Ears spiral computed tomography of the temporal bones. Indications and methods of CT scan of the temporal bones. Where to do a CT scan of the temporal bones in St. Petersburg
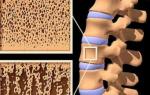
The temporal bone of the skull is a complex paired structure containing many anatomical structures, having an intricate relief of many ducts, mastoid cells, auditory ossicles, the inner ear, and the tympanic membrane.
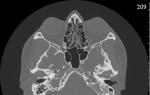
CT anatomy of the temporal bones
Near the pyramid of the temporal bone is the saddle-shaped fossa of the Turkish saddle, where the important endocrine gland, the pituitary gland, is located. The body regulates the state of the endocrine glands. Computed tomography (CT) shows well the structure of the area, allows you to determine the size of the Turkish saddle, identify tumors, calcification, inflammation of the pituitary gland.
The temporal bone is connected to the movable jaw through the temporomandibular joint. Near the area are arteries, nerve fibers. Damage to the segment causes multiple pathologies leading to inflammation of the inner and middle ear (otitis media), impaired swallowing, and inflammatory processes inside the esophagus and stomach.
CT scan of the temporal bones is normal
Computed tomography of the temporal bones normally shows the following anatomical structures:
- Smooth, clear walls;
- Physiological lumen width;
- Sclerotic type of cell structure;
- Normal pneumotization;
- Soft tissue structures of the mouth of the auditory tube;
- Clear visualization of the auditory ossicles;
- Normal pass configuration;
- Clear smooth walls.
CT-signs of bilateral otitis media with a chronic course are often combined with increased sclerotization, a decrease in pneumotization of the cells of the mastoid process. Purulent, inflammatory processes in the area are well visualized on a computed tomogram.
CT of the temporal bones - what shows
X-ray computed tomography is prescribed to examine the bones. Soft tissues are better analyzed by MRI.
CT-signs of pathology of the tympanic cavity:
- Assessment of the condition of the walls;
- Visualization of neural structures;
- Analysis of vascular formations;
- Determination of the anatomy of the mastoid process, pyramids.
The middle ear is located near the meninges, facial nerve, large blood vessels. Computer scanning allows you to clearly identify purulent-inflammatory processes of the middle ear (otitis media).
Computed tomography of the temporal bones clearly tracks tumor, traumatic injuries. Neoplasms of the vestibular and auditory parts of small sizes do not lead to hearing loss.
Computed tomography shows the degree of mineralization (density of calcium salts), otosclerosis of the inner and middle ear. The deposition of sclerotic tissue is observed in chronic processes.
On computed tomograms, tumors are determined - osteomas, fibromas, angiomas. Neoplasms grow slowly, may be accompanied by hemorrhages.
Prolonged suppurative otitis media leads to cancer of the middle ear. The tumor is malignant, has infiltrative growth, is characterized by spread to neighboring areas, is characterized by a tendency to spread to the surrounding anatomical structures, to the lymph nodes.
Pathology leads to severe pain in the head, purulent bloody discharge, concomitant inflammation of the facial nerve. Timely CT allows you to determine the nosology at an early stage, reduce mortality.
Any pathological changes in the temporal bone, pyramid, mastoid process leads to impaired blood supply. High probability of pathology of the microcirculation of the brain due to the proximity of the cerebral arteries. Ingestion of a purulent clot, thrombus, embolus into the vessel leads to blockade of the blood supply, the occurrence of a bleeding area.
Indications for CT of the temporal bones:
- Intra-ear secretions;
- Loss of hearing and vision;
- Traumatic lesions of the temporal bones;
- Pathology of the temporomandibular joint (TMJ);
- Before surgery.
Tomography of the temporal bone is a fast, informative method for diagnosing most types of nosologies.
What is better CT or MRI of the temporal region
The effectiveness of computed and magnetic resonance imaging of the temporal region varies significantly. The difference between CT and MRI is not only in the physical basis of the method. Radiation exposure of tissues in high doses does not allow the use of computed tomography repeatedly for a short period of time.
Magnetic resonance imaging is harmless to human health in the absence of metal objects in the body. Modern innovative tomographs are able to track even the pathology of bone tissue. The price of the equipment is high enough for peripheral medical institutions to purchase MRI scanners.

Jugular glomus tumor on CT scan of the temporal bones
CT with contrast also allows you to study arteries, veins, nerves, other vascular formations, tumors, and measure sizes.
