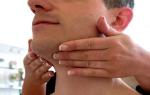
How to remove an inflamed lymph node in the neck. Treatment of inflamed lymph nodes in the neck at home. Herbal decoctions and tinctures
Enlarged lymph nodes are considered normal if they are painless, the skin over them has its usual color, and the body temperature does not rise. Treatment of lymph nodes at home should be carried out as prescribed by a doctor and under his supervision, since inflammation can serve as a symptom of a dangerous disease.
Functions of the lymphatic system
The human lymphatic system is made up of:
- accumulation of lymphatic tissue in the nasopharynx (tonsils);
- spleen;
- Bone marrow;
- thymus (thymus gland);
- accumulations of lymphoid tissue in the intestine;
- lymph nodes
The elements of the lymphatic system are connected to each other by ducts through which approximately 1.5 liters of lymph circulates - liquid connective tissue that provides protective, transport, and immune functions.
Normally, lymph freely penetrates into intercellular spaces, tissue cells and ducts, removes excess moisture, metabolic products, dead cells, and toxic substances that interfere with the functioning of internal organs. Lymphocytes are cells contained in lymph that neutralize viruses and bacteria.
On the neck, under the jaw, and in the armpits, lymphatic vessels form lymph nodes - clusters of tissue that perform barrier and protective functions.
In normal condition, the lymph nodes have an oval shape and a diameter of up to 1 cm. After cleansing in the lymph nodes, the blood enters the subclavian veins.
Why do lymph nodes enlarge in children?
In childhood, quite often the lymph nodes in the neck can be enlarged, but, at the same time, there is no inflammation.
Pay attention to the health of the child and consult a pediatrician if:
- Palpation causes pain, swelling is felt;
- The body temperature rises;
- The skin in the lymph node area is red and hot.
Inflammation of the lymph nodes indicates inflammatory processes in the nasopharynx, oral cavity, and nasal sinuses. The initial diagnosis consists in examining the child by a specialist and a general blood test.
Why do cervical lymph nodes become inflamed?

Lymphadenitis– inflammation of one or more lymph nodes located nearby.
Lymph nodes are enlarged, painful, the skin is hyperemic, general health worsens, and body temperature rises. The inflammatory process is the body’s response to a viral infection of acute respiratory infections, influenza, pharyngitis, herpes. Toxins produced by the virus enter the lymph nodes through the bloodstream and lead to the development of inflammation.
Bacteria and fungi can enter the bloodstream through blood, microtraumas, and cuts; in some cases, the infection is of a mixed nature.
A bacterial infection requires appropriate treatment - antibiotics. Symptomatically inflamed lymph nodes are treated with heat - compresses and heating pads relieve swelling and pain.
If inflammation lasts more than 14 days, you should undergo a full examination to exclude the possibility of malignant neoplasms.
Prevention of inflammation

To prevent inflammation, the lymphatic system needs regular cleaning: removal of metabolic products, toxins, protein fragments, starchy compounds. Their accumulation is facilitated by poor nutrition, unfavorable environmental conditions, and stress.
Slowing metabolism leads to fluid retention in tissues and swelling.
Pathological processes in the body are evidenced by frequent colds, chronic rhinitis, proliferation of lymphatic tissue in the nasopharynx, inflammation, etc.
Promotes liver and kidneys - the organs that take the brunt.
- Freshly squeezed citrus juices – lemon and orange – help cleanse the lymph. The high content of vitamin C stimulates the immune system;
- The removal of toxins is facilitated by a sauna, steam bath, hot baths with baking soda. It should be taken into account that these procedures have contraindications.
Folk remedies for treating inflamed lymph nodes

- A decoction of pine needles is rich in vitamin C, stimulates increased lymph flow and increases performance. To prepare it, 1 tbsp. l. Wash young pine needles, add ½ liter of cold water and cook over low heat for 20 minutes. then cool, strain, take the hot decoction three times a day, 0.1 liter on an empty stomach;
- Fresh beets, crushed to a pulpy state, are squeezed out, wrapped in several layers of gauze and applied to the lymph nodes in the form of a warm compress 2-3 times a day for 30 minutes;
- drink ½ tbsp on an empty stomach. At the initial stage of treatment, it can cause a sharp decrease in blood pressure, weakness, and dizziness. When such symptoms appear, the juice is diluted with warm boiled water 1:1. During treatment, it is recommended to avoid acidic foods and foods that contain yeast. For kidney diseases, urolithiasis, increased stomach acidity, beetroot juice is contraindicated;
- 2 tbsp. l. black currant leaves pour 0.2 liters of boiling water, leave for 15-20 minutes, strain, take 1/3 tbsp. 3 times a day. The drug is recommended for the treatment of lymph node tuberculosis;
- leaves, 2 tbsp. l., pour 0.2 liters of boiling water, leave for five minutes, put on low heat, without bringing to a boil, simmer for 2 minutes, remove, cool, strain. Take 1 tbsp 3 times a day on an empty stomach. l., the product can be used as warm lotions on the area of inflammation.
Sage is contraindicated for people with thyroid dysfunction, low blood pressure, kidney disease, pregnant and lactating women.
100 jumps technique - exercises for inflammation of the lymph nodes
But still, the most common cause of enlarged and inflamed lymph nodes is improper circulation and stagnation of lymph in the body. Swelling, excess weight - all these are also sad consequences of disruption of this process. How to fix everything? This will be discussed.
To get your lymphatic system to work properly and lymph to circulate as it should, you will need lymphatic drainage techniques.
One of the simplest and most effective - jumping in place. This exercise not only makes the lymphatic system work well, but also helps eliminate swelling in the legs and face.
What do we have to do? Everything here is simple to the point of banality. Stand on your toes, practically without lifting your toes from the floor, and perform small jumps.
No need to jump high. The jumps should be fast and much lower than when you jump rope. Women can support their chests with their arms bent at the elbows when performing the exercise.

