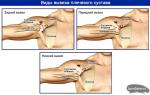
Increasing creatine. Creatinine level in renal failure
At the heart of a biochemical blood test is one of the important components - creatinine. Its content in the body has an important function for the diagnosis of kidney diseases and is used to examine such pathologies. It is imperative to determine why creatinine in the blood is elevated and what are the reasons for exceeding the indicator in order to stop its further rise and reduce the concentration.
The formation of creatinine occurs due to the breakdown of protein molecules and is a continuous process. is one of the toxic waste products that are regularly excreted from the body. The organs and tissues that are responsible for its metabolism are the kidneys, liver and muscles. In the absence of violations of the work of these organs, the substance is excreted from the body with urine. When creatinine in the blood is elevated, toxins will accumulate in the body, poisoning it.
In a healthy person, the amount of creatinine is kept at a constant level, the process of its production and excretion occurs continuously. However, with some violations, the concentration increases, which can lead to intoxication of the body.
There is no specific norm for the content of creatinine in the blood; it cannot be the same for everyone. The size of the norm is individual - the norm is affected by gender and age, the patient's physique, his food preferences. Accordingly, the results of the analyzes take into account all of these factors.

Thus, in order to determine in which direction the deviation is observed, it is necessary to take into account the individual established limits of the norm, namely the age, sex and complexion of the patient. There are generally accepted norms - average indicators, from which it is necessary to build on when evaluating this component in a biochemical analysis:
- Infants - 46-106 mmol / l;
- Schoolchildren - 28-63 mmol / l;
- Women - 45-80 mmol / l;
- Men - 74-110 mmol / l.
For example, the level of creatinine in women will be lower than in the blood of men. This is due to physiological characteristics. If we consider childhood, then as the child grows up, an increase in the concentration of such a substance in the blood will be observed, since muscle mass will increase.
It should be borne in mind that the creatinine level alone is not the complete necessary information for diagnosing kidney disease. It is worth considering other indicators, namely.

To avoid errors in the result and evaluation of a blood test by creatinine concentration, the general rules for preparing an analysis should be followed. Blood is given in the morning on an empty stomach. It is necessary to exclude the day before the test, sports training and physical activities, to prevent overheating and hypothermia of the body, taking alcohol-containing drinks.
In case of non-compliance with the rules for passing the analysis, an incorrect false result can be obtained and, accordingly, the wrong treatment is prescribed.
Symptoms when creatinine in the blood is elevated
high creatinine and significant deviations of the content of this substance in the blood from the norm are the result of the development of various disease states and pathologies. Serious ailments and pathologies are manifested in conjunction with other symptoms. Accordingly, a thorough examination is required to capture the manifestation of all symptoms and correctly establish the cause of the increase in this substance.
Clinical signs when the concentration increases are the following:
- Pain in the lumbar region and muscles;
- Chronic fatigue, apathy;
- Change in the amount of urine output - decrease / increase, complete cessation of urination.
- Increased .
- The appearance of swelling of the lower extremities.

Why is high creatinine dangerous?
An increased level of creatinine in the blood does not always mean the development of pathology, but can be expressed for subjective reasons (strong abruptly started physical activity, unbalanced nutrition, and other reasons). But if the increase in creatine is critical, it is observed two or more times, while other indicators according to laboratory analysis do not correspond to the norm - they indicate the development of a pathological process.
A high concentration is dangerous for the development of various pathologies, namely the following:
- Renal failure. When kidney disease occurs, the body does not completely get rid of creatinine, as a result of which the substance accumulates in the plasma. Thus, the kidneys, as an independent organ, cannot cope with their functions - remove harmful substances.
- Violation of cardiac activity. With an increase in creatinine levels, blood circulation is disturbed, heart muscle cells are destroyed, which affects the development of heart failure.
- Endocrine disorders.
- Oncology. In the presence of malignant tumors and metastasis, muscle tissue is destroyed, which negatively affects organs such as the kidneys and liver, and an increase in creatinine in the blood.
- A large injury to muscle tissue, which can provoke the removal of a substance from damaged cells. After healing of such injuries, the level, as a rule, returns to normal.
- Removal of one of the kidneys.

Since the kidneys play the main role in the process of removing creatinine from the body, the level of this substance in the blood indicates the functioning of the renal and urinary systems.
Clearance, what is it?
What to do to determine how much creatinine is in the blood? For these purposes, a special test is carried out - clearance.
A significant excess of the concentration of the substance occurs with the loss of about half of the renal function. Clearance is indicated for all hospitalized patients, as well as women during pregnancy and people with suspected renal failure.
Clearance is the volume of blood plasma that is cleared by the kidneys from creatine in 1 minute.

Possible causes when creatinine in the blood is elevated
Why can there be increased creatine, because its level does not increase in the body on its own. The reasons for the increase in creatinine in the blood may be its enhanced process of formation or a decrease in its excretion from the body.
Also, the level when creatinine in the blood is elevated can be affected by “extrarenal” factors, physiological causes:
- gender of the patient;
- Age category;
- Hormonal imbalance;
- Dehydration of the body;
- Muscle mass;
- The nature of nutrition, namely the consumption of large amounts of meat and protein;
- The use of certain dietary supplements and medications.
Thus, the increase in the level of this substance may be temporary. Such factors and lifestyle considerations should be taken into account by the physician when reviewing test results.

