Major sexually transmitted diseases. Sexually transmitted diseases (STDs)
Home doctor (handbook)
Chapter XI. SEXUALLY TRANSMITTED DISEASES
Venereal diseases no longer cause fear. In any case, the majority: "It's not about me, it's about homosexuals and prostitutes. Even if you get infected (of course, not AIDS), being cured is a couple of trifles. With modern means!" The successes of medicine create the illusion that you can do without a doctor - you just need to take antibiotics and everything will pass. A dangerous delusion - not only will it not go away, but it can go into a more difficult stage and manifest itself when it becomes very difficult, and sometimes even impossible, to do something.
General symptoms. The first sign is discharge from the genital organs, sores and "abrasions" on their surface, but sometimes the disease does not manifest itself for the time being. It happens that it does not develop at all, but a person carries a pathogen in himself and can infect his sexual partners, intrauterine transmission of the microbe from mother to child is also possible.
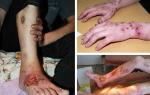
Serious consequences should be remembered: in newborns - eye damage (conjunctivitis), pneumonia, sepsis and meningitis, birth defects, disability and even death; in women - inflammatory diseases of the pelvic organs, ectopic pregnancy, miscarriages, premature births and stillbirths; in men - narrowing of the urethra, impotence, comfort and other infertility. Some types of pathogens contribute to the development of cancerous tumors of the cervix, skin and internal organs.
Sexually transmitted diseases have never been considered only from a medical point of view, they have always been associated with ethical standards: the infected person is to blame. The sexual revolution, having radically changed views on sexual life, has led to a significant increase in such patients - there are about 1 billion of them in the world. In other words, every fifth inhabitant of the Earth suffers from sexually transmitted diseases. Recently, the most formidable - AIDS - has been added to them. The danger is great enough. Therefore, it is necessary to have at least a minimum of knowledge about these diseases - their manifestations, course and consequences, means of treatment and prevention.
Gardnerellosis.
Inflammation of the vagina (vaginitis). Transmitted sexually. It has now been established that the cause is a special microorganism called gardnerella. The patient develops foul-smelling leucorrhoea (the smell of rotten fish), which intensifies after intercourse. With such secretions, it is imperative to consult a doctor, and the sexual partner should also be treated so as not to get infected from him again.
Hepatitis B.
One of the serious diseases of the liver. It is transmitted through blood, as well as sexual contacts, which are the ones that "supply" a significant number of patients. The risk of contracting hepatitis B is extremely high in people who have promiscuous sex. It was found in 1/3 of homosexuals and bisexuals (who have sex with both men and women), while among men who have intercourse only with women - only 6%. Almost 300 million people in the world are carriers of the disease virus.
In patients with hepatitis B, yellowness of the skin, eyes, pain in the liver, changes in the color of urine, feces, deterioration in general well-being are observed. However, often the disease is asymptomatic, without jaundice and other signs. A severe complication is primary liver cancer, which in some regions of the world is the most common form of malignant neoplasms, especially among men (see also Chapter Infectious Diseases).
Genital herpes (genital herpes, HSV-2). In recent years, it has become increasingly common in many countries around the world. For example, in the United States, 200-500 thousand patients are registered annually. According to the UK Venereology Service, women are 6 times more likely to get genital herpes than men.
Symptoms and course. Usually 3-6 days after infection, blisters appear on the skin and mucous membranes. Sometimes there are no signs of the disease for quite a long time. In men, blisters appear on the penis, especially on the glans and foreskin. Before this, patients feel a burning sensation, itching, tingling. The same eruptions can occur in the mouth as a result of sexual intercourse through the mouth. Bubbles, merging and bursting, turn into small wounds. Some patients develop discharge from the urethra, pain during urination, and even urinary retention. The temperature may rise, headache, general malaise, enlarged lymph nodes.
In women, blisters and ulcerations appear on the genitals, in the perineum and near the anus. Then the bubbles disappear, and after a while they reappear.
A sick woman during childbirth infects her child. The newborn may develop damage to the nervous system, skin, mouth and internal organs. Most children who get herpes die. The survivors have severe complications from the nervous system. If in the later stages of pregnancy, genital herpes is found in women, they try to do a caesarean section in order to protect the child from infection during passage through the birth canal.
Gonorrhea. An infectious disease it is also called gonorrhea, a change caused by gonococcus. Neisser, the scientist who discovered this pathogen in 1879, said: "I do not hesitate to declare that, in terms of its consequences, gonorrhea is a disease incomparably more dangerous than syphilis."
Indeed, gonorrhea brings a lot of suffering to people of sexually active age. This was especially noticeable in a period when there were no antibiotics in medical practice. Its main danger stems from a frivolous attitude that it is possible to recover easily, even without a doctor - with the help of the advice of "experienced" friends and acquaintances. Of course, gonorrhea is not as destructive as syphilis, but the likelihood of infertility (both in men and women), sexual disorders in men, infection of children during childbirth is extremely high.
It should be added that gonorrhea is much more common than syphilis. She, as well as syphilis, can be ill several times. Many, not suspecting that they are sick, continue to live sexually, infecting their partners, are not treated, and the disease progresses, leading to severe complications. Infection occurs with various forms of sexual intercourse: with "normal" sexual intercourse, with "incomplete" (when there is only mutual contact of the genital organs, without the introduction of the penis into the vagina), with orogenital (contact of the genital organs and oral mucosa), with anal.
Men do not always get infected from women with gonorrhea. With a small number of gonococci, they may not enter the narrow opening of the urethra. If nevertheless hit, they can be thrown away or washed away with urine. Most often, a woman infects a man during menstruation or immediately after it, with prolonged sexual intercourse, with its rapid end, when gonococci are taken out of the deep sections of the glands.
Unlike men, women "catch" gonorrhea in almost all cases of sexual intercourse with the patient.
