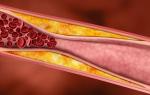
Which spiral is the best for women. What types of intrauterine devices are there? Contraindications to installing a contraceptive
Sooner or later, every woman has to decide the issue of contraception. It is important that contraception is reliable and as safe as possible. The most effective methods of protection against unwanted pregnancy are considered to be hormonal pills and intrauterine systems. Which is better, the IUD or oral contraceptives? This is the age-old dilemma that ladies face. To understand which protection option to choose from the two most reliable, you need to understand all the pros and cons of the methods.

A gynecologist will help you choose a remedy on an individual basis.
Oral contraceptives (OCs) contain female hormones. They are responsible for the occurrence/non-occurrence of pregnancy. Hormone-containing pills can slow down ovulation. This eliminates the possibility of fertilization.
Contraceptive drugs have an effect on the uterine mucus. It thickens. Because of this, the movement of sperm is significantly hampered: they cannot reach the goal and die without fertilizing the egg. Even if sperm managed to penetrate the fallopian tube, pregnancy still will not occur. Under the influence of hormonal drugs, the lining of the uterus becomes thin. This makes consolidation of the embryo impossible.
There are several types of oral contraceptives. The principle of their “work” is slightly different. But the main thing is that the “target audience” is different. Tablets are divided into:
- combined;
- progestational.
Combined ones contain two types of hormones: estrogen and progestin. Preparations of this type are micro-, low- and high-dose. Tablets with microhormone content are optimal for protecting young nulliparous girls. However, they may not be suitable. Then low-dose drugs are prescribed. This type of COC can be called universal: women who have given birth can also take them. Drugs with a high dose of hormones can only be taken after a doctor’s prescription. They are designed to correct hormonal imbalances.
Progestogen-type drugs are also called “mini-pills”. These drugs contain one hormone – progestin. Tablets are prescribed if there are contraindications to taking combined (estrogen-containing) drugs. “Mini-pills” also provide protection to nursing women: they do not affect lactation and do not harm the baby.
Pros OK
Oral contraceptives have many advantages, thanks to which they have gained such enormous popularity. The advantages of such funds include:

Another important plus: when taking OCs, ectopic pregnancy cannot develop. The principle of action of the drugs excludes implantation in principle.
Disadvantages of tablets
OKs work well and have many advantages, but they also have disadvantages. Otherwise, the question of choosing between a spiral and pills would not be so pressing. What are the disadvantages of OK? The disadvantages include:
- Features of reception. Oral contraceptives should be taken at approximately the same time every day. If the schedule is disrupted at least once, the likelihood of conception increases.
- Contraindications. Hormonal pills have a number of contraindications. They should not be taken if you have liver problems, kidney pathologies, heart disease, or high blood pressure. If a woman smokes a lot, then she will have to look for another method of contraception. Combination drugs should not be used during lactation, although this fact is balanced by the fact that nursing mothers can take “mini-pills”. Naturally, if they are suitable.
- Side effects. The pills can cause a number of unpleasant symptoms. The beginning of use is almost always accompanied by spotting in the middle of the cycle. OCs can cause headaches, apathy, and decreased libido. Many drugs increase appetite and retain fluid, which can lead to weight gain if you don’t watch your eating habits.
The disadvantages include the fact that OCs lose a large percentage of their effectiveness if a woman takes antibiotics at the same time. Not everyone knows about this, which leads to unwanted pregnancy.
The principle of operation of the uterine device

When solving the age-old question “IUD or birth control pills?”, it is important to remember that IUDs are recommended only for women who have given birth. The system can thin the endometrium, which increases the risk of miscarriages in nulliparous women in the future. If complications arise, the woman may be left without offspring.
How does the spiral work? It prevents egg implantation. The foreign body leads to thickening of the uterine tissue, which makes the implantation of the fertilized egg impossible.
Modern copper coils are focused not on an abortifacient effect, but on a spermicidal one. They contain hormones that thicken cervical fluid and suppress sperm activity. The presence of such substances increases the contraceptive effect of the IUD.
The IUD is not inferior in effectiveness to birth control pills, but, like drugs, the system does not protect against sexually transmitted infections. Such contraceptive methods are relevant if you have a permanent partner: only as a way to prevent unwanted pregnancy.
Benefits of the IUD
The IUD is a popular method of contraception. Women choose it because of its numerous benefits. The advantages of the IUD include:
- High efficiency. Installation of an intrauterine system eliminates conception by 95–97%.
- Long lasting. Contraception will allow you to forget about the worries associated with an unwanted pregnancy for three to five years.
- Cost-effective and convenient. IUDs, unlike pills, do not need to be purchased regularly or follow any schedule. In fact, after installation you can forget about the presence of the system.
- Action without conventions. The spiral does not interact with medications, that is, a high level of protection is maintained regardless of the circumstances.
- Does not affect reproductive function in the future. If no complications arise after installation of the IUD, reproductive function resumes immediately after removal of the system. True, the body often needs time to recover.
The IUD can be considered as a postpartum method of contraception. It does not affect lactation, so it is suitable for nursing mothers. The contraceptive system can be installed six weeks after delivery, provided that the birth was not accompanied by complications. Only a gynecologist can determine the possibility of installation.
Disadvantages of intrauterine contraception
All contraceptive methods have their drawbacks. The Navy is no exception. It must be remembered that this method does not exclude the occurrence of infectious diseases. There are other disadvantages:

