How is a kidney injury treated?
The kidneys are paired organs of the urinary tract that perform a cleansing function. The kidneys are located symmetrically with respect to each other, the right organ is one level lower than the left one, has a smaller diameter, and therefore is more prone to injury. The kidney has a bean-like shape with smooth and dense film coatings of the fibrous capsule. Organs are located in a relatively protected space. Protection is represented by a fatty layer, ribs and a muscle layer. The fixed position of the organs in the abdomen is provided by Gerota's rigid fascia. Kidney contusion can occur due to lesions on the sides of the abdomen or during penetrating wounds.
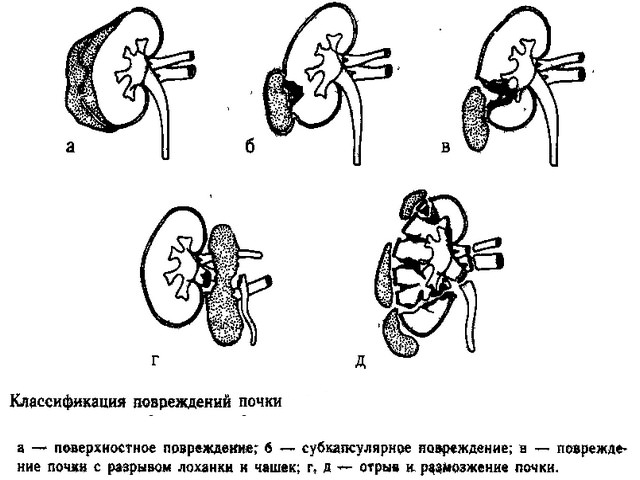
A kidney injury is a traumatic injury to an organ. When bruised, tissue ruptures can occur from a collision with ribs or vertebrae. A bruise is characterized by the formation of numerous bruises caused by capillary damage, internal hemorrhages and deformity of the pelvis.
The anamnesis distinguishes between two types of damage:
- isolated contusion (no surgery required, the patient is treated in the urology department);
- combined (deformities of several organs are diagnosed, most often with damage to the fibrous tissue of the kidneys, surgery is required).
Factors of the occurrence of pathology
Injury occurs as a result of mechanical action:
- physical violence;
- bruises from falls;
- concussion of the body;
- prolonged compression pressure;
- traffic accidents;
- environmental disasters;
- sport games;
- inserting a catheter, crushing kidney stones.
Congenital and acquired pathologies of the kidneys can be a provoking factor. In these diseases, kidney injury occurs from slight physical pressure.

