Abnormal growth of the chest bone in boys. Chest deformities. At what stage can you start physical therapy?
If the chest protrudes, the condition may be the result of hereditary or acquired defects in the bone and cartilage system.
Physiologically, this condition can be provoked by a hypersthenic constitution. In people with broad bones, the sternum protrudes slightly forward. It can be mistaken for a pathological change, but it returns to normal when a person loses a little weight.
Why does the sternum protrude?
With Poland syndrome in children, other stigmas of disembryogenesis are observed:
- underdevelopment of the subclavian artery;
- testicular hypoplasia;
- leukemia;
- paralysis of the facial and optic nerves.
Poland's symptom causes pronounced cosmetic defects. If they are not treated early, compression of the lungs and heart occurs.
Zhen's syndrome is characterized by progressive breast dystrophy and intrauterine growth disorder of the bone structure. As the pathology progresses, it is inherited according to an autosomal recessive principle and is associated with chromosomal abnormalities.
How does a protruding bone appear on the chest?
In newborns, a bone on the chest is observed in the presence of a congenital anomaly of the osteoarticular system of the following type:
- funnel-shaped;
- keeled deformity.
The cause of the pathology is genetic abnormalities that lead to disruption of the formation and development of the bone and cartilage systems. The use of orthoses helps support the chest wall in the correct position and, in young children, promotes the normal development of the chest cavity. However, these devices are only effective when the disease is detected in the early stages.
If the bone in the middle of the sternum (keel) protrudes without a pronounced displacement of the ribs, the pathology can be corrected with the help of physical therapy. Some doctors recommend that patients in this situation constantly press on the protrusion. This procedure is enough to return the curved sternum to its normal position.
A barrel-shaped chest in a child and an adult occurs due to increased airiness of the lungs and expansion of the intercostal spaces against this background.
When barrel deformation appears:
- congenital anomalies of the skeletal system;
- excessive growth of cartilage tissue (hyperostosis);
- displacement of the heart (ectopia);
- congestive changes in the pleural and pericardial sac.
Diseases such as rickets, bone tuberculosis, syphilis also provoke breast expansion. However, it takes some time for the lungs to become more airy.
A barrel-shaped hump in men also forms with the following diseases:
- cerebral paralysis;
- inflammation of the lungs and pleura;
- syringomyelia;
- scoliosis (lateral curvature of the spinal column).
Thus, the barrel-shaped bulge is a consequence of the pathology of the osteoarticular system.
The convex sternum resembles a hump at the front of the upper torso. During an external examination of the patient, one can note not only protrusion of the sternum, but also forward displacement of several ribs. 
A bulge (hump) is more characteristic of an adult. An experienced smoker often experiences chronic changes in the lung tissue against the background of constant inflammation. Because of this, the alveolar acini swell, which leads to expansion of the chest cavity.
Convex (chicken) breasts in a child may be due to. Pathology in the initial stages can be treated with conservative methods. Simply applying pressure to the keel over a period of several months can often return the sternum to its original position.
When the anteroposterior and transverse dimensions of the chest cavity lengthen with an acute angle of the sternum, correction of the defects may be necessary surgically. For these purposes, replacement of bone defects with external or internal plates is used.
If a man has a barrel-shaped chest, the pathology can be eliminated surgically. With this type of disease, doctors suggest correcting the sternum using plastic surgery.
The decision on the method of treating the pathology must be made by the doctor. You won't be able to fix it on your own.
What is emphysematous breast
Emphysematous breasts are different from barrel chests. Doctors clearly understand the difference between these concepts.
Emphysematous chest cavity most often develops with an acquired disease - emphysema. It appears against the background of chronic changes in lung tissue and leads to expansion of the pulmonary alveoli. As a result, the respiratory excursion decreases.
When emphysematous breasts appear:
- chronic pulmonary diseases;
- underdevelopment of surfactant;
- pathology of lung tissue.
Emphysematous breasts appear with respiratory diseases.
Emphysematous breasts often occur in men. It is a consequence of smoking, inhalation of toxic substances, and weakness of the alveolar acini.
