Insidious disease frontitis. Symptoms of frontitis in adults treatment and diagnosis How frontitis is treated
When the paranasal sinus in the frontal part of the head becomes inflamed, frontal sinusitis (or frontal sinusitis) begins. The sinus cavity is covered with a mucous membrane from the inside, with frontal sinusitis it becomes inflamed, but the causes of its inflammation can affect how severe the disease will be and in what form.
Reason one: infection
It is the entry of microbes from the nasal cavity into the pelvis of the sinuses that most often leads to sinusitis. Moreover, both the frontal and maxillary cavities can become inflamed at the same time. Causative agents of viral frontitis:
- Coronaviruses
- Family Adenoviridae
- Rhinoviruses
- Respiratory Syncital Virus Infectious
Reason two: bacteria
A bacterial infection occurs when it enters the cavity: Streptococcus pneumoniae; Pyogenes; haemophilus influenzae; Staphylococcus aureus. The fungus can also cause acute frontal sinusitis, infection with fungi and microbes can happen through their entry into the bloodstream.
Reason three: allergies
For example, swelling of mucosal tissues can be caused by prolonged, asthma-incessant allergic rhinitis. Puffiness is so strong that it does not allow fluid to exit from the sinus, blocking the desired opening, which this exit provides.
Reason Four: Polyps
Polyps are benign neoplasms, have a rounded shape and result from the degeneration of cells of the mucous membranes. Due to polyps, there is severe swelling and blockage of the outflow in the sinuses.
Reason five: injuries and curvature
In adults, bruises and fractures of the bones of the skull often cause swelling, impaired blood circulation and, as a result, inflammation of the sinuses. A deviated septum can be a congenital anomaly or the result of trauma. In any case, the curvature also does not allow mucus with microbes to freely come out.
Reason six: foreign bodies in the nose
More often, children suffer from pushing small objects into the nose: various beads and parts from toys cause inflammation first in the nasal passages. And then it spreads to the rest of the cavity and into the sinuses.

Frontitis is a rather dangerous and serious disease, it is not easily tolerated in relation to other forms of sinusitis. Acute and protracted forms of frontal sinusitis each have their own characteristics.
Acute frontal sinusitis causes the following complaints in patients:
- the forehead area becomes sharply painful, the sensations intensify if you press or tap on the front wall of the forehead;
- eyes hurt, tears flow non-stop, daylight irritates;
- discomfort in the area of \u200b\u200bthe inner corners of the eyes;
- the classic symptoms of frontal sinusitis are swelling in the nose and the inability to breathe normally;
- nasal discharge at first muco-transparent, and after a while cloudy-purulent;
- the whole face swells;
- the skin over the sinus may be hyperemic;
- the temperature can be either subfebrile or rise to 39.5 C and stay for more than one or two days;
- acute frontitis gives severe weakness.
The peculiarity of pain in acute form is their cyclicity. While the outflow of fluid is disturbed, the pain is unbearable, it can radiate to the temporal part of the head or to the eyes. As soon as the sinus is freed from the accumulated mucus, the pain subsides.
Chronic frontal sinusitis begins about two months after the onset of the acute process. Usually a chronic disease becomes from incorrect treatment, or as a result of frankly ignoring a painful condition.
The symptoms of chronic sinusitis are:
- pain in the forehead is no longer strong, but dull and aching, but with a slight tapping it gets worse;
- if you press on the nose, then the pain radiates to the inner corner of the eye, and quite sharply;
- nasal discharge often foul-smelling, cloudy, purulent. In the morning, the discharge is especially plentiful.
Despite the fact that the symptoms of frontal sinusitis have somewhat weakened, this has nothing to do with improvement. Moreover, it is chronic sinusitis that is dangerous to health, and even life, with complications and consequences.

How to treat sinusitis, what drugs and when it is better to start treatment will tell the attending physician. For example, with a viral or allergic etiology, antibiotics will be powerless, moreover, they can aggravate the course of the disease by causing dysbacteriosis and lowering the immune barrier. Antibiotics for frontitis can only be prescribed by a doctor.
Treatment of frontal sinusitis in adults with antibiotics is advisable in the case of purulent, stagnant processes. Discharge with pus means that their origin is bacterial.
In the clinic, samples of secretions should be taken from the patient to determine the type of bacteria and their sensitivity to antibacterial drugs. It is laboratory studies of discharge from the nose that are the key to successful therapeutic therapy. Chronic frontitis makes this procedure mandatory.
The use of antibacterial agents is justified in case of severe headaches, a very severe general condition, and if sparing methods of treatment have not given positive dynamics.
How to do without AB?

Treatment of frontal sinusitis with sparing methods involves the use of drops in the nose, which have a vasoconstrictive effect. After the vasoconstrictor has been instilled, the next agent is applied (antibacterial or antiseptic aerosols).
Treatment of frontal sinusitis in an acute form is carried out with the use of antihistamines (Erius, Diphenhydramine) to eliminate puffiness, prevent allergic reactions and better remove mucus accumulated in the sinuses.
It will not be possible to cure the disease in two days, especially if the inflammation process has dragged on. But, the sooner you start therapy, the more chances you have to avoid complications and recover quickly.
Let's visit a physiotherapy room

Treatment of frontitis is often not complete without physiotherapy. The nose of the patient is washed with medicines, antiseptics. You can speed up the recovery of adults by prescribing procedures such as electrophoresis with iodine (2%), laser irradiation, salt room and UHF.
All these procedures are carried out to warm the frontal zone, to ensure an easy outflow of sinus contents, as well as to relieve inflammation and improve local blood circulation.