Diseases of the genitourinary system:
- dystopia;
- urolithiasis disease;
- pyelonephritis;
- neoplasms in organs;
- horseshoe shape;
- hydronephrosis;
- prolapse of the kidneys;
- kidney failure.
Determining the level of severity
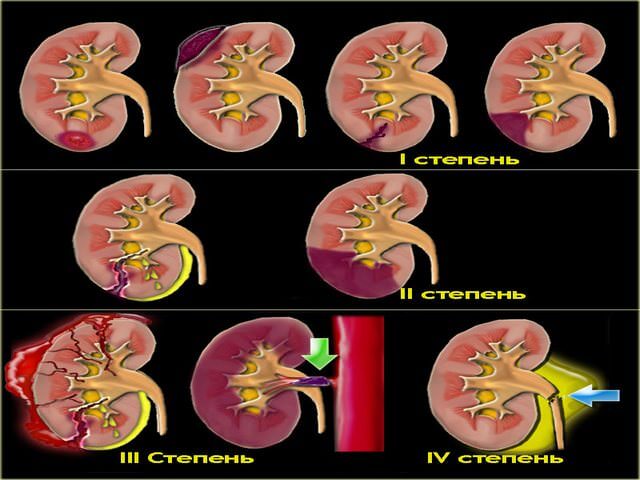
With a kidney injury, the symptoms differ according to several levels of severity of the pathology:
- Mild - minor changes in the state of health of the victim. Hematuria is not observed or is present in moderate mode.
- The average level of severity is the symptomatology of severe hematuria, the presence of red blood cells in the urine, or the complete cessation of urination. A significant hematoma forms in the area of injury.
- A severe level of injury is expressed in a state of shock, increasing gross hematuria, fever, convulsions.
Symptoms of injury
The organs are characterized by a strong blood supply, any damage to the genitourinary system is manifested by hypovolemia. Blood begins to seep into the urinary tract and is excreted in the urine. One of the main symptoms of tissue rupture is hematuria. By the duration, intensity of excretion and the number of blood inclusions in the urine, one can judge the severity of the bruise.
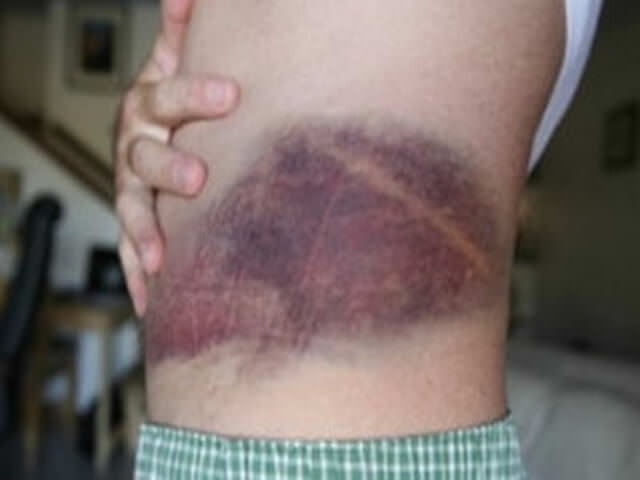
Pain signals can be stabbing, sharp. Not always complex kidney damage is expressed by characteristic signs. For example, if the ureters rupture, blood discharge in the urine may not appear. An important sign of pathology is swelling of the lower back on the side of the injury. The tumor occurs as a result of the accumulation of blood in the perirenal or retroperitoneal tissues. If the integrity of the tissue is damaged, urine can enter the peritoneum, which causes swelling and swelling of the affected area. The occurrence of a subcapsular hematoma provokes a rupture of the walls of the capsule, which, without competent treatment, can be complicated by the development of peritonitis.
The main signs of kidney pathology due to trauma:
- strong pain impulses in the back;
- urinary disorder;
- increase in hyperazotemia;
- hematuria with different levels of urine color;
- swelling in the damaged area;
- chills, fever.
Important! If you suspect a traumatic injury to the kidneys, you should immediately contact a nephrologist.
Differential Diagnosis
Kidney contusion is suspected in patients with blunt or penetrating injuries to the lateral abdomen. Also, the presence of a pathological condition is indicated by soreness or bruising on the lower back. The diagnosis is made on the basis of the results of a comprehensive examination: interviewing the patient, biochemical analysis of blood, urine.
To accurately identify the degree of injury, instrumental diagnostic methods are used:
- kidney x-ray with contrast;
- ultrasound procedure;
- excretory urography;
- magnetic resonance therapy;
- intravenous urography;
- chromocystoscopy.
Ultrasound is the most effective method for urgent diagnosis of trauma: parenchymal deformities, locations, and the presence of bruising are determined. In the event that it is impossible to determine the nature and severity of the bruise, and the condition of the victim worsens, there is a need for urgent surgical intervention.
In the case of a stable state of health, computed tomography is performed to prevent possible pathologies. The severity level of the pathology is determined by the results of severe damage to the vessels and parenchyma.
According to the indications, an emergency laparotomy of the parenchyma and the vascular system is performed. In case of failure of one kidney and to identify the functionality of the other, nephrectomy and internal pyelography are performed.
Therapeutic methods of treatment
After a preliminary diagnosis, treatment is prescribed according to the level of damage. For uncomplicated bruises, complex therapeutic measures are carried out: 15 days of bed rest, dietary nutrition, anti-inflammatory drugs, hemostatic therapy. Uncomplicated injuries can be treated at home on their own, but only after examination and doctor's recommendations.
Basic rules for treating a kidney injury:
- Immediately after injury, apply a cold compress to the injured area. This procedure is performed to relieve pain and prevent the development of kidney edema.
- Compliance with strict bed rest. A bruised organ becomes vulnerable to any impact, therefore, for optimal tissue healing, one should be at rest for the entire regeneration period.
- Antibacterial drugs: Amoxicillin, Ciprofloxacin, Levofloxacin, Maxifloxacin to exclude the possibility of developing an inflammatory process in the organs.
- Hemostatic drugs to stop internal bleeding: Dicinon, Etamzilat.
- For pain, it is recommended to take only antispasmodics: No-shpa, Drotaverine.
- Strong painkillers can be taken only as a last resort and according to the doctor's indications: Ketanov, Ketorol, Nise.

Possible consequences of injury
- Kidney contusion can be manifested by microscopic bruising on the skin or internal hemorrhages without visible hematomas and ruptures of the renal tissues.
- When falling, there is a possibility of rupture of the parenchyma, this is due to the fact that the kidney consists of hollow organs: the renal pelvis with fluid that, when shaken, can break the fibrous wall and seep into the peritoneum.
- Rupture of the ligament of the kidney with the vascular pedicle provokes the development of severe internal bleeding.
Important! Physical damage to the kidneys due to bruising is always accompanied by deformation of neighboring organs in the peritoneum.
Without competent kidneys can lead to extremely negative consequences:
- blood poisoning;
- suppuration of the perirenal areas;
- decrease in the level of hemoglobin and erythrocytes in the blood;
- pyelonephritis;
- urolithiasis disease;
- rupture of the vascular pedicle, urinary duct or pelvis.

If symptoms of damage to the parenchyma tissue, an increase in hematoma near the kidneys, or internal bleeding appear, an urgent operation is required.
Important! Kidney bruises can be combined with damage to the respiratory system, liver, spleen, intestines, bladder.
Control and management of therapy
After significant traumatic injuries, hospitalized patients require constant monitoring by a nephrologist for a year. Repeated studies are indicated every two weeks after injury. With favorable events, medical monitoring can be carried out once a month. The development of a feverish state, the appearance of pain in the back or the development of hematocrit are the first indicators for an extraordinary examination.
- physical diagnostics;
- biochemical analysis of urine;
- radiation methods of examination;
- careful control of blood pressure;
- the presence of creatinine in the blood.
Long-term observation is established by the attending physician; in the absence of indications, it is necessary to check the level of blood pressure.
The prognosis of kidney injury depends entirely on the level of mechanical damage and associated injuries. With a bruise of the first and second degrees of severity without developing complications, it is usually favorable. Severe level 3 injuries or serious complications can lead to nephrectomy and subsequent disability. A high level of risk of complications is observed in patients after a serious injury to the kidneys, regardless of the treatment used. It is possible to prevent the development of complications only with the help of constant monitoring and preventive medical examination.