What does holding your breath lead to? Holding your breath has benefits for human health. Holding your breath: harm and danger. Breath holding training underwater
Today's lesson topic is holding your breath.
It is an important component of the Bodyflex technique. It is this part of the technique that has the most enemies. An article by a certain Fileev about the dangers of holding your breath has been wandering on the Internet for many years, and for a very long time I began to study this issue and, accordingly, found a complete refutation of it. The author of the article deliberately kept silent about the Verigo-Bohr effect; its essence is that it is when you hold your breath that the blood begins to be enriched with oxygen.
TOI’ll briefly describe the physiology of breathing, taking into account the Verigo-Bohr effect:
During breathing, gas exchange occurs in the lungs. Oxygen combines with hemoglobin to form oxyhemoglobin. Due to the continuous breakdown of substances in the cells of the body, carbon dioxide is constantly formed and oxygen is used, which comes with the bloodstream. In order for us to start losing weight, we try to inhale as much of the oxidizing agent as possible - oxygen, which breaks down fats into CO2 + H2O + energy (everyone felt the heat and sweating?). Hemoglobin is separated from oxygen, and carbon dioxide takes its place - dissociation of oxyhemoglobin.
It would seem that in order to consume more oxygen, you need to inhale as much of it as possible. What does slow exhalation, sharp inhalation and holding your breath have to do with it?
But for what - the Verigo-Bohr effect, translated for those who don’t particularly understand: O2 is separated from hemoglobin only with the help of CO2; it is this that destroys the unstable compound of O2 and hemoglobin. The more CO2 in the blood, the more O2 molecules will enter the cell.
We lose weight while inhaling at stage 5.
A little about the meaning of CO2:
1. Hemoglobin exchanges oxygen for CO2 and vice versa.
2. CO2 normalizes smooth muscle tone.
3. Reduces the viscosity of colloidal cell solutions.
4. Restores adequate susceptibility of the central nervous system
Moreover, Bodyflex is making life difficult for the author of this article, because he sells his own method for 4,500 rubles (this was eight years ago, not a small amount of money). And who will buy if you can lose weight completely free? Well, when his criticism extended to yoga and he said that yoga leads to cancer, I realized that we were dealing with an abnormal person with delusional ideas. So I decided to throw his article out of my memory, due to lack of evidence.
Breath-holding is practiced by doctors treating complex respiratory diseases such as asthma. And I know cases of relief or complete recovery from these problems during Bodyflex classes. Well, my own grandmother became an example for me, who simply used diaphragmatic breathing with a delay in exhalation and cured a bunch of her chronic ailments. All materials that you read below were borrowed from yoga websites. This practice is inextricably linked with yoga.
Pranayama.
Prana is one of the central concepts of yoga and Indian medicine. Translated from Sanskrit, “prana” means “breath” or “constant movement.” By prana we mean the totality of energies that exist in the universe; a certain total energy that gives people life. The manifestation of this energy can be observed and controlled through breathing. It is on breathing techniques that many yoga exercises are based, designed to control energy (including that generated during exercise) and, thus, achieve harmony with the outside world.
Pay attention to this yogi. This is what our stomach looks like when we hold our breath.
Pranayama is the control of prana, a kind of breathing exercise.Pranayama allows you to regulate and control the length of prana. Usually “pranayama” is translated as “breath control”: from the words “prana” (breath) and “yama” (control). However, the true meaning of the concept, the purpose of pranayama, is to expand prana, spreading it to passive areas of the body and inactive areas of the brain to awaken various innate abilities and further develop perception.
This is achieved by regulating breathing and conserving prana. Medieval yogis believed that breathing was closely related to the state of consciousness and sought to control the psyche by mastering breathing. Pranayama, which is primarily an energetic practice, also brings visible physiological effects.
Pranayama affects human physiology by changing the concentration of oxygen and carbon dioxide. During the breathing process, different muscle groups are used. There is a reflex effect on the brain through an effect on the olfactory and other receptors. With proper breathing, a kind of hydraulic massage of the brain and internal organs is carried out. Pranayama also affects the nervous system.
Purpose of holding your breath- gradual adjustment of the nervous system.
The main thing in the mastery of holding your breath- this is the ability to hold your breath while inhaling or exhaling correctly.
CORRECT EXECUTION . Instead, you can properly train your subconscious so that it will serve you even when you are not consciously directing your breath. Holding your breath means relaxing the muscles of the diaphragm, ribs and abdominal cavity, which are responsible for the constant movement of breathing.
To hold your breath while exhaling:
Start by exhaling completely.
Draw the Navel Center toward the spine.
Lift your lower chest and diaphragm.
Allow your upper ribs to relax.
Do not bend your spine when you try to exhale completely - this will disrupt the functioning of the diaphragm.
Tuck your chin in.
Calm down.
If your muscles begin to urge you to inhale, consciously exhale a little more. This technique can significantly increase the duration of the hold without tension or struggle.
Delays must be done on an empty stomach, when the stomach is already empty. Depending on the type of food, this occurs approximately 3-5 hours after eating.
Benefits of Holding Your Breath.
Holding your breath allows you to integrate the body's systems.
Holding your breath while inhaling can temporarily raise your blood pressure.
Holding your breath as you exhale lowers blood pressure, facilitating blood circulation.
Holding your breath while inhaling affects the sympathetic nervous system.
Holding your breath while exhaling affects the parasympathetic nervous system.
1.Breath-holding, ancient and very effective methods for cleansing your body of various energy blocks. Even karmic ones, which are sometimes not only not cleared by other methods, but simply not noticed.
2. Many manuals on breath holdings say that they are not compatible with alcohol, tea, coffee and other things. That drinking the above drinks, even in small quantities, leads to unpleasant sensations in the body.
Relax and don't think about changing your diet. If the body deems it necessary, it itself will cease to feel the need for this or that drink or this or that food, and your diet will change automatically, without effort or violence on your part.