Treatment of frontal sinusitis can be carried out not only in the clinic, but also at home.
- Wash potato peelings, boil, lightly knead in a saucepan and carry out steam inhalation. To do this, the pot with hot cleanings should be placed on a stable surface, lean over the pan, cover with a towel and inhale the hot steam with your nose for about 10 minutes;
- At home, you can prepare a decoction of medicinal herbs (sage, eucalyptus, chamomile), put a couple of drops of lemon oil into the still hot decoction and breathe in the steam from the decoction for 20 minutes;
- Treating sinusitis at home may include nasal washes, soda solution, saline solution, or special isotonic sea water. It can be purchased at a pharmacy;
- Onions and honey have long been used at home as remedies for many diseases. In the case of treatment of frontal sinusitis, the onion is rubbed on a fine grater. One tablespoon of grated onion is diluted with a glass of boiling water. After the mixture has cooled, one tablespoon of honey is added to it. The nasal cavity is washed with this solution.
Whether home conditions are suitable for the treatment of frontal sinusitis can be assessed by the doctor. In any case, all folk remedies must be examined and approved by a doctor. Home treatment can be of an auxiliary nature, but by no means be the main treatment, especially when it comes to acute, purulent processes and severe inflammation.
You can help a patient with frontal sinusitis by doing a massage at home to improve blood circulation in the right areas of the face.
Before starting therapy at home, you need to carefully weigh your own well-being and the effectiveness of procedures performed at home. If there is no relief in two days of treating the disease at home, then the methods of therapy should be changed to others.
Everyone has a runny nose and nasal congestion at least a few times a year, and the number of episodes of headaches is difficult to count, but most people do not pay any attention to it. Nevertheless, a very dangerous ailment frontitis can begin to manifest itself, the symptoms and treatment of which have a number of features.
What is frontitis and why is it dangerous?
Often found in professional athletes, frontal sinusitis is the most severe type of sinusitis, manifested by inflammation of the mucous membrane of the frontal sinus. It causes a violation of the general condition of the body, so many patients lose their ability to work and are forced to undergo long-term treatment.
If you ignore its signs for a long time, this can cause the development of severe complications, including:
- meningitis;
- pneumonia;
- sepsis;
- osteomyelitis;
- phlegmon of the orbit, etc.
Thus, when symptoms of frontal sinusitis appear, you should immediately contact the ENT and begin treatment. Otherwise, the patient may require serious surgical intervention, and developing complications can cause death.

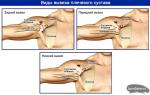
Varieties of frontal sinusitis
Traditionally, the disease can occur in acute and chronic forms. Depending on the symptoms accompanying it, the following types of frontal sinusitis are distinguished:
- catarrhal;
- purulent;
- polyposis;
- polyposis-purulent;
- complicated.
Also inflammation can be:
- left-sided;
- right-handed;
- bilateral.
Spicy
Acute frontal sinusitis in many (more often in young men) begins against the background of a common cold or flu. It is typical for him:
- an increase in body temperature up to 39 ° C;
- malaise;
- severe headaches;
- cough;
- a feeling of fullness in the mid-eyebrow;
An acute inflammatory process is accompanied by the production of a large amount of secretion and a significant decrease in the rate of its outflow. Therefore, acute frontal sinusitis without discharge from the nose is often observed. In this form, the process persists only for 3 weeks, after this time the disease is considered chronic.
Chronic
Chronic sinusitis is called inflammation that persists for a long time in the paranasal sinuses, which does not appear too pronounced. Often it develops in the absence of acute treatment, but it is much more difficult to diagnose it. Chronic frontal sinusitis in most cases is unilateral, and is typical for it:
- periodic aching pain in the corresponding part of the forehead;
- the constant presence of mucous discharge from the nose;
- thickening of the mucosa;
- the formation of granulomas and polyps;
- morning cough with the separation of a large amount of sputum with impurities of pus.
left hand
For the left-sided process, a dull pressing pain in the left half of the forehead is typical. It worsens in the evenings, after physical exertion, long reading, computer work, or other activity that requires the head to be tilted.
In addition, she can give to the right eyebrow or temple, as well as the crown. As a rule, it is constant, but sometimes it can become pulsating. In addition, discharge and congestion are also observed only on the left. Source: website
Right handed
Inflammation of the right frontal sinus is accompanied by almost continuous discomfort in this part of the forehead, which increases significantly when pressed. There was also an increase in discomfort in the evening, after physical exertion and work with the head bowed. By analogy with the left-sided lesion, discomfort can be felt in the left temple and brow, sometimes in the crown, and nasal congestion and discharge are present only in its right side. 
What are the symptoms and complaints of frontal sinusitis?
For frontal sinusitis, both local and general clinical manifestations are characteristic, the intensity of which is directly dependent on its form and the age of the patient. The first ones include:
- difficulty in nasal breathing;
- sudden headaches in the brow from the infected paranasal sinus, often aggravated in the morning or when pressing on the corner of the eye or between the eyebrows;
- runny nose;
- a feeling of fullness in the bridge of the nose, growing during the day;
- feeling of heaviness behind the eyes;
- swelling of the eyelids and soft tissues between the eyebrows.
The most specific feature is frontal headaches. If the pathology has managed to become chronic, it can be diffuse, and not clearly localized.
 This is a consequence of a violation of the cerebral lymph and blood circulation, a deterioration in the outflow of contents from the frontal sinuses, mechanical irritation of the endings of the trigeminal nerve, poisoning of the body with the waste products of pathogens, etc.
This is a consequence of a violation of the cerebral lymph and blood circulation, a deterioration in the outflow of contents from the frontal sinuses, mechanical irritation of the endings of the trigeminal nerve, poisoning of the body with the waste products of pathogens, etc.
Attention
With an exacerbation of this type of sinusitis, arching pain occurs in the forehead, which increases significantly during eye movements or when the head is tilted forward. But applying cold usually brings relief.
The discharges present are viscous, thick and have an unpleasant odor, and the use of traditional remedies for the common cold usually does not work. Initially, they are transparent, but as the disease progresses, they acquire a yellow or greenish color, which indicates the beginning of a purulent process. Although often there is frontal sinusitis without discharge from the nose.
This occurs with a serious violation of the outflow from the affected sinuses. In such cases, the main symptom of the pathology is severe headaches, and a visual examination of the nasal cavity reveals deformations of the anatomical structures provoked by the pressure of accumulated pus.
Sometimes patients note that the symptoms that characterize frontal sinusitis disappear. , and treatment is unreasonably stopped. This is a huge mistake, as the disappearance of typical symptoms does not always indicate recovery. After all, they may be absent when the outflow from the sinuses is normalized, despite the preservation of their purulent lesion.
Also, patients suffer from violations of the general condition, in particular:
- temperature increase;
- weaknesses;
- dizziness;
- sleep problems;
- apathy;
- loss of appetite, etc.
In rare cases, there is:
- decrease or even disappearance of smell;
- lacrimation;
- photophobia;
- deterioration of vision.
Causes of Frontal Sinusitis
 The causative agents of sinusitis are various types of staphylococci and streptococci, which can live on the mucous membranes even in absolutely healthy people. But with the development of various diseases, immunity decreases, as a result of which bacteria get the opportunity to actively multiply and, therefore, provoke the development of frontal sinusitis.
The causative agents of sinusitis are various types of staphylococci and streptococci, which can live on the mucous membranes even in absolutely healthy people. But with the development of various diseases, immunity decreases, as a result of which bacteria get the opportunity to actively multiply and, therefore, provoke the development of frontal sinusitis.
In recent years, data have also appeared that Haemophilus influenzae, some fungi, etc., can become pathogens of pathology. There is also a clear connection between its development and environmental pollution with dust, toxins, etc.
As an impetus to the onset of the disease can be:
- untreated rhinitis;
- injuries and anomalies in the structure of the nose, causing difficulty in breathing;
- infectious diseases, in particular, tonsillitis, scarlet fever, diphtheria;
- proliferation of tissues of the pharyngeal tonsil.
They create good conditions for the formation of inflammation and diseases such as:
- the presence of polyps, tumors and other neoplasms in the nose;
- violation of the culture of blowing your nose;
- immunodeficiencies of various nature.
Features of the disease
Frontitis, especially purulent, is very often combined with sinusitis or damage to the cells of the ethmoid labyrinth. For this reason, the pathology is difficult and gives patients a lot of trouble.
Indeed, the symptoms of frontal sinusitis are joined by signs of these ailments, and patients suffer from severe discomfort not only in the forehead and eyebrows, but throughout the face. Also, the disease often provokes the occurrence of conjunctivitis and a persistent cough that cannot be treated. 
It is especially difficult to timely diagnose frontal sinusitis in children, which is quite dangerous for them. Moreover, it is in children that, due to the excessive use of various medicines, the disease imperceptibly becomes chronic and, due to the specifics of the anatomy, often provokes the development of otitis media. And one of the reasons for its formation may be the ingress of foreign bodies into the nose.
The main methods for diagnosing frontal sinusitis
 A significant role in identifying the disease is given to the questioning of the patient and palpation. To confirm the diagnosis allow:
A significant role in identifying the disease is given to the questioning of the patient and palpation. To confirm the diagnosis allow:
- rhinoscopy;
- radiography;
- diaphanoscopy (more often used when examining pregnant women and children);
- sinoscopy;
- thermography;
- scintigraphy (used to detect complications and diagnose a latent form of pathology);
What does frontal sinusitis look like on an x-ray? The radiograph helps to establish the presence of pathological formations, fluid, and deformation of the structure of the frontal sinuses. This is one of the most reliable ways to detect pathology at an early stage. Flaw- radiation exposure. An x-ray of the frontal sinuses shows:
- nature of inflammation (presence of fluid and its amount)
- any darkening indicating any formation in the frontal sinuses
- cushion-like protrusion in chronic hyperplasia.
- absence of cysts