For this type of pathology, surgical operations are not performed, since they do not bring a therapeutic effect. With chronic changes in lung tissue, its volume increases on both sides of the lungs.
Depending on the cause of the pathology, specialists decide what to do.
is a congenital or acquired change in the shape of the chest. It manifests itself as a change in the shape of the musculoskeletal frame of the upper body. Negatively affects the condition of the chest and spine organs, can provoke curvature of the spinal column, complications of the heart and lungs. Diagnosed based on the results of a physical examination and data from hardware studies (radiography, MRI, CT, etc.). For severe deformities, surgical treatment is indicated.
General information
Chest deformity is a congenital or acquired change in the shape of the chest. The term “chest” refers to the musculoskeletal frame of the upper body that protects the internal organs. Deformation of the chest inevitably affects the heart, lungs and other organs located in the chest cavity, causing disruption of their normal functioning.
Causes
All chest deformities are divided into two groups: dysplastic (congenital) and acquired. Congenital deformities are less common than acquired ones.
- Acquired deformities develop as a result of various diseases (chronic lung diseases, bone tuberculosis, rickets and scoliosis), injuries and burns of the chest area.
- Congenital deformities are caused by underdevelopment or abnormal development of the spine, ribs, sternum, shoulder blades and chest muscles. The most severe deformities occur when the development of bone structures is impaired.
Types of deformations
Depending on the location, disturbances in the shape of the anterior, posterior and lateral walls of the chest are distinguished. The severity of the deformation can vary: from an almost imperceptible cosmetic defect to a gross pathology that causes disruption of the heart and lungs. With congenital deformities, as a rule, the shape of the anterior surface of the chest changes. Violation of the shape is accompanied by underdevelopment of the sternum and muscles, absence or underdevelopment of the ribs.
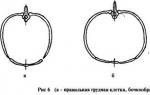
Funnel chest deformity
Abnormal breast shape caused by retraction of the sternum, anterior ribs and costal cartilages. Pectus excavatum is the most common malformation of the sternum. It is assumed that funnel-shaped deformity occurs due to a genetically determined change in the normal structure of cartilage and connective tissue. Children with pectus excavatum often have multiple malformations, and family history reveals cases of similar pathology in close relatives.
Retraction of the sternum with this malformation leads to a decrease in the volume of the chest cavity. A pronounced violation of the shape of the breast causes curvature of the spine, displacement of the heart, disruption of the heart and lungs, and changes in arterial and venous pressure.
Subsequently, the deformation becomes fixed. The depth of the funnel gradually increases, reaching 7-8 cm. The child develops scoliosis and thoracic kyphosis. A decrease in respiratory excursions of the chest by 3-4 times compared with the age norm is revealed. Disorders of the cardiovascular and respiratory systems are increasing.
In order to diagnose changes in the heart and lungs caused by chest deformation, the patient undergoes a whole range of examinations: chest X-ray, echocardiography, ECG, etc.
Treatment
Conservative therapy for this congenital chest deformity is ineffective. For degrees II and III deformity, surgical reconstruction of the chest is indicated to create normal conditions for the functioning of the heart and lungs. Operations are carried out when the child reaches the age of 6-7 years. Traumatologists manage to achieve the desired result only in 40-50% of patients.
In recent years, the two-magnetic plate method has been used to treat this malformation. One plate is implanted behind the sternum, the second is installed externally on a special corset. The outer magnet pulls the inner plate anteriorly, gradually eliminating the deformation of the patient's chest.
Pileated chest deformity (chicken breast)
The pathology is caused by excessive growth of costal cartilage. Usually the cartilage of the V-VII ribs grows. The patient's sternum protrudes forward, giving the chest a characteristic keel shape. A keeled chest is accompanied by an increase in the anteroposterior size of the chest.
As the child grows, the irregularity in shape becomes more pronounced and a significant cosmetic defect occurs. Internal organs and spine suffer slightly. The heart takes on the shape of a drop (a hanging heart). Patients complain of shortness of breath, fatigue, and palpitations during physical activity.
The operation is indicated only for dysfunction of internal organs and is not performed on children under 5 years of age.
