Blood sugar level: acceptable fasting rate, measurement methods. The difference between blood plasma and serum
High blood sugar is the main symptom of diabetes. A certain amount of glucose is always present in the body of any person, as it is the most important source of vital energy. The sugar level is unstable and fluctuates throughout the day. But in a healthy person, it keeps within the limits that are commonly called the norm. And diabetics have higher values.
The level of blood sugar does not depend on gender and age of a person. The rules are the same for men, women and children. However, doctors note some relationship between sugar levels and the age of the patient. As a rule, glycemic (blood glucose) levels are slightly higher in older people. This is understandable: the older the patient, the more depleted his pancreas and the worse it copes with the production of the hormone insulin, which regulates sugar.
Elevated blood glucose levels are called hyperglycemia. Most often, it is a sign of diabetes mellitus, but it can also occur with exacerbation of chronic pancreatitis (pancreatogenic diabetes), hypercortisolism (adrenal or pituitary gland disease), thyrotoxicosis (increased release of thyroid hormones), pheochromocytoma (adrenal gland disease), acromegaly (pituitary disease).
Symptoms of hyperglycemia
With severe hyperglycemia (high blood sugar), a person may experience the following sensations:
- dry mouth;
- thirst;
- frequent urination (including at night);
- an increase in the volume of urine excreted;
- weakness, lethargy, fatigue, decreased performance;
- weight loss against the background of increased appetite;
- poor healing of wounds, skin lesions, inflammatory diseases;
- itching of the skin and mucous membranes (most often the perineum);
- the appearance of a specific taste in the mouth and the smell of "baked apples" due to acetone. This is a sign of a clear decompensation of diabetes.
However, high sugar does not always mean the presence of diabetes or some kind of disorder in the body. There is a so-called physiological hyperglycemia - a condition in which an increase in blood glucose is due to natural causes. These include: eating a meal rich in carbohydrates, severe emotional stress, stress, some surgical interventions.
In order to accurately know the amount of sugar, you can take an empty stomach blood test. By the way, when doctors say “on an empty stomach”, they mean early in the morning, at least 8, but not more than 14 hours should pass from the last meal. If this time interval is not observed, the results of the analysis may be false, uninformative. And by the phrase “after eating,” doctors usually mean a period of 2-4 hours after eating.
It is important to note that you can measure glucose both in venous blood (from a vein) and in capillary blood (taken from a finger). In each of these cases, their sugar norms.
In the venous blood of a healthy person, the normal level of sugar will be within 6.1 mmol / l on an empty stomach and up to 7.8 mmol / l 2 hours after a meal. In capillary blood (from a finger), it is believed that this indicator should not exceed 5.6 mmol / l, and a couple of hours after eating - no more than 7.8 mmol / l.
The doctor assumes that the patient has diabetes mellitus when the level of glycemia is equal to or exceeds 7 mmol / l on an empty stomach and more than 11.1 mmol / l 2-3 hours after a meal in venous blood and 6.1 mmol / l on an empty stomach and 11.1 mmol / l a couple of hours after eating in the capillary. And what is in the interval between the norm and diabetes?
prediabetes
This is a simplified name for a condition in which glucose tolerance is impaired. The pancreas still produces insulin, but in small quantities. And the hormone is not enough for the normal functioning of the body. Such a diagnosis reflects the possibility of developing diabetes in the future with an indifferent attitude to one's health and adverse circumstances (overeating, sedentary lifestyle, bad habits, non-compliance with diet and medical recommendations).
When a patient is suspected of an initial or latent form of carbohydrate metabolism disorders (with a moderate increase in blood sugar levels, with the periodic appearance of glucose in the urine, symptoms of diabetes with acceptable sugar, against the background of thyrotoxicosis and some other diseases), a so-called glucose tolerance test is performed. This study allows you to clarify the diagnosis or confirm its absence.
Carbohydrate tolerance stress test
3 days before the analysis, a person does not limit himself in the use of carbohydrates, eats in his usual mode. Physical activity should also remain habitual. The last evening meal the day before should contain 50 g of carbohydrates and be no later than 8 hours before the test (drinking water is allowed).
The essence of the analysis is as follows: the patient's blood glucose level is measured on an empty stomach, then for 5 minutes they are allowed to drink a glass (200-300 ml) of warm water with 75 g of glucose dissolved in it (in children, at the rate of 1.75 g per kilogram of weight, but not more than 75 g). Then, blood sugar is measured an hour later and 2 hours after drinking glucose. For the entire time of the analysis, the patient is not allowed to smoke and actively move. The load test result is evaluated as follows: 
If glucose tolerance is low (sugar level does not drop fast enough), this means that the patient is at risk for developing diabetes.
Gestational diabetes
This term refers to the increased level of glucose in the blood of a pregnant woman. For diagnosis, only venous blood is examined. Recently, absolutely all pregnant women have been tested for diabetes to detect carbohydrate tolerance between 24 and 28 weeks of pregnancy (optimally 24-26 weeks). This measure allows you to identify the disease at an early stage and prevent possible consequences for the mother and fetus.
Decreased glucose level
With long-term treatment of diabetes with insulin or oral medications, hypoglycemia can occur, a condition in which blood sugar is very low (below 3.3 mmol / l).
Causes of occurrence:
- An overdose of insulin resulting from a violation of the tactics of administering the hormone (incorrect dose set for injection, erroneous repeated intake, injection with short insulin instead of prolonged, etc.);
- deficiency of carbohydrates in the diet, skipping meals, a long interval between insulin injections and meals;
- greater than usual physical activity;
- alcohol intake.
Like high blood glucose, hypoglycemia can be physiological due to various natural causes. For example, with stress, intense physical exertion, in newborns - in the first hours of life.
Symptoms of hypoglycemia:

What to do with mild hypoglycemia
If symptoms are detected, you need to eat 4 pieces of sugar, or drink a glass of sweet tea, carbonated drink (lemonade, fanta) or juice (preferably grape). It is also necessary to analyze the reasons that led to a strong drop in sugar, so that such mistakes do not happen again. Perhaps the physical load was calculated incorrectly, a meal was missed, or there were errors in taking or injecting insulin. In case of severe hypoglycemia and the patient faints, call an ambulance.
Permissible indicators in diabetics
With diabetes, you should strive to keep blood glucose as close to normal as possible. This is the basis for the prevention of complications and the guarantee of relative health in this disease. It is necessary to achieve indicators of glycemia before meals no higher than 6.1 mmol / l, and 2-3 hours after a meal - up to 7.8 mmol / l. Relying only on your feelings is completely wrong, since most people do not feel the difference between sugar values \u200b\u200bfrom 4.5 to 12 mmol / l. In addition, if the amount of glucose in the blood is almost always elevated (as happens in diabetics), the body's susceptibility to sugar levels goes astray. Habitually high values begin to feel normal, and normal ones are confused with hypoglycemia. That is why it is important to carry out self-monitoring with a glucometer in order to know exactly how much sugar is in the blood.
The procedure consists in regularly checking the blood on your own at home. The meaning of self-control is that a person can track sugar fluctuations in a timely manner and adjust their treatment if the measurement results are unsatisfactory. The value of readings obtained under familiar conditions during self-monitoring is much higher, since they reflect the patient's condition in a calm environment.
 A special tool with which a diabetic can measure blood sugar on their own is called a glucometer. The device is easy to use, convenient and accurate. It works like this: the patient applies a drop of his blood to a special test strip, which is then inserted into the device. And within a minute, the device displays the measurement result on the screen.
A special tool with which a diabetic can measure blood sugar on their own is called a glucometer. The device is easy to use, convenient and accurate. It works like this: the patient applies a drop of his blood to a special test strip, which is then inserted into the device. And within a minute, the device displays the measurement result on the screen.
 Currently, there are a large number of different glucometers. The patient chooses the product that is convenient for him. There are devices with the function of remembering the last measurements, with the option of evaluating the result (poor, satisfactory), with the possibility of transferring data to a personal computer with subsequent processing, etc. Some devices, in addition to sugar levels, can measure cholesterol and acetone in the blood. Even talking devices for people with reduced vision are sold, as well as glucometers combined with a tonometer - to determine blood pressure. Each device has an error in the measurement, both plus and minus. An acceptable error is considered to be a deviation within +
20%.
Currently, there are a large number of different glucometers. The patient chooses the product that is convenient for him. There are devices with the function of remembering the last measurements, with the option of evaluating the result (poor, satisfactory), with the possibility of transferring data to a personal computer with subsequent processing, etc. Some devices, in addition to sugar levels, can measure cholesterol and acetone in the blood. Even talking devices for people with reduced vision are sold, as well as glucometers combined with a tonometer - to determine blood pressure. Each device has an error in the measurement, both plus and minus. An acceptable error is considered to be a deviation within +
20%.
The patient records the results of self-control in a diary for further discussion with the doctor.
You can also buy test strips for determining the level of sugar in the urine, but they lose significantly in accuracy to glucometers. Firstly, the measurements will only reflect the level that was in the blood at the time this urine was formed, which means that the result obtained does not reflect the glucose level at the moment. Secondly, sugar appears in the urine when it is above 10 mmol / l in the blood. If the blood glucose level is low, the test strip will show a negative result. Well, and thirdly, the result of the measurement is determined by comparing the resulting color with a palette on a special scale, and people with poor eyesight or in poor lighting can see a completely unreliable result there.
Self-monitoring with a glucometer will allow you to:
- determine whether you have achieved the goals set for you by your doctor at this stage of diabetes treatment;
- assess how effective the doctor's recommendations and prescriptions are;
- timely carry out correction of treatment - independently or in consultation with a doctor;
- actively participate in the treatment process, personally manage the situation.
To determine what level of sugar in the blood once a week or even a month (as they do in the clinic) is completely insufficient. Such control does not reflect the whole picture of the state of the body in full. In type 1 diabetes, people need glucose measurements several times a day - before meals, on an empty stomach, and at bedtime. After the optimal sugar values \u200b\u200bare reached, the results of the diet and therapy are stable, it is advisable to periodically (once a week or two) take such multiple measurements during the day to make sure that everything is in order.
Glycated hemoglobin
There is another parameter by which doctors evaluate the presence of diabetes in a person, as well as the effectiveness of the prescribed treatment. This is glycated hemoglobin. It reflects the average blood sugar level over the past 3 months. For example, if you have tested 8% glycated hemoglobin, this means that in the last 3 months your blood glucose level has been in the range of 7.5 mmol/l to 9 mmol/l. What this individual indicator should be for you, based on the clinical picture of the course of your disease, the doctor knows. He will comment on the results and give further recommendations for treatment. The value of glycated hemoglobin depends on age, the presence and nature of complications of diabetes, concomitant diseases. It is necessary to control this parameter once every 3 months by donating blood from a vein in a special laboratory.
Every patient with diabetes should set himself the task of bringing his blood sugar values as close to normal as possible, because excess glucose leads to many unpleasant, and sometimes fatal consequences. For example, it causes damage to blood vessels and nerves.
Consequences
Diabetes is a very serious disease. And if it is not treated, the consequences will be severe both for individual internal organs and for the whole organism as a whole. Here is a list of some of the complications: 

The main condition for the prevention of complications of diabetes is the compensation of carbohydrate metabolism, that is, a set of measures that allow bringing sugar levels in the blood of a sick person closer to normal. If you control your diabetes, follow a strict diet, carefully take all the right medications and lead a healthy lifestyle, you are protected from the severe consequences of the disease in the long term.
In order for the human body to work without failures, it needs, first of all, the energy that it receives along with incoming food. At the same time, glucose is the main source of energy for cells, tissues and the brain.