To avoid the development of such an unpleasant pathology, you should be attentive to the treatment of acute rhinitis, various acute respiratory viral infections, influenza. It is also necessary to restore the normal anatomy of the nasal structures in the presence of septal deformities, etc. And if, nevertheless, it was not possible to avoid its occurrence, it is necessary to immediately begin treatment.
How should frontitis be treated?
 Frontitis can greatly reduce a person’s ability to work and disrupt the usual course of his life, but the main danger of the disease is the appearance of complications. Therefore, the diagnosis of pathology should be carried out as early as possible, and treatment should begin just as early.
Frontitis can greatly reduce a person’s ability to work and disrupt the usual course of his life, but the main danger of the disease is the appearance of complications. Therefore, the diagnosis of pathology should be carried out as early as possible, and treatment should begin just as early.
When the first symptoms of frontitis appear, you should seek medical help. Only a specialist, taking into account the stage, severity and all the characteristics of the patient, will be able to prescribe a correctly justified therapy.
Rationale for treatment directions
Treatment of frontal sinusitis in adults and children after 12 years of age (up to 12 years of age, the frontal sinuses are not formed anatomically) is based on the etiology and pathogenesis of the disease. That is, each medication or procedure is aimed either at eliminating the provoking factor of the pathology, or at stopping its symptoms.
The vast majority of cases of the disease occur due to the introduction of bacterial microflora into the mucous membrane, leading to inflammation of an infectious origin. Much less often - due to sensitization of the body to a certain antigen, which is the cause of inflammation of allergic origin.
Having diagnosed an infectious or allergic frontal sinusitis, the ENT doctor determines the main direction of therapy - etiological. In case of bacterial inflammation, antibacterial agents are prescribed.
With the allergic nature of the pathology, antihistamine, hormonal, barrier drugs, as well as cell membrane stabilizers are necessary.
The pathogenesis of inflammation of the frontal sinuses develops in the following areas:
- expansion of the capillaries of the mucous membrane of the sinuses and excretory channels;
- the release of blood plasma into the intercellular space with the formation of a significant edema of the membrane;
- blockage of the drainage channels increased in volume by the mucous membrane;
- increased production of mucopurulent contents in the frontal cavities;
- impaired drainage of discharge into the nasal passages.
The appointment of medications or procedures that can stop the development of the inflammatory process at these stages is symptomatic therapy.
It includes:
- the use of vasoconstrictor drugs;
- restoration of drainage function, cleansing the sinuses from purulent contents and treating them with antiseptics;
- normalization of local immunity of the mucous membrane, acceleration of the regeneration of the destroyed epithelium.
Early appeal for help, as well as the appointment of competent therapy, allow the treatment of frontal sinusitis without a puncture, which can be carried out both through the nasal cavity and directly through the frontal bone.
A complex of medications, optimally selected for each patient, is able to cure acute inflammation in 7-10 days, and in the case of chronic inflammation, to lengthen the remission as much as possible.
How to treat sinusitis with antibiotics?
Treatment of bacterial infection is the mainstay of therapy. Antibacterial drugs are presented in an extensive range, it is necessary to choose the most effective of them in each case.
The best option is to inoculate the detachable frontal sinus on a nutrient medium, followed by determining the sensitivity of the pathogen to antibiotics. This method will give results in 24 hours and will avoid the appointment of ineffective funds.
But in practice, in medical institutions it is often not possible to carry out such a study at all in the first days of the disease. Or the material is taken, but sent to distant laboratories.
Therefore, the medical tactic is as follows: a broad-spectrum antibiotic is prescribed as the first course; if recovery does not occur, then a narrow-spectrum antibiotic is used in the second course (a strictly defined remedy is prescribed upon receipt of results from the laboratory). 
Antibiotics for frontitis, prescribed in the first course, take into account the fact that the disease is most often caused by Haemophilus influenzae or pneumococcus. Therefore, from a wide range of funds, preference is given to the penicillin group, macrolides and cephalosporins.
From penicillins more often amoxicillin derivatives (Amoxiclav, Augmentin, Doxycycline) are used in the form of tablets or injections, the dosage is calculated depending on the patient's weight.
From cephalosporin antibiotics of the latest generation are prescribed Cefaclor, Cefotaxime, Ceftriaxone.
Funds from the group macrolides can be used not only in the first course, but also in the second, with a low effectiveness of penicillin or cephalosporin antibiotics. An example of macrolides is Sumamed containing azithromycin.
It has a bactericidal effect on streptococci, pneumococci, Haemophilus influenzae, fusobacteria, clostridia, and some protozoa. The drug is used for intramuscular or intravenous administration.
There are antibacterial agents for topical use. This is Bioparox nasal spray containing fusafungin, which is very effective in acute and chronic frontal sinusitis, as well as Isofra and the combined preparation Polydex (a complex with a vasoconstrictor and hormonal component).
Symptomatic treatment of frontitis
Etiological therapy should be supplemented with symptomatic treatment. To reduce swelling of the mucous membrane, vasoconstrictors (vasoconstrictors) are needed for topical application.
Their choice, the appointment of the dosage and the duration of the course must be carried out by the doctor, since any violation can lead to damage to the epithelium.
The drug is selected from the groups of short, medium or long-acting. Examples:
- Galazolin
- Nazol
- Rinostop
- Nazivin
- Polydex is very effective.
Treatment of frontal sinusitis can be carried out using homeopathic remedies, for example, Sinuforte. This preparation, produced on the basis of the active substances of cyclamen, is an absolutely natural herbal medicine. Sinuforte, as well as Echinacea, Traumeel or Engystol, has a complex effect (antimicrobial, vasoconstrictor and immunomodulatory).
The most important direction of therapy is hot or cold inhalations and washing the sinuses with special solutions. At home, this is easy to do, but it must be remembered that the procedures are not carried out at elevated body temperature. To reduce it, you can use antipyretics based on Paracetamol.
Inhalations are carried out both through a nebulizer and with the help of ordinary hot decoctions (chamomile, calendula, boiled potatoes, sage). Washing is carried out with a saline solution (2 teaspoons of salt per 2 liters of water) or pharmaceutical preparations
- Dolphin
- Aqua Maris
- Marimer
- Physiomer
- Otrivin Sea
- Quicks
In the conditions of a medical institution, the “cuckoo” procedure is carried out, or the supply of a solution under pressure through one nostril, and the removal of wash water through the other. In this case, drainage and cleansing of all paranasal sinuses occurs. Very effective and the use of the Yamik sinus catheter
Frontal sinusitis - inflammation of the paranasal sinuses has a second name - frontal sinusitis. The disease manifests itself equally in males and females.
Any sinusitis appears due to infection in the paranasal sinus, as a result of which the movement of fluid is disturbed. These processes provoke the rapid multiplication of pathogenic microbes in the sinus, which becomes apparent by the formation of pus. The main sign of frontitis is the accumulation of purulent-mucous substance. Frontitis in adults manifests itself in 2 forms - chronic and acute. Each form of the disease has its own severity of symptoms.
Frontite types
Symptoms of an acute illness
Frontitis symptoms and treatment in adults in the acute stage:
- Severe soreness in the sinuses, near the eyes, on the forehead and bridge of the nose (caused by the accumulation of a large amount of pus). When you press these places, the pain intensifies.
- Also, the pain increases when the patient's torso is tilted forward and the period of sleep. This is the main external difference between frontal sinusitis and sinusitis. With sinusitis, the pain decreases when the patient assumes a supine position. The reasons for this dependence have not been fully identified, although many studies have been conducted.
- There is a feeling in the bridge of the nose, as if it were bursting. This symptom is especially acute in the evenings. Later, this unpleasant sensation moves to the forehead and infraorbital region.
- It's difficult to breathe.
- Mucus comes out of the nose. At first, the discharge is translucent, but the bacteria multiply, pus begins to stand out. If the outflow of secretions does not occur, this is a threatening phenomenon, indicating a blockade of the sinus. All other symptoms increase and complications develop over time.
- Cough at night. Its occurrence is caused by the flow of mucus down the throat, which stimulates the mucosal receptors.
- Tearing, pain in the inner corner of the eye. Both eyes can be affected, as well as one - it depends on the spread of the lesion.
- The patient's temperature is elevated to 38.5°C. Sometimes the temperature rises above the focus of inflammation.
- Puffiness is noticeable under the eyes and in the forehead area.
- There are symptoms of intoxication: weakness, reduced performance, do not want to eat.
The acute phase lasts up to 21 days, resulting in fatigue and irritability of the patient. Often, frontal sinusitis is aggravated by sinusitis (pathology of the sinuses of the upper jaw). Symptoms of frontal sinusitis are complemented by manifestations of sinusitis.
Chronic disease symptoms
If the acute form is poorly treated, chronic frontal sinusitis occurs. When a month has passed from the onset of the disease, and the symptoms do not disappear, the doctor speaks with confidence about the transition of the disease to the chronic stage.
Frontitis symptoms and treatment in adults in the chronic phase:
- Mucus becomes very thick, smells unpleasant. Usually the left or right sinus is prone to inflammation (a runny nose flows from one nostril).
- The sense of smell is reduced, the patient is not able to distinguish smells. But if properly treated, the sense of smell is restored.
- A strong swelling is noticeable above the eyebrows, especially in the morning. This symptom indicates inflammation in the walls of the orbit.
- There is conjunctivitis.
- The cough is aggravated in the supine position, it cannot be cured with antitussive medications, because the root cause is irritation of the throat mucosa with secretions from the sinuses.
- In the morning, sputum with a smell is expectorated.
- Sometimes there is pain in the ears and throat or teeth ache.
- Bad smell from the mouth.
- The patient feels tired and apathetic.
- Periodic increase in temperature up to 37.5°C is not ruled out.
Complications with frontitis
You should not expect that the disease will be cured on its own, it is treated without fail. Lack of treatment and illiterate use of medications, interruptions in the treatment course lead to complications.
- The infection spreads to other sinuses. Frontitis with other types of sinusitis.
- Inflammation passes to the eye area, an abscess may begin, inflammation of the periorbital tissue and phlegmon will form.
- The pus can spread to the brain, causing meningitis.
- Sepsis rarely develops.
Frontitis treatment methods
After a visual examination, ultrasound of the sinuses and x-ray of the skull, the doctor can diagnose frontal sinusitis. Some other additional studies are also being ordered. The treatment is carried out by a specialist.
Having found out the cause of the inflammatory reaction, the doctor selects medications. To do this most fully, a bacteriological study of secretions is carried out in a special laboratory and the sensitivity of this type of bacteria to a particular antibiotic is clarified. After such a study, it becomes clear which antibiotics should be used for a particular patient.
To completely cure frontal sinusitis, it is necessary to purposefully achieve the following results:
- Eliminate inflammation.
- Reduce puffiness.
- Improve the outflow of accumulated pus.
- Destroy fungi, bacteria and viruses.
- Improve ventilation and breathing process.
To achieve these goals, the doctor prescribes antibiotics if bacteria that cause serious complications have been found in the smear. Antibiotics are used for internal use (tablets, injections) and local (sprays, drops, aerosols, swabs saturated with the drug). For a full recovery, you will need to use other groups of medications. Often combine local and systemic antibiotics.
antibiotics for sinusitis
It is possible to use any medications for frontal sinusitis only as prescribed by the attending physician, who selects an antibiotic in accordance with the individual characteristics of the patient's body. Keep in mind that antibiotics have no effect on viruses. The use of antibiotics for a virus does not give the desired effect, but it is addictive and allergic reactions and dysbacteriosis. When a viral infection is detected, antiviral medications are prescribed, the fungus is removed with special antifungal agents.
If it is not possible for any reason to conduct research in the laboratory, then broad-spectrum antibiotics are prescribed. These drugs affect almost all bacteria, so the pathogens of frontitis will also fall under their action. They usually begin to treat with a group of penicillins, macrolides and cephalosporins.
According to statistical information, pneumococci and Haemophilus influenzae most often provoke frontal sinusitis. These organisms are sensitive to penicillin and cephalosporin. When treating at home, doctors prescribe antibiotics in tablet form. For babies, it is most convenient to use suspensions and soluble pills.
Penicillin antibiotics
With frontal sinusitis, synthetic and semi-synthetic medications are used. In order for the medicine to be effective, some substances are added to it that protect the antibiotic from bacterial enzymes present in the body. The dosage is calculated by the otolaryngologist individually for each patient.
Cephalosporin antibiotics
An equal alternative to penicillin are cephalosporin antibiotics, which have a similar molecular composition and act on bacteria in a similar way. In order for the molecules of the medicinal substance to be destroyed by enzymes to a lesser extent, it is necessary to use medications of the II-III generation. All such antibiotics are produced in injections, they are the ideal choice for severe frontal sinusitis or subsequent complications. The disadvantage of this antibiotic is its negative impact on the microflora of all parts of the intestine. Inaccurate use of the drug leads to dysbacteriosis.
macrolide antibiotics
These medications are chosen for treatment if the patient has intolerance to the two previous groups of antibiotics, or they have shown themselves to be ineffective. Macrolides practically do not harm the microflora and intestinal mucosa. But they have a strong anti-inflammatory effect.
Local antibiotics
These therapeutic medications are delivered directly to the nasal cavity by various methods.
- Drops.
- Aerosol.
- Nasal spray.
- Medicated tampons.
This method of delivery of a therapeutic substance completely eliminates toxic renal damage.
Other drugs
In addition to antibacterial, antiviral and antifungal therapy, other medications are also prescribed.
- Vasoconstrictor drops for easier breathing. They should not be used for more than five days.
- Antihistamine medications - reduce swelling in the nose, facilitating the general condition.
- Antipyretic drugs at temperatures above 38.5 ° C.
- ACC is prescribed to speed up and facilitate the elimination of mucus.
- Homeopathic medicines have an anti-inflammatory effect and increase mucus waste.
- Antispasmodics and analgesics are used in the presence of severe pain.
In addition to medicines, a course of physiotherapy is attributed, and if conservative therapy does not lead to any results, then the ENT doctor prescribes a sinus puncture.
Inhalation with frontal
The patient's condition noticeably improves after inhalation over essential oils and herbal decoctions. During frontitis, you need to drink a lot of fortified liquid: freshly squeezed juices, tea with lemon, rosehip broth, compote. A large amount of fluid improves well-being, because toxins are released from the body with it. The course prescribed by the otolaryngologist must be followed very precisely. Only full compliance with the prescribed and performed treatment will help normalize the processes and prevent complications.
Frontitis is treated within a few weeks, sometimes months. Much easier to prevent. It is necessary to avoid hypothermia of the body, harden and exercise. It is useful for prevention to carefully monitor the normal state of immunity, maintain it with vitamins and a healthy diet. If a person is still sick, then treatment should be started at an early stage.
Inflammation of the paranasal sinuses is denoted by the general term - sinusitis. Frontitis is characterized by severe symptoms - inflammation of the mucous membrane of one or two frontal sinuses.
This disease is also called frontal sinusitis, and it occurs with the same frequency in men and women.
Symptoms indicating inflammation of the frontal sinus
Any sinusitis occurs due to the fact that an infection gets into the paranasal sinus, and the outflow of fluid from the cavity is disturbed. Such changes contribute to the rapid multiplication of pathogenic microflora in the sinus, which causes the formation of pus.
Puffiness, a large accumulation of mucopurulent secretion, an inflammatory reaction affect the appearance of all the symptoms of the disease.
Frontitis in adults occurs in two forms - acute and chronic. Each of these forms has its own characteristics of the course, and the severity of the main symptoms also changes.
Symptoms of acute frontal sinusitis in adults