The child can become infected from the mother when passing through the birth canal. At the same time, the mucous membrane of the eye is affected, and in girls, the genitals are also affected. Blindness in newborns in 56% of cases is caused by gonorrhea. Gonococci can also be brought into the genitals of girls by contaminated hands of the mother, a towel, sponge, bed linen, etc.
Symptoms and course. Gonorrhea affects the genitourinary organs, rectum, mucous membranes of the eyes, oral cavity and pharynx, sometimes joints, heart and other organs. In men, usually 3-5 days after infection, abundant purulent, mucopurulent discharge appears, accompanied by itching, pain or pain when urinating. Allocations are either spontaneous or appear when pressure is applied to the glans penis. Yellow-green stains remain on the underwear. The lips of the urethra become inflamed, swollen, slightly painful.
If the disease is not treated, then the process extends to the entire canal, prostate, seminal vesicles, testicles. Painful, frequent, difficult urination. The temperature may rise, chills, pain during bowel movements. A serious complication of gonorrhea, often leading to infertility, is the defeat of the testicle. Usually there is swelling, sharp pain, it increases in size.
After gonorrheal inflammation of the epididymis (epididymitis), the formation of spermatozoa is disrupted and, with a bilateral process, the possibility of fertilization drops sharply. Undesirable consequences can be avoided only with timely treatment, strict adherence to the doctor's recommendations, temporary cessation of sexual activity, refusal of alcohol, etc.
"A 29-year-old man was transferred to the venereology department of the hospital from a surgical hospital. He moved on crutches due to an increase and sharp pain in the ankle joint. He had slight cloudy mucous discharge from the urethra. He fell ill suddenly: he went to bed healthy, and in the morning he had pain in the joint, fever, chills, weakness made him call an "ambulance", which took him to the surgical department. The patient is not married, often engages in promiscuity. 3 years ago he had trichomoniasis. It turned out that a few days after sexual contact with an unfamiliar woman for 3-4 weeks, he had a slight discharge from the urethra.Determining that this was again trichomoniasis, he began to take the medicines that he was prescribed for this disease, and continued to lead his former lifestyle: playing sports, sex, drinking. In the venereology department, a patient was diagnosed with gonorrhea.
Sometimes a person who has had sexual contact with a known gonorrhea patient does not show any signs of the disease. This does not mean that he was not infected. It is imperative to do research. The so-called asymptomatic course of gonorrhea is dangerous both for the sick person and for those who come into contact with him. It is of particular importance during pregnancy, as it is possible to infect the child. 50-70% of women with gonorrhea have no discomfort. The rest may have purulent or mucopurulent discharge from the vagina, frequent urge and pain when urinating. Late seeking medical help with asymptomatic gonorrhea leads to the fact that the disease passes from the cervix to the uterine mucosa, fallopian tubes, ovaries. There is a risk of ectopic pregnancy, infertility, complications during childbirth.
Often, complications of gonorrhea occur in women almost imperceptibly. Only a few have pain in the lower half of the abdomen, bleeding from the vagina, fever, headache, general malaise. If a patient with gonorrhea is pregnant, then she has a high risk of miscarriage, fetal death and postpartum infection.
A very unpleasant complication of gonorrhea in women is inflammation of the large vestibular glands (bartholinitis), which usually begins 2-3 weeks after infection. Gonococci, penetrating into the duct of the gland, cause inflammation, and a painful cord or nodule appears in the groin: when pressed, pus can be released. If the mouth of the gland is closed, pus, accumulating in the excretory duct, stretches it. Then a painful, mobile tumor, ranging in size from a cherry to a large egg, protrudes from the genital slit. The woman feels pain in the vulva, it is difficult for her to walk, sit. When other microorganisms are attached to the gonococcus, the temperature rises to 38-39°C. The tumor bursts, pus pours out of it, the pain disappears, the temperature decreases, but after a while, if treatment is not carried out, pus accumulates again, redness of the skin, soreness, swelling appear, and everything starts all over again. Often, patients with such complications have to undergo surgery.
With sexual intercourse through the mouth, gonorrhea of the oral cavity and pharynx occurs. Signs of it are redness and sore throat, sometimes severe, with high fever. For the most part, gonorrhea of the genital organs also occurs at the same time.
If there is a discharge from the rectum and discomfort in this area, you should also consult a doctor and be examined. Gonorrhea of the anus is possible not only in homosexual and bisexual men, but also in women, after sexual intercourse through the anus or as a result of leakage of infected vaginal discharge.
Gonorrhea is especially dangerous for children. Only a few become infected through a common bed due to poor hygiene. In most cases, they are "rewarded with a bad disease" by older family members or friends at home, forcing them to cohabit.
The initial manifestation of gonorrhea in a newborn is usually eye disease. A few days after birth, the child's eyes turn red, yellow or green discharge begins from them.
It is necessary to immediately consult a doctor and begin treatment in order to prevent damage to the cornea and all tissues of the eye, leading to blindness. Children often pay for the mistakes of adults or become their victims.
Infection caused by immunodeficiency viruses (HIV). Another name is AIDS (AIDS, Acquired Immune Deficiency Syndrome). In recent years, it has become epidemic in the world; it is caused by human immunodeficiency viruses found in the saliva and mucous secretions of patients. This infectious disease, which develops when the pathogen enters the bloodstream, is most often transmitted sexually. Infection with HIV infection is also observed during intravenous administration of drugs during blood transfusion and its preparations due to a non-sterile instrument, especially a needle.
AIDS pathogens are destroyed by boiling, ether, acetone, ethanol (20%), sodium hypochlorite (0.2%). For the first time this disease was detected in homosexuals and drug addicts. It was even called at first "the disease of homosexuals." Mostly men were ill (9 out of 10). In the future, it began to spread widely also among people who have promiscuity. Transmission of the virus from mother to child during pregnancy and childbirth has been proven.