CT of the pyramids of the temporal bones
A thickening in the middle of the temporal bone called the pyramid contains the anatomical structures of the middle and inner ear. The area includes many vessels, nerves. X-ray layer-by-layer scanning of the pyramidal part of the temporal bone reveals tumors, purulent infiltrates, pathological accumulation of cerebrospinal fluid.
Purulent and bacterial inflammatory processes, bleeding into the pyramid are well diagnosed after contrasting. The procedure involves the intravenous administration of a reinforcing drug, followed by the manufacture of layer-by-layer sections. Each tomogram shows the anatomical structures in a section, but with the help of three-dimensional modeling, it is possible to create a spatial representation of the object. The picture allows you to identify the smallest cavities, internal ducts, plan the course of surgery.
CT for otitis media
Bacterial inflammation of the middle ear leads to damage to the mucous membranes, accumulation of pus inside the cells of the mastoid process, the tympanic cavity. Long-term persistence of chronic inflammation leads to the release of pus, the appearance of a perforation in the eardrum. Pathology forms dangerous complications:
- hearing loss;
- Infiltration of the inner ear;
- Spread of pus through the circulatory system;
- Destruction of the walls of the mastoid process;
- Destruction of internal cavities;
- Thrombosis of the sigmoid sinus;
- Development of an abscess;
- epidural hematoma;
- empyema;
- Involvement in the inflammatory process of the auditory ossicles with hearing loss.
The conclusion of computer and magnetic resonance imaging often ends with the diagnosis of mastoiditis. The erroneous interpretation arises from the detection of aseptic fluid inside the mastoid cells that occurs after simple exudative otitis media. Correctly diagnosing mastoiditis is possible only after the detection of an inflammatory lesion of the bony septa.
Computed tomography of the temporal bone of a child
The presence of radiation exposure when using the method of computed tomography (CT) requires a careful attitude to the use of examination in a child. Only in the presence of life-threatening diseases, the lack of effectiveness of the conservative treatment of diseases of the mesotympanum, epitympanum, hypotympanum, according to indications, children are scanned.
Epitympanum - the upper part of the tympanic cavity, consisting of the auditory canal, auricle and tympanic cavity. Inflammatory and purulent processes in the area are well detected after examination by an otolaryngol (ENT doctor). There is no need for computed tomography to diagnose the pathology of the area.
Mesotympanum is the middle part of the tympanic cavity. The region consists of the Eustachian, auditory tube. The area is not available for inspection, so the examination is carried out by radiation methods.
The lower part of the tympanic cavity (hypotympanum) can only be examined with a CT scan. The department contains important anatomical structures - three semicircular canals (lateral, posterior, superior), cochlea, vestibule.
Otosclerosis on CT
Hereditary genetic disease - otosclerosis occurs due to metabolic disorders. The exact cause of the disease could not be established. Morphological changes in pathology are accompanied by the growth of bone tissue with the filling of the cells of the mastoid process. Resorption is due to the activity of bone cells - osteoblasts and osteoclasts. The places of destruction are filled with connective tissue fibers. Sclerosis of the inner ear leads to hearing loss (conductive). In young people, nosology is characterized by the formation of a sclerotic focus near the anterior edge of the vestibule. A novice radiologist does not always detect changes. The process is bilateral, therefore it is taken as an anatomical norm.
Cholesteatoma on CT scans
A tumor-like formation (cholesteatoma) consists of epithelial tissue, connective tissue fibers located in the middle ear. The danger of the disease lies in the sclerosis of the mastoid cells of the pyramid of the temporal bone. ENT doctors believe that there is no rationality for diagnosing cholesteatoma using CT, since part of the tumor is detected during the examination. Three-dimensional modeling after computed tomography reveals a small formation in the auditory canal at an early stage of development.
On CT cholesteatoma appears as a soft tissue mass with accompanying bone erosions.
Tomographic signs of cholesteatoma:
- Location inside the ear canal;
- soft tissue education;
- Displacement of the auditory ossicles;
- Erosive defects in the walls of the epitympanum, lateral semicircular canal.
During scanning, other tumors of the temporal bone - hemangioma, osteoma, neurinoma, glomus formations - may be an additional finding.