The acute form of frontal sinusitis in most cases in adults occurs as a result of an untreated cold. It manifests itself with pronounced symptoms:
- Intense pain. With inflammation of the frontal sinuses and the accumulation of pus in them, the pain will be localized around the eyes, in the region of the bridge of the nose and forehead. When tapping or pressing on the forehead, the pain increases markedly.
- Feeling of growing fullness in the bridge of the nose. Usually this symptom intensifies in the evening and the swelling from the nose passes to the infraorbital region and forehead. The pressure in the inflamed sinus increases when the head is tilted, which leads to increased pain.
- Labored breathing.
- Discharge of mucus from the nasal passages. At first, the discharge is transparent, but as the bacteria multiply, they become purulent. It is also necessary to know that the absence of secretions indicates a complete blockade of the outflow of fluid from the frontal sinus, and this only aggravates all other manifestations of the disease and contributes to the development of serious complications.
- Night cough. A cough occurs due to the fact that in a horizontal position, mucus begins to flow down the back of the throat and this irritates the receptors of the mucous layer.
- Photophobia, the appearance of a large number of continuously running tears, pain from the inner corner of the eye. All these symptoms develop on the side of the lesion or immediately on both eyes if the inflammation spreads simultaneously to two frontal sinuses.
- An increase in body temperature. Inflammatory reaction in the sinuses and the accumulation of purulent mucus cause the temperature to rise to 38-39 degrees. Often there is an increase in local temperature over the focus of inflammation.
- Visually, puffiness can be noted in the forehead and under the eyes.
Acute frontal sinusitis almost always occurs with symptoms of intoxication. A sick person has a pronounced weakness, a sharp decrease in working capacity, and there is no appetite.
The duration of the acute phase of the disease reaches up to three weeks, it is clear that this negatively affects the general well-being, causes irritation and fatigue.
Often inflammation of the frontal sinuses is combined with sinusitis, that is, damage to the maxillary sinuses. At the same time, changes characteristic of sinusitis are added to the symptoms of frontal sinusitis.
Symptoms of chronic frontal sinusitis in adults

