In what cases does a pregnant woman need to urgently consult a doctor? Emergency conditions during pregnancy: types of pathologies and assistance Features of treatment of heat stroke during pregnancy
First aid for ectopic pregnancy
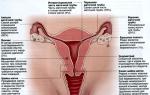
- a process in a woman's body when a fertilized egg develops outside the uterine cavity - usually in the fallopian tube, ovary or abdominal cavity. If you suspect an ectopic pregnancy, you should immediately consult a doctor. They do not take any measures to eliminate pain on their own. The only way to treat this dangerous complication is surgery, which is performed immediately after diagnosis. Hospitalization in the gynecological or surgical department. The woman is carried on a stretcher. If you faint, give ammonia to sniff.
The reason for this is most often inflammatory diseases of the female genital organs, and primarily the fallopian tubes, as a result of which they lose the ability to “capture” and “carry” a fertilized cell into the uterine cavity.

Symptoms depend on the type of ectopic pregnancy. If the fertilized egg develops in the tube, then in the 6th to 8th week of pregnancy its walls become thinner and rupture. Sharp pain occurs in the lower abdomen, which radiates to the bladder or rectum. After some time, signs of acute anemia appear: pale skin, cold sweat, rapid pulse (up to 160 beats per minute) and weak filling. The abdomen is painful and tense. Minor bleeding from the vagina.
When an egg is expelled through the free end of the fallopian tube into the abdominal cavity, they speak of an ectopic pregnancy as a tubal miscarriage. It proceeds slowly, as the fertilized egg peels off gradually. In this case, cramping pain occurs in the lower abdomen. When pain appears, fainting is possible. There is dark bloody discharge from the vagina.
First aid. If you suspect an ectopic pregnancy, you should immediately consult a doctor. They do not take any measures to eliminate pain on their own. The only way to treat this dangerous complication is surgery, which is performed immediately after diagnosis. Hospitalization in the gynecological or surgical department. The woman is carried on a stretcher. If you faint, give ammonia to sniff.
Prevention. The main means of preventing ectopic pregnancy is timely treatment of inflammatory processes of the female genital organs.
With the onset of spring and warm weather, we begin to move more and go on trips, vacations, to the countryside or anywhere else. Accordingly, expectant mothers will also not sit at home, and can go to nature or outside the city on vacation. But, before you go on vacation, it is worth considering the issues of providing first aid in case of health problems. It is about providing first aid in some situations that we will talk today.
What do you need to think about?
If you are going out of town or to the country, just in case, it is worth finding out in advance where the nearest pharmacies, clinic or hospital are located in this area, and what types of medical care they can provide, whether there is a gynecology department and a maternity hospital. If you are outside the city, it is worth keeping in mind that in the region, if you call an ambulance, local ambulance teams arrive and will deliver all patients only to the nearest regional hospital or hospital. The city ambulance team can go to the country house or out of town only in cases where such a service is specified in the paid contract for childbirth and prenatal care.
Before your trip, pack a first aid kit for yourself, taking into account your health characteristics, having discussed with your doctor the medications that will be allowed for you. You will definitely need to take with you your passport and insurance policy, as well as those documents that you have at the time of the period in which you will go on vacation. This can be an exchange card, which, if necessary, can be issued at your antenatal clinic upon your request from the 22nd week of pregnancy. It is also worth taking with you a birth certificate, which is usually issued to pregnant women at 30 weeks or after attending a consultation for at least 12 weeks. It is also worth taking along ultrasound or CTG data, the results of all other studies during pregnancy, as well as the results of all tests performed on you with an extract from your chart. If you have a contract for childbirth or for prenatal care under a VHI policy, you must take it with you, in parallel with the contract for childbirth, if you have concluded one.
When collecting a first aid kit for your trip to the country or out of town, you need to put in it your vitamins for pregnant women, antispasmodics ("No-shpa" or "Papaverine"), a sedative ("Valerian" or "Motherwort"), as well as all those medications medications that are additionally prescribed to you on the recommendation of a doctor. Don’t forget about seasonal medications - you need to put in insect repellents (repellents), as well as substances to relieve itching and speed up the healing process of the area of insect bites. It is also worth bringing with you medications to protect against UV rays and to treat sunburn, antihistamines and products to normalize digestion. Before leaving, visit a doctor and discuss with him the nuances of treating your health problems, if necessary, whether it is worth taking maintenance medications, as well as recommendations on how to behave on vacation, nutrition, and set a date for your next visit to the doctor . If appropriate, ask your doctor for a phone number where you can reach him if you have questions or concerns. Let's discuss with you those problems that may arise as emergencies and require first aid in pregnant women.