When creatinine in the blood is elevated, the following factors can also affect:
- Pronounced changes in the functioning of the liver (acute and chronic liver diseases);
- Heart diseases;
- Pneumonia;
- kidney failure;
- Intestinal obstruction;
- Dehydration of the body;
- The presence of stones in the urinary tract;
- Diabetes;
- Long term diet
- Increased physical activity, provoking the destruction of muscle tissue;
- Pregnancy period;
- Exposure to certain types of drugs.
Of course, the results of the analyzes should take into account how much the indicator is increased. Small deviations from the established norms are not an indicator for diagnosing kidney pathology. However, in most cases, especially with an increase of more than twice the indicator, it indicates the development of a violation in the functioning of the kidneys, which do not cope well with the excretion of this substance.

How to lower blood creatinine levels
It should be borne in mind that it is absolutely impossible to select any drugs on your own, as well as a technique for lowering the level of creatinine in the blood. A preliminary consultation with a doctor and a complete diagnostic examination are required. Any treatment will be effective when the cause is correctly established, which led to an increase in the concentration of the substance.
Possible treatments:
- The attending physician may recommend a hospital or hospitalization in a medical institution of the appropriate profile. In this case, the patient is treated with the help of intravenous administration through droppers of special medicinal solutions.
- Taking medications designed to normalize protein metabolism and get rid of toxic products.
- Normalize water metabolism by drinking enough fluids.
- Normalize your diet.
- Make lifestyle adjustments and reduce physical activity.
- Use the means of traditional medicine (in the absence of contraindications).

To treat this pathology, it is necessary to eliminate the cause that influenced increased creatinine. Follow all doctor's recommendations. After the course of treatment, it is necessary to retake a laboratory analysis.
Diet food
Diet modification is a must. You should first consult with a nutritionist about proper nutrition.
If creatinine in the blood is elevated, the following recommendations should be followed:
- Reduce meat consumption by eating no more than 3 times a week. Preference should be given to rabbit, veal, turkey.
- Increase the intake of dairy products, eggs, fish, nuts to get the required dose of protein.
- Salt intake should be completely eliminated or reduced.
- Be sure to include fruits and vegetables rich in fiber in your diet.
- Alcoholic drinks, spicy foods, strong tea and coffee should be excluded from the diet.
- It is useful to use cereals cooked in water.
- Control the required daily water intake - at least 1 liter. Drinking water should be carried out on an empty stomach or in between doses, it is not recommended to drink water during meals.

In addition, you need to know the use of which foods can increase the content of creatinine in the blood in order to try to remove them from your diet:
- High-protein foods, because protein increases the workload on the kidneys and, consequently, the level of creatinine. Therefore, legumes, fish, dairy products in use must be limited.
- Foods with a high content of phosphorus and potassium: pumpkin and sunflower seeds, various types of nuts, sesame seeds, dried apricots, chocolate products and other foods should be limited in use.
Compliance with proper nutrition with an overestimated indicator acts as a kind of protection for the residual functioning of the kidneys, which has a beneficial effect on reducing the load on the organs and normalizing the level of creatinine in the blood.
Folk methods
It is possible to reduce or normalize the level of creatinine in the blood by using traditional medicine. The most common natural remedies for raising blood creatinine are:
- Decoctions and teas with the addition of various herbs that have a diuretic effect.
- Eating boiled rice for breakfast. In advance, rice groats must be left overnight soaked in water.
- Green tea also helps to reduce blood creatinine. Such a drink helps to stimulate the kidneys and increase urination.
- Cinnamon in the form of seasoning or added to tea helps to reduce creatinine.

Before using any type of herb, you should consult your doctor, as many herbal remedies have contraindications.
Preventive measures
To prevent when creatine is elevated in the blood, and also, if necessary, to help reduce it, simple preventive measures should be followed:
- Moderate physical activity and sports training;
- Full and regular rest;
- Maintaining a proper balanced diet and controlling water intake throughout the day;
- Prevent the development of chronic diseases, regularly undergo medical examinations;
- Try to avoid stressful situations whenever possible.

In custody
Accurate determination of the concentration of creatinine is one of the main aspects of the diagnostic examination of the organs of the urinary system, which helps to confirm or refute the preliminary diagnosis.
In such a situation, it is necessary to consult a doctor, diagnose and establish the cause that led to an increase in the concentration of this substance. It is necessary to lower the level, following the recommendations of the doctor and the prescribed course of treatment.
Self-treatment in such a case is not allowed.
Currently, all medicine is becoming standardized. This indicator is of paramount importance for assessing the functioning of the renal filter, diagnosing chronic diseases of this organ, and choosing a method of therapy.
Even 20 years ago, in order to check the functioning of the kidneys, doctors had to conduct complex tests and take a large number of tests: urea, creatine, uric acid, etc. However, with the development of methods for determining the level of creatinine, these problems have become a thing of the past. For a modern person, this indicator is enough to draw a conclusion about the state of kidney function.
What is creatinine
In the body, a huge number of chemical processes proceed non-stop. Their result is the production of not only useful substances for humans, but also various by-products. Creatinine is one of these “natural waste products”. It is obtained from creatine (more specifically, creatine phosphate), after it has been used to fuel the muscles with energy. When creatine phosphate realizes its beneficial effect, it turns into creatinine, which is easily removed from the body.
Almost 100% of this substance is excreted through the kidneys along with urine. If it accumulates in excess, human tissues begin to suffer from this toxin. In addition to the fact that this compound directly poisons cells, increased creatinine in the blood changes its normal acid-base balance. Acidifying biological fluids, it disrupts the normal metabolism in every organ, which can lead to a serious condition of the patient and even death. The greatest danger lies in the damage to the brain, respiratory and circulatory systems.
With a significant excess of normal values, it is necessary to reduce the concentration of elevated creatinine in a timely manner.
