Erythrocytes, or red blood cells, serve to carry oxygen from the lungs to tissues and organs. human body. Moving on bloodstream, these particles saturate the cells with oxygen, leading to light carbon dioxide gas. Therefore, the content of erythrocytes in the fluid used by the body - urine, should be minimal. Their appearance indicates a violation of the barrier between the circulatory and urinary systems, which is unacceptable when normal operation organism.
Note that this depends on the method of urine collection, as these cells will be clogged during bladder catheterization. If in doubt, perform a urine cytology. They may or may not be keratinized. They are larger than transitional cells and have small central nuclei. They may be round or have one or more flat borders. Keratinized squamous epithelial cells are from the skin or vulva and are large cells with angular borders.
Causes of change in the smell of urine
They may or may not have nuclei. If you are in doubt about the origin of the cells, Wright's stain can be performed on the urine sediment and demonstrates the central nuclei and angular borders of squamous epithelial cells. Squamous cells are often considered as contaminants in urinary micturition specimens and may also contaminate specimens collected by catheterization. Urine collected by cystocentesis should not contain any squamous epithelial cells.
The presence of red blood cells in the urine small quantities not always identified with diseases. It could be temporary caused by taking certain drugs that increase vascular permeability, stress, excessive physical exertion.
Determine which organ genitourinary system an error occurred, the method helps "three-glass sample". It consists in the sequential selection of urine in numbered containers. All three portions are collected during one urination.
Note that while these cells are considered pollutants, large quantities may represent abnormal conditions of the genitourinary system, in particular, squamous metaplasia prostate at the dog. This occurs secondary to excess estrogen normally secreted by testicular tumors.
renal tubular epithelial cells
Renal tubular epithelial cells are rare in urine and, as mentioned above, are very difficult to distinguish from transitional epithelial cells. If a large number of small epithelial cells with a uniform appearance are noted in the urine, these cells are suspected to be renal. Transitional epithelial cells tend to be more variable in size and shape. browning a large number renal tubular epithelial cells will indicate renal tubular injury.
The study is determined in each serving. If a blood cells most of all in the first container, the cause of the increase in erythrocytes in the urine should be sought in urinary tract if in the second, the kidneys suffer.
Elevated red blood cells in the urine in the third container they talk about problems with bladder. The same number of red blood cells in all three containers may indicate problems in the kidneys and ureters.
Neoplastic cells, usually of transitional epithelial origin, may be shed into the urine. The presence of these cells may be diagnostic of urinary neoplasia, but they are not always seen in the urine of affected animals. Thus, the absence of these cells on urinalysis does not rule out neoplasia.
The diagnosis of neoplasia depends on the identification of cytological criteria for malignancy in epithelial cells, for example. Marked changes in the size of nuclei and cells, multiple nucleoli with variable size in one nucleus, multinucleation with intracellular anisocarosis, macronucleoli. These features are clearly visible in cytological smears and are difficult to reliably identify in unstained urine preparations. Thus, urine cytology should be performed on animals with suspected tumors.
In case of questionable test results, the specialist prescribes additional examination : ultrasound diagnostics and more detailed analyzes urine and blood to make an accurate diagnosis.
Causes of increased red blood cells in the urine of a woman conditionally can be divided for 4 groups:
1. kidney disease leading to an increase in red blood cells:
They may also become secondarily inflamed from necrosis or superimposed bacterial infection. Rarely, other tumors that originate in the bladder or kidney may exfoliate in the urine. Pictured at right are images from unstained and Wright-stained urine sediment from a cat with renal lymphoma. Neoplastic lymphoblasts stratified in the urine and provided the diagnosis in this case.
Sperm in the urine is usually only of value as evidence of the donor's intact masculinity. They can be seen in the urine of men collected by urination, catheterization, or cystocentesis. Rarely, they can be observed in the urination of urine in a newly grown woman. The presence of semen is reported as part of a complete examination of the sediment, the purpose of which is to report all microscopic findings.
- glomerulonephritis. The disease leads to a breakdown in the filtering function of the kidneys, due to which red blood cells seep into the urine;
- pyelonephritis. An illness of an infectious nature that provokes an inflammatory process in the kidney and increases vascular permeability;
- hydronephrosis. Difficulty in the outflow of urine leads to stretching of the organ and microdamage to the vessels;
- tumors. Neoplasms of various nature can compress or destroy blood vessels, causing bleeding;
— urolithiasis disease. Violation metabolic processes leads to the formation of stones in the renal pelvis. The edges of the stones scratch the walls of the mucosa, causing bleeding;
- as a result of injury to the organ, the blood directly enters the urine.
Laboratory blood and urine tests can depict and evaluate the health of any individual. There are many reasons that can lead to results outside of the "normal range". These results can help you identify potential problems.
Blood - biochemical parameters
Low values are usually a sign of anemia or blood loss due to bleeding. A result lower than the limit value is often a sign viral infection, higher bacterium. More high values may have healthy people. . Serum appearance is normal: bright and light yellow.