The chronic form of inflammation of the frontal sinuses occurs due to insufficient treatment of an acute disease. If the symptoms of the disease do not completely disappear for more than a month, we can already say that acute inflammation has passed into chronic.
Chronic frontal sinusitis can be suspected by several signs, the most basic of which is a runny nose. A thick, viscous mucus is secreted, in which pus periodically appears. Nasal discharge also has an unpleasant odor.
It is worth knowing that in most cases with chronic frontal sinusitis, only one sinus is inflamed, so the mucus will flow and blow out from one nostril.
In addition to a runny nose, chronic frontal sinusitis is indicated by:
- Decreased sense of smell. A person ceases to distinguish many odors, if the treatment is carried out on time, then this function of the nose will be fully restored.
- Severe swelling of the area above the eyebrows and eyelids. This symptom is especially noticeable in the morning and indicates the spread of inflammation to the walls of the orbit.
- Intermittent conjunctivitis.
- Persistent cough, aggravated by lying down. Cough with frontal sinusitis cannot be treated with antitussive drugs, as it occurs due to irritation of the throat with viscous mucus from the sinuses.
- Expectoration of viscous mucus with a smell in the morning.
- A constant feeling of lethargy, fatigue, not wanting to do the usual work and household chores.
In chronic frontal sinusitis, a periodic increase in body temperature of about up to 37.5 degrees.
Possible complications in acute and chronic frontal sinusitis