Norm
Despite the fact that creatinine is an end product and is not used in chemical reactions, normally its amount in the blood is not zero. The body constantly maintains a certain concentration of this compound, not allowing it to be excreted without a trace. For what? This allows you to maintain the necessary acid-base balance and adequate metabolism in tissues.
In different laboratories, creatinine norms may differ, which is associated with the peculiarities of the operation of the equipment, its calibration and the opinion of specialists. As a rule, reference (normal) values are additionally printed on the sheet with the result of the analysis.
Any deviation from normal indicators is a reason to repeat the analysis and find out the cause of this condition. It is very important to do this as early as possible so that if a pathology is detected, therapy can be started in a timely manner and such deadly complications as chronic / acute renal failure can be prevented.
Reasons for the increase
In any population, there are two main causes of increased creatinine - excessive intake of precursor substances and impaired removal of toxins from the body. In the first case, the change in indicators is temporary and, as a rule, is not associated with the presence of kidney disease. Insufficient excretion of creatinine is always a companion of any renal pathology.
Excessive intake of creatinine
Before looking for a disease in a person, it is necessary to exclude this particular group of causes. Where can the precursors of this substance get into the blood?
| Source | Creatinine precursors |
Foods high in protein:
|
Amino acids - any proteins and complex compounds with proteins (glycoproteins, proteids, nucleoproteins, etc.) in the digestive system break down into amino acids. Being absorbed, they first turn into creatine in the liver, then in the muscles into creatine phosphate and decompose to creatinine. |
| Injured muscles. | Creatine and creatine phosphate - a large amount of these substances are found in muscle tissue. When it is damaged, they enter the bloodstream and break down to creatinine. |
| Muscle or connective tissue in severe hyperthyroidism. |
The presence of one of these factors can cause high creatinine. In this case, the indicator does not reflect the work of the kidneys and, as a rule, quickly returns to normal - within a few days. To confirm the absence of pathology, it is enough to pass a second analysis after 7-10 days.
Causes of impaired excretion
Damage to the renal filter and insufficient excretion of toxic substances is the main cause of the increase in creatinine. If the patient has properly prepared and passed the analysis, or he has repeatedly found an excess of the norm for this indicator, the probability of damage to the organ is extremely high.
There are a large number of diseases that can lead to creatinine retention. It can be quite difficult to detect them, since pathologies often proceed hidden and the first signs are found only in the analysis of urine. The most common of these diseases and their characteristic symptoms are:
| Disease affecting the kidneys | Brief description of the disease | Characteristic features |
| Glomerulonephritis |
A chronic disease that develops due to a constant inflammatory process in the kidneys. The exact cause of its occurrence is not known to date. Unfortunately, this pathology is incurable. The main thing the patient must do is to slow it down with medication and lifestyle changes. |
In some forms, symptoms may be completely absent - changes are determined only in the urine (the appearance of protein, blood cells and other pathological elements). However, the following signs of damage to the renal tissue are often observed:
|
| Damage to the kidney tissue in hypertension |
All human organs suffer from high blood pressure, but first of all, the heart and kidneys. Due to constant hypertension, the kidney tissue begins to wrinkle, be replaced by connective fibers and lose its function. |
|
| diabetic nephropathy |
Elevated blood sugar is dangerous because it begins to be deposited in small vessels that feed human tissues. With their significant defeat, irreversible changes begin to occur, and the organs lose their ability to perform their function. |
The presence of diabetes of any type, before the onset of signs of chronic kidney disease. In the absence of a diagnosis of diabetes, you should pay attention to the symptoms characteristic of elevated glucose levels:
|
Renal amyloidosis, including:
|
Amyloidosis is a chronic disease with an unknown cause. It is reliably known that it is a frequent companion of any long-term inflammation. With this pathology, a person has the formation and accumulation in the organs of an atypical (wrong) protein - amyloid. It is he who damages the kidney filter and is the cause of an increase in the level of creatinine in the blood. |
The risk group for the presence of amyloidosis includes all people with chronic, poorly controlled inflammatory diseases. Unfortunately, there are no characteristic signs of this disease. With it, the same symptoms are observed as with glomerulonephritis or diabetic nephropathy. The final diagnosis can only be made after performing a biopsy - examining part of the organ under a microscope with special staining. |
| Ischemic disease (with narrowing / damage to the renal arteries) | The kidneys produce a biologically active substance that can significantly increase blood pressure. Its amount increases with their "oxygen starvation", which occurs against the background of blockage of the arteries. | Ischemic kidney disease is characterized by a combination of the following symptoms:
|
| Poisoning by nephrotoxic substances | There is a whole group of compounds that can damage the kidney cells and cause acute renal failure with a significant increase in creatinine. | This condition can be suspected only with the use of nephrotoxic substances. These include:
|
Infections that occur with kidney damage:
|
Contrary to popular belief, these diseases exist in Russia and are constantly circulating among rodents (mainly in rats and mice). Often the disease begins like a normal ARVI. And only after some time a person develops characteristic signs of pathology. |
|
Increased creatinine in children
The presence of this change in the analysis of the child requires a thorough diagnosis. First of all, in order to exclude a false result, it is recommended to once again explain to the parents the preparation algorithm before blood sampling and re-conduct the study. If the laboratory once again detects an excess of the norm, this means that there are clear signs of a pathological process.