What to remember when holding your breath!
Remember that the brain will signal to inhale when the level of carbon dioxide (CO2) in the blood rises too high. It does not respond to oxygen levels. The fact is that it reacts to the level of carbon dioxide. If you are prepared to hold your breath with a full exhalation as you exhale the carbon dioxide, you will be able to hold your breath longer and feel comfortable doing so.
If you feel dizzy and disoriented, stop. Dizziness is not enlightenment. You must build this practice regularly and patiently. Drastically pushing beyond your capabilities will not help.
As you practice, create a place of calm in your mind and observe the changes in your body and mind.
In the practice of holding your breath as you exhale, remember that the goal is to switch metabolic activity, balance the nervous system and emotional control.
Different opinions of different schools and yogis on holding the breath.
Andrey Lapin.
Breath-holding is the most powerful type of exercise that causes changes in the energy structure and in a person’s condition. “Do not inhale too hastily, inhalation gives strength and a controlled and purified body, retention gives equal consciousness and longevity, and exhalation is completely cleansing.”
Robert E. Svoboda "Aghora II: Kundalini"
Siddha Chauranginath was a student and contemporary of Gorakhnath. Legend says that he was the son of the Bengali king Devapala. Devapala's first wife died when Chauranga was still a child, and his father took a new wife, who resorted to deception to bring her own son to the throne. Chauranga was taken to a forest clearing where his arms and legs were cut off. Here he was found by Matsyendranath, who instructed Gorakhnath to take care of the limbless youth. Gorakhnath taught him the yoga of "holding the breath in a bowl" (kumbhaka), and after twelve years of this practice his limbs were miraculously restored by the power of his consciousness...
The section of pranayama that deals with holding the breath is called kumbhaka, from the word kumbha, pot. What kind of pot is this? Here the pot refers to the torso, chest and abdominal cavity in which prana can be retained. You have seen how a potter makes pots. Here you “make” a potty, giving your body complete stability. Having achieved this, you can move on to the Kevala Kumbhaka stage, in which breathing may be interrupted for several minutes. Only by mastering Kevala Kumbhaka can you make your mind completely stable. Your worship can only be stable to the extent that your mind is stable. 378. Exhalation destroys sins. One who practices breathing yoga can stop even death.
379. The natural flow of air should be delayed as much as strength allows. Exhalation should be practiced through the path of the "moon" (i.e. lunar swara) and inhalation through the "sun" (i.e. solar swara).
380. The one whose “moon” drinks from the “sun” from time to time, and the “sun” from the “moon”, will live as long as the moon and stars exist.
Six Yogas of Naropa
If the practitioner is able to hold his breath without strain for two minutes, he is considered to have fulfilled the minimum requirement on the path to mastery of the pranas; a delay of four minutes is considered average; six or more minutes is already the highest requirement.
There are many scientific opinions about breathing exercises about the unconditional benefits for the body. The development of physical abilities, holding your breath for the benefit of internal organs and the treatment of various diseases does not lose its relevance. A large influx of oxygen promotes the breakdown of fat molecules and helps get rid of extra pounds.
Breath holding training for health benefits
Breathing training is practiced by those who support a healthy lifestyle, adherents of yoga and Pilates. Breathing exercises develop the lungs. Thanks to the practice of deep breathing, metabolic processes in the body are accelerated. To do this, just straighten up and take a slow breath for 5 seconds, hold your breath and slowly exhale all the air.
To thoroughly cleanse the body of carbon dioxide, perform the “Cleansing” exercise. Slowly enter, and as you exhale, pause for 5 seconds and forcefully push the remaining air in the lungs to the exit.
Managing the respiratory process and controlling breath holding is necessary during activities such as:
· Yoga. Kumbach is the main element in such exercises; this is holding your breath.
· Diving and snorkeling. Professionals learn to concentrate and listen to their body, increase their lung capacity and hold their breath under water for a long time.
· Breathing practice. Some directions recommend the practice of stopping inhalation and exhalation to improve quality of life and spiritual balance. For example, bodyflex, rebirthing.
Benefits of holding your breath for the body
· When you hold your breath, the pressure changes: when you inhale, the blood pressure rises, when you hold your breath while exhaling, it decreases.
· With the correct technique of performing exercises based on holding your breath, a person’s physical and mental health is strengthened.
· Blood circulation improves.
· To saturate cells with oxygen, sugar is broken down, thereby increasing the level of carbon dioxide molecules in the blood and increasing body temperature, which promotes the breakdown of fat. Thus, the vacuum exercise is the most effective for restoring the abdominal muscles and breaking down fatty tissue in the waist area.
· Holding your breath with benefits for the body can last 20 seconds; such training has no contraindications.
· Regularly performing breath-holding exercises increases life expectancy.
· If the carbon dioxide level rises high, the brain sends a signal to inhale. Therefore, to hold your breath deeply, it is recommended to exhale the accumulated carbon dioxide twice.
· Dizziness is a signal to stop. Abruptly holding your breath without first preparing the body is harmful.
· Long-term breath holding is performed only on an empty stomach. Increased blood flow should flow unhindered to all internal organs and cells and saturate them with oxygen.
Harm from holding your breath
Health status indicates possible harm and threat to the body. Breath-holding practices are contraindicated for people with:
· Diseases of the endocrine system;
· Serious mental disorders;
· During pregnancy;
· Serious diseases of the heart and blood vessels;
· Difficult rehabilitation period after a long illness.
The presence of bad habits in a person can also have a detrimental effect on well-being. Stimulants in the form of tea, coffee, tobacco affect health; it will be extremely difficult to perform techniques with holding your breath. It has been noticed that with constant monitoring of health, performing long-term breath-holding techniques, a person gradually abandons the above-mentioned stimulants. The load should be increased gradually.
Breath holding technique
For beginners, practicing prolonged breath-holding is dangerous to health. It is necessary to prepare the body with a special set of physical exercises. The spine will acquire the necessary flexibility, the muscles will receive a charge of tone, and the capillaries will prepare for the load on the vessels.