Fainting and dizziness in pregnant women
During pregnancy, expectant mothers may experience fainting or dizziness, and dizziness can be considered sensations in which the body itself or objects around the body seem to move. In this case, fainting may also occur - this is a short-term and shallow loss of consciousness, lasting from several seconds to one to three minutes. This occurs due to special changes occurring in the body associated with pregnancy. During the development of the fetus, a woman develops a whole system of blood vessels in the pelvic area for adequate nutrition of the fetus. The area of the uterus during pregnancy can account for up to 30% of all circulating blood, and outside of pregnancy only up to 2% of the blood. As a result of the development of pregnancy, the heart of the expectant mother will work with increased loads so that a sufficient amount of blood can be provided in the uterine area while the volume of blood in the vessels increases. At the same time, there may not be enough oxygen to the mother’s organs and tissues, which can result in hypoxia, especially in the area of brain tissue, which causes attacks of dizziness, which can sometimes result in fainting. This is quite acceptable in isolated cases during pregnancy, but such a condition cannot be ignored.
Why may dizziness occur?
The main causes of dizziness in pregnant women can be cramped or stuffy rooms that are poorly ventilated, and therefore you should avoid large crowds of people in small and stuffy rooms; under such environmental conditions, the body receives less oxygen and poorly delivers it to the tissues. A state of toxicosis with bouts of vomiting and, as a result, dehydration of the body can lead to fainting. A state of dehydration can have an extremely negative effect on blood circulation in the area of small vessels and the cerebral cortex. The causes of fainting can be a sudden change in body position - usually this is abruptly getting out of bed, changing from a horizontal position to a vertical position. This is called orthostatic collapse, when the vessels simply do not have time to contract when changing body position and the blood flows into the lower half of the body. You should avoid sudden movements and getting out of bed; you need to do this slowly and carefully, rising sideways from a lying position or getting up smoothly from a chair.
Also, the causes of fainting can be an increase in the size of the uterus with compression of large venous vessels - the inferior vena cava in particular. Such compression leads to difficulty in the outflow of blood from the lower extremities, which also causes swelling in the lower body, and also causes problems with the outflow of blood from the internal organs, which leads to disruptions in their functioning. Fainting can also be caused by pathophysiological problems such as attacks of vegetative-vascular dystonia, manifestations of osteochondrosis or pathologies of the heart and blood vessels. Usually, expectant mothers know about such problems before pregnancy and it will be necessary to conduct an examination in the initial stages of pregnancy and prescribe adequate therapy for the pathology. Also, fainting can be caused by a decrease in hemoglobin levels with the development of anemia in pregnant women. This leads to a deficiency of hemoglobin to carry oxygen in the blood, leading to hypoxia and fainting. You always need to find out in detail the causes of fainting and deal with them quickly and effectively, as well as know the warning signs of fainting in order to quickly provide help.
Signs of impending fainting
It is important to recognize the approach of fainting, so as not to fall and injure yourself, or to avoid fainting if possible. The main signs of impending fainting will be dizziness with attacks of headache and pulsation in the temples, as well as an attack of sudden weakness with general malaise. Nausea with blurred vision and blurred vision, noise or congestion in the ears, chills or body heat, a feeling of lack of air and a sharp drop in blood pressure to critical levels may occur.
If such symptoms appear, you need to sit down or lie down, and if possible, call for help. If fainting occurs, it is worth laying the pregnant woman down on a flat surface, placing a bolster or pillow, a blanket under her feet, or simply giving them an elevated position to allow blood to drain out. It is important to immediately provide fresh air into the room if a woman faints in a stuffy room. You need to unbutton the collar of your clothes to make breathing easier, let them smell a piece of cotton wool soaked in a sharp-smelling liquid - vinegar or ammonia. You can sprinkle the woman’s face with cool water, give her a sweet liquid or strong tea to drink.
How to prevent fainting in pregnant women?