Symptoms and course. First, the temperature rises to 38-40 ° C at any time of the day, profuse sweating appears, and physical activity sharply decreases. At the same time, loose stools, weight loss, shortness of breath, inflammatory changes in the skin of the face, hair loss, and swollen lymph nodes can be observed. This may go on for several years. Patients then develop various concomitant infections that are rare in people with normal immunity. They can affect the skin, lymph nodes, eyes, various parts of the gastrointestinal tract, lungs, and central nervous system. In this case, various rashes appear on the skin (spotty, nodular, vesicular, etc.), often accompanied by itching. The severe course of these diseases is due to the extremely limited protective forces of the body. Most often, AIDS patients develop bilateral persistent pneumonia. Often there is oral candidiasis, which, spreading, leads to the appearance of ulcers of the esophagus and lungs. Bubble rashes appear on the mucous membrane of the mouth, genitals and perineum. Many are affected by the central nervous system, eyes (chorioretinitis). Diarrhea is often noted, which is quite difficult, with frequent watery stools (up to 15 liters per day). In most patients, immediately after recovery from one infectious disease, another begins, or a combination of various infections is observed.
Approximately 40% of AIDS patients develop malignant tumors. Often they are diagnosed at a late stage or after the death of the patient. Approximately 1/3 Kaposi's sarcoma occurs, in which not only the skin is often affected, but also the lymph nodes, mucous membranes and internal organs.
Quite often, those infected with the virus for several years, in addition to an increase in the cervical, axillary or occipital lymph nodes, have no other symptoms of the disease with a further classic picture.
Human immunodeficiency viruses, like war, affect people of the most active age.
Candidiasis. Inflammation caused by Candida yeast. Candidiasis ("thrush") is one of the most common infections, especially in women.
The occurrence of candidal inflammation of the vagina is promoted by increased skin moisture (when wearing nylon tights); violation of carbohydrate metabolism; the use of antibiotics or other chemotherapeutic agents, including drugs prescribed for trichomoniasis, which eliminate other microorganisms that are natural antagonists of fungi; the use of hormones (taking steroid drugs and birth control pills); diseases that weaken the body's immune system; infection from a sick man.
Symptoms and course. A third of sick women become infected with candidiasis during sexual intercourse. They develop cheesy discharge from the genital tract, itching and pain, aggravated by urination and sexual intercourse. The vaginal vestibule becomes dark red, and redness may spread to adjacent areas of the skin, in particular around the anus.
In men, the glans penis and the skin covering it usually turn red, covered with a white coating, sometimes wounds appear on them, patients are worried about itching and burning. It happens that inflammation of the urethra begins with mucous discharge from it and the presence of flakes in the urine.
Molluscum contagiosum. It spreads through close contact, including sexual contact. Children become infected when they are breastfed by an ill mother and through household items. In terms of up to 3 months after infection, small nodules appear on the skin of patients ranging from a pinhead to a pea with an impression in the center. In children, rashes are more often located on the skin of the hands, face, neck; in adults - on the skin of the trunk and genitals, the inner surface of the thighs, pubis and abdomen. These nodules are painful.
Treatment - see Ch. Skin diseases, section 5, Molluscum contagiosum.
Pubic lice (pediculosis). Lice is spread not only sexually, but also through underwear. The pubic louse lives in pubic hair, in the armpits, as well as in the beard, mustache, eyebrows and eyelashes.
It does not affect the hair of the head, which distinguishes it from the head louse. On the affected areas of the hairline, mainly the perineum, thighs, anus, small hemorrhages, cyanotic spots, signs of inflammation, scratching appear. In the future, small nodules, vesicles, pustules may form. Patients are worried about constant itching. Lice can be seen at the roots of the hair, small nits are found on the hair.
The topic is very prosaic - sexually transmitted diseases (STDs). In recent years, the rates of infection with sexually transmitted diseases have been steadily increasing. Unfortunately, this applies primarily to adolescents, due to the lack of proper sex education in schools and families. Statistics say that every 10 people on our planet suffer from STDs, not excluding children and the elderly.
Sexually transmitted diseases (STDs) are a whole group of infectious diseases with a variety of clinical manifestations, united by sexual transmission and high social danger. The term appeared in 1980, and to date, more than 20 types of infections and viruses are classified as STDs: from deadly HIV infection to banal chlamydia, which, by the way, cannot be called trifling either. Moreover, in terms of prevalence in Russia, it is in second place after the flu.
According to the type of causative agent, STDs are divided as follows:
The World Health Organization classifies STDs as follows:
Common sexually transmitted infections
- gonorrhea;
- syphilis;
- lymphogranulomatosis (inguinal form);
- chancroid.
- granuloma of the venereal type.
Other STDs
that affect mainly the organs of the reproductive system:
- urogenital shigellosis (occurs in persons with homosexual sexual intercourse);
- trichomoniasis;
- candidal lesions of the genital organs, manifested by balanoposthitis and vulvovaginitis;
- mycoplasmosis;
- herpes type 2;
- gardnerellosis;
- scabies;
- genital warts;
- chlamydia;
- flatheads (pubic pediculosis);
- molluscum contagiosum.
that affect mainly other organs and systems:
- sepsis of newborns;
- Hepatitis B;
- lamblia;
- cytomegalovirus;
- AIDS;
- amoebiasis (typical for persons with homosexual contacts).
Often, STDs are asymptomatic and are detected only at the stage of development of complications. Therefore, it is very important to pay due attention to their prevention: use contraceptives, avoid casual sexual contact, observe hygiene and take tests twice a year in the direction of a gynecologist or urologist.
Of course, most STDs are curable, but not all. For example, it will never be possible to part with genital herpes - treatment only softens the course of the disease and reduces the frequency and severity of relapses. Only those under the age of 25 have a chance to permanently get rid of the human papillomavirus (HPV).
