Mirena coil how to install. The effectiveness of the Mirena IUD during endometriosis: advantages and disadvantages. What signs can be used to judge that Mirena is in place
Mirena spiral with menopause - consequences, reviews, cost, rules of use, you need to find out in advance. The contraceptive is different from the usual spiral, which prevents pregnancy. It contains a synthetic hormone - progesterone. Mirena normalizes hormonal levels, protects against unwanted pregnancy.
The action of the Mirena coil
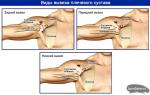
T-shaped device with 2 antennae. In the body of the Mirena spiral there is a cavity filled with hormones. The body receives an equal amount of progesterone daily in the form of levonorgestrel - 20 mcg each. The hormone belongs to the group of gestagens. Prevents the formation of the endometrium, the growth of cancer cells. The Mirena coil balances progestins and estrogens. Does not interfere with ovarian function. Prevents the development of pathological processes in the pelvic organs, reduces the manifestation of menopause. Used as a means of contraception. Its action is especially useful at the initial stage of menopause, when it is still possible to become pregnant. The spiral thickens the discharge, prevents sperm from entering the uterine cavity. Prevents the development of hyperplasia, endometriosis.
Mirena and uterine fibroids
 One of the reasons for the development of fibroids is hormonal disorders. The likelihood of a tumor appearing in the process of menopause is high. Uterine fibroids provoke painful, heavy periods, bleeding during menopause. The Mirena spiral evens out the hormonal background, prevents the development of a neoplasm or helps to reduce it. While the conventional coil is contraindicated, Mirena is recommended by doctors for the prevention of many diseases. The tool regulates estrogens, prevents the development of the endometrium. Menstruation scanty may be present in the first months of treatment, then disappears altogether.
One of the reasons for the development of fibroids is hormonal disorders. The likelihood of a tumor appearing in the process of menopause is high. Uterine fibroids provoke painful, heavy periods, bleeding during menopause. The Mirena spiral evens out the hormonal background, prevents the development of a neoplasm or helps to reduce it. While the conventional coil is contraindicated, Mirena is recommended by doctors for the prevention of many diseases. The tool regulates estrogens, prevents the development of the endometrium. Menstruation scanty may be present in the first months of treatment, then disappears altogether.
An increased amount of estrogen provokes the growth of fibroids. In the process of fading reproductive functions, the amount of estrogens in a woman's body decreases, but they replenish it with drugs containing a synthetic hormone. As a result, there is a situation with a high rate of estrogen. The spiral allows you to balance this level. Since it contains progesterone, it is possible to use drugs with estradiol. But the treatment regimen should be selected by the doctor, taking into account the individual characteristics of the organism. According to women, Mirena copes quite well with fibroids. It either stays the same or disappears completely.
Abundant discharge after the installation of the spiral
 When using this remedy, spotting may be present for the first 4 months, which is the norm for menopause. So the body adapts to the new conditions of existence, the hormonal background stabilizes. At the same time, the risk of developing inflammation is high. Often, pathology is the cause of bleeding after the installation of the spiral. Firstly, the body is trying to get rid of a foreign object, and secondly, the hormonal background is changing. If bleeding occurs, consult a specialist. Even if there are no other warning signs.
When using this remedy, spotting may be present for the first 4 months, which is the norm for menopause. So the body adapts to the new conditions of existence, the hormonal background stabilizes. At the same time, the risk of developing inflammation is high. Often, pathology is the cause of bleeding after the installation of the spiral. Firstly, the body is trying to get rid of a foreign object, and secondly, the hormonal background is changing. If bleeding occurs, consult a specialist. Even if there are no other warning signs.
How long does the bleeding last
With menopause, the Mirena spiral helps to avoid spotting, spotting. For the first 2 months, there may be abundant spotting if the spiral was placed at the beginning of menopause. But after 4 months everything returns to normal - there are no discharges or they come too scarce. The bleeding lasts from 5 to 7 days. After installing the Mirena spiral, the doctor should advise the woman. Tell what consequences await her. In what cases to seek help from gynecologists. In general, you should visit a doctor 2 times a year. And also 1-2 months after the installation of the spiral.
Contraindications
The tool is not suitable for everyone. Before installing the Mirena spiral, it is necessary to undergo an examination of the whole body. Contraindications are:

The consequences of installing a spiral
Side effects may appear at first. If they are not significant, continue to use the remedy. Otherwise, you will have to refuse it. What could be?

If the body has taken the remedy without side effects, the disappearance of menopause symptoms can be felt immediately. Headache, excessive sweating, hot flashes, irritability, and other unpleasant manifestations of menopause pass.
However, there is another side of the coin. Progesterone promotes fluid retention, possibly swelling of the legs, weight gain. An allergic rash, acne appears on the skin. There is constant nausea, an incomprehensible state, a clouded state, laziness, apathy appear. Hair on the face may grow, fall out in bunches on the head. Doctors usually say that the condition of the hair and skin improves from the system, fewer wrinkles appear. If the above symptoms are present, you need to double-check the hormonal background, consult with specialists. You may have to take it out. Hormone deficiency and excess negatively affects the body. Doctors allow such a negative impact of the system for 3 months. Then the body adapts to the new conditions of existence, excess weight goes away, and the woman feels healthy again, without side effects, symptoms of menopause.
Mirena use for menopause
The doctor installs the remedy after a preliminary examination of the woman's body. The procedure itself does not take much time. Immediately after installation, a woman can leave the gynecologist's office. Within 2 weeks it is forbidden to lift weights. In the future, when using the spiral, heavy physical exertion should be avoided. There are no discharges during menopause. The use of Mirena provides for constant monitoring by the gynecologist, the woman herself. If pink, bloody discharge appears, you should consult your doctor. The rest of the woman leads a full life.
 The use of Mirena prevents unwanted pregnancy. In the first years of the extinction of reproductive functions, conception is quite possible. However, it is almost impossible to determine pregnancy by your own feelings - they resemble the manifestations of menopause. Menstruation may be absent due to menopause. The pregnancy test is also not as accurate as before. Since the level of hCG during menopause in women is increased. Corresponds to the first weeks of pregnancy. Thus, a negative test result can mean pregnancy, and a positive one can deny it. Using Mirena allows a woman to have sex without the threat of conception.
The use of Mirena prevents unwanted pregnancy. In the first years of the extinction of reproductive functions, conception is quite possible. However, it is almost impossible to determine pregnancy by your own feelings - they resemble the manifestations of menopause. Menstruation may be absent due to menopause. The pregnancy test is also not as accurate as before. Since the level of hCG during menopause in women is increased. Corresponds to the first weeks of pregnancy. Thus, a negative test result can mean pregnancy, and a positive one can deny it. Using Mirena allows a woman to have sex without the threat of conception.
Intrauterine contraception immediately became popular among women, because it gives a high result and is very convenient to use. One of these contraceptives is the Mirena spiral, which is effective for, but before using it, you need to familiarize yourself with the reviews and consequences. It also does not hurt to find out the features of the remedy and its effect on the body.
Use in menopause
Mirena with menopause, or rather in its initial stages, helps a woman prevent unwanted pregnancy and normalize the hormonal balance of the body. In the initial stages of the process of ovarian failure, the likelihood of conception remains. But it can be very difficult, because the symptoms are very similar to the manifestation of menopause. Yes, and the absence of menstruation may be associated with the approach of menopause.
In addition, you can not be one hundred percent sure of the result of a pregnancy test. The fact is that the level of hCG during menopause is increased, and its indicators correspond to those of the first weeks after conception. It turns out that the test may be negative, but in fact there is a pregnancy.
Therefore, women decide to use Mirena to continue an active sex life without the threat of conception. At the same time, the spiral does not affect the quality of sexual relations. It is installed for a long period of time with minimal control requirements.
It is worth noting that this spiral differs from the usual options, because its composition includes progesterone of synthetic origin. Due to this, the hormonal balance is stabilized, which leads to the elimination of unpleasant symptoms of menopause.
Spiral features
The hormonal contraceptive comes in the form of a T-shaped device with two special antennae. Thanks to this shape, the spiral can be securely fixed in the uterus. In addition, a loop of threads is provided, with the help of which the system is removed.
In the body of the device itself, a cavity is provided in which the hormonal component, represented by levonorgestrel (52 milligrams), is located. The product itself is stored inside a special tube protected by a vacuum package consisting of plastic and paper. It must be stored at 15-30 degrees for no more than three years from the date of manufacture.
How it works
The active substance of the spiral belongs to the gestagens. Hormone:
- blocks the growth of the endometrium;
- prevents cancer cells from multiplying;
- normalizes the balance between estrogen and progesterone;
- does not affect the normal functioning of the ovaries;
- blocks the appearance of pathologies of the pelvic organs;
- reduces the symptoms of menopause;
- protects against unwanted conception;
- acts as an excellent means of preventing endometriosis.
After the system is installed, the woman's body receives a certain dose of levonorgestrel (20 mcg) every day. By the end of the five-year period of use, this figure drops to 10 mcg per day. It is important to note that almost the entire dose of the hormone is concentrated in the endometrium, and the hormone content in the blood does not exceed the microdose.
The active substance does not begin to flow into the blood immediately. This happens after about an hour, and after 14 days the blood contains the highest concentration of levonorgestrel, but this figure depends on the weight of the woman. If a woman weighs no more than 54 kilograms, then this figure will be 1.5 times more.
According to reviews, after installing the system, unstable discharge of a smearing nature may be noted, but only during the first few months. This is due to the restructuring of the endometrium, after which the duration and volume of bleeding are significantly reduced. And sometimes they stop altogether.
