A sharp drop in air temperature. Temperature fluctuations A sharp drop in air temperature
Why does a change in weather affect a person's well-being?
If you are a person whose well-being can predict the weather, then this article is for you.
In my article, I want to talk about how fluctuations in temperature, air humidity and atmospheric pressure affect human health and how you can avoid the negative impact of weather conditions on your body.
Man is a child of nature and is an integral part of it!
Everything in this world has its balance and a clear relationship, in this case, we will talk about the relationship between weather conditions and human well-being.
Some people, often moving in time and climatic zones (frequent flights), constantly change the climate and feel very comfortable doing so.
Others, on the contrary, “lying on the couch” feel the slightest fluctuations in temperature and atmospheric pressure, which in turn negatively affects their well-being - it is this sensitivity to changes in weather conditions that is called meteorological dependence.
Weather-dependent people or people - "barometers" - are most often sick, suffering from diseases of the cardiovascular system, often working a lot, constantly overworking and not resting enough.
Meteorologically dependent people include people with diseases of atherosclerosis of the vessels of the heart, brain and lower extremities, patients with diseases of the respiratory system, musculoskeletal system, allergy sufferers and patients with neurasthenia.
How do changes in atmospheric pressure affect on a person's well-being?
In order for a person to be comfortable, atmospheric pressure should be equal to 750 mm. rt. pillar.
If atmospheric pressure deviates, even by 10 mm, in one direction or another, a person feels uncomfortable and this may affect his state of health.
What happens when atmospheric pressure decreases?
With a decrease in atmospheric pressure, air humidity rises, precipitation and an increase in air temperature are possible.
The first to feel the decrease in atmospheric pressure are people with low blood pressure (hypotension), "cores", as well as people with respiratory diseases.
Most often, there is general weakness, shortness of breath, a feeling of lack of air, shortness of breath occurs.
A decrease in atmospheric pressure is especially acute and painful for people with high intracranial pressure. They get worse migraine attacks. In the digestive tract, too, not everything is in order - there is discomfort in the intestines, due to increased gas formation.
How to help yourself?
- The important point is to normalize your blood pressure and maintain it at the usual (normal) level.
- Drink more fluids (green tea, with honey)
- Don't Skip Your Morning Coffee These Days
- Don't Skip Your Morning Coffee These Days
- Take tinctures of ginseng, lemongrass, eleutherococcus
- After a working day, take a contrast shower
- Go to bed earlier than usual
What happens when atmospheric pressure rises?
When atmospheric pressure rises, the weather becomes clear and does not have sudden changes in humidity and temperature.
With an increase in atmospheric pressure, the state of health worsens in hypertensive patients, patients suffering from bronchial asthma and allergies.
When the weather becomes calm, the concentration of harmful industrial impurities in the city air increases, which are an irritating factor for people with respiratory diseases.
Frequent complaints are headaches, malaise, pain in the heart and decreased overall ability to work. An increase in atmospheric pressure negatively affects the emotional background and is often the main cause of sexual disorders.
Another negative characteristic of high atmospheric pressure is a decrease in immunity. This is due to the fact that an increase in atmospheric pressure lowers the number of leukocytes in the blood, and the body becomes more vulnerable to various infections.
How to help yourself?
- Do some light morning exercise
- Take a contrast shower
- Morning breakfast should contain more potassium (cottage cheese, raisins, dried apricots, bananas)
- Do not overeat during the day
- If you have increased intracranial pressure, take the medication prescribed by your neuropathologist beforehand.
- Take care of your nervous and immune system - do not start important things on this day
- Try to spend this day with minimal physical effort and emotions, because your mood will leave much to be desired.
- Upon arrival home, rest for 40 minutes, go about your daily activities and try to go to bed early.
How do fluctuations in air humidity affect on a person's well-being?
Low air humidity is considered to be 30 - 40%, which means that the air becomes dry and can irritate the nasal mucosa.
Dry air affects allergy sufferers and asthmatics.
What to do?
- In order to moisturize the mucous membrane of the nasopharynx, rinse through the nose with a slightly salty solution or ordinary non-carbonated water.
- Now there are many nasal sprays that contain mineral salts, help moisturize the nasal passages, nasopharynx, relieve swelling and improve nasal breathing.
What happens to the body when air humidity rises?
Increased air humidity, it is 70 - 90%, when the climate is characterized by frequent precipitation. An example of weather with high air humidity can be Russia and Sochi.
High humidity adversely affects people with respiratory diseases, because at this time the risk of hypothermia and colds increases.
High humidity contributes to the exacerbation of chronic diseases of the kidneys, joints and inflammatory diseases of the female genital organs (appendages).
How to help yourself?