To reduce the likelihood of fainting, you should change the position of your body in space smoothly and slowly; if you are lying down, you don’t need to get up right away, roll onto your side, sit in bed with your legs dangling, and sit silently, try not to bend over. Then slowly rise to your feet. Constantly ventilate the room in which you are, and also avoid inhaling strong odors; carry ammonia with you if you are prone to fainting. Eat regularly, avoid long hungry breaks and drink enough fluids, in hot weather do not stay in the sun for a long time and wear a hat. It is important to wear clothes that do not restrict movement, that will not interfere with movement and free breathing, only made from natural, breathable fabrics. It is important to avoid confined spaces with large crowds of people - transport during rush hour, queues in stuffy rooms. You should also avoid strenuous physical activity. If signs of imminent fainting occur, immediately ask for help from others.
You should not sit for a long time with your legs crossed or tucked under you, do not take a hot bath, replace it with a cool shower, go for walks in the company of someone, and be sure to see a doctor in case of fainting.
More articles on the topic “Treatment of pregnant women”:
Ecology of life. Health: An ectopic pregnancy is a process in a woman's body when a fertilized egg develops outside the uterine cavity - usually in the fallopian tube, ovary or abdominal cavity. If you suspect an ectopic pregnancy, you should immediately consult a doctor.
Ectopic pregnancy is a process in a woman’s body when a fertilized egg develops outside the uterine cavity- usually in the fallopian tube, ovary or abdominal cavity.
The cause of this is most often inflammatory diseases of the female genital organs, and primarily the fallopian tubes, as a result of which they lose the ability to “capture” and “carry” a fertilized cell into the uterine cavity.
Symptoms depend on the type of ectopic pregnancy. If the fertilized egg develops in the tube, then in the 6th-8th week of pregnancy its walls become thinner and rupture. Sharp pain occurs in the lower abdomen, which radiates to the bladder or rectum. After some time, signs of acute anemia appear: pale skin, cold sweat, rapid pulse (up to 160 beats per minute) and weak filling. The abdomen is painful and tense. Minor bleeding from the vagina.
When an egg is expelled through the free end of the fallopian tube into the abdominal cavity, they speak of an ectopic pregnancy as a tubal miscarriage. It proceeds slowly, as the fertilized egg peels off gradually. In this case, cramping pain occurs in the lower abdomen. When pain appears, fainting is possible. There is dark bloody discharge from the vagina.
First aid. If you suspect an ectopic pregnancy, you should immediately consult a doctor. They do not take any measures to eliminate pain on their own. The only way to treat this dangerous complication is surgery, which is performed immediately after diagnosis. Hospitalization in the gynecological or surgical department. The woman is carried on a stretcher. If you faint, give ammonia to sniff.
Prevention. The main means of preventing ectopic pregnancy is timely treatment of inflammatory processes of the female genital organs. published
Other emergency conditions in obstetrics include placental abruption, complicated toxicosis, eclampsia, eclamptic attack and other pathologies, any of which not only complicates the bearing of the fetus and darkens the joy of future motherhood, but also poses a serious threat to the child and his mother. The pathological course of pregnancy is a cause for serious concern and constant monitoring.
Pathology of pregnancy toxicosis: late diagnosis
Toxicosis in late pregnancy is a serious pathology, manifested by an edematous-neurotic and hypertensive symptom complex, which leads to damage to the nervous system and the development of convulsive syndrome and is accompanied by fetal suffering.
The clinical picture of toxicosis in the pathology of pregnancy is as follows:
- swelling;
- hypertensive syndrome;
- in advanced stages - pain in the epigastric region, which depends on liver damage and tension of the hepatic capsule;
- headache;
- blurred vision due to spasm of cerebral vessels;
- cerebral edema;
- edema is generalized; on the lower and upper extremities, on the anterior abdominal wall, in the form of swelling or puffiness of the face.
- When diagnosing this pathology of pregnancy, systolic blood pressure is recorded in non-severe cases of 130-140 mg Hg. Art., with severe flows - 150-160 mm Hg. Art.;
- diastolic pressure is respectively 90-110 mmHg. Art.;
- tachycardia up to 100 beats per minute or more.
Such a pathological condition during pregnancy as insufficiency of the uteroplacental circulation leads to the development of malnutrition, acute and chronic hypoxia of the fetus and is accompanied by abruption of the normally located placenta. manifested by a significant increase in body weight and a decrease in urine volume.