Hormonal spiral against menopausal diseases
Symptoms of menopausal syndrome are caused by destabilization of the hormonal background. But not always this problem can be solved by taking hormonal drugs with estrogen. The fact is that many diseases in the female body provoke the predominance of estrogen over progesterone. Here, the use of estrogen-containing drugs only exacerbates the problem, increasing the speed and neglect of the disease.
Levonorgestrel, which is contained in the Mirena spiral, can help in the fight against the following problems:
endometrial hyperplasia
Estrogen provokes excessive division of tissue cells, which can cause cancer. In addition, hormone surges can increase the symptoms of hyperplasia. In this case, the spiral reduces the effect of estrogen on the endometrium, but at the same time does not prevent the hormone from having a positive effect on the work of the heart, blood vessels, urinary system, bone tissue, etc.
endometriosis
This disease is a direct consequence of a lack of progesterone against the background of an excess of estrogen. Mirena blocks the development of endometriosis, and also contributes to the subsidence of the disease. Levonorgestrel has a beneficial effect on the uterine mucosa, blocking the further spread of endometriosis foci and the risk of developing cancer. It can be noted a huge number of positive reviews about the Mirena spiral for endometriosis in premenopause without negative consequences for women's health.
Myoma
We note right away that with such a disease it is not always possible to use a spiral. Everything will depend on the characteristics of the tumor (location and size). Here, the agent significantly reduces the supply of nutrition to the tumor.
Bleeding
Mirena contains an analogue of progesterone, which can reduce the activity of bleeding and their volume. But its use is allowed only if the bleeding is not associated with cancer.
A change in the hormonal background always leads to a decrease in the body's defenses, which is why these diseases often occur precisely with the approach of menopause. Mirena and premenopause are connected in such a way that the spiral itself significantly reduces the risk of various pathologies due to the support of the vaginal microflora and the stabilization of hormonal balance.
The main indications and contraindications for use
Unfortunately, not every woman can use the tool. To begin with, it is worth noting that a prerequisite is the examination of the whole organism.
In this case, contraindications are:
- malignant tumors;
- breast oncology;
- bleeding associated with serious illness;
- individual intolerance to gestagens;
- vein thrombosis;
- inflammation of the pelvic organs;
- infection in the urinary system;
- endometritis;
- liver problems (hepatitis, cirrhosis);
- heart and kidney disease;
- recent abortion (three months ago).
Important! Any inflammatory pathology of the pelvic organs are indications for the removal of the spiral. In addition, intrauterine contraceptives are contraindicated at a high risk of infectious diseases (problems with immunity, lack of a permanent partner).
Despite the minimal effect of levonorgestrel on the functioning of the body, it is contraindicated in all cancers. Relatively contraindicated diseases include migraines, arterial hypertension, thrombophlebitis and diabetes mellitus. In these cases, the possibility of using an intrauterine hormonal contraceptive is determined by the doctor, but only after a comprehensive laboratory diagnosis.
Main indications for use:
- Contraception. The main purpose of the installation of the IUD remains the prevention of unwanted conception.
- Idiopathic menorrhagia. The IUD is used as an element of therapy only in the absence of hyperplastic processes in the uterine mucosa, as well as extragenital pathologies.
- Prevention of endometrial hyperplasia. It is used when prescribing estrogen replacement therapy when it is necessary to balance estrogens and progestins in the body.
- Profuse bleeding with no clear cause. After installing the spiral, or rather after 4 months, the amount of discharge should return to normal.
Side effects of the Mirena coil
It is worth noting that often side effects appear only in the first few months after the doctor has installed the system. Here you need to pay attention to the strength of their manifestation. If the side effects are minor, then the woman can continue to use the remedy, but this issue is resolved with the attending physician.
Among the side effects it is worth highlighting:
- migraine;
- headache;
- ectopic pregnancy;
- jumps in blood pressure;
- nausea;
- vomit;
- the appearance of excess weight;
- dizziness;
- allergic rashes;
- breast pain;
- unstable emotional state;
- irritability;
- insomnia.
These side effects most often appear only at the very beginning of using the remedy. Judging by the reviews, most women who have undergone a preliminary examination and installed a spiral with an experienced specialist do not suffer from side effects. , hot flashes and irritability disappear almost immediately.
Very rarely, the use of a spiral can cause:
- tumor development;
- stroke
- myocardial infarction;
- formation of cysts in the ovaries;
- jaundice.
Abundant discharge after the installation of the spiral
A certain number of women's reviews contain information about spotting after the installation of Mirena. During premenopause, the coil can cause spotting and spotting, but this is normal only in the first four months after the procedure.
Similarly, the female body adapts to changes and normalization of hormonal balance. In addition, in the first few months after the installation of the spiral, there is a significant risk of inflammatory processes. Therefore, with any complaints, you should consult a doctor to eliminate other causes of bleeding, even if there are no other painful symptoms.
As for the duration of bleeding, it is within five or seven days. But soon Mirena should reduce the abundance of secretions, gradually bringing them closer to normal.
For more information about , follow the link.
Possible side effects of Mirena
According to reviews and studies, the following consequences, although they appear very rarely, still take place:
- ectopic pregnancy. At risk are women who suffered from protracted infectious diseases and inflammatory processes. In this case, immediate surgical intervention is required. Symptoms of complications include dizziness, nausea, pain in the lower abdomen, delayed menstruation, pallor of the skin and general weakness.
- Penetration. Ingrown means in the walls of the uterus occurs very rarely. This is possible against the background of lactation, the recent birth of a child, or a non-standard location of the uterus.
- The fall of the Navy. Spiral fallout is quite common. The likelihood of this undesirable process increases during menstruation, and it can go unnoticed. Women are advised to immediately consult a doctor to remove the product and install a new system.
- Inflammatory processes and infectious diseases. High probability of development in the first month after the installation of the system. A woman needs to see a doctor who will prescribe treatment and decide whether the coil needs to be removed.
- Amenorrhea. Possible six months after using the IUD. The first thing to do here is to rule out pregnancy. Note that after removing the remedy, the cycle becomes normal if the cessation of menstruation is not caused by other reasons.
- . Occur in only 12% of patients (approximately). It is also worth noting that enlarged follicles independently acquire normal sizes after a few months.
Nothing more can be said about the consequences. This is due to the individuality of each case and the impossibility of collecting information about every woman who used Mirena. Note that this IUD with levonorgestrel is relatively safe, like all drugs containing hormones. In most cases, patients successfully endure all five years with this system, but subject to a responsible attitude to their health and passing the necessary examination.
Installation, removal and features of the spiral
It is worth noting that not all doctors have sufficient experience in installing the Mirena coil. A woman needs to find a specialist who has already worked with this type of IUD and knows the features of this procedure.
The product is available in sterile packaging that cannot be opened at home. This is done by a specialist immediately before installation. If the integrity of the package has been violated, then the installation of the spiral is not allowed. It is destroyed as medical waste. The same applies to the removal procedure, because the used spiral still contains hormones.
Examination before the installation of Mirena
Before buying a Mirena spiral, you should check your health in advance. First you need to visit the attending doctor, who will advise:
- examine the vagina;
- visit a mammologist;
- examine the microflora of the vagina;
- do an ultrasound of the genitals.
In addition, it is worth taking tests for hormones in order to accurately determine the state of the hormonal background of the body.
Features of using the tool for various purposes
There is a list of prescriptions for the date of installation of the IUD:
- For contraception. The procedure should be carried out in the first week of the cycle. But the replacement of the IUD is performed on any day of the menstrual cycle.
- After childbirth. Here you should wait for the complete involution of the uterus, but even with this factor, Mirena is contraindicated during the first six weeks after the birth of the child. In addition, if severe pain occurs, the pelvic organs should be examined to exclude perforations.
- To protect the endometrium. Can be used in conjunction with HRT. The procedure is carried out in the last days of the cycle. With amenorrhea, the coil can be installed at any time.
How often to visit the doctor after the installation of the spiral
Without fail, a woman must appear at a gynecologist's appointment no later than 3 months after the installation of Mirena. Then you can visit the doctor once a year, and if you have complaints, you should immediately go to the hospital.
If the doctor has allowed the installation of the spiral to a woman suffering from diabetes, then she needs to closely monitor the level of glucose in the blood. The fact is that levonorgestrel still negatively affects glucose tolerance. Any ailments should not be ignored.
Spiral Removal
The system is removed by gently pulling on specially designed threads using sterile forceps. Sometimes it is impossible to see the threads, then the doctor resorts to using a traction hook for safe extraction. In addition, in some cases, the specialist expands the cervical canal.
Important! The system is removed after five years of use when the patient feels normal. For any serious complaints, the IUD should be removed from the body immediately.
As for the re-installation of a new tool, the procedure can be carried out almost immediately. Here everything will depend on the monthly. When saving menstrual flow, the installation of a new system is carried out on the days of menstruation in order to eliminate the risk of fertilization of the egg.
The doctor should warn the patient that the insertion or removal of an intrauterine hormonal contraceptive may cause certain pain and bleeding. Particular caution should be shown to women with epilepsy and cervical stenosis. Syncope, bradycardia or convulsive seizures are possible here.
After Mirena is removed, the system is checked for integrity in order to exclude slippage of the hormonal cavity of the spiral. Once the physician confirms the integrity of the remedy, no further action is required.
What the reviews say
Mirena solves several women's problems at once. Premenopause brings some discomfort, which is associated not only with unpleasant symptoms, but also with the need to select the optimal contraceptive. Most women note the practicality of this tool.
Often, patients wonder if they will be able to become pregnant after removing the system. So, 80% of women were able to conceive a child (planned) in the first year after the removal of the IUD. In other cases, diseases interfered or pregnancy occurred a little later.