The spiral is inserted only in a medical facility. The procedure must be carried out by a specialist, but even this is not always a guarantee that the introduction of the spiral will not lead to complications. Among the possible complications, the greatest danger is inflammatory processes and incessant bleeding. After the procedure, severe pain may occur, and cycle disorders are often recorded. The appearance of pathological signs serves as a reason to remove the foreign body. The spiral cannot be installed in the presence of diseases of the pelvic organs, benign tumors, or discharge of unknown origin.
What's better?
When choosing a contraceptive method, it is important for a woman to know which one is the safest, most effective, and most economical. Only a gynecologist can find out which is better; IUDs or birth control pills have their pros/cons for each specific case. The doctor selects the method of protection individually. When choosing a contraceptive method, the following are taken into account:
- health status;
- presence of contraindications;
- age;
- presence/absence of pregnancy history.
It should be remembered that nulliparous women are extremely rarely given the IUD. Doctors dissuade patients from such an undertaking, arguing the possibility of infertility as a result of uterine deformation. Therefore, the choice for women who have not yet experienced the happiness of motherhood is obvious - oral contraceptives. They should not be taken without prior consultation with a gynecologist. The doctor will select the best option for tablets, taking into account the characteristics of the female body. You should consult your doctor both when changing pills and when giving them up.
The spiral is often chosen because of its ease of use. This method is especially relevant for active women who may simply forget to take pills. If a couple has a child and they want to conceive the next one no sooner than in three years, then the IUD is the best protection option. The IUD comes to the rescue when it is impossible to find pills: for example, the body reacts to hormonal drugs with persistent side symptoms. It is undesirable to take OCs if you are prone to gastrointestinal diseases: during the adaptation period, they can provoke stomach pain and cause vomiting, and this can lead to intestinal diseases or their exacerbation.
When to choose other methods of protection
Oral contraceptives and intrauterine systems are relevant only with regular sexual activity. If sex occurs with the same partner (subject to trust), then these methods can solve the main problem - to protect against “strays”. But with promiscuous sex life, there is another issue that needs to be resolved: protection from infections. The best solution in this case is barrier methods of protection (diaphragms, condoms). If sexual contacts occur regularly, but with different partners, a woman can choose to protect against pregnancy with the help of an OC or IUD, but insist on using a condom at each contact.
If a woman has serious health problems and a possible pregnancy poses a risk to her life, then irreversible methods of contraception are recommended - sterilization. The procedure involves artificially creating obstruction of the tubes, which leads to the impossibility of conception. The operation is carried out according to medical indications. If desired, only women of older reproductive age (after 35) who have fulfilled their maternal mission are enrolled in the procedure.
Protection from unwanted pregnancy helps to preserve women's health for a long time, because abortions cause irreparable harm to the body and undermine psychological balance. Finding the optimal contraceptive option requires an individual approach, but among the variety of methods, there is sure to be one that suits you.
Anna Mironova
Reading time: 9 minutes
A A
Is it worth or not to install a spiral? This question is asked by many women who choose a method of protection against unwanted pregnancy. An intrauterine device is a device (usually made of plastic with gold, copper or silver) that serves as a fertilization blocker and (if fusion does occur) as a barrier to the entry of an egg into the uterine cavity or its attachment to the walls of the uterus.
What types of intrauterine device are offered today? , what is better to choose, and what might the installation entail?
Types of intrauterine devices today
Of all the known contraceptives, the spiral is today one of the three most effective and popular. There are more than 50 types of spirals.
They are conventionally divided into 4 generations of this device:
- Made from inert materials
An option that is no longer relevant in our time. The main disadvantage is the risk of the device falling out of the uterus and an extremely low degree of protection.
- Coils containing copper
This component “fights” sperm that has entered the uterine cavity. Copper creates an acidic environment, and due to inflammation of the uterine walls, the level of leukocytes increases. Installation period is 2-3 years.
- Spirals with silver
Installation period – up to 5 years. Very high level of protection.
- Spirals with hormones
The leg of the device is in the shape of a “T”, and it contains hormones. Action: a certain amount of hormones are released into the uterine cavity every day, as a result of which the process of release/maturation of the egg is suppressed. And due to the increase in the viscosity of mucus from the cervical canal, the movement of sperm slows down or stops. Installation period is 5-7 years.
The shapes of the intrauterine device (IUD) are an umbrella, a direct spiral, a loop or a ring, the letter T. The latter is the most popular.
The most popular types of IUDs today
- IUD Mirena
Features: T-shape with levonorgestrel hormone in the shaft. The drug is “thrown out” into the uterus at a dose of 24 mcg/day. The most expensive and effective spiral. Price – 7000-10000 rub. Installation period is 5 years. The IUD helps treat endometriosis or uterine fibroids (plus), but also leads to the formation of follicular ovarian cysts.
- IUD Multiload
Features: oval shape with spikes-protrusions to reduce the risk of falling out. Made from plastic with copper wire. Cost – 2000-3000 rubles. Prevents fertilization (sperm die due to the inflammatory reaction caused by copper) and implantation of the embryo (when it appears) in the uterus. It is considered an abortifacient method of contraception (as, indeed, any other IUD). Use is permitted for women who have given birth. Side effects: increased duration and pain of menstruation, pain in the lower abdomen, etc. The contraceptive effect can be reduced when taking antidepressants.

- Navy Nova T Cu
Features: shape – “T”, material – plastic with copper (+ silver tip, barium sulfate, PE and iron oxide), installation period – up to 5 years, average price – about 2000 rubles. For easy removal of the spiral, the tip has a thread with 2 tails. The action of the IUD: neutralizes the ability of sperm to fertilize an egg. Disadvantages: does not exclude the possibility of an ectopic pregnancy; there are known cases of uterine perforation during installation of the IUD; it causes heavy and painful periods.
- Navy T-Copper Cu 380 A
Features: shape – “T”, installation period – up to 6 years, material – flexible polyethylene with copper, barium sulfate, non-hormonal device, German manufacturer. Action: suppression of sperm activity, prevention of fertilization. Recommended for women who have given birth. Special instructions: heating of fragments of the spiral (and, accordingly, their negative impact on surrounding tissues) is possible during thermal procedures.
- Navy T de Oro 375 Gold
Features: contains 99/000 gold, Spanish manufacturer, price – about 10,000 rubles, installation period – up to 5 years. Action: protection against pregnancy, reducing the risk of uterine inflammation. The shape of the IUD is a horseshoe, T or U. The most common side effects are increased intensity and duration of menstruation.
The pros and cons of intrauterine devices
The advantages of the IUD include the following:
- A long period of validity - up to 5-6 years, during which you can (as the manufacturers say) not worry about other methods of contraception and accidental pregnancy.
- The therapeutic effect of some types of IUDs (bactericidal effect of silver ions, hormonal components).
- Saving on contraceptives. Buying an IUD is cheaper for 5 years than constantly spending money on other means of contraception.
- The absence of side effects that occur after taking hormonal pills - obesity, depression, frequent headaches, etc.
- The ability to continue breastfeeding. The spiral will not affect the composition of the milk, unlike tablets.
- Restoring the ability to conceive from 1 month after removal of the IUD.