Flat chest
It is caused by uneven development of the chest with a decrease in its anteroposterior size. Does not cause changes in the organs of the chest cavity.
Acquired deformities arise as a result of previous diseases (rickets, bone tuberculosis, lung diseases, etc.) As a rule, the posterior and lateral surfaces of the chest are involved in the process.
Emphysematous chest
Develops in chronic pulmonary emphysema. The anteroposterior size of the chest increases, the patient's chest becomes barrel-shaped. A decrease in respiratory excursions is due to lung disease.
Paralytic chest
Characterized by a decrease in the anteroposterior and lateral size of the chest. The intercostal spaces are widened, the shoulder blades lag behind the back, and the collarbones are clearly visible. There is an asymmetrical retraction of the sub- and supraclavicular fossa and intercostal spaces, asynchronous movement of the shoulder blades during breathing. The pathology is caused by chronic diseases of the pleura and lungs.
Scaphoid chest
Occurs in patients with syringomyelia. It is characterized by a scaphoid depression in the middle and upper parts of the sternum.
Kyphoscoliotic chest
It develops as a result of a pathological process in the spine, accompanied by a pronounced change in its shape, which is confirmed by x-rays and CT scans of the spine. May occur with spinal tuberculosis and some other diseases. Severe kyphoscoliotic deformity causes disruption of the heart and lungs. Difficult to treat.
Instructions
Conservative pectus excavatum deformity is possible only on the deformity. During this period, you can try to delay the development of the disease with the help of special gymnastics and certain sports (volleyball, basketball, swimming, rowing). At the second and third stages of deformation, surgical treatment is prescribed. The operation is performed on patients aged 3 to 14 years. The child must be carefully examined to ensure that there are no other diseases that could cause the deformity.
Pectus carinatum or “chicken breast” is an increase in the size of the chest. In this case, the sternum protrudes significantly forward, and is attached to it at an acute angle. Treatment for such chest deformity is as follows: physiotherapy, swimming and physical therapy are prescribed. If the patient’s condition still worsens or changes appear in the cardiovascular system, then plastic surgery (thoracoplasty) may be necessary.
No amount of physical exercise can correct chest deformation; you can only slow it down or even stop it. In addition, all this is possible only at the first stage of the disease. Bodybuilding, in addition to slowing down the process of deformation, also allows you to hide it due to muscle mass. When correcting the deformity, special attention is given to exercises on the chest: push-ups, bench press, half-belt, lying dumbbell flyes and exercises that affect its expansion indirectly: pull-ups, rows of the lower and upper blocks. The stronger the chest muscles are, the better. That is why the most effective exercises are: bench press on inclined boards and on a horizontal surface.
note
Keeled breast deformity. A keeled chest of only pronounced degrees can somehow affect health; a slightly pronounced keeled chest does not pose a threat to health and usually does not require correction. Physical exercise is unlikely to change the keeled shape of the chest.
Helpful advice
Keeled breast (chicken breast, pectus carinatum) is a congenital deformity of the chest caused by anterior protrusion of the sternum and the ribs articulated with it. Pileated chest deformity is a disease that manifests itself at the birth of a child. Among the causes of disruption of intrauterine development of the fetus, there may be various factors that adversely affect the mother’s body during pregnancy.
Sources:
- curvature of the chest
Improving your own body is an art known to people since ancient times, and today many men pay a lot of attention to their body, keeping themselves in shape and developing all muscle groups. Most often, both beginners and experienced athletes try to develop the pectoral muscles, which allows them to expand the chest. In order to expand your chest, you can perform physical exercises that are accessible to everyone, training the chest muscles and allowing you to form a harmonious figure.
Instructions
The bench press has a lot of benefits and possibilities - if you change the angle of the bench press, performing it on an incline bench instead of a flat one, you can develop additional muscle and build muscle mass.
As you press, spread your arms with the dumbbells as wide as possible to give them the greatest load.
Movements while lying down will allow you to expand the volume of the chest - raise your arms with dumbbells from behind your head and bring them together on your chest, and then return them back, straightening your arms behind your head.