Of course, with the approach of menopause, many women no longer plan to have a child. It is important to carry out the installation of the spiral at the right time.
In fact, the reviews are contradictory. The main group of women is not satisfied with the unstable emotional background in the first month of using the IUD. But here you need to take into account the restructuring of the body, which is trying to get used to the changes and the influence of the hormone.
In addition, women note that the Mirena spiral is much more convenient than oral ones, which require a strict regimen. If we take the price of the system, then it ranges from 9-13 thousand rubles. With the expectation of a five-year period, you can save a good amount in contrast to spending on contraceptives.
The Mirena intrauterine hormonal contraceptive is a real find during premenopause, when the likelihood of conception remains, and the hormonal balance needs to be normalized. In addition, Mirena shows itself well together with estrogen-based HRT. It remains only to follow the recommendations and monitor your health in order to avoid possible consequences.
What is the Navy?
An intrauterine device (IUD) is a small plastic device inserted into the uterus to prevent pregnancy. Modern models are made of plastic and contain metal or a drug (copper, silver, gold, or progestin).
What types of intrauterine devices exist?
Modern intrauterine devices are small plastic or plastic-metal devices. Their dimensions reach approximately 3x4 cm. Usually, copper, silver or gold is used to make spirals.
The appearance of most spirals resembles the shape of the letter "T". The T-shaped form of spirals is the most physiological, as it corresponds to the shape of the uterine cavity.
1-27 - variants of spiral shapes. One thing in common is that they all play the role of a “foreign body”.
28 - Lipps loop. Spirals of just this form were common in the USSR. They were produced in three sizes. It was very inconvenient to insert them, since the disposable conductor, which is now attached to each spiral and is made of a transparent polymer, was absent, a metal conductor was used, with which it was difficult to control the insertion process. Therefore, complications such as perforation (perforation) of the uterus occurred more often than at present.
29-32 - T-shaped spirals or "teshki" - modern modifications of metal-containing spirals. 33 - also "teshka". An extremely convenient insertion and removal option. Due to the fact that the "shoulders" are drawn into the conductor, the manipulation is almost painless.
34-36 - multiloads or umbrella spirals. They perform their function perfectly, however, when they are inserted and removed, the cervical canal is often injured. There are also cases of defragmentation (when the "shoulders" come off the rod).

What are the best spirals?
There is no perfect spiral that would suit everyone without exception. This issue is decided by the gynecologist individually for each woman.
How does the Navy work?
The action of the IUD consists of several factors:
- thickening of cervical mucus (i.e. cervical mucus), which makes it difficult for sperm to enter the uterine cavity;
- a change in the properties of the endometrium (mucous cavity of the uterus), which makes it unsuitable for the introduction () of the egg;
- due to the effect of a foreign body, the peristalsis of the fallopian tubes increases, which accelerates the passage of the egg through them, during which time it does not have time to reach the degree of maturity necessary for implantation.
How to use the Navy?
During a short, simple procedure, the doctor inserts an IUD into the uterine cavity.
If you want to make sure that the IUD is in the uterus, you can insert your fingers into the vagina and feel for the plastic threads attached to the IUD.
If pregnancy is desired, you can ask your doctor to remove the IUD. Your ability to conceive will be restored immediately.
What are the advantages of this method of contraception?
- High efficiency, comparable to the effectiveness of hormonal contraceptives. To some extent, IUDs are more reliable than hormonal pills, since there is no danger of missing pills. When using a spiral on the part of a woman, absolutely no action is required to maintain the contraceptive effect, and, therefore, any possibility of error or accident is excluded.
- Provides protection from pregnancy for a long time (from 5 to 7 years, depending on the type of IUD).
- Application is not associated with sexual intercourse.
- Compared to all other methods of contraception, the intrauterine device is the cheapest contraceptive method. Despite the fact that the cost of one spiral is many times higher than the cost of one package of contraceptive pills or one regular package of condoms, recalculating its cost for 5 years (the usual period of wearing one spiral) shows its undeniable superiority in economic terms.
- Unlike birth control pills, metal or plastic coils that do not contain hormones have absolutely no general "hormonal" effect on the body, which (in some cases justifiably) many women fear. For this reason, IUDs, which do not contain hormones, are recommended as the primary contraception for women over 35 years of age, with active smoking or other conditions that make it impossible to use birth control pills, but require a very high level of protection against unwanted pregnancy.
- The spiral is not felt at all during intercourse and does not interfere with partners.
What are the disadvantages of the method?
- Unlike, for example, a condom, the IUD does not protect against sexually transmitted diseases.
- Insertion and removal of the IUD is performed only by a doctor.
- After the installation of the IUD, side effects are possible.
What can be side effects?
The installation of an intrauterine device can lead to some complications, however, not all women who wear the device develop complications. Modern research shows that more than 95% of women who wear the IUD find them to be very good and convenient methods of contraception and are satisfied with their choice.
During or immediately after installation (for all types of coils):
- Perforation of the uterus (extremely rare);
- Development of endometritis (very rare).
During the entire period of use of the spiral (for metal-containing or plastic spirals without hormones):
- Your periods may become more heavy and painful.
- There may be bloody discharge from the vagina between periods.
- Women with sexually transmitted infections (STIs) are at greater risk of developing pelvic inflammatory disease.
- In some cases, expulsion (complete or incomplete prolapse) of the IUD from the uterus is possible.
When is it not possible to install an IUD?
Contraindications for the installation of the spiral are determined by the gynecologist. Only a specialist can determine exactly how safe the installation of a spiral is in your case.
An IUD cannot be installed if:
- You think you may be pregnant.
- You have more than one sexual partner.
- There is an acute form of inflammatory diseases of the cervix or pelvic organs, including STIs.
- During the last three months, inflammatory diseases of the pelvic organs were observed.
- Vaginal bleeding of unknown origin is observed.
- There is a fast-growing, also, if the myomatous node deforms the uterine cavity.
- Has cancer of the genitals.
- There is a severe form of anemia (hemoglobin<90 г/л).
There is a high risk of contracting an STI.
How to prepare for the installation of the spiral?
The procedure for inserting an intrauterine device cannot be performed in the presence of any genital infections or other gynecological diseases, therefore, before installing the device, the gynecologist performs a general gynecological examination, taking swabs for the degree of purity of the vagina and a smear for oncocytology, in some cases it is necessary to conduct an ultrasound scan. research. If any infections or gynecological diseases are detected, the insertion of the IUD is postponed until the cure.
Before installing the coil:

How to behave after the introduction of the spiral?
Within 7-10 days after the installation of the spiral, it is impossible:
- Have sex;
- Do douching;
After 7-10 days it is necessary to undergo a control examination.
Be sure to see your doctor early if:
- Within a few days of having the coil inserted, you develop a fever, very heavy vaginal bleeding, abdominal pain, or unusual, foul-smelling vaginal discharge.
- At any time after the insertion of the coil, you feel the coil in the vagina, notice that the coil has shifted or fallen out, and also if you notice a delay in menstruation by 3-4 weeks.
What is follow-up?
If menstruation has not occurred within 4-6 weeks after the insertion of the IUD, contact the consultation. You should contact the consultation for preventive examination at least once a year, and in case of questions or problems - at any time.
What symptoms should you see a doctor for?
Appeal is required if:
- You suspect pregnancy.
- You have heavy vaginal bleeding (more heavy or longer than usual).
- Are you experiencing severe abdominal pain?
- pain is felt and bleeding occurs during sexual contact.
- There are signs of infection, unusual vaginal discharge, chills, fever.
- You do not feel the IUDs or feel that they are shorter or longer than before.
Will there be any changes in the state of health and the nature of menstruation after the introduction of the IUD?
After installing spirals without hormones, the following changes are possible:
- Menstruation becomes more painful, somewhat longer and more plentiful than before the installation of the spiral.
- Spotting bloody discharge from the vagina may be observed, before or after menstruation, sometimes (less often) and in the interval between two periods.
- In some cases, due to increased menstrual pain and irregular bleeding, women are forced to stop using the coil and remove it before the expiration date.
After installing a spiral with hormones (in particular):
- Perhaps a significant shortening of menstruation and a decrease in the total amount of bleeding during menstruation.
- Approximately 20% of women using Mirena experience the complete disappearance of menstruation (amenorrhea). The restoration of menstruation in this case occurs only after the expiration of the spiral and its removal from the uterus. It is reliably known that the disappearance of menstruation in women using Mirena is not associated with inhibition of the ovaries (as when using oral contraceptives), but with the suppression of the development of the uterine mucosa with small doses of hormones.
- Despite the fact that many women are afraid of the disappearance of menstruation, there is no reason to consider it dangerous to health. Moreover, this effect of hormonal coils may even be beneficial, as it significantly improves a woman's quality of life and is an effective treatment for anemia, which many women have with long and heavy periods. IUD Mirena is just used to treat severe uterine bleeding.
How is an intrauterine device removed?
Removal is usually done after 5-7 years (depending on the modification of the spiral). But at the request of a woman, this can be done at any time. The reason may be the desire to have a pregnancy or the occurrence of any complications.
Before removal, the same examination is performed as before the introduction of the spiral. If necessary, sanitation (improvement) of the vagina is prescribed.
Removal is done by pulling the tendrils of the spiral at a certain angle. In some cases, for example, in the case of wearing a spiral over the prescribed period, the removal has to be carried out in stationary conditions, with anesthesia, by scraping the uterine cavity.
Within 4-5 days after the removal of the spiral, you can not:
- Have sex;
- Use vaginal tampons (regular pads can be used);
- Do douching;
- Take a bath, visit a sauna or bath (you can take a shower);
- Engage in heavy physical labor or intense physical exercise.