Arguments against the use of the IUD - disadvantages of the IUD
- No one gives a 100% guarantee of protection against pregnancy (maximum 98%). As for ectopic pregnancy, the IUD increases its risk by 4 times.
- No IUD guarantees the absence of side effects. In the best case – pain and increase in the duration of menstruation, abdominal pain, discharge (bloody) in the middle of the cycle, etc. In the worst case – rejection of the device or serious health consequences.
- Risk of spontaneous removal of the IUD from the uterus. Typically after lifting weights. This is usually accompanied by cramping abdominal pain and fever (if there is an infection).
- The IUD is prohibited if at least one item from the list of contraindications is present.
- When using an IUD, regular monitoring of its availability is required. More precisely, its threads, the absence of which indicates a shift in the spiral, its loss or rejection.
- One of the most significant disadvantages is the risk of prematurity in the future due to depletion of the endometrium in the uterus.
- Experts advise terminating a pregnancy that occurs while using an IUD. Preservation of the fetus depends on the location of the IUD itself in the uterus. It is worth noting that when pregnancy occurs, the IUD is removed in any case, and the risk of miscarriage sharply increases.
- The IUD does not protect against sexually transmitted diseases and the penetration of various types of infections into the body. Moreover, it promotes their development, because the body of the uterus remains slightly open when using the IUD.
- When inserting an IUD, there is a risk (0.1% of cases) that the doctor will puncture the uterus.
- The mechanism of action of the spiral is abortifacient. That is, it is equivalent to an abortion.
- Any pathology of the pelvic organs.
- Diseases of the pelvic and reproductive organs.
- Tumors of the cervix or the uterus itself, fibroids, polyps.
- Pregnancy and suspicion of it.
- Cervical erosion.
- Infection of the internal/external genitalia at any stage.
- Defects/underdevelopment of the uterus.
- Tumors of the genital organs (already confirmed or if their presence is suspected).
- Uterine bleeding of unknown origin.
- Allergy to copper (for IUDs containing copper).
- Adolescence.

Relative contraindications:
- Ectopic pregnancy or suspicion of it.
- Diseases of the cardiovascular system.
- Poor blood clotting.
- Endometriosis (whether past or present).
- No history of pregnancy. That is, for nulliparous women, the IUD is not prohibited, but is categorically not recommended.
- Menstrual irregularities.
- Little uterus.
- Venereal diseases.
- Scars on the uterus.
- The risk of catching a sexually transmitted disease. That is, several partners, a partner with diseases, promiscuity, etc.
- Long-term treatment with anticoagulants or anti-inflammatory drugs, which continues at the time of installation of the spiral.
- It is not uncommon for a spiral to grow into the uterus. Sometimes women simply forget about it, and as a result they have to cut out the spiral along with the uterus.
Doctors' opinions about the IUD - what experts say
After installation of the IUD
- Not a 100% contraceptive method, the benefits of which are outweighed by side effects and the risk of serious consequences. Definitely not recommended for young nulliparous girls. The risk of infection and ectopic infection increases significantly. Among the advantages of the spiral: you can safely engage in sports and sex, obesity is not a threat, the “antennae” does not even bother your partner, and in some cases there is even a therapeutic effect. True, sometimes it is crossed out by consequences.
- There have been many studies and observations regarding the IUD. Still, there are more positive aspects. Of course, no one is immune from the consequences, everyone is individual, but for the most part, spirals today are quite safe means. Another question is that they do not protect against infections and diseases, and if there is a risk of developing cancer, their use is strictly prohibited. It is also worth mentioning the use of medications in combination with the use of hormonal IUDs. For example, regular aspirin significantly reduces (by 2 times!) the main effect of the IUD (contraception). Therefore, when treating and taking medications, it makes sense to use additional contraceptives (condoms, for example).
- Whatever you say, regardless of the elasticity of the IUD, it is a foreign body. And accordingly, the body will always react to the introduction of a foreign body according to its characteristics. One has increased pain during menstruation, the second has abdominal pain, the third has problems with bowel movements, etc. If the side effects are severe, or they do not go away after 3-4 months, then it is better to abandon the IUD.
- The use of an IUD is definitely contraindicated for nulliparous women. Especially in the age of chlamydia. The spiral can easily provoke an inflammatory process, regardless of the presence of silver and gold ions. The decision to use an IUD must be made strictly individually! Together with a doctor and taking into account ALL nuances of health. The spiral is a remedy for a woman who has given birth, who has only one stable and healthy partner, good health in the female part and the absence of such body features as allergies to metals and foreign bodies.
- In fact, making a decision about an IUD - to have it or not to have it - must be done carefully. It’s clear that this is convenient - once you install it, you don’t have to worry about anything for several years. But there are 1 – consequences, 2 – a wide list of contraindications, 3 – a lot of side effects, 4 – problems with bearing a fetus after using the IUD, etc. And one more point: if the work involves lifting heavy objects, you should absolutely not mess with the IUD. It would be good if the IUD turns out to be the ideal solution (in any case, it is better than an abortion!), but you should still carefully weigh all the possible problems and advantages.
Possible consequences of intrauterine devices
According to statistics, most refusals from the IUD in our country are for religious reasons. After all, the IUD is actually an abortifacient method, because most often the fertilized egg is expelled at the approaches to the uterine wall. Others refuse the IUD because of fear (“an unpleasant and slightly painful installation procedure), because of side effects and because of possible consequences.
Is it really worth worrying about the consequences? What can the use of an IUD lead to?
First of all, it is worth noting that complications of various types when using the IUD are associated with an illiterate approach to decision-making, both by the doctor and the woman: due to underestimation of risks, due to negligence when using the IUD (non-compliance with recommendations), due to low qualification of the doctor who installs the spiral, etc.