By the way, it is believed that the human papillomavirus can cause cancer of the cervix, vagina, vulva and penis. The genital herpes virus also affects sperm, and if a woman becomes infected with it during pregnancy, it can cause severe congenital diseases of the fetus.
Note: almost all viral and bacterial sexually transmitted diseases penetrate the placental barrier, that is, they are transmitted to the fetus in utero and disrupt its physiological development. Sometimes the consequences of such infection appear only a few years after the birth of a child in the form of dysfunction of the heart, liver, kidneys, developmental disorders.
Treatment will be successful only if it is started without delay and completed. How to spot the very first danger signals?
An alert has been declared!
There are eight main signs, having discovered which, you should not delay a visit to the doctor.
- Itching and burning in the intimate area.
- Redness in the genital area and anus, sometimes - sores, vesicles, pimples.
- Discharge from the genitals, smell.
- Frequent, painful urination.
- Enlarged lymph nodes, especially in the groin.
- In women - pain in the lower abdomen, in the vagina.
- Discomfort during intercourse.
- Cloudy urine.
However, for example, syphilis or chlamydia may appear several weeks after infection, and sometimes STDs can generally be hidden for a long time, turning into a chronic form.
Regardless of the presence of discomfort in the genital area, a preventive visit to the doctor is necessary twice a year, as well as after casual sexual contact, sexual violence, in case of infidelity of your regular partner. If you notice any STD symptoms, go to your appointment the same day.
Symptoms of sexually transmitted diseases in women
The presence of certain symptoms of STDs in women is explained by the peculiarities of their physiology.
The following signs should alert a woman and become a reason for an extraordinary visit to the gynecologist:
- pain and dryness during sex;
- single or group enlargement of lymph nodes;
- dysmenorrhea (violations of the normal menstrual cycle);
- pain and discharge from the anus;
- itching in the perineum;
- anus irritation;
- rash on the labia or around the anus, mouth, body;
- atypical vaginal discharge (green, frothy, odorous, bloody);
- frequent painful urge to urinate;
- swelling of the vulva.
Sexually transmitted diseases in men: symptoms
You can suspect an STD in men by the following signs:
- blood in semen;
- frequent and painful urge to urinate;
- low-grade fever (not with all diseases);
- problems with normal ejaculation;
- pain in the scrotum;
- discharge from the urethra (white, purulent, mucous, with a smell);
- rash of various kinds on the head of the penis, the penis itself, around it.
Let's get to know each other better
- Chlamydia
Symptoms. 1-4 weeks after infection, patients develop purulent discharge, painful urination, as well as pain in the lower abdomen, in the lower back, bleeding between menstruation in women, in men - pain in the scrotum, perineum.
What is dangerous? In women, it can lead to inflammation of the fallopian tubes, cervix, pathologies of pregnancy and childbirth, diseases of the liver, spleen.
In men - to inflammation of the epididymis, prostate gland, bladder, impaired potency. Newborns may develop conjunctivitis, nasopharyngeal lesions, pneumonia.
- Trichomoniasis
Symptoms. They can appear on the 4-21st day after infection, sometimes later. Women have abundant foamy discharge of white or yellowish-green color with a pungent odor, causing severe itching and irritation of the genital organs, as well as pain, burning during urination, pain during intercourse. In men, there is a burning sensation during urination, mucopurulent discharge from the urethra. However, this disease is often asymptomatic.
What is dangerous? In women, the cervix and inner layer of the uterus, fallopian tubes, ovaries, and urinary tract are affected. The infection can even cause peritonitis!
In men, the prostate gland, testicles and their appendages, and urinary tract are affected.
- Mycoplasmosis (in men - ureaplasmosis)
Symptoms. It can detect itself 3 days after infection, or maybe even a month later, manifesting itself as itching and discomfort in the genital area, scanty clear discharge, painful urination.
What is dangerous? A frequent complication in women is inflammation of the genital organs, in men - a violation of spermatogenesis.
- Gonorrhea
Symptoms. 3-7 days after infection, women develop yellowish-greenish vaginal discharge, frequent, painful urination, pain in the lower abdomen, and sometimes bloody discharge. However, in most of the fairer sex, the disease goes unnoticed for a long time. Men have pain and burning sensation during urination, yellowish-greenish purulent discharge from the urethra.
What is dangerous? In women, the urethra, vagina, anus, uterus, ovaries, and fallopian tubes are affected. In men - internal genital organs, chronic inflammation of the epididymis, seminal vesicles, prostate develops, which threatens impotence, infertility.
- Syphilis
Symptoms. The incubation period of the disease is 3 to 6 weeks. The first sign is a rounded sore (hard chancre). In women, it lives on the labia or vaginal mucosa (sometimes in the anus, in the mouth, on the lips), in men - on the penis or scrotum. By itself, it is painless, but a week or two after its appearance, the nearest lymph nodes increase.
This is the time to start treatment! This is the first stage of the disease, when it is still reversible.
2-4 months after infection, the second stage develops - a rash “spreads” all over the body, high fever, headache appear, almost all lymph nodes increase.
In some patients, hair falls out on the head, wide condylomas grow on the genitals and in the anus.
What is dangerous? This disease is called slow death: if not fully cured in time, serious problems arise with the musculoskeletal system, irreversible changes occur in the internal organs, the nervous system - the third stage of the disease begins, in which about a quarter of patients die.
Forget about the Internet!
Did you notice that something is wrong? It is better to play it safe and hurry to the doctor, rather than looking on the Internet for symptoms and treatments.
How are STDs diagnosed? First - an examination by a doctor, then - tests and studies. The most modern method of DNA diagnostics: PCR (polymerase chain reaction). For research, scrapings are taken from the urethra, vagina and cervix.