When choosing dumbbells or a bench press barbell, make sure the weight is right for you - otherwise you risk injury and sprains. On the last lift, to increase the efficiency of the work done, hold the dumbbells at the bottom.
Raise the dumbbells as you exhale, and as you lower the dumbbells down, take a powerful inhale.
Another time-tested method of training the pectoral muscles is classic push-ups, as well as swimming underwater while holding your breath.
A wide male chest is a symbol of reliability, strength and protection. But wide breasts are not only beautiful. A wide chest means additional lung capacity, which means the ability to perform heavy physical work for a long time. In order to make your chest wide, you need to perform special breathing exercises. They can be aimed at working different muscle groups, but the combination of physical activity with proper breathing leads to the desired result - an increase in chest volume.

You will need
- - vertical support;
- - light dumbbell;
- - rod;
- - gymnastic bench
Instructions
Perform Rader rows to increase chest volume. Stand facing a vertical support at arm's length. Place your feet shoulder-width apart. Grab a support with your hands just above your head. Take a deep breath and pull your arms towards you and down, without letting go of the support. While holding your breath, tighten your chest and neck muscles. Make sure your abdominal muscles remain relaxed. Hold the load for 4-6 seconds, then relax. A sign of a correctly performed exercise will be a feeling of temporary discomfort in the chest and difficulty breathing.
Lie down on a gymnastic bench, bend your knees and place it on the bench. Raise a light dumbbell above your chest with your arms outstretched. Inhale and slowly lower the weight with straight arms behind your head. Don't lower the weight too low. At the lowest point, take one more extra breath and straighten your chest as much as possible. Slowly return to the starting position. Do the next repetition after a pause. Do not perform breathing pullovers with heavy weights; the main thing in this exercise is execution.
Set the barbell to a weight with which you can squat 15-17 times. Now stand under the barbell and squat. After each squat, take 3-5 deep breaths. Breathe deeply, trying to expand your chest to the maximum. Most likely, you can do 12-14 squats without any problems, and then the work will get more difficult. But you need to do 20 squats. Make sure your heels don't leave the floor. Every week, increase the weight of the barbell by 2.5 - 10 kg, depending on your level of training.
Come close to the barbell lying on the floor. Your shins should touch the bar. Moving your pelvis back, squat and bend over. Grab the bar with an overhand grip. Straighten your legs, straightening your body and moving your pelvis forward. Lift the bar off the floor and straighten up. Then return the bar to the floor and take 3-5 deep breaths. Repeat. Inhale and exhale after each repetition. Do 20 reps with a weight that you would normally lift 16-17 times.
note
Breathing training is strictly contraindicated for beginners and those who have had a break from training for more than a month. Before starting exercises using this method, consult a doctor, preferably at a sports and physical education clinic. These exercises are also contraindicated for people with problems with the eyes, cardiovascular system and musculoskeletal disorders.
Chest deformity can be of two types: congenital funnel-shaped and keeled. Most often, these deformities occur in children who are characterized by asthenic development. In this case, the disease progresses as the child’s body gradually grows and causes a noticeable cosmetic defect in the appearance of the anterior chest wall. As a rule, deformation of the chest can be combined with curvature of the spine.

The chest helps protect internal organs from external influences. Deformation of the chest can affect the further development of the quality of organ function. What can cause chest deformation and how to fix it later in the article.
The disease can be caused by the following reasons:
- Congenital deformity of the chest or resulting from spinal injury:
- Atrophied tissues;
- Changes associated with age;
- Spinal fractures;
- Displacement of intervertebral discs;
- Tumor;
- Osteoporosis.
Congenital
Appears as a result of improper skeletal development or poor genetics during pregnancy. Among the causes of chest deformation in children, Marfan syndrome is common. Improper development of costal cartilages or breasts becomes one of the causes of the disease. In most cases, the deformity becomes noticeable immediately after birth. Sometimes it appears after a few years.
During the development of the embryo, a defect may occur in the connection of the left and right buds, which will cause the appearance of a gap in the thoracic region. In very rare cases, a gap in the entire chest may appear together with a heart defect.