1. Take a normal breath and exit at your usual pace. Relax your muscles. The ribs need to relax, the abdominal muscles should not give sudden impulses.
2. Take a deep breath and hold your breath for 10 seconds. Exhale slowly. As you exhale, it is important to control the spine - not to allow it to sag.
3. Take a deep breath and hold your breath for 15 seconds. Slowly exhale almost all the air and hold your breath for 5 seconds. Exhale.
This is the simplest exercise for those who want to improve their health. When finishing your workout, exit slowly. The subsequent inhalation should occur without a sharp intake of air. Stopping your breathing by straining the muscles of your neck and throat is dangerous. Proper holding of the breath occurs by stopping and relaxing the muscles of the diaphragm and abdominal cavity. By holding your breath as you inhale and exhale, you will calm your nervous system.
Breathing training to combat excess weight
This is actually a very easy technique to keep your figure in shape. Even if you love sweets and homemade cakes, doing this exercise regularly will keep your weight normal.
1. Straighten up, feet shoulder-width apart.
2. Take a deep breath through your nose and into your stomach.
3. Hold your breath for 16 seconds.
4. Exhale slowly for 8 seconds.
5. After exhaling, repeat the inhalation.
It is recommended to perform such exercises after eating, then excess fat deposits will not have time to form. All unhealthy products will burn out faster and will not be deposited on your waist. Holding your breath while drawing air from your stomach helps you lose weight. Holding your breath with benefit while inhaling starts the process of removing toxins from the body.
Breathing exercises should be done in a calm state, with relaxed muscles. If you do them regularly for a month or more, you can achieve weight loss results without harm to your health.
Secret techniques for holding your breath with benefits for the body
Yoga states that you need to hold your breath correctly, then all body systems begin to work correctly, stimulating cellular respiration. A powerful secret yogi technique of holding your breath for 30 minutes or more is now available for mastering. Previously, only teachers shared it with their best students.
Gradually mastering the technique of performing many yoga exercises, you can feel that you can hold your breath for a longer time with each new exercise. The distribution of energy in the body increases cell viability.
Holding your breath is a useful skill that will improve your health, replenish your strength and energize you. For lovers of scuba diving, holding your breath for a long time is simply necessary. Exercise can also kick-start your weight loss process. There are special techniques for influencing different internal organs and muscle groups to relax and relieve tension.
The answer to the question “is holding your breath beneficial or harmful?” lies in how correctly you do it and what results you want to achieve. In modern society, it is becoming common to constantly visit gyms, go for morning jogs, and master sports equipment at home. Breathing is the most important factor in maintaining health and achieving sports results; by controlling breathing, you can effectively speed up or slow down metabolism and the overall tone of the body.
Is holding your breath beneficial or harmful?
Psychological calm. An experienced yogi who practices a variety of pranayama techniques and masters them perfectly, can easily amaze an ordinary person with his seemingly supernatural abilities to hold inhalation for several minutes without any unpleasant consequences for himself.
Is it good to hold your breath?
Such breathing exercises lead to the acceleration of metabolic processes in the body; all cells, including stem cells, divide more actively. They are the indispensable “building” material for the human body. Mastering one or more techniques and regular practice helps to increase life expectancy and improve its quality. Many eastern techniques for physical and spiritual development necessarily pay attention to breathing control.
The harm of holding your breath
- Bad habits.
If, in the process of mastering the techniques, you take various stimulants (tea, coffee, tobacco or alcohol), even rarely and little by little, or have other addictions that affect your health, then you are not in danger of unpleasant consequences for the body or difficulties in performing the practices. During the training process, without any struggle, any desire to take all of the above disappears, body functions are normalized, and psychological relief from addictions occurs. Only excessive efforts at the limit of your capabilities can cause harm; by observing a smooth and gradual increase in load, you will ensure your safety and only positive results. - Diseases
Long delays should not be practiced if you suffer from heart disease or cerebrovascular accidents. If you have recently suffered from an illness and have not yet recovered, do not force things, progress smoothly and gradually. It is also worth refraining from practice if you have diseases of the internal secretion organs, so as not to cause harm to yourself. - Pregnancy
Proponents of using practices during pregnancy as an opportunity to prepare the body of mother and baby for childbirth are taking a risk. But even the slightest inaccuracy in dosage - and the harm from using the techniques will more than outweigh the benefits. You will never be able to know exactly at what point the positive effect of practice will change to a destructive one. The maximum time can be dangerous not only for the mother, but also for the child. So, if you are an expectant mother, exclude any extreme stress until 12–14 weeks, so as not to harm your baby. - Dream
During sleep, involuntary stopping may occur. It’s good if this happens for 20–30 seconds. But it happens that the duration of such a stop reaches three minutes. If you suffer from night snoring, you often (up to 400 times) stop breathing during your sleep. Such delays can easily cause harm, and even be very dangerous. Headaches, irritability, memory loss are just some of the problems that await you.
Breath holding technique
You can easily find out if you are doing the right thing. It is enough to measure your pulse to make sure that your heart beats have become less frequent, but stronger, that your chest is almost shaking from the pulsations. When completing the exercises, you need to exhale slowly (this will involve the abdominal muscles), and while exhaling, stop yourself briefly. The next inhalation should occur automatically. Calmly and without harshness.
Is holding your breath beneficial or harmful?
The answer to the question “is holding your breath beneficial or harmful?” lies in how correctly you do it and what results you want to achieve.
In modern society, it is becoming common to constantly visit gyms, go for morning jogs, and master sports equipment at home.
Breathing is the most important factor in maintaining health and achieving sports results; by controlling breathing, you can effectively speed up or slow down metabolism and the overall tone of the body.
But all this will bring tangible health benefits only if performed correctly technically. You know that you should start any exercise while inhaling, and end with exhaling, and nothing else; this is required when performing many exercises.