Doctors also use the ELISA method (blood is taken from a vein or a scraping is done and the presence of antibodies to STDs is determined), bacterioscopy (most often it detects gonococci and Trichomonas) and many other diagnostic methods.
STDs are treated with antibacterial drugs, as well as local procedures (washing the urethra in men, sanitation of the vagina in women and other procedures).
At the end of the course of treatment, it is imperative to undergo a control examination - to pass several tests to make sure that there is no infection in the body.
What is important to know
- Is it possible to get infected in a bath or pool?
In fact, the likelihood of catching STDs in everyday life is very low. Microorganisms that cause venereal diseases are unstable in the external environment. In the pool, for example, it is almost impossible to pick up such an infection (unlike fungal or intestinal). Even if an HIV-infected or syphilis patient swims in the water next to you, chlorinated water will quickly kill pathogens.
However, in public toilets, if surfaces are not monitored there, there is a risk of infection with the papillomavirus or herpes virus. But the classic venereal diseases - syphilis, chlamydia, gonorrhea and trichomoniasis - require contact with blood or mucous membranes.
The exception is syphilis: it can be transmitted through saliva if you use the same dishes with the patient and do not wash them well. So, in any case, you should not forget about the rules of hygiene.
Keep in mind: for a short time, microorganisms that cause "bad" infections can survive on warm, damp clothes. Therefore, in the bath or pool (and at home too), do not use someone else's wet towel, washcloth or other personal hygiene items.
- Symptoms of sexual disease appear immediately?
Not always. With good immunity, a disease (for example, chlamydia) can proceed for years without symptoms. The person may not even know they are sick. And the only way to detect such a latent infection is through laboratory tests.
The first signs of infection in women are unusual vaginal discharge. In men, urethritis (inflammation of the urethra). Its symptoms are urinary incontinence and purulent discharge. All other symptoms (rashes, swollen lymph nodes, etc.) appear when the infection has already spread in the body.
- Condom - reliable protection against STDs?
Yes. If it is of good quality, has not expired, is properly sized and used correctly, then the risk of contracting most STDs is reduced to zero.
The exception is external warts and severe herpetic infection.
Incidentally, nonoxynol-9 spermicidal lubricant used on condoms does not protect against STDs, according to a 2001 WHO report. By damaging cell membranes, nonoxynol-9 spares neither spermatozoa, nor infections, nor the mucous membranes of the genital organs. By damaging the mucous membrane of the vagina and cervix, nonoxynol-9 "opens the gate" to infections.
While the condom is not the ideal way to prevent STDs, it is considered the most effective. Therefore, it is necessary to use condoms for all types of sex: vaginal, anal and oral.
In order not to increase the risks, you should buy condoms only in reputable pharmacies. To avoid damaging the condom, do not open the package with a file or fingernails.
It must be remembered: a condom can only be used with special lubricants. Ordinary creams and ointments are not suitable for this.
A common mistake is to use birth control pills, vaginal pills, or spermicidal creams with a condom. Gynecologists warn that these drugs disrupt the microflora of the vagina and provoke the development of candidiasis (thrush). Thus, instead of getting rid of problems, you can acquire them.
If you want to protect yourself as much as possible, it is enough to use a condom correctly and follow personal hygiene measures. A high degree of protection and the almost complete absence of side effects is a definite plus of condoms. However, it should be remembered that the condom can break, in which case you should have emergency prophylaxis on hand.
Emergency drug prophylaxis is also used - a single dose or injection of antibacterial drugs, which can only be prescribed by a dermatovenereologist. The procedure helps to prevent gonorrhea, chlamydia, ureaplasmosis, mycoplasmosis, syphilis and trichomoniasis. But this method should not be used frequently.
But you should not count on various gels, suppositories and vaginal tablets in terms of protection against STDs. These products contain spermicidal substances in insufficient quantities to secure at least 80-90%. In addition, the causative agents of many STDs do not live in seminal fluid, but on the genitals and are insensitive to spermicides.
The same applies to douching after intercourse with special gels or chlorine-containing antiseptics.
Remember!
Sexually transmitted diseases are dangerous, first of all, with complications: infertility, impotence, chronic inflammatory processes, lesions of the nervous system and internal organs. Improper treatment, ignoring symptoms, neglecting preventive measures can adversely affect your health.
What can be done in an emergency?
So, what to do after unprotected intercourse if you have no confidence in the health of your partner?
- Urinate profusely.
- Wash hands and external genitalia with soap.
- Treat the genitals, pubis and thighs with an antiseptic (miramistin, chlorhexidine and others). This technique helps to reduce the risk of STDs by 80-90%. But not 100%. So the best prevention is a condom and common sense.
- If it is not possible to visit a doctor in the next 24 hours, take a “shock” dose of antibiotics.
- Seek medical attention as soon as possible.
It makes sense to see a doctor within 5 days of having unprotected sex. There are emergency drug treatments that can prevent the development of syphilis, gonorrhea, chlamydia, and other sexually transmitted diseases.
But it will not help against HIV and the human papillomavirus (HPV).
Blood for hepatitis, syphilis and HIV is taken 3 months after contact. It makes no sense to be examined before: antibodies to these diseases do not appear in the blood immediately after infection.
Following these precautions will reduce the likelihood of infection and the severity of its possible consequences.
The sexual freedom that modern man is accustomed to using has its own “pitfalls”: according to WHO, at present, every tenth, including children and the elderly, suffer from one or another STD. Every 15 seconds, someone in the world is diagnosed with a sexually transmitted infection. In order to maintain your health and not endanger your partner, timely prevention and treatment are required.
The constant increase in the number of sexually transmitted diseases does not indicate the complexity of prevention, but the irresponsible attitude of most people to their health and their ignorance in this matter. Often, patients are embarrassed to see a doctor when symptoms occur and try to get by with folk remedies. This is fraught with irreversible consequences for their health.