Creatinine in children rarely increases due to acquired chronic diseases such as glomerulonephritis, diabetic or hypertensive nephropathy, amyloidosis, etc. In most cases, the following conditions are the cause of its delay:
- hyperthyroidism. This disease is not uncommon among young patients. An excess amount of thyroid hormone leads to the breakdown of proteins throughout the body, which leads to an increase in the activity of the creatine kinase enzyme. As a result, there is an increase in the concentration of metabolic products;
- Alport syndrome(synonymous with "hereditary nephritis"). This is a congenital disease in which there is a primary lesion of two organs: the kidneys and the hearing aid. In this case, the child develops glomerulonephritis and hearing loss;
- Congenital anomalies of the kidneys. These include such pathologies as insufficient development / absence of an organ (respectively, hypoplasia or aplasia), polycystosis, the presence of a solitary cyst, and others. In most cases, an ultrasound scan is sufficient to make a diagnosis.
Reasons for the decline
Reduced creatinine does not harm the human body, however, such data make it possible to suspect the presence of a pathological condition or an unhealthy lifestyle. The presence of such a connection is explained quite simply:
- In organs and tissues, a certain balance is constantly maintained between chemical processes, various substances and energy exchange;
- To maintain it, a certain amount of various substances is required: amino acids, glucose, fatty acids, trace elements and vitamins. Their number can be judged by the well-being of a person and the "by-products" of metabolism;
- Creatinine is a product of amino acid metabolism. A decrease in its concentration, in most cases, indicates an insufficient amount of protein (amino acids) or a lack of muscle mass.
There are not many conditions in which a person has low creatinine. These include starvation, a strict vegetarian diet, or myodystrophy (a pathological condition of the muscles in the body). Also, lower values in the analysis can be determined with heavy drinking or intravenous infusions of solutions, due to the "dilution" of the blood. Other causes are extremely rare.
Preparation for analysis
To obtain an adequate result, a person needs to try to exclude all factors that affect this indicator. Standard preparation for analysis includes:
- Exclusion of eating. It is recommended to take blood for research not earlier than 4 hours from the last meal. A prerequisite is a small intake of protein in the body. This means that a person should not consume a large amount of meat, fish or dairy products before the examination (no more than 100-200 g);
- Limitation of physical activity. Any strength exercise with sufficient load leads to muscle microtrauma. This may affect the results of the study, slightly increasing the rate;
- Restriction of the drinking regime. Before the diagnostic procedure, it is not recommended to drink a large amount of liquid (more than 1.5-2 liters for several hours). This can lead to false results in the form of low blood creatinine.
What is creatinine used for?
The glomerular filtration rate (GFR for short) is the most important indicator of kidney function. It demonstrates how well toxins are removed from the body and quite accurately reflects the state of this organ. Only by GFR it is possible not only to determine the presence / absence of chronic kidney disease, but also to determine its degree.
To calculate this indicator, it is enough to know your creatinine level and a few elementary data, such as age, gender and race. Glomerular filtration is calculated using complex formulas that are available in almost any online service or program dedicated to the functioning of the urinary system. There are several calculation options, but at the moment, the most relevant are the MDRD and CKD-EPI formulas.
To interpret the results, just use the table below. The presence of chronic kidney disease (or CKD) is a reason to contact your doctor in order to conduct additional diagnostics and determine further tactics.
| CKD stage | GFR level, ml/min | Additional risk of heart and vascular disease |
| Absence of pathology | More than 90 in the absence of signs of kidney damage, such as:
|
Virtually absent |
| CKD I | More than 90 in the presence of adverse prognostic factors and markers of kidney damage. | There is little risk |
| CKD II | 60-89 | Above average risk |
| CKD IIIa | 45-59 | High |
| CKD IIIb | 30-44 | Extremely high probability of occurrence of a disease or complications from the cardiovascular system. |
| CKD IV | 15-29 | |
| CKD V | Less than 14 |
Methods for lowering creatinine levels
When pathological changes are detected in the tests, people ask themselves the question “How to lower blood creatinine?”. However, the excess of the norm of this substance is not the main problem for a person - this is only the "tip of the iceberg". An increase in its concentration indicates, as a rule, a serious renal pathology, which for a long time remained without proper treatment. Therefore, the main thing is not to get rid of high creatinine, but to slow down / stop the course of the underlying disease.
How to do it? Only the attending physician can answer this question. Tactics will be determined by the type of disease from which the patient suffers. However, we can name the general approaches to therapy used for these pathologies:
- Lifestyle change. The main thing at this point is quitting smoking and alcohol, limiting the intake of NSAIDs (Paracetamol, Ketorol, Citramon, Coldrex, Antigrippin and others), gradual weight loss. These activities help to slow damage to the kidney cells and are of fundamental importance in the treatment;
- Water regime correction. This nuance is determined individually for each patient. In the first stages of diseases and in the absence of significant fluid retention, a standard scheme is proposed - “volume of fluid consumed = the amount of fluid excreted in the urine over the past day + 500 ml”;
- Diet with restriction of salt (usually up to 5 g / day) and protein (up to 300-400 g / day);
- Drug therapy. The medications that the patient should take are determined individually. However, the treatment regimen, in the absence of contraindications, should include “protective drugs” that slow down the progression of CKD. These include two main groups: ACE inhibitors and Sartans (synonymous with angiotensin receptor inhibitors).
The need for surgery and dialysis is determined depending on the type of pathology and the condition of the person. In the presence of a significant narrowing of the renal arteries, surgical intervention is recommended, which will expand their lumen and restore the nutrition of the organ. With low GFR, in some cases, hemodialysis remains the only option. Therefore, the question "how to reduce creatinine?" the best answer would be to adequately treat your underlying disease.
FAQ
Question:
What to do if an increased level of creatinine is found in the blood, but doctors did not find pathological changes in the urine and on ultrasound?
