Necrosis of the kidneys or the process of necrosis of the cells of the kidney tissue
Every person suffering from at least some chronic pathology should be aware of the first signs of death of kidney tissue, which is called renal necrosis.
kidney necrosis
Necrosis of the kidneys is the process of necrosis of the cells of the kidney tissue. As a result of the research, it was found that kidney necrosis is characterized by swelling of cells and protein structures in them, followed by destruction (lysis).
Necrotic changes in the kidneys can occur due to severe intoxication with any poisonous substances, as a result of the development of autoimmune processes in the human body. Quite often, the cause of the destruction of kidney cells is a decrease in blood flow in the organ itself. With a decrease in the degree of blood supply, ischemia and hypoxia of the cellular system of the kidney develops, and then the destruction of cells.
Violation of blood flow to the kidney may occur due to thrombosis of the renal vessels or obstruction of the urinary tract by a stone or neoplasm.
Often, kidney necrosis develops in pregnant women and parturient women, this is due to heavy bleeding from the uterine cavity or premature detachment of a normal or pathologically placed placenta.
In children, this pathology occurs against the background of a viral or bacterial disease as a complication of dehydration (with profuse vomiting or diarrhea).
Kinds
Necrosis of epithelial cells of convoluted tubules
Toxic substances affect the most sensitive areas of the kidneys - the epithelium of the tubular apparatus.
The role of toxic substances can be:
- Pesticides that are part of various toxic substances or detergents;
- Heavy metal compounds, often mercury, lead and arsenic;
- Ethylene glycol is a representative of organic solvents.
In the photo, necrotic changes in the epithelial cells of the convoluted tubules of the kidneys or acute tubular necrosis - micropreparation
A. - Non-nuclear cells; B. - Preserved nuclei in the cells of the loop of Henle; B. The vessels are filled with blood and dilated.
Also, a possible cause of acute tubular necrosis can be an injury, which consists in strong squeezing of the organ, as a result of which blood flow to the tubules of the kidneys is disturbed.
In case of blockage of the ureter due to a violation of the outflow of urine, the tubules expand, their epithelium becomes necrotic and desquamated.
This type of necrosis manifests itself with acute or gradual urinary retention, blood initially appears in the urine, and the frequency of urination per day decreases. Very often, patients feel discomfort and sharp pain in the lumbar region. The patient may have a fever. Such symptoms occur due to the development of a dangerous pathological condition with kidney dysfunction - renal failure.
Acute tubular necrosis of the kidneys - macropreparation 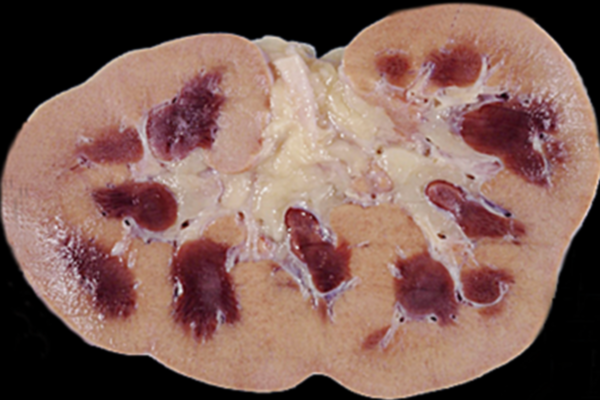
cortical
Necrosis of the cortical substance of the kidneys (cortical) is more common in newborns or in pregnant women.
Pathogenetically, necrosis of the cortex is due to increased intravascular coagulation locally in the kidneys or totally (in the bloodstream of the whole organism). The blood coagulates intensively due to a decrease in the level of fibrinogen and an increase in the concentration of thromboplastin and thrombin. There is a blockage of the blood-carrying (afferent) renal arterioles, which leads to disruption of the blood supply and shrinkage of the kidney.
As a result of criminal abortion under inappropriate conditions, bacteria enter the bloodstream and release toxins. A sharp intake of such toxins in large quantities into the blood provokes the development of a shock state (endotoxic shock).
In shock conditions, the blood flow becomes centralized, blood does not enter the cortical layer of the kidneys in a normal amount, and necrosis occurs.
Quite often, necrotic changes in the cortical layer end with the deposition of calcifications.
Symptoms for this type of pathology can be varied: there is urination with blood, the frequency of urination decreases until it is completely absent. There may be pain in the back (lower part), in the abdomen, vomiting and severe nausea, fever. If the process of intravascular coagulation is total, symptoms of damage to other organs join. Hemorrhages appear on the skin.