During the main period, we control the inhalation unconsciously, but sometimes we consciously monitor the frequency. When the body is normal, impulses from the brain cause the diaphragm and chest muscles to contract. This is how air enters the lungs.
When the exit of carbon dioxide through the lungs is blocked, it accumulates in the blood, as happens in the process of stopping the movement of air in the lungs. The activity of oxygen consumption by tissues increases, and as a result, progressive hypoxia.
Typically, the time for which a person, without special training, can consciously hold his breath while inhaling is up to one minute. After this time, the brain will be forced to take a breath. Extending this time may result in dizziness or fainting.
To correctly stop while exhaling, it is better to master one of the existing special techniques.
One of the techniques is Pranayama; it is considered one of the main techniques that yoga uses to control energy in the body. By performing it, you will ensure the normalization of all functions and renewal of the body., psychological calm.
An experienced yogi who practices a variety of pranayama techniques and masters them perfectly, can easily amaze an ordinary person with his seemingly supernatural abilities to hold inhalation for several minutes without any unpleasant consequences for himself.
This technique has not always been so popular. Only initiates used it, passing on valuable information from mouth to mouth. In the modern world, anyone who devotes enough time and effort to training can learn to stop breathing for a long time; let's consider whether this is beneficial or harmful.
By holding your breath as you exhale, you stimulate metabolism for a long time, and at the same time the body receives the energy it needs. Such the practice is useful for relieving stress, overcoming depression and excessive aggression.
It will help improve digestion and regulate the functioning of the sweat and sebaceous glands. But, the main thing is that this technique helps to reveal the reserve capabilities hidden in the body, literally renewing the nervous system.
There are a variety of delay techniques, and they are performed in different ways. Each of them is aimed at achieving a specific goal:
- Holding your exhalation for up to 20 seconds will help the body optimally absorb oxygen. This technique has no contraindications and is accessible to everyone.
- A delay for a longer time, up to 90 seconds, has an enhanced effect on the entire body, bringing significant improvements in its functions, is safe for a healthy person, however, it may pose a danger for people with vascular diseases, heart diseases, circulatory disorders, and similar diseases. It should only be performed under the supervision of an experienced mentor.
- Holding the breath for more than 90 seconds helps to renew and activate the capabilities of the body and psyche. Its consequence is the accumulation of carbon dioxide in the blood and increased absorption of oxygen by all cells of the body, which leads to accelerated regeneration, metabolism and overall restoration of the body. But strict control over your condition and preliminary preparatory training with a gradual increase in the duration of the cycle are necessary.
Such breathing exercises lead to the acceleration of metabolic processes in the body; all cells, including stem cells, divide more actively. They are the indispensable “building” material for the human body.
Mastering one or more techniques and regular practice helps to increase life expectancy and improve its quality.
Many eastern techniques for physical and spiritual development necessarily pay attention to breathing control.
The harm of holding your breath
Anyone who has decided to master the technique of holding their breath wonders whether they will harm themselves and how to do it so as to bring only benefit to the body and not harm. In any case, it is worth remembering that training at the limit, including for the maximum time, can be dangerous.
- Bad habits. If, in the process of mastering the techniques, you take various stimulants (tea, coffee, tobacco or alcohol), even rarely and little by little, or have other addictions that affect your health, then you are not in danger of unpleasant consequences for the body or difficulties in performing the practices. During the training process, without any struggle, any desire to take all of the above disappears, body functions are normalized, and psychological relief from addictions occurs. Only excessive efforts at the limit of your capabilities can cause harm; by observing a smooth and gradual increase in load, you will ensure your safety and only positive results.
- Diseases Long delays should not be practiced if you suffer from heart disease or cerebrovascular accidents. If you have recently suffered from an illness and have not yet recovered, do not force things, progress smoothly and gradually. It is also worth refraining from practice if you have diseases of the internal secretion organs, so as not to cause harm to yourself.
- Pregnancy Those who support the use of practices during pregnancy, as an opportunity to prepare the body of mother and baby for childbirth, are at risk. But even the slightest inaccuracy in dosage - and the harm from using the techniques will more than outweigh the benefits. You will never be able to know exactly at what point the positive effect of practice will change to a destructive one. The maximum time can be dangerous not only for the mother, but also for the child. So, if you are an expectant mother, exclude any extreme stress until 12–14 weeks, so as not to harm your baby.
- Sleep During sleep, involuntary stopping may occur. It’s good if this happens for 20–30 seconds. But it happens that the duration of such a stop reaches three minutes. If you suffer from night snoring, you often (up to 400 times) stop breathing during your sleep. Such delays can easily cause harm, and even be very dangerous. Headaches, irritability, memory loss are just some of the problems that await you.
Breath holding technique
Before you start doing the exercises, you should know some rules.
- First, you need to prepare your body with physical exercise for several weeks so that all your organs and tissues receive a good blood supply, providing them with everything they need, the network of capillaries is activated, the spine gains the necessary flexibility and the muscles are toned, this will help avoid unwanted problems.
- Performing techniques goes better if you are completely relaxed, down to a single muscle. This ensures blood access even to the farthest parts of the body, without kinking or squeezing important arteries
- Make sure you do your classes on an empty stomach. A full stomach significantly complicates blood flow in the abdominal area, impairing the access of nutrients to the internal organs.
- Pre-oxygenation will help you practice for a longer period of time. The more deep breaths you take beforehand, the longer you can expect to stop breathing.
For someone just starting out, holding your breath is the most versatile and most suitable technique for improving your health. Experienced yogis recommend first getting to the two-minute stop, and only after that learning other types of delays. Many practitioners, when determining the consequences of holding an exhale, focus on the benefits.
You can easily find out if you are doing the right thing. It is enough to measure your pulse to make sure that your heart beats have become less frequent, but stronger, that your chest is almost shaking from the pulsations.