Glucose is a nutrient delivered to organ tissues by blood molecules. In the blood, in turn, it enters from the liver and intestines. And today we will touch on the topic: "Glucose in the blood: the norm." In parallel, the reasons for the rejection will also be considered.
The amount of sugar in the blood is the most important indicator
Low glucose levels in expectant mothers
No less common in pregnant women and low blood glucose levels. This is due to the fact that she has to provide nutrients, including glucose, to two organisms: her own and the future baby. Since the child takes the sugar he needs, the lack of glucose is felt, first of all, by the mother herself.

This manifests itself in a reduced emotional and physical tone of a woman, drowsiness, apathy. The above symptoms quickly disappear after eating, so doctors recommend that a woman eat several times throughout the day in small portions to avoid the development of hypoglycemia or a lack of blood glucose.
Blood from a vein: sugar indicators
Along with the common method of capillary blood analysis, the method of calculating the level of sugar by taking the patient's venous blood is considered no less reliable. Blood glucose from a vein (the norm in this case is generally accepted) during the analysis should not exceed 6.10 mmol / l. The analysis is carried out by intravenous blood sampling, and in the laboratory determine the level of glucose.
Home glucometers
Glucose is the source of vital energy. A blood test (the norm of the permissible amount of sugars you already know), carried out at home, will help you independently control possible deviations.

Modern medical technology has special devices that allow you to determine the amount of blood glucose at home. Such devices are easy to use and reliable in performance, if the examination is carried out correctly and in compliance with all these recommendations. Such devices measure, as a rule, the level of glucose in capillary blood, therefore, the existing standard norms listed above are applicable to the results.
Glucose tolerance test
If a patient is suspected of having endocrine disorders, experts also recommend undergoing a special test using pure glucose. A blood test (the norm of sugar after a glucose load is no more than 7.80 mmol / l) allows you to determine how efficiently the body processes the glucose that came with food. This study is ordered by a doctor in the presence of alarming symptoms.
Now you know what the blood glucose level should be, the norm for men, women and children. Be healthy!
28.11.2017
One of the main roles in the metabolic processes of the human body is played by the level of glucose in the blood, the norm for which for an adult is in the range 3.5 - 5.5 mmol/l. What are the criteria for diagnosing diabetes mellitus? And most importantly, what are the main causes of excessive increase or decrease in sugar levels and how can this be prevented? Is it always to blame that a person consumes too much sweets?
What determines the level of glucose?
Glucose is a derivative of carbohydrates (sugar). In the human body, through complex biochemical reactions, it is subsequently transformed into pure energy. Doing without it is impossible. And in order to start this whole process of splitting glucose, the body needs insulin, produced by the pancreas. It is a protein hormone that fully regulates carbohydrate metabolism.
But according to numerous studies, the average human blood sugar level has increased significantly over the past 100 years. This is due to the fact that in the diet of a modern person, food rich in carbohydrates, and even of non-vegetable origin, significantly predominates. And the pancreas simply cannot fully produce such a large amount of insulin, with which it will be possible to normalize blood glucose levels to a reference value of 5.5 mmol / l. Moreover, a constant load on it can provoke a number of diseases that ultimately cause hypo- and hyperglycemia (low and high glucose levels, respectively).
By the way, even before the middle of the 19th century, traditional sugar was very expensive due to the complex technology of its production. Further, this process was automated, they began to massively grow sugar beet, from which the cost of sugar decreased significantly. And along with this, it began to be more actively used in cooking. This, too, has played a role in why the number of diabetic patients has risen nearly 200-fold since the 20th century. According to statistics, for every thousand people today there are 6 patients with diabetes mellitus, and two of them are insulin dependent.
So what determines the level of sugar in the blood? There are several key factors:
- the amount of carbohydrates present in the daily diet;
- performance of the pancreas;
- the presence of chronic diseases of the gastrointestinal tract or liver;
- physical activity.
And, by the way, diabetes in almost 80% of cases is inherited. Therefore, the level of sugar is also influenced by the genetic factor.
Normal blood glucose levels. Table
The norms of sugar for both women and men are identical, but the indications differ by age:
The indicators in the table are reference, so they should not be considered normal for all people. In addition, during the day, the sugar level can drop below 3.5 and rise above 5.5 mmol / l. But if over the next few hours it normalizes, then this is not a deviation. Naturally, if a person eats something sweet (chocolate, for example), this will also lead to an increase in blood glucose levels (after about 1-2 hours). Even short-term increases in the rate to 11.1 mmol / l are considered the norm.
Blood glucose is the sugar that the bloodstream carries to all the cells in the body for energy. The body regulates blood glucose levels so that they remain moderate: enough to fuel cells, but not enough to overload blood flow.
The internal environment of the blood must remain stable in order to maintain the vital functions of the body. Glucose levels fluctuate throughout the day. After a meal, the levels rise and then settle, after about an hour, and are at their lowest point before another meal.
When there is a violation of glucose metabolism in the body - this manifests itself in an increased content of glucose called, maybe a low content -.
Glucose levels fluctuate throughout the day. After a meal, the levels rise and then settle, after about an hour, and are at their lowest point before another meal.
In this article, we'll look at high and low glucose levels, as well as how to stay within a healthy blood sugar range.

Hyperglycemia is an increased level of sugar in the blood plasma. Elevated blood sugar may look normal, while it will be a kind of adaptive reaction of the body that provides energy material to the tissues, when it is consumed, it can be increased muscle activity, fear, arousal, severe pain etc. Such rises in blood sugar usually last for a short time, this, as already explained earlier, is associated with the stresses of the body.
Hyperglycemia usually develops when there is not enough insulin in the body or when cells become less sensitive to insulin. Without insulin, glucose cannot enter cells and accumulates in the bloodstream.
Hyperglycemia can also occur in people who do not have diabetes. Your blood sugar levels can skyrocket if you are sick or under a lot of stress. This happens when hormones the body makes to fight disease raise blood sugar levels. Such rises usually last a short time.
If hyperglycemia continues for a long time with a sufficiently high concentration of glucose, at which the rate of release of sugar into the blood exceeds the rate at which the body manages to absorb it, then this, as a rule, is due to diseases of the endocrine system. This can also have detrimental consequences, which will be reflected in the form of damage to the insular apparatus of the pancreas and the excretion of glucose in the urine.
A mild degree of hyperglycemia practically does not harm the body, and when sugar exceeds the norm, a person begins to suffer from, because of which he begins to drink a lot of fluids, frequent urination occurs, in which sugar is excreted from the body along with urine, as a result of which the mucous membrane of the body becomes dry, just like the skin. A severe form of hyperglycemia can lead to nausea, vomiting, a person becomes drowsy and lethargic, loss of consciousness is possible, this already indicates the onset of a hyperglycemic coma, which can lead to death.
As a rule, hyperglycemia is characteristic only for endocrine diseases, such as diabetes mellitus, increased thyroid function, for diseases of the hypothalamus, the area of \u200b\u200bthe brain that is responsible for all the work of the endocrine glands, in rare cases it may be due to some. With prolonged hyperglycemia, a persistent disturbance of metabolic processes begins, which leads to a feeling of severe weakness, the immune system begins to falter, regular purulent inflammatory processes begin in the body, sexual dysfunction occurs and the blood supply to all tissues is disturbed.
Other possible causes of high blood glucose include:
hyperthyroidism, or an overactive thyroid gland;
pancreatitis, or inflammation of your pancreas;
pancreas cancer;
prediabetes, a high-risk condition for developing type 2 diabetes;
stress to the body from illness, injury or surgery;
medicines such as steroids.
In rare cases, hyperglycemia can be a sign of a hormonal disorder called acromegaly or Cushing's syndrome, which occurs when the body produces too much cortisol.
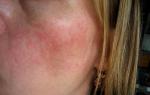
Symptoms of High Sugar
Typically, a person does not experience overt symptoms until their blood sugar levels are significantly above normal.
Early symptoms:
Strong thirst;
Frequent urge to urinate;
The skin is dry, itchy;
Fatigue, drowsiness;
The longer the condition is left unattended, the more severe the symptoms can become. If left untreated, toxic acids will accumulate in the blood or urine.
More serious signs and symptoms:
-
Wounds, scratches do not heal well;
dry mouth;
The smell of acetone on the breath;
-
Abdominal pain.
The person may also experience:
blurred vision;
Headache;
weight loss;
Weakness;
Unstable emotional state.
Persistently elevated blood sugar can also lead to insulin resistance, which reduces the amount of glucose your cells take up. Eventually, the condition can progress to type 2 diabetes.
The long-term complications of uncontrolled diabetes affect the small blood vessels that supply the nerves, kidneys, retina, and other organs.
Some serious complications that can develop from persistent hyperglycemia include:
Damage to blood vessels, which increases the risk of heart disease and stroke
nerve damage;
kidney damage or failure;
Damage to blood vessels in the retina, potentially leading to vision loss or blindness
Cataract, or clouding of the lens in the eye
Foot problems that can lead to serious infections
Problems with bones and joints;
Skin problems, including infections and non-healing wounds;
Infections of the teeth and gums.
Using neural imaging, the researchers showed that people with diabetes and cognitive dysfunction also have reduced blood flow to the brain and a number of other abnormalities that affect thought processes.
If sugar is above 5.5 mmol/l(on an empty stomach) is hyperglycemia (high sugar). The diagnosis is made.
Risk factors
Hyperglycemia can also occur in people who do not have diabetes.
You are at risk if:
Lead a sedentary lifestyle;
Have a chronic or severe illness;
Use steroids;
Recently had surgery.
If you have diabetes, your blood sugar levels can skyrocket if you:
Don't follow your diabetes meal plan;
Do not use insulin correctly;
You are taking medication incorrectly.
One study has shown that work, life, and relationship stress can also release hormones that keep blood glucose levels high.
Even an illness like the flu can lead to stress, which causes a spike in blood sugar.
Medical identification bracelet
A person with hyperglycemia should consider wearing a necklace or bracelet that provides information about their health condition. For example, whether the patient has diabetes, allergies, or whether insulin needs to be taken.
A medical identification bracelet can save lives in situations where a person is unable to speak on their own, such as after a traffic accident or severe DKA (diabetic ketoacidosis).
Video: Dr. Myasnikov - popular questions about diabetes:
low sugar
Hypoglycemia is a low level of sugar in the blood plasma. It should be noted that hypoglycemia is much less common in healthy people than hyperglycemia. This happens for various reasons, for example, with malnutrition, when there is an overstrain of the insulin apparatus of the pancreas, in simple terms, when a person eats too much sweet food, hypoglycemia develops. Since the pancreas begins to work at its maximum capacity, it begins to secrete more insulin (), glucose begins to be completely absorbed by the tissues, which leads to hypoglycemia.
If sugar is below 3.3 mmol/l(on an empty stomach) is hypoglycemia (low sugar)
Causes of hypoglycemia:
-
Some medicines, such as quinine to treat malaria
Too much insulin taken;
Drinking alcohol without food, as the liver may not release glycogen;
Certain diseases, particularly severe hepatitis and kidney disease;
Anorexia.
Permanent hypoglycemia can also begin due to severe ones, in which digestion processes are disturbed and glycogen is released into the blood, as well as diseases of the kidneys, adrenal glands and hypothalamus.
Excessive production of insulin or insulin supplements can lead to hypoglycemia.
Some tumors can severely lower blood sugar levels because they produce chemicals like insulin. The tumor can also consume so much glucose that it is not enough for the rest of the body.
People who undergo gastric bypass surgery may also experience hypoglycemia, as they take in less food than they did before the surgery.
Nesidioblastosis, a rare condition associated with an increase in beta cells, often leads to an overproduction of insulin. Beta cells produce insulin in the pancreas.