Removal of the IUD does not cause changes in the menstrual cycle. The exception is the Mirena Navy, when worn, there is no menstruation or poor cyclic spotting. After removal of Mirena, the menstrual cycle usually recovers in about 3-6 months.
Be sure to see your doctor if you develop a fever, very heavy vaginal bleeding, abdominal pain, or unusual, foul-smelling vaginal discharge within a few days of removing the coil.
Can I remove the coil myself?
Do not under any circumstances try this!
The coil is removed by pulling on the tendrils, which may break before it is removed. After that, the IUD can be removed only instrumentally and only with penetration into the uterine cavity. In addition, the mustache may break off at the moment the spiral passes through the cervical canal and it will get stuck there. Trust me, it hurts a lot.
To remove the spiral, be sure to consult a gynecologist.
How often should the coil be changed?
Metal-containing coils (for example, copper or gold) can be used for 5-7 years without replacement. Spirals with hormones (for example, Mirena) require replacement every 5 years.
Can I get pregnant if I am wearing an intrauterine device?
The occurrence of pregnancy in women wearing an intrauterine device is extremely rare. The probability of pregnancy in the case of using copper coils is no more than 8 chances out of 1000 during the year. When using spirals with hormones, the chance of getting pregnant is reduced to 1 chance in 1000 within a year.
At the same time, the course of pregnancy is no different from the course of a normal pregnancy, the spiral is located behind the fetal membranes, and during childbirth is born along with the afterbirth. Many women are afraid that the spiral can grow into the child's body. These fears are unfounded, since the child's body is surrounded by and. Pregnant women with a spiral are observed as threatened by.
The risk of pregnancy is greatly increased if the coil shifts or falls out of the uterus. This happens, especially often after menstruation, when the coil can be thrown out of the uterine cavity along with the rejected tissues.
In this regard, all women who wear a coil are advised to check for the presence of a coil in the uterus at least once a month by feeling for the tendrils of the coil in the depths of the vagina. If earlier you felt the antennae of the spiral well, but you can no longer find them, contact your gynecologist, as the spiral may have fallen out and you did not notice it.
How do I know if I'm pregnant while wearing a IUD?
If while wearing a non-hormonal intrauterine device, there is a delay in menstruation by more than 2-3 weeks, it is necessary to do a home pregnancy test and consult a doctor.
Can a spiral impair the ability to become pregnant in the future?
The contraceptive effect of intrauterine devices is easily reversible and disappears soon after they are removed from the uterine cavity. The probability of pregnancy within 1 year after the removal of the spiral reaches 96%.
Planning for pregnancy is possible as early as the next month after the removal of the intrauterine device.
Good afternoon
Due to the myomatous nodes formed during pregnancy, the gynecologist recommended installing the Mirena intrauterine hormonal system. Bought it in Ukraine. With a discount, the cost was 2365.50 UAH.
The packaging was tightly sealed to keep the contents sterile.
You won't even be able to read the instructions until you open the box.
Initially, I wanted to attach instructions to the review, but when I saw its scale, I realized that it was pointless. You can see for yourself:

Installation.
It took : Mirena spiral, gynecological examination set with a mirror.
I was seated on a chair, a mirror was installed, excess bloody discharge was blotted with cotton swabs, disinfected with an alcohol solution, the cervical canal was opened with long forceps, a spiral was installed, the excess part of the thread was cut off and the mirror was removed. All! It took no more than 5 minutes. But if we take into account the time when we went for sterile tongs and scissors, filled out the card, etc. It all lasted 20-25 minutes.
As such, there was no pain. It was a little hot from alcohol, and it was unpleasant when opening the cervical canal with forceps (but this is because I could not relax in any way).
It was a little scary to go to the toilet for the first time. But inside of me I absolutely do not feel anything foreign.
Do not live sexually for 10 days;
Do not lift weights, including a child, for at least 10 days (later it turned out that it is better not to lift anything at all ...);
Do not bathe in the bath for 10 days;
After 10 days, come for an inspection to check the correct installation.
Feelings after installing Mirena.
Self-hypnosis is a terrible thing! I constantly thought about the possible displacement of the spiral, it constantly seemed to me that I felt it touching the walls ... until I got distracted. My daughter got sick and not before. By chance, I remembered the intrauterine system (the child cannot be lifted). Then I realized that while I do not think about a foreign body, I do not feel it. Not at all.
I also noticed that a day after the installation, the pigmentation on the nipples increased a little, they became darker and stretched out like after feeding a child (although I turned off the guards more than 4 months ago). Then it passed.
Bloody discharge at the time of installation was very plentiful. Immediately after the procedure, they became scarce.
Throughout all 10 days, scanty spotting continued.
Re-inspection after 10 days.
It was a routine examination with a speculum. The doctor checked the presence of threads and the location of the spiral itself, asked about the sensations and the presence of discomfort. I had no complaints, so the next examination is scheduled in three months.
The withdrawals never stopped. The instructions indicate that the norm is up to three months. I also want to note that spotting does not go constantly, but periodically during the day. Enough pads for two or three drops.
After 22 days from the beginning of the cycle, the discharge intensified and acquired a more familiar color for menstruation. This went on for five days, then the intensity decreased again. I don't know what it was. Maybe menstruation is going on like this now, maybe something else. Further it will be seen.
The first sex after the installation of Mirena.
Naturally, no one was going to wait three months. Therefore, we decided to test the system on the 13th day. No one felt any foreign body. So there is no need to worry about this. But it’s better to spread the diaper…
Impressions and observations after the installation of the Mirena spiral.
And now let's talk about the specific disadvantages for me, which I was not ready for. This is a ban on lifting weights. Complete ban. And how is this even possible, having a one-year-old child??? And someone has two children ... As I was told, with muscle tension, the system can be pushed out of the uterus. Great! Nothing to say...
Of course, the first week I was completely replaced by my husband (sickness, bathing a child, walking, shopping, throwing garbage, etc.), but then I had to distribute responsibilities. After all, he needs to go to work sometime ... a month later, I already entered the usual mode. Of course, I try not to lift the winter stroller with the child, but otherwise everything is the same.
Also, the sex drive is completely gone. After giving birth, I’m already used to the fact that “appetite comes with eating”, but then it’s hard to swing at all ... Well, okay, there will be another reason to somehow diversify your sex life.😊
It's too early to talk about weight, only half a month has passed. My appetite hasn't increased, but soon the New Year holidays, my birthday... I'll try to control myself.😁
A month later and New Year's holidays - minus half a kilo. This makes me happy!))))
!!!UPDATE (04/16/2018)
For 10 days there were scanty spotting. For a week there was no discharge at all. Then they started again: for two days, barely noticeable, spotting, for 9 days, moderate, typical for menstruation, and again, slightly spotting, residual.
In total, periodic discharges took about 70 days.
After 3 months.
For two days there was a barely noticeable daub. After 10 days, spotting began, which lasted a little more than a week. At this time, I did ultrasound. It turned out that it was already the middle of the cycle, and those two days earlier were monthly ...
The next menstruation began according to the schedule day to day. The discharge lasted 5 days. Not plentiful, not painful (although there were tingling sensations in the area of the “acting” ovary, but quickly passed). There were no more pulling pains on the first day of the cycle. I'll save on spazmalgon))).
Myoma has noticeably decreased (almost twice), and the forming node has generally resolved. The gynecologist said that for now it is necessary to spend money on pads, and when the fibroids disappear, the spiral can be removed.
The attraction returned a month and a half after installation.
Spiral FEEL partner in some positions. I don't know how, but we do. Unpleasant sensations it does not deliver, according to the husband. And, to be completely frank, the male genital organ feels movement along some kind of foreign tube. P.S.: only the first months are felt)))
The weight stays the same. I’m thinking of losing weight by the summer ... some)).
After 9 months!!!
The fourth month after the installation of the spiral went perfectly! The cycle was clear, the discharge went on for 6 days (as before the spiral), there were no painful sensations.
BUT! Before starting the next cycle got chest pain, the mammary gland noticeably increased and a painful nodule appeared on the left. I started to google (it’s not destined to go to the doctor right away). According to the description, it looked like a cyst and it was said that there was nothing to worry about, they resolve themselves after the release of the egg, there was not a word about their connection with Mirena).
I am waiting for the next cycle .. A few days earlier, the discharge began, 10 days passed. The soreness in the chest disappeared, but the lump remained. I called the gynecologist. She said - it's prolactin increased, this happens after childbirth. Drink Mastodinon.
I bought Mastodinone, but decided to wait until the next cycle to get tested for prolactin levels. I waited... I waited... I waited... But I didn't get my period... I started buying up all the pregnancy tests I could find in stores - everything was negative.
The next step is a pelvic ultrasound. Result - OVARIAN CYST. I'm shocked. For some reason, I decided that the hormonal spiral would protect against such formations ... I don’t know where I got this from. I started to google again ... someone turn off the Internet for me! Nowhere did I find any mention that the Mirena intrauterine device causes the formation of cysts in the ovaries.
The test results for progesterone showed a good level of the hormone, TSH - also normal.
I went to the gynecologist. She canceled Mastodinon (which I never started taking) and prescribed Distreptase suppositories (for resorption of cysts), Amelotex suppositories (painkillers and anti-inflammatory) and Tazalok drops (to normalize hormonal levels). After the first menstruation, do a control ultrasound.
It's been a month and a half. The cycle never started. Again there were very painful seals in BOTH mammary glands. I - again to the gynecologist. She pointed to the ultrasound of the pelvis and mammary glands.
It's summer, holiday season. I found a mammologist in the regional oncology, and decided to do an ultrasound there. And... for good reason. Painful lumps in the chest growth of glandular tissue, it is treated by the same Tazalok with prolonged use. But they accidentally found a painless lump in the left breast, made a puncture and - TUMOR!