- If possible, change the climate to dry
- Reduce exposure to damp and wet weather
- Warm up when you leave the house
- Take vitamins
- Treat and prevent chronic diseases in a timely manner
How do fluctuations in air temperature affect human well-being?
For the human body, the optimum ambient temperature is 18 degrees, it is this temperature that is recommended for maintaining in the room where you sleep.
Sudden temperature changes are accompanied by a change in the oxygen content in the atmospheric air, and this significantly depresses a person's well-being.
Man is a living being who needs oxygen in order to live and naturally feel good.
When the ambient temperature drops, the air is saturated with oxygen, and when it warms, on the contrary, there is less oxygen in the air, and therefore it is difficult for us to breathe in hot weather.
When the air temperature rises and atmospheric pressure decreases, people with cardiovascular and respiratory diseases suffer first of all.
When, on the contrary, the temperature drops and atmospheric pressure rises, it is especially difficult for hypertensive patients, asthmatics, people with diseases of the digestive tract and those who suffer from urolithiasis.
With a sharp and significant fluctuation in ambient temperature, by about 10 degrees during the day, a large amount of histamine is produced in the body.
Histamine is a substance that provokes the development of allergic reactions in the body in healthy people, not to mention allergy sufferers.
How to help yourself?
- In this regard, before a sharp cold snap, limit the use of foods that can cause allergies (citrus fruits, chocolate, coffee, tomatoes)
- During a strong heat, the body loses a large amount of fluid, and therefore drink more purified water in the summer - this will help save your heart, blood vessels and kidneys.
- Always listen to weather forecasts. Possession of information about temperature changes will help you reduce the likelihood of exacerbations of chronic diseases, and maybe save you from the appearance of new health problems?!
What are magnetic storms And How do they affect a person's well-being?
Solar flares, eclipses and other geophysical and cosmic factors affect human health.
You have probably noticed that over the past 15 - 25 years, along with the weather forecast, they talk about magnetic storms and warn of possible exacerbations of diseases in certain categories of people?
Each of us reacts to magnetic storms, but not everyone notices it, much less associates it with a magnetic storm.
According to statistics, it is during the days of magnetic storms that the greatest number of ambulance calls occur for hypertensive crises, heart attacks and strokes.
These days, not only the number of hospitalizations in cardiology and neurology departments is increasing, but the number of deaths due to heart attacks and strokes is also growing.
Why do magnetic storms prevent us from living?
During magnetic storms, the work of the pituitary gland is inhibited.
The pituitary gland is a gland located in the brain and produces melatonin.
Melatonin is a substance that, in turn, controls the work of the sex glands and the adrenal cortex, and the metabolism and adaptation of our body to adverse environmental conditions depend on the adrenal cortex.
Once upon a time, even studies were carried out in which it was proved that during magnetic storms the production of melatonin is suppressed, and more cortisol, the stress hormone, is released in the adrenal cortex.
Prolonged or frequent exposure to magnetic storms on the body can lead to disruption of biorhythms, which are also controlled by the pituitary gland. The result of this can be not only a deterioration in well-being, but also serious health problems (for example: neuroses, chronic fatigue syndrome, hormonal imbalances).
In conclusion, I want to say that people who spend little time outdoors suffer from weather changes more often, and therefore even slight weather fluctuations can cause poor health.
"11 ways to get rid of weather dependence"
1. Hardening
2. Swimming
3. Walking, running
4. Frequent walks in the fresh air
5. Healthy and nutritious food
6. Enough sleep
7. Correction of the emotional sphere (autogenic training, relaxation, yoga, massage, conversation with a psychologist)
8. Taking vitamins
9. Eat seasonal foods
10. Refusal of bad habits
11. Weight normalization
Tips for sudden weather changes
- Limit physical activity.
- Avoid additional both emotional and physical stress.
- Control your blood pressure and do not forget to take the medicines prescribed by your cardiologist. Neurologist, pulmonologist or allergist.
- Do not overeat or abuse salt.
- Walk outdoors for at least 1 hour before bed.
- With an increase in blood pressure, massage the neck and thoracic spine.
- Take tranquilizers.
- Don't forget about vitamins C and B.
If you have read the article to the end, then you are really worried about your health and you clearly feel the fluctuations in the weather.
But what if the mood does not deteriorate when environmental changes prevent us from living? And if this happens often, we are exposed to constant negativity, of which there is already a lot around us, and then there is the weather ....
Olga Lukinskaya
It is generally accepted that going to the bath is useful, and a contrast shower helps to "harden" the immune system - but at the same time they say that for an unprepared person, diving into cold water can provoke a heart attack. We tried to figure out what science says about the dangers and benefits of temperature changes for the body - does the bath really “remove toxins”, is it useful to leave to “warm up” from winter to summer, and can food at contrasting temperatures harm.