Every morning you need to perform 100 jumps. If you feel discomfort during the exercise, stop at this number of jumps for a while and increase it gradually. The stomach should be pulled in throughout the entire exercise.
Make sure that there is no tension in the spine. This exercise will help disperse lymph throughout the system and prevent its stagnation.
Now do it exercise to help relieve swelling in the legs. The same 100 jumps, only with your heels hitting the threshold. You will need a threshold or other surface that rises 5 cm above the floor (book, balcony threshold). You stand on your toes and perform 100 jumps with your heels. Make small and quick jumps, carefully and without strain.
These exercises are recommended for everyone. People who lead a sedentary lifestyle and abuse alcohol and fatty foods especially suffer from lymph stagnation. And also for women, because the bra interferes with the normal outflow of lymph.
Agree, there is nothing complicated in this exercise. But thanks to it, you can ensure healthy lymph flow and, as a result, get rid of excess weight and. To me, it sounds very attractive, it’s worth a try!
An increase in the lymph nodes of the neck - lymphadenitis, they always signal the onset of the inflammatory process. This happens against the background of colds, including long-term ones, with a sharp decrease in the body's immunity. It is important to properly treat the lymph nodes in the neck so as not to face even more serious consequences.
Why are the lymph nodes in the neck enlarged and inflamed?
Being actively attacked by pathogenic viruses and bacteria, the body may not be able to cope with them. The immune system fails, and the lymph nodes begin to increase. The process can happen very quickly: in a few hours, the lymph nodes in the neck can swell up to the size of a quail egg. The lymphatic glands of the neck are close to the head, the brain, which is fraught with very negative consequences for the movement of the infection.
All pathogenic microorganisms are delivered by the lymph flow to the node, where the viruses are destroyed. With a weakened immune system, the lymph nodes can not cope with the amount of work, they begin to increase in size due to the resulting overload and inflammation. Factors affecting the enlargement of the lymph nodes of the neck:
- oncological diseases;
- tuberculosis;
- syphilis;
- infectious bacterial inflammation of the throat, oral cavity - tonsillitis, flux;
- purulent swelling of the inner ear - otitis;
- influenza, pneumonia (right, left, bilateral);
- changes in the functioning of the endocrine organs, more often the thyroid gland;
- frequent, uncontrolled use of alcoholic beverages.
Symptoms that will help you understand that the lymph nodes in the neck are in the stage of inflammation:
- soreness and discomfort in the area from the chin to the auricles;
- the appearance of bulges in places where the lymph nodes are located
- difficulty turning the head;
- body temperature with an increase to 37.8 C;
- general weakness, rapid fatigue, accompanied by severe headache.
Which doctor treats lymph nodes
To determine the source of the infection that has arisen and how to treat the lymph nodes in the neck so that the result of recovery comes as soon as possible, you need to go to the therapist initially. After a tactile examination of the submandibular region on the right and left, a number of laboratory blood tests, the doctor, based on their results, will be able to determine the diagnosis of lymphadenopathy. In the event of more serious situations than the usual suspected cold, it is recommended to consult an immunologist, an infectious disease specialist, an endocrinologist, an otolaryngologist, an oncologist.
How to treat lymphadenitis on the neck

The correct approach to the question of how to treat lymphadenitis determines the time spent on restoring health. Comprehensive treatment prescribed after a detailed examination and an accurate diagnosis will be more beneficial. The time after which the size of the lymph node returns to normal depends on the severity of the disease and the time that has passed since the first symptoms. It is important to remove the cause that provoked inflammation of the lymph nodes in the neck.
Drug therapy
In order to stop the rate of infection, the doctor prescribes broad-spectrum antibiotics of the tetracycline group, which are sold in pharmacies by prescription. Treatment with drugs requires at least two weeks. For treatment, antibiotics have proven themselves well for inflammation of the lymph nodes of the neck:
- Amoxiclav.
- Ampicillin.
- Oracillin.
- Amoxicillin.
- Flemoxin.
- Ceftriaxone.
Auxiliary medicines to enhance the effect of antibiotic exposure, a professional physician will definitely prescribe:
- Antifungal drugs:
- Clotrimazole.
- Diflucan.
- Ketoconazole.
2. Antihistamines that reduce the risk of an allergic reaction:
- Cetirizine.
- Eden.
- Diazolin.
- Tavegil.
- Suprastin.
3. Immunomodulatory agents to increase the body's resistance to diseases:
- Immunal.
- Echinacea tincture.
- Ginseng tincture.
- Eleutherococcus.
- Viferon.
- Interferon.
- Arbidol.
- Amiksin.
4. Vitamin complexes, with the obligatory inclusion of vitamin C, minerals to maintain immunity.
Physiotherapy procedures

How to treat inflammation of the lymph nodes with the help of physiotherapy, the attending physician should tell in detail. Any actions that have a warming effect on the neck are strictly prohibited. With an increase in temperature in the lymph nodes, an active spread of infection occurs, which can result in blood poisoning. For the treatment of inflamed enlarged lymph nodes in the neck that do not have oncological prerequisites, the following procedures are suitable:
- phonophoresis;
- laser radiation.
Folk remedies and herbs

There are many ways to treat lymph nodes in the neck with the help of traditional medicine in combination with drugs. Here are some recipes that give good results when used at home:
- Grind yarrow leaves, add a little honey. Apply as an ointment to enlarged lymph nodes in the neck area. In addition, you can take one tablespoon of the juice of this plant daily.
- Collection of herbs of pharmaceutical chamomile, mint, calendula, pour hot water and insist. Use for drinking and gargling.
- A decoction of the echinacea plant, taken every day, will give strength and speed up recovery. Dried root 6 tablespoons pour water (500 ml) and bring to a boil over low heat.
- Golden root, which has antiseptic properties, will help cure an enlarged lymph node in the neck. Pour the plant in a frayed state (one spoonful) with boiling water (one glass) - the norm for one day. It is recommended to follow the advice - to drink fermented milk products in parallel.
- In equal proportions, take dried calendula flowers, wormwood grass, blackcurrant leaves with a total volume of 3 tablespoons, which are poured into 1.5 liters of boiling water. The infused drink is used as a tonic tea.
- Horsetail at the rate of one spoon per 230 ml of boiled water, insist until the grass settles to the bottom. Drink several times a day, 2 teaspoons with an increase in the lymph nodes of the neck.
What to do if the lymph node in the child's neck is inflamed