***
The only effective folk remedy for preventing STDs is complete sexual abstinence :).
Plus: it's free. Minus: does not exclude the possibility of infection by domestic means and in case of violence.
Based on materials
List of STDs, how they are transmitted, signs and treatments
STD(explanation: sexually transmitted diseases) - this category includes diseases that are transmitted through sexual contact. They affect not only the genitals, but the entire body, which often leads to quite serious consequences.
According to statistics, about half of Russians are infected or have ever been infected with at least one type of STD. This prevalence is due to the frequent change of partners, as well as the beginning of early sexual relations. Also, the spread of these diseases is facilitated by new contraceptives that have replaced the condom.
Sexually transmitted diseases include diseases caused by various pathogens.
STDs are spread exclusively through sexual contact - vaginal, anal or oral, in this case the gender of the person does not matter. Many STDs are spread through genital contact, even if there is no penetration. Genital herpes, for example, can be transmitted through skin-to-skin contact: only minor damage to the skin's surface is enough to become infected.
There are STDs that can be transmitted to humans in other ways. For example, hepatitis B and HIV can be transmitted through blood transfusions and through the use of needles during injections.
The use of barrier methods of contraception is not always a guarantee of safety. When using this method of protection, it is important to follow the instructions on the packaging.
Symptoms

In medicine, the main signs indicating the presence of STDs are distinguished. Their appearance serves as a reason for contacting a gynecologist or urologist. The specialist will conduct an examination and prescribe further examination.
List of STD symptoms:
- redness and rashes in the intimate area;
- itching in the intimate area;
- enlarged lymph nodes;
- discomfort during intimate relationships;
- painful, frequent urination;
- altered discharge from the genitals;
- pain in the lower abdomen or groin.
There are a lot of venereal infections, and each of them has its own characteristics of manifestation.
Most Common STDs

Each person can become infected with these diseases, regardless of gender, age and social status:
- Chlamydia- an insidious disease that is transmitted exclusively through sexual contact. Most patients in the early stages of the disease have virtually no symptoms. In men, chlamydia is manifested by characteristic symptoms: cutting pain during urination and the act of ejaculation. This is due to inflammation of the urethra and epididymis, which is caused by pathogenic bacteria. In women, signs of infection are less noticeable, and may not appear at all. However, chlamydia is one of the causes leading to inflammatory processes, ectopic pregnancy, and female infertility.
- Trichomoniasis- bacterial infection. At the initial stage, the disease does not manifest itself. The incubation period is about two weeks. Men may experience a characteristic discharge from the penis, as well as a burning sensation in the urethra. Women have a more pronounced manifestation of trichomoniasis. One of the characteristic symptoms is a yellow-green discharge that has an unpleasant odor and cutting pain during sex.
- - a fairly common STD, often found among people whose age is from 15 to 24 years. The infection spreads through all types of intimate relationships. In men, gonorrhea appears 1-2 days after infection. Patients have painful and frequent urination, profuse discharge of pus from the urethra is disturbing. Gonorrhea requires effective and rapid treatment. In the absence of timely therapy, various complications arise. In women, the temperature rises, spotting and pain during sex are observed, the condition of the body as a whole worsens.
- - is a viral disease, which is characterized by a high susceptibility to pathogens. The virus is transmitted during sexual intercourse and during skin-to-skin contact, the causative agent is HSV-2 (decoding - herpes simplex virus type II). About a day after infection, small blisters appear on the genitals, their formation is accompanied by a slight tingling and itching. Over the next few days, the blisters turn into painful sores, swollen lymph nodes, and fever. Rashes are the visible part of the disease. After their disappearance, the virus can remain in the body for many years, and sometimes for life. Lack of timely treatment in pregnant women can lead to various complications, including fetal death.
- Syphilis- an infectious disease, the excitation of which provokes a bacterium called "pale spirochete". You can become infected with this disease through sexual contact of any form. The first symptoms occur within ten days after infection - a hard chancre appears on the perineum or genitals (less often on other parts of the body). Over time, such rashes appear on the fingers and in the oral cavity. There is an increase in lymph nodes, especially in the cervical and inguinal. In medicine, 3 stages of syphilis are distinguished. In the absence of timely treatment, the disease can become severe: ulcers spread throughout the body, including mucous membranes. The patient is concerned about aching bones, inflammatory processes and deterioration in general well-being. In the third stage of the disease, meningitis may occur. Complications of syphilis can lead to the most severe consequences, such as paralysis or death.
- are sexually transmitted viruses. Regardless of gender, the disease manifests itself in the same way - in the form of warts in the anus and perineum. In men, warts can hide in the urethra and behind the foreskin. Human papillomavirus types 16 and 18 are one of the main causes of cervical cancer. An asymptomatic course of the disease is not excluded, in this case, it is possible to find out about the presence of an infection only after diagnosis.
- Ureaplasmosis – a disease that is characterized by a chronic course. Its causative agent is ureaplasma, a unicellular microorganism belonging to the conditionally pathogenic flora. This means that ureaplasma is present in small quantities in a healthy person. The disease begins to progress when microbes begin to multiply rapidly, crowding out healthy microflora. Symptoms appear after 2-3 weeks, patients experience burning during urination, inflammation of the genitourinary system and cloudy discharge from the vagina. Often women are worried about pain in the lower abdomen. If left untreated, the disease becomes chronic and leads to complications: endometritis, colpitis, narrowing of the urethra, cystitis, inflammation of the fallopian tubes, etc. Untimely treatment of ureaplasmosis can lead to premature birth, missed pregnancy and infertility.
- Mycoplasmosis- Caused by opportunistic pathogens. They can be in the body of an absolutely healthy person and provoke many diseases of the genitourinary system. In men, the disease is asymptomatic, in women there is a burning sensation during urination, pain during sexual intercourse and pain in the lower abdomen.
- Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV)- the most dangerous of all sexually transmitted diseases. The disease does not appear immediately, its incubation period lasts from three weeks to three months. Symptoms appear only at the stage of manifestation of the process. Patients complain of chronic weakness, inflammation of the lymph nodes, loss of appetite, headaches. The main characteristic symptom of HIV is tonsillitis (inflammation of the palatine tonsils), which does not go away for a long time. In patients, the body temperature rises to 37.5 ° C, which cannot be normalized with the help of antipyretic drugs. The lack of adequate antiretroviral therapy negatively affects the general condition of the patient. The body is attacked by various bacterial and viral diseases: herpes, candidiasis, pneumonia, tuberculosis. And as a result, AIDS develops.
Diagnostics

There are a lot of pathogens included in the STD group. Medicine offers many diagnostic methods to detect them and prescribe a treatment regimen.
Conventionally, these methods are divided into several groups:
- blood tests;
- STD test;
- microscopic methods;
- crops and cultural methods;
- DNA diagnostics.
After the onset of symptoms indicating the presence of any sexual infection, you should consult a specialist. Male patients should make an appointment with a urologist, and women with a gynecologist. If there are obvious signs of a sexually transmitted disease (rashes on the genitals or chancre), you need to consult a venereologist.
In modern medicine, there are many diagnostic methods, but the exact universal method does not yet exist. When examining for the presence of STDs, you cannot use only one method.
As a rule, a complex of various measures is used to identify the pathogen, so diagnosis often takes a long time.
- The first thing to do in case of symptoms that indicate a sexual infection is to take it to the clinic smear for microflora. This is a procedure that is performed annually during a routine examination by a gynecologist or urologist. In women, a swab is taken from the urethra and vagina, in men - from the urethra.
- One of the simplest methods is bacterial culture. The doctor takes the secret of the genital organs from the patient for analysis. The material is placed in a special nutrient medium, which promotes the reproduction of pathogenic and "correct" bacteria.
- If necessary, in addition to microbiological analysis, linked immunosorbent assay, which allows you to identify active antibodies that help the body fight STDs. For certain diseases that affect the entire body (syphilis, HIV), an additional blood test is performed (Wasserman reaction and HIV determination).
- The most accurate diagnostic method polymerase chain reaction(PCR), which allows to reveal hidden diseases that are characterized by an asymptomatic course.
- The presence of an infection is detected by DNA analysis. As a rule, this method is most effective for suspected diseases that are in the body for a long time in a "sleeping" state.
In addition to being examined by specialized specialists, patients with STDs may need to be seen by other doctors, since some diseases also affect other organs. These infections include:
- herpes, HPV;
- syphilis, etc.
They can affect the skin, joints, affect vision, the circulatory system. Depending on the degree of complications, you need to contact a dermatologist, infectious disease specialist, immunologist, proctologist and other highly specialized specialists.
It is important to remember that only a doctor can make an accurate diagnosis, since many diseases have similar symptoms. Self-medication can only aggravate the development of the disease and lead to serious complications.
Treatment

Treatment of STDs implies an individual approach to each patient. Methods for the treatment of such ailments include the following types of therapy:
- antiviral;
- immunostimulating;
- antibacterial;
- vitamin therapy;
- physiotherapy.
Effective treatment should be aimed not only at the genitals, but also at correcting the state of the body as a whole. Local treatment gives only a short-term result and in most cases does not eliminate the infectious disease by 100%.
A lasting effect can only be achieved with the help of drug therapy. In this case, the patient is prescribed local antibacterial agents (gels, suppositories, ointments and creams) and oral preparations for oral administration. In some cases, invasive treatments such as drips or injections may be indicated.
Treatment is prescribed by a venereologist, it includes:
- a course of antibacterial drugs - penicillin, erythromycin, tetracycline, etc .;
- imidazole drugs;
- sulfa drugs;
- antifungal drugs.
Before taking any medicines, it is necessary to pass special tests for the body's susceptibility to antibiotics.
Properly selected treatment with antiviral drugs and antibiotics lasts 10-12 days. If the disease becomes chronic, the duration of treatment is at least three weeks. In special cases, a second course of drug therapy is prescribed, but the treatment regimen changes somewhat.
Prevention

If an STD occurs, both partners must be treated, otherwise there is a risk of re-infection. It is not so difficult to get infected with such diseases; almost every person who has an intimate relationship is at risk. The main method of prevention is a trusting relationship, the rejection of promiscuity and the use of contraceptives.
In order to avoid a recurrence of the disease, after the course of treatment it is necessary to be observed by a specialist, periodically handing over. The last test, which completely excludes the remainder of the infection in the patient's body, includes provocation. If the body withstands such a test, it means that the person is absolutely healthy.
Modern pharmacology offers a large selection of antibiotics against STDs of various forms of release, but not all of them are effective enough. It is strictly forbidden to self-medicate such diseases; only a specialist should select drugs.
Our expert - gynecologist Marina Vedeleeva.
Dangerous Thirty
The topic is very prosaic - sexually transmitted diseases (STDs). Almost all of us have met them personally at least once in our lives. By the way, there are more than 30 of them: from the deadly HIV infection to the commonplace chlamydia, which, by the way, cannot be called trifling either. Moreover, in terms of prevalence in Russia, it is in second place after the flu.
Of course, most STDs are curable, but not all. For example, it will never be possible to part with genital herpes - treatment only softens the course of the disease and reduces the frequency and severity of relapses. Only those under the age of 25 have a chance to get rid of (HPV) forever. Later, it will not be possible to destroy the virus, the point of treatment is to eliminate tissue changes affected by the virus. By the way, it is believed that the human papillomavirus can cause cancer of the cervix, vagina, vulva and penis. The genital herpes virus also affects sperm, and if a woman becomes infected with it during pregnancy, it can cause severe congenital diseases of the fetus.
