Bladder tumor in men and women: treatment, symptoms
In the case of pathological changes in the cells of the mucosal epithelium, doctors diagnose a tumor of the bladder. With an illness, an increase in the number of cells is observed, the pathological process is characterized by a change in their composition. Neoplasms in the bladder are benign or malignant in nature. If a malignant tumor of the bladder has arisen, then the cells in which the changes have occurred penetrate into the submucosal layer. Gradually, the disease progresses and harms the entire wall of the bladder. Doctors have noticed that a tumor of the bladder in men is diagnosed more often than in women.
Benign formations and their classification
Tumors of the bladder of a benign nature occur on the walls of the internal organ and neck. In medicine, there is a classification of bladder tumors into epithelial and non-epithelial. Benign formations lead to polyps, adenomas, pheochromocytomas, and papillomas. The above formations are characterized by epithelial nature. Such a tumor in the bladder is endowed with the ability to degenerate into a malignant one.
There are also non-epithelial neoplasms of the bladder. Often there are neoplasms of the bladder called sarcomas, which provoke lymphogenous and hematogenous metastases in the initial stages. All other formations of a non-malignant nature, as a rule, do not lead to metastases and do not injure nearby tissues. After the patient has removed the formation, metastasis does not occur.
epithelial
Bladder polyps
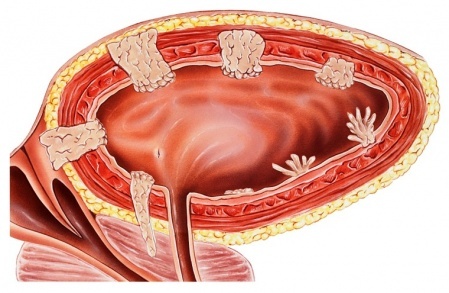 If left untreated, polyps can develop into malignant tumors.
If left untreated, polyps can develop into malignant tumors. When forming, connective tissue cells grow with defects. They are attached to the mucous membrane of the organ with the help of a small leg. Polyps look like mushrooms. The pedicle of the formation is directed into the cavity of the urea. Often the disease does not make itself felt, and there are no obvious signs of polyp formation.
Pathology is detected in most cases during an ultrasound examination. Only in the case of formation in the ureter or in the presence of a tumor of the urethra, the pathology makes itself felt. The first sign of a polyp in this area is considered to be a violation of urine excretion - outflow delays occur. During urination, the direction of the jet changes and it splashes. The color of the urine changes, it becomes pinkish, and sometimes red. This is due to the destruction of the posterior wall of the urinary cavity and bleeding. The patient complains of pain during the excretion of urine.
Papillomas
Papilloma is a benign tumor, the surface of which is rough. This formation has a pink color and is soft in structure. In medicine, there are multiple and single papilloma. They are prone to recurrence. When re-germination occurs in the bladder, their modification is noticed. When atypical papillomas occur, doctors talk about an early stage of malignancy.
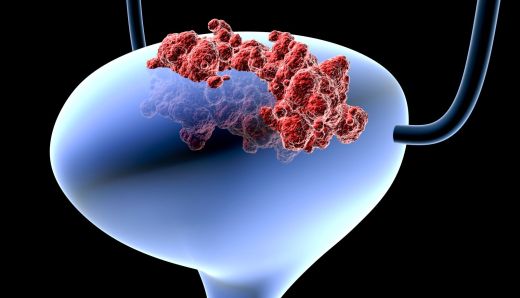 Papilloma refers to a benign tumor.
Papilloma refers to a benign tumor.
At the initial stage, this pathology does not manifest itself in any way. Just like polyps, it makes itself felt in the later stages. Against the background of papilloma, cystitis often develops, especially in women. The patient eventually complains of problematic urination, there is a delay in outflow. When passing urine for a laboratory test, blood will be found in the tests.
Prostate adenoma in men
Bladder adenoma or prostatic hyperplasia occurs in the stronger sex. The disease is characterized by the growth of prostate tissues and the formation of tumors and nodular neoplasms in them. Due to the fact that the prostate partly consists of the urethra, in the case of an increase in education, it puts pressure on the bladder and makes it difficult to urinate. Often, adenoma occurs due to hormonal failure, which is observed in aged men. After the age of 50, the likelihood of getting sick increases. Pathology in young guys is practically not observed.
 Pheochromocytoma is a tumor of the adrenal glands.
Pheochromocytoma is a tumor of the adrenal glands. Very rarely, pheochromocytoma affects the walls of the bladder. As a rule, pathology is observed in the adrenal glands or in other organs. Education consists of cells that are part of the chromaffin tissue. With the appearance of this type of formation, excessive release of catecholamines is observed. Pathology in the internal organ leads to seizures during urination. During the excretion of urine, there is no pain, but blood is observed.
endometriosis tumors
An endometriosis neoplasm jeopardizes the walls of the bladder. The composition of this tumor includes small cysts that protrude into the luminal region of the internal organ. Endometriosis is associated with dyshormonal metaplasia, in the case when the body has a large amount of estrogen and a lack of progesterone.
Doctors identify the growth of an endometrial tumor in a single and multiple type.
Bladder tumors in women of this type are more common than in men. Most often manifested during the menstrual cycle. This neoplasm tends to grow and injure neighboring tissues and organs. Often, an endometriosis tumor develops into a malignant tumor in the bladder. Therefore, it is extremely important to identify the pathology in time and remove the formation.