Conclusion: A proliferative form of mastopathy with foci of pronounced proliferation of the epithelium and stroma of the mammary gland.


Soon the operation ... And the treatment.
Ultrasound of the small pelvis was done in a private clinic. The cyst did not disappear after the treatment, new ones did not form either. There the doctor told me that Mirena intrauterine device very often leads to the formation of cysts in the ovaries! This is due to the fact that the progesterone hormone contained in it is secreted in large quantities and prevails over estrogen. The brain perceives this signal as if ovulation has already occurred and does not give a command to release the egg from the ovary. She stays there and grows into a cyst. Usually such cysts are small in size and resolve themselves, and later appear again. It's not scary, but you have to watch. that is why with the Mirena spiral, menstruation may not go at all.
Regarding the main reason why I installed the spiral - UTERINE MYOMA:
- A small (9.0x0.8 mm) incipient subserous-interstitial myomatous node has disappeared.
- A large (30.x25.0 mm) subserous-interstitial myomatous node - decreased in 9 months to 21.x19.0 mm, the walls thickened and it is considered "old", not dangerous to the body.
Thus, the spiral performs its main task. But according to the result - one heals, the other - cripples!
I won’t extract it yet, I’ll see if Tazalok helps to normalize the hormonal background. For my age, such a reaction to Mirena is rare. But I want you to be aware of the possible consequences as well.
That's all for me. This post will be updated as time goes by. Add to bookmarks so as not to lose 😉
Intrauterine contraceptive
Active substance
Levonorgestrel (micronized) (levonorgestrel)
Release form, composition and packaging
Intrauterine Therapy System (IUD) is a T-shaped levonorgestrel-releasing construct, placed in the conductor tube (conductor components: insertion tube, plunger, index ring, handle and slider). The IUD consists of a white or almost white hormonal elastomeric core placed on a T-shaped body and covered with an opaque membrane that regulates the release of levonorgestrel (20 µg/24 h). The T-body is provided with a loop at one end and two arms at the other; threads are attached to the loop to remove the system. The IUD is free from visible impurities.
Excipients: core made of polydimethylsiloxane elastomer; a membrane of polydimethylsiloxane elastomer containing silicon dioxide colloidal anhydrous 30-40% of the mass.
Other components: T-shaped polyethylene body containing 20-24% wt., a thin thread of brown polyethylene, dyed with iron oxide black ≤1% wt.
Delivery device: conductor - 1 pc.
Navy (1) - sterile blisters (1) - cardboard packs.
pharmachologic effect
Mirena is an intrauterine therapeutic system (IUD) that releases levonorgestrel and has mainly a local gestagenic effect. The progestogen (levonorgestrel) is released directly into the uterine cavity, which allows it to be used at an extremely low daily dose. High concentrations of levonorgestrel in the endometrium contribute to a decrease in the sensitivity of its estrogen and progesterone receptors, making the endometrium immune to estradiol and exerting a strong antiproliferative effect. When using Mirena, morphological changes in the endometrium and a weak local reaction to the presence of a foreign body in the uterus are observed. Increasing the viscosity of the cervical secretion prevents the penetration of sperm into the uterus. Mirena prevents fertilization due to inhibition of sperm motility and function in the uterus and fallopian tubes. Some women also experience suppression of ovulation.
Previous use of the drug Mirena does not affect the childbearing function. Approximately 80% of women who want to have a baby become pregnant within 12 months after the IUD is removed.
In the first months of using Mirena, due to the process of inhibition of endometrial proliferation, there may be an initial increase in spotting bloody discharge from the vagina. Following this, a pronounced suppression of endometrial proliferation leads to a decrease in the duration and volume of menstrual bleeding in women using Mirena. Scanty bleeding often transforms into oligo- or amenorrhea. At the same time, ovarian function and the concentration of estradiol in the blood remain normal.
Mirena can be used to treat idiopathic menorrhagia, i.e. menorrhagia in the absence of hyperplastic processes in the endometrium (endometrial cancer, metastatic lesions of the uterus, submucosal or large interstitial node of uterine fibroids, leading to deformation of the uterine cavity, adenomyosis), endometritis, extragenital diseases and conditions accompanied by severe hypocoagulation (for example, von Willebrand disease, severe thrombocytopenia ), the symptoms of which are menorrhagia.
After 3 months of using Mirena, menstrual blood loss in women with menorrhagia is reduced by 62-94% and by 71-95% after 6 months of use. When using Mirena for 2 years, the effectiveness of the drug (reducing menstrual blood loss) is comparable to surgical methods of treatment (ablation or resection of the endometrium). A less favorable response to treatment is possible with menorrhagia due to submucosal uterine myoma. Reducing menstrual blood loss reduces the risk of iron deficiency anemia. Mirena reduces the symptoms of dysmenorrhea.
The efficacy of Mirena in preventing endometrial hyperplasia during chronic estrogen therapy was equally high with both oral and transdermal estrogen.
Pharmacokinetics
Suction
After the introduction of the drug Mirena, levonorgestrel begins to be immediately released into the uterine cavity, as evidenced by the measurement data of its concentration in the blood plasma. The high local exposure of the drug in the uterine cavity, which is necessary for the local effect of Mirena on the endometrium, provides a high concentration gradient in the direction from the endometrium to the myometrium (the concentration of levonorgestrel in the endometrium exceeds its concentration in the myometrium by more than 100 times) and low concentrations of levonorgestrel in blood plasma (the concentration of levonorgestrel in the endometrium exceeds its concentration in blood plasma by more than 1000 times). The rate of release of levonorgestrel into the uterine cavity in vivo is initially approximately 20 mcg/day, and after 5 years decreases to 10 mcg/day.
After the introduction of the drug Mirena, levonorgestrel is detected in the blood plasma after 1 hour. Cmax is reached 2 weeks after the administration of the Mirena drug. In line with the declining release rate, the median plasma concentration of levonorgestrel in women of reproductive age with a body weight above 55 kg decreases from 206 pg / ml (25th-75th percentiles: 151 pg / ml - 264 pg / ml), determined by at 6 months, up to 194 pg/ml (146 pg/ml-266 pg/ml) at 12 months and up to 131 pg/ml (113 pg/ml-161 pg/ml) at 60 months.
Distribution
Levonorgestrel binds nonspecifically to serum and specifically to sex hormone-binding globulin (SHBG). About 1-2% of circulating levonorgestrel is present as the free steroid, while 42-62% is specifically bound to SHBG. During the use of Mirena, the concentration of SHBG decreases. Accordingly, the fraction associated with SHBG during the period of use of the drug Mirena decreases, and the free fraction increases. The average apparent V d of levonorgestrel is about 106 liters.
It has been shown that body weight and plasma SHBG concentration affect the systemic concentration of levonorgestrel. those. with low body weight and / or high concentration of SHBG, the concentration of levonorgestrel is higher. In women of reproductive age with low body weight (37-55 kg), the median plasma concentration of levonorgestrel is approximately 1.5 times higher.
In postmenopausal women who use Mirena simultaneously with the use of intravaginal or transdermal estrogen, the median plasma concentration of levonorgestrel decreases from 257 pg / ml (25th-75th percentile: 186 pg / ml - 326 pg / ml), determined at 12 months, up to 149 pg/ml (122 pg/ml-180 pg/ml) at 60 months. When Mirena is used concomitantly with oral estrogen therapy, the plasma concentration of levonorgestrel, determined after 12 months, increases to approximately 478 pg / ml (25th-75th percentile: 341 pg / ml - 655 pg / ml), which is due to induction synthesis of SHPG.
Metabolism
Levonorgestrel is largely metabolized. The main metabolites in plasma are unconjugated and conjugated forms of 3α, 5β-tetrahydrolevonorgestrel. Based on the results of in vitro and in vivo studies, the main isoenzyme involved in the metabolism of levonorgestrel is CYP3A4. The isoenzymes CYP2E1, CYP2C19 and CYP2C9 may also be involved in the metabolism of levonorgestrel, but to a lesser extent.
breeding
The total clearance of levonorgestrel from blood plasma is approximately 1 ml / min / kg. In unchanged form, levonorgestrel is excreted only in trace amounts. Metabolites are excreted through the intestines and kidneys with an excretion rate of approximately 1.77. T 1/2 in the terminal phase, represented mainly by metabolites, is about a day.
Linearity/Nonlinearity
The pharmacokinetics of levonorgestrel depends on the concentration of SHBG, which, in turn, is influenced by estrogens and androgens. When using Mirena, a decrease in the average concentration of SHBG by approximately 30% was observed, which was accompanied by a decrease in the concentration of levonorgestrel in the blood plasma. This indicates the non-linearity of the pharmacokinetics of levonorgestrel over time. Given the predominantly local action of Mirena, the effect of changes in systemic concentrations of levonorgestrel on the effectiveness of Mirena is unlikely.
Indications
- contraception;
- idiopathic menorrhagia;
- prevention of endometrial hyperplasia during estrogen replacement therapy.
Contraindications
- pregnancy or suspicion of it;
- inflammatory diseases of the pelvic organs (including recurrent);
- infections of the external genital organs;
- postpartum endometritis;
- septic abortion within the last 3 months;
- cervicitis;
- diseases accompanied by increased susceptibility to infections;
- cervical dysplasia;
- diagnosed or suspected malignant neoplasms of the uterus or cervix;
- progestogen-dependent tumors, incl. ;
- uterine bleeding of unknown etiology;
- congenital and acquired anomalies of the uterus, incl. fibromyomas leading to deformation of the uterine cavity;
- acute liver disease, liver tumors;
- age over 65 years (no studies have been conducted in this category of patients);
- Hypersensitivity to the components of the drug.