Cost of CT scan of the temporal bones
Experts recommend performing tomography of the temporal region after inflammatory processes, skull injuries, hearing loss, suspected tumors. The price of a survey in Moscow varies from 2,500 to 6,000 Russian rubles. A large range is determined by the type of equipment, the qualifications of doctors, the use or absence of contrast.
The cost of the service includes the need for anesthesia (for a child), recording the results on an optical disc, the need to obtain a second opinion. Obtaining several conclusions of radiologists is required for patients with identified inflammatory processes (chronic mastoiditis, otitis media).
Where to do a CT scan of the temporal bone in Moscow and St. Petersburg
Most of the clinics in Moscow and St. Petersburg were brought together by the Unified Consultative Center. We invite readers to choose the best diagnostic center near their place of residence, next to work. Sorting is carried out by dozens of parameters. Our partners have licenses, modern equipment, qualified personnel. Institutions offer not only CT scans of the head, neck and MRI, but also a free preliminary consultation, a second opinion when deciphering tomograms made in other institutions.
There are no alternatives to X-ray computed tomography in diagnosing the pathology of the pyramids, mastoid cells of the temporal bones. Magnetic resonance imaging is used to determine soft tissue pathology. Turning to professionals, you protect yourself not only from unreasonable exposure, but also from unnecessary financial costs.
9-04-2014, 19:26 22 095
The temporal bone of the human skull is a complex bone formation of a paired composition. This bone structure has a complex shape and no less complex internal relief. In addition to the fact that the temporal bones are the bearing parts of the cranium, parts of the hearing aid are attached to them, they protect the vestibular apparatus and the inner ear.
The bone serves as a support for the chewing apparatus - it is articulated with the movable part of the jaw. According to its structure, it consists of three parts, each of which performs its functions and somewhat differs in the structure of the fabric from its neighbors. From the inside, arteries and nerve fibers adjoin the temporal bone. The role of the temporal bone is very great, therefore, its damage invariably leads to damage to the inner part of the head, replete with vital organs.
Any change in the structure or shape of the temporal bone affects the circulatory system that feeds the brain, either on the organs of hearing and vision, or directly on the brain. The same danger is borne by inflammation of the cellular structures of the mastoid bone (one of the constituent parts), neoplasms on the inside of the bone, changes in the external auditory canal.
Computed tomography of the temporal bones is used for such indications:
- Hearing or vision impairment of unknown origin;
- Pain in the middle ear;
- discharge from the ears;
- Traumatic lesions of the temporal part of the head;
- problems with jaw movement;
- Preparation for surgical intervention and control over the postoperative condition.
In long-term treatment, along with computed multislice tomography, MRI of the temporal bones is widely used. It is also preferable to MRI if there is a need for frequent monitoring of the patient's condition.
What does CT and MRI of the temporal bone show
With the help of computer or magnetic resonance imaging, the following are determined:- Otitis and other inflammatory diseases of a chronic and acute nature;
- Traumatic injuries of bone and soft tissues of the temporal region;
- Abscesses and other infectious lesions;
- Tumors of a different nature;
- Otosclerotic and other degenerative phenomena;
And there is very little water and other solutions in the bones, so the MRI image of the temporal bones is less informative than the spiral computed tomography of the temporal bone if the bone base itself is examined. But in the case of diagnosing a disease of surrounding organs, blood vessels, and, especially, neoplasms, then MRI is preferable.
When contrasting the image, neoplasms of a different nature and metastases from other organs are very well localized. A feature of tumors is a well-branched own circulatory microsystem, which differs in structure from the vascular network of surrounding tissues. In the presence of a contrast fluid that is injected into a vein, these vessels are clearly visible, and it becomes possible not only to visually identify the tumor, but also to measure its size.
MRI of the temporal bone is very well used in the diagnosis of diseases of the eye sockets and sinuses. The presence of abscesses and tumors, secretions during inflammatory processes of the middle ear and canal, disturbances in the apparatus for maintaining balance of traumatic or other origin are determined with high accuracy and are well visualized.
The ability to obtain a large number of sections facilitates accurate diagnosis. Often, pain in the temporal bone is caused by completely different reasons, which are very difficult to determine with conventional diagnostic methods. Repeated studies are often required. In this case, CT is not recommended - the use of X-rays, even of such low intensity, in the brain area is very undesirable.