Symptoms of low blood sugar
Symptoms of hypoglycemia may come on suddenly.
They include:
-
Dizziness;
excessive sweating;
difficulty sleeping;
skin tingling;
trouble thinking clearly or concentrating;
Loss of consciousness, convulsions, coma.
blurred vision;
fast heartbeat;
sudden mood changes;
sudden nervousness;
unexplained fatigue;
Pale skin;
Headache;
Severe sweating, trembling in the arms, legs, the whole body, increased heart rate, the appearance of fear of death, a constant and strong feeling of hunger, after which there may be a loss of consciousness. This state of a person is called. A person suffering from or prone to this disease should always have sweets with him, which must be taken at the first sign of hypoglycemia.
Another possible cause of low blood sugar is drinking too much alcohol, especially for long periods of time. This can affect the liver's ability to store glucose and then release it into the blood when you need it.
Very low blood sugar is a clear symptom for a medical emergency!
However, contrary to popular belief, low blood sugar is not exclusive to diabetes, although it is rare. This can happen if your body produces more insulin than it should.

In a healthy person who does not suffer from diabetes, the normal blood sugar content is 3.3-5.5 mmol/l on an empty stomach. If the cells of the body fail to absorb the sugar that enters the bloodstream during the digestion of food, the level of sugar in the blood slowly but surely begins to rise. As already known, it is glucose that is the main source of energy.
In a person with insulin-dependent type 1 diabetes, the pancreas produces little or no insulin. In the second type of insulin-dependent diabetes, the pancreas secretes enough insulin, but it is not able to work as it should.
To keep sugar normal, you need to combine several methods at once. This, of course, is a healthy diet, as well as regular monitoring of sugar levels. The healthy diet that is prescribed for diabetes is similar to the diet that is prescribed for any healthy person, just to maintain health.
3.3-5.5 mmol / l (on an empty stomach) - the norm!
In a sick person with diabetes, the sugar rate, of course, can have a fairly wide range than the sugar content in a healthy person. Ideally, you should strive only for a result of 3.3-5.5 mmol / l. It is almost impossible to achieve such a result in practice, for this reason, if a sick person's glucose level ranges from 4 to 10, and only occasionally goes beyond these limits, the patient can be satisfied with this result.
With a blood glucose level between 4 and 10, a person with diabetes will not have serious complications for more than 10 years. In order to always maintain this level of sugar in the blood, a person with diabetes should definitely purchase a glucometer.
How to determine the exact level of sugar in the blood?
Before testing, tell your doctor about the drugs you are taking, including prescription, over-the-counter, and herbal supplements. Some medicines can affect blood glucose levels. Your doctor may ask you to stop taking a certain medication or temporarily change your dosage before the test.
Medications that can affect blood glucose levels:
-
tricyclic antidepressants;
Monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOIs);
Phenytoin;
epinephrine (adrenaline);
Sulfonylureas.
corticosteroids;
potassium-sparing diuretics;
Birth control pills;
hormone therapy;
Aspirin (bufferin);
You should also tell your doctor if you have had an injury, heart attack, or surgery in the recent past.
Fasting Plasma Glucose Test (FPG)
A fasting plasma glucose (FPG) test is a blood test that is performed after you have been fasting all night or 8 hours before the test. Do not eat or drink anything other than water.
This method has a number of disadvantages:
It shows the glucose level only at that particular moment. You can go to donate blood every week and the sugar level will always be different!
You can wake up with high sugar levels, but if the clinic is far away, and you decide to take a walk in the fresh air for half an hour, then most likely, when you get to the clinic, your sugar will already be normal! Because walking in the fresh air is good for lowering sugar levels. Or you can drink water in the morning, which will dilute the blood and the sugar will drop again.
You may have a high blood sugar level for a long time, but if you accidentally lower it (for example, spend the weekend in the country as an employee), then your sugar may return to normal and this type of analysis will show you that everything is in order , but in fact it is not.
If your result is 7 mmol/l or higher, you will be retested on another day to confirm the diagnosis.
Random Plasma Glucose Test (RPG)
A random blood glucose test (RPG - Random Plasma Glucose) is a blood test that can be done at any time of the day. It measures the level of sugar in the blood at a given time.
An RPG result that is greater than 11.02 mmol/L is indicative of diabetes, especially if you have symptoms such as excessive thirst, hunger, or urination.
Oral glucose tolerance test (OGTT)
The oral glucose tolerance test (OGTT - Oral glucose tolerance test) takes a little longer than the previous two. In this test, blood is taken after an overnight fast and then again two hours after you drink a sugary drink.
After the sweet, the sugar level will rise. But for the norm, within two hours, it should fall below 7.71 mmol / l.
If you have blood sugar:
Between 7.8 and 11 mmol / l - prediabetes is diagnosed;
If 11 mmol / l and above, type 2 diabetes is diagnosed.
A1C test (glycated hemoglobin)
The A1C test is a blood test that measures the percentage of sugar that is attached to hemoglobin, a protein in red blood cells. The higher the A1C, the higher your average blood sugar over the past two or three months.
The A1C test is also known by these names:
Hemoglobin A1c test;
HbA1c test;
Glycated hemoglobin test.
To date, the most accurate method for determining blood sugar levels is an analysis for!
The level of glycated hemoglobin does not depend on the time of day, physical activity, food intake, prescribed medications, or the emotional state of the patient.
An analysis of glycated hemoglobin shows the number of candied red blood cells in the blood and is displayed as a percentage. Below is a comparison table:
Glycated hemoglobin |
Average blood glucose |
| 4% | 2,6 |
| 5% | 4,5 |
| 6% | 6,7 |
| 7% | 8,3 |
| 8% | 10,0 |
| 9% | 11,6 |
| 10% | 13,3 |
| 11% | 15,0 |
| 12% | 16,7 |
Since erythrocytes live up to 120 days, it is enough to do this type of analysis once every 4 months.
Glucometer
You can also measure your blood sugar at home with a glucometer. The accuracy of readings depends on the type of glucometer.
The procedure involves pricking a finger and putting blood on a test - a glucometer strip. The results will be shown on the screen in 10-20 seconds.
Continuous Glucose Monitoring (CGM)
CGM (Conscious glucose monitoring) systems have appeared relatively recently. A glucose sensor is inserted under the skin and reads sugar from body tissue continuously. It warns if the blood sugar level is too low or too high.
The term of use of the sensor lasts from several days to a week. Then it needs to be replaced. Also, in order to calibrate the CGM, you must use a glucometer.
However, the system has a number of disadvantages:
The accuracy of the indication is lower compared to blood;
CGM devices are not as reliable for acute problems such as low blood sugar detection;
The data shown by CGM lag behind reality by an average of 10 - 15 minutes.
7 ways to prevent blood sugar spikes
Consult with a nutritionist to develop a meal plan. Meal planning will help you avoid unexpected spikes in blood sugar.
Reduce excess weight. Losing weight will help your body use insulin better.
Learn about the glycemic index. Research shows that not all carbohydrates are equal. The glycemic index (GI) measures how various carbohydrates can affect blood sugar levels. Foods with a high GI rating can affect blood sugar levels more than lower GI ratings.
When the insular apparatus malfunctions, the concentration of glucose in the blood increases. Pathology has several stages of varying complexity, to detect pathology, patients are prescribed laboratory blood tests to determine the level of glycemia.
Sugar analysis
Before taking tests, patients should refrain from eating for 10 hours, the day before this, alcohol and coffee should not be consumed. Blood is taken in the morning on an empty stomach.
Such a study allows you to determine the state of metabolic processes in the body, the degree of deviation from the norm of glycemia, diagnose a pre-diabetic state and type 1 or type 2 diabetes mellitus.
How much sugar is in the blood serum of healthy people? The fasting glycemic index is normally in the range of 3.3-5.5 mmol / l. With an increase in these values, a re-analysis and several more studies are prescribed to establish the correct diagnosis.
If the fasting result ranges from 5.5 to 6.9 mmol/l, prediabetes is diagnosed. When glycemia reaches a value exceeding 7 mmol / l, this indicates the presence of diabetes mellitus.
How long does high blood sugar last after eating sweets? The increase in glycemia after light carbohydrates persists for 10–14 hours. Therefore, it is this period of time that should be refrained from eating before taking the test.
Fasting serum sugar is increased to 5.6 - 7.8, this is a lot, what does this mean and what should be done? Hyperglycemia can be caused by:
- diabetes;
- stressful state of the patient;
- physical stress;
- taking hormonal, contraceptive, diuretic drugs, corticosteroids;
- inflammatory, oncological diseases of the pancreas;
- condition after surgery;
- chronic liver diseases;
- pathology of the endocrine system;
- improper preparation of the patient before taking the test.
Stress and excessive physical activity stimulate the secretion of the adrenal glands, which begin to produce contrainsular hormones that promote the release of glucose by the liver.
If the patient is taking medication, please inform your doctor. To establish the diagnosis, the study is carried out twice. In order to exclude or confirm an endocrine disease in a patient, a test for the body's tolerance to glucose and a study on glycated hemoglobin are done.
Glucose sensitivity test
If fasting blood serum sugar increased to 6.0 - 7.6, what should be done, how much and how dangerous it is, how to treat the pathology? Patients are scheduled to perform a glucose tolerance test with a sugar load if the results of previous tests are in doubt. This study allows you to determine how much glycemia rises after the intake of carbohydrates in the digestive tract and how quickly the level normalizes.
First, blood is taken from the patient on an empty stomach, after which they are given a solution of glucose with water to drink. The material sampling is repeated after 30, 60, 90 and 120 minutes.
2 hours after drinking a sweet solution, the level of glycemia should be below 7.8 mmol / l. An increase in the level to 7.8 - 11.1 mmol / l is diagnosed as impaired glucose tolerance, metabolic syndrome or prediabetes. This is a borderline condition that precedes type 2 diabetes.
Pathology is treatable. Patients are prescribed a strict low-carbohydrate diet, exercise, weight loss. Most often, such measures are enough to restore metabolic processes in the body and delay or completely prevent the development of diabetes for a long time. In some cases, drug therapy is carried out.
With results exceeding 11.1 mmol / l, a diagnosis is made - diabetes mellitus.
Analysis for the level of glycated hemoglobin
Diabetes mellitus can have a latent course, and at the time of testing it does not manifest itself as an increase in glycemia. To determine how much sugar has increased in the body over the past 3 months, an analysis is carried out for the concentration of glycated hemoglobin. The answer of the study allows you to determine the percentage of hemoglobin that has reacted with glucose.
Special preparation before passing the analysis is not required, it is allowed to eat, drink, play sports, lead a normal lifestyle. Do not affect the result and stressful situations or any diseases.
How much glycated hemoglobin is in the blood serum of a healthy person? Normally, this substance is contained in the range of 4.5 - 5.9%. An increase in this level indicates that there is a high percentage of the likelihood of developing diabetes. A disease is detected if the content of glycerinated hemoglobin is more than 6.5%, which means that the blood contains a lot of hemoglobin associated with glucose.
Which doctor to contact
What does the analysis say if the blood sugar level is increased to 6.4 - 7.5 mmol / l on an empty stomach, is it a lot, what does it mean and what should be done? These are high glycemic levels, which require additional research. After the appearance of suspicions of diabetes mellitus, you should seek help from an endocrinologist.
If the doctor diagnosed prediabetes based on the results of the tests, you should follow a low-carbohydrate diet, exclude sweets and foods containing easily digestible sugars from the diet.
The menu should be fresh vegetables, fruits, healthy foods. Physical activity improves the absorption of insulin by the tissues of the body, this helps to reduce the level of glycemia and restore metabolic processes.