Cold and hot shower
A soul with an alternating change in water temperature (from hot to cold and vice versa) is often credited with magical properties: it should strengthen the immune system, train muscles and even regulate the endocrine system. A couple of years ago, a study was conducted in the Netherlands with the participation of three thousand people who took either the usual shower or a contrast shower in the morning. It turned out that the number of days when people were ill (mostly with colds) was the same in all groups, but those who took a contrast shower were 29% less likely to miss work, because they tolerated viral infections much more easily. By the way, the timing of the study coincided with the influenza epidemic in Holland.
According to the authors of the study, the mechanisms of this effect are not yet clear - but it is not associated with the "strengthening" of immunity; it turned out that the cold simultaneously causes reactions that enhance and suppress immune function. Possible explanations include psychological expectations (a placebo effect when a person is confident of a recovery with a contrast shower) and an improvement in overall fitness. The 29% reduction in sick leave is comparable to the effect of physical activity: people who exercised regularly had 35% fewer sick days than those who did not exercise or take contrast showers.
The general condition improves due to temperature contrasts because the cardiovascular system is trained: under the influence of cold, the superficial vessels narrow to protect the body from heat loss. In the heat, on the contrary, there is an expansion of blood vessels close to the surface of the body - this avoids overheating. As with any other workout, this should be accustomed to the body gradually, starting with mild temperature changes and short intervals.
Bath and cold water
With scientific confirmation of the benefits of the bath, everything is not so simple: on the one hand, saunas and baths are associated with a healthy lifestyle, and a couple of years ago, in another study, they confirmed that their regular visit correlates with a decrease in the risk of heart disease and even mortality. On the other hand, the official commentary on these results states that people at risk of cardiovascular complications may experience discomfort in the bath, as a result of which they simply refuse to visit it.
Changes in atmospheric pressure are one of the most common causes of deterioration in well-being in weather-dependent people. A sharp change in weather primarily negatively affects the health of those who suffer from cardiovascular diseases. Their well-being may worsen due to decrease in atmospheric pressure.
How does temperature change affect pressure?
Severe frosts in winter are traditionally brought by anticyclones - areas of high atmospheric pressure. Anticyclones are characterized by clear or slightly cloudy weather and the absence of precipitation. And now in the European territory of Russia, which carries warmer air. This cyclone is a giant atmospheric vortex, in the center of which is dominated by low pressure.
But how are atmospheric and blood pressure related? Despite the fact that we do not feel and do not see the air, it is not incorporeal. This gas has a weight that would flatten us if human bodies did not maintain their own pressure - arterial pressure. It gets higher or lower, depending on how the atmospheric changes. The so-called "baroreceptors" located in the vessels are responsible for this process.
In healthy people, they easily adapt to what is happening around, but in weather-sensitive people, unfortunately, they do not cope with the task as well as we would like. When the atmospheric pressure increases, their baroreceptors do not just increase the pressure, but provoke a real jump. As a result, a person begins to have a headache, nausea appears, and flies flash before his eyes. Sometimes a slight chill joins these sensations. Weather-sensitive people react to a decrease in atmospheric pressure in the same way as to an increase. At first, their baroreceptors begin to reduce arterial parameters, but at some point it seems to the body that they are becoming too low, and it.
What to do? It is necessary to exclude from the diet foods that can further increase blood pressure (strong meat and fish broths, strong tea, coffee, beans, peas, carbonated drinks).
Do not overeat, it is better to make a diet of vegetable and fish dishes, eat more greens.
You also need to moderate physical activity, abandon any hard work. In general, this day needs to be unloaded as much as possible so that it goes smoothly.
We are afraid of a cold
It was during warming, and not in severe frosts viruses and pathogenic bacteria are activated. Increased air humidity reduces the body's resistance to disease. Therefore, it is easier to catch a cold or flu, which will lead to bronchitis. The incidence of pneumonia is also on the rise.
What to do? Dress warmly enough so you don't get windy, but not too warm so you don't overheat. You should also try not to get your feet wet in puddles of melted snow and, at least for a while, give up cigarettes or smoke less.
During a thaw, some people may experience shortness of breath, suffocation, and even develop hypoxia - oxygen starvation. This is due to the fact that a cyclone carrying warm air and snow leads to a decrease in atmospheric pressure, therefore, the oxygen content in the air decreases.
Breathing can become more difficult even for a healthy person, what then to say about patients with bronchial asthma. Therefore, asthmatics these days should not forget about the inhaler.
We follow the mood
Natural disasters affect the mental state of people. Abnormal atmospheric pressure turns some people into somnambulists. Someone, on the contrary, appears inexplicable aggression. It is very important for such people to learn to relax after a busy day.