Examination of the pyramids of the temporal bones
A massive thickening on the inside of the temporal bone, called the pyramid, is the location of the inner and middle ear. In addition, it is replete with channels in which important blood vessels and nerve branches are located. Computed tomography of the pyramids of the temporal bones allows you to study their structure throughout the depth, determine the presence of tumors and neurinomas, developmental anomalies, purulent and cerebrospinal fluid. With the help of MRI of the temporal bone, this is difficult to do, due to the complexity of the bone structure.Also, CT is very good at detecting the presence of fresh bleeding, even in the case of internal injuries. Most pyramid studies are done using contrast.
The complexity and great importance of the temporal zone of the head requires a very careful approach to conducting research and deciphering its results. Therefore, the information obtained during the diagnosis should be provided to a doctor who specializes specifically in diseases of this area.
Computed tomography (CT) of the temporal bones is a modern and accurate way to diagnose the condition of the temporal bones, adjacent soft tissues, the auditory canal and the middle ear. CT is performed by means of exposure to x-rays, the data obtained are displayed on the monitor screen in the form of images. As a rule, CT is the final stage of the examination. It is used when other diagnostic methods have not been effective enough.
If you are thinking about where to do a CT scan of the temporal bones, it is worth choosing a clinic where this study is carried out professionally. Stolitsa specialists have been practicing CT for many years, they have hundreds of cases of high-quality diagnostics, which then served as the basis for further effective treatment.
Diagnosis of the state of the temporal bones is very important, since many vessels, nerve fibers adjoin them, and the performance of the masticatory apparatus depends on them. The pyramid of the temporal bones is also a protection for the normal functioning of the vestibular and hearing aids. CT of the temporal bones shows:

- consequences of injuries (hematomas, fluid in the middle ear, purulent discharge);
- the presence, size and rate of development of neoplasms (including malignant ones);
- anatomy of the temporal bone, the structure of the middle ear and the bony walls of the inner ear;
- localization and degree of development of inflammatory processes;
- the presence of metastases;
- the presence of foreign bodies in the ear canal, etc.
CT of the temporal bones with contrast
The state of the bones can be fully assessed without the introduction of a contrast agent. It is used in order to more accurately visualize the structure of soft tissues and blood vessels, to determine the location and size of neoplasms. The substance is administered intravenously, does not harm the health of the patient and leaves the body on its own within the next couple of days. The time of injection of a contrast agent is determined individually: shortly before the procedure or during it, after a number of images have already been taken.
Indications and contraindications for CT of the temporal bones
Computed tomography is an extremely effective method of research, through which many diseases can be detected. Indications for its implementation are:
- pain symptoms in the temples of unknown etiology;
- frequent dizziness;
- discharge from the ear;
- sudden loss of vision or hearing;
- the presence of neoplasms and metastases;
- inflammatory processes;
- infectious diseases;
- mechanical damage to the bone;
- hemorrhage of soft tissues;
- otosclerosis, etc.
Often, CT is used in preparation for an upcoming operation or in order to evaluate the results after it.
Important! The method has no age restrictions, you can do a CT scan of the temporal bones of a child or an elderly person with a referral from the attending physician.
Contraindications for CT of the temporal bones are:
- pregnancy (undesirable at any time);
- allergy to the composition of the contrast agent;
- excessive weight of the patient (the maximum allowable weight of the patient during CT scan on closed-type equipment is 120-130 kg.).
If the patient suffers from mental illness associated with uncontrolled physical activity or fear of enclosed spaces, a sedative may be used.
The possibility of performing CT of the temporal bones in Moscow is not available in every clinic. There are even fewer places where the examination and interpretation of the results will be performed professionally. Turning to the network of clinics "Capital", you can be sure of the high qualification of doctors and the accuracy of the examination. Take a step towards effective treatment right now!
Make an appointment
Preparation for the examination
Special preparation for CT of the temporal bones is not required. If you plan to enter a contrast agent, you must completely refuse to eat no later than 5-6 hours before the procedure. Before the CT scan, the specialist also collects the necessary anamnesis about the patient's health, identifies possible contraindications to the procedure.

The procedure lasts no more than 30 minutes. All metal jewelry, prostheses and devices must be removed, as they can distort the results of the study. The patient lies with his back on the tomograph table, the head is fixed motionless (if necessary, with straps), the table is pushed into the apparatus. The staff leaves the room and observes the procedure from an adjacent room.