Inflammation of the frontal sinuses, like other types of sinusitis, must be treated. Lack of timely therapy, misuse of drugs or interruption of the course of treatment lead to:
- Spread of infection to adjacent sinuses. Therefore, frontal sinusitis can be complicated by sphenoiditis, ethmoiditis, sinusitis.
- The transition of inflammation to the orbit and periorbital areas. Perhaps the development of an abscess of the eyelids, inflammation of the tissue around the orbit can lead to the formation of phlegmon.
- Spread of pus into the brain, which causes abscess formation and meningitis.
Cases of the development of sepsis against the background of frontal sinusitis have also been registered.
Frontitis treatment methods

The diagnosis of frontal sinusitis is established on the basis of complaints, examination and after such instrumental methods as skull radiography And sinus ultrasound. If possible, conduct additional surveys. The treatment of frontal sinusitis must be dealt with by a narrow specialist - an ENT doctor.
In order for the prescribed medications to be beneficial, they must be selected correctly, and this can only be done by finding out the nature of the development of the inflammatory reaction. This requires bacteriological examination of mucus and determination of its sensitivity to antibiotics.
The main goals of the treatment of frontal sinusitis include:
- Elimination of the inflammatory response.
- Reducing swelling of the mucous layer.
- Improving the outflow of accumulated mucus from the sinuses.
- Destruction of bacteria, viruses or fungi.
The use of antibiotics and other drugs

To achieve complete recovery, it is sometimes necessary to simultaneously use several groups of drugs at once. Antibiotics are prescribed only if bacteria are detected in the smear or when there is a high probability of developing severe complications. Most often, a combination of local and systemic antibiotics is used.
From the means with local effects, the drug is used Bioporox, spray Isofra . Inside with ENT diseases, most patients are prescribed Augmentin, Amoxicillin, Ampisid, Flemoxin Solutab, Cefaclor, Ceftriaxone, Summamed, Azithromycin .
The type of antibiotic, as well as its dosage and general course of application, are selected by the doctor for each patient individually. If it is established that the inflammation is caused by viruses, then drugs with antiviral properties are needed. Fungal infection is destroyed by antifungal agents.
In addition to antibiotic therapy, patients with frontal sinusitis are also prescribed:
- Vasoconstrictor drops - Nazivin, Galazolin, Vibrocil . These drops are needed to ease breathing, but they should not be dripped for more than 5 days.
- Antihistamines - Tavegil, Suprastin, Diphenhydramine . The use of these drugs affects the reduction of swelling in the nasal passages, which facilitates the course of sinusitis.
- Antipyretics are used when the temperature rises above 38.5 degrees.
- ACC. This medicine is prescribed for frontal sinusitis in order to accelerate and facilitate the removal of a viscous, purulent secret from the inflamed sinus.
- Homeopathic remedies. For any type of sinusitis, drugs such as Sinuforte, Sinupret, Cinnabsin . They have anti-inflammatory properties and effectively increase mucus discharge.
Can be used for severe pain analgesics and antispasmodics. The doctor can prescribe a course of physiotherapy, and if conservative therapy is ineffective, puncture of the frontal sinus.
Inhalation with frontal