If diet therapy and physical activity do not give results, an additional intake of sugar-lowering drugs is prescribed. Treatment should take place under the strict supervision of a physician.
If fasting blood sugar has risen to 6.3 - 7.8, this is a lot to do, does this mean that diabetes has developed? If a glucose tolerance test and a glycated hemoglobin test confirm high glycemic levels, diabetes is diagnosed. Patients should be observed by an endocrinologist, take medication, follow the prescribed diet.
Symptoms of diabetes:
- increased urge to urinate;
- polyuria - an increase in the volume of urine;
- constant feeling of thirst, drying of the mucous membranes of the oral cavity;
- severe hunger, overeating, as a result of a rapid increase in body weight;
- general weakness, malaise;
- furunculosis;
- long-term regeneration of abrasions, wounds, cuts;
- dizziness, migraine;
- nausea, vomiting.
In many patients, symptoms in the initial stages are blurred or absent at all. Later there are some complaints, worse after eating. In some cases, there may be a decrease in the sensitivity of some parts of the body, most often these are the lower limbs. Wounds do not heal for a long time, inflammation, suppuration is formed. This is dangerous, gangrene can develop.
An increase in blood sugar levels on an empty stomach is a signal of a violation of metabolic processes in the body. Additional studies are being carried out to confirm the results.
Timely detection of the disease, strict control over nutrition and therapy will normalize the patient's condition, stabilize glycemia, and prevent the development of severe diabetic complications. Violation of metabolic processes causes a malfunction of the digestive, nervous, cardiovascular system and can cause a heart attack, atherosclerosis, stroke, neuropathy, angiopathy, coronary heart disease. If the level of glycemia is too high, the patient plunges into a coma, which can lead to severe disability or death.
Glycemia refers to the amount of glucose in the blood. This is a physiological state that is responsible for the regulation of vital processes in the body of living beings. Quantitative indicators of sugar can fluctuate up or down, which can also have a physiological and pathological character. The level of glucose rises after food enters the body, with insufficient insulin synthesis, and decreases as a result of catabolism, hyperthermia, stress and significant physical exertion.
The norm of glucose in the blood is an important diagnostic point that allows you to clarify changes in carbohydrate metabolism and the level of energy consumption by cells and tissues of the body. Indicators of norm and pathology are considered in the article.
Glucose in human blood
All carbohydrates supplied to the body cannot be absorbed in their original form. They are broken down to the formation of monosaccharides with the help of special enzymes. The rate of this reaction depends on the complexity of the composition. The more saccharides are included in the carbohydrate, the slower the processes of breakdown and absorption of glucose from the intestinal tract into the blood.
For the human body, it is important that the amount of glucose in the blood is constantly at a normal level, because it is this saccharide that provides energy to all cells and tissues. First of all, it is necessary for the functioning of the brain, heart, and muscular apparatus.
Maintaining optimal glycemic levels is the key to health
What happens if the glucose level is out of range:
- hypoglycemia (below the norm) causes energy starvation, as a result of which the cells of vital organs atrophy;
- hyperglycemia (sugar levels above normal) provokes damage to blood vessels, leads to a decrease in their lumen and further pathology of tissue trophism up to the development of gangrene.
Norm indicators
Blood sugar levels are determined in several ways. Each of them has its own normal numbers.
Clinical Analysis
A general blood test allows you to clarify the quantitative indicators of formed elements, hemoglobin, the coagulation system, to clarify the presence of allergic or inflammatory processes. This diagnostic method does not show the level of sugar, but is a mandatory basis for the rest of the studies indicated below.
Sugar analysis
The examination determines how much monosaccharide is in the capillary blood. The results of the analysis are the same for adult men and women, for children they differ by age. To get the correct data, you must give up the morning meal, brushing your teeth, chewing gum. During the day do not drink alcohol and medicines (after discussion with your doctor). Blood is taken from a finger. Results can be in the following units: mmol/l, mg/100 ml, mg/dl, mg/%. The table shows possible answers (in mmol/l).
Biochemical analysis
Biochemistry is a universal diagnostic method, since, in addition to glycemia, it allows you to determine the numbers of a significant number of indicators. The study requires blood from a vein.
Blood is a biological fluid, changes in indicators of which indicate the presence of pathology in the body
The normal content of monosaccharide in a biochemical analysis differs from the diagnosis from a finger by about 10-12% (mmol / l):
- upon reaching 5 years of age and older - 3.7-6.0;
- borderline condition upon reaching 5 years of age and older - 6.0-6.9;
- diabetes mellitus is questionable - above 6.9;
- the norm for infants is 2.7-4.4;
- the norm during pregnancy and in the elderly is 4.6-6.8.
In venous blood plasma, not only sugar indicators are determined, but also cholesterol levels, since the relationship between these two substances has long been proven.
Such an analysis is carried out in the following cases:
- medical examination of the population;
- obesity;
- pathology of the endocrine apparatus;
- presence of signs of hypo- or hyperglycemia;
- observation of the patient in dynamics;
- during pregnancy to exclude the gestational form of the "sweet disease".
Definition of tolerance
Glucose tolerance is the state of the cells of the body, in which their sensitivity to insulin is significantly reduced. Without this pancreatic hormone, glucose is not able to penetrate the cells to give the necessary energy. Accordingly, with impaired tolerance, an increase in the amount of sugar in the blood plasma occurs.
If such a pathology is present, it can be determined using a “load” test, which allows you to clarify the indicators of the monosaccharide on an empty stomach and after consuming fast carbohydrates.
The study is prescribed in the following cases:
- the presence of symptoms of "sweet sickness" with normal numbers of glucose in the blood;
- intermittent glucosuria (sugar in the urine);
- increased urine volume per day;
- pathology of carbohydrate metabolism;
- the presence of relatives with diabetes;
- pregnancy and childbirth with a history of macrosomia;
- severe disruption of the visual apparatus.
Blood is taken from the patient, they are given to drink glucose powder diluted in a glass of water or tea, and at certain intervals (according to the doctor's instructions, but in the standard - after 1, 2 hours), blood is taken again. What is the permissible limit of the norm, as well as the pathology numbers can be seen in the table below.
Indicators of the results of the glucose tolerance test
Glycosylated hemoglobin
Using this diagnostic method, you can evaluate the blood sugar content for the last quarter. The hemoglobin of erythrocytes binds to monosaccharides, forming glycated hemoglobin, therefore, it is possible to derive average values for the life cycle of red blood cells, which is 120 days.
Indicators are measured as a percentage (%) of the total amount of hemoglobin in the bloodstream. Figures below 5.7% are considered the norm, indicators up to 6% indicate an average risk of developing the disease and the need to correct the diet. 6.1-6.5% - high risk of the disease, above 6.5% - the diagnosis of diabetes is questionable. Each percentage corresponds to certain glucose numbers, which are average data.
HbA1c Compliance with Glycemic Indicators
Fructosamine
This analysis shows the content of monosaccharide in the blood serum for the last 2-3 weeks. The norm indicators should be less than 320 µmol / l. The examination is important in cases where the attending physician decided to change the treatment tactics, to control the degree of compensation for diabetes mellitus in pregnant women, in people suffering from anemia (glycosylated hemoglobin indicators will be distorted).
Numbers above 370 µmol/l indicate the presence of conditions:
- the degree of decompensation of diabetes;
- kidney failure;
- hypofunction of the thyroid gland;
- high level of IgA.
A level below 270 µmol/L indicates the following:
- hypoproteinemia;
- diabetic nephropathy;
- hyperfunction of the thyroid gland;
- intake of high doses of vitamin C.
Pathology of blood sugar level
Hyperglycemia, in addition to diabetes, may accompany inflammation of the pancreas of acute and chronic course, diseases of the adrenal glands, liver, long-term use of combined oral contraceptives in women, the use of diuretics and steroids (in men).
The state of hyperglycemia develops even when the sugar levels on an empty stomach are above 6.7 mmol / l. Figures exceeding 16 mmol / l indicate the beginning of precoma, more than 33 mmol / l - ketoacidotic coma, above 45 mmol / l - hyperosmolar coma. The states of precoma and coma are considered critical, requiring emergency assistance.
Hypoglycemia develops when sugar levels are less than 2.8 mmol / l. This is an average figure, but acceptable limits can vary within 0.6 mmol / l in one direction or another. In addition, the causes of low blood glucose can be various types of intoxication (ethyl alcohol, arsenic, drugs), hypothyroidism, fasting, excessive physical activity.
The attending physician is the main “evaluator” of glycemic indicators and changes in the body
During the period of bearing a child, hypoglycemia may also develop. It is associated with the consumption of part of the monosaccharide by the baby. Hyperglycemia during pregnancy indicates the development of the gestational form of diabetes (similar in pathogenesis to the non-insulin-dependent form and is accompanied by impaired glucose tolerance). This condition goes away on its own after the baby is born.
Blood sugar indicators, as well as further tactics for introducing the patient, should be evaluated and selected by a specialist. Self-interpretation of numbers can lead to a misunderstanding of the state of personal health, excessive excitement, untimely start of therapy if necessary.
What does blood sugar 7.7 mean, causes and treatments
If blood sugar has reached a value of 7.7, what does this mean? Is it dangerous for a diabetic? Indeed, with diabetes, it is important to constantly check the readings of glucose in the blood. Patients periodically take a fasting blood test in the laboratory or independently measure sugar several times a day using a glucometer. It can be used at home. Therefore, every diabetic should know which indicator is considered too high and is an excuse for an immediate visit to the doctor.
Normal values
Diabetes mellitus is considered a serious disease in which patients need to monitor the amount of sugar in the blood. This value refers to glucose. There are special rules that a diabetic must rely on. These values are influenced by age and diet, but blood sugar should not rise above 7 mmol/liter. Its composition is constantly changing throughout the day.
If you take the analysis immediately after eating, the indicator will be high. Therefore, blood should be taken in the morning on an empty stomach.
The amount of sugar in the blood in adults is considered normal from 3.6-5.2 mmol / liter. If the patient consumed carbohydrates, then the value may increase to 6.8 mmol / liter. As a rule, after a few hours the indicator will return to normal. These parameters apply to a person between the ages of 14 and 59. In people older than sixty years, the normal blood glucose parameter varies between 4.6-6.5 mmol / liter.
- In pregnant women, a value of about 3.4-6.7 mmol / liter is allowed.
- In children under two years old - 2.6-4.4 mmol / liter.
- From two to seven years of age - 3.2-5.0 mmol / liter.
- From seven to fourteen years, 3.2-5.6 mmol / liter is allowed.
While waiting for the baby, you need to monitor the amount of sugar in the blood, because an increased rate can affect the development of the fetus. Therefore, a woman should periodically donate blood, so doctors monitor her health.
If the accumulation of glucose in the blood shows 7 mmol / liter or more, then you should immediately consult a doctor and undergo an appropriate course of therapy.
Reasons for the increased parameter
It is known that with an increase in blood sugar in a patient with diabetes, the state of health worsens, and complications may appear. And if all measures are not taken, then death may occur.
There are symptoms by which you can notice an increased rate:
- dry mouth and constant thirst;
- dizziness;
- itchy burning of the skin;
- frequent urination, especially at night;
- deterioration in visibility;
- tendency to frequent infectious diseases;
- poor healing of cuts on the skin;
- taken pills do not have the appropriate effect.
In these cases, you need to consult a doctor and take a blood test. If an increase in glucose is confirmed, it is necessary to start therapy that will help reduce blood sugar. You will also need to strictly follow the diabetic diet, exclude carbohydrates from the diet.