Children who do not yet have a stable immune system in their bodies develop lymphadenitis much more often than adults. At the first signs of inflammation of the neck area, it is worthwhile to urgently visit a medical facility, not forgetting the condition that it is forbidden to heat the lymph nodes. The doctor, having examined, will tell you how to treat the lymph nodes in the child's neck. It is important not to miss the moment of the initial stage of the disease. The main reason that can provoke inflammation of the lymph nodes of the neck are frequent tonsillitis, tonsillitis, untimely treatment of dental caries.
Disease prevention
Knowing how to treat enlarged lymph nodes in the neck is good, but it is better to prevent the occurrence of a dangerous disease by observing preventive measures. This will require simple but effective methods to increase immunity by hardening the body, eating a sufficient amount of vegetables and fruits containing vitamins, especially C and group B.
By avoiding hypothermia regardless of the time of year, it is possible to reduce the risk of colds. Inflammation of the lymph nodes of the neck can be avoided if you do not ignore regular medical examinations with a careful examination of specialists in various fields, which will help identify emerging diseases at an early stage. In these cases, the treatment will be quick, with a good result, without complications associated with lymphadenitis in the neck.
Before determining how to treat the lymph nodes, it is recommended to visit a general practitioner, who will refer you to the appropriate specialist, if necessary. How to cure a disease in a particular person depends on the extent of the lesion, as well as the form of inflammation. In most cases, treatment of affected lymph nodes involves the use of conservative measures. Purulent lesions can only be excluded through surgery.
Medicines
Treatment of lymph nodes can be carried out using the following medications:
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. As soon as they enter the body, in particular, the lymph system, they produce a sharp decrease in the production of prostaglandins - mediators of the inflammatory process. Thanks to such medications, disturbing symptoms are eliminated: hyperemia, pain and swelling, fever. Therapy of lymph nodes in children and adults can occur through the use of ointment or cream, as well as taking tablets.
Long-term use of NSAIDs causes irritation of the gastrointestinal mucosa and internal bleeding. This group includes Nimesil, Ibuprofen, Diclofenac, etc.
- Analgesic. Therapy for lymph nodes includes taking analgesics, which are prescribed in case of individual intolerance to NSAIDs. For example, it could be Analgin, Efferalgan or Panadol. It is advisable to use the latter drug for a child in the form of rectal suppositories or syrup.
- Glucocorticosteroids. Effective for inflammation of the lymph nodes and their vessels, which is accompanied by severe swelling. Thanks to the substances included in the composition, the intensity of pain is reduced and local reactions are eliminated.
The most effective glucocorticoid drugs for the treatment of nodes behind the ears, under the chin, on the shoulder and in other areas are Prednisolone and Dexamethasone. Improper use of such medications will only intensify the inflammation. For this reason, a doctor should prescribe the dosage and method of administration.
- Antiviral. If the lymph nodes are inflamed in a child whose immune system is not yet fully formed, such remedies will become an indispensable assistant in the treatment of pathology occurring in any area (behind the ear, on the neck, etc.). These drugs include Arbidol, Kagocel, etc.
- Antibiotic. If an infection has entered the lymph area or blood, antibiotics are prescribed: Cefixime, Azithromycin, Sumamed, etc.
Ointments
 Local remedies in the form of ointments or creams are also prescribed. These are applied to the affected node (ear, neck, etc. areas) in the form of a compress or lotion.
Local remedies in the form of ointments or creams are also prescribed. These are applied to the affected node (ear, neck, etc. areas) in the form of a compress or lotion.
Local remedies that allow you to fight diseases such as lymph node hyperplasia, lymphadenitis, etc. include Ichthyol ointment and Vishnevsky ointment. The components included in the products ensure deep penetration into the dermis, relieving inflammation and providing an antimicrobial effect.
Treatment of lymphangitis (vascular damage) can be carried out with the help of Heparin ointment, which helps to cope with stagnant processes and speed up lymph flow. Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are used to get rid of pain and swelling. These include Ketoprofen, Piroxicam, etc.
It is not recommended to leave a bandage with ointment on all night, because the affected area must breathe, and the fabric is an obstacle to this. The duration of use of ointments is determined in accordance with the recommendations of the attending physician. In any case, the doctor will be able to find out how to treat inflammation of the lymph nodes only after eliminating acute symptoms, for example, fever.
Physiotherapy
In most cases, physiotherapeutic procedures are used to treat a disease of the nodes such as lymphadenitis (for example, in the ear area, on the neck, etc.). Since the pathology is caused by infectious pathogens, it is necessary to act not only on the lymph node, but also on the direct infection. Physiotherapeutic procedures are effective in combating any inflammatory process in this area, and also help eliminate pain.
So, the following types of physiotherapy are most often prescribed for lymph node damage: 
- Irradiation of the affected area with ultraviolet rays. At the beginning of treatment, 2 procedures are performed per session, increasing over time to 8. In total, approximately 5 procedures will be required to eliminate the inflammatory process.
- Ultrahigh frequency therapy (UHF). This method of physical treatment helps to get rid of the inflammatory process in a short period of time. The affected area is treated for 7-15 minutes. per session. UHF therapy is contraindicated for use in the presence of symptoms of general intoxication.
- Carrying out fluctuarization. During treatment, the inflamed lymph nodes are exposed to a sinusoidal alternating current of medium or high dose (depending on the severity of the disease).
The total duration of exposure per session is no more than 10 minutes. 5 sessions are enough to get rid of the inflammatory process.
- Impact of ultrasound. Helps resolve the inflammatory infiltrate in the affected lymph node. The duration of exposure is no more than 7 minutes. Number of sessions – up to 10.
- Laser exposure. The therapy technique helps improve blood circulation in the affected area, eliminate inflammation and pain, and also accelerate the regeneration processes of affected tissues.
Each method of physiotherapy has its own contraindications. For this reason, only a specialist should prescribe them.
Folk remedies
Treatment of lymph nodes can also be carried out at home through the use of folk remedies.
So, to get rid of the inflammatory process (be it near the ear, on the neck or in another area), you can use the following traditional medicine:
- Nettle, yarrow, oregano, horsetail. This collection of herbs is effective in the treatment of inflammation of the lymph nodes of chronic recurrent treatment. The infusion is made as follows: the ingredients are mixed in equal parts and poured with boiling water. After infusing for 1 hour, the product is filtered and consumed orally, half a glass before meals.
- Dandelion . Soak a piece of gauze folded in five with freshly squeezed juice from the plant and apply it to the inflamed area. The procedure is carried out several times a day for 3-4 days.
- Internal fat and scavenger. Local ointment is prepared as follows: after melting the fat in a water bath, add dry herb norichnik (3 tablespoons) and place it back in the bath for another few hours. After filtering the product, it is poured into another container and stored in a cool place. The ointment must be applied to the inflamed area several times a day.
- Knotweed. 1 tbsp The ingredient is poured with boiling water in a volume of 500 ml and left to infuse for half an hour. After cooling and straining, the product is taken orally before meals several times a day.
It is worth noting that before carrying out such therapy you need to consult a doctor, because some drugs may be contraindicated in a particular case and will only aggravate the course of the underlying disease.
Lymphadenitis (inflammation of the lymph nodes) is not an independent disease, but a concomitant one, signaling that unusual changes are occurring in the body.
What are our lymph nodes responsible for?
Lymph nodes are our filter, protection and degree of immunity. In the lymph nodes, the process of cleaning lymph occurs (from bacteria, microbes, foreign substances, viruses, toxins), which is responsible for the performance of the entire body as a whole. The state of our health can be judged by the condition of the lymph nodes.
Reasons for the development of inflammation
Treatment of lymphadenitis cannot be carried out without determining the cause of the disease; only after determining the main problem can one understand whether antibiotics will be needed in this case or whether local procedures will be sufficient. It is possible to detect the disease not only by palpation, but often even visually - there will be a noticeable increase in the submandibular lymph nodes. Additionally, in case of a complicated course of the disease or to clarify the diagnosis, clinical laboratory tests, radiography, MRI, CT or biopsy of the affected lymph node may be prescribed.
Enlarged lymph nodes may be due to the following reasons:
- teething;
- infectious diseases;
- lesions in the oral cavity (stomatitis, gingivitis, periodontitis);
- decreased immunity;
- injuries to the lymph node area;
- venereal diseases;
- tumor processes in the body.