The condition of a sick person is alleviated after inhalation, these procedures can be carried out over decoctions of anti-inflammatory herbs, solutions of essential oils.
During the treatment period, it is necessary to drink as much healthy liquid as possible.- rosehip broth, tea with lemon, compotes, freshly squeezed juices. Sufficient drinking regime facilitates well-being, and contributes to the rapid removal of all accumulated toxins.
The course of treatment prescribed by the doctor for acute or chronic frontal sinusitis must be fully observed by the patient. Only this will help to completely normalize the state of the frontal sinus, and prevent the occurrence of complications.
Inflammation of the paranasal sinuses (paranasal sinuses) has a common name - sinusitis. With the localization of inflammation in the frontal sinuses, we can talk about frontal sinusitis. These include at least 10% of all cases of sinusitis. Although the proportion of inflammation of the frontal sinuses in the total number of sinusitis is not large, however, frontal sinusitis is fraught with the most unpleasant complications and is accompanied by a severe form of leakage.
During the disease, the mucous membrane that lines the sinus becomes inflamed. The disease can affect one sinus (unilateral sinusitis) or both (bilateral).
Acute sinusitis, symptoms and treatment of which are ignored, often becomes chronic. Like any chronic disease, chronic sinusitis is treated for a long time and diligently.
Frontitis disease is caused by various reasons. Most of them are similar to the causes of inflammation in other parts of the respiratory system.
The main reason for such phenomena is infection. Pathogenic bacteria, viruses and fungi, getting into the frontal sinuses, cause painful processes. The situation is aggravated by the fact that the duct from the frontal sinus to the nasal passage is thin and tortuous. Even a small edema can block it and create a favorable environment for further reproduction of the infection.
Streptococcal, staphylococcal and other gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria lead to multiple inflammations of the sinuses, including frontal sinusitis.
Against the background of SARS and influenza, the disease can be caused by viruses of various etiologies (adenoviruses, rhinoviruses, influenza viruses). Fungal sinusitis is rare and often appears against the background of systemic diseases (severe diabetes mellitus, HIV infection, the effects of chemotherapy).
- In the frontal sinuses, the infection can get with the blood flow from other organs that have been infected.
- The cause of frontal sinusitis can be allergic reactions that lead to swelling and further closure of the nasal passages.
- Not infrequently, frontitis is a companion of polyps in the nose. With polyps, there is swelling of the mucosa, a change in breathing and a deterioration in the drainage of the nasal sinuses.
- Injuries of the nose and sinuses, congenital anomalies of the anatomy of these organs and the presence of foreign bodies in them, as a rule, sooner or later lead to inflammation of the sinuses, including the frontal ones.
Frontitis in adults is diagnosed much more often than in children. Frontitis in children before puberty is extremely rare, since the frontal sinuses have not yet fully developed during this period of life.
However, it should be noted that the symptoms of frontal sinusitis in adults are more pronounced and easier to diagnose without the use of additional methods (ultrasound, tomography, X-ray). Frontitis during pregnancy is especially fraught with negative consequences for the embryo in the initial stages and requires urgent therapy with all possible medicines and methods in this state.
The international classifier ICD classifies frontal sinusitis according to two codes: ICD-10: J01.1 Acute frontal sinusitis and ICD-9: 461.1 Acute frontal sinusitis.

Frontitis symptoms
Acute frontal sinusitis is characterized by the following symptoms:
- Intense pain localized in the area above the bridge of the nose, possibly in one of the sides. Pain with frontal sinusitis tends to increase in the morning, as at night the outflow of mucus and pus from the sinuses is disturbed. They also increase with sharp turns of the head, leaning forward, shaking, vibration, with pressure over the bridge of the nose. There is a spread of pain in the temple and corners of the eyes.
- Nasal congestion, sometimes on one side with unilateral inflammation.
- Nasal discharge, especially intense in the morning with an unpleasant odor
- Lachrymation and pain in the eyes.
- Raising the temperature above subfebrile.
- General malaise and intoxication, which is growing rapidly.
In the chronic form, the signs of frontal sinusitis are less pronounced. So the temperature may not rise or remain at around 37.1-37.4 C, the pain may also be less pronounced. However, purulent discharge from the nose is diagnosed, as well as a cough at night and a runny nose that does not go away. The sense of smell is reduced. There are reviews that with chronic frontal sinusitis there are no symptoms at all, and this is very dangerous, since untreated inflammation of the frontal sinuses can lead to sad consequences.
At the slightest suspicion of frontal sinusitis, it is urgent to contact an ENT specialist. Everyone should understand why sinusitis is dangerous and take responsibility for their health and their loved ones, especially children.
Frontitis in children symptoms are often atypical, more common:
- headache without a specific localization,
- general intoxication,
- fever,
- Pain in the eyes,
- fear of bright light
- runny nose with discharge of pus,
- swelling of the upper eyelid.
The disease in children often occurs as a complication after suffering the flu, SARS, measles, scarlet fever, so it is very important to pay attention to the change in the child's condition in time. Practice shows that in children from 7-12 years old, frontal sinuses are more difficult than in adults, this is due to the immature immunity, the presence of adenoids and the underdevelopment of the nasal sinuses themselves. In preschool children, the frontal sinuses are not yet formed.
How to treat sinusitis depends on the results of laboratory tests. In bacterial forms of the disease, antibiotics are mandatory. In addition to analysis, x-rays are needed. The x-ray will clearly show the localization of inflammation, that the patient has sinusitis or frontal sinusitis. Modern method of diagnosis - tomography without errors will confirm the symptoms and treatment in adults and children will be aimed at eliminating the focus of the disease.

