Ultrasound of the bladder: how to properly prepare for the study?
Ultrasound of the bladder (MP) is a painless, non-invasive, informative examination method. That is why it is resorted to if any pathology associated with this organ is suspected. Preparation for an ultrasound examination of the bladder is almost the most important component in the examination. Together with the study of the MP, visualization of the kidneys and urinary ducts is mandatory. The MP is, in a sense, a window through which the prostate gland can be visualized.
Bladder
Indications for the study
- Pain in the pelvic area.
- Rare or, conversely, frequent urination.
- Recurrent cystitis in adults.
- Acute infection in children.
- The appearance of blood in the urine.
- Urinary retention.
- Education.
- Suspicion of prostate pathology (applies to men).
- Cancer suspicion.
- Any kidney disease (allows you to make a diagnosis in the complex).
Study preparation
If the patient is not properly prepared, the doctor will not be able to correctly conduct the examination. The bladder is a hollow organ, it is crushed in an unfilled state, and it will be simply impossible to see anything, as well as measure it on an ultrasound scan. Follow the directions of the doctor who directs you to the procedure. A specialist can refer you to an ultrasound of the kidneys, because these two organs are closely related.
Adult training

1.5 hours before the ultrasound of the bladder, you need to drink up to 1 liter of water
The goal of training for both women and men is to fill the MP. To do this, you need to urinate an hour and a half before the ultrasound, and then gradually drink a liter of water (on average, this is 4-5 glasses). If there is an urge to urinate, they do not empty, but wait for the study. Due to the fact that the road to the clinic or hospital where an ultrasound scan is scheduled can take more than an hour, and there is also a queue there, and you will not be accepted quickly, many take water with them and drink it while waiting for the turn to the doctor. Preparation for an ultrasound of the bladder in women and men is fundamentally no different.
Preparation in children
The preparation of children is complicated due to the fact that it is difficult for a child to drink just water, children often refuse to do this. We need to explain to him what it is for. One and a half to two hours before the examination, the child should urinate. Instead of water, you can give him tea or compote, but in no case milk or sparkling water (these drinks cause gas formation, which will make it difficult for the ultrasound doctor to visualize the bladder in the future). How much water to give the child before the ultrasound? The norm of the liquid that the child should drink is 5-10 ml per kilogram of his weight. It is not necessary for newborns to drink. Children under two years old should be allowed to drink at least half a glass (you can use a nipple), from three to seven years old - a glass, from seven to eleven years old and a half, and teenagers full two.
General points
When preparing, it is necessary to maintain a balance, because if you do not drink enough water, you will not be able to fill the bladder, and the doctor will not be able to adequately assess the parameters necessary for the study. If, on the contrary, you drink too much, then the doctor will diagnose a pathology that is not really there (dilation of the renal pelvis or residual urine) or simply do not wait until the study. If you suffer from bloating, then two days before the study, remove milk, cabbage, citrus fruits, nuts, bread and pastries, onions from the diet.
It is necessary to prepare for an ultrasound of the bladder, otherwise the results of the study will be distorted! How much water you drink depends on the success of the ultrasound! Pay due attention to the preparation for the procedure.
How is the research going?
The patient usually lies on his back, however, sometimes the doctor needs to turn him into an inclined position. The patient should be relaxed and breathe calmly. The doctor applies a gel to the lower abdomen and begins the study. After examining the bladder in a full state, the patient should urinate and then the doctor examines the empty bladder. On average, the procedure is quick (takes 15 to 20 minutes). In addition to the bladder itself, the doctor scans the kidneys and ureters. Ultrasound can be both external and internal. An internal ultrasound is done for special indications, so your doctor will inform you about this before the appointment of the study.
Bladder ultrasound
What might be the results
The doctor sees a filled MP as an anechoic formation emerging from the small pelvis. The norm is when the internal contour of the organ is even, and the transverse sections are symmetrical. The wall thickness is individual, depending on the fullness, but it should be the same throughout. The wall thickness in the filled state is about 4 mm. After the examination, the patient needs to urinate. The norm is when there is no residue, if there is residual urine, then its volume should be measured. After examining the bladder, the kidneys and ureters are visualized.
Diseases of the bladder and its structures, detected by ultrasound
Ultrasound shows the following signs that play a role in determining the pathology and making a diagnosis:
- Changes in wall thickness.
- detection of trabecularity.
- Asymmetry.
- The presence of internal cysts.
- Tumor structures in the cavity of the bladder or at its base.
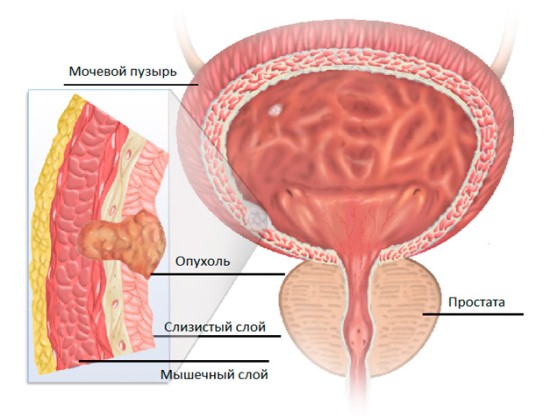
Bladder tumor
A very thick trabecular wall is defined as:
- External obstruction by the posterior urethral valve or in the presence of the urogenital diaphragm in children.
- Neurogenic MP (accompanied by ureterohydronephrosis).

urinary disorder
Local wall thickening is checked especially carefully to rule out cancer.
Causes of local thickening:
Echogenic masses associated with the wall:
- "Soldered" to the mucous stones.
- Cyst "urethrocele".
- Polyp on leg.
- Enlargement of the prostate gland in men.
- Enlargement of the uterus in women.
Mobile echogenic formations in the cavity:
- Stones.
- Foreign bodies.
- Thrombus (blood clot).
- Air.
Increased or overstretched MR shows:
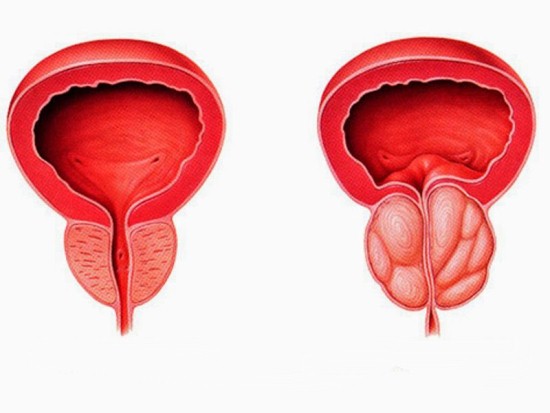
Normal and enlarged prostate
- Strictures or stones of the urethra in men.
- Injury of the urethra in women.
Small MP:
- Cystitis (because of this, the patient cannot hold urine for a long time).
- Damage or fibrosis of the wall (the volume of the bladder decreases).
- Crayfish. Radiation therapy and surgical treatment.
- Rare infiltrating cancer. Such cancer makes the bladder asymmetrical, which can be seen on ultrasound.
Study accessibility
An ultrasound costs from 700 to 900 rubles, depending on the clinic and the city where you live. The price may seem high to many patients, but ultrasound reveals so many diseases that this method is simply indispensable if you want to have a healthy bladder. If an ultrasound of the bladder and kidneys was prescribed to you by the attending physician of the budgetary clinic to which you are attached, then the study will be done free of charge. Today, there is an ultrasound machine in every medical institution. It is more logical to conduct a study in conjunction with ultrasound of the kidneys and urinary tract, because this will allow us to assess the pathology of the excretory system, as well as the prostate gland in men in combination.