So, the most common complications and consequences when using an IUD:
- Infection/inflammation of the pelvic organs (PID) – up to 65% of cases.
- Rejection of the IUD by the uterus (expulsion) – up to 16% of cases.
- Spiral ingrowth.
- Very heavy bleeding.
- Severe pain syndrome.
- Miscarriage (if pregnancy occurs and the IUD is removed).
- Ectopic pregnancy.
- Depletion of the endometrium and, as a result, a decrease in the ability to bear a fetus.
Possible complications from using copper-containing IUDs:
- Long and heavy menstruation - more than 8 days and 2 times stronger. In most cases, they can be normal, but they can also be a consequence of an ectopic pregnancy, an interrupted normal pregnancy, or perforation of the uterus, so don’t be lazy about going to the doctor again.
- Cramping pain in the lower abdomen. Similarly (see point above) - it’s better to play it safe and get checked by a doctor.
Possible complications from using an IUD containing hormones:
- The most common complication is amenorrhea. That is, the absence of menstruation. If the culprit of amenorrhea is not an ectopic pregnancy, but an IUD, then the reason is reversible atrophy of the uterine epithelium.
- A disrupted menstrual cycle, the appearance of spotting in the middle of the cycle, etc. If such symptoms are observed for more than 3 months, a gynecological pathology should be excluded.
- Symptoms of the action of gestagens. That is, acne, migraines, breast tenderness, “radiculitis” pain, vomiting, decreased libido, depression, etc. If symptoms persist for 3 months, gestagen intolerance can be suspected.
Possible consequences of violating the IUD installation technique.
- Perforation of the uterus. Most often observed in nulliparous girls. In the most difficult cases, the uterus has to be removed.
- Cervical rupture.
- Bleeding.
- Vasovagal reaction
Possible complications after removal of the IUD.
- Inflammatory processes in the pelvic organs.
- Purulent process in the appendages.
- Ectopic pregnancies.
- Chronic pelvic pain syndrome.
- Infertility.
Content
Pregnancy and the birth of a baby are an important and significant event in the life of every woman, but it must be planned and desired. For those girls who are not yet ready to become mothers or who already have children, the use of intrauterine devices (IUDs) is best as a contraceptive. When used correctly, their effectiveness reaches 98 percent. What types of intrauterine devices are there and how do they work? How much does such a tool cost and what is the cost of installing it? Many women ask these questions.
What is an intrauterine device and how does it work?
An IUD is a special small device for effectively preventing pregnancy, which a gynecologist, using a guide, inserts into the uterine cavity through the vagina. This device is popular in modern medicine due to a number of advantages:
- affordable price;
- after removal of the product, the ability to bear children is quickly restored;
- allowed for use during breastfeeding;
- high effectiveness of the drug (pregnancy occurs in only 2% of cases);
- hormonal balance is not disturbed;
- long (from 3 to 10 years) period of use;
- easy to install and remove;
- does not cause discomfort and is not felt during sexual intercourse;
- there is no need to take oral contraception.
Depending on the type of intrauterine device, the principle of its operation is as follows:
- Copper and other metals in IUDs have a detrimental effect on sperm.
- Promotes the secretion of viscous mucus, which interferes with the movement of sperm and fertilization of the egg.
- Hormone-containing IUDs suppress ovulation.
- If fertilization of the egg has occurred, then VSM increases the contractile activity of the uterus, and the egg dies.
Classification by composition
There is no one universal VSM suitable for all girls. Depending on the physiological state of the patient and the structural features of the uterus, the gynecologist selects the optimal type of intrauterine devices. There are more than 50 types of contraceptive devices on the market today. Their creation and improvement took place in stages, so all types of IUDs are divided into 4 generations: inert, copper, silver and gold, hormone-containing. Let's look at each of them in more detail.
Inert

An outdated version of intrauterine devices (invented about a century ago), it belongs to the first generation. Inert IUDs are low-effective and have a high risk of dislodging or falling out, which is why their use is prohibited in many countries. Representatives of this group are:
- Lips plastic loop made in the shape of the letter S.
- Steel Mauch ring with two scrolls.
- Double helix Saf-T-Coil.
- Dalkon's shield.
This second generation of vaginal devices is a small T-shaped or semi-oval device, the rod of which is wrapped in copper wire. The product is easy to install and remove. Due to the presence of copper, an acidic environment is created in the uterine cavity, which significantly slows down the activity of sperm. Copper intrauterine contraceptives are installed for a period of 3-5 years. The most popular models are:
- Multiload;
- Nova T;
- Juno Bio;
- Para Grand.
With silver
Any metal tends to oxidize and deteriorate, so in order to extend the life of the copper IUD, manufacturers began to use silver in its rod. At the same time, the spermatostatic effect is doubled, and silver ions, which have antibacterial and disinfectant effects, have a beneficial effect on the woman’s body. Intrauterine contraceptives containing pure silver or with copper are allowed to be inserted into the uterine cavity for 5-7 years.
From gold

As an alternative to silver and copper products, an improved gold version was developed. The main advantages of the gold IUD are absolute biological compatibility with the female body, the absence of allergic reactions, and the resistance of gold to damage by corrosion. Products of this type have anti-inflammatory properties and effectively protect against unwanted pregnancy. Golden spirals are installed for a long period - from 5 to 10 years. Women's ability to bear children, after their removal, remains normal.
The fourth generation of intrauterine devices includes products containing hormones. According to doctors, this is the best means of contraception. This new generation IUD has the shape of the letter T, in the stem of which there is a hormonal drug (levonogrestrel, progesterone), which is evenly released in small doses into the uterine cavity. This contraception has no contraindications, since the hormone does not enter the blood, but has only a local effect: it relieves inflammation, slows down ovulation, and prevents the fertilization of the egg. You can wear an IUD for 5-7 years.
Shapes of contraceptive devices
It is impossible to say which IUD is better. Depending on the anatomical features of the uterus and the personal preferences of each woman, the form of the contraceptive product is individually selected. Before choosing the ideal contraceptive and deciding to use it, you should consult a gynecologist. Let's look at the main forms of intrauterine devices, how they look in the photo and their distinctive features.

- T-shaped
The most popular type of intrauterine device among women. They are easy to use and easy to install and remove. The T-shaped IUD has the form of a rod from which two flexible shoulders extend. With the help of hangers, the product is fixed in the uterine cavity. A special thread is attached to the end of the rod, allowing the doctor, if necessary, to easily remove the spiral from the uterus.
- Ring shaped
The ring-shaped intrauterine device is a modern method of contraception that is recommended for patients who have had an abortion. This product is made of plastic and contains gold, silver or copper. The product is securely attached to the uterus and is easily removed, so the presence of special ropes attached to the contraceptive product is not necessary.
- Loop or umbrella shaped
The outer edges of the umbrella-shaped spiral have protrusions in the form of spikes, due to which the product is securely fixed inside, this reduces the risk of its spontaneous falling out. The umbrella-shaped contraceptive device is used by women who have a non-standard uterine structure, which makes it impossible to install a T-shaped intrauterine device.
The most popular IUDs for contraception
Pharmacies offer a wide range of different contraceptives. Contraceptive IUDs are in particular demand among women all over the world. Depending on your financial capabilities and the characteristics of your body, your doctor will determine which model is best for you. Let's look at the most popular types of intrauterine devices, their photos and descriptions.