Treatment of lymph nodes using traditional methods
Treatment of inflammation of the lymph nodes consists of identifying the primary source of the disease (there is no point in treating the lymph node itself), removing the infectious focus (if this is not done, serious complications cannot be avoided), relieving inflammation and increasing immunity.
Medications are prescribed (antibiotics that stimulate the immune system, antifungals, antihistamines, multivitamins), and physiotherapeutic procedures are performed.
Traditional methods of treating lymph nodes
When the main treatment has already been prescribed by the doctor, you can additionally add traditional methods to it, which will help speed up the healing process, relieve pain and discomfort, and strengthen the immune system.
Decoctions for lymph nodes
Inflammatory processes can be controlled well if you follow the correct drinking regime. Drinking plenty of warm drinks is the key to a faster recovery. Take herbal decoctions prepared by yourself from mint, horsetail, elderberry, chamomile, currant leaves, calendula, and be sure to add honey and lemon.
Tinctures for lymph nodes
The recovery process from lymphodenitis will go faster if you take immunity-boosting vitamins and tinctures - propolis, ginseng or echinacea. Take any of the drugs, 10-13 drops, 3-4 times a day, diluted in water.
Rinse for lymph nodes
When the cause of swollen lymph nodes is infectious diseases of the oral cavity, good results can be achieved by rinsing.
Use the following recipes:
1. Pour boiling water over a mixture of soda, salt (1 tsp each) and iodine (3-5 drops). Rinse with warm solution as often as possible.
2. A decoction of chamomile flowers and oak bark (1:1). Pour boiling water over a mixture of one teaspoon, let it brew, rinse every 2-3 hours.
3. Dissolve half a teaspoon of hydrogen peroxide, pharmaceutical alcohol tincture of chamomile or calendula in 200 ml of warm water.
Massage for lymph nodes
A light and gentle massage performed with olive, peach or any of the essential oils (lavender, tea tree oil, eucalyptus) will help speed up the healing and recovery process.
When performing a massage, observe the following conditions:
- You need to massage the lymph nodes carefully no more than twice a day, without pressure, gently stroking the skin, starting from the base of the neck, smoothly moving through the area of the lymph nodes to the ears.
- The duration of the procedure should not exceed 10 minutes.
Ointments for lymph nodes
After the massage procedure, the area of the lymph nodes can be lubricated 2-3 times a day with Vishnevsky’s liniment (relieves inflammation and reduces pain) or Ichthyol ointment (relieves swelling and severe pain).