Question:
How often should this indicator be checked for a healthy person?
It is included in the screening standards for all patients over 39 years of age. In the absence of pathologies, diagnostics is carried out once every 6 years.
Question:
Do I need to contact a nephrologist if creatinine concentration increases?
To begin with, with this problem, you should contact the local therapist, who will conduct the necessary diagnostics. If necessary, he will refer the patient to a nephrologist or other subspecialists.
Question:
Can the menstrual cycle affect a woman's creatinine levels?
At the moment, there are no studies that would prove the connection between these two conditions.
Examinations, in particular analyzes, are necessary for the timely detection of deviations and proper treatment of a person. When creatinine in the blood is elevated, the reasons may be different. Depending on the values, we can talk about both a physiological (natural) increase and a pathological one, which is a sign of a disease.
Creatinine in the blood: what is it
Before talking about the level of creatinine, you need to understand what kind of substance it is. This chemical compound is formed from creatine, its function is to deliver the proteins needed for nutrition to the muscles. After the protein is broken down, muscle and other tissues receive the necessary energy, the creatinine resulting from this reaction is excreted from the body.
Since it is produced during metabolism, it is also defined as a metabolite. Concentration is measured in µmol/l. Since the production of creatinine and its excretion are a continuous biochemical process, the content of this substance in the blood is constant.
Important! The physical activity of a person and the use of meat food affect the concentration of creatinine, this may affect the results of the tests.
The level of creatinine in the blood depends on:
- age;
- muscle mass;
- the amount of protein consumed.
Since women have less muscle mass than men, their norm is lower. In people with one kidney, the creatinine level should not exceed 190 µmol/L.
The reasons for the increase in creatinine can be physiological (transient) and pathological. The first ones include:
- physical exercise;
- dense protein foods (meat and fish);
- the use of substances to build muscle mass (for example, creatine, a drug taken by bodybuilders);
- drug treatment - antibiotics (cephalosporins, tetracyclines) and NSAIDs (Ibuprofen, Diclofenac);
- surgery with extensive damage to muscle tissue.

Increased creatinine during pregnancy with toxicosis and in lactating women, in senile people and in children during the period of active growth. A very high concentration (at the level of adults) in a child at birth is due to the fact that during childbirth he experiences a strong physical load. For newborns, this figure can be up to 48.0.
In different groups, creatinine in the blood is as follows:
The level fluctuates depending on the complexion and age values within the same group, it can increase with exercise (for example, up to 120–122 in men). The level of this substance differs in a big way in those who do not receive a complete protein diet or are on a strict diet. This is explained by the fact that the body, not receiving protein from the outside, begins to produce it, splitting its own muscle tissue. If the diet or vegetarianism is continued, the amount of the metabolite will gradually decrease.
Important! Restriction in nutrition, in particular, refusal or a sharp decrease in protein foods with various diets lead to a change in the level of creatinine, people after such diets need to be restored or even treated.
Pathological increase in the concentration of this metabolite occurs primarily in diseases of the urinary system. Creatinine is excreted from the body only with urine, through the kidneys. An increase in concentration means that it is not filtered. This is also indicated by an increase in the level of urea in the blood. In acute renal failure, creatinine increases and can reach values of 800–1000 µmol/l and higher. Such patients need to undergo hemodialysis. An indicator of more than 1000 µmol / l is an indication for an urgent dialysis procedure for health reasons, such a high level of creatinine threatens coma.
Clearance is very important for the accuracy of diagnosis - a value that shows the effectiveness of the purification of blood by the kidneys from protein breakdown products. The average creatinine clearance is 125 ml / min. The upper limit in young men is 140 ml / min, in women - 105 ml / min. A clearance rate of 40 ml / min in adults indicates serious kidney problems.
However, an increase in creatinine concentration is observed only if the functionality of the kidneys decreases by almost half (40-60%). Therefore, for the early diagnosis of renal failure, the level of a substance in the blood (serum) is an insufficient diagnostic method.
High creatinine is also observed:
- with oncological diseases;
- with pathologies of the endocrine system (acromegaly, gigantism, hyperthyroidism and Basedow's disease);
- with extensive radiation damage.
Creatinine also increases with muscle inflammation (myositis), myasthenia gravis, poliomyelitis, and severe burns. Increased rates are possible with cholelithiasis, cystitis, prostatitis in men, congestion in the bladder.
Important! In order for the blood test to give an accurate picture, you need to take it in the morning on an empty stomach, you can drink weak tea without sugar. A light dinner is allowed 8 hours before pickup. Do not drink alcohol, meat and fatty foods. If these conditions are violated, an increase in creatinine is possible in the analyzes.
Symptoms and treatment
Concomitant symptoms with elevated creatinine:
- myalgia (lower limbs and back in the kidney area);
- increased blood pressure;
- swelling (face, legs);
- decreased work capacity, rapid fatigue;
- pallor of the skin.

Often, an increase in creatinine is accompanied by dysuria, manifested both in rare urination (up to anuria), and in polyuria over 2 liters of daily urine. It may be cloudy due to protein impurities, and also contain blood (hematuria). All clinical manifestations are not associated with a change in the content of the metabolite, but with the underlying disease that caused its fluctuations. Tests can help you understand the symptoms. The decoding of the analysis should be done only by the attending physician, who fully knows the medical history.
Important! The results of creatinine tests taken a day apart can vary by up to 15%.
Treatment with folk remedies
To reduce creatinine and improve kidney function, infusions, decoctions and other herbal remedies from medicinal plants are used.
