Bladder and blood in urine in women and men: causes, treatment
Among the pathologies of the urinary system, doctors distinguish such a pathology as hematuria of the bladder. This deviation does not proceed as an independent disease, hematuria signals an inflammatory process in the pelvic organs. The pathological process is characterized by the release of blood during urination. The causes of its occurrence may lie in oncological diseases. And in some cases, red urine is only a consequence of eaten beets. But do not turn a blind eye to this fact, if you find spotting during urination, you should consult a urologist. Comprehensive diagnosis and timely treatment will affect the symptom and help avoid pathological complications.
General information
Hematuria is a sign of a pathological process in the genitourinary system, in which there is a discharge of blood during urination. In medicine, there are several types of hematuria, with which you can install? what kind of illness does the person have? With a deviation in the human body, the number of red blood cells in the blood increases. At the first appearance of this symptom, the patient should consult a doctor, even if the problem itself has disappeared.
It is important to understand that the release of blood during urination in most cases signals serious abnormalities, such as urolithiasis, trauma to internal organs, an infection of the urinary system, or malignancy. Hematuria in the bladder has several types, which manifest themselves in different ways.
Varieties
 There are different types of diseases, which a specialist will help to diagnose.
There are different types of diseases, which a specialist will help to diagnose. Doctors distinguish between temporary and permanent hematuria, the latter is difficult to treat and manifests itself at the slightest inflammation or hypothermia of the body. Given the reasons that result in blood in the urine, the pathology is divided into extrarenal, renal and postrenal. The first hematuria is not associated with injury or kidney disease. Renal hematuria is diagnosed when there is a failure in renal function. Postrenal pathology is observed in case of injuries in the bladder, ureter and other organs of the genitourinary system. Given the intensity of the pathological process, micro- and macrohematuria are distinguished.
Microhematuria
With microhematuria, there is a slight discharge of blood, which is almost imperceptible. Blood can only be detected with the help of laboratory tests. Microhematuria occurs against the background of inflammation in the organs of the genitourinary system. Often this type of hematuria is observed with cystitis, pyelonephritis. In most cases, a deviation of this type is the only sign of the presence of a neoplasm in the urinary system.
Gross hematuria
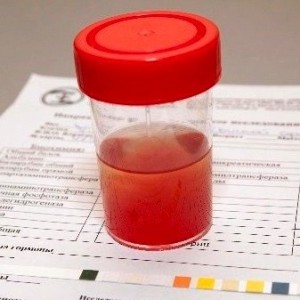 With gross hematuria, you can visually determine the admixture of blood in the urine.
With gross hematuria, you can visually determine the admixture of blood in the urine. Gross hematuria is noticeable even without laboratory tests, because when a person deviates, urine with blood clots is released. With such a deviation, the patient is often diagnosed with an oncological disease in the kidneys or bladder. In turn, macrohematuria is divided into three types:
- initial;
- total;
- terminal.
Terminal pathology is observed in pathologies of the urea, urethra or prostate gland. In this case, the patient has a blood clot in the last portion of urine. With initial hematuria, malignant neoplasms in the urethra, injuries of the urethra occur. Often, macrohematuria of this type suffers after an unsuccessful instrumental examination, as a result of which the urethra was damaged. With total hematuria, bleeding in most cases occurs due to pathology in the kidneys. In this case, the patient releases blood clots from the bladder.
The main causes of blood in the urine and in the bladder
The source of this deviation is the pathological processes occurring in the organs of the genitourinary system. Hematuria is extremely rare in a healthy person and does not indicate a serious disorder in the body. Some people experience microhematuria after jogging or walking for a long time. With active physical exertion, a person increases the number of red blood cells in the blood, which leads to temporary hematuria. If urine with blood is constantly observed, then this indicates such pathologies:
- injury to the organs of the genitourinary system;
- inflammatory diseases;
- malignant neoplasms;
- varicose veins;
- papillomas;
- appendicitis.
 With the defeat of the tubercle bacillus of the urea, blood is observed in the urine.