Acquired
It appears as a result of diseases affecting the chest or spine:
- Scoliosis;
- Rib tumor;
- Tuberculosis;
- Osteomyelitis in the ribs;
- Rickets;
- Purulent inflammation of tissue in the chest;
- Severe burns or injuries;
- Thoracoplasty.
The most common are funnel-shaped and protruding (keeled) deformities.
Types of disease:

With this type, urgent surgery is necessary.
- Arched chest or Currarino-Silverman syndrome. A rare type of disease.
- Poland syndrome. It affects the ribs, spine, muscles and neighboring organs. Usually there is a displacement of the spine.
The disease has different locations:
- Front;
- Side;
- Behind.
Pathology is classified according to its complexity:
- Stage I - the heart is not displaced. The depth of deformation is up to 2 cm.
- Stage II - the heart is displaced no more than 3 cm. The depth of deformation is up to 4 cm.
- Stage III - the heart is displaced more than 3 cm. Depth of deformation is more than 4 cm.
- Congenital pathology
 They don't happen that often. Its further development and consequences may depend on the degree of the disease. If you take timely measures, you can avoid serious consequences and completely get rid of deformation. Basically, this disease occurs due to genetics. During the formation of the embryo, cartilage appears in the thoracic and dorsal regions. Poor genetics can cause them to not fully develop. The chest is disproportionate in size. You should immediately go to the doctor and start treatment on time. In the future, the deformation of the chest can progress and cause problems with the heart, lungs, compression or displacement. Possible curvature of the spine, inhibition of development, increased fatigue, and frequent occurrence of colds.
They don't happen that often. Its further development and consequences may depend on the degree of the disease. If you take timely measures, you can avoid serious consequences and completely get rid of deformation. Basically, this disease occurs due to genetics. During the formation of the embryo, cartilage appears in the thoracic and dorsal regions. Poor genetics can cause them to not fully develop. The chest is disproportionate in size. You should immediately go to the doctor and start treatment on time. In the future, the deformation of the chest can progress and cause problems with the heart, lungs, compression or displacement. Possible curvature of the spine, inhibition of development, increased fatigue, and frequent occurrence of colds.
- Acquired
It is usually caused by illness or external damage in the form of trauma, which may affect the side or back of the chest. An advanced disease can create a reduction in the chest, scoliosis, and a decrease in the space between the ribs.
This disease is treated depending on the stage of development and consequences in disrupting the functioning of the lungs and heart. Drug treatment only eliminates the symptoms of the disease and does not cure the disease itself. At the first stage, therapeutic methods can be applied. These include massage, wearing a corset, physical therapy, and physiotherapy. They will not correct bone deformities, but they will help keep the body in good shape.
 Funnel-shaped pathology can be eliminated using a vacuum bell. This method creates a vacuum over the deformation site, which pulls the funnel back. In cases where the method does not help, sternochondroplasty is used. During the procedure, a plate is inserted after making local incisions in the chest area and cutting the cartilage. This is an effective method, but after the intervention there will be scars.
Funnel-shaped pathology can be eliminated using a vacuum bell. This method creates a vacuum over the deformation site, which pulls the funnel back. In cases where the method does not help, sternochondroplasty is used. During the procedure, a plate is inserted after making local incisions in the chest area and cutting the cartilage. This is an effective method, but after the intervention there will be scars.
At stages 2 and 3 of the disease, only surgery can help. In the past, the operation was often performed using the Ravich method. He showed good results without complications, but could cause many injuries. In the present tense, the Nuss method is used.
The operation for chest deformation proceeds as follows:
3 cm wide incisions are made on both sides of the chest. An introducer is inserted into the incision. It is carried into the subcutaneous space behind the muscles. In the thoracic space it is moved behind the sternum in front of the pericardium. Along this path, a steel plate is inserted inside. The plate is fixed using clamps on the ribs. This helps align the chest to normal. Upon completion of the operation, the patient takes strong painkillers for a week.
Among the retainers, there are those that are removed after 3 years of use, and there are also implants intended for lifelong use.
Chest deformity is a serious disease requiring immediate action. If you consult a doctor in a timely manner, you can avoid serious complications and further development of the disease.