Mint infusion
An infusion is made from dried peppermint (2 tablespoons) and 500 ml of boiled water: the leaves are poured into a thermos, the container is closed for 2 hours. Strained infusion to drink in small portions during the day.
Infusion of stinging nettle leaves
In a glass of boiling water, take 2 tbsp. l. dry nettle and leave for an hour, wrapped. Strained nettle infusion is taken after and before going to bed for half a glass.
lingonberry leaves
1 st. l. dried lingonberry leaves pour a glass of boiling water and cook for half an hour in a water bath. Strained broth drink three times a day for a third of a glass.
Collection based on sage
Sage (4 tablespoons) is mixed with dandelion leaves, birch bark and burdock root (3 tablespoons each). Mixture pour 1 liter of boiling water and keep in a thermos for 3 hours. Strained infusion take at night for 3 tbsp. l. Not recommended for pregnant women.
Decoction of dandelion roots
For 1 st. l. root 2 cups of water, simmer until boiling, after 5 minutes remove from heat and cool. Drink 2 tbsp. l. half an hour before meals 3-4 times a day.
Diet
Nutrition with increased creatinine should be reviewed in the direction of reducing the amount of animal proteins in the diet. At the same time, you need to eat a lot of vegetables and fruits. Meat products are consumed in the amount necessary for the protein norm (it may differ depending on the type of activity, age, physiological state).
What to Avoid:
- meat in large quantities;
- fatty, fried foods;
- strong rich broths;
- spicy food;
- smoked meats, pickles, marinades;
- baking, white fresh bread;
- oily fish;
- strong tea, black coffee;
- fat milk, cream.
The basis of the diet should be cereals, vegetable products, butter and vegetable oil, lean meat (600 g per week), dairy products, cottage cheese, eggs (1 piece every two days), bran bread (no more than 100 g per day). Very well helps to reduce creatinine rice water, mucous soups.
An increased concentration of creatinine in the blood may indicate a malfunction of the kidneys and excretory system, therefore, when the first symptoms appear, you should consult a doctor in order to establish a diagnosis in time and begin treatment.
Creatinine is a metabolic product that is in the blood of every person. Normally, the kidneys filter and excrete creatinine in the urine, but some diseases can disrupt this process and lead to the accumulation of creatinine in the body in dangerous amounts. There are several ways to lower creatinine levels, including dietary and lifestyle changes, medications, and certain medical procedures.
Steps
About Creatinine
- The kidneys normally filter creatinine from the blood and pass it into the urine.
- High creatinine levels often indicate kidney disease.
- Creatinine levels can rise as a result of strenuous exercise or regular high protein intake.
- Taking creatine supplements can also lead to increased levels of creatinine in the blood and urine.
-
Understand how a creatinine test is done. The test measures the amount of creatinine in the blood.
- Your doctor may also order a urine test to check your creatinine level. The amount of creatinine in the urine should be high, and in the blood - low.
- These tests allow you to quickly assess the condition of the kidneys. Urine or blood creatinine levels are usually analyzed by the laboratory within 24 hours.
-
Interpret the results. Creatinine levels vary by age and gender. In addition, the level of creatinine is affected by a person's weight. Below we give the standard values.
Find out what causes creatinine levels to rise. There are several reasons. Some of them are more dangerous than others, however, you should deal with this problem, regardless of the reason.
- Deterioration of kidney function or kidney failure. If the kidneys are not working at full capacity, they cannot remove creatinine through the glomerular filtration process as they should. Glomerular filtration is the outflow of fluid that has been filtered in the kidneys.
- Destruction of muscle tissue. If you have a disease that causes muscle breakdown, pieces of muscle tissue can get into your bloodstream and impair kidney function.
- Eating a lot of meat. If you regularly eat cooked meat in large quantities, the level of creatinine in the blood will increase.
- Hypothyroidism. Thyroid disorders can affect the functioning of the kidneys. Hypothyroidism impairs the filtering ability of the kidneys.
Folk remedies
-
Drink herbal teas. Some herbal teas are believed to lower blood creatinine levels. Studies have not confirmed a clear link, but they have not refuted this theory either.
- Drink two large cups (250 milliliters) of herbal tea daily.
- Try nettle leaf and dandelion root tea.
- These teas stimulate the kidneys and cause increased urine output. As a result, creatinine excretion increases.
-
Try nettle supplements. Nettle can increase the amount of urine, due to which the concentration of creatinine will decrease. Nettle contains histamines and flavonoids, which increase blood flow to the kidneys, improving urine filtration.
- Nettle leaves can be taken as a tablet or brewed as a tea.
-
Discuss with your doctor if you should take sage. Sage is a plant that can increase the glomerular filtration rate of the kidneys, speeding up the removal of creatinine from the body. Sage contains lithospermate B, which improves kidney function.
- Be sure to consult your doctor. Do not take sage without his consent.
Lifestyle changes
-
Watch how much water you drink. As a general rule, you should drink 6 to 8 glasses of water every day. Dehydration causes an increase in creatinine levels, so it is important to maintain adequate water levels in the body.
- With insufficient water intake, the amount of urine decreases. Creatinine is excreted in the urine, so when the volume of urine decreases, this process becomes more difficult, and the level of creatinine rises.
- At the same time, excess water negatively affects kidney function. Excessive water intake leads to an increase in blood pressure, and increased pressure increases the load on the kidneys.
- It is best to drink water in moderation unless your doctor tells you otherwise.
-
Limit physical activity. When you exercise, your body converts food into energy faster. As a result, more creatinine is formed, and its level in the blood rises.
