Back osteochondrosis
Osteochondrosis of the back is a disease associated with damage to the intervertebral discs, vertebral bodies, nearby articular surfaces and the ligamentous apparatus of a degenerative-dystrophic nature. The pathological process primarily develops in the cartilaginous tissue with a gradual transition to the bones and ligaments. The first symptoms, as a rule, appear in the later stages, when the progression of the disease leads to the infringement of the nerve roots, resulting in pain.
Osteochondrosis is quite widespread. According to statistics, up to 90% of the adult population suffer from it to one degree or another.
Stages
In its development, spinal osteochondrosis goes through four main stages.
Stage one
Three types of back osteochondrosisIt is characterized by the onset of dehydration of the nucleus pulposus, as a result of which the height of the intervertebral disc decreases. Small cracks appear in the fibrous ring, however, the pathological process develops within the disc.
Stage two
A reduction in the standing height of the discs brings the points of attachment of the ligaments and muscle fibers of two adjacent vertebrae closer together. As a result, muscles and ligaments begin to sag, excessive mobility and displacement of the vertebrae relative to each other develop. The instability of the segments leads to the formation of spondylolisthesis.
Stage three
The main symptom of this stage of osteochondrosis of the back is the development of morphological changes in the intervertebral discs: the formation of prolapses and protrusions. The articular apparatus of the vertebral segment is also affected. Both in the joints and in the uncovertebral joints, subluxations and arthrosis can occur.
Stage four
This stage is characterized by the appearance of adaptive changes in the affected areas, through which the body tries to eliminate the excessive mobility of the vertebrae and maintain the supporting and protective function of the spine. This process leads to the appearance of osteophytes (marginal bone growths) on adjacent surfaces of the vertebrae. Osteophytes lead to trauma to the nerve roots. As a rule, it is at the fourth stage of spinal osteochondrosis that the process of fibrous ankylosis begins in the joints and intervertebral discs. As a result, the affected segment seems to be walled up in a shell, which leads to the disappearance of symptoms.
Development of the disease
Osteochondrosis is primarily a degenerative-dystrophic, and not an inflammatory process. Its main cause is malnutrition of tissues with subsequent degeneration of their structure. Cartilage and bone tissues, like any other, are in a constant process of restructuring and self-renewal. Physical activity contributes to an increase in their strength and elasticity, and their absence leads to weakening of tissues and disruption of their structure.
Degenerative processes in spinal osteochondrosis are primarily due to the peculiarities of the blood supply and nutrition of cartilage and bone tissues. Intervertebral discs are not supplied with their own vessels. Their nutrition occurs by diffusion - in other words, the disks receive oxygen and other necessary substances from neighboring tissues. For this reason, the main condition for their proper nutrition is the activation of blood circulation in the surrounding tissues, and it can be achieved primarily as a result of intensive muscle work.
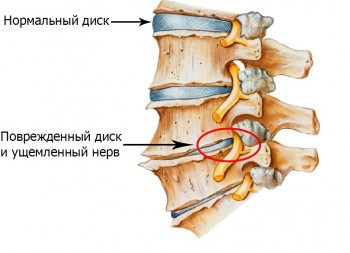
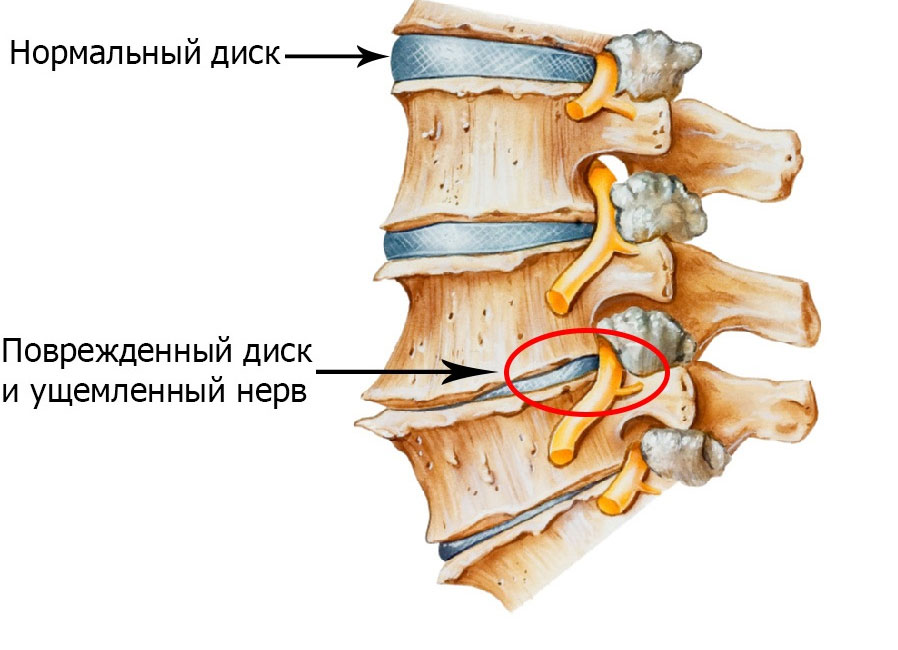 The development of osteochondrosis disease
The development of osteochondrosis disease The intervertebral disc consists of two main parts: the nucleus pulposus (it is located in the center) and the elastic fibrous ring surrounding it. Deterioration in the nutrition of the disks leads to the destruction of the complex biopolymer structures that make up the nucleus pulposus. As a result of gradual dehydration, the nucleus pulposus becomes brittle and can undergo defragmentation even at low loads. The strength of the fibrous rings is also reduced. These factors gradually lead to the development of osteochondrosis of the back.