Carefully and only after consultation with a specialist should the drug be used in the following conditions:
- congenital heart defects or heart valve disease (in view of the risk of developing septic endocarditis);
- diabetes.
Consideration should be given to removing the system if any of the following conditions are present or first occur:
- migraine, focal migraine with asymmetric loss of vision or other symptoms indicating transient cerebral ischemia;
- Unusually severe headache
- jaundice;
- severe arterial hypertension;
- severe circulatory disorders, incl. stroke and myocardial infarction.
Dosage
Mirena is injected into the uterine cavity. Efficiency is maintained for 5 years.
The release rate of levonorgestrel in vivo at the beginning of use is approximately 20 μg / day and decreases after 5 years to approximately 10 μg / day. The average rate of release of levonorgestrel is approximately 14 mcg / day for up to 5 years.
The Mirena IUD can be used in women receiving oral or transdermal estrogen-only hormone replacement therapy (HRT).
With the correct installation of Mirena, carried out in accordance with the instructions for medical use, the Pearl index (an indicator reflecting the number of pregnancies in 100 women using a contraceptive during the year) is approximately 0.2% for 1 year. The cumulative rate, reflecting the number of pregnancies in 100 women using a contraceptive for 5 years, is 0.7%.
Rules for the use of the Navy
Mirena is supplied in a sterile package, which is opened only immediately before the installation of the IUD. Asepsis must be observed when handling an opened system. If the sterility of the packaging appears to be compromised, the IUD should be disposed of as medical waste. The same should be done with the IUD removed from the uterus, since it contains hormone residues.
Insertion, removal and replacement of the IUD
Before installation Mirena drug woman should be informed about the effectiveness, risks and side effects of this IUD. It is necessary to conduct a general and gynecological examination, including an examination of the pelvic organs and mammary glands, as well as an examination of a smear from the cervix. Pregnancy and sexually transmitted diseases should be excluded, and inflammatory diseases of the genital organs should be completely cured. Determine the position of the uterus and the size of its cavity. If it is necessary to visualize the uterus before the introduction of the Mirena IUD, an ultrasound of the pelvic organs should be performed. After a gynecological examination, a special instrument, the so-called vaginal mirror, is inserted into the vagina, and the cervix is treated with an antiseptic solution. Mirena is then injected into the uterus through a thin, flexible plastic tube. The correct location of the Mirena preparation in the bottom of the uterus is especially important, which ensures a uniform effect of the progestogen on the endometrium, prevents the expulsion of the IUD and creates conditions for its maximum effectiveness. Therefore, you should carefully follow the instructions for installing Mirena. Since the technique of insertion in the uterus of different IUDs is different, special attention should be paid to working out the correct technique for inserting a particular system. The woman may feel the insertion of the system, but it should not cause her much pain. Before the introduction, if necessary, you can apply local anesthesia of the cervix.
In some cases, patients may have cervical stenosis. Do not apply excessive force when administering Mirena to such patients.
Sometimes after the introduction of the IUD, pain, dizziness, sweating and pallor of the skin are noted. Women are advised to rest for some time after Mirena is administered. If these phenomena do not go away after a half-hour stay in a calm position, it is possible that the IUD is not positioned correctly. A gynecological examination must be performed; if necessary, the system is removed. In some women, the use of Mirena causes allergic skin reactions.
The woman should be re-examined 4-12 weeks after insertion, and then once a year or more often if clinically indicated.
In women of reproductive age Mirena should be inserted into the uterine cavity within 7 days from the onset of menstruation. Mirena can be replaced with a new IUD on any day of the menstrual cycle. IUD can also be installed immediately after an abortion in the first trimester of pregnancy in the absence of inflammatory diseases of the genital organs.
The use of an IUD is recommended for women with a history of at least one birth. Installation of the Navy Mirena in the postpartum period should be carried out only after the complete involution of the uterus, but not earlier than 6 weeks after birth. With prolonged subinvolution, it is necessary to exclude postpartum endometritis and postpone the decision to administer Mirena until the involution is completed. In the event of difficulty inserting an IUD and/or severe pain or bleeding during or after the procedure, a pelvic exam and ultrasound should be performed immediately to rule out perforation.
For the prevention of endometrial hyperplasia when conducting HRT with drugs containing only estrogen, in women with amenorrhea, Mirena can be installed at any time; in women with preserved menstruation, the installation is performed in the last days of menstrual bleeding or withdrawal bleeding.
Delete Mirena preparation by gently pulling on the threads captured by the forceps. If the threads are not visible and the system is in the uterine cavity, it can be removed using a traction hook to remove the IUD. This may require the expansion of the cervical canal.
The system should be removed 5 years after installation. If a woman wants to continue using the same method, a new system can be installed immediately after the previous one is removed.
If further contraception is needed, in women of childbearing age, removal of the IUD should be performed during menstruation, provided that the menstrual cycle is maintained. If a system is removed in the middle of a cycle and a woman has had sexual intercourse within the previous week, she is at risk of becoming pregnant, unless the new system was installed immediately after the old one was removed.
The insertion and removal of an IUD can be accompanied by some pain and bleeding. The procedure may cause syncope due to vasovagal reaction, bradycardia or seizures in patients with epilepsy, especially in patients with a predisposition to these conditions or in case of cervical stenosis.
After removing Mirena, the system should be checked for integrity. In case of difficulties with the removal of the IUD, isolated cases of slipping of the hormonal-elastomer core on the horizontal arms of the T-shaped body were noted, as a result of which they were hidden inside the core. Once the integrity of the IUD is confirmed, this situation does not require additional intervention. Limiters on the horizontal arms usually prevent the core from completely separating from the T-body.
Special patient groups
Children and teenagers Mirena is indicated only after the onset of menarche (establishment of the menstrual cycle).
women over the age of 65 therefore, the use of Mirena is not recommended for this category of patients.
Mirena is not a first choice drug for postmenopausal women under the age of 65 with severe uterine atrophy.
Mirena is contraindicated in women with acute diseases or tumors of the liver.
Mirena has not been studied in patients with impaired renal function.
Instructions for the introduction of the IUD
It is installed only by a doctor using sterile instruments.
Mirena is supplied with a guidewire in a sterile package that must not be opened prior to insertion.
Should not be re-sterilized. The IUD is for single use only. Mirena should not be used if the inner packaging is damaged or open. Mirena should not be installed after the month and year indicated on the package.
Before installation, you should read the information on the use of Mirena.
Preparation for the introduction
1. Conduct a gynecological examination to determine the size and position of the uterus and to exclude any signs of acute inflammatory diseases of the genital organs, pregnancy or other gynecological contraindications for the installation of Mirena.
2. The cervix should be visualized with the help of mirrors and the cervix and vagina should be completely treated with an antiseptic solution.
3. If necessary, use the help of an assistant.
4. Grab the anterior lip of the cervix with forceps. Straighten the cervical canal by gentle traction with forceps. The forceps must be in this position during the entire time of insertion of the Mirena preparation to ensure gentle traction of the cervix towards the inserted instrument.
5. Carefully moving the uterine probe through the cavity to the bottom of the uterus, determine the direction of the cervical canal and the depth of the uterine cavity (the distance from the external os to the bottom of the uterus), exclude septa in the uterine cavity, synechia and submucosal fibroma. If the cervical canal is too narrow, widening of the canal is recommended and pain medication/paracervical block may be used.
Introduction
1. Open the sterile package. After that, all manipulations should be carried out using sterile instruments and sterile gloves.
2. Move the slider forward at the very distant position in order to draw the IUD into the guide tube.
You should not move the slider in a downward direction, because. this may lead to premature release of Mirena. If this happens, the system will not be able to be placed inside the conductor again.
3. While holding the slider in the farthest position, set upper edge index ring in accordance with the measured probe distance from the external pharynx to the bottom of the uterus.
4. Keep holding the slider in the farthest position, you should advance the conductor carefully through the cervical canal into the uterus until the index ring is about 1.5-2 cm from the cervix.
Do not push the conductor with force. If necessary, expand the cervical canal.
5. Holding the conductor still, move the slider to the mark to open the horizontal shoulders of the Mirena preparation. You should wait 5-10 seconds until the horizontal hangers are fully opened.
6. Gently push the conductor inwards until index ring will not come into contact with the cervix. Mirena should now be in the fundal position.
7. Holding the conductor in the same position, release the Mirena preparation, moving the slider as far down as possible. While holding the slider in the same position, carefully remove the conductor by pulling on it. Cut the threads so that their length is 2-3 cm from the external os of the uterus.
If the doctor has doubts that the system is installed correctly, the position of Mirena should be checked, for example, using ultrasound or, if necessary, remove the system and insert a new, sterile system. The system should be removed if it is not completely in the uterine cavity. The remote system must not be reused.
Removal/replacement of Mirena
Before removing / replacing Mirena, read the instructions for use of Mirena.
The Mirena preparation is removed by gently pulling on the threads grasped by the forceps.
The doctor can install a new Mirena system immediately after removing the old one.
Side effects
In most women, after the installation of Mirena, a change in the nature of cyclic bleeding occurs. During the first 90 days of using Mirena, an increase in the duration of bleeding is noted by 22% of women, and irregular bleeding occurs in 67% of women, the frequency of these phenomena decreases to 3% and 19%, respectively, by the end of the first year of its use. At the same time, amenorrhea develops in 0%, and rare bleeding in 11% of patients during the first 90 days of use. By the end of the first year of use, the frequency of these phenomena increases to 16% and 57%, respectively.