Therapy
Treatment of frontal sinusitis can take place both on an outpatient basis and in a hospital. It all depends on the severity of the patient's condition. Sometimes, in particularly complex and advanced cases, it is necessary to resort to surgical intervention. In such situations, punctures are used to remove the contents of the sinuses. With a high density of mucus in the sinuses and the impossibility of removing it with a puncture, they resort to more serious surgical intervention. In most cases, frontitis can be treated without a puncture. Medicines, physiotherapy, homeopathy, washings, folk remedies, massage with frontal sinusitis are far from all methods of treatment.
Treatment of frontal sinusitis in adults begins with the use of vasoconstrictor drugs to relieve swelling from the mucous membrane of the anastomosis, sinus and nasal cavity. Hormonal drugs may be prescribed to reduce inflammation. With bacterial frontal sinusitis, antibiotics are prescribed both locally (in drops, sprays) and general.
To cure sinusitis, like other sinusitis, you can use the homeopathic preparation Sinupret.
Treatment at home is quickly possible only if you strictly follow the recommendations and prescriptions of the doctor.
Diagnosis of frontal sinusitis makes it possible to determine the range of pharmacological preparations necessary for treatment. Carrying out a series of manipulations at the final stage of the disease (physiotherapy) is an excellent prevention of frontal sinusitis.
Antibacterial therapy
When pathogenic bacteria are detected in laboratory tests, antibiotic therapy should be started immediately and carried out in a full course without interruptions and premature cancellation, even with a significant improvement in the patient's condition. If the disease is not started, on the recommendation of a doctor, you can limit yourself only to drops and sprays containing an antibiotic:
- "Tsiprolet";
- Normax.
At high temperature, headaches are prescribed tablets or injections of drugs such as:
- "Ceftriaxone";
- "Cefatoxime";
- "Ciprofloxacin";
- "Lincomycin".
In parallel with the course of antibiotics, antifungal drugs, probiotics are prescribed (to restore the intestinal microflora).

Vasoconstrictors
Vasoconstrictor drugs should be used only when necessary and when prescribed by a doctor. Uncontrolled use of drugs in this group is fraught with unpleasant consequences - atrophy of the mucosa, the occurrence of vasomotor rhinitis.
The list of vasoconstrictor drugs used for frontal sinusitis is extensive. Here are the old preparations "Galazolin" and "Naphthyzin" and more modern ones:
- "Sanorin";
- "Nazivin";
- "Otrivin";
- "Nazol";
- "Rinazolin".
Vasoconstrictor drops are selected by a doctor with different duration of action - from 4-6 hours (short duration), up to 6-10 hours (medium) and more than 10 hours - long-term.
Proper instillation is of great importance for successful treatment. The nose is buried lying down. The right nostril is buried when the head is tilted to the right side, the left - to the left. After instillation of the first nostril, it is necessary not to change the position for 10 minutes so that the drops get to their intended purpose, and not run down the back wall of the larynx. Only after this is the other nostril buried.

Nasal lavage
Vacuum nasal lavage treats frontal sinusitis very effectively. This procedure is called "cuckoo" and consists in pumping a solution for washing into one nostril and simultaneously taking it from the other nostril. During the procedure, the syllables “cuckoo” are repeated, which makes it possible to block the message between the nose and throat. At this point, the solution enters the sinuses, washes out the pathogenic contents and exits. Anti-inflammatory and antibacterial drugs are added to the washing solution.

Inhalations
Inhalation should be treated with great care. The presence of pus in the sinuses and elevated body temperature are contraindications for inhalation. It is advisable to carry out inhalations at the initial stages of the disease, if there is inflammation, but there is no purulent discharge, or at the final stages of aftercare.
For the preparation of infusions for inhalation, both medicinal herbs, such as chamomile, sage, and essential oils, bay leaf are used, you can use the Asterisk balm in a small amount.
Inhalations have a mild and lasting effect not only on the frontal sinuses, but also on other parts of the respiratory tract.

Physiotherapy procedures
- electrophoresis;
- magnetotherapy
Electrophoresis makes it possible to accumulate drugs in the frontal sinuses.
Thus, UHF heating with a preparation that generates ultra-high frequencies makes it possible to influence a limited area without heating adjacent tissues and organs.
The magnetic field created during magnetotherapy helps to activate local blood circulation, kill infectious agents and relieve edema, and hence the outflow of contents from the sinus, relieve inflammation,
Treatment with folk remedies
Treatment with folk remedies should not be carried out uncontrollably, but only under the supervision of a doctor and possibly with mild forms of the disease. It is important to monitor whether the patient's condition worsens.
To ensure the outflow of contents from the sinuses, a solution consisting of 200 ml of saline and 15-20 ml is used. alcohol infusion of chlorophyllipt. Before using the solution, the nose is first washed with saline solutions, then vasoconstrictor drops are instilled, and only after the onset of their action, the prepared antibacterial solution is instilled. One ampoule of "Lincomycin" can be added to it.
- Rinse your nose with a saline solution, add a few drops of iodine and tea tree oil.
- You can wash your nose with a decoction of chamomile, cooked in a water bath.
- Honey with onions is a well-known folk remedy for the treatment of inflammation in the sinuses. No nasal drops are prepared on their basis. Black radish juice is also used to prepare drops for frontal sinusitis.
Kalanchoe juice, as well as Kalanchoe juice mixed with aloe juice, are powerful antibacterial agents. Based on these ingredients, ointments can also be prepared. Turundas are impregnated with ointments and placed in the nostrils alternately.

Complications with frontitis
Complications with frontal sinusitis are very dangerous, since the frontal sinuses are adjacent to the eyeballs, brain and other vital organs, and a bacterial infection located in any organ can provoke a general blood poisoning - sepsis.
Frontitis complications include:
- cellulitis of the eye tissue;
- sinusitis, sphenoiditis, ethmoiditis;
- osteomyelitis, periostitis;
- meningitis;
- sepsis.
Most of these diseases pose a threat not only to health, but also to the life of the patient.
Disease prevention
Prevention of any respiratory diseases consists in strengthening the immune system, a balanced diet, regular walks in the fresh air, reasonable physical activity.
If you stay outdoors for a long time, you should dress according to the weather, do not overcool. A very important role in the prevention of frontitis is played by timely oral care, mandatory examinations at the dentist, and timely treatment of diseased teeth.