- Physical exercise is important for health, so you should not completely exclude physical activity. You should play sports, but at the same time choose types of load with low intensity. Instead of running and basketball, take up walking or yoga.
-
Get enough sleep. During sleep, most processes in the body slow down. As a result, the process of converting creatine to creatinine is slower, which contributes to more efficient filtration of creatinine in the kidneys.
- Try to sleep 6-9 hours at night. 7-8 hours is usually enough for most people.
- In addition, lack of sleep is a physical stress, and this contributes to more active muscle work during normal exercise. This can put the kidneys under stress, impairing their ability to filter out creatinine.
Medical treatment
-
Talk to your doctor about stopping any medications you are taking. Some medicines increase creatinine levels. Not only drugs that can harm the kidneys are dangerous, but also some drugs that are prescribed for kidney diseases.
Explore medications and supplements that can help. Depending on the underlying cause of your high creatinine levels, your doctor will prescribe certain medications or supplements to lower your blood creatinine levels.
- Before prescribing a drug that is right for you, your doctor will need to determine what disease is causing the increase in creatinine, since many drugs affect both the underlying disease and creatinine levels.
-
Take hypoglycemic medications. One of the causes of kidney disease and, as a result, elevated creatinine levels is diabetes. If you have diabetes, it's important to keep your insulin levels up to prevent further damage to your kidneys. There are drugs that will help you with this.
- In such cases, repaglinide is often prescribed. The initial dose is 0.5 milligrams, and the medicine should be taken before meals. The maximum daily dose is 4 milligrams (before meals). Even if you skip a meal, you need to take a pill.
-
Lower your blood pressure with medication. High blood pressure is another factor that causes kidney problems. Blood pressure control will help prevent the disease from progressing, so that the level of creatinine will decrease.
Some antibiotics can be dangerous if taken incorrectly. People with kidney disease should take lower doses of antibiotics than those with healthy kidneys.
Take medications that lower your creatinine levels. Often in such cases, ketosteril is prescribed. Talk to your doctor about this drug - it may be right for you. It is usually prescribed at a dosage of 4-8 tablets three times a day with meals. You may also be prescribed nutritional supplements:
Medical procedures
- The most common cause of high creatinine is a malfunction or chronic kidney disease. Damage can be caused by disease, a potentially fatal infection, shock, cancer, or reduced blood flow to the kidneys.
- Type 2 diabetes also contributes to increased creatinine levels.
- Other possible causes: heart failure, dehydration, blood loss and, as a result, shock, as well as gout, exhausting physical exertion, muscle injuries, muscle pathology, burns.
Treat the disease that caused the increase in creatinine levels. Creatinine rarely rises on its own. Most often, its increase is a symptom of a more serious disease. Get tested to find the cause of the increase in creatinine and begin treatment.
-
Try laser physiotherapy. Studies have shown that the use of a cold or low-wavelength laser improves kidney function. As a result, the kidneys filter and excrete creatinine better.
- The application of a cold laser to the adrenal region relieves stress and improves sleep.
- The use of a cold laser on the vagus nerve improves blood flow in all organs, including the kidneys.
-
Try a massage. Massage also helps blood circulation, reduces stress, which promotes sleep and relaxation.
Learn blood purification methods. Hemodialysis, or dialysis, may be indicated for people with severe kidney disease with persistently elevated creatinine levels. This method is quite extreme, but extremely effective.
Consider alternative treatments. In particular, consider using micro-Chinese medicine - osmotherapy. This method is based on traditional Chinese medicine and can help heal minor kidney damage. This method makes extensive use of medicinal baths, which are part of traditional Chinese medicine.
Find out what creatinine is. Creatinine is a breakdown product of creatine, a substance that allows food to be converted into energy through metabolism.
The list of standard biochemical tests includes a blood test for creatinine. This substance is a product formed after muscle contraction during the breakdown of creatine phosphate. In this case, there is a rapid receipt of energy for the movement. Therefore, the concentration of this substance indicates whether the functional activity of the organism is preserved or impaired.
What does elevated blood creatinine mean in men, what are the symptoms and treatment? Understanding!
Characterization of creatinine
The human body constantly produces creatinine in a certain amount, because its content in the blood serum is almost constant. This value depends on the amount of human muscle mass. Therefore, in men, the creatinine content is usually significantly higher than in women. This is explained by the fact that the indicator expressing the ratio of muscle mass to total body mass is higher for them.
In general, the substance under study belongs to the group of slags - substances formed as a result of the breakdown of molecules in the body and excreted unchanged. In particular, creatinine is synthesized during the breakdown of proteins. It is formed in muscle tissue, after which it enters the bloodstream. This substance must be removed from the body, as it adversely affects the tissues.
Creatinine is excreted by the kidneys, it completely passes from the blood capillaries to the renal tubules. Thus, if the content of this substance in the blood increases, then a violation of glomerular filtration will be the likely cause of this. Blood creatinine is an important diagnostic indicator that determines the exact diagnosis in the presence of renal pathologies.
Normal creatinine content
Due to the fact that the level of creatinine in the blood is determined by the volume of muscle mass, this indicator differs both by sex and by age. For women, the normal value is:
- At the age of 60-65 years - 53-100 mmol per liter;
- After 65 years - 50-110 mmol per liter.
For men, the physiological content of creatinine is:
- Up to 60-65 years - 80-120 mmol per liter;
- After 65 years - 70-120 mmol per liter.
It can be seen that with age, the content of creatinine decreases slightly. This is because older people develop senile muscle atrophy and use less creatine phosphate.