Choose any way of relaxation - whatever you like. It can be yoga, meditation, auto-training, add to them walking around the house for the coming dream. These days, you need to try to pull yourself together and not quarrel with anyone, because stress aggravates the painful condition.
Those who feel excitement, aggression, nervousness, in no case need to drive these days, do dangerous work, plan complex negotiations, and so on.
We take care of the joints
People suffering from joint pain are keenly aware of the slightest changes in the weather. Cooling or warming, as well as high humidity, adversely affect the condition of patients with rheumatoid arthritis. The pain will pass at least for a while if you use warming ointments and dressings made of natural wool.
We don't fall
During the thaw, ice often forms. As a result, more and more people who slip on icy sidewalks end up in emergency rooms with bruises, fractures, and even concussions. The hospitals also receive victims of falling icicles and ice from the roofs. The number of traffic accidents is also on the rise as cars skid on slippery roads. Therefore, carefully look under your feet and do not walk near buildings. Choose non-slip shoes with flat soles. And stay away from houses with icicles hanging from their roofs.
The impact of weather on healthHow often do we blame the weather for bad mood, poor health, unwillingness to do anything and other troubles. But can weather conditions really have such an active influence on our health, and what is it really - meteorological dependence?Atmosphere pressure
In order for a person to feel comfortable, atmospheric pressure should be 750 mm Hg, if this value deviates even by only 10-15 points, the human body reacts with a deterioration in well-being.
Cyclone
A cyclone is a decrease in atmospheric pressure, which is accompanied by cloudiness, high humidity, precipitation and an increase in air temperature.
Who is affected by the cyclone?
The cyclone is dangerous for people suffering from low blood pressure, for those who have problems with the heart and blood vessels, as well as impaired respiratory function.
The negative influence of the cyclone is manifested in a feeling of general weakness, shortness of breath, lack of air, and shortness of breath. The thing is that on such days the air is depleted of oxygen. And people who have increased intracranial pressure may suffer from migraines. With the advent of the cyclone, the condition of the gastrointestinal tract also worsens, the discomfort in which is associated with stretching of the intestinal walls due to increased gas formation.
How to alleviate the impact of the cyclone?
The most important thing is to keep your blood pressure at an acceptable level, for this you need to drink more water (2 glasses more than usual). A morning cup of coffee, tinctures of Eleutherococcus, lemongrass, pantocrine or ginseng will benefit. Facilitate the state of a contrast shower and a good long sleep.
Anticyclone
An anticyclone is an increased atmospheric pressure that brings with it calm, clear weather, without sudden changes in temperature and humidity.
Who is affected by the anticyclone?
The risk group includes people with high blood pressure, asthma and allergies, who suffer from the fact that the city air is saturated with harmful impurities, which are especially abundant in calm weather.
The influence of the anticyclone is characterized by pain in the heart, headaches and malaise, which contributes to a decrease in efficiency and general well-being. High pressure negatively affects the character and can cause sexual frustration in men. Under the influence of the anticyclone, immunity weakens, the number of leukocytes in the blood decreases and the body becomes susceptible to infections.
How to alleviate the influence of the anticyclone?
In the morning it is advisable to take a contrast shower, perform several morning exercises, do not overeat during the day, giving preference to bananas rich in potassium, raisins, you can take vitamin E. With increased intracranial pressure, it is important to follow the recommendations of a neurologist.
With pressure drops, it is not recommended to start any important business, so as not to overload the immune and nervous systems of the body. But if it is impossible to completely abandon the loads, then you need to at least minimize them and be prepared for the fact that your health may not be the best.
The danger for a person lies not only in atmospheric, but also in his own blood pressure, because often high blood pressure has absolutely no manifestations. A person may not be aware of the problem of high blood pressure at all, exposing himself to the risk of a stroke or heart attack. Therefore, it is very important to regularly measure blood pressure in order to prevent the development of unpleasant diseases, and you also need to be careful about your weight.
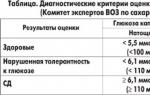
It is important to know that the optimal indicators of blood pressure are the numbers - 120/80, the pressure of 130/85 is considered normal. Normally high readings are 130/85 and 139/89, normal low readings are 100/60.
It is also important to measure blood pressure correctly, especially if you feel unwell during weather changes and take into account that the result will be overestimated in the cold, so it is best to take measurements at room temperature (20 ° C). The results will be inflated immediately after smoking, drinking alcohol or tea and coffee, under stress, after physical exertion, taking a shower or bath, and also if you cross your legs, sit in a Turkish position or bend your back during the measurement .