The deviation of blood sugar is called hyperglycemia. During its course, sugar accumulates, resulting in a metabolic failure. A person develops drowsiness, fatigue, nausea, and in some cases fainting.
If, during the test, blood sugar has a value of 5.8 to 7.8 mmol / liter, then you should find out the reasons for this phenomenon. Hyperglycemia can be caused by a variety of factors.
- diabetes;
- overeating, including a large amount of carbohydrates in the diet;
- severe stress;
- various infectious diseases;
- taking medications and hormonal drugs;
- improper preparation for blood donation.
If blood sugar is 7.7 mmol / l, what does this mean? Usually, after such conclusions, they suggest taking a test for a reaction to glucose and glycated hemoglobin. Only then is a diagnosis of diabetes mellitus made. Patients should regularly visit an endocrinologist, take medication and follow an appropriate diet.
Elevated blood sugar should definitely be reduced. If this is not done, acute and chronic manifestations of diabetes may occur. They are expressed by loss of consciousness, fainting, damage to the nervous system and internal organs. Therefore, medical attention is needed. Often, the lack of proper treatment can lead to the death of a patient with diabetes.
Test results
This type of examination helps to recognize the state of metabolism in the body, the magnitude of the deviation from normal values, to diagnose pre-diabetic syndrome and type 1 or type 2 diabetes mellitus.
In ordinary people, the glycemic index when donating blood in the morning is about 3.2-5.5 mmol / l. If the parameter is increased, then for a reliable diagnosis, a secondary analysis and additional examination are carried out. The glucose sensitivity test allows you to determine the degree of development of glycemia.
The test is carried out in this way:
- Do blood sampling on an empty stomach.
- After that, the patient should drink a mixture of glucose.
- Then they take blood every half hour, up to two hours (4 times).
Based on the results of the test, a diagnosis is made. The degree of glucose in the blood reaches up to 7.5 mmol / l - this means a normal value; if the value fluctuates from 7.6 to 11.0 mmol / l - this is prediabetes; values above 11.1 are considered a symptom of the disease.
However, this test is not enough - it is also necessary to determine the level of glycated hemoglobin, since diabetes mellitus can manifest itself in a latent form and do not show signs when donating blood. To check whether blood sugar has risen, an analysis is made for the concentration of glycated hemoglobin. The results reveal the percentage of hemoglobin contained that entered into a chemical reaction with glucose.
Additional preparation for this analysis is not necessary, a person can eat, drink, and exercise. Taking medications and nervous experiences do not affect the performance. In a normal person, the level of this substance should be in the range of 4.5-5.8%. An increased value indicates the development of diabetes mellitus. If this parameter reaches a value above 6.5%, then this means one thing - there is a large amount of hemoglobin combined with glucose in the blood.
Glucose reduction methods
At the risk of illness, when blood sugar reaches a value of 8-11 mmol / l, it is necessary to go to an endocrinologist and get advice on subsequent actions. These parameters indicate a metabolic disorder. If all measures are not taken, then a person may develop such a serious disease as diabetes mellitus.
In such cases, it is recommended to lose weight first. A nutritionist can help you adjust your diet. With prediabetes, it is recommended to remove dairy products from the diet, as it affects the flow of insulin into the blood. It is also necessary to abandon certain foods that contribute to the rapid formation of glucose in large doses.
- pumpkin, potatoes, zucchini;
- watermelons, pineapples, raisins, dates;
- honey, sugar, sweets;
- cereals: oatmeal, rice;
- pasta, muffin;
- liver;
- butter;
- mayonnaise.
At the risk of diabetes in the diet should be present: meat and fish of low-fat varieties, bread from coarse coarse fibers, permitted vegetables and fruits, cereals, eggs and greens. When following a diet, as a rule, after a certain time, the patient loses weight, and the glycemic index returns to normal.
If there are no contraindications, then it is advisable for a diabetic to engage in light physical education daily. This improves metabolism and reduces excess weight.
People who have diabetics in the family, with a high content of glucose in the blood, are prescribed hypoglycemic drugs to eliminate the risk of developing this disease. After all, the disease can be inherited.
What is blood sugar 7
We will talk about what should be the blood sugar content, how it is measured and how to reduce the high sugar content.
What is the normal blood sugar level
The expression "blood sugar" refers to the concentration of glucose in it. For this indicator, there are strictly defined standards. These figures depend on the age of the person, as well as on the diet, but this figure should not rise above 7 mmol / liter. The concentration of sugar in the blood changes throughout the day. If you donate blood for analysis immediately after eating, then the value will be higher than a few hours later. It is necessary to regularly monitor this indicator. This is very important, because if you do not notice its increase in time, you can get irreversible consequences.
Norm for adults
The unit of measure for the amount of sugar in the blood is mmol/liter. In an adult healthy person, this indicator, as a rule, always fluctuates between 3.7-5.3 mmol / liter. Immediately after eating fast carbohydrates, it can rise to 6.9 mmol / liter, but not higher than 7. After a short time, the value returns to normal. When collecting blood from a finger, the figure will be about 20% lower than when taken from a vein. The given values are relevant for people of any gender from 14 to 59 years.
In people over 60 years of age, a glucose content of 4.7-6.6 mmol / liter is considered normal. During pregnancy, women's blood sugar levels can change. The norm of glucose concentration in a future mother is considered to be 3.3-6.8 mmol / liter. It is especially important for a pregnant woman to control changes in sugar levels, since its increase can adversely affect the health of the unborn baby. The value of the blood sugar concentration, equal to 7 mmol / liter and above, is considered elevated and is the reason for an immediate visit to the doctor.
Norm for children
The level of glucose depends on the age of the child. In children under 2 years old, the rate is from 2.7 to 4.4 mmol / liter. From 2 to 7 years - 3.2-5.1 mmol / liter. In children from 7 to 14 years old, the level is 3.2-5.5 mmol / liter. If the sugar level in children rises to 7 mmol / liter and above, it is necessary to consult a doctor as soon as possible and undergo a course of treatment.
Blood sugar test
You need to regularly monitor blood sugar to prevent the development of serious diseases. To do this, you need to know your blood sugar level.
In order to find out this amount, a laboratory blood test is used. In order for the results of the analysis to be reliable, the following rules must be strictly observed:
- The analysis is given on an empty stomach. This means that you should not eat at least 8 hours before taking blood for analysis. Do not brush your teeth or use chewing gum.
- It is better to donate blood for sugar in the morning - from 8 to 11 o'clock.
- For 2-3 days before donating blood for analysis, it is better to refrain from eating fatty foods.
- It is strictly forbidden to drink alcoholic beverages for at least a day before taking blood.
- In addition, physical activity, as well as thermal procedures, such as a bath or sauna, are not recommended a day before the analysis.
- Before taking the test, you can not take any medications and carry out medical procedures.
- People over 40 years old need to be analyzed three times a year.
How to measure your blood sugar yourself
There is a way to measure glucose levels at home. This is a special device called a glucometer. It is used by people with diabetes to control changes in sugar levels several times a day. A modern electronic glucometer is equipped with a display and a device for piercing the skin. Separately, you need to purchase special test strips. The device is very easy to use.
In order to measure blood sugar levels with a glucometer, you just need to pierce the skin on the tip of your finger, squeeze out a drop of blood, and attach a test strip to it. The result will be known in just a few seconds. The procedure is absolutely painless and does not cause discomfort. Currently, there is a very large selection of glucometer models, all of which are very compact in size and weigh no more than 100 grams. This allows you to take the glucometer with you anywhere, it fits easily in your pocket or bag.
Causes and symptoms of high blood sugar
There are various reasons for high sugar levels:
- the main one is diabetes mellitus. In this case, the elevated sugar level is permanent, often causing great harm to the body;
- the cause may be overeating, eating a large amount of fast carbohydrates;
- sugar levels can rise in stressful situations;
- Another reason may be various past infectious diseases.
How to spot high blood sugar levels
There are several main symptoms of high blood sugar:
- frequent feeling of thirst;
- prolonged headaches and dizziness;
- skin itching;
- frequent and painful urination, including at night;
- dry mouth;
- decreased vision;
- frequent infectious diseases;
- increased fatigue;
- prolonged healing of wounds;
- increase in treatment.
Why is high blood sugar dangerous?
An increase in blood glucose levels is called hyperglycemia. It is observed in diabetes mellitus, dysfunction of the thyroid gland, disruption of the hypothalamus, liver diseases, and some others.
Excess glucose accumulates in the blood, thereby disrupting metabolism. Very severe hyperglycemia can cause nausea, vomiting, drowsiness, and in some cases even loss of consciousness.
How to Lower Your Blood Sugar
If the blood sugar level exceeds 7 mmol / liter, it is necessary to take measures to reduce it. This can be achieved at home. To do this, first of all, you need to pay special attention to the foods you eat. It is useful to eat fish and seafood, meat, poultry, eggs, cheese, butter, fresh green vegetables, mushrooms. Following such a low-carb diet, you can bring your sugar levels back to normal in a few days. The general principles of a low-carbohydrate diet at a sugar level of 7 mmol/liter and above are as follows:
- The amount of carbohydrates consumed in food should not exceed 120 g per day.
- It is necessary to exclude from the diet foods that contain sugar in its pure form or are quickly converted into glucose. These include not only sweets and sweets, but also foods containing starch, as well as pasta or porridge from various cereals.
- It is better to eat not 3, but 4-5 times a day, but in small quantities.
After 5-7 days of such a diet, the level of blood sugar concentration should return to normal.
Also, physical activity contributes to lowering blood sugar below 7 mmol / liter. They are simply necessary at a glucose level of 7 mmol / liter and above. Physical activity should be moderate and selected taking into account the characteristics of the body. You should not overload the body with physical activity at an elevated sugar level above 7 mmol / liter, this can be harmful to health.
To control the level of sugar, you need to use a glucometer several times a day. Be sure to do this after 5-7 minutes, after a minute, after 30 minutes and 2 hours after eating. New foods in a low-carbohydrate diet should be introduced gradually, and blood glucose levels should be monitored after eating them. It should not rise above 7 mmol / liter.
Products, the use of which is highly undesirable for blood sugar levels above 7 mmol / liter:
- sugar;
- sweets and sweets;
- cereals and other cereal products, as well as bread and pastries;
- potato;
- almost all fruits and fruit juices;
- beet;
- pumpkin;
- carrot;
- paprika;
- legumes;
- tomatoes;
- milk;
- yoghurts and curds with fruit;
- cottage cheese;
- condensed milk;
- semi-finished products (dumplings, pizza, dumplings);
- chips and other snacks;
- sauces and ketchups;
- sweeteners.
This list can also include products that are sold as diabetic. Their use is prohibited when the sugar content is above 7 mmol / liter.
Blood sugar levels should be checked regularly and kept in the normal range. When raising it to 7 and above mmol / liter, you must immediately go to the doctor to avoid serious illness. If the level does not fall below 7 mmol / liter for a long time, a very serious examination is required.
Krasnoyarsk medical portal Krasgmu.net
Blood sugar is normal 3.3-5.5 mmol / l - the norm regardless of age;
blood from a finger (on an empty stomach):
3.3-5.5 mmol / l - the norm, regardless of age;
5.5-6.0 mmol / l - prediabetes, intermediate state. It is also called Impaired Glucose Tolerance (IGT) or Impaired Fasting Glycemia (IFG);
6.1 mmol / l and above - diabetes mellitus.