- Newborns - 30-90 mmol per liter;
- Infants (children under the age of 1 year) - 20-35 mmol per liter;
- From 1 to 10 years - 30-60 mmol per liter.
In adolescents, the creatinine content ranges from 40 to 80 mmol per liter.
Physiological increase in creatinine
In some cases, the analysis for creatinine shows an excess of the normal level, but there is no pathology in the body. Sometimes a high concentration of this substance in the blood can be physiological. So, in children during periods of active growth, the functional activity of the muscles increases significantly, which means that the production of creatinine also increases. Therefore, in their blood it is possible to detect a higher concentration of it than is normal.
A physiological increase in concentration is also observed in old age. It is worth noting that the indicator should not be much more than the norm. A significant increase in the level of a substance in the blood is already considered a sign of pathology.
Creatinine production is increased in people engaged in heavy physical labor. With intensive loads on the muscles, they use more creatinine phosphate, which means that the creatinine content also increases. The work of the kidneys in this case may be normal, however, due to the large amount of the substance in the blood, they do not have time to filter and excrete it. Therefore, elevated creatinine is determined in the analysis.
The hormonal background also has a great influence on the indicator. This factor is especially relevant for women. The level of creatinine in the blood may vary slightly depending on what phase the patient's menstrual cycle is in. A physiological change in the indicator also occurs during pregnancy. In the body of the expectant mother, protein metabolism is more intensive, so the release of creatinine will also be accelerated.
An increased level of the laboratory indicator is also characteristic of people professionally involved in sports. This is due to the fact that their muscles have a lot of physical activity, and with the type of nutrition of athletes. Usually their diet contains a large amount of proteins, which are destroyed in the body with the formation of creatinine. In addition, many biological supplements taken by athletes for accelerated weight gain contain a specific amino acid - creatine, which in its structure is a precursor of endogenous creatinine.
Thus, an increase in the level of creatinine in the patient's blood serum is not always a sign of any pathology. Age and gender characteristics, the level of physical activity, and the nature of nutrition have a great influence on the result of the analysis. All these factors should be taken into account when deciphering the results of the analyzes.
Pathological increase in creatinine
A persistent increase in creatinine levels is a sign that there is some kind of pathological process in the body. This symptom is called hypercreatininemia. Depending on how much the indicator has increased, there are 3 degrees of the state:
- 1 degree - slight hypercreatininemia;
- Grade 2 - moderate hypercreatininemia;
- Grade 3 - severe hypercreatininemia.
1 and 2 degrees can be caused by the following factors:
- Unbalanced nutrition. Increased consumption of proteins, especially of animal origin, leads to an increase in blood creatinine.
- Prolonged fasting. In the absence of energy supply, the body first decomposes sugars and fats. After their reserves in the body run out, proteins begin to break down. This process leads to a change in the laboratory value.
- Bleeding from the digestive system due to ulcers, erosions, tumors. In this case, the blood flowing into the lumen of the gastrointestinal tract enters the process of digestion. It contains a lot of protein, which is decomposed into amino acids and absorbed into the body. The decomposition of these elements leads to an increase in the level of creatinine.
- Severe dehydration. When the blood plasma leaves the vascular bed, the blood becomes more “concentrated”, therefore all biochemical parameters, including the creatinine content, increase significantly.
A mild degree of creatininemia is also associated with a number of diseases:
- Renal insufficiency of a mild form;
- Liver diseases associated with toxic or infectious damage (hepatitis, cirrhosis);
- Gangrene or other massive processes of necrosis of muscle tissue;
- Increased functional activity of the adrenal glands - hypercortisolism syndrome;
- Extensive muscle injury;
- severe burns;
- kidney damage (nephropathy) due to diabetes;
- Increased formation and massive release of thyroid hormones into the blood;
- Myasthenia gravis is a severe hereditary disease that affects muscle tissue;
- Syndrome of intoxication in infections and purulent-septic pathologies;
- Autoimmune diseases (rheumatism and arthritis, vasculitis, lupus);
- Toxicosis in pregnant women.
A significant increase in the level of creatinine is observed with a pronounced form of hypercreatininemia. This condition may be associated with the presence of the following pathologies in the patient:
- Severe kidney damage, accompanied by severe renal failure and a sharp decrease in their functional activity;
- Muscular dystrophies, which are accompanied by active destruction of muscle tissue in the patient's body;
- Condition after prolonged muscle compression (positional compression syndrome);
- Reperfusion syndrome - the appearance of pathological symptoms after the removal of blood clots from the vessels supplying the muscles;
- Severe infectious lesions of the body, including a generalized infection - sepsis.
These conditions require emergency treatment, as they threaten the health and life of the patient.
Treatment of elevated creatinine in men
If an elevated creatinine content is found in the analysis, it is necessary to consult a doctor and undergo a complete examination. Only a specialist is able to establish the origin of this symptom and start treatment on time.
You can remove a small increase in creatinine levels by changing the patient's lifestyle. In this case, doctors recommend:
- Choose the right diet containing the optimal amount of protein substances;
- Limit alcohol intake;
- Limit physical activity;
- Drink enough water.
The same measures will be effective in the prevention of hypercreatininemia.
Thus, creatinine is a breakdown product of protein molecules in the human body. Its level in the blood depends on the coordinated work of several body systems (kidneys, liver, intestines). If the regulation of this indicator is disturbed, hypercreatininemia occurs - an increased content of a substance in the blood serum.
This is an important diagnostic feature that indicates the presence of a severe pathology in the patient's body. Therefore, if a high creatinine is detected in the analysis, it is recommended to consult a specialist and undergo a full examination in order to establish the cause of this symptom.