Kidney dysfunction
The kidneys perform several vital functions in the body. If there are problems with the kidneys, then this may indicate the presence of a pathological condition characterized by a partial or complete loss of the functionality of this organ to maintain the chemical balance in the body. When a person's kidney function is disturbed, all organs suffer to one degree or another.
Causes of dysfunction
If the kidney does not function in a child or an adult, then there are many reasons why this happens, and each can lead to the most unpredictable consequences. Possible causes of kidney dysfunction can be combined into 3 groups, each of which, one way or another, reveals the secrets of the appearance of such dysfunctions in the human body.
Renal
Studies have shown that pathologies affecting the parenchyma of the organ belong to this type of provoking factors. The most likely are:
- poisoning with nephrotropic poisons;
- jade;
- thrombosis of the vessels of the kidneys, which occurs with extensive hemolysis or crush syndrome;
- kidney infarctions;
- trauma;
- removal of both kidneys.
Prerenal
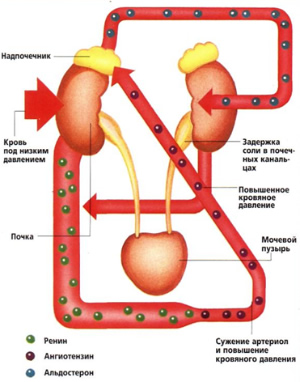 Hypofunction of the kidneys is the inability of blood vessels to maintain blood pressure.
Hypofunction of the kidneys is the inability of blood vessels to maintain blood pressure. Hypofunction, i.e., a decrease in kidney activity, occurs due to problems with blood vessels. Urine filtration directly depends on the volume of blood entering the organ, and it is determined by the value of blood pressure. Most often, one kidney does not function, or two in this case, with a sharp decrease in pressure and, as a result, a decrease in blood flow through the vessels.
The main root cause of the pressure drop is a state of shock with severe circulatory disorders, which is possible under such circumstances as:
- severe blood loss;
- burns, injuries;
- development of sepsis;
- introduction to a person of specific allergens that provoke anaphylactic shock in him;
- malfunctions of the heart (for example, myocardial infarction).
Postrenal
This type of causes primarily includes an acute form of obstruction of the ureters of two kidneys, which is caused by factors such as:
- the presence of a tumor;
- getting an injury that provokes the formation of a hematoma;
- the formation of stones in the genitourinary system;
- squeezing the ureters with a ligature during surgery.
Simultaneous failures in the work of both ureters is an extremely rare occurrence. Most often, a chronic form is observed, which proceeds slowly and can not be detected immediately. Hypofunction occurs due to chronic pathologies that gradually destroy the active parenchyma of the kidneys, replacing it with connective tissue. These diseases include:
- urolithiasis disease;
- chronic pyelonephritis;
- chronic glomerulonephritis.
There are cases of the development of a chronic form against the background of damage to the renal vessels as a result of the development of diabetes mellitus or atherosclerosis. Less commonly, these are hereditary diseases (for example, polycystic). Possible postrenal causes include the following pathogenic mechanisms:
- clogging of the tubules in the kidneys and necrosis of their epithelium in case of poisoning, hemolysis;
- decrease in the filtration process due to poor circulation and damage to the glomeruli;
- the impossibility of excreting urine due to its non-conductivity through the urinary canals.
Clinical signs and symptoms
 General weakness, fever, migraine - a reason to pay attention to the work of internal organs.
General weakness, fever, migraine - a reason to pay attention to the work of internal organs.
The first signs that the kidneys are not working normally are quite typical and make it clear that you should immediately contact a specialized specialist. Poor kidney function is determined by the following signs:
- minor manifestations of intoxication: general weakness, fever, migraine;
- edema appears, in the area of \u200b\u200bwhich the tissues become white and become slightly loose, pain is felt;
- cutting or aching pain in the lower back, which is felt only in an upright position;
- integration of pain at the top of the thigh, in the groin and pubis shows the path of passage of stones through the urinary tract;
- blood appears in the urine, the cause of which is a kidney injury of a different nature;
- - a hallmark of inflammation or necrotic process in hemolysis, tumors or abscess;
- poor outflow of urine with frequent urges, along with which pains are felt, cramps in the lower abdomen;
- a person has a reduced volume of daily urine, the reason for this is poisoning with poisons or drugs, renal colic;
- increased dryness in the mouth and thirst may show failures in the excretion of fluid;
- high blood pressure in case of problems with the kidneys, which for a long time is not reduced by medicines - a sign of pathology of the renal arteries;
- urinary retention will show that prostate adenoma, urolithiasis, etc. are developing;
- worried about such nervous disorders as overexcitation with a possible loss of consciousness, involuntary urination, or, conversely, drowsiness and lethargy;
- weight gain;
- poor appetite.