If blood was taken from a vein (also on an empty stomach), the norm is about 12% higher - up to 6.1 mmol / l (diabetes mellitus - if above 7.0 mmol / l).
blood glucose
blood glucose level for humans,
not suffering from diabetes
Before breakfast (on an empty stomach):
Before lunch or dinner:
1 hour after eating:
2 hours after eating:
Between 2 and 4 am:
Diabetes Diagnosis Test: Sugar Load Test. They determine the level of sugar in the blood on an empty stomach, then you drink 75 g of glucose in the form of syrup (75 g of glucose per glass of water) and after 2 hours again donate blood for sugar and check the result:
up to 7.8 mmol / l - the norm;
above 11.1 mmol / l - diabetes.
Before the test, you can eat as usual. Within 2 hours between the first and second tests, you can not eat, smoke, drink; it is undesirable to walk (physical activity reduces sugar) or, conversely, to sleep and lie in bed - all this can distort the results.
Glycemia. Normal fasting blood glucose when determined by the glucose oxidase or orthotoludin method is 3.3-5.5 mmol / l (mg / 100 ml), and when determined by the Hagedorn-Jensen method - 3.89-6.66 mmol / l (mg /100ml). According to WHO (1980), in adults, the normal level of glucose in plasma obtained from fasting venous blood is 6.4 mmol/l (<115 мг/100 мл), в цельной венозной крови – 5,6 ммоль/л (< 100мг/100мл) и в цельной капиллярной крови – 5,6 ммоль/л (<100мг/100мл).
As recent studies have shown, with age, the normal content of glucose in the blood serum increases, therefore, after 60 years, it is necessary to carry out a correction, which is 0.056 mmol / l (1 mg / 100 ml) for each subsequent year. In apparently healthy elderly people, fasting glycemia can range from 4.4 to 8.0 mmol / l (mg / 100 ml).
The diagnostic criterion for diabetes mellitus is an increase in the concentration of glucose in the plasma of venous and capillary blood on an empty stomach > 7.8 mmol / l (140 mg / 100 ml) or in whole venous or capillary blood > 6.7 mmol / l (120 mg / 100 ml); 2 hours after a load of 75 g of glucose, the level of glucose in venous blood plasma> 11.1 mmol / l (200 mg / 100 ml) and in capillary blood plasma> 12.2 mmol / l (220 mg / 100 ml); in venous whole blood >10.0 (180 mg/100 ml) and in capillary whole blood >11.1 mmol/l (200 mg/100 ml).
Impaired glucose tolerance, or latent diabetes mellitus, is characterized by the following indicators: on an empty stomach, the concentration of glucose in venous or capillary blood plasma is<7,8 ммоль/л (140 мг/100 мл), а в цельной венозной или капиллярной крови <6,7 ммоль/л (120 мг/100 мл). Через 2 ч после приема 75 г глюкозы эти показатели соответственно составляют 7,8-11,0 ммоль/л (мг/100 мл) в плазме венозной крови и 8,9-12,1 ммоль/л (160,0-179,0 мг/100 мл) в плазме капиллярной крови; тогда как в цельной венозной крови – 6,7-9,9 ммоль/л (мг/100мл) и в цельной капиллярной крови – 7,7-11,0 ммоль/л (мг/100 мл).
A repeated (after a certain period of time) increase in the concentration of glucose in plasma obtained from venous or capillary blood above 7.8 mmol / l or in whole venous or capillary blood above 6.7 mmol / l is a sign of diabetes mellitus, and in this case there is no need to do a glucose tolerance test.
With an increase in blood glucose above 8.88 mmol / l, glucosuria appears, which, together with hyperglycemia, serves as an objective criterion for the disease. In rare cases, glucosuria can occur at normal blood glucose concentrations due to a decrease in the permeability threshold of the kidney tubules for glucose (renal diabetes). Such normoglycemic glucosuria can be primary (idiopathic) or secondary (with kidney disease). It can also occur during pregnancy and De Toni-Fanconi-Debre syndrome (enzymatic tubulopathy, in which there is a violation of the reabsorption of glucose, amino acids, phosphates and bicarbonates in the renal tubules). In diabetes mellitus, combined with nephrosclerosis (or functional insufficiency of the kidneys of another etiology), with high hyperglycemia, on the contrary, minimal glucosuria or its absence is detected. With age, there is an increase in the renal threshold for glucose, so in patients with type II diabetes, compensation of carbohydrate metabolism is better controlled by blood glucose (glycemia) rather than by glucose excretion in the urine (glucosuria).
In the event that there are no clinical symptoms of diabetes, and the blood glucose level is below the above, a glucose tolerance test (PTH) with a single dose of glucose is performed to detect diabetes mellitus. The WHO Expert Committee (1980,1985) recommends a glucose load of 75 g (in children - 1.75 g per 1 kg of ideal body weight, but not more than 75 g) followed by blood sampling for 2 hours.
Impaired glucose tolerance is characterized by the following parameters.
1. The concentration of glucose on an empty stomach should be below those values that are regarded as diabetes, i.e. the level of glucose in venous blood plasma is not higher than 7.8 mmol / l, in venous whole and capillary blood is not higher than 6.7 mmol / l.
2. Glucose level 2 hours after taking 75 g of glucose should not be between normal values and figures characteristic of diabetes, namely in plasma of venous blood 7.8-11.1 mmol / l, in whole venous blood 6.7- 11 mmol / l and in whole capillary blood 7.8-11.1 mmol / l.
The determination of insulin and C-peptide in the blood serum during PTH provides additional information about the state of the insular apparatus, which may be of prognostic value.
Naturally, in addition to glycemia, indicators of glucosuria are widely used in the diagnosis of the disease, which until recently was practically the only indicator of diabetes compensation. The introduction of simplified methods for determining the content of glucose in the blood using portable glucometers (domestic glucometer "Satellit"), as well as indicator strips for visual determination, allows for constant monitoring of the state of carbohydrate metabolism in diabetic patients.
Ketonuria or acetonuria. With insulin deficiency, there is an accumulation of "ketone bodies" - products of fat metabolism: b-hydroxybutyric acid, acetoacetic acid and acetone. The presence of ketone bodies in the urine indicates decompensation of diabetes mellitus and dictates the need to change insulin therapy. It should be noted that ketonuria can occur, in addition to diabetes , and in other pathological conditions: fasting, a diet high in fat, alcoholic ketoacidosis and infectious diseases that occur with a high temperature.
Microalbuminuria and proteinuria. In apparently healthy individuals, the kidneys excrete only a small amount of protein, which is less than 15 μg / min or less than 30 mg per day during the night and is called normoalbuminuria. An increase in albumin excretion from 20 to 200 µg/min or higher (30 to 300 mg/day) leads to microalbuminuria, which indicates the initial form of diabetic nephropathy. Albumin excretion over 300 mg/day - proteinuria indicates the progression of diabetic nephropathy. In severe cases, high proteinuria (3-6 g/day) is combined with edema, hypoalbuminuria, anemia, hypercholesterolemia, indicating nephrotic syndrome.
Glycosylated hemoglobin or glycohemoglobin. It has been established that in human blood hemolysates, along with the main fraction of hemoglobin (HbA), there is an insignificant amount of other fractions called "minor" (HbA1a, A1b, A1c). In healthy adults, HbA accounts for 90%, HbA1a - 1.6%; HvA1v-0.8%, HvA1c-3.6%, HvA2-2.5% and HvF-0.5% Glycosylated hemoglobin is hemoglobin in which the glucose molecule condenses with the b-terminal valine of the b-chain of the HvA molecule. This non-enzymatic process proceeds slowly, during the entire life of the erythrocyte (about 120 days).It has been established that glycosylation occurs through the formation of aldimine (“Schiff bases” between the carbohydrate aldehyde and the amino group), a relatively unstable, “reversible” compound. transformation (transformation Amadori) turns into a relatively stable, "irreversible" compound ketoamine. The resulting ketoamine remains attached to the protein for the entire period of its life. Glycosylation undergoes many body proteins (proteins of blood, lens, kidneys, nerves, blood vessels, etc.). The rate of glycosylation and the amount of glycosylated proteins depends on the magnitude and duration of hyperglycemia.
HbA1c makes up 4-6% of total hemoglobin in the blood of practically healthy individuals, while in diabetic patients the level of this protein is increased by 2-3 times. In patients with initially diagnosed diabetes mellitus, the content of HbA1c was 11.4±2.5% (in the control group 4.3±0.7%), and after prescribing an appropriate diet and insulin therapy to these patients, it was 5.8±1.2% . Thus, glycated hemoglobin has a direct correlation with the level of glucose in the blood and is an integrated indicator of the compensation of carbohydrate metabolism over the past few days. The rate of formation of HbA1c, as well as HbA1, depends on the magnitude of hyperglycemia, and normalization of its blood level occurs 4-6 weeks after reaching euglycemia. In this regard, the content of this protein is determined if it is necessary to control carbohydrate metabolism and confirm its compensation in patients with diabetes for a long time. According to the WHO recommendation, the determination of the content of glycosylated hemoglobin in the blood of patients with diabetes mellitus should be carried out 1 time per quarter. This indicator is widely used both for screening the population and pregnant women to detect disorders of carbohydrate metabolism, and to control the treatment of patients with diabetes mellitus.
Fructosamine. This is a group of glycosylated blood proteins, and partly tissue proteins. It was noted above that glycosylation of hemoglobin passes through the stage of conversion of aldimine to ketoamine. Ketoamines (protein containing glucose) are fructosamines. The content of fructosamine reflects the state of carbohydrate metabolism over the previous 1-3 weeks due to the shorter half-life of glycosylated blood proteins compared to hemoglobin. In the blood serum of practically healthy individuals, the concentration of fructosamine is 2-2.8 mmol / l, in diabetic patients with satisfactory compensation of carbohydrate metabolism - 2.8-3.2 mmol / l, and with decompensation of diabetes - above 3.7 mmol / l .
Determination of other glycosylated proteins. The disadvantage of methods for determining the content of HvA1c, HvA1 and fructosamine is that the obtained indicators, indicating the state of carbohydrate metabolism for the previous 3-9 weeks, cannot be used for short-term monitoring of the state of carbohydrate metabolism in patients after changing the regimen of insulin therapy or other types of treatment. In this regard, the search for new possibilities for determining the amount of other glycosylated proteins continues. So, M. Hammer et al. (1989) proposed a new method for controlling glycemia in diabetic patients - determination of the content of glycosylated fibrinogen in the blood. The half-life of fibrinogen is 4 days, so the amount of glycosylated fibrinogen is a reflection of the compensation of carbohydrate metabolism in a shorter period of time compared to the level of HbA1c or fructosamine.
Determination of glycosylated albumin in blood serum allows to control glycemia for the previous 7 days. Indicators of glycosylated albumin in the blood of diabetic patients correlate with the degree of glycemia.
An unusual technique for controlling glycemia was proposed by M. Oimomi et al. (1988) - determination of the level of furosin (fructosolizin) in the hair. The authors emphasize that this technique is very promising for identifying the initial slowly progressive forms of IDD and especially IDD.
Determination of the thickness of the basement membrane of capillaries. M. Siperstein et al. (1968) reported on a morphometric electron microscope method for determining the thickness of the basement membrane of the capillaries of the quadriceps femoris. It has been shown that % of diabetic patients have a thickening of the basement membrane, while in the control group such a thickening of the membrane was found only in 2-8% of the examined. However, in recent years it has been established that basement membrane thickening is detected only in % of diabetic patients, and the determination of the membrane thickness is a valuable diagnostic method for detecting microangiopathy. Moreover, as studies by S. Aronoff et al. (1976), basement membrane thickness is not a marker of diabetes and depends on age and sex. With age, the thickness of the basement membrane of capillaries increases, and in men it is greater than in women before menopause. With the onset of menopause, the thickness of the basement membrane increases faster than in men, and the differences in these values are almost erased in the future.