Reduced air humidity
If the air humidity is low, then it is 30-40%. And dry air irritates the nasal mucosa, which does not allow harmful microbes to enter the body during breathing. Allergy sufferers are especially at risk, and in order to avoid increased dryness in the nasopharynx, it is recommended to wash with a solution of lightly salted or non-carbonated mineral water.
High humidity
With a large amount of precipitation, air humidity can reach 80-90%. Such weather is characteristic of subtropical zones, in Russia - the cities of Sochi and Vladivostok.
The risk group is made up of people with respiratory diseases, for whom spring is especially dangerous due to snowmelt. High humidity is often accompanied by frequent changes in weather conditions, when the risk of hypothermia and colds is especially high. High humidity can exacerbate the inflammatory processes of the joints and kidneys. With high humidity combined with high air temperatures, it is better to limit exposure to the open air.
Temperature
The most comfortable temperature is considered to be from 16 to 18 degrees. The same value is recommended for nighttime sleep and should be maintained in the bedroom.
Sharp changes in temperature lead to a change in the oxygen content in the air: when it gets colder, it is saturated with oxygen, and when it gets warmer, on the contrary, it becomes depleted. When atmospheric pressure decreases against the background of high air temperature, people with disorders of the respiratory and cardiovascular systems fall into the risk group.
If, against the background of high pressure, the air temperature drops and is accompanied by cold rains, then hypertensive patients, asthmatics, people with kidney stone and cholelithiasis suffer it especially hard. With sudden changes in temperature (8-10 ° C per day), histamine is released in the human body, provoking the appearance of allergic reactions, sometimes even in those who have never suffered from them before. Trying to protect yourself from unwanted reactions, before a cold snap, stick to a sparing diet that excludes chocolate, citrus fruits, spices and red wine. 
Weather sensitivity - a disease or a natural condition?
Healthy people almost do not react to weather changes. But since when the weather changes in a healthy body, there are rapid changes in the blood count, enzyme activity, hormone production, the heart rate, blood pressure and mood may change slightly. This is the protective reaction of the body to changes in nature. Otherwise, healthy people do not notice the difference in their condition during meteorological cataclysms.In medicine, dependence on the weather by the human body is divided into meteosensitivity, meteorological dependence and meteopathy.
weather sensitive you can name almost the entire population of our planet (statistics call the figure 75%). Such people react with malaise to the manifestation of changes in the weather. It can be said of such a person that he is not yet sick, but is no longer healthy. That is, it is in a state of pre-illness. More often meteosensitivity affects people with a type of character weak and unbalanced (melancholic and choleric). Sanguine people - people of a strong balanced type can react to weather changes only when the body is weakened.
Weather dependent people who react with changes in blood pressure, cardiograms, general malaise, etc. are called.
Meteopathy- it's a disease. Such patients during weather changes do not leave pain in the heart, shortness of breath, headaches and dizziness, noise in the head, neurasthenia, insomnia, weakness, aching joints and muscles, etc. This condition requires medical treatment and constant medical supervision.
The problem of weather dependence is very serious. Because more and more chronic patients suffering from vascular diseases, during the so-called magnetic storms, end up in hospital beds and the number of heart attacks and strokes on such days is growing.
How can a person help himself to endure changes in the weather without significant losses?
A healthy lifestyle, strengthening the immune system will help nullify the body's reaction during adverse weather forecasts.
On normal days:
1. Mode of work and rest
2. Balanced diet
3. Sufficient night sleep in a cool room and short breaks during the day
4. Physical activity that trains the respiratory and cardiovascular systems: swimming, walking (especially before bedtime)
5. Massage and self-massage
6. Hardening
7. Shower, therapeutic baths
8. Walk in the air, but not in the sun
In the event of a sudden change in weather:
1. Avoid overwork - if possible, you need to give up hard physical and intellectual work
2. Eat in moderation
3. Try to avoid conflict situations
4. Take soothing herbal teas
5. Strictly observe the regimen of taking medications prescribed by the doctor
6. Always have an ambulance on hand
During the full moon, oriental medicine advises, especially hypertensive patients, to reduce physical activity.
Traditional medicine recipes for weather-dependent people:
Infusion from a mixture of herbs:
Hawthorn flowers - 4 parts
t. Rava motherwort - 4 parts
. rose hips - 4 parts
. chamomile flowers - 1 part
. mint leaves - 1 part
Pour 1 tablespoon with one glass of boiling water, let it brew and drink as instead of tea 3 times a day.
Aromatherapy:
The smell of rosemary and lavender helps with increased excitability
. The smell of lemon and eucalyptus will improve your mood
Take care of yourself and be attentive to the changes taking place in the body, mood and well-being. 


To begin with, it would be nice to understand whether the weather affects a person, and if so, how?
A person has long felt like a "master of nature", and sometimes even tries to curb the elements. And then there's this question...