2. Diseases bladder and urethra:
- cystitis. Inflammation of the bladder mucosa contributes to the infiltration of red blood cells into the urine unchanged;
- tumor processes in the urea and urethra, leading to a violation of the integrity of the walls of blood vessels;
- passing stones urethra injures the walls of the mucosa, causing bleeding;
- damage to organs of a traumatic nature.
Often these results are due to the fact that the patient does not comply with the rules not to eat at least 12 hours before donating blood. Serum may turn red due to hemolysis and jaundice due to increased bilirubin values. Higher values are found in diabetics and decrease with hypoglycemia according to different reasons. Increase in urea and normal creatinine may be the result of diet, rich in proteins. Elevated creatinine values may be due to increased physical activity or taking steroids. Increases the risk of developing cardiovascular diseases especially atherosclerosis. Higher values indicate significant liver damage or other diseases. Higher values usually occur in alcoholics and are a sign of liver damage.
- Maybe indicating an increase in blood fat.
- Elevated values are manifested in kidney disease.
- Decreased values are observed in pregnant women and women in general.
- Low values in patients with kidneys.
- Increased values appear with gout.
- The decrease in concentration has no diagnostic value.
- Higher values are usually associated with malnutrition and stress.
- Do not respect not eating 12 hours before blood removal.
- Elevated values occur with liver damage and biliary obstruction.
- Low values have no diagnostic value.
3. Diseases organs of the reproductive system:
- cervical erosion;
- Uterine bleeding.
The ingress of blood into the urine in these diseases is explained by the structural features of the female genitourinary system.
4. Reasons somatic origin- pathologies of organs that are not associated with the urinary system, but leading to changes in its work. Namely:
Elevated values may indicate increased bone degradation and possible development osteoporosis. Enhanced Level indicates dysfunction of the pancreas. . Together with hemoglobin, erythrocytes and parameters that determine the morphology of erythrocytes, it is possible to trace the state bone marrow. Iron analysis alone is not important for diagnosing anemia.
This is a non-specific parameter. Decreased levels, a sign of damage to liver function, except during pregnancy, when often reported low values. The prothrombin time is normal. Normal urine is clear, yellow with an acid reaction. Anything that deviates from this is possible sign the appearance of the disease.
- hemophilia or thrombocytopenia. Both diseases reduce blood clotting and lead to its penetration into the urine during its filtration in the glomeruli of the kidneys;
— general intoxication the body increases the permeability of the protective membrane of the kidneys for red blood cells.
You can often find similar queries, which is displayed in the title, in the Yandex and Google search engines. Indeed, not all people are urologists, nephrologists or just general practitioners. Before we talk about the reasons, let's think about whether it is legitimate to put the question like that at all? It turns out not.
Appearance - normal: bright appearance. Urine urine - indicates an increase in the number of leukocytes, in some kind of inflammatory process, as well as fungi, bacteria, mucus and other elements that can be found in urine sediment. Dark brown urine - indicates an increase in bilirubin, which is usually a sign of liver damage or jaundice. Some people usually have increased bilirubin so that they look like normal urine. Red urine - indicates the presence of hemoglobin, which usually indicates damage to the kidneys, blood appears in the urine, but also in various inflammatory processes, injuries. The reaction is normal: acid reaction.
There are no reasons for an increase in the number of red blood cells in the urine and cannot be. This is the correct answer to the question.
And now let's change the question itself so that it makes sense: "what are the reasons for the appearance of red blood cells"?
Now everything is correct. But, in order not to confuse the minds, we will use the familiar term "increase in red blood cells."
The kidneys are unique filter factories, and their the main task- separate useful substances from harmful ones. Useful material are again returned to the blood from the primary urine, and the harmful ones are concentrated and excreted. This applies to molecules, but not to huge (compared to molecules) blood cells.
Alkaline reaction - usually indicates a bacterial infection. . Relative density- reference value from 012 to 025. increased density may be a sign of diabetes, hypertension, adrenal hormone dysfunction, kidney damage. May be positive due to increased physical activity or during pregnancy when it is not a sign pathological changes. The appearance of protein in the urine in all other conditions is a sign inflammatory process. Positive results glucose in the urine is mainly associated with increased values this parameter in the blood, which usually occurs in diabetics.
- And it is due to increased water loss - vomiting, diarrhea and high fever.
- Usually decreases with increased urine output.
According to the norms of microscopy of a sediment taken from a whole test tube, no more than 1-2 erythrocytes, and no more than 3 leukocytes in men and 6 leukocytes in women, should be in the field of view of the microscope. In women, additional leukocytes appear due to the proximity of the genitals. What are the reasons high content erythrocytes in urine?
A lot of red blood cells in urine - what does this mean?
- Positive results may be a sign of liver or bile damage.
- A positive finding is present in diabetics.