This indicator is the same in men and women with diabetes mellitus, and always exceeds the values observed in healthy individuals of the corresponding age, and the frequency of thickening of the basement membrane in patients with diabetes depends on the age and duration of the disease. So, with a duration of diabetes up to 4 years, thickening of the basement membrane is detected in 26% of patients under 40 years of age and 50% of patients over 40 years of age; with a duration of diabetes of 5-9 years, these figures are 58 and 44%, and 44 and 64%, respectively. As a result, this indicator cannot serve as a marker of predisposition or the presence of diabetes. Its determination is a valuable method for detecting and monitoring the progression of microangiopathies.
In patients with diabetes, a reduced ability of erythrocytes to deform was found as a result of an increase in the amount of HbA1c and an increase in the viscosity of the erythrocyte. It has been suggested that the resulting difficulty in blood circulation in the capillaries and the change in pressure in them stimulate the thickening of the basement membrane.
Reducing sugar folk remedies. Lowering (normalizing) blood sugar
Folk method to lower blood sugar
Of the medicinal plants most often used to normalize blood sugar levels are immortelle, veronica, St. , wild rose and elderberry, roots of burdock, dandelion, couch grass, knotweed, Jerusalem artichoke and chicory, buds of lilac and birch, aspen bark, young leaves and partitions of walnuts.
Cooking. 1-2 tbsp chop the bark (leaves) of mulberries, pour 1.5-2 tbsp. steep boiling water, leave to infuse for 2 hours. Ready to take the infusion during the day for 3-4 times.
Oats. Oat grains and husks are used to regulate blood sugar levels.
Cooking. 1 st. l. Husks (grains) of oats pour 1.5 tbsp. water and cook for 15 minutes. Take 3-4 times a day in equal portions 15 minutes before meals. Store the decoction in the refrigerator.
Cinnamon. Just half a teaspoon of cinnamon a day can significantly lower blood sugar levels in diabetics. Cinnamon is an effective means of regulating blood glucose levels. The therapeutic effect is manifested even when cinnamon is added to tea; it is useful not only for diabetics, but also for those who have hidden problems with blood sugar. The active component of cinnamon was the water-soluble polyphenol MHCP. In laboratory experiments, this substance has demonstrated the ability to mimic insulin, activate the receptor that perceives it, and work in cells on an equal footing with insulin. Human trials have shown the ability of one, three, six grams of cinnamon to lower blood sugar levels by 20% or more. In addition, it turned out that cinnamon reduces blood fat and "bad cholesterol", and neutralizes free radicals. Cinnamon also has unique properties that prevent blood clotting and has an antibacterial effect, stopping the growth of bacteria.
Blueberries are a well-known remedy for lowering blood sugar. Blueberry leaves and berries are used as a hypoglycemic agent. Cooking. Prepare a decoction of blueberry leaves according to the following recipes: take 1 tbsp. l. finely chopped blueberry leaves, pour boiling water (2 cups), boil for 4 minutes. Take ½ cup 15 minutes before meals. Blueberries are prepared according to this recipe: for 25 g of berries 1 tbsp. water, boil for 15 minutes, take 2 tbsp. spoons 2-3 times a day 10 minutes before meals. To be treated for 6 months, to follow a diet. Sugar will drop to normal.
Blueberry juice contains glycosides anthocyanosides, which reduce the risk of vascular thrombosis by reducing the ability of platelets to aggregate and stick to the inner wall of blood vessels.
Oak acorns. For diabetes, grind ripe oak acorns in a coffee grinder and take this powder inside 1 tsp. an hour before meals in the morning and at night. Drink water. Drink a week, then 7 days break and repeat the weekly treatment.
Aspen bark. To reduce blood sugar, pour two tablespoons of aspen bark into 0.5 liters of water, bring to a boil and cook over low heat for 10 minutes. Then insist until completely cooled. Strain. Drink 0.5 cup 30 minutes before meals. Good for lowering blood sugar quickly.
Walnut. A decoction of walnut partitions for diabetes helps maintain health. 40 g of raw materials simmer for an hour on low heat in 0.5 liters of water. Drink 1 tbsp. before every meal.
Infusion of May walnut leaves: finely chop the dried leaves, 1 tbsp. crushed leaves, pour 1 cup of hot water and boil for 1 minute, then insist until the water cools down. Strain and drink this infusion evenly throughout the day. This treatment can be carried out throughout the year. In addition to diabetes, this tea perfectly treats goiter, thyroid gland, high blood pressure, atherosclerosis, fibroids, cysts, etc.
Bought medicinal. A decoction of the roots and a tincture of the plant should be drunk with insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. For treatment, take 10 drops of tincture in the morning and afternoon for 2 weeks. The tincture is prepared with 70% alcohol. Pour 100 g of root with a liter of alcohol, leave for 20 days. Kupena tincture must be dripped into water, rosehip infusion or green tea. A decoction of the roots is bought medicinal: pour 2 tablespoons of the crushed root with a liter of water, boil for half an hour in an enameled saucepan with the lid closed over low heat. Time to insist. Drink 1/3-1/2 cup 4 times a day, regardless of meals.
A decoction of the root, bought in milk, will help reduce blood sugar. 50 g of crushed root are placed in a 5-liter saucepan, pour 3 liters of fresh milk and boil over low heat in a water bath so that the milk does not burn until the volume reaches 1 liter. Make sure that the milk does not run away and does not burn. Stir the broth more often. Cool, strain through 2 layers of gauze, squeeze, discard the roots after squeezing. A decoction of milk is ready for use.
Carnation. To cleanse the blood vessels and reduce blood sugar, take 20 pieces of cloves (spices that are sold in the store), pour a glass of boiling water, close the lid and leave to infuse overnight. Drink 1/3 cup 30 minutes before meals 3 times a day. And in the evening, add 10 more to these 20 cloves and pour boiling water again, insist and take the next day. Then make a new infusion. Drink this medicine for 6 months.
Stinging nettle (leaf) -3 parts, mountain ash (fruits) -7 parts; mix, brew the mixture in the amount of 2 tablespoons with two cups of boiling water, boil for 10 minutes, leave for 4 hours in a sealed container, store in a dark place. Take -1/2 cup 2-3 times a day.
The burdock root contains up to forty percent of inulin, which helps in the treatment of diabetes, as well as gallstone and urolithiasis, rheumatism and gastritis.
Burdock large (roots) -20 g pour a glass of boiling water, boil for 10 minutes. in a water bath, cool, filter. Take 1 tablespoon 3-4 times a day for 30 minutes. before meals.
Bay leaf lowers blood sugar. Take 8-10 pieces of bay leaf, brew 200 ml of boiling water in a thermos and leave for a day. Take warm, each time straining from a thermos, 1/4 cup 3-4 times a day 30 minutes before meals. The course is 3-6 days.
Black currant. Long-term use of blackcurrant leaf tea will help in the treatment of diabetes. Pour 1 pinch of leaves into a teapot and pour boiling water over it. After 10 minutes, the tea is ready, you can drink it.
Goat's rue (Galega officinalis) has properties similar to insulin, it is effective in mild forms of diabetes. After taking an infusion from this plant, after three to four hours, a decrease in sugar in the patient's body occurs, and the result obtained lasts more than nine hours. To prepare a decoction, you need to take one tablespoon of finely ground goat's rue, pour 1.5-2 cups of boiling water, wrap and insist for four hours, then strain. The prepared portion is designed for one day: divide it into equal parts and take fifteen to thirty minutes before meals.
Lilac lowers blood sugar. The leaves of any lilac can be brewed and drunk as tea without the norm and regardless of the meal in diabetes. This tea lowers blood sugar levels. To normalize blood sugar, drink an infusion of lilac buds, which are harvested at the stage of their swelling. 2 tbsp kidneys pour 2 tbsp. boiling water, leave for 6 hours and strain. This is the daily rate, which you need to drink 3-4 times.
Japanese Sophora. Sophora japonica seed tincture should be taken for diabetes: 2 tbsp. tablespoons of seeds should be insisted on 0.5 liters of vodka for a month, then take 1 teaspoon 3 times a day for 1 month.
Levzeya. A decoction of the root is drunk in diabetes mellitus. 1 tbsp raw materials for 1 tbsp. water, simmer on low heat for two hours, strain. Drink 1 tbsp. three times a day before meals.
Elder herbaceous. 2 teaspoons of grassy elderberry root, brew cups of boiling water, take 1 tbsp. spoon before meals 3-5 times a day.
Dandelion officinalis. To reduce sugar, it is recommended to take an infusion of dandelion roots: one tablespoon of fresh washed roots should be poured with two glasses of boiling water, wrapped and infused for two hours, then strained. The prepared portion is designed for one day, the infusion should be divided into three equal parts and taken orally thirty minutes before meals.
Horseradish lowers blood sugar. Grate horseradish root, mix horseradish with sour milk. Not with kefir, but with sour milk. The ratio is 1:10. This medicine should be taken 1 tablespoon 3 times a day before meals. Sugar does not drop immediately, but gradually. But the effect must come.
Exotic medicinal plants that regulate blood sugar levels
Cactus treatments have been extensively documented for over 500 years. According to legend, the Aztecs used a type of Mexican cactus, prickly pear, to control or actually cure the "sweet pee" disease (diabetes) in adults.
The Mexican cactus continues to be a traditional remedy for diabetes in Mexico and other Latin American countries.
The Mexican cactus lowers blood sugar levels by blocking the absorption of sugar in the intestinal tract. It lowers total cholesterol levels, improves the ratio of high-density cholesterol to low-density cholesterol - "bad cholesterol" and lowers triglycerides by preventing the conversion of blood sugar into fat, and by eliminating excess bile acids, which eventually , will be converted to cholesterol. It also lowers blood pressure and curbs appetite, and makes it easier to break down and remove fat from the body.
American ginseng or American ginseng (Panax quinquefolium). American ginseng is native to North America and is chemically similar to ginseng that grows in Asia.
Until recently, American (five-leaf) ginseng was not widely used in its homeland and was used mainly as a mild stimulant. However, even at the very beginning of the development of America, European colonists added it to tea to increase appetite and improve digestion, especially in the elderly and sickly children. Today, in the United States and Canada, five-leaf ginseng is becoming an increasingly popular therapeutic and especially preventive remedy.
In 1992, the American Ginseng Society published a book entitled "American Ginseng in America", which gives numerous examples of the use of ginseng pentaphyllum for medicinal purposes. Thus, the consequence of taking its preparations (root powder, fresh root, etc.) is a decrease cholesterol levels, the disappearance of addiction to alcohol, it helps women during menopause, probably by increasing the level of estrogen (female sex hormone); the dry root improves sleep, while the raw one, on the contrary, has a stimulating effect; it is used for colds, warts, sore throats, arthritis and other diseases.
Quite a wide application has a five-leaf ginseng in China. It is indicated for mental and physical fatigue, lung diseases, tumors, anemia, insomnia, gastritis, neurasthenia.
Ginseng is a powerful plant adaptogen - a plant capable of increasing the body's nonspecific resistance to a wide range of harmful effects of physical, chemical and biological nature.
Ginseng is useful in the treatment of diabetes, fatigue, stress relief and during convalescence. It increases stamina and well-being, which is why athletes take ginseng to increase both endurance and strength. Ginseng helps to focus your thoughts and improve memory. It has antiviral and antibacterial properties. And amazingly, there are no known side effects of ginseng.
American ginseng is a highly effective anti-diabetic agent that significantly reduces blood sugar levels in people with diabetes.
Bitter Melon. Bitter melon grows in tropical areas, including areas in the Amazon, East Africa, Asia, and the Caribbean. In addition, it is cultivated in South America, in particular for the production of medicines. It has been used for over 5000 years in China.