It is considered the most effective hormone-containing IUD. It has a T-shape, consists of a vertical membrane, inside of which there is a hormone and two horizontal hangers (attached to the uterus). The product provides a high degree of protection against unwanted conception, suppresses the ovulation process, reduces the risk of ectopic pregnancy, relieves inflammation of the woman’s genital organs, and regulates the menstrual cycle. The cost of the product ranges from 7-10 thousand rubles, the validity period is 5-7 years.
Multiload
This spiral has the shape of an umbrella, on the side elements of which there are spike-like protrusions used for reliable fixation on the walls of the uterus. The leg of the spiral is wrapped in copper, which has a depressing effect on sperm and suppresses their ability to fertilize. Multiload is allowed to be installed by nulliparous girls. The cost of the spiral is from 3.5 thousand rubles.
This intrauterine device is T-shaped. The products are made of plastic and copper; in more expensive versions, it is possible to add silver. Nova T has a detrimental effect on sperm, slows down their movement and reduces the ability to fertilize an egg. The cost of the spiral is from 2 thousand rubles, the shelf life is up to 5 years.

Invention of Belarusian doctors. Pharmacies sell many varieties of Juno spirals. There are options for both women who have children and those who have not. The cost of a contraceptive varies from 250 to 1000 rubles. We list the common types of contraceptive devices of the Juno model:
- Juno Bio-T is a budget option. A spiral in the shape of an anchor, the rod of which is covered with copper thread.
- Juno Bio-T Super. Identical to the previous model, but has an antimicrobial composition.
- Juno Bio Multi Ag. A T-shaped product, the leg of which is wrapped with copper and silver thread.
- Juno Bio Multi. It has an F-shape with jagged edges. Suitable for use by women after childbirth or girls who have had an abortion.
- Juno Bio-T Au. An expensive spiral containing gold. Designed for patients with allergies to metals.
Where to buy and how much does it cost to install a spiral?
You can purchase an intrauterine device at any pharmacies in your city or order it from specialized online catalogues. The cost of a vaginal contraceptive depends on many factors: model, material, manufacturer, shape, presence or absence of side effects. Intrauterine devices are sold in the following retail outlets in Moscow:
- "Lepharm". Customs Prospect, 9, building 8. Price 700-9000 rub.
- "Omega". st. Skobelevskaya, 25. Cost – 169-10000 rubles.
- "Social Pharmacy". st. Dubninskaya, 44a. Price 200 -5000 rub.
Online stores where you can order a spiral:
- vsepessarii.ru. Cost from 300 to 5500 rub.
- brief-med.ru. Price 250-6000 rub.
In order to correctly install the spiral, you must contact an experienced gynecologist. There are many gynecological offices in Moscow where they will provide you with this service, but pay attention to the following factors:
- How many years has the clinic been operating?
- Experience of a gynecologist, and what patient reviews about him.
- Service cost.
The price for installing an intrauterine device in some Moscow clinics is as follows:
- LLC Medical Clinic "NORMA", Nikitsky Boulevard 12, building 3. Price - 2000-3000 rubles.
- Gynecology Sikirina O.I., Bolshoi Demidovsky Lane, 17/1. The cost of the service is 1500 rubles.
- MEDICAL CENTER, st. Koktebelskaya, house 2, bldg. 1. Price – 2500-3500 rubles.
- ON clinic. Tsvetnoy Boulevard, building 30, building 2. Cost from 5,000 rubles.
Video: doctors’ opinion on installing an intrauterine device
The IUD is a reliable method of preventing unplanned pregnancy. You can learn about the principle of operation of this contraceptive device by reading an article with instructions on the Internet, going to a consultation with a gynecologist, or watching the following video. TV presenter Elena Malysheva will tell you how effective the use of intrauterine devices is, what the possible consequences are, how to place them correctly and when.
This is a small device placed in the uterus in the form of a spiral or the letter T, at the end of which there are antennae. The presence of a foreign body in the uterine cavity does not allow the egg to attach and makes it possible to prevent pregnancy.
This phenomenon was discovered a long time ago, by camel drivers in the Middle East. During long treks through deserts, they inserted a small stone or pebble into the females' uterus in order to avoid unwanted pregnancy. Let's talk more about intrauterine device- types, principle of action and installation in the body.
There are a large number of spirals of different shapes and different sizes. All are made of plastic, some have a copper or silver thread, others contain a reservoir of progesterone.
It is generally accepted that the spiral causes inflammatory processes and promotes the penetration of microinfections into the uterine cavity. For the purpose of self-defense, the uterus produces a large number of leukocytes designed to destroy the pathogen, in this case it is sperm or a fertilized egg.
The inner surface of the uterus, irritated by the presence of the spiral, creates and maintains in constant readiness an environment unfavorable for the egg or sperm. The spiral can also help to increase the mobility of the tubes, which leads to the release of the germ cell before the fertilized one and doubles the speed of sperm movement.