Cortical necrosis of the kidney 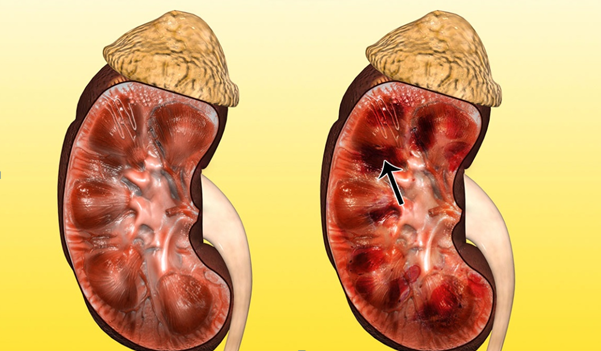
Papillary
The main etiological factor in the development of necrotic changes in the cells of the papillae of the kidneys is a bacterial infection. Bacteria can enter the pelvis from outside through the urinary tract, and are also transferred to the kidney with blood (hematogenous route). With an increase in urine pressure in the pelvis, bacteria spread to one or more papillae. As a result, cell lysis develops, blood flow to the kidney pyramids is disturbed.
The symptomatology is represented by a pronounced febrile state, pain syndrome, pronounced intoxication signs.
Papillary necrosis of the kidneys 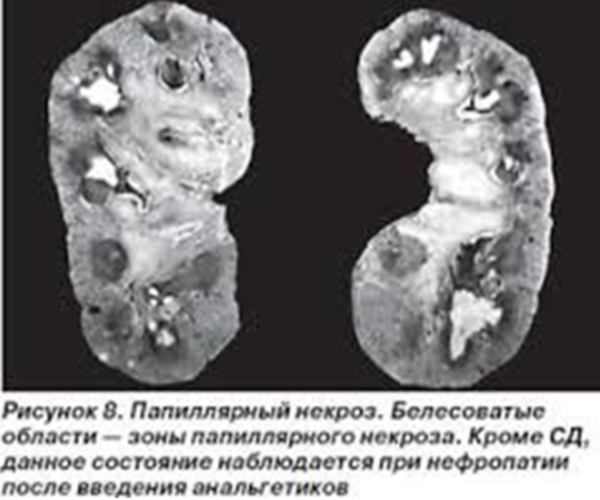
Cheesy
Necrosis of the renal tissue of the caseous type usually develops at the site of growth and development of tuberculous or syphilitic granulomas (growths). Often the cause of this pathology can be a disease such as leprosy. Caseous areas resemble curdled mass on examination. Under the microscope, the homogeneous nature of the kidney tissue, destroyed cells and connective tissue fibers are noted.
Diagnosis of tuberculosis and syphilis by initial clinical manifestations is quite difficult. There may be periods of a significant rise in body temperature, for a long time leukocytes and erythrocytes can be detected in the urine in large quantities.
The diagnosis can be confirmed by laboratory and instrumental studies. The most informative diagnostic method is considered to be a puncture biopsy of the kidney.
Caseous nephrosis 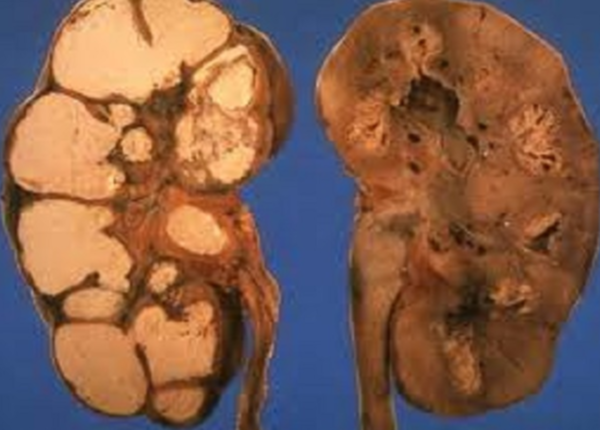
Focal
Focal necrosis of the renal tissue is usually caused by bacterial flora (syphilis, tuberculosis, leprosy and some other diseases). Symptoms are similar to those in the above forms of kidney necrosis.
Treatment
The main principles of the treatment of kidney necrosis are to eliminate the root cause of the pathological process. For this, it is necessary to carry out a complete clinical and laboratory examination.
Therapeutic measures depending on the etiology and pathogenetic mechanisms of the development of the disease:
- Antibacterial therapy;
- Improvement of hemodynamics (anticoagulant therapy);
- Elimination of obstructive urinary tract syndrome (possible and formation of a nephrostomy).
- Elimination of signs of renal failure and elimination of toxic substances (using hemodialysis);
- To relieve pain, antispasmodics or non-narcotic / narcotic analgesics are prescribed.
Surgical interventions are carried out only in severe cases of the development of the disease. If necrosis covers almost the entire area of \u200b\u200bthe kidney, then it is completely removed ().
If the cause of necrosis is vascular thrombosis, then thrombectomy and angioplasty with a balloon are widely used.
The prognosis for early detection of signs of ischemia of the renal tissue is quite favorable. Areas of necrosis as a result of timely and proper treatment are compacted and turn into a scar. And the surrounding active kidney cells compensate for their work.
Attention! In order to prevent necrosis of the renal tissue, it is recommended to be attentive to your health, to control the state of the cardiovascular, endocrine, and genitourinary systems. And when the slightest alarming symptoms appear, you should immediately consult a doctor!