Within an hour, the patient can pick up the CT results along with a detailed transcript, often for convenience they are issued on electronic media. Based on these data, the doctor prescribes further treatment.
Advantages and disadvantages of CT of the temporal bones
The advantages, undoubtedly, include the high accuracy and information content of the method. If necessary, on the basis of the obtained images, a 3D model of the study area can be compiled. CT of the temporal bones involves the use of x-rays, but its dose is so small that it does not harm the patient's body. Important positive aspects are also the short duration of the procedure (if contrast is not used, the diagnosis can last no more than 5 minutes) and its affordability (the cost of CT is much lower than that of MRI).
As for the disadvantages, the main risks in performing CT are associated with the possible reaction of the body to the contrast agent. However, this issue is resolved by conducting preliminary tests and analyzes. In addition, it is undesirable to expose yourself to x-rays too often. The exposure dose is small, however, the shortest recommended interval between CT scans should be at least 3 weeks.
CT of the temporal bones is often the final diagnostic method, so it should be treated with special attention. Our clinics use only the most modern equipment, and the study is performed by highly qualified specialists. If you want the diagnostics to be really high-quality, contact the "Capital"!
Make an appointment
CT scan of the temporal bones
CT of the temporal bones is a modern research method. It allows you to achieve a clear visualization of all structures. Due to the fact that the thickness of the layered sections is about 1 mm, it is possible to study in detail the state of the external auditory canal, the pyramids of the temporal bones, the middle and inner ear and to achieve the identification of various disorders. You can count on the visualization of not only bone tissues, but also soft ones, due to which all kinds of inflammatory processes, neoplasms, infectious processes, as well as injuries and their consequences will be detected.
When is the examination scheduled?
Computer is necessary in a large number of cases. This study will provide information for establishing different diagnoses, namely:
- chronic or acute inflammatory diseases, for example otitis media, mastoiditis;
- trauma;
- infectious diseases;
- hearing impairment and the work of the vestibular apparatus;
- neoplasms and foreign bodies in the ear;
- abscesses and tumors;
- congenital malformations of the ear;
- vascular disease in the temporal region;
- degenerative and necrotic processes;
- and much more.
CT scan of the temporal bones: what does it show?
The result of the work of a radiologist is clear pictures that show the structure of all structures of the ear and temporal bones. CT of the pyramid of the temporal bone also allows you to examine the adjacent soft tissues, so you can get the necessary information and make the correct diagnosis. If we are talking about images that were obtained using a contrast agent during the study, it will also be possible to examine the meninges, temporal cerebral lobes, the walls of the orbits and much more.
With the help of tomography, it will also be possible to plan an operative intervention, and based on its results - to evaluate the effectiveness. After the patient receives the images and the report from the radiologist, he should go to his doctor.
Preparation for the procedure
The procedure involves a minimum of preparation. When pathologies are detected in the area of the temporal bones, CT scan is performed, as a rule, without a contrast agent. In this case, it will be enough to visit the diagnostic center and remove all metal-containing elements from yourself.
If the use of contrast is prescribed, you need to pass special tests. This will eliminate the possibility of allergic reactions to the drug. Before CT, in this case, you can not eat for 6 hours, this will minimize the side effects from the contrast.
How is a CT of the temporal bones performed?
 If you don’t know how it goes, what this study shows and what you need to be prepared for, you should know that tomography does not cause any discomfort. This study does not require surgical intervention in the body. All you need to do is change into medical clothes, remove all jewelry and put accessories and gadgets aside. After that, the patient lies on the movable table of the apparatus. Parts of the body that will not be examined are covered with a special apron to reflect excess radiation. Then the table is pushed into the ring of the tomograph and the study begins, which lasts 5-20 minutes, depending on whether contrast was used (with it, the examination is longer).
If you don’t know how it goes, what this study shows and what you need to be prepared for, you should know that tomography does not cause any discomfort. This study does not require surgical intervention in the body. All you need to do is change into medical clothes, remove all jewelry and put accessories and gadgets aside. After that, the patient lies on the movable table of the apparatus. Parts of the body that will not be examined are covered with a special apron to reflect excess radiation. Then the table is pushed into the ring of the tomograph and the study begins, which lasts 5-20 minutes, depending on whether contrast was used (with it, the examination is longer).
When is contrast needed?