It needs to be sorted out.
Healthy and strong people feel only strong changes in the weather, sick and weakened people react even to small weather changes.
Photo: Shutterstock.com
It's no secret that the human body, like animals and vegetation, coexists in a close relationship with nature. Whether we like it or not, we still feel (feel) its impact on us. Healthy and strong people feel only strong changes in the weather, sick and weakened people react to small weather changes.
For more than three thousand years, people have been trying to understand and study the issue of the influence of natural factors on the human body. In ancient Tibet, diseases were associated with meteorological phenomena. Hippocrates (460-377 BC) in his writings described the relationship between the physical and mental well-being of a person and climate change. He wrote in his work "Aphorisms" that human organisms behave differently in relation to the seasons: some are closer to summer, others to winter, and diseases proceed differently (good or bad) at different times of the year, in different countries and conditions. life.
Thus, there is no doubt that the weather has a direct and tangible effect on the human body and its well-being. Then it is necessary to understand in more detail what forces of nature affect our body, and how the weather affects the health and well-being of people?
Atmosphere pressure
Atmospheric pressure is one of the most influential weather factors. The nature and strength of the influence of atmospheric pressure depend on the magnitude of deviations from the norm (amplitude of fluctuations) and the rate of change. The area of influence extends to almost all organs of our body.

Atmospheric pressure is one of the most influential natural factors.
Photo: Shutterstock.com
Changes the pressure in the cavities of our body
With a change in atmospheric pressure, the pressure in the cavities of our body also changes, which causes mechanical irritation of the nerve endings (baroreceptors) of the respiratory organs (pleura), abdominal cavity, joints, and blood vessels. Receptors perceive external influences and transmit this signal to the brain, where this information is processed. The back reaction of the body is provided by the vegetative-vascular system. It is responsible for the connection of the internal organs with the central nervous system, for vascular tone and blood pressure, for the work of the heart, and also controls the activity of the glands (endocrine, sweat, sebaceous). It is this response of the body that is observed in weather-sensitive people with jumps in atmospheric pressure.
With this phenomenon, reactions are observed:
- joints - exacerbation of arthritis, joint pain;
- cardio - vascular system - sudden changes in blood pressure, rhythm and heart rate disturbances, general deterioration of well-being;
- gastrointestinal tract - bloating in the stomach and intestines. Quite healthy people may complain of similar symptoms, this is due to a change in pressure in the abdominal cavity.
People are susceptible to such reactions to changes in atmospheric pressure:
- suffered traumatic brain injury;
- suffering from intracranial pressure;
- with chronic diseases of the upper respiratory tract.
Reduces the partial pressure of oxygen in the blood
In addition, with jumps in atmospheric pressure, there is a simultaneous decrease in the partial pressure of oxygen in the blood, which causes hypoxia of the organs and tissues of our body. Our brain cells suffer the most from "oxygen starvation". Therefore, even healthy people often get headaches from pressure drops.
The most prone to headaches in this case are people:
- suffering from chronic diseases of the respiratory tract, who have had severe diseases of the lungs and bronchi;
- suffering from heart disease;
- having general or local circulatory disorders (for example, in the vessels of the brain, chronic heart failure);
- suffering from anemia.
What indications are considered a deviation from the norm in central Russia?
High a pressure above 755 mmHg is considered. With such readings of the barometer, asthmatics, "cores", and people with mental disabilities are the first to suffer. Low pressure below 748 mmHg is considered. At low pressure, hypotensive patients have no strength, they tend to sleep, feel sick, and feel dizzy. In hypertensive patients, it begins to knock in the temples, the headache intensifies.
temperature fluctuations

A sharp temperature drop in itself gives a serious burden on the body.
Photo: Shutterstock.com
The most comfortable temperature for a resident of the middle latitudes of Russia is 16-18 C 0. It is this temperature that is recommended to maintain indoors during sleep.
A temperature drop in the region of 3-4 degrees C 0 is considered normal and does not cause any discomfort to anyone. A sharp cold snap or sudden warming (temperature change of 7-8 or more degrees C 0 within 12 hours) can cause serious complications in people suffering from vascular diseases or who have had a heart attack or stroke.
A sharp temperature drop in itself gives a serious burden on the body. Therefore, doctors do not recommend people suffering from chronic diseases, especially the nervous and endocrine systems, heart and blood vessels, autoimmune diseases, to change climatic zones (in winter, go to warm climes, in summer to zones with cold temperatures).
Cold snap adversely affects the body's immune system. For this reason, the largest bursts of colds and infectious diseases are observed at times of severe cooling. Therefore, doctors recommend that people suffering from chronic infectious and inflammatory diseases, especially ENT organs (chronic pharyngitis, tonsillitis, sinusitis, etc.) take special care during cold snaps to protect themselves from the possibility of a relapse of the disease.