With the defeat of the tubercle bacillus of the urea, blood is observed in the urine. Bleeding from the urea occurs when the organ is infected with a tubercle bacillus. In the case of renal pathologies, urine with blood is observed, namely, with polycystosis, hemangioma, and renal failure. For men and women, the sources for deviation are slightly different. This is due to the different structure of the organs of the genitourinary system.
Causes in men
The bladder in men bleeds if there are inflammatory processes in the genitals, in which pus is released. Hematuria is provoked by prostatitis, prostate cancer, congenital renal abnormalities, inflammatory processes in the seminal vesicles. Often the cause of hematuria in men is papillary necrosis or problems with blood clotting.
Hematuria in women
In women, hematuria is manifested due to improper hygiene of the anus, cystitis, gynecological diseases, urethritis. Very often, pathology occurs when carrying a child or in the postpartum period, when a woman has an increased number of red blood cells in the body. A deviation can be provoked by surgery in the uterus or vagina. The source of spotting in women can be wearing tight and unnatural underwear. Blood in the urine indicates the menstrual cycle.
Symptoms
 Symptoms of hematuria appear depending on the cause of the disease.
Symptoms of hematuria appear depending on the cause of the disease. A person manifests various symptoms depending on the source of the lesion, the degree and severity of the accompanying pathology. Most often, the patient complains of problematic and painful urination, which indicates an inflammatory process in the bladder or urethra. A patient with hematuria has the following symptoms:
- excretion of reddish urine;
- difficult urination, urine comes out in a thin stream;
- pain on the side of the abdomen;
- constant feeling of a full bladder;
- feverish state.
Very often, bleeding from the urea is manifested by general weakness and dizziness.
The patient experiences constant thirst, his skin turns pale, sometimes there is a greenish-yellow hue of the skin and the membranes of the eyes. Noticeable discharge of brown clots that have an unpleasant odor. At the first symptoms listed above, you should seek help and undergo a complete diagnosis of the pelvic organs.
Hematuria and pregnancy
In a pregnant woman, urine with blood can appear in any trimester. This fact should alert the pregnant woman and the attending physician, since this deviation is not the norm when carrying a child. But you should not immediately sound the alarm, because only in rare cases, hematuria during pregnancy indicates a serious deviation.
 Blood in the urine during pregnancy can be a symptom of the development of an infectious disease of the urinary system.
Blood in the urine during pregnancy can be a symptom of the development of an infectious disease of the urinary system. Bloody discharge often disappears after the birth of the child on its own. In rare cases, in the postpartum period, repeated hematuria is noted, which indicates an inflammatory process in the kidneys, ureter and other organs of the genitourinary system. Sources for the appearance of hematuria during childbearing are the following factors:
- the growing uterus puts pressure on the ureter, as a result of which the kidneys are disrupted;
- urolithiasis disease;
- inflammatory processes in the kidneys or insufficiency of this organ;
- hormonal changes.
In some cases, bleeding in the bladder indicates rupture of the veins that are located around the renal calyces. The growing fetus has a mechanical effect on the function of the kidneys and urinary tract. A woman in position should not be condescending to this symptom and, at its first manifestations, contact a gynecologist. Timely diagnosis of deviations will help to avoid complications that will affect the health of the mother and the growing fetus.
Pathology in children
 Hematuria in children may indicate serious disorders in the urinary system, hematopoiesis, or trauma.
Hematuria in children may indicate serious disorders in the urinary system, hematopoiesis, or trauma. Bladder hematuria affects infants and older children. With the timely detection of the pathology of the child, it is possible to completely cure and get rid of unpleasant symptoms. In children, this deviation manifests itself as a result of impaired functioning of the kidneys or urinary tract. Often the following factors become the source of pathology:
- kidney stones;
- infectious diseases or injuries of the excretory tract;
- increased amount of calcium in urine;
- increased salt concentration;
- malignant education.
In many cases, pathology occurs due to disorders that appear in the process of intrauterine development. In infants and young children, in addition to spotting, there is a high body temperature and pain in the lower abdomen. Pain is associated with the formation of stones in the kidneys or ureter. A child with these manifestations should be immediately shown to a pediatric urologist.