A contrast agent is used quite rarely, this is justified by the fact that CT of the temporal bones shows a more than complete picture. Doctors usually decide on the introduction of contrast before computed tomography in the event that there is a suspicion of oncology.
The contrast agent accumulates in the area of neoplasms and other tissues where pathological processes take place. This substance allows you to examine their structure in detail, as well as assess the state of the vessels through which the contrast will pass, which provides additional information about the patient's condition.
Contraindications for CT of the temporal bones
CT shows pathologies of the temporal bones, the procedure is safe and does not cause discomfort, but there are still a number of limitations to its appointment. As a rule, tomography is not prescribed for children under 14 years of age, since the effect of X-ray radiation on a growing organism is much stronger than on an adult. In some cases, the attending physician decides to prescribe a CT even for children under 14 years of age, since the benefits of the procedure will outweigh the possible risks.
Pregnancy is an absolute contraindication, since there is a risk of fetal developmental disorders due to X-ray exposure. Nursing mothers should not breastfeed their baby for about 2 days after the CT scan. The examination becomes impossible even if the patient suffers from hyperkinesis (involuntary movements) of the head. In this case, it is impossible to get clear pictures, and the study will not bring results.
The use of contrast has even more contraindications, for example, diseases of the endocrine system, renal failure and severe patient conditions, which include shock or coma. In these cases, a sharp deterioration in well-being is possible, since the contrast gives a large load, and there is a threat to the patient's life.
How often can a CT of the temporal bones be done?
It is not recommended to study the anatomy of the pyramid of the temporal bone on CT more than once a year. If we are talking about emergency situations, the procedure can be prescribed up to 3 times a year with an interval of at least 4 weeks. It will also be necessary to evaluate the radiation exposure from other studies so that the diagnosis does not lead to a deterioration in well-being and diseases.
CT interpretation
The decoding is done by a radiologist, who, based on the results of a CT scan, will draw up a conclusion. It takes up to half an hour, after which the results are handed over to the patient. In difficult cases, other specialists, for example, a neuropathologist, may be involved in the decoding process.
Modern high-quality computed tomography of the temporal lobes of bone tissue is carried out in all medical centers equipped with innovative equipment. This procedure is carried out both for children and adults and allows you to accurately determine the various pathological changes in this part of the skull or congenital, as well as acquired structural anomalies. Modern CT of the temporal bones for a child and an adult does not require special training, and there is also a minimum number of contraindications.
The essence of CT of the temporal part of the skull
In humans, the temporal bones perform a large number of different rather important functions. It is to them that the arteries, numerous nerve fibers, as well as the movable part of the upper jaw are attached. In fact, this is a natural protection of the inner ear, as well as a complex system of the vestibular apparatus, which is important for the body.
Important! Various kinds of damage to the temporal bones are very dangerous for humans, injuries and diseases are fraught with various serious consequences. It can be a hearing impairment, vision problems, as well as a malfunction in the brain.
For the reason that there are quite a lot of diseases in this area, and in order to make their accurate diagnosis, one cannot do without such a procedure as CT scan of the temporal bone. The CT procedure is completely painless and takes a minimum amount of time. As a rule, this is 5-10 minutes if no contrast is used, and approximately 30 minutes if this substance was used. During the examination, a person is exposed to a minimum amount of x-ray exposure. Despite the relative safety, the procedure is often not recommended. At a minimum, at least 3 weeks must pass from one to the other procedure.
Indications for examination
Children and adults are referred for CT by an ENT or maxillofacial plastic surgeon. Among the main indications of this procedure are:
- Deterioration of hearing and vision for no apparent reason.
- Dizziness and various painful sensations in the temples.
- Pain and unpleasant discharge from the ear cavity.
- Acute and chronic otitis.
- Penetration into the ear of foreign objects.
- Injuries of the temporal parts.
- Jaw mobility disorders.
- Tumor suspicion.
- The presence of cysts.
- The styloid process is examined.
- Congenital destruction of the temporal bones.
An indication is also the preoperative preparation of a person who is planned to install an electrode and then monitor him after implantation of the implant. It is impossible to do without CT when examining the pyramids - a special part of the temporal bone. It is here that the middle and inner ear are located, as well as nerve fibers and vessels with veins that are important for humans.
Important! A feature of this procedure is the use of a special contrast during the study.
What does CT show?