As a result, the level of prostaglandin increases, which prevents the egg from attaching to the walls of the uterus. The copper compound released from the copper threads changes the mucous membrane, making it harmful to sperm.
The effectiveness of this contraceptive. In terms of reliability, the IUD is in second place after birth control pills. The effect is achieved in 96% of cases. For 100% safety, spermicides should be additionally used.
Reversibility of the process. The spiral can have an adverse effect on the female body and its reproductive ability. Its consequences:
- Disease and infection of the pelvic organs.
- Perforation of the uterus.
- Ectopic pregnancy.
However, in most cases such problems do not arise and residual effects are impossible.
How to install a spiral?
Insertion of the IUD is a routine medical procedure that is performed in the office and does not require anesthesia or special preparation. However, in order to identify possible contraindications, it is necessary to undergo a preliminary gynecological examination and a smear test.
If possible, in addition to this, it is advisable to undergo a clinical examination, talk with a doctor, do a cytobacteriological analysis of vaginal discharge and tissue, and a blood test to identify possible sexually transmitted diseases.
During the first visit, the doctor examines the depth and position of the uterus in order to select the spiral needed in a particular case. If the uterus is small or the woman has never given birth, his choice will be a small spiral. In the decision, the doctor indicates the number of the spiral and the medications that must be brought with you on the appointed day.
And now this day has come. You are nervous and even afraid. In practice, it turns out that the insertion of the spiral occurs very quickly, in 3 minutes, and is absolutely painless. The doctor inserts a surgical speculum into the vagina. Then he disinfects the cervix (the first tangible touch) and places the forceps on one of her lips (a slight tingling sensation is felt) to penetrate through the cervix to the body of the uterus.
The doctor inserts a small probe through the cervical canal and measures the depth of the uterine cavity (hysterometry). This way he knows what size spiral to choose. Immediately before installation, the spiral is placed in a small tube of small diameter, penetrating into which it is deformed and becomes tense, like an elastic band.
Now you need to act very quickly to prevent its shape from changing.
Having installed the device in place, the gynecologist moves the inserted part a few centimeters into the uterine cavity. This forces the spiral to return to its original shape.
The doctor carefully removes the pusher and device for inserting the coil. The procedure is completed.
This truly simple operation may be accompanied by mild, dull pain or simply discomfort. Women who gave birth naturally find the insertion of the IUD absolutely painless. Those who have never given birth or have a very narrow cervical passage are more sensitive. Some women experience painful cramps within a few minutes.
And finally, all that remains is to cut the thread. The head of a man's penis risks getting tangled in threads that are too long, and too short ones can get pricked! The doctor cuts the threads at a distance of 2-3 centimeters from the entrance to the cervix. Usually the woman is too excited to feel for these threads, indicating the presence of a spiral, so this can be done later, in a calmer environment.
How to make sure that the spiral is in place?
Check the availability of the IUD immediately before the first sexual intercourse after its insertion (if you lack the courage, ask your partner to do it); check how it stands every time after the end of menstruation, and then from time to time. This can be done with your finger:
- Pull your feet as close to your buttocks as possible to reduce the length of your vagina.
- Insert the previously disinfected middle finger. The finger spreads the vaginal lips and touches the convex part of the cervix.
- Feel for the hole (small depression) where the threads are located.
- On certain days, the uterus may move in such a way that it is very difficult to detect the cervix or find the opening.
Try repeating the operation the next day. If you cannot feel the protruding threads after several days, or if they seem shorter or longer than they should be, or if you feel a protruding plastic part with your finger, make an appointment with your doctor.
It is advisable to have a special mirror at home and periodically conduct self-examination. With its help, you can also examine threads. Typically, a month after insertion of the IUD, you must undergo a medical examination. Then it is advisable to see a doctor every six months.
Possible reaction of the body to the establishment of a spiral
Minor bleeding without complications is observed. If it does not stop or turns into severe open bleeding, consult a doctor.
By prescribing a simple treatment, he will stop it. Cramping or intrauterine pain may occur. They will disappear after using antispasmodic drugs prescribed by the doctor, and after 2 months they will completely go away on their own.
There is always a danger of the spiral coming out. It is for this reason that self-monitoring is recommended. The body has a unique ability to reject foreign bodies. If he cannot tolerate the IUD, then rejection will occur within the first three months. This often occurs during menstruation. Sometimes a woman does not notice that the spiral has fallen out.
Observe yourself carefully and pay attention to the bottom of the toilet or sanitary napkins.
Using hygienic tampons, it is impossible to inadvertently remove the IUD. The coil cannot get tangled or caught on the tampon. Signs of rejection are:
- Unusual vaginal discharge.
- Spasms and severe pain.
- Bleeding.
- Too long threads when palpated with a finger or a heightened sensation of the presence of a foreign object in the cervical canal or in the vagina.
- Partner complaints (irritated tip of the penis).
- Painful sensations during sexual intercourse.
Symptoms indicating the presence of an infection (fever, unusual bleeding, colic, pain in the pelvic area) should make you contact your gynecologist immediately.
When to install a spiral?
This is usually done before or at the very end of menstruation. It all depends on the doctor and his skill.
Those doctors who prefer to insert the IUD during or immediately after the end of menstruation believe that the cervical passage is slightly open during this period, which allows the IUD to be inserted with less pain.
Moreover, you can be sure that there is no pregnancy. Is it possible to insert an IUD immediately after childbirth or abortion? That's what they did before. But now many doctors are afraid of infection, or perforation of the uterus, or rejection of the device, since the cervix at this time is softer and the uterine cavity is enlarged.
Thus, it is better to insert the IUD 2-3 months after the birth of the child and a month after an artificial termination of pregnancy or a delay in menstruation. Advantages of the spiral:
- The IUD provides very effective and permanent protection against pregnancy from the very moment it is inserted.
- The IUD has little effect on the body’s natural hormonal balance.
- The spiral allows you to have a carefree sex life: you do not need to take, administer spermicidal capsules and ointments, or measure body temperature.
- The presence of a spiral facilitates the process of familiarization with the genitals, since it requires constant palpation with a finger.
- The spiral does not need to be changed often. Plastic IUDs are changed every 3-4 years in order to prevent and eliminate the possibility of inflammatory processes in the pelvic organs (if not for this danger, one IUD could be installed for life).
- If desired, immediately after removing the IUD, you can think about conceiving a child.
Spirals with copper wire are also removed every 3-4 years. They probably lose their reliability after this period, since the onset of oxidative processes does not allow copper ions to be active. And sometimes it simply dissolves and is absorbed by the body when it is deficient. IUDs containing progesterone last for a year.
What are the contraindications to installing an IUD?
Absolute contraindications:
- Pregnancy.
- Acute or chronic genital infection.
- Underdeveloped uterus.
- Unreasonable bleeding from the genital tract of unknown origin.
- Postpartum period (recent birth).
General contraindications:
- Coagulation problems (poor blood clotting).
- Cardiovascular diseases.
- Diabetes.
Relative contraindications:
- Fibroma.
- A woman who has not given birth (the device is placed only after the consent of the woman, who has been warned about the possible consequences, and only in the case of a complete ban on the use of contraceptive hormonal drugs). The patient's condition is being closely monitored.
- Some malformations of the uterus.
- Previous operations on the uterus (presence of scars).
- Cases of ectopic pregnancy or plastic surgery on the uterine lips in the past.
Pregnancy with an IUD, fortunately, is quite rare. If your period is late, take a pregnancy test immediately.
If the result is positive, undergo an ultrasound examination to clarify the location of the spiral in relation to the uterine cavity and embryonic sac.
If the IUD is located under the embryo sac and the pregnancy is progressing normally, the gynecologist can carefully remove it to avoid infectious complications (this, of course, applies to women who want to continue the pregnancy).
If the IUD is located above the embryo sac, it must be left in place and ensure normal pregnancy. It is necessary to make an appropriate entry in the patient’s personal card so as not to forget to remove the IUD from the placenta after birth.
One midwife even witnessed a newborn baby holding the coil in his small clenched fist. And finally, if a woman does not want to continue the pregnancy, you can resort to artificial termination in the appropriate manner.
The most common cases of spontaneous miscarriage are in early pregnancy. The incidence of ectopic pregnancy is 2.9%. This is a very serious and dangerous complication. If it is not detected in time, then first there is a hole in the fallopian tube, then it ruptures (the fallopian tube is too narrow to accommodate a growing egg), after which bleeding opens, inflammatory processes worsen, infection occurs and as a result - loss of the tube, which leads to infertility, and sometimes (in the past) to death.
The symptoms are the same as in early pregnancy (fatigue, vomiting, breast pain). Sometimes there is continuous black bleeding, absence of menstruation, abdominal pain of varying degrees of intensity (mild, dull, cutting), increasing as pregnancy progresses.
One or all of these symptoms occur suddenly, so you need to be very careful and consult a doctor as soon as possible. An ectopic pregnancy is a “bomb” inside that will explode at any moment.
Perforation most often occurs during insertion of the IUD due to clumsiness or lack of experience on the part of the physician. A poorly installed IUD rests against the wall of the uterus, with part of the IUD halfway passing through the mucous membrane of the uterus, or the IUD “goes” into the abdominal cavity.
What happens next? The spiral can move from organ to organ and penetrate them, which, naturally, requires urgent surgical intervention. Unfortunately, perforation does not have any special symptoms that would allow it to be detected.
Therefore, the first signal of concern may be threads that are too short or completely absent during self-examination. The second sign of perforation, paradoxically as it may seem, is pregnancy. The fact is that once the spiral has disappeared, the woman is no longer protected.
So, if the threads of the spiral cannot be felt and are invisible when examined with a mirror, it means that either the spiral has fallen out, which was not noticed, or perforation has occurred. The doctor has a number of tools for a more accurate determination.
He may examine the uterine cavity using a probe or a biopsy instrument. It is necessary to undergo fluorography (all plastic spirals are coated with barium so that they can be detected using X-rays), or even better - echography.