Bitter melon is used medicinally to treat tumors, injuries, inflammation, malaria, menstrual problems, as an antiviral agent for measles and hepatitis, for flatulence, and as an antihelminthic.
For many decades, bitter melon fruit has been used as an effective means to enhance cellular glucose uptake, which is especially important for normalizing blood sugar levels.
Bitter melon reduces the level of triglycerides in the blood (Triglycerides (TG) or neutral fats are derivatives of glycerol and higher fatty acids. Triglycerides are the main source of energy for cells. Triglycerides enter our body with food, are synthesized in adipose tissue, liver and intestines. Level triglycerides in the blood depends on the age of the person.The analysis of triglycerides is used in the diagnosis of atherosclerosis and many other diseases.)
Bitter melon stabilizes blood glucose levels while lowering levels of "bad" cholesterol (low-density cholesterol, known as LDL cholesterol, the most harmful form of cholesterol) and as such, bitter melon improves overall cardiovascular health.
Gymnema Sylvestre. Gymnema Sylvestra is a woody plant that grows in the rainforests of central and southern India. Gymnema has been used in India to treat diabetes for over 2,000 years. The leaves of the plant are also used to treat stomach ailments, constipation, liver disease and for the production of herbal medicines.
According to current research, Gymnema Sylvestre improves the uptake of glucose into cells and prevents the action of adrenaline to stimulate the liver to produce glucose, thereby lowering blood sugar levels.
Gymnema Sylvestra has the important property of increasing cell permeability to insulin, as well as assisting in the regeneration of beta cells in patients with type 1 diabetes mellitus. Gymnema Sylvestre works by stimulating the activity of enzymes necessary for the absorption of glucose.
Fenugreek hay or Greek fenugreek (Trigonella foenum-graecum L). Fenugreek is a genus of plants of the legume family. The homeland of the plant is the eastern part of the Mediterranean, Asia Minor. It grows in Southern Europe, Asia Minor, Iran, Syria, Iraq, Pakistan, Mongolia, Japan, North Africa, Ethiopia, USA. It is grown in the Mediterranean countries, Ethiopia, India, China and Argentina, in the south of Transcaucasia.
In the wild, fenugreek is preserved in the mountains of Turkey, Iran and Iraq. As a fodder, food and medicinal plant, it is grown in Southern and Central Europe, India, China, South Africa and Ethiopia, and in America. In the CIS it is cultivated in South Transcaucasia.
Fenugreek is used as a spice and as a medicinal herb throughout the world. Traditional Chinese herbalists use it for a variety of purposes, including kidney problems, male genital infections, constipation, atherosclerosis, high triglycerides and high cholesterol. However, the number one reason why fenugreek is widely used is the problems associated with diabetes and sugar intolerance in the body.
Based on exhaustive scientific research, the European Herbal Science Society has concluded that fenugreek is an adjunct in the treatment of diabetes mellitus and hypercholesterolemia. It also has an effect on lipid oxidation, thereby reducing the level of free radicals in the blood.
The German Food and Drug Administration, similar to the FDA (USA), recognized the usefulness of fenugreek and approved it as one of the plants used for medicinal purposes, in particular, to dissolve mucous and other secretions, to increase blood flow and inhibit growth infections.
A proven way to lower blood sugar levels (folk remedies):
Dry blackberry leaves, chop. 2 tsp brew 1 tbsp. boiling water. Infuse for an hour, strain and drink three times a day.
A decoction of young blueberry shoots: 1 tbsp. chopped twigs, 1 tbsp. boiling water, cook over low heat for 10 minutes, insist until cool and strain. Drink 1-2 tbsp. three times a day.
1 tsp dry crushed blueberry leaves pour 1 tbsp. boiling water, wrapped to insist an hour, strain, squeeze, drink four times a day for 1/4 tbsp.
Each of the above remedies should be used in courses of 3-4 weeks, with intervals between courses of 5-10 days, and the next course, start drinking the drug with another component.
Equal parts of the lure leaf, mulberry and walnut, bean leaves, St. For 1 tbsp. collect 250 ml of water, bring to a boil and cook for 3-5 minutes, cool, strain. Drink 1/3 tbsp. three times a day courses for 3 weeks with a week break between them.
Nigella Damascus or Nigella Damascus effectively lowers blood sugar and strengthens the immune system. Collection: 1 tbsp. (ml) nigella, 1 tbsp. elecampane roots, 1 cup of oregano herb, 1 cup of dried pomegranate peels. Grind everything very finely and pour into a bowl. 1 st. Coarsely chop the pomegranate peel, then grind it very finely and add to the first three components. Store this mixture in a dark screw-on jar in a cool place. Apply 15 minutes before meals 3 times a day, 1 tbsp. this mixture for 4 weeks in a row, then gradually reduce the dose. Carry out 2-3 courses of treatment. With the composition of this wonderful recipe, you can reduce blood sugar from 16 mmol to 5.0 mmol in just one course of treatment.
In equal quantities, mix blueberry leaves, juniper fruits, flax seeds, lingonberry leaves. 1 st. pour a spoonful of the mixture with a glass of boiling water. Take 2-3 times a day for a glass before meals.
Rose hips (fruits) - 3 parts, blackcurrant (fruits) - 1 part, carrots (root) -3 parts, lingonberries (fruits) - 1 part, nettle (leaves) - 3 parts. Brew one tablespoon of the mixture with 2 cups of boiling water, boil for 10 minutes, leave for 4 hours in a tightly closed container and cool place, strain through cheesecloth. Take 1/2 cup 2-3 times a day. Reduces blood glucose levels.
Blueberries (leaves) - 60 g, beans (pods) g, corn (stigmas) g, clover (inflorescences) g, dandelion root -20 g, nettle leaves - 25 g. Collect brew in 1 liter of boiling water, keep warm 5 -8 ocloc'k. Then, over low heat, bring to a boil, strain, cool. Take 1 glass 4 times a day.
Mix equal amounts of blueberry leaves, bean pods, nettle leaves, dandelion root, St. John's wort. 2 tbsp. spoons of the mixture pour 3 cups of boiling water, leave for 30 minutes, take 1/4 cup 4-6 times a day before meals.
Mix equal amounts of blueberry leaves, bearberry leaves, valerian root, dandelion root. 2 tbsp. Spoons of the mixture pour 2 cups of boiling water, leave for 1 hour. Take 1/3 cup 3 times a day, preferably before meals.
Folk remedies to lower blood sugar:
Stone oil is a reliable, folk medicine proven way to treat type 2 diabetes. Stone oil dissolves in boiled water at room temperature, merges after 2-3 days, the sediment can be used for lotions and compresses. At the beginning of treatment (2-3 days), it is better to use stone oil in small doses (a glass during the day) and a low concentration (1 g per 3 liters of water) after meals. Then before meals. Every day increase the concentration, bringing to 3 g per 2 liters of water, drink 1 glass 3 times a day. The course of treatment is 80 days. The course of treatment requires 72 g of stone oil. Watch your sugar drop! Insulin is used if necessary as directed by a doctor. Depending on the severity of diabetes, 1-4 courses of treatment will be required. Break between courses - 1 month. During treatment, exclude pork, lamb, fatty poultry, as well as alcohol, antibiotics, strong tea, coffee, cocoa from the diet. The return of diabetes under the above conditions will not occur.
The easiest way to lower blood sugar to normal is to eat baked onions in the morning (on an empty stomach). It's baked. Eat every day for a month. In addition to baked onions, mustard seeds are good at reducing sugar (eat a pinch of seeds daily). In addition, mustard seeds have a great effect on digestion, relieve constipation, increase bile secretion, so that your well-being and mood will noticeably improve. Mustard seeds can be successfully replaced with flax seeds, which have all of the above medicinal properties of mustard seeds.
It happens that a diabetic has eaten some of the forbidden foods, but if he drinks tea from his cuff, the sugar will not jump! Recipe for making cuff tea: 1 des.l. herbs with flowers brew 300 ml of boiling water, bring to a boil. Then cool, strain, divide into two parts and drink in two doses before meals. The cuff cures a lot of other diseases. It heals all inflammations, tumors, hernias, suppresses fermentation processes, relieves pain in the heart, treats rheumatism, dropsy and much more. By the way, she enlarges breasts for young girls.
The juice of a number of vegetables, berries, and fruits has a sugar-lowering effect. It is recommended juice of fresh potato tubers, juice from fresh leaves of white cabbage, juice from fresh fruits of raspberry, dogwood and pear, garden salad, peas, alfalfa, mushrooms have a sugar-reducing property.
Micronutrients and macronutrients that affect blood sugar
Chromium was first discovered as an essential trace element for the life of any organism in 1955.
It is also present in many foods - brewer's yeast, wheat germ, liver, meat, cheese, beans, peas, whole grains, spices, mushrooms.
The body of a healthy person contains on average only a few milligrams of chromium and it plays a big role in human health.
The main role of chromium in the body is the regulation of blood sugar as a "glucose tolerance factor". Chromium works with insulin to move sugar from the blood to the body's tissues for use or storage. This micronutrient is so important for sugar tolerance that its severe deficiency leads to the development of a diabetes-like disease. Chromium levels decrease during and after childbearing, in childhood diabetes, in coronary artery disease (hardening of the arteries leading to the heart). Chromium deficiency during pregnancy may explain the diabetes that develops during pregnancy (gestational diabetes), and the interaction of chromium with insulin may also contribute to the rapid weight gain, fluid retention, and increased blood pressure that some women experience during pregnancy and later. Chromium is necessary for normal fat metabolism (“fat burning”) in the body and its deficiency unequivocally leads to overweight and obesity.
Manganese helps reduce blood sugar and has a lipotropic effect (lowers cholesterol), promotes protein synthesis.
Sorbitol (sugar substitute) does not cause the need for insulin, and is deposited in the liver in the form of glycogen. It has an antiketogenic, choleretic, vitamin-sparing (B vitamins) and mild laxative effect, promotes the development of beneficial intestinal flora capable of synthesizing choline, its precursors and vitamins, and enhances the antitoxic function of the liver.
Citric acid and other organic acids have a detoxifying effect - they remove toxins from the body, cholesterol, and reduce the risk of oncogenic nitrosamine synthesis. Fruit acids have a choleretic, anti-inflammatory effect, stimulate the secretion of juice in the gastrointestinal tract, improve digestion, activate intestinal motility, normalizing stools, and inhibit putrefactive processes in the large intestine.
Pectins, inulin (a soluble form of plant fibers) reduces the digestibility of carbohydrates (starch) and fats from the gastrointestinal tract, remove cholesterol, promote the reproduction of bifidoflora in the large intestine, preventing the growth of putrefactive bacteria. They prevent obesity, normalize intestinal motility, regulate stool.
Vitamins normalize carbohydrate, fat and protein metabolism, have antioxidant activity, stabilize cell membranes, lower blood cholesterol levels, stimulate the immune system, increasing the body's resistance, improve the function of the cardiovascular, nervous - vitamins B1, B6, B12 (polyneuropathy, encephalopathy ), digestive, excretory (nephropathy) systems. Normalize vision - vitamins A, E, C (retinopathy); sexual function - vitamins A, E, zinc, selenium; eliminate trophic changes in the skin - vitamins B2, B6, etc.
Ferrous iron, together with vitamin B12, stabilizes the level of hemoglobin in the blood, improving the supply of oxygen to tissues, will promote hematopoiesis, improve the activity of the liver and kidneys, normalize metabolic processes in the nerve trunks and the central nervous system.
Blood sugar is normal. Blood sugar reduction folk remedies
The blood sugar level is normal. Blood glucose, fasting sugar, blood and sugar