Heat (high temperature)- the ability to tolerate heat is directly dependent on wind and humidity. The more windy and humid, the more difficult the heat is tolerable. For a resident of middle latitudes, an air temperature of 27 C 0 is considered comfortable. Asthmatics, people with overweight, metabolic disorders, autoimmune diseases, endocrine and cardiovascular diseases suffer the most from heat.
Air humidity

Particularly unfriendly to humans is a combination of the following factors: high (or low) temperature, high humidity and strong winds. Photo: Shutterstock.com
Humidity is the amount of water vapor in the air. Comfortable indicators for a resident of middle latitudes is considered to be air humidity of 50%.
In conditions low humidity the air becomes dry, which causes the mucous membranes of the body to dry out and exposes it to the risk of developing infectious diseases. Often this happens in the cold season, with the beginning of the heating season, when the air in the rooms becomes dry.
high humidity in nature gives rise to dampness. Dampness, in turn, directly affects the body's ability to withstand temperature, since water has a heat capacity. Particularly unfriendly to humans is a combination of the following factors: high (or low) temperature, high humidity and strong winds.
high humidity during the hot season reduces the body's heat transfer and causes the risk of overheating and heat stroke. IN cold season, with high humidity, there is a threat of hypothermia, since water literally draws heat from the body. There are cases when frostbite of limbs occurred even at temperatures above 0C 0 . High humidity can also provoke attacks of bronchospasm and jumps in blood pressure in people suffering from bronchopulmonary and cardiovascular diseases.
Meteorological dependence on indicators of air humidity also affects people with skin diseases, suffering from pathologies of the respiratory and cardiovascular systems.
Movement of air masses (wind)

Movements of air masses (wind) of different density also cause a lot of anxiety
Photo: Shutterstock.com
Movements of air masses (wind) of different density also cause a lot of anxiety. First of all, people with pathologies of the nervous system suffer from the wind. This is due to the fact that the wind has an irritating effect on the receptors of the skin and unprotected mucous membranes. Therefore, people suffering from diseases of the skin and eyes are prone to relapse, due to the fact that the wind mechanically affects the affected areas.
Strong wind can cause migraine attacks, anxiety attacks in children under 3 years of age, as well as severe depression in people with an unbalanced psyche.
Complete calm on the contrary, it causes anxiety attacks in people suffering from neurosis, people of the older generation (45-60 years old) and adolescents. This phenomenon is directly related to age-related hormonal fluctuations in the body.
Solar Activity

Solar radiation - has a direct effect on the systems and organs of the human body.
Photo: Shutterstock.com
solar radiation
Solar radiation - has a direct effect on the systems and organs of the human body, depresses the immune system. Excessive UV radiation and overheating adversely affect the functioning of the immune system.
This can exacerbate chronic diseases of the ENT organs, diseases of the upper and lower respiratory tract, skin diseases, as well as other infections that have a chronic form of the course, including herpes virus infections.
Lack of sunlight gives rise to a lack of vitamin D in the body and leads to a decrease in the protective functions of the body, weakening of the immune system, the occurrence of neurosis and depression. Children and the elderly are especially susceptible to this.
Excess solar radiation It has an adverse effect on the course of skin diseases, and is also fraught with sunburn and favors the development of malignant tumors. Therefore, doctors categorically forbid people with suspected malignancy to be in direct sunlight for a long time.
Meteorological dependence on sunlight affects children, the elderly, people with skin diseases, as well as diseases of the nervous, endocrine and immune systems.
Electromagnetic radiation
The sun also changes the electromagnetic field of the Earth, sometimes so much that it creates real "magnetic storms", which directly affects the human body and the processes occurring in it.
The electromagnetic waves of the magnetic field of our Planet are invisible to the human eye, with rare exceptions (Northern Lights), but this does not mean that they do not affect us. The influence is in two directions:
- effects on the central nervous and endocrine systems;
- impact on the cardiovascular system (directly on vascular tone).
Those. people are at risk of meteorological dependence from "magnetic storms":
- elderly (from 55 and older), because increases the sensitivity of the neuro-endocrine system;
- with diseases (or suspicions of them) of the central nervous system (craniocerebral trauma, strokes;
- with cardiovascular diseases (hypertension, atherosclerosis, coronary heart disease);
- with diseases of the nervous system (vegetative-vascular dystonia, migraine, neurosis, depression);
- with endocrine diseases (diabetes mellitus, thyroid disease, premenstrual syndrome, pathological menopause);
- suffering from severe chronic diseases leading to nervous exhaustion.