Prevention of inflammation of the lymph nodes
Preventing a disease is easier than treating it later, so try to take preventive measures:
- pay attention to the appearance of bacterial and viral infections in a timely manner and treat them;
- avoid hypothermia and exposure to drafts;
- toughen up;
- get plenty of rest;
- go in for sports.
Improper treatment of inflamed lymph nodes can lead to irreversible consequences, therefore, during treatment procedures, it is strictly forbidden to apply warm compresses to the area of the lymph nodes, rub them, make meshes from iodine, or engage in self-medication without coordinating your actions with a doctor.
Inflammation of the lymph nodes in the neck means a pathology associated with the immune system, which means you can’t just leave this disease to chance.
In general, cervical lymphadenitis has a very wide etiology; infectious, autoimmune, oncological diseases and many others can be the causes.
Therefore, it is important to diagnose in time and eliminate the cause of inflammation, that is, treatment in this case will be etiotropic (we act on the cause). Lymph nodes are natural barriers in our body, and when pathogenic or foreign agents enter, they actively begin to “work”, and, accordingly, become inflamed.
That is, the very fact that the lymph nodes are inflamed indicates pathological processes in the body. The article provides lists of possible causes of inflammation, symptoms and treatment methods. The information may be useful for mothers, because cervical lymphadenitis often affects children, accompanying influenza or ARVI.
Inflammation of the lymph nodes in the neck - characteristics


If a person notices lumps appearing on his neck just below the ear or lower jaw, he should immediately consult a doctor. Most likely, cervical lymphadenitis may manifest itself in this way.
This is by no means a reason to panic, but timely diagnosis of the disease is the key to successful treatment. The patient's condition, accompanied by a sharp increase in lymph nodes, is called lymphadenopathy in medicine.
Inflammation of the lymph nodes in the neck is a fairly general name, rather describing the clinical picture of the development of the disease. But its causes can be a variety of diseases, including lymphadenitis. Lymphadenitis is an infection of large lymph nodes. As a rule, the disease has a fairly clearly defined localization.
Typically, an increase in nodes is noticeable in the armpits, groin, and in the area of the elbow or knee joints. Cervical lymphadenitis is also quite common, due to the close location of the retropharyngeal lymph nodes (between the angle of the lower jaw and the ear), submandibular and superficial cervical (in the area of the collarbone) to the surface of the body.
Inflammation of the lymph nodes in the neck or cervical lymphadenitis is not an independent disease, but a symptom that accompanies many infectious diseases and a number of other pathological conditions. Enlarged cervical lymph nodes are a sign of the development of an infection in the body or a manifestation of a disease of the lymphatic system.In the human body, lymph nodes play the role of biological filters and are organs of immune defense. With the flow of lymph, pathogenic microorganisms are delivered to special formations that delay the infection and prevent it from spreading throughout the body.
It is here, in the lymph nodes, that pathogenic bacteria and viruses are destroyed, as well as the fight against degenerated cancer cells. As a rule, the cause of inflammation of the nodes is the penetration of an external infection into the lymphatic system - various types of pathogenic microorganisms.
There are cases of the onset of inflammation from products of organic tissue decay or even microscopic foreign bodies entering the vessels. In the normal development of the disease, when lymphadenitis is the main disease, as a rule, there is a history of skin wounds, purulent wounds or severe inflammatory processes (boils, abscesses).
However, manifestations of lymphadenitis can also be a consequence of chronic or acute diseases occurring in the body, such as tuberculosis, influenza, inflammation of the lungs and upper respiratory tract, tonsillitis.
What are lymph nodes needed for?
To find out why the lymph nodes in the neck hurt, first let’s understand what lymph and lymph nodes are and what function they perform in the body. Lymph is a special fluid that resembles blood, except that it lacks red blood cells.
The main type of cells found in lymph are lymphocytes. This type of cell is responsible for the body's immune response. Lymph nodes are a collection of lymphatic vessels. The nodes perform a dual function - on the one hand, they are a barrier to the penetration of various infectious agents into the body, and also prevent the proliferation of pathological cells of the body itself.
On the other hand, lymph nodes are the site of development of new lymphocytes. Antibodies and phagocytes can also be produced in the lymph nodes. In addition, these organs are responsible for the outflow of intercellular fluid. Lymph nodes (lymph glands) are organs of immune defense and act as unique biofilters from pathogenic microorganisms.It is in them that the destruction of pathogenic viruses and degenerated cancer cells is carried out. The main part of the lymph nodes is located in the groin, neck and armpits. Inflamed lymph nodes, as a rule, indicate that an infection has “settled” somewhere nearby.
That is, if it is inflamed in the neck, then most often this indicates a sore throat or ear infection. Lymph nodes are the organs that are the first to give a signal to turn on protection when faced with something potentially dangerous.
Immediately, without waiting for a response from their central organs, they “preserve” the dangerous agent inside and begin to attack it with their own forces, while simultaneously sending lymphocytes to the source of the problem. This assault causes enlargement of the lymph nodes.
That is, lymphadenitis - and this is what is called when they reach size when they are visualized or can be felt - almost always means that there is a problem in the place from which these formations collect lymph. The name of this disease can be either ARVI, inflammation in the area of the dental system, or even cancer - only a doctor can find out the cause.

There are many lymph nodes in the human body, but they are most densely located in the neck, groin area and armpit. Lymph nodes vary in size. The largest of them have a diameter of approximately 1 cm. In the neck area there are the following groups of lymph nodes:
- anterior cervical superficial and deep;
- posterior cervical superficial and deep;
- submandibular;
- chin;
- ear;
- occipital
They are soft and elastic, slightly smaller in size than a bean, mobile and painless. The largest ones and those located close to the surface of the skin can be felt with your fingers. They have a round shape to the touch and can roll slightly. However, in normal condition, the lymph nodes do not cause pain when touched.