Main stages
 Violation of the kidneys damages the state of all systems of the human body.
Violation of the kidneys damages the state of all systems of the human body. Kidney dysfunction comes in two forms: chronic and acute. They, in turn, are divided into 4 stages:
- Conservative. With it, dysfunction occurs gradually and does not flow into the next stage quickly. Mild symptoms appear associated with chronic pathologies, which are the root causes of the fact that the kidneys do not work well. If you ignore the symptoms of the disorder and do not start treatment, then it is possible to flow into the terminal stage, which is more dangerous for the body.
- Terminal. It is characterized by the development of uremic syndrome with its characteristic:
- general weakness;
- headache and muscle pain;
- itching of the skin with the formation of ulcers;
- the appearance of puffiness;
- vomiting, nausea;
- ammonia smell from the mouth;
- hearing and smell disorders;
- increased irritability;
- insomnia; high blood pressure;
- malfunctions of the kidneys and liver, lungs and heart.
- Latent, characterized by minimal manifestations in the form of increased fatigue during physical exertion, evening weakness, the composition of urine changes, in which the presence of protein is detected.
- Compensatory, in which complaints of poor health become more frequent, the feeling of discomfort does not leave, the composition of urine and blood changes.
Consequences of kidney failure
Even a moderate impairment of kidney function with untimely treatment can develop into a more serious pathology or lead to death. If the kidneys work poorly, then:
- there is a risk of developing an infectious process;
- decreased production of sex hormones;
- there is bleeding in the gastrointestinal tract;
- hypofunctionality is exacerbated by hypertension.
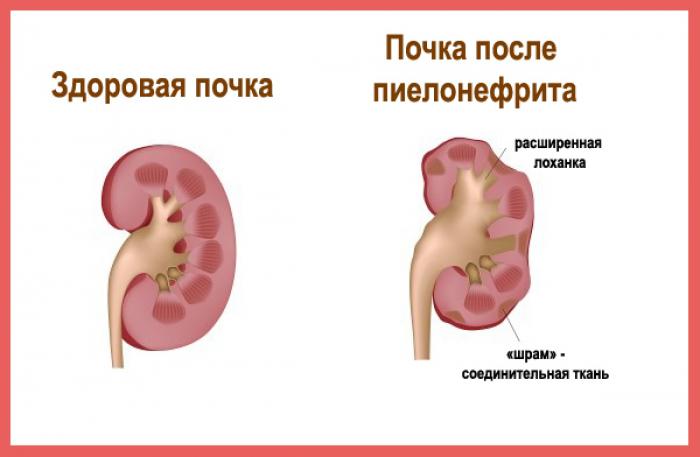 Pyelonephritis is a consequence of impaired renal function.
Pyelonephritis is a consequence of impaired renal function. Many complications of kidney failure depend on the form of failure:
- Acute renal disorders give impetus to the development of necrosis of the cortical substance due to circulatory failures, edema appears in the lungs during the recovery period, infections and pyelonephritis are often observed.
- Chronic renal failure can lead to the accumulation of harmful substances, which provokes problems with the nervous system in the form of seizures, tremors of the limbs, mental disorders. Perhaps the development of anemia, a decrease in bone strength, the occurrence of a stroke or heart attack.
Diagnosis: how to determine malfunctions in the kidneys?
Kidney dysfunction in the early stages is practically not diagnosed without pronounced symptoms, since it proceeds sluggishly and often a person does not pay due attention to these signs. To confirm an accurate diagnosis, the patient must contact a nephrologist or urologist, who then prescribe the following procedures:
- urine analysis (urinalysis checks its osmolarity, glomerular filtration rate) and blood (creatinine in it);
- blood biochemistry;
- tests for immunological disorders and TORCH - infections;
- MRI and CT of the kidneys;
- excretory urography;
- radiological research.