A white blood cell count of up to 50 or more than 50 is usually a sign of an inflammatory process. The most positive sign due to infection or chronic kidney disease. . Epithelial cell panel - normal: small. Their appearance in the urine to any extent has no more significant diagnostic value. These cells line up the urinal. . Round epithelial cells - normal: negative.
First of all, there may be "travel" blood in the urine, for example, with bleeding from the urethra. In this case, they will be fresh. In the event that there is no bleeding, the appearance of red blood cells is called hematuria. If it is visible only under a microscope, it is microhematuria, and if the color of the urine changes, it is macrohematuria.
Sometimes, if the patient has urinary catheter that hurts bladder may cause hematuria. Additionally, women and men have their own special reasons, the source of which are the genitals.
A positive result is usually a sign of a bacterial infection, and can also be the result of improper urine intake - non-sterile vessels. A positive result indicates the greatest damage to the kidneys. . Amorphous urates - normal: negative.
A positive conclusion has no diagnostic value. . Calcium oxalate crystals are normal: small. A positive finding does not necessarily indicate a disease, but may be a sign of the kidneys. crystals uric acid- normal: negative.
A positive result indicates kidney disease. . Triple phosphate crystals - normal: negative. Positive results may be a sign of a bacterial infection. . Mucus - normal: negative or slightly. A positive finding is the most common sign of a fungal infection and can occur in diabetics. A positive finding occurs in older men and indicates damage to the prostate gland.
- A positive conclusion is of little diagnostic value.
- Positive results show chronic illness kidneys.
The reasons for the increased content of red blood cells in the urine in women is the time of menstruation, diseases such as cervical erosion, malignant neoplasms, dysfunctional uterine bleeding, metrorrhagia.
The reasons for the increased content of red blood cells in the urine in men can be tumors of the prostate gland, as well as its calculi, which are sometimes called prostate stones.
If there was an increase in red blood cells in the urine of a child, then perhaps this was the result blunt trauma kidneys that children can get during active games, since there are no other, specifically “childish” reasons. However, you need to know that the appearance of hematuria in infants from the very first days of life may indicate serious violation renal function: perinatal trauma, about sepsis, and about intrauterine infections, as well as about drug intoxications.
In order to separate “high” urine from “low”, that is, urine from the kidneys and pelvis from the bladder part, a Nechiporenko test is used, in which an average portion is collected. The reasons for the increase in erythrocytes in the urine when taking a sample according to Nechiporenko are usually kidney pathology: acute glomerulonephritis, nephrotic syndrome, or acute disorder renal blood flow - kidney infarction.
Pour into three glasses
There is the famous "three-glass test", in which the entire portion of urine is distributed into three different transparent vessels (glasses). First, a person urinates in the first glass, continues in the second, and finishes in the third.
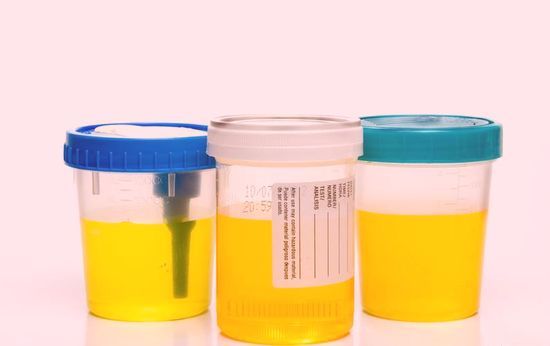
In the event that blood is contained only in the first portion - hematuria is called initial, if in the last - terminal. Most often, this is due to various urological diseases not related to kidney function. If urine is in the first glass, you need to look for the pathology of the urethra, if in the last glass, then you need to examine the bladder, prostate in men. If there is total hematuria, that is, blood is contained in all three glasses, then diagnostic value of this sample falls, since the source can be both the ureter and the kidney, pelvis, or all together, with the urethra and bladder.
About protein boost
Unlike erythrocytes, protein is sometimes present in the urine, since there is a lot of it in the blood plasma. But protein is “valuable” for the body, and therefore its amount in urine should not exceed 0.33 grams per liter, that is, 0.03%. Anything above is called proteinuria.
The reasons for the increase in protein in healthy people are:
- after a long and intense physical tension in healthy individuals (marching proteinuria);
- in fever, especially in children and the elderly;
- with excessive protein food;
- after stress.
Much more dangerous development proteinuria associated with an increase in the filtration capacity of the renal glomeruli. This occurs with glomerulonephritis, with diabetic sclerosis of the kidneys, with arterial hypertension, thrombosis of the vessels of the kidneys, with other diseases.
What are the reasons if it occurs in the urine elevated protein, and with it - erythrocytes?
In the event that cylindruria is added to proteinuria and hematuria, then this pathology is called urinary syndrome. Cylinders are called tiny casts of the renal tubules, which are clogged with hyaline and other substances.
The most common causes of urinary syndrome, or a simultaneous increase in protein and red blood cells, will again be acute and chronic glomerulonephritis, pyelonephritis, different kinds nephropathy, cardiovascular and chronic heart failure, as well as congestive kidney.