A little more about the chest deformation in the video:
They are reading now.
Chest deformity in a child is a characteristic change in the shape of the chest, which can be either congenital or acquired. If parents notice that their baby’s posture is different from normal, it is necessary to take a number of important measures, otherwise the curvature of the sternum can cause a host of other defects and disruption of the normal functioning of organs such as the heart and lungs. In addition, as children grow up, they will begin to develop various complexes about their appearance, which is why they will develop psychological and social problems, represented by isolation and distance from their peers.
Is there an effective solution for this situation and how to avoid a disastrous outcome in the future? Fortunately, today you can find a number of high-tech corrective methods that will be an effective means of combating deformation. But before we move on to discussing good solutions, we should carefully study the types and causes of such problems as chest deformation.
Why do children suffer from chest deformities?
It is known that deformation of the chest can be both congenital and acquired. Problems of the first type are often explained by genetic changes, when some malfunctions occur during the intrauterine formation of the embryo. There are cases that a defect is inherited, but the probability of such a course of events is 20-60%. Among hereditary types of deformation, Marfan pathology should be highlighted, which is a congenital syndrome that damages the musculoskeletal system and disrupts the functioning of the nervous and cardiovascular systems. It also affects the condition of the eyes.
In most cases, the presence of curvatures of the chest is noticed only as the baby grows up, namely during the period of active growth, which occurs from 5 to 8 years, as well as at the stages of puberty at the age of 11-15 years. Often changes are caused by uneven growth of the costal cartilages and sternum or various pathologies of the diaphragm, which lead to underdevelopment of cartilage and connective tissue.
In addition, the deformation of the HA can be explained suffering from various complex diseases, including:
- skeletal damage (tuberculosis, scoliosis, rickets);
- tumor type diseases (osteoma, chondroma, mediastinal tumor);
- systematic diseases;
- emphysema;
And others.
Types of chest deformities
A significant part of such changes is represented by a funnel-shaped or keeled deformity of the chest. The features of each type will be discussed below. In rare cases, children are exposed to the following types of curvature:

Funnel-shaped (sunken) chest deformity
 Funnel chest deformity occurs in 90% of cases of congenital deformities. If we compare males with females, then in representatives of the first group the problem occurs approximately 3 times more often than in the other. It looks like a sunken chest in a child, which is why it is popularly called “shoemaker’s chest.” The anomaly often occurs in representatives of different generations, so experts attribute it to genetic changes.
Funnel chest deformity occurs in 90% of cases of congenital deformities. If we compare males with females, then in representatives of the first group the problem occurs approximately 3 times more often than in the other. It looks like a sunken chest in a child, which is why it is popularly called “shoemaker’s chest.” The anomaly often occurs in representatives of different generations, so experts attribute it to genetic changes.
Patients suffering from pectus excavatum have reduced volume of the sternum, which soon causes curvature of the spine, represented by scoliosis or kyphosis, problems with blood pressure and poor functioning of important organs. Also, the child is often exposed to colds, the quality of the immune system deteriorates, and autonomic disorders manifest themselves in a particularly strong way. Clear signs of deformation are noticed at puberty, when the deformation becomes very noticeable when inhaling. To eliminate the pathology, surgical correction must be used. Funnel-shaped deformations are presented in three degrees of severity:

Carinatum deformity
Pileated chest deformity presented in the form of a kind of keel, which appears in the process of excessive growth of costal cartilages. People call it “chicken breast”, which is explained by its characteristic shape. In the early stages of development, the curvature may be barely noticeable, but with maturity it turns into a clearly visible defect. The child begins to suffer from heart pain, rapid fatigue during physical activity, shortness of breath and rapid heartbeat.
You can notice the presence of any defects during a routine examination by a pediatrician, who should determine the presence of changes in the size, shape and symmetry of the chest. When listening to the heart and lungs, wheezing and murmurs will be noticeable. After the specialist notices any oddities, he should refer the baby for further in-depth examination to an orthopedic traumatologist or thoracic surgeon.