If the IUD is still in the uterus, after opening the cervix (which is painful in itself), you can pull on the threads to remove it. If the spiral has settled in the abdominal cavity, it must be removed, since in this case there is a danger of an infectious disease, as well as difficulties in the functioning of organs that encounter the spiral, the presence of which leads to tingling and even pinching (for example, the intestines).
In such a situation, surgical intervention is necessary, the operation is often performed using abdominal endoscopy. Inflammatory processes in the uterus and pelvic organs are the most common complication and one of the least treatable, which in the future will affect the full functioning of the reproductive organs.
On average, when using a spiral, this danger increases by 3 times, 7 times if a woman has not given birth, and 1.7 times if she already has more than three children. It is for this reason that many doctors refuse to insert the IUD into young women who do not have children and have irregular sex lives with multiple partners, which increases the risk of infection or sexually transmitted viruses.
The prospect of entering sexual maturity with an infection of the fallopian tubes, which will ultimately lead to complete infertility, cannot satisfy either the doctor or the woman herself.
There may be cases where the uterine mucosa accumulates around the IUD, partially covering it, which prevents the IUD from performing its functions. Removing an encapsulated coil is very painful; sometimes you have to resort to curettage.
Inconveniences when using a spiral
They are not systematic, and in most cases they are completely absent. But nevertheless, under certain circumstances they can bother a woman. During installation of the IUD, rupture of the cervix with forceps is not possible if all actions and stretching are performed carefully. If the cervix is damaged, it is first treated. Perforation of the uterus is a very serious complication, especially not a pleasant one, since it cannot be detected immediately, since it is painless. Perforation occurs due to inaccurate hysterometry or careless insertion of the spiral. In case of complications, the woman needs rest, ice on the stomach and a course of antibiotic treatment.
More than 60 million women in the world prefer such a means of birth control as an intrauterine contraceptive. Which ones are better, for how long are they installed, is this a painful procedure? These questions interest many women.
IUD classification
This type of contraception is used by more than 16% of Russian women of reproductive age. To find out what is good about an intrauterine device and which one best protects against pregnancy, you need to know which devices can be purchased on the domestic market.
There are several types of intrauterine contraceptives:
- non-medicinal;
- first generation medications - “Multiload”, “Nova”, “Junona Bio”;
- third generation medications - Mirena.
The first ones are made of synthetic materials with the addition of They come in various shapes: T-shaped or S-shaped. These ineffective doctors report that they are not currently used due to frequent inflammatory complications after their administrations.
The second group is represented by those containing copper, gold, and silver. In this case, it is possible to have one metal or a combination of several: the rod is silver, and the winding is copper. Intrauterine devices with silver and other metals do not corrode, help prevent various inflammations of the internal genital organs and are installed for a fairly long time - for 5 years.

Contraceptives belonging to the third group are similar in form to the previous ones, but contain a container with a synthetic gestagen, which is released in microdoses - up to 20 mcg daily. Such spirals are installed for 7 years. They not only have a contraceptive effect, preventing the attachment of a fertilized egg, but are also used to treat various diseases: endometriosis, dysfunctional uterine bleeding and during hormone replacement therapy with estrogen to prevent endometrial hyperplasia. Such spirals are suitable for women with religious prejudices, since fertilization does not occur due to changes in hormonal balance under the influence of the constant release of progestogens.
Mechanism of action
To decide which intrauterine devices are better, you need to know how they work. This method of contraception leads to the development of specific inflammation as a reaction to a foreign body: leukocyte infiltration of the endometrium, morphofunctional changes that are unusual for the normal menstrual cycle and in which the introduction of a fertilized egg is impossible.