In people of any age, lymphadenitis is divided into:
- Acute, caused by highly contagious flora or caused by injury directly to the lymph node.
- Chronic, which develops when weakly virulent microflora penetrates into the node, when the acute process is not treated. Specific processes immediately acquire a chronic course: tuberculosis, brucellosis, syphilitic.
According to the nature of the process occurring inside the lymph node, lymphadenitis occurs:
- Catarrhal. This stage is characteristic of an incipient infectious disease. Here the lymph node is soaked in blood plasma.
- Hyperplastic, occurring at a late stage of the process. The lymph node grows due to the abundant proliferation of immune cells in it.
- Purulent. It develops only during a bacterial process, when the lymph node is filled with a large amount of pyogenic microflora, or the lymph node is injured by infected material. When filled with a large amount of pus, the latter can also saturate the tissue surrounding the node. And if the body does not decide to cover it with a capsule, then the pus can “spread” throughout the neck (phlegmon), but if the focus of pus is surrounded by a capsule, then an abscess can develop.
Causes of the inflammatory process
Cervical lymphadenitis in adults is an organismal response to an infectious agent that has entered it: a virus, fungus or bacterium. In this case, the latter can be:
- nonspecific: staphylococci, Proteus, clostridia, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, staphylococci;
- specific: Mycobacterium tuberculosis, the causative agent of syphilis, gonococcus, Brucella, actinomycete fungus, the bacterium that causes tularemia.
At primary school age, the lymph nodes become inflamed during lacunar tonsillitis, when ulcers are found on the tonsils. An increase in the number of lymph nodes can be accompanied by rare diseases such as histioplasmosis or coccidioidomycosis.
Up to three years, and then at 6–10 years, an increase in a large number of lymph nodes in the absence of symptoms of the disease can be a symptom of a physiological phenomenon called “lymphatism” if: the child’s rapid growth is noted, if animal proteins predominate in his food.
Treatment for this type of cervical lymphadenitis is not necessary, but observation by a pediatrician is mandatory here: this is not necessarily lymphatism, but a manifestation of hypersensitivity. If, in addition to lymphadenopathy, the thymus gland (this is the same organ of the immune system as the lymph nodes) becomes greatly enlarged, this is a dangerous signal.
The causes of enlarged lymph nodes in the neck are always caused by an infectious bacterial disease. To know exactly how to treat enlarged lymph nodes, you need to understand the causes of their appearance and inflammation.
Infectious diseases of the respiratory tract
This group of diseases is the most common cause of inflammation of the lymph glands located in the neck. Infectious diseases of the respiratory tract include:
- influenza (inflammatory damage to the mucous membrane of the upper respiratory tract);
- tonsillitis (inflammation of the tonsils);
- rhinitis (inflammation of the nasal mucosa);
- sinusitis (inflammation of the sinuses);
- laryngitis (inflammation of the larynx);
- tracheitis (inflammation of the trachea).
Such a dangerous disease as tuberculosis can also cause lymphadenitis. In tuberculosis, inflammation of the lymph nodes has some characteristics - they enlarge, but are not painful and do not cause any discomfort.
As a rule, with respiratory tract infections, the submandibular lymph glands become inflamed. It is possible to determine that the cause of lymphadenitis is inflammation of the respiratory system by a number of additional symptoms:- cough, redness and sore throat;
- runny nose, nasal congestion, loss of smell;
- severe muscle pain (typical of influenza);
- high temperature, chills, fever.
Mouth infections
They are also a common cause of inflammation of the lymph nodes (usually anterior cervical and submandibular). This group of infections includes:
- gingivitis (inflammatory disease of the gums);
- caries (destruction of dental tissue);
- stomatitis (inflammation of the oral mucosa, namely the inside of the cheeks, lips, palate);
- glossitis (inflammation of the tongue);
- periodontitis (inflammation of the tooth root).
A characteristic symptom of oral infections is bad breath.
Common infectious diseases
The lymph glands in the neck can become inflamed not only when the infection is localized in organs located in close proximity to them. Together with lymph, pathogenic viruses or bacteria spread throughout the body.
An infection localized, for example, in the liver or lungs, can cause inflammation of the nodes in the neck. Common infectious diseases that are accompanied by lymphadenitis include:- mumps (viral inflammation of the salivary, seminal and pancreatic ducts);
- measles (a viral infection of the skin manifested by a rash);
- diphtheria (a bacterial disease in which a fibrous plaque in the form of a film forms in the throat, and sometimes on the skin);
- AIDS (irreversible loss of immunity);
- mononucleosis (an infection in which the body begins to produce atypical cells, the localization of which is the lymph nodes, liver, spleen).
In general infectious diseases, as a rule, the lymph nodes located at the back of the neck become inflamed. Mononucleosis is characterized by a very strong enlargement of the lymph glands, the size of which can reach the size of a chicken egg.
Autoimmune diseases
Autoimmune diseases are pathologies in which the body, for unknown reasons, perceives its cells as foreign and begins to fight against them. Symptoms characteristic of this group of diseases include lymphadenitis. There are more than eighty types of autoimmune diseases. The most common include:
- lupus erythematosus (destruction of connective tissue that affects all organs and systems of the body);
- rheumatoid arthritis (joint damage);
- sarcoidosis (formation of dense nodes in various organs, including the lymph glands);
- Sjögren's syndrome (chronic inflammation of the salivary and lacrimal glands, which, as it progresses, spreads to the lymph nodes).
There are no characteristic general symptoms for this group of diseases, and lymphadenitis is not a mandatory sign. Therefore, only a doctor can determine that autoimmune pathology is the cause of inflammation of the lymph nodes in the neck.
Decreased immune function - when the barrier function is weakened, the lymph nodes begin to produce more protective cells, as a result of which they can increase in size. In this case, the lymph glands are not painful, but hard to the touch.Constantly enlarged lymph nodes can be observed in people suffering from vitamin deficiency, chronic inflammation, and general fatigue of the body. Especially often, weak immunity is the cause of enlarged lymph nodes in a child.
Oncological diseases
The cause of inflammation of the organs of the lymphatic system can be malignant neoplasms. Nodes can enlarge both due to a tumor in the lymph gland itself (lymphoma), and in the presence of neoplasms in other organs of the body (most often in the brain). As a rule, lymph nodes in cancer are not painful and do not cause any discomfort.
allergic reactions
An allergy is an increased sensitivity of the immune system to allergenic foods. Upon contact with an allergen, the lymph nodes begin to produce specific cells aimed at neutralizing the allergen. Therefore, with prolonged allergies, the lymph nodes in the neck begin to become inflamed. You can determine that the cause of lymphadenitis is an allergy by the following symptoms:
- redness of the skin, itching, burning sensation;
- rash, blisters, blisters;
- nausea, vomiting;
- cough, throat swelling.
Causes of cervical lymphadenitis in a child