When completing the exercises, you need to exhale slowly (this will involve the abdominal muscles), and while exhaling, stop yourself briefly. The next inhalation should occur automatically.
Calmly and without harshness.
Train progressively, increasing the duration of the delays each time, and then each next time the exercises will be easier for you. Only in this way will the result be benefit, not harm. You will be helped by a constant improvement in your well-being, muscle tone and good mood.
You should understand the main thing. The maximum stop is dangerous. There is no need to conduct drastic experiments. If you learn to do this correctly, you will improve your health, become a more balanced person, and discover new sources of energy in yourself. And for divers and anyone interested in scuba diving, being able to hold your breath is not only useful, but even necessary.
Source:
Holding your breath: benefits. What does holding your breath do? Breath-holding exercises
In this article we will talk about what breath holding (Kumbhaka) is, what it is intended for and what effect it has on a person’s physical, mental and spiritual state.
Benefits of holding your breath
Holding your breath has a beneficial effect on the body, because during the process of temporarily stopping breathing, the body has the opportunity to distribute the accumulated energy throughout all organs of the body. We are talking here about a special type of energy - Prana.
This concept comes from yogic practice and has not yet been studied by modern medicine, but this does not mean that such energy does not exist.
The fact that the phenomenon has not been studied simply means that at the stage of development at which the science of our days is, we have not yet reached the level to evaluate and study more complex phenomena than those that can be easily studied by empirical methods.
What is Prana
Prana is the basic energy from which everything consists. It is no coincidence that people mentally associate this energy with the breathing process, because...
saturation with Prana occurs largely thanks to it, but one should not understand by Prana the filling of the body with oxygen. Prana reaches us not only through the respiratory tract, but also through the skin and eyes.
Reducing the concept of Prana to the level of gas exchange would be a great underestimation of cosmic energy.
During inhalation and exhalation, along with oxygen and other chemicals, we receive the type of energy without which it is impossible to live. To clearly illustrate the integral role of Prana for a person, remember yourself in an office with the air conditioner on.
The air is clean and its volume is sufficient, the temperature is optimal, everything seems to be fine, but... There is one thing. Why do many people sometimes want to go out and “get some fresh air”? Is it due to oxygen starvation? Of course not. There is O2, but there is no Prana.
So we want to go out and take a deep breath.
Benefits of holding your breath for the body
Without a brief introduction explaining the energy of Prana, it would be unreasonable to start talking about breath retention, since the very benefit of holding the breath is that the Prana absorbed during the inhalation process is distributed throughout the body during the delay.
Here the practitioner’s mental processes come into play, his trained awareness, which will help him stay concentrated during the practice of holding his breath and, through mental effort, send Prana energy to those parts of the body that most need it.
What benefits does the body receive through the practice of holding the breath - Kumbhaka
- An intensive cleansing process of the entire body is underway.
- Blood flow to the heart and lungs, and with it the delivery of oxygen.
- The transition of O2 from alveolar air to blood is more efficient.
- Intensification of gas exchange processes.
- CO2 concentration increases. This gives a signal to the body that it needs to add O2, thus improving the consumption and absorption of the same oxygen. This is not a paradox, but a law. The fact is that a lack of O2 is not a signal for the body that the composition of these two gases in the body needs to be balanced; Only if the CO2 concentration increases does the body receive a command to continue the gas exchange process - this is how it becomes saturated with O2.
- Temporary acidification of the blood, which occurred due to an increase in CO2 content, facilitates the easy release of oxygen by hemoglobin.
What happens when you hold your breath
While holding your breath while inhaling, the work of internal processes in the body is activated. There are 2 types of breathing: external and internal.
Inhalation and exhalation are primarily responsible for the first type of breathing, which is necessary for the functioning of the nervous system and muscles, and the second is responsible for all cells in the body.
It is holding the breath that activates cellular respiration, which receives less attention, which leads to the aging of the physical body and an imbalance in the internal functioning of the body's systems. There is no need to explain that a lack of cellular respiration is the cause of the development of pathologies.
Holding your breath while exhaling
Holding your breath while exhaling is much more important than holding your breath while inhaling; it is more difficult to perform, and it is shorter in time than holding your breath while inhaling.
What the time parameter depends on is easy to understand if we remember that after inhalation, oxygen is still in the lungs, so gas exchange processes occur, the body does not clearly feel a lack of O2.
While when exhaling, there is no more air in the lungs, the blood is filled with CO2 and signals the body that O2 is required. Therefore, it is more difficult for us to hold our breath as we exhale.
But it is the duration of holding your breath while exhaling that is an excellent indicator of the general condition of the body. If at rest, on an empty stomach and with the correct position of the spine (fully straight), holding your breath on exhalation does not exceed 40 seconds, then everything in your body is not as good as you would like.
Ideally, you should be able to hold your breath as you exhale for at least 40 seconds, preferably longer.
What does holding your breath do as you exhale?
It is believed that if you can hold your breath as you exhale for at least 40 seconds, then your body is in excellent shape and your carbon dioxide levels are at the proper level.
Let us remember that it is vital that this level does not fall below 6-7%, because CO2 is responsible for metabolic processes in the body and the synthesis of amino acids, is a vasodilator and an excellent sedative.
The psychological state depends on the ratio of oxygen and carbon dioxide in the body. While holding your breath, the work of the vagus nerve, which is responsible for the respiratory, digestive organs, heart and blood vessels, is stimulated.
Unlike the sympathetic system, which activates the body, the vagus nerve calms the heart rate and slows the pulse, but it also has a beneficial effect on the digestive system, increasing salivation and sweating.
This suggests that the Yang process predominates in the body. It is associated with heat production. It is no coincidence that when you start practicing pranayama with Kumbhaka while exhaling, then even in a cool room you will feel warm.
This is the body’s reaction associated with the activation of the vagus nerve.
How to increase breath retention
In order to increase breath retention, you can start practicing pranayama. This is a technique for controlling and managing breathing. It is part of the eight limb yoga system and directly follows the practice of asanas.