The IUD causes contractions of the uterus, prevents the normal growth of the endometrium for egg implantation, promotes peristalsis and negatively affects sperm with copper, gold and silver ions.
Each theory of contraceptive action should not be considered as prevailing; the mechanism of action consists of several components.
Advantages
To find out which intrauterine device is the best, you need to familiarize yourself with the advantages of all types of IUDs:
- efficiency up to 98%;
- ease of use;
- minimum of adverse reactions;

- restoration of the ability to fertilize after removal of the IUD during the first month;
- breastfeeding is not affected (not suitable for IUDs with gestagens);
- is administered for a long time;
- low cost;
- There is no need to take pills daily and monitor their use when using oral contraceptives.
Flaws
Among the disadvantages, it should be noted nagging pain in the lower abdomen, especially in the first days, heavy menstruation, a high risk of developing inflammation, constant monitoring of the mustache, restrictions for young women.
Contraindications
Which intrauterine devices are better: “Multiload”, “Junona Bio”, “Nova”? Are there any contraindications for a certain type of IUD? It should be noted that for all types there are relative and absolute contraindications.

Absolute contraindications include acute inflammatory process, oncological neoplasms of the cervix and uterine body, bleeding from the vagina of unknown origin, suspected or existing pregnancy. With these symptoms, insertion of the IUD is strictly contraindicated.
Relative contraindications are those symptoms in which the introduction of an IUD is possible after appropriate examination or treatment, or when the contraceptive will not contribute to the progression of the process. This:
Exacerbation of chronic diseases and six months after treatment;
. venereal diseases;
. cervicitis, vaginitis;
. heavy menstruation, intermenstrual bleeding;
. endometrial hyperplasia or polyps;
. uterine fibroids with submucous nodes;
. some forms of endometriosis;
. malformations of the uterus: insufficient development, abnormal structure;
. changes in the cervix that make it impossible to insert an IUD;
. ectopic pregnancy six months before insertion;
. history of IUD expulsion (self-removal);
. infectious and inflammatory complications after abortion during the last three months;
. if there are many sexual partners;
. somatic diseases: chronic inflammation, incl. tuberculosis; anemia or coagulopathy; rheumatic heart disease, valve defects;
. allergy to metal ions;
. Westphal-Wilson-Konovalov disease is a hereditary disease in which copper metabolism is disrupted;
. treatment with immunosuppressants.
In each specific case, after identifying all unfavorable factors and a thorough examination, the doctor determines the possibility of using an IUD. Pharmacies sell various intrauterine devices. Photos of the packaging are presented above. Their cost varies from 200 to 10,000 rubles.
Examination before insertion of the IUD
Before using this method of contraception, you must have an individual consultation with your gynecologist and perform the required minimum of examinations:
- clinical blood test;
- examination;
- examination for syphilis, hepatitis B and C, HIV carriage;
- extended colposcopy;
- Ultrasound of the uterus and appendages.
Time of IUD insertion
According to WHO experts, the IUD can be inserted on any day, but the most favorable days are considered to be days 4-7 of the menstrual cycle. This is explained by the fact that at the specified time the uterine mucosa has been restored after rejection of the endometrium, is slightly open, the presence of menstruation is a reliable sign of the absence of pregnancy, and minimal bleeding that occurs after insertion does not bring discomfort to the woman.

After an induced abortion or self-abortion, the IUD can be inserted immediately or within 4 days if there are no signs of bleeding or inflammation.
Complications
Complications are possible immediately and some time after the intrauterine device is installed. Which is better in terms of minimal unpleasant side effects? Often after insertion of the spiral, a pain symptom occurs, which can last for an hour. This is reported in the reviews. Most often, the discomfort goes away after taking analgesics. If the pain is not relieved by taking analgesics and antispasmodics, then it is necessary to perform an ultrasound or hysteroscopy to determine the correct insertion of the IUD and diagnose the presence of a spiral in the uterus or outside it (if the uterus is perforated during insertion).
Expulsion of the IUD is most often observed in young nulliparous women due to increased contractility of the uterus. It occurs mainly in the first days after administration. Moreover, the frequency of this complication depends on the type of IUD: copper-containing devices remove themselves in 6-16% of cases, progestogen-containing devices - in 3-6.5%. With age and an increase in the number of births and abortions, the likelihood of this complication decreases.
Inflammatory diseases are complications that are observed in 3.8-14.5% of cases when the IUD of the second group is inserted. Moreover, if inflammation occurs in the first 3 weeks, then its occurrence can be associated with the introduction of an IUD; if after 3 months, then this is a newly emerging disease. The formation of a purulent tubovarial formation is the most dangerous inflammatory complication. It occurs with prolonged use of the spiral - more than 6-7 years.

Bloody discharge is possible in the first days after administration (2.1-3.8% of cases) and can be stopped by prescribing hemostatic agents. If bleeding continues, is accompanied by pain, or occurs between menstruation and does not respond to treatment, then it is necessary to remove the coil.
In 0.5-2% of cases, pregnancy may occur. This occurs with full or partial expulsion of the IUD. Most often, such a pregnancy ends in spontaneous abortion, even if the woman wants to keep it.
And which intrauterine devices are better in terms of complications, a gynecologist will help you decide.
The effectiveness of intrauterine contraceptives
Many types of IUDs pose the following questions to a woman: how to avoid complications, and which intrauterine device is better? Reviews from doctors and patients speak in favor of copper- or silver-containing IUDs.
The addition of copper and silver reduced the incidence of complications by 2-10 times. Moreover, the effectiveness of such IUDs is 93.8%. Inert coils have an efficiency of 91-93%. Currently, copper-containing IUDs are the most acceptable due to the low percentage of complications and high percentage of contraceptive activity.
The Mirena hormonal releasing system is the most effective contraceptive and is considered almost biological sterilization, since it has many actions aimed at preventing the fertilization of the egg, attaching it to the endometrium, increasing the viscosity of mucus in the cervical canal to protect against sperm entering the uterus.
We looked at the positive and negative effects that the intrauterine device has. Which one is better? This issue should be resolved together with a gynecologist. At the same time, the price that the woman expects is determined, and the indications that the doctor identifies after the examination.