The most common cause of inflammation of the lymph nodes in the neck in a child, as in an adult, is various respiratory infections. The second most common factor that provokes childhood lymphadenitis is weak immunity.
Very often in children, inflammation of the lymph nodes in the neck is caused by abrasions, scratches, and open wounds. This happens because when the skin is damaged, a foreign agent enters the body, and the immune system begins to fight it, which is accompanied by an enlargement of the lymph glands.A lymph node in a child’s neck may become inflamed after playing with cats, dogs and other animals. Animal saliva, penetrating into the child’s body through scratches, is identified by the immune system as an “enemy”, and it begins to fight against it, as a result of which the lymph nodes enlarge.
If this condition is caused by low-grade inflammation of the head and neck area, or the immune system is not strong enough to quickly overcome the infection, chronic cervical lymphadenitis occurs.
It manifests itself only by randomly detected enlarged lymph nodes, which are almost not painful to touch. At the same time, the baby’s health is good, the temperature is not elevated. If lymphadenitis develops as a result of an acute - bacterial or viral - process localized in the oral cavity, soft tissues of the head or neck, the following symptoms are detected:
- a sharp rise in temperature to high numbers;
- swelling of the neck;
- refusal to eat.
- The older children say, pointing to the neck area, that it has become difficult even to drink;
- sleep disturbance;
- Nausea, lethargy, and weakness may develop in infants.


The main symptoms depend on the local manifestation or are caused by general signs of another more severe disease. At the site of the inflamed lymph node, the following appear:
- pain when swallowing on the right and left, pain on palpation of the submandibular nodes are characteristic of a respiratory infection, sore throat;
- painful nodules on the back of the neck appear with rubella measles;
- enlarged compacted formation - the size of the submandibular lymph nodes can vary from the size of a pea (can be palpated) to a walnut or egg (visible visually).
- General symptoms - the condition may be accompanied by headache, general malaise, weakness, fever, and rashes on the body.
In the presence of a long-term chronic infection, the symptoms of lymphadenitis are mild, there is a slight increase in regional nodes, and there is slight pain on palpation or when swallowing. The condition worsens with hypothermia and colds.
To treat lymphadenitis, it is necessary to undergo a full examination, identify foci of infection and carry out their complete sanitation. If the lymph node is dense, hard, painless to the touch, and inflammation of the lymph nodes in the neck lasts for more than six months, the doctor suspects a tumor.
The patient is examined by an oncologist, tests for tumor markers are checked, and a biopsy is performed. In such cases, a delay in examination or the patient’s refusal may cost him his life. A general blood test will reveal a picture of inflammation: leukocytosis, accelerated ESR.
Algorithm of actions when one/several enlarged lymph nodes are detected


If you feel (or your child complains to you) local pain in the neck or under the jaw: Examine this area. There you can find a soft tissue injury or an abscess. Gently, with two fingers, feel and “roll” the tissue in the painful area: with lymphadenitis, you will feel a “ball”.
If it is myositis, no local formation will be palpable. If you feel a “ball”, note the following facts for yourself: pain when pressed, displacement of this formation relative to the skin above and muscles on the sides, skin temperature above it.If the lymph nodes are small, painless, “roll” with your fingers, there are many of them at once, this indicates pathologies of the immune system. The consultant who will help you understand the pathology is an infectious disease specialist. An uneven contour, palpable “bumps”, poor mobility of the formation and its painlessness are serious signs.
You need to visit an oncologist who will prescribe the necessary examinations. If we are talking about the purulent process of the lymph node itself, it can become very painful and hot. Your specialist is a surgeon. Inflammatory pathologies of the throat, oral cavity and neck will be characterized by increased pain on palpation and slight “rolling” under the fingers.
Here you need to visit an ENT doctor, a therapist (for children - a pediatrician), and sometimes a dentist. The next point in the “program” is self-examination. You need to look at your teeth, gums and throat in the mirror so that the mucous membranes are clean, free of plaque and ulcers, and your teeth are free of signs of damage. You also need to examine the soft tissues of the face and neck - for ulcers, injuries, dense painful areas.
If any of this is present, then most likely you have found the cause of lymphadenitis. All that remains is to contact the appropriate specialist and undergo treatment. The lymph nodes are clearly divided into groups for a reason: each one collects lymph from a designated area of the head and neck, so the focus of infection or atypical cells can be found.
But there is a “but”: with a pronounced inflammatory process, as well as systemic (they affect many organs at once) diseases or damage to the immune system, several groups are affected at once, which makes diagnosis much more difficult.
Diagnosis of pathology
Diagnosis of enlarged lymph nodes in the neck begins with finding out the cause. Any process in the body that causes tissue to swell or swell is inflammation. When the lymph nodes become inflamed, they increase in size.
With pronounced or advanced enlargement of the lymph nodes, patients complain of persistent pain in the affected area. Please note that if the process of lymph node enlargement occurs very quickly and violently, then the cause of the disease can be diagnosed.As a rule, this is a wound into which germs or infection have entered and traveled through the lymphatic channels to the lymph nodes in the neck. If we are talking about acute inflammation of the lymph node, then the reaction manifests itself throughout the body:
- Heat.
- Decreased appetite.
- Chills.
- General weakness and fatigue.
- Headache.
It is very easy to diagnose the inflammatory process, thanks to enlarged lymph nodes. But sometimes, enlarged lymph nodes are not associated with inflammatory processes. Therefore, it is necessary to diagnose enlarged lymph nodes taking into account other signs that may be the cause of this symptom.
As soon as you notice enlarged lymph nodes, it is important to seek advice from your GP. He will conduct the necessary diagnostics, send you for an ultrasound of the lymph nodes of the neck, based on the results of which he will give a referral to a specialist: dentist, surgeon, hematologist, otolaryngologist or oncologist.
In general, there are about a hundred diseases that are accompanied by a reaction of the lymphatic system. Therefore, it is important to pay attention to other symptoms associated with lymphadenitis. If the lymph node does not acquire normal size despite treatment within 2-3 months, then this is a characteristic sign of a chronic infection.Time should be taken for a complete medical examination to determine the root cause of the inflammatory process. If the inflammation does not subside within six months, and the lymph node is hard and painful to the touch, then there is reason to worry about the possible presence of a lymph tissue tumor. You need to make an appointment with a specialist, get tested, and have a biopsy. Under no circumstances should you let everything take its course!
Inflammation of the lymph nodes in the neck - treatment