Before you start practicing pranyama, perform a set of asanas for the spine. It is very important. Many beginners are often unaware of how important it is to prepare the spine before practicing breathing exercises, since the breathing process is connected to the spinal cord.
It is necessary not only to perform pranayama in the correct position - in Padmasana or Siddhasana, but also to prepare the spinal column itself. Let us remember that the energy channels Ida, Pingala and Sushumna are located along the spine. By performing asanas, you will also activate the flow of Prana through the nadi channels, including the three most important ones.
Inhale - and God will let you in, hold your breath - and God will remain with you. Exhale - and you will let God come to you, hold your exhalation - and you will merge with Him. Krishnamacharya
Breath-holding exercises
Once you have prepared, you can perform pranayama. To begin with, it is better to opt for simpler pranayama, such as Samavritti, or “square” breathing, and Anuloma Viloma.
At first, you can omit holding your breath while exhaling and perform only Kumbhaka while inhaling.
This will allow you to prepare for more complex pranayamas, and later you can complicate the performance by doing both Kumbhakas - on inhalation and on exhalation.
Other pranayamas include Viloma and Ujjaya, Surya Bhedana and Chandra Bhedana pranayama. When holding your breath, it is better to focus on the classic proportion 1:4:2 (1 is inhalation, 4 is holding your breath, 2 is exhaling). The unit of counting can be taken as pulse beats or steps if you perform pranayama while walking.
Before performing pranayamas with Kumbhaka, it is better to prepare the lungs by “ventilating” them with the help of Bhastrika or similar pranayamas.
Why hold your breath in pranayama?
The important role of Kumbhaka in pranayama is to increase, redirect and redistribute the Prana received during inhalation in the body.
You consciously regulate the flow of Prana in a more effective way, preventing it from settling and stagnating in the lower chakras.
Redistribution of Prana energy
Now that the energy is concentrated in the higher parts, your consciousness begins to work differently. It is no coincidence that pranayama practitioners notice how their interests in life change.
The spiritual sphere is activated, so what previously would have seemed like something speculative, devoid of connection with real life, begins to look different - now it truly interests you, and all because your understanding of life and its values has changed.
If in the past your consciousness was centered in the area of the three lower chakras, then after practicing holding your breath in pranayama, you noticed changes in your psychological state and life values.
This effect also occurred as a result of simultaneous meditation practice. When you concentrate on your breathing and working with Prana, your brain is at its most efficient.
Its untapped possibilities are opening up.
This is not siddhi yet, but even such small changes will indicate to you the extent to which we underestimate our abilities, considering analytically acquired knowledge to be the only reliable support in life.
You will understand that a person can rely not only on logic, but also on what is called direct knowledge. Gradually it will become more accessible to you. The main thing is to practice and everything will come. But do not be zealous in practice, exploiting only the volitional factor. May you enjoy watching your breath and learning how to perform Kumbhaka correctly. Love what you do.
What does holding your breath do?
The practice of pranayamas is based on holding the breath. If it weren’t for it, then all that would be left of pranayama would be breathing exercises for rhythmic breathing and ventilation of the lungs. Pranayama would cease to exist, because its meaning is Kumbhaka - holding the breath.
When you hold your breath, all processes in the body are activated: physiological, mental, and energetic.
Correctly performed breath holding is one in which the practitioner increases Prana and distributes it throughout the body. His consciousness is one-pointed and concentrated, so at the same time he practices mindful directed attention, which is a form of meditation. The rest of the thoughts leave the mind, and nothing remains for the practitioner except the breathing process.
Remember the wisdom that Buddha said: “The mind is everything. You become what you think about." Become the very breath and Prana, then you will find yourself. They are the source of life for body and soul.
Source:
Holding your breath has benefits for human health. Holding your breath: harm and danger
There are many scientific opinions about breathing exercises about the unconditional benefits for the body. The development of physical abilities, holding your breath for the benefit of internal organs and the treatment of various diseases does not lose its relevance. A large influx of oxygen promotes the breakdown of fat molecules and helps get rid of extra pounds.
Breath holding training for health benefits
Breathing training is practiced by those who support a healthy lifestyle, adherents of yoga and Pilates. Breathing exercises develop the lungs. Thanks to the practice of deep breathing, metabolic processes in the body are accelerated. To do this, just straighten up and take a slow breath for 5 seconds, hold your breath and slowly exhale all the air.
To thoroughly cleanse the body of carbon dioxide, perform the “Cleansing” exercise. Slowly enter, and as you exhale, pause for 5 seconds and forcefully push the remaining air in the lungs to the exit.
Managing the respiratory process and controlling breath holding is necessary during activities such as:
· Yoga. Kumbach is the main element in such exercises; this is holding your breath.
· Diving and snorkeling. Professionals learn to concentrate and listen to their body, increase their lung capacity and hold their breath under water for a long time.
· Breathing practice. Some directions recommend the practice of stopping inhalation and exhalation to improve quality of life and spiritual balance. For example, bodyflex, rebirthing.
Benefits of holding your breath for the body
· When you hold your breath, the pressure changes: when you inhale, the blood pressure rises, when you hold your breath while exhaling, it decreases.
· With the correct technique of performing exercises based on holding your breath, a person’s physical and mental health is strengthened.
· Blood circulation improves.
· To saturate cells with oxygen, sugar is broken down, thereby increasing the level of carbon dioxide molecules in the blood and increasing body temperature, which promotes the breakdown of fat. Thus, the vacuum exercise is the most effective for restoring the abdominal muscles and breaking down fatty tissue in the waist area.
· Holding your breath with benefits for the body can last 20 seconds; such training has no contraindications.
· Regularly performing breath-holding exercises increases life expectancy.
· If the carbon dioxide level rises high, the brain sends a signal to inhale. Therefore, to hold your breath deeply, it is recommended to exhale the accumulated carbon dioxide twice.