Treatment will be successful only if it is started without delay and completed. How to spot the very first danger signals?
An alert has been declared!
There are seven main signs, having discovered which, you should not delay a visit to the doctor.
Itching and burning in the intimate area.
Redness in the genital area and anus, sometimes - sores, vesicles, pimples.
Discharge from the genitals, smell.
Frequent, painful urination.
Enlarged lymph nodes, especially in the groin.
In women - pain in the lower abdomen, in the vagina.
Discomfort during intercourse.
However, for example, syphilis or chlamydia may appear several weeks after infection, and sometimes STDs can generally be hidden for a long time, turning into a chronic form.
Let's get to know each other better
Chlamydia
Symptoms. 1-4 weeks after infection, patients develop purulent discharge, painful urination, as well as pain in the lower abdomen, in the lower back, bleeding between menstruation in women, in men - pain in the scrotum, perineum.
What is dangerous? In women, it can lead to inflammation of the fallopian tubes, cervix, pathologies of pregnancy and childbirth, diseases of the liver, spleen; in men - to inflammation of the epididymis, prostate, bladder, impaired potency. Newborns may develop conjunctivitis, nasopharyngeal lesions, pneumonia.
Trichomoniasis
Symptoms. They can appear on the 4-21st day after infection, sometimes later. Women have abundant foamy discharge of white or yellowish-green color with a pungent odor, causing severe itching and irritation of the genital organs, as well as pain, burning during urination, pain during intercourse. In men, there is a burning sensation during urination, mucopurulent discharge from the urethra. However, this disease is often asymptomatic.
What is dangerous? In women, the cervix and inner layer of the uterus, fallopian tubes, ovaries, and urinary tract are affected. The infection can even cause peritonitis! In men, the prostate gland, testicles and their appendages, and urinary tract are affected.
Mycoplasmosis (in men - ureaplasmosis)
Symptoms. It can detect itself 3 days after infection, or maybe even a month later, manifesting itself as itching and discomfort in the genital area, scanty clear discharge, painful urination.
What is dangerous? A frequent complication of trichomoniasis in women is inflammation of the genital organs, in men - a violation of spermatogenesis.
Gonorrhea
Symptoms. 3-7 days after infection, women develop yellowish-greenish vaginal discharge, frequent, painful urination, pain in the lower abdomen, and sometimes bloody discharge. However, in most of the fairer sex, the disease goes unnoticed for a long time. Men have pain and burning sensation during urination, yellowish-greenish purulent discharge from the urethra.
What is dangerous? In women, the urethra, vagina, anus, uterus, ovaries, and fallopian tubes are affected. In men - internal genital organs, chronic inflammation of the epididymis, seminal vesicles, prostate develops, which threatens impotence, infertility.
Syphilis
Symptoms. The incubation period of the disease is 3 to 6 weeks. The first sign is a rounded sore (hard chancre). In women, it lives on the labia or vaginal mucosa (sometimes in the anus, in the mouth, on the lips), in men, on the penis or scrotum. By itself, it is painless, but a week or two after its appearance, the nearest lymph nodes increase. This is the time to start treatment! This is the first stage of the disease, when it is still reversible. 2–4 months after infection, the second stage develops - a rash “spreads” all over the body, high fever, headache appear, almost all lymph nodes increase. In some patients, hair falls out on the head, wide condylomas grow on the genitals and in the anus.
What is dangerous? This disease is called slow death: if not fully cured in time, serious problems arise with the musculoskeletal system, irreversible changes occur in the internal organs, the nervous system - the third stage of the disease begins, in which about a quarter of patients die.
Forget about the Internet!
Did you notice that something is wrong? It is better to play it safe and hurry to the doctor, rather than looking on the Internet for symptoms and treatments.
How are STDs diagnosed? First - an examination by a doctor, then - tests and studies. The most modern method of DNA diagnostics: PCR (polymerase chain reaction). For research, scrapings are taken from the urethra, vagina and cervix.
Doctors also use the ELISA method (blood is taken from a vein or a scraping is done and the presence of antibodies to STDs is determined), bacterioscopy (most often it detects gonococci and Trichomonas) and many other diagnostic methods.
STDs are treated with antibacterial drugs, as well as local procedures (washing the urethra in men, sanitation of the vagina in women and other procedures). At the end of the course of treatment, it is imperative to undergo a control examination - to pass several tests to make sure that there is no infection in the body.
How to protect yourself?
The classic self-defense against STDs is the condom. Good quality and true to size.
Emergency medical prophylaxis is also used - a single dose or injection of antibacterial drugs, which can only be prescribed by a dermatovenereologist. The procedure helps to prevent gonorrhea, chlamydia, ureaplasmosis, mycoplasmosis, syphilis and trichomoniasis. But this method should not be used frequently.
But as for douching after intercourse with special gels or chlorine-containing antiseptics, most experts believe that this does not reduce the risk of infection.
The world of sexually transmitted infections is very diverse and in some places not well understood. There are infections that do not cause illness in humans at all, but there are also those that are deadly for him.
Hoping for a favorable outcome of chlamydia without treatment is to expose yourself to the risk of severe complications for the sake of a illusory hope of recovery.
Scabies and pubic pediculosis are, of course, not sexually transmitted diseases, but they are transmitted very well through sexual contact. We will not dwell on them in particular, we will only note that these insects have no reason to leave their main habitat. Human skin is home to scabies mites and pubic lice. This is how nature made them. And why should they leave this house?
Considering most of the known STI, we can conclude that trying to sit at home in the hope of "maybe it will blow over" is not worth it. Yes, there is a certain probability that some diseases will go away on their own, but is it worth hoping for this and endangering your health?