Treatment of lymph nodes in the neck begins with procedures and methods that will help relieve pain. It is also very important to determine the cause of inflammation and enlargement of the lymph nodes in the neck. An infectious disease specialist, a surgeon and an oncologist will help you in this matter.
In general, there are many issues associated with the treatment of lymph nodes in the neck. Before treatment, it is necessary to find out why the lymph nodes are inflamed. These problems can be solved using various treatment methods. Enlarged lymph nodes in the neck are responsible for ear diseases, head diseases and diseases associated with the respiratory system. Enlargement can also be caused by dental infections.
- Echinacea is considered the best remedy that helps fight an inflamed lymph node in the neck. Echinacea is a plant that has an anti-inflammatory and antiseptic effect on the affected area. Echinacea infusion must be diluted with boiled water. The approximate ratio is 10 drops of tincture per 100 grams of water. You need to take the tincture 3 times a day. This treatment for enlarged lymph nodes is most often used for colds.
- Another way to cure lymph nodes in the neck is to use compresses and rubbing. You will need camphor oil or ichthyol ointment. The oil is used for compresses, and the ointment must be gently rubbed into the affected area.
- Please note that if the lymph nodes in the neck are enlarged, it is better to stop using creams and perfumes for a while. Since this can provoke further inflammation.
- The easiest way to relieve pain in the lymph nodes is to take a terry towel, soak it in hot water, wring it out well and apply it to the neck and enlarged lymph nodes. Keep the compress for no longer than 15 minutes.
- Daily consumption of vitamin C can return enlarged lymph nodes to their normal appearance. Eat more vegetables and fruits, drink juices, especially orange.
- It is strictly forbidden to make an iodine grid. Since it can cause severe inflammation of an already enlarged lymph node.
Enlarged lymph nodes in the neck are not a fatal diagnosis, but it is a disease that requires immediate treatment. There is no need to wait until the disease becomes irreversible, seek help from a doctor and take care of your health.
ethnoscience
Folk remedies can both contribute to drug treatment, accelerating the healing process, and harm. Taking various tinctures and decoctions, of course, will not help you heal completely, but it can significantly alleviate the condition. Here are a few proven recipes that have repeatedly proven their effectiveness:
- Echinacea tincture. This excellent antiseptic is considered one of the most effective remedies for inflammation of the lymph nodes. Add 10 drops of tincture to 50 ml of boiled water. Take 4 times daily;
- Green jadeite. This miracle stone is famous for its ability to cleanse the body. It should be approximately the same size as a swollen lymph node. You just need to apply it to the inflamed area for 10 minutes several times a day;
- Dried Canadian goldenseal powder. One tsp dilute powder in 1 tbsp. water. Drink 1 tbsp every day, additionally including fermented milk products in your diet to avoid stomach upset;
- Mint, calendula, chamomile. Brew the decoction, cool and gargle 3-4 times a day;
- Soda and salt. Dissolve in 1 tbsp. hot water 0.5 tsp. soda and salt. Cool to room temperature. Use to rinse 3-4 times a day;
- Aloe juice. Every day take 1 tbsp. l. freshly squeezed juice;
- Massage with essential oils. It helps reduce discomfort and speed up recovery. Dissolve 1 part each of lavender, eucalyptus and tea tree oil in 20 parts of almond or olive oil. Massage movements should be gentle, directed along the neck from top to bottom. If painful sensations occur, slightly release the finger pressure.
If you have swollen lymph nodes in your neck, then under no circumstances trust advice related to:
- using heating pads or warming compresses;
- rubbing the inflamed areas;
- applying iodine nets.
This is strictly prohibited, because such techniques only accelerate the spread of infection through the blood vessels, aggravating the condition. In addition, such self-medication can be fatal!


Mothers know their child’s body like no one else and subconsciously “scan” it during daily care. Having discovered a certain dense lump on the neck and not finding an explanation for this, it is important not to panic, but to consult a pediatrician in a timely manner.
Most often, inflammation of the lymph nodes is observed in children aged 5-7 years. This is due to the fact that their lymphatic system has not yet fully formed, and therefore the barrier function is not fully realized.As already noted, lymph nodes are responsible for the body’s anti-infective defense. Their increase indicates an intense fight against viruses and bacteria. Enlarged lymph nodes in a child’s neck occur for the same reasons as in an adult (infectious diseases, mechanical damage, protracted infectious and inflammatory processes). If you find an inflamed lymph node in your baby, you should not:
- warm it up;
- endlessly touch;
- torment yourself with thoughts on this topic.
It is advisable to contact a pediatrician who can examine the child, make a correct diagnosis and prescribe treatment. When going to an appointment at the clinic, it’s a good idea to prepare answers to the questions that a specialist will most likely ask you:
- Has your child recently had injuries in the area of the inflamed nodes?
- Was your child scratched by a cat?
- Does inflammation continue to grow and localize?
- Is the lymph node painful?
- When was your last vaccination (possibly an allergic reaction to the vaccine)?
In children, swollen lymph nodes often occur as a result of a cold and go away on their own. However, nodules in the neck with sizes different from the norm do not always indicate that the baby is sick. Lymph nodes, due to their special location, may appear slightly enlarged due to the individual characteristics of the child.
If they bother the baby for quite a long time and for no apparent reason, it means that an inflammatory process is going on in the body. Only a doctor can determine what caused this reaction and prescribe treatment.