Progressive toxicosis with prolonged disruption of microcirculation contributes to deepening changes in the brain, the development of cerebral edema, acute cerebrovascular accident, increased convulsive readiness, the development of an eclamptic attack, eclamptic status, and coma.
Before transporting a patient with toxicosis to a hospital, preliminary administration of sedatives is necessary in order to ensure a therapeutic and protective regime and prevent seizures. Most often, it is customary to administer 2 ml intramuscularly or intravenously of a 0.25% solution of droperidol in combination with 2 ml of a 0.5% solution of diazepam (Relanium); in severe cases, the administration of a number of barbiturates is indicated.
Pathologies during pregnancy: placental abruption (with photo)
Premature abruption of a normally located placenta is another pathology during pregnancy that is a cause for serious concern.
This emergency condition of a pregnant woman is characterized by separation of the placenta before the birth of the fetus - during gestation and at the beginning of labor. This is a violation of the uteroplacental circulation due to late toxicosis of pregnancy and kidney disease.
Signs of such an obstetric emergency are:
- weakness, dizziness;
- pale skin;
- peripheral cyanosis;
- tachycardia;
- if the detachment occurs over a significant extent, abdominal pain and uterine tension are bothersome;
- characterized by local pain depending on the placenta insertion site;
- Blood appears from the external genital tract, but the degree of external bleeding does not correspond to the patient’s anemia, because a significant part of the blood accumulates between the uterus and placenta (retroplacental hematoma);
- sometimes anuria and coma are observed simultaneously;
- with significant placental abruption develops (pallor of the skin, threadlike rapid pulse, low blood pressure).
In a fetus with this pathology, symptoms of intrauterine hypoxia rapidly increase during pregnancy:
- the heartbeat cannot be heard or there are signs of impairment;
- tachycardia more than 160 beats/min;
- bradycardia less than 120 beats/min.
The causes of this pregnancy pathology are the following factors:
- late gestosis;
- hypertonic disease;
- kidney diseases;
- complicated obstetric and gynecological history;
- uterine fibroids;
- uterine injuries;
- rapid emptying of the uterus with polyhydramnios, multiple pregnancies, large fetuses.
See what this pregnancy pathology looks like in these photos:


Pathology of pregnancy - eclamptic attack: signs of diagnosis
Such a pathology of pregnancy in obstetrics, such as an eclamptic attack, often develops against the background of symptoms of preeclampsia (high blood pressure, headache, blurred vision, pain in the epigastric region), which can also occur against the background of mild clinical symptoms of toxicosis.
An eclamptic attack lasts 1.5-2 minutes and is characterized by four phases:
- pre-convulsant period - the appearance of small fibrillary twitching of the facial muscles, descending to the muscles of the neck and upper limbs, the eyelids close, loss of consciousness occurs lasting up to 30 s;
- period of tonic convulsions - convulsive contractions of the muscles of the whole body, as in opisthotonus: the body is tense, stretched, the head is thrown back (tonic convulsions); breathing stops, the pulse is weak, and cannot be detected in peripheral vessels. - 200/100; peripheral cyanosis develops, duration - 30-40 s;
- period of clonic convulsions - the appearance of strong convulsive contractions of all muscle groups of the face, body, limbs, after 30-40 s the convulsions weaken, stop, and convulsive breathing is restored. Also signs of this pathology of pregnancy in this phase are tachypnea, separation of foam from the mouth with a pink tint due to tongue bite;
- seizure resolution period - cessation of convulsions, consciousness may be restored, but a transition to a coma or another convulsive attack may be observed.
The most dangerous periods for the mother are the second and third periods, as breathing stops and cerebral hemorrhage and cardiac arrest may develop.
When making a diagnosis, it should be taken into account that in the pathology of pregnancy, in some cases, a coma can develop without previous eclamptic attacks.
 First, a coma develops, then turns into stupor, then a partial restoration of consciousness occurs, and in the end a complete restoration of consciousness is observed, but persistent neurological damage may remain.
First, a coma develops, then turns into stupor, then a partial restoration of consciousness occurs, and in the end a complete restoration of consciousness is observed, but persistent neurological damage may remain.
According to the degree of increase in blood pressure, changes in urine, the severity of edema syndrome, the appearance of complaints in the patient and the development of eclamptic convulsions during late toxicosis, the following stages are distinguished:
- nephropathy stage I,
- nephropathy II degree,
- nephropathy stage III,
- preeclampsia and eclampsia.