In the process of performing a CT scan of the temporal region, a doctor who specializes in images analyzes not only this part, but also examines the general appearance of the bones, the position and functioning of the inner and middle ear, pyramids, the heart-shaped process in the ear, as well as the main auditory canal. Based on the obtained images, the doctor can diagnose the following pathologies, that is, he answers the request:
- Abscesses;
- Acute and chronic otitis;
- The development of various infections;
- Cracks in the bones and fractures;
- The presence of tumor formations;
- Cartilage and soft tissue injuries;
- Hemorrhages.
Tomography is able to show such indicators as the general structure of the pyramids, the development of tumors and neuromas, anomalies in the structure and the causes of adverse discharge from the ears. If internal injuries were received as a result of an injury, then the procedure makes it possible to identify foci and sources of bleeding. The tomography procedure takes an average of 30 minutes, and an hour is spent on decoding.

In order to increase the information content of CT of the temporal bones, iodine-based contrast agents are used.
Preparation for tomography
During the procedure, the patient lies on a special moving table. In the process of work, he slowly moves to the main capsule, where the process of obtaining images is carried out. It is worth being prepared for the fact that the rotation of the tomograph is performed around the head with little noise. X-ray radiation is directed strictly to the temporal lobes. In some cases, you can ask the patient to turn his head a little and hold his breath. To get the most accurate shots, be sure to remain still.
Important! When examining the temporal parts of the skull, a study with contrast is often performed. This is an ideal opportunity to get an analysis of soft tissues, to identify various tumors, as well as infectious and inflammatory processes.
It is mandatory to examine the pyramids of the temporal bone elements during MRI. Answering the question of how the check is done, it can be noted that contrast is also used here. The substance used contains iodine and is administered intravenously approximately 30 minutes before the examination. In some cases, the agent is administered directly during an already performed tomography. When conducting research through the introduction of this substance, you need to be prepared for the fact that it is quite heavy.
Contrast causes severe allergic reactions and, in milder cases, can cause nausea and dizziness. With a significant increase and a serious increase in side effects, you should immediately inform your doctor about it. It is not difficult to do this, since a two-way connection is established between the room with the tomograph and the doctor's office.
Speaking about the need for preparation, it can be noted that it is quite simple. If no contrast is injected, no action is taken at all. If contrast is needed, you need to follow the meals, the last of which should be taken at least 6 hours before the event. As for drinking, the last drink should be consumed approximately 2 hours before. At least a day before, you need to completely eliminate smoking and alcohol.
These preparations are necessary for the reason that during the process of contrast administration, as few side effects as possible occurred. This is an ideal opportunity to avoid itching, nausea, dizziness, and there will also be no negative impact on the vascular system. As a preparation, a rule is noted for removing all metal objects from the body. The doctor must be aware of all implanted metal products and implants. The pictures will then turn out to be clear, the decoding is very fast, the description is handed out in just an hour.
Contraindications for use
Even if there is no contraindication to the use of a contrast agent, there are undesirable moments that are a contraindication to the procedure itself. An unconditional contraindication to conducting a CT scan of the temporal bones is pregnancy and hyperkinesis of the head. Patients who are overweight are absolutely not allowed to be examined on a tomograph, as there will be a risk that their anatomy will damage the mechanical properties of the apparatus. Most of the devices are able to withstand a person's weight of 120 kg. Women who experience quite painful PMS should also refrain from computerized research.
If the tomography of the temples is performed on young children, there may be some difficulty in ensuring immobility. For this reason, babies are put into a light state of drug-induced sleep. This is a procedure that is completely harmless to the health of the child, which ensures the complete immobility of the baby. Pictures and conclusions are issued very quickly.
The procedure for examining the temporal part of the skull for adults and children is not carried out if they have such pathological conditions as:
- Acute and chronic renal failure.
- Disorders in the work of the cardiac and endocrine system.
- Allergy to contrast, which contains iodine. It is not difficult to recognize such a reaction, if it is, then a person has a negative reaction to seafood.
Of particular note is the procedure for women who are breastfeeding babies. If a woman has undergone such an examination, it is shown to refrain from feeding for two days after it. This time will be quite enough for the complete removal of the substance from the body.
Summing up
The temporal region of the skull during normal functioning performs quite a lot of important functions for a person. If it is damaged, there is a risk of problems with vision, hearing and other functions. If the cost seems high, you should immediately correlate it with the guaranteed benefits.