The ongoing structural changes are irreversible. The goal of treating the disease is to minimize them and prevent further development of the pathological process.
The reasons
Spinal osteochondrosis develops as a result of a number of factors. They can be divided into endogenous (internal) and exogenous (external).
 Osteochondrosis occurs due to metabolic disorders
Osteochondrosis occurs due to metabolic disorders Endogenous include:
- genetic predisposition;
- features of cartilage tissue;
- metabolic disorders (mainly phosphorus and calcium)
- violation of the development of the spine in the prenatal period;
- age changes.
The main reason for the exogenous nature is the uneven distribution of the load on the spine, leading to a pathological change in the cartilage in areas of high pressure. Spinal osteochondrosis can be triggered by:
- spinal injuries;
- insufficient development of back muscles;
- incorrect posture (S-shaped curvature of the spine or stoop);
- prolonged stay in an uncomfortable position;
- infections;
- unbalanced diet with insufficient content of certain trace elements and vitamins;
Lifting weights, jumping, falling, static loads lead to microtrauma of the intervertebral discs. The frequent impact of these factors against the background of reduced elasticity of the discs, their loss of depreciation qualities and a reduction in the distance between the vertebrae provokes infringement of the nerve roots, which leads to the appearance of osteochondrosis back pain.
 Osteochondrosis has many symptoms
Osteochondrosis has many symptoms Clinical manifestations
Symptoms of osteochondrosis of the back can vary significantly depending on the location of the lesion. The main symptom of the disease is discomfort and pain. Pain may be intermittent, intermittent, dull or sharp, mild or intense. They are provoked by significant physical exertion, sudden movement, falling, etc.
Other symptoms of spinal osteochondrosis include:
- increased fatigue (physical and mental);
- decreased sensitivity of the limbs and individual parts of the body;
- chilliness of the legs and hands;
- pain radiating along the nerve trunks to the shoulder, shoulder blade (mainly manifested in the cervical form of the disease) or to the leg (occur with lumbar osteochondrosis).
With cervical localization of the lesion, the following symptoms also occur:
- dizziness;
- headache;
- deterioration of vision and hearing;
- visual fatigue.
In case of damage to the lumbosacral zone of the back, there may be a violation of the functioning of the pelvic organs, the reproductive sphere, and various sexual dysfunctions.
With thoracic localization of spinal osteochondrosis, pain appears in the region of the heart, in the intercostal space. Sometimes they are quite difficult to differentiate with pain in heart disease. A distinctive feature of osteochondrosis pain is their connection with the movements of the spine (for example, an increase in the intensity of unpleasant sensations during a sharp turn, tilt, etc.).
Diagnostics
To select the correct treatment for spinal osteochondrosis, it is first necessary to clarify the diagnosis.
Sufficiently informative and the most accessible diagnostic method is radiography. There are several types of X-ray examinations:
 X-ray required for diagnosis
X-ray required for diagnosis - Plain radiography is the simplest method, the essence of which is the x-ray of individual sections of the spinal column or the spine as a whole. In most cases, a targeted x-ray examination is prescribed, based on the patient's complaints and symptoms of the disease.
- Myelography is a more complex and rather dangerous diagnostic method. A contrast fluid is injected into the spinal canal. The danger lies in the possibility of damage to the spinal cord during puncture and (or) the manifestation of an allergic reaction to the composition used. With the help of myelography, the internal structure of the canal can be determined. This method has the maximum informativeness for the detection of hernias.
- Computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging are the most modern, but at the same time the most expensive diagnostic methods. Their use is advisable if it is necessary to differentiate spinal osteochondrosis from other pathologies of the spine with similar symptoms (for example, tumors of the spinal canal).
- Neurological examination - is carried out for a comprehensive assessment of the patient's condition. Neurological consultation allows you to clarify the localization and degree of sensory and motor disorders.
Treatment Methods
How can osteochondrosis of the back be treated? Modern medicine offers an integrated approach aimed at eliminating the symptoms and causes of the disease. Both pharmacological and non-pharmacological methods of treatment are used.
Medical therapy
With spinal osteochondrosis, several groups of medicines are prescribed:
 Treatment with ibuprofen
Treatment with ibuprofen 
Physiotherapy and other methods
An effective way to improve the patient's condition is physiotherapy and a number of other non-drug methods for treating back diseases. The most popular of them are:
- vacuum therapy;
- acupuncture;
- laser therapy;
- electrical stimulation;
- dry traction of the spine;
- ultrasound therapy;
- vibrostimulation;
- isometric kinesitherapy;
- physiotherapy;
- underwater hydromassage;
- manual therapy;
- medical diet;
- psychotherapy.
What to do if, with osteochondrosis of the back, the use of medicines and physiotherapy is not effective enough or, for one reason or another, their appointment is undesirable? In the absence of positive dynamics, as well as when the disease becomes severe, surgical intervention is recommended.
Prevention
To prevent spinal osteochondrosis and other pathologies of the spine, experts advise:
- Actively engage in sports to form a strong muscle corset and improve metabolic processes.
- From early school age, monitor posture and correct spinal curvatures.
- Avoid increased physical activity.
- If you need to carry heavy objects, evenly distribute the load on both hands.
- Eat foods rich in trace elements (calcium, magnesium, phosphorus) and vitamins.
- Fight overweight.