Pathological condition during pregnancy: eclampsia
This pathological condition during pregnancy, such as eclampsia, is an acute cerebral edema, accompanied by gestosis: high intracranial hypertension, failure of autoregulation and impaired cerebral circulation, ischemic and hemorrhagic damage to brain structures.
Emergency care during pregnancy with gestosis includes: the creation of a therapeutic and protective regime; restoration of the function of vital organs; quick and gentle delivery.
The volume of prehospital care is determined by the patient’s condition and the severity of the clinical manifestations of late gestosis:
I degree:
- slight swelling; transient hypertension, blood pressure increases by no more than 30% (BP 140/90 - 150/90 mm Hg); A feature of hypertension at this stage is its inconstancy and lability; Traces of protein may be present in the urine.
II - III degrees:
- increased swelling; proteinuria more than 10 g/l; increase in blood pressure to 150/90 - 170/110 mm Hg. Art.
This type of pregnancy pathology, preeclampsia, is characterized by:
- an increase in blood pressure to 170/110 mm Hg. Art. and higher;
- dysregulation of cerebral blood flow;
- oliguria (diuresis 600 ml/day or less);
- low hourly diuresis (less than 60 ml/h);
- generalized edema (anasarca);
- motor and mental agitation or depression.
Emergency care for pregnant women during an attack of eclampsia, coma:
- the woman should be placed on her right side with the head end raised;
- tilt your head back to prevent tongue retraction, insert an air duct;
- mask fluorotane anesthesia against the background of neuroleptics - intravenously 4 ml of a 0.25% solution of droperidol, 2 ml of a 0.5% solution of seduxen and 2 ml of a 2.5% solution of pipolfen along with 20 ml of a 40% solution of glucose ;
- Sodium hydroxybutyrate, hexenal or sodium thiopental are used as basic anesthesia;
- artificial ventilation of the lungs in the mode of moderate hyperventilation, if necessary, tracheal intubation;
- after the end of the seizure, it is necessary to clear the mouth and nose of mucus and saliva, and remove removable dentures;
- catheterization of the main vein, bladder, insertion of a gastrointestinal tube through the nasal passage;
- with severe neurological symptoms and high intracranial pressure - diagnostic and therapeutic lumbar puncture;
- to improve the activity of the cardiovascular system, 0.25-0.5-1 ml of a 0.05% solution of strophanthin is administered intravenously, 0.5-1 ml of a 0.06% solution of corglicon is administered intravenously along with 20 ml of 40% glucose solution;
- strict control of blood pressure and diuresis.
Indications for artificial ventilation of the lungs when providing emergency care in obstetrics are:
- lack of consciousness outside of seizures;
- , not amenable to antihypertensive therapy;
- convulsive readiness that is not relieved by anticonvulsant therapy;
- repeated seizures;
- combination of seizures and bleeding.
Hospitalization is possible only after persistent relief of attacks of eclampsia and the patient’s recovery from a coma. During transportation, care should be taken because of the possibility of renewed seizures, so the patient should be placed on a stretcher and carefully transferred to an ambulance. Patients are transported on stretchers with the upper body elevated, and artificial ventilation is performed.
What other pathologies may there be in obstetrics: ectopic pregnancy
One of the causes of “acute abdomen in gynecology” is ectopic pregnancy. Acute pain in the lower abdomen, in addition to ectopic pregnancy, is possible with the following diseases: acute inflammation of the uterine appendages, malnutrition of the myomatous node, torsion of the pedicle of the ovarian tumor, acute appendicitis, renal colic, ovarian apoplexy, pelvioperitonitis, etc.
In an ectopic pregnancy, the fertilized egg implants and develops outside the uterine cavity, as a tubal abortion or as a rupture of the fallopian tube. Risk factors for ectopic pregnancy include previous salpingoophoritis, endomyometritis, abortion, surgery on the internal genital organs, hormonal disorders, etc.
In a tubal abortion, the fertilized egg is peeled off from the walls of the fallopian tube and expelled into the abdominal cavity. Since the fallopian tube contracts rhythmically, the flow of blood into the abdominal cavity is periodic.
When the fallopian tube ruptures (if menstruation is delayed by 3-4 weeks), blood enters the abdominal cavity from vessels damaged by the villi of the fertilized egg, located in the thin wall of the fallopian tube.