Seasonal weather dependence

According to statistics, the largest outbreak of seasonal diseases occurs in the autumn-winter period.
Photo: Shutterstock.com
There is such a thing as seasonal weather dependence. What it is? This is the dependence of a person’s well-being on weather factors that are characteristic of a particular time of the year. For example, chronic diseases often sharply worsen at the turn of the seasons: winter and spring, summer and autumn, etc. for this reason, we see seasonal spikes in respiratory illnesses in the spring and fall. According to statistics, the largest outbreak of seasonal diseases occurs in the autumn-winter period.
Diseases that are characterized by seasonal exacerbations include:
- peptic ulcer of the stomach and duodenum (spring and autumn);
- depression and neurosis (spring and autumn);
- chronic infectious and inflammatory diseases (autumn and winter);
- severe pathologies that occur with depletion of the body (spring and autumn).
Climatic weather dependence

Photo: Sphinx Wang / Shutterstock.com
There is also climatic meteorological dependence, this is the dependence of a person's well-being on the totality of weather factors characteristic of a particular region. For example, changing climatic zones (moving from winter to summer and back) is quite painful for children, the elderly, those suffering from chronic diseases and / or people with weakened immune systems.
Climatic conditions can also positively influence human health. It should be noted that in many clinical cases climate change is indeed able to bring healing to the patient.
Long before modern discoveries about climatic meteorological dependence were made, doctors recommended that patients “change the climate”. For example, with nervous diseases, patients were sent "to the waters" (warm thermal springs, with a high concentration of bromine in the fumes). Patients with an "ulcer" were also sent to be treated "at the waters" (mineral springs). Patients suffering from respiratory diseases were sent to resorts surrounded by dense coniferous forests (pine, fir, spruce, eucalyptus), the air of which is rich in phytoncides * - here the patients received significant relief, and often healing.
Climatic resorts to this day help the sick to restore shaky health, and the healthy to strengthen the immune system.
* Phytoncides (from Greek. ????? - "plant" and lat. Caedo- "kill"- biologically active substances formed by plants that kill or inhibit the growth and development of bacteria, microscopic fungi, and protozoa.
"Meteorological Neurosis"

Meteoneurosis is a condition when a person really feels terrible during weather changes (irritability, bad mood, shortness of breath, palpitations, dizziness), while real health indicators (pressure, heart, temperature, etc.) remain normal. Photo: Shutterstock.com
It must be said that meteorological dependence occurs not only due to the presence of certain diseases in the human body. The ability to resist the influence of weather conditions of the organism is also affected by its adaptive capabilities.
Sometimes, patients with chronic diseases quite successfully resist the influence of weather on the body, and sometimes quite healthy and full of strength people suffer from meteorological dependence. In this case, we can talk about such a phenomenon as "meteorological neurosis". Meteoneurosis is a violation of neuroenocrine regulation, leading to a significant decrease in the body's ability to resist and adapt to the influence of the weather.
Simply put, meteoneurosis is a kind of neurotic disorder when a person really feels terrible during weather changes (irritability, bad mood, shortness of breath, palpitations, dizziness), while real health indicators (pressure, heart, temperature, etc.) remain normal .
Risk factors that contribute to the occurrence of meteoneurosis include:
- hereditary predisposition;
- physical inactivity - a sedentary lifestyle;
- rare exposure to fresh air;
- overweight;
- bad habits (smoking, caffeine and alcohol abuse);
- intellectual overload (exams, "parks" at work);
- repetitive stress.
Meteoneurosis is a fairly common ailment of our time. They often affect residents of large cities. It also often develops in sensitive people under the influence of geomagnetic forecasts.
Some patients even complain that they are not given sick leave, although they really feel disgusting. Indeed, the manifestations of meteoneurosis cannot be measured with instruments, just as it is impossible to measure melancholy, apathy or boredom. It is also quite difficult to get to the bottom of the true causes of meteoneurosis. Often these reasons are purely psychological in nature, for example, a small child willingly takes over from adults to be upset because of “bad” weather, observing this phenomenon in his family for more than one year in a row. Sometimes the cause of meteoneurosis can be an innate need for a lot of sunlight. It is especially difficult for such a person to live in cloudy, northern and low-sun regions, he literally “gets sick” from a lack of sunlight.
Despite the fact that this ailment looks like laziness from the outside, it poses a very real danger. Motorists can get into an accident, employees can lose valuable data or make mistakes, because of frustration and absent-mindedness, you can simply not carefully look at your feet and fall.
Order yourself good weather!

What kind of weather awaits us in the near future?
After the May rains, of course, we all want good weather. We make plans, prepare for trips to the countryside or to the country, and maybe even on vacation. How can the weather affect our plans and do we need to make adjustments to the weather forecast?