Non-epithelial
Fibroma of the bladder
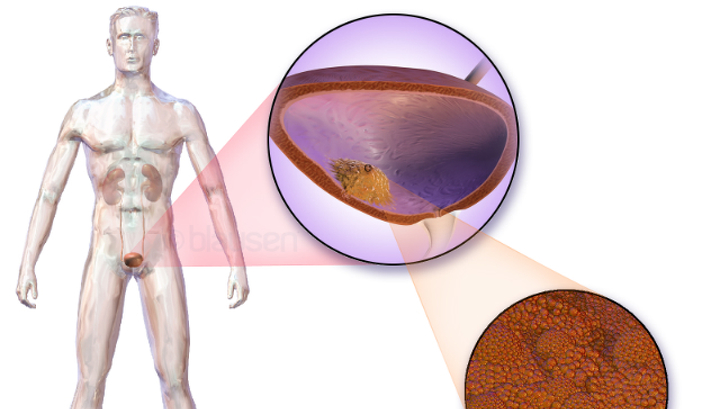 Fibroma for a long time does not give any symptoms.
Fibroma for a long time does not give any symptoms. Fibroma is small and has a spherical shape. Often the formation is similar to a pinkish ellipse. As the neoplasm grows, its color changes. The cause of fibroma is the uncontrolled reproduction of cells. Education of this type does not make itself felt and does not cause concern to a person. If necessary, it can be easily removed surgically.
Leiomyoma
Leiomyoma of the bladder is extremely rare and is characterized by the formation of a non-malignant nature in the structure of smooth muscles. As a result of the pathological process, the immune system weakens, disturbances occur in the functioning of the bladder and neighboring organs. In most cases, the patient has pain during urination. It is recommended to treat leiomyoma with the help of surgical therapy.
Hemangioma
Hemangioma of the internal organ is a neoplasm located in the vessels of a reddish-blue hue. As a rule, this pathology is congenital in nature and can progress very quickly if the hemangioma is not eliminated in a timely manner. The presence of this formation is indicated by blood from the urethra.
Other formations
 Prolonged stagnation of urine can provoke the formation of tumors.
Prolonged stagnation of urine can provoke the formation of tumors. Non-epithelial neoplasms include fibroids of the internal organ. The composition of fibroids includes cells of different tissues. It mainly contains fibrous and connective tissues. Often this formation grows to a significant size. Fibromyxoma is rare and is spherical. The structure of the formation is soft and there is a leg. Another non-epithelial tumor is a neurinoma, which resembles a ball. Volumetric formation of the bladder has a bumpy surface and is composed of auxiliary cells of the nervous tissue.
Types of malignant tumors of the bladder
Malignant tumors are distinguished by the fact that the formed cells can penetrate into other layers of the organ, and not be located only on the surface. When covering the entire organ, metastases occur, which are difficult to treat. Malignant tumors are more often diagnosed in men. Depending on the type of pathology, special therapy is prescribed.
Varieties
Considering the morphological components, cancer is divided into pathology of the transitional cell, squamous cell type and adenocarcinoma. The first type is the most common. With pathology, a modification of the cells of the organ and their further growth occurs. In squamous cell carcinoma, epithelial cells are affected. The cause of the pathology is protracted inflammatory processes. In the case of adenocarcinoma, mutational processes of cells are observed as a result of constant stagnation of the secretion of the glands.
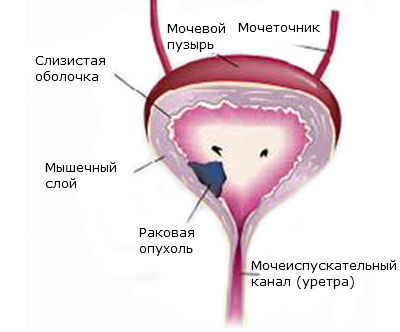 There are various types of pathology.
There are various types of pathology. Subdivide the cancer of the internal organ based on the type of manifestation of the disease. There is solid and papillary pathology. Solid cancer has an exophytic and endophytic form. With an exophytic tumor, hilly formations appear, and in the case of an endophytic pathology, the structure of the formation is flat. Papillary cancer is observed frequently and is characterized by the growth of papillomas, which have become malignant. It is mainly localized near the neck of the bladder or in the region of the bottom.
In medicine, bladder cancer is distinguished between highly differentiated and low-differentiated species, it all depends on the deformation of the formation.
Given the depth of injury to the mucosa of the internal organ, cancer is classified into invasive and non-invasive. The first type injures the internal structure of the urea and spreads to adjacent organs. With superficial or non-invasive cancer, the pathology does not spread to other organs, but injures the mucous and submucosal membranes.
Main reasons
Medicine has not yet been able to finally investigate all the possible causes of tumors in this organ. Often, pathology occurs due to prolonged stagnation of urine in the internal organ. Due to the large number of different substances in it, the urothelium is transformed into a malignant one. It is important to timely eliminate the causes of congestive processes, this may be due to cystitis, inflammation, stricture of the urethra and other pathologies. The occurrence of tumors is preceded by other reasons:
Often the cause of a bladder tumor is the use of poor-quality drinking water. A liquid that contains a large amount of chlorine increases the chance of pathology. Doctors are inclined to believe that the disease is preceded by a papillomavirus infectious deviation.