When Mirena is used in combination with long-term estrogen replacement therapy in most women, cyclic bleeding gradually stops during the first year of use.
The following are data on the incidence of adverse drug reactions that have been reported with Mirena. Determining the frequency of adverse reactions: very often (≥1/10), often (from ≥1/100 to< 1/10), нечасто (от ≥1/1000 до <1/100), редко (от ≥1/10 000 до <1/1000) и с неизвестной частотой. Hежелательные реакции представлены по классам системы органов согласно MedDRA . Данные по частоте отражают приблизительную частоту возникновения нежелательных реакций, зарегистрированных в ходе клинических исследований препарата Мирена по показаниям "Контрацепция" и "Идиопатическая меноррагия" с участием 5091 женщин.
Adverse reactions reported during clinical trials of Mirena for the indication "Prevention of endometrial hyperplasia during estrogen replacement therapy" (involving 514 women) were observed with the same frequency, except for cases indicated by footnotes (*, **).
| Often | Often | Infrequently | Rarely | Frequency unknown |
| From the side of the immune system | ||||
| Hypersensitivity to the drug or a component of the drug, including rash, urticaria and angioedema | ||||
| Mental disorders | ||||
| Depressed mood Depression |
||||
| From the side of the nervous system | ||||
| Headache | Migraine | |||
| From the digestive system | ||||
| Abdominal/pelvic pain | Nausea | |||
| From the skin and subcutaneous tissues | ||||
| acne hirsutism |
Alopecia Itching Eczema Skin hyperpigmentation |
|||
| From the musculoskeletal system | ||||
| Backache** | ||||
| From the genital organs and mammary gland | ||||
| Changes in the volume of blood loss, including an increase and decrease in the intensity of bleeding, "spotting" spotting, oligomenorrhea and amenorrhea Vulvovaginitis* Discharge from the genital tract* |
Pelvic infections ovarian cysts Dysmenorrhea Breast pain** Breast engorgement IUD expulsion (full or partial) |
Uterine perforation (including penetration) *** | ||
| Laboratory and instrumental data | ||||
| Elevated blood pressure | ||||
* "Often" according to the indication "Prevention of endometrial hyperplasia during estrogen replacement therapy".
** "Very common" for the indication "Prevention of endometrial hyperplasia during estrogen replacement therapy".
*** This frequency is based on data from clinical studies that did not include women who were breastfeeding. In a large prospective, comparative, non-interventional cohort study of women using an IUD, uterine perforation in women who were breastfeeding or who had an IUD inserted up to 36 weeks postpartum was reported with an "infrequent" frequency.
MedDRA terminology is used in most cases to describe certain reactions, their synonyms, and related conditions.
Additional Information
If a woman with an established Mirena drug becomes pregnant, the relative risk of ectopic pregnancy increases.
The partner can feel the threads during intercourse.
The risk of breast cancer when Mirena is used for the indication "Prevention of endometrial hyperplasia during estrogen replacement therapy" is unknown. Cases of breast cancer have been reported (frequency unknown).
The following adverse reactions have been reported in connection with the insertion or removal of Mirena: pain during the procedure, bleeding during the procedure, insertion-related vasovagal reaction accompanied by dizziness or fainting. The procedure can provoke an epileptic seizure in patients suffering from epilepsy.
infection
Cases of sepsis (including group A streptococcal sepsis) have been reported following IUD insertion.
Overdose
With this method of application, an overdose is impossible.
drug interaction
It is possible to increase the metabolism of gestagens with the simultaneous use of substances that are enzyme inducers, especially isoenzymes of the cytochrome P450 system involved in the metabolism of drugs, such as anticonvulsants (for example, phenytoin, carbamazepine) and agents for the treatment of infections (for example, rifampicin, rifabutin, nevirapine, efavirenz). The effect of these drugs on the effectiveness of the drug Mirena is unknown, but it is assumed that it is not significant, since Mirena has a mainly local effect.
special instructions
Before installing Mirena, pathological processes in the endometrium should be excluded, since irregular bleeding / spotting is often noted in the first months of its use. Pathological processes in the endometrium should also be excluded if bleeding occurs after the start of estrogen replacement therapy in a woman who continues to use Mirena, previously prescribed for contraception. Appropriate diagnostic measures should also be taken when irregular bleeding develops during long-term treatment.
Mirena is not used for postcoital contraception.
Mirena should be used with caution in women with congenital or acquired valvular heart disease, bearing in mind the risk of septic endocarditis. When inserting or removing an IUD, these patients should be given antibiotics for prophylaxis.
Levonorgestrel in low doses can affect tolerance to, and therefore its plasma concentration should be regularly monitored in women with diabetes using Mirena. As a rule, dose adjustment of hypoglycemic drugs is not required.
Some manifestations of polyposis or endometrial cancer may be masked by irregular bleeding. In such cases, additional examination is necessary to clarify the diagnosis.
The use of intrauterine contraception is preferred in women who have given birth. IUD Mirenana should be considered as the method of choice in young nulliparous women and should be used only if it is impossible to use other effective methods of contraception. IUD Mirenana should be considered as the method of first choice in postmenopausal women with severe uterine atrophy.
Available data indicate that the use of Mirena does not increase the risk of developing breast cancer in postmenopausal women under the age of 50 years. Due to the limited data obtained during the Mirena study for the indication "Prevention of endometrial hyperplasia during estrogen replacement therapy", the risk of breast cancer when Mirena is used for this indication cannot be confirmed or refuted.
Oligo- and amenorrhea
Oligo- and amenorrhea in women of childbearing age develops gradually, in approximately 57% and 16% of cases by the end of the first year of using Mirena, respectively. If menstruation is absent within 6 weeks after the start of the last menstruation, pregnancy should be excluded. Repeat pregnancy tests for amenorrhea are not necessary unless there are other signs of pregnancy.
When Mirena is used in combination with permanent estrogen replacement therapy, most women gradually develop amenorrhea during the first year.
Inflammatory diseases of the pelvic organs
The guidewire helps protect Mirena from infection during insertion, and the Mirena injection device is specifically designed to minimize the risk of infection. Inflammatory diseases of the pelvic organs in women using intrauterine contraception are often caused by sexually transmitted infections. It has been established that the presence of multiple sexual partners is a risk factor for infections of the pelvic organs. Pelvic inflammatory disease can have serious consequences: it can impair fertility and increase the risk of ectopic pregnancy.
As with other gynecological or surgical procedures, severe infection or sepsis (including group A streptococcal sepsis) can develop after IUD insertion, although this is extremely rare.
With recurrent endometritis or inflammatory diseases of the pelvic organs, as well as with severe or acute infections that are resistant to treatment for several days, Mirena should be removed. If a woman has persistent pain in the lower abdomen, chills, fever, pain associated with sexual intercourse (dyspareunia), prolonged or heavy spotting/bleeding from the vagina, a change in the nature of the discharge from the vagina, you should immediately consult a doctor. Severe pain or fever that occurs shortly after IUD insertion may indicate a severe infection that needs to be treated promptly. Even in cases where only a few symptoms indicate the possibility of infection, bacteriological examination and monitoring are indicated.
Expulsion
Possible signs of partial or complete expulsion of any IUD are bleeding and pain. Contractions of the muscles of the uterus during menstruation sometimes lead to displacement of the IUD or even to pushing it out of the uterus, which leads to the termination of the contraceptive effect. Partial expulsion may reduce the effectiveness of Mirena. Since Mirena reduces menstrual blood loss, its increase may indicate the expulsion of the IUD. A woman is advised to check the threads with her fingers, for example, while taking a shower. If a woman finds signs of displacement or prolapse of the IUD or does not feel the threads, sexual intercourse or other methods of contraception should be avoided, and a doctor should be consulted as soon as possible.
If the position in the uterine cavity is incorrect, the IUD must be removed. At the same time, a new system can be installed.
It is necessary to explain to the woman how to check the threads of Mirena.
Perforation and penetration
Perforation or penetration of the body or cervix of the IUD is rare, mainly during insertion, and may reduce the effectiveness of Mirena. In these cases, the system should be removed. With a delay in diagnosing perforation and migration of the IUD, complications such as adhesions, peritonitis, intestinal obstruction, intestinal perforation, abscesses or erosion of adjacent internal organs can be observed.
In a large prospective comparative non-interventional cohort study in IUD users (n=61448 women), the incidence of perforations was 1.3 (95% CI: 1.1-1.6) per 1000 insertions in the entire study cohort; 1.4 (95% CI: 1.1-1.8) per 1000 injections in the Mirena study cohort and 1.1 (95% CI: 0.7-1.6) per 1000 injections in the copper IUD cohort.
The study demonstrated that both breastfeeding at the time of insertion and insertion up to 36 weeks postpartum were associated with an increased risk of perforation (see Table 1). These risk factors were independent of the type of IUD used.
Table 1. Perforation rate per 1000 insertions and hazard ratio stratified by breastfeeding and time postpartum at insertion (parous women, entire study cohort).
An increased risk of perforation with IUD insertion exists in women with fixed malposition of the uterus (retroversion and retroflexion).
Ectopic pregnancy
Women with a history of ectopic pregnancy, tubal surgery, or pelvic infection are at higher risk of ectopic pregnancy. The possibility of ectopic pregnancy should be considered in the case of lower abdominal pain, especially if it is combined with the cessation of menstruation, or when a woman with amenorrhea begins to bleed. The frequency of ectopic pregnancy when using Mirena is approximately 0.1% per year. In a large prospective comparative non-interventional cohort study with a follow-up period of 1 year, the incidence of ectopic pregnancy with Mirena was 0.02%. The absolute risk of ectopic pregnancy in women using Mirena is low. However, if a woman with an established Mirena drug becomes pregnant, the relative likelihood of an ectopic pregnancy is higher.