To determine the parameters of the chest and various changes in its structure, they use thoracometry. In addition, diagnostic work may include characteristic displacement of the heart and disruption of the lungs. However, at the stage of planning surgical treatment, the child is given a CT scan. The procedure allows you to determine the exact degree of compression, displacement of the heart and compression of the lungs. The asymmetry of deformation is also clarified here.
 There are a number of conservative methods for treating chest deformity in a child. Considered one of the most effective physiotherapy, which includes a series of physical exercises, swimming or comprehensive prevention of sternum curvature. Of course, this method will not be able to completely correct bone defects, but the functioning of the cardiovascular system will be improved. Also, after complex measures, good air exchange in the lungs and an increase in body tone are noticed. For this purpose, many doctors recommend the use of children's orthoses and appropriate compress-based systems.
There are a number of conservative methods for treating chest deformity in a child. Considered one of the most effective physiotherapy, which includes a series of physical exercises, swimming or comprehensive prevention of sternum curvature. Of course, this method will not be able to completely correct bone defects, but the functioning of the cardiovascular system will be improved. Also, after complex measures, good air exchange in the lungs and an increase in body tone are noticed. For this purpose, many doctors recommend the use of children's orthoses and appropriate compress-based systems.
The characteristic vacuum suction cup has good results - vacuum bell method. The structure is installed over the deformity, which allows you to pull the funnel outward and make the elements of the chest more mobile. But you should not expect high effectiveness from the use of such treatment.
Surgery
As for grade 2 and 3 deformities, they cannot be treated conservatively. To improve the normal functioning of the body surgical methods will have to be used. In most cases, sternum realignment surgery is performed between the ages of 12 and 15 years.
Several decades ago, surgery involved the use of the Ravitch method during open operations. Despite excellent effectiveness and the absence of serious complications, such methods were considered very traumatic. Currently, thoracoscopic intervention using the Nuss method is in great demand.
 The essence of the operation is represented by the following points: 2 incisions with a diameter of 2-3 centimeters are made on both sides of the sternum. The pericardium is passed through one of them, resulting in a special channel through which a steel or titanium plate is inserted. After completion of the action, it is fixed by suturing it to the ribs or muscles using clamps.
The essence of the operation is represented by the following points: 2 incisions with a diameter of 2-3 centimeters are made on both sides of the sternum. The pericardium is passed through one of them, resulting in a special channel through which a steel or titanium plate is inserted. After completion of the action, it is fixed by suturing it to the ribs or muscles using clamps.
Eventually, the chest regains its normal shape and becomes natural. After the operation, the patient must be given powerful painkillers for one week. It is important to note that some retainers are removed after 3 years, while others are intended to last a lifetime.
If the patient suffers from carinatum deformity, the main solution is to remove the overgrown cartilage, so the operation is carried out in one stage. As for chest clefts, in this case, surgical operations should be done as quickly as possible. For this reason, even children under one year of age are subject to intervention.
The procedure involves partially cutting the sternum and suturing it in the midline. It is important to understand that in young children the bones remain very elastic and flexible, so they quickly “grow together.” In the period from one to three years, the sternum is also excised, and the missing elements are filled with special autografts. To make the fixation as reliable as possible, doctors install titanium plates.
Surgical chest wall reconstruction has a positive prognosis for quality of life. According to statistics, in 95% of cases the patient’s complete recovery is observed. However, sometimes it is necessary to do repeated operations.
Means and methods for preventing deformation in a child
 There are many recommendations that will help avoid the development of deformity and protect the child from such a dangerous pathology.
There are many recommendations that will help avoid the development of deformity and protect the child from such a dangerous pathology.
First thing, you should regularly take your baby for examination to a therapist and carry out comprehensive prevention of any chronic respiratory diseases. It is also important to protect the baby from injuries and burns in the sternum area.
From an early age, you need to accustom your baby to regular physical exercise and different sports, especially swimming. This will strengthen your abs, spinal muscles and maintain muscle tone in your back. In addition, sports will prevent the development of childhood rheumatism.
An important element of healthy chest development is proper and balanced nutrition.
Currently, in official medicine there are no exact factors that can lead to the appearance of congenital deformity of the funnel-shaped type, so there are no effective methods for preventing the anomaly yet.