· Dizziness is a signal to stop. Abruptly holding your breath without first preparing the body is harmful.
· Long-term breath holding is performed only on an empty stomach. Increased blood flow should flow unhindered to all internal organs and cells and saturate them with oxygen.
Harm from holding your breath
Health status indicates possible harm and threat to the body. Breath-holding practices are contraindicated for people with:
· Diseases of the endocrine system;
· Serious mental disorders;
· During pregnancy;
· Serious diseases of the heart and blood vessels;
· Difficult rehabilitation period after a long illness.
The presence of bad habits in a person can also have a detrimental effect on well-being. Stimulants in the form of tea, coffee, tobacco affect health; it will be extremely difficult to perform techniques with holding your breath.
It has been noticed that with constant monitoring of health, performing long-term breath-holding techniques, a person gradually abandons the above-mentioned stimulants.
The load should be increased gradually.
Breath holding technique
For beginners, practicing prolonged breath-holding is dangerous to health. It is necessary to prepare the body with a special set of physical exercises. The spine will acquire the necessary flexibility, the muscles will receive a charge of tone, and the capillaries will prepare for the load on the vessels.
1. Take a normal breath and exit at your usual pace. Relax your muscles. The ribs need to relax, the abdominal muscles should not give sudden impulses.
2. Take a deep breath and hold your breath for 10 seconds. Exhale slowly. As you exhale, it is important to control the spine - not to allow it to sag.
3. Take a deep breath and hold your breath for 15 seconds. Slowly exhale almost all the air and hold your breath for 5 seconds. Exhale.
This is the simplest exercise for those who want to improve their health. When finishing your workout, exit slowly. The subsequent inhalation should occur without a sharp intake of air.
Stopping your breathing by straining the muscles of your neck and throat is dangerous. Proper holding of the breath occurs by stopping and relaxing the muscles of the diaphragm and abdominal cavity.
By holding your breath as you inhale and exhale, you will calm your nervous system.
Breathing training to combat excess weight
This is actually a very easy technique to keep your figure in shape. Even if you love sweets and homemade cakes, doing this exercise regularly will keep your weight normal.
1. Straighten up, feet shoulder-width apart.
2. Take a deep breath through your nose and into your stomach.
3. Hold your breath for 16 seconds.
4. Exhale slowly for 8 seconds.
5. After exhaling, repeat the inhalation.
It is recommended to perform such exercises after eating, then excess fat deposits will not have time to form. All unhealthy products will burn out faster and will not be deposited on your waist. Holding your breath while drawing air from your stomach helps you lose weight. Holding your breath with benefit while inhaling starts the process of removing toxins from the body.
Breathing exercises should be done in a calm state, with relaxed muscles. If you do them regularly for a month or more, you can achieve weight loss results without harm to your health.
Secret techniques for holding your breath with benefits for the body
Yoga states that you need to hold your breath correctly, then all body systems begin to work correctly, stimulating cellular respiration. A powerful secret yogi technique of holding your breath for 30 minutes or more is now available for mastering. Previously, only teachers shared it with their best students.
Gradually mastering the technique of performing many yoga exercises, you can feel that you can hold your breath for a longer time with each new exercise. The distribution of energy in the body increases cell viability.
Holding your breath is a useful skill that will improve your health, replenish your strength and energize you.
For lovers of scuba diving, holding your breath for a long time is simply necessary. Exercise can also kick-start your weight loss process.
There are special techniques for influencing different internal organs and muscle groups to relax and relieve tension.
Source: zhenskoe-mnenie.ru
Source:
Breathing exercises for weight loss - benefits and exercises
Breathing is muscular work. During breathing, a person's lungs do not work spontaneously. The rib cage, intercostal muscles, and diaphragm expand the rib cage, reducing air pressure in the lungs. This causes air to be sucked into the lungs. As you exhale, other muscles compress the chest and force air out of the lungs.
A person who wants to develop eventually comes to breathing exercises. It includes correct breathing, the ability to work with the energy of the elements and the ability to integrate into the Bi-field structure.
This is an intermediate stage in the mental, biofield and physiological development of a person. It is often missed in the process of self-development, but if it is mastered, a person has the ability to perceive the world more broadly. Breathing techniques are sometimes taught in pranayama and yoga.
Breathing is associated with the movement of certain resources in the body.
If the air in the environment is bad, then the way you breathe does not matter. If you have a normal environment with clean air, then pranayama will preserve energy resources and help develop abilities.
Subconsciously, a person himself uses correct breathing and some elements of pranayama.
But if you have knowledge, then this can be deepened and brought to a subtle level, when, with the help of breathing, you will solve problems that cannot be solved in a simple way.
With the help of breathing exercises you can cure many diseases and get rid of excess weight.
When using breathing exercises for weight loss, you need to know the principle of its action. During deep breathing, there is a large influx of oxygen to the cells. Oxygen oxidizes fat molecules and turns fat into carbon dioxide, which is expelled when you exhale. The most effective exercise for reducing waist size and burning belly fat is “Vacuum”.
How to do:
Perform the exercise on an empty stomach or 3 hours after eating.
- Half an hour before performing the exercise, drink a glass of water at room temperature.
- To feel the degree of tension in the internal abdominal muscles, place your hands on the back of a chair or wall.
- Take a deep breath.
- Slowly exhale the air from your lungs while drawing in your stomach.
- After you have completely exhaled all the air, hold your breath for a few seconds.
- Take a breath.
- Do the exercise 15 minutes a day. You can divide this time into three five-minute periods and do a “vacuum” in the morning and evening.
An equally effective exercise for losing weight is the “Fire Breathing” exercise. This is the breathing element of Kundalini yoga. With its help, decay products are removed from the body, carbon dioxide processed from fat is sent to the lungs and expelled.
It is not advisable to practice “Fire Breathing” during pregnancy and during menstruation.
How to do:
- Stand straight, back straight.
- Inhale through your nose.
- Contract your abdominal muscles.