Loss of threads
If, during a gynecological examination, the threads for removing the IUD cannot be found in the cervical region, pregnancy must be excluded. The threads can be drawn into the uterine cavity or cervical canal and become visible again after the next menstruation. If pregnancy is excluded, the location of the threads can usually be determined using careful probing with an appropriate instrument. If the threads cannot be detected, perforation of the uterine wall or expulsion of the IUD from the uterine cavity is possible. To determine the correct location of the system, an ultrasound can be performed. If it is unavailable or unsuccessful, an X-ray examination is performed to determine the localization of the Mirena preparation.
ovarian cysts
Since the contraceptive effect of Mirena is mainly due to its local action, women of childbearing age usually experience ovulatory cycles with rupture of the follicles. Sometimes the atresia of the follicles is delayed, and their development can continue. These enlarged follicles are clinically indistinguishable from ovarian cysts. Ovarian cysts have been reported as an adverse reaction in approximately 7% of women using Mirena. In most cases, these follicles do not cause any symptoms, although sometimes they are accompanied by pain in the lower abdomen or pain during intercourse. As a rule, ovarian cysts disappear on their own within two to three months of observation. If this does not happen, it is recommended to continue monitoring with ultrasound, as well as carrying out therapeutic and diagnostic measures. In rare cases, it is necessary to resort to surgical intervention.
The use of Mirena in combination with estrogen replacement therapy
When using the drug Mirena in combination with estrogens, it is necessary to additionally take into account the information specified in the instructions for use of the corresponding estrogen.
Excipients contained in Mirena
The T-shaped base of the Mirena preparation contains barium sulfate, which becomes visible on x-ray.
It must be borne in mind that Mirena does not protect against HIV infection and other sexually transmitted diseases.
Influence on the ability to drive vehicles and control mechanisms
Not observed.
Additional information for patients
Regular checkups
The doctor should examine you 4-12 weeks after the insertion of the IUD, and then regular medical examinations are required at least once a year.
Consult your doctor as soon as possible if:
You no longer feel the threads in the vagina.
You can feel the bottom end of the system.
You assume you are pregnant.
You experience persistent abdominal pain, fever, or a change in your normal vaginal discharge.
You or your partner experience pain during intercourse.
You have noticed sudden changes in your menstrual cycle (for example, if you had few or no periods and then had persistent bleeding or pain, or if your periods became excessively heavy).
You have other medical problems such as migraine headache or severe recurring headache, sudden visual disturbances, jaundice, high blood pressure, or any of the other diseases and conditions listed in the "Contraindications" section.
What to do if you are planning a pregnancy or want to remove the drugMirenafor other reasons
Your doctor can easily remove the IUD at any time, after which pregnancy becomes possible. Usually, the removal is painless. After removal of the Mirena drug, reproductive function is restored.
When pregnancy is not desired, Mirena should be removed no later than day 7 of the menstrual cycle. If Mirena is removed later than the seventh day of the cycle, use barrier methods of contraception (for example, a condom) for at least 7 days before removing it. If there is no menstruation when using Mirena, 7 days before the removal of the IUD, you should start using barrier methods of contraception and continue their use until menstruation resumes. You can also install a new IUD immediately after removing the previous one; in this case, no additional measures of protection against pregnancy are required.
How long can Mirena be used
Mirena provides protection against pregnancy for 5 years, after which it should be removed. If you wish, you can install a new IUD after removing the old one.
Restoration of the ability to conceive (Is it possible to become pregnant after stopping the use of Mirena?)
Yes, you can. Once Mirena is removed, it will no longer interfere with your normal reproductive function. Pregnancy may occur during the first menstrual cycle after Mirena is removed
Effects on the menstrual cycle (Can Mirena affect your menstrual cycle?)
Mirena drug affects the menstrual cycle. Under its influence, menstruation can change and acquire the character of "smearing" discharge, become longer or shorter, flow with more abundant or less than usual bleeding, or stop altogether.
In the first 3-6 months after the installation of Mirena, many women experience, in addition to their normal menstruation, frequent spotting or scanty bleeding. In some cases, very heavy or prolonged bleeding is noted during this period. If you experience any of these symptoms, especially if they persist, tell your doctor.
It is most likely that with the use of Mirena, the number of days of bleeding and the amount of blood lost will gradually decrease every month. Some women eventually find that their periods have completely stopped. Since the amount of blood lost during menstruation with the use of Mirena usually decreases, most women experience an increase in hemoglobin in the blood.
After removing the system, the menstrual cycle is normalized.
No periods (Is it normal not to have periods?)
Yes, if you are using Mirena. If, after installing Mirena, you noted the disappearance of menstruation, this is due to the effect of the hormone on the uterine mucosa. There is no monthly thickening of the mucous membrane, therefore, it is not rejected during menstruation. This does not necessarily mean that you have reached menopause or that you are pregnant. The plasma concentration of your own hormones remains normal.
In fact, the absence of menstruation can be a big advantage for a woman's comfort.
How can you know you are pregnant
Pregnancy in women using Mirena, even if they do not have menstruation, is unlikely.
If you haven't had a period in 6 weeks and you're concerned about it, take a pregnancy test. If the result is negative, no further tests are needed unless you have other signs of pregnancy such as nausea, fatigue, or breast tenderness.
Can Mirena cause pain or discomfort?
Some women experience pain (similar to menstrual cramps) for the first 2-3 weeks after IUD insertion. If you feel severe pain, or if the pain continues for more than 3 weeks after the system was installed, contact your doctor or the hospital where you had Mirena installed.
Does Mirena affect sexual intercourse?
Neither you nor your partner should feel an IUD during intercourse. Otherwise, sexual intercourse should be avoided until your doctor is satisfied that the system is in the correct position.
How much time should elapse between the installation of Mirena and sexual intercourse
The best way to give your body a rest is to refrain from sexual intercourse for 24 hours after Mirena is inserted into the uterus. However, Mirena has a contraceptive effect from the moment of installation.
Can tampons be used
What happens if Mirena spontaneously passes out of the uterine cavity?
Very rarely, during menstruation, IUD expulsion from the uterine cavity can occur. An unusual increase in blood loss during menstrual bleeding may mean that Mirena has fallen out through the vagina. Partial expulsion of the IUD from the uterine cavity into the vagina is also possible (you and your partner may notice this during intercourse). With the complete or partial exit of Mirena from the uterus, its contraceptive effect immediately stops.
What signs can be used to judge that the Mirena drug is in place
You can check for yourself if the Mirena threads are in place after your period has ended. After the end of menstruation, carefully insert your finger into the vagina and feel for the threads at the end of it, near the entrance to the uterus (cervix).
Shouldn't be pulled threads, because You may accidentally pull Mirena out of your uterus. If you can't feel the threads, see your doctor.
Pregnancy and lactation
Pregnancy
The use of the drug Mirena is contraindicated in pregnancy or suspicion of it.
Pregnancy in women who have Mirena installed is extremely rare. But if the IUD falls out of the uterus, the woman is no longer protected from pregnancy and must use other methods of contraception before consulting a doctor.
During the use of Mirena, some women do not have menstrual bleeding. The absence of menstruation is not necessarily a sign of pregnancy. If a woman does not have periods, and at the same time there are other signs of pregnancy (nausea, fatigue, soreness of the mammary glands), then it is necessary to consult a doctor for examination and a pregnancy test.
If pregnancy occurs in a woman during the use of Mirena, it is recommended to remove the IUD, because. any IUD left in situ increases the risk of spontaneous abortion and preterm birth. Removing Mirena or probing the uterus can lead to spontaneous abortion. If careful removal of the intrauterine contraceptive is not possible, medical abortion should be discussed. If a woman wants to keep the pregnancy and the IUD cannot be removed, the patient should be informed about the possible risk of septic abortion in the second trimester of pregnancy, postpartum purulent-septic diseases that can be complicated by sepsis, septic shock and death, as well as the possible consequences of premature birth for the child. In such cases, the course of pregnancy should be carefully monitored. An ectopic pregnancy must be ruled out.
A woman should be explained that she should inform the doctor about all symptoms suggesting complications of pregnancy, in particular, the appearance of spastic pain in the lower abdomen, bleeding or bloody discharge from the vagina, and fever.
The hormone contained in the Mirena preparation is released into the uterine cavity. This means that the fetus is exposed to a relatively high local concentration of the hormone, although through the blood and the placental barrier the hormone enters it in small quantities. Due to intrauterine use and local action of the hormone, the possibility of a virilizing effect on the fetus must be taken into account. Due to the high contraceptive efficacy of Mirena, clinical experience related to pregnancy outcomes with its use is limited. However, the woman should be informed that at this point in time there is no evidence of congenital effects caused by the use of Mirena in cases of continuation of pregnancy until delivery without removal of the IUD.
breastfeeding period
Breastfeeding a child while using Mirena is not contraindicated. About 0.1% of the dose of levonorgestrel can enter the child's body during breastfeeding. However, it is unlikely that it poses a risk to the child at doses released into the uterine cavity after the installation of Mirena.
It is believed that the use of Mirena 6 weeks after birth does not adversely affect the growth and development of the child. Monotherapy with gestagens does not affect the quantity and quality of breast milk. Rare cases of uterine bleeding have been reported in women using Mirena during lactation.
Fertility
After the removal of the drug Mirena in women, fertility is restored.
For impaired liver function
Contraindicated in acute liver diseases, liver tumors.
Terms of dispensing from pharmacies
The drug is dispensed by prescription.
Terms and conditions of storage
The drug should be stored out of the reach of children, protected from light at a temperature not exceeding 30°C. Shelf life - 3 years.