Ectopic pregnancy in the stage of peritoneal shock (rupture of the tube) is characterized by:
- sudden intense pain in the lower abdomen;
- irradiation of pain to the epigastric region (gall bladder, stomach);
- feeling of pressure on the rectum;
- nausea, vomiting;
- phrenicus symptom;
- frequent weak pulse;
- drop in blood pressure;
- tension and pain in the abdominal wall, Shchetkin-Blumberg symptom in the lower abdomen.
With an ectopic pregnancy, the size of the uterus is less than the expected pregnancy period, pain when the cervix is displaced, and a unilateral tumor-like formation in the area of the uterine appendages, detected during a gynecological examination.
Percussion during intra-abdominal bleeding reveals dullness in sloping areas (iliac regions), which moves with changes in body position.
This article has been read 2,561 times.
Convulsions- These are involuntary muscle contractions. Pregnant women most often experience cramps in the calf muscles (calf muscles); less often, other muscles of the legs, arms, and neck may spasm. During a cramp, a woman feels a strong, sharp pain in the muscle, mainly occurring at night during sleep or in the morning when waking up.
Information The most severe muscle spasms during pregnancy appear in the second trimester, when the fetus is actively growing and its nutritional needs increase.
Causes of cramps during pregnancy
Main reasons The appearance of muscle spasms in pregnant women are:
- Decreased micronutrient levels in the mother's body (potassium, magnesium) and vitamins(mainly vitamin B);
- Decreased glucose levels(sugar) in the blood. Glucose is the main energy source for the body; during pregnancy, it is intensively spent on the needs of the mother and the growing fetus. A pronounced lack of glucose occurs with rare and large meals, so pregnant women are advised to eat often, but in small portions;
- Decreased hemoglobin levels in blood;
- Varicose veins. During pregnancy, increased blood flow in the pelvis increases the load on the veins of the lower extremities. Due to deterioration of blood circulation in the veins, muscle nutrition is disrupted, which is a favorable background for the development of seizures;
- Inferior vena cava syndrome(observed only in the third trimester). When a woman lies in a supine position for a long time, the large uterus puts pressure on the inferior vena cava. In this regard, there is a violation of venous circulation and, consequently, a violation of the nutrition of the calf muscles;
- . When smoking 10 or more cigarettes per day, chronic oxygen deficiency develops, which has a negative effect on the condition of the muscles;
- Consuming more and other caffeinated drinks (provokes muscle tension and cramps).
First aid for seizures
If an attack of convulsions occurs, it is necessary:
- Try not to panic breathe deeply and calmly;
- Pull your toes towards you several times (repeat until muscle pain decreases);
- Carefully massage the muscle from the periphery to the center, so as not to provoke a new attack;
- Lie down with your legs raised up to improve blood circulation in the calf muscle.
Treatment of seizures in pregnant women
If cramps occur, you must immediately notify the obstetrician-gynecologist in charge of the pregnancy. If necessary, the doctor will prescribe additional diagnostic measures (biochemical blood test, blood test for glucose, general blood test, etc.) and consultations with specialized specialists (therapist, surgeon).
Treatment for seizures depends on the cause that causes them. Yes, when lack of microelements and vitamins in the body, therapy will consist of normalizing nutrition and taking a complex of multivitamins to normalize their deficiency:
- Normalization of potassium levels in the body. The richest in potassium are bananas, potatoes, broccoli, and beef liver. If there is insufficient intake of potassium from food, drug treatment is prescribed: Asparkam,;
- Replenishment of calcium deficiency. This microelement is found in larger quantities in dairy products, green vegetables (cauliflower, asparagus, broccoli), beans, eggs, and nuts. Of the medications most often used during pregnancy;
- Increasing the amount of magnesium in the body. Magnesium is found in many foods (seeds, nuts, legumes, greens, carrots, buckwheat porridge). Drug treatment includes taking.
For supporting sufficient level of glucose in the body The pregnant woman is prescribed fractional meals. The basis of the daily diet should be complex carbohydrates (brown bread, cereals, pasta, fruits and vegetables). You should avoid taking simple carbohydrates (sweets, cakes), because. with a large intake of sugar from the outside, the level of glucose in the blood drops, which leads to severe cramps.
With severe anemia treatment consists of taking iron supplements (for example,), which normalize the level of hemoglobin in the blood. light stroking from the feet to the thigh;