- Exhale sharply through your nose, pressing your abdominal muscles with your hands.
- Do belly breathing at intervals of 2 times per second. The chest is in place and does not move.
- After a few minutes, feel the heat throughout your body.
Breathing exercises for weight loss burn 140% more body fat than jogging and maintain a high metabolic rate.
The popularity of breathing exercises by Alexandra Nikolaevna Strelnikova is justified by scientific evidence. It helps heal many diseases, such as hypertension, ischemia, osteochondrosis, heart failure, asthma, excess weight, nervous diseases, stuttering and sexual disorders.
Strelnikova was an opera singer, so her breathing technique is used to restore her voice, as well as for cardiovascular diseases.
Warm-up exercise “Palms”
- Bend your elbows and open your palms. Press your elbows towards your body. Shoulders slumped.
- Take 8 noisy, sharp breaths while bending your palms.
- Pause for 3-5 seconds and catch your breath.
- Repeat the exercise 12 times.
Exercise "Hug your shoulders"
- Bend your elbows in front of you, as if hugging yourself.
- Place your right hand on top of your left.
- Take 8 sharp, noisy breaths, while slightly spreading your arms and hugging yourself again.
- Don't change hands. The right one should be on top all the time.
- Repeat the exercise 12 times.
Exercise "Epaulettes"
- Lower your arms down and clench your fists.
- Take 8 sharp breaths, straightening your fists and slightly bending your elbows, as if suddenly throwing something out of your hands.
- Pause for 3-5 seconds.
- Repeat 12 times.
Exercise "Pump"
- Stand up straight with your torso slightly bent.
- Extend your arms perpendicular to the floor.
- Take 8 sharp breaths, raising and lowering your arms and tilting your body, as if pumping a pump.
- Take a break.
- Repeat 12 times.
Exercise "Cat"
- Stand straight with your elbows bent 90 degrees.
- Take 8 sharp breaths, while squatting slightly and turning your body to the right and left alternately.
- Take a break.
- Repeat 12 times.
Exercise "Turns"
- Stand up straight, arms down.
- Take 8 sharp breaths, rotating your head left and right with each one.
- Take a break.
- Repeat 12 times.
Exercise “Chinese dummy”
It’s done the same way as turns, only you don’t need to turn your head, but tilt it left and right. Shoulders are motionless.
Exercise "Steps"
- Stand up straight, arms down.
- Take 8 sharp breaths, with each breath lifting your legs alternately.
- Take a break.
- Repeat 12 times.
Exercises should be done in 3 sets of 32 times without breaks.
You need to approach breathing practices carefully. The body is designed in such a way that during physical activity the heart rhythm changes and breathing movements become greater.
If we do breath-holding exercises in a calm state for a month, lengthen the exhalation or inhalation, changes in blood pH and other indicators of the body occur.
The endocrine system and immune system functions change.
At the beginning of classes, a person may experience an influx of energy and an increase in energy abilities. After some time, a sharp decline and weakness may appear.
Symptoms similar to those of chronic fatigue appear. In a relaxed state, a person’s breathing is almost not felt and the need for oxygen is sharply reduced.
If we carry out deep breathing at this time, we harm the body.
People with the sympathetic nervous system, which is associated with increased blood pressure - a red face, flushed cheeks and tachycardia - should not hold their breath while inhaling. They will stimulate increased blood pressure and can lead to a stroke. It is better for such people to hold their breath while exhaling.
Suitable exercise:
- Take as full and quick a breath as possible through your nose.
- Relax your abdominal muscles to get as much air into your lungs as possible.
- While holding your breath, pull in your abdominal muscles, lifting your stomach.
- Place your hand on your stomach for better control of the movement.
- Bend your torso forward as much as possible, and slightly round your shoulders.
- Squeeze your gluteal muscles.
- Hold this position for 10 seconds.
- Straighten up without exhaling.
- Exhale slowly with resistance. It's like you're blowing through a straw.
- Do not relax your abdominal and gluteal muscles until you finish exhaling.
Do this exercise for 15 minutes a day, three sets of 5 minutes each.
The main thing is to do all breathing exercises in a calm emotional state. Before starting gymnastics, consult your doctor to avoid negative results.
Source:
Bodyflex for the abdomen and sides - a set of breathing exercises for weight loss with video
Special breathing exercises have a great impact on the process of losing weight, so bodyflex exercises for the abdomen and sides are very effective.
They help tighten problem areas by saturating tissues and cells with oxygen. This technique works great even for those who have never been an athlete or who are prohibited from intense training.
How to do breathing to lose belly fat and several effective exercises are described in detail in the information below.
Do not underestimate breathing exercises for losing weight in the abdomen and sides. They help get rid of extra pounds just as much as physical exercise.
A set of exercises based on holding your breath for a few seconds in combination with stretching is called bodyflex for the abdomen and sides, or bodyflex.
This training program is very popular along with oxysize, because it also helps you lose weight without dieting or daily visits to the gym. The basis of bodyflex is active diaphragmatic breathing, i.e. belly breathing, which promotes:
- expansion of lung volume;
- saturation of blood with oxygen;
- acceleration of metabolism;
- increased fat burning.
To really lose weight using this technique, it is important to follow its technique and a few more basic rules. The main thing is to start exercising only on an empty stomach. The optimal time for training is considered to be the first half hour after waking up. Other recommendations for beginners:
- Regular training. It is necessary to determine a time that is convenient for you so that you can practice bodyflex daily during the selected period. It only takes 15 minutes a day. There should be no absences from classes.
- Changes. To track the effectiveness of bodyflex, it is recommended to take measurements with a centimeter tape of the main volumes of the figure - the abdomen and sides, hips, chest. You can check them every week.
- Nutrition. Breathing exercises do not require dieting, but you should still avoid junk food.
- Time. If you don’t have time for bodyflex in the morning, you can do it in the evening, but your last meal should be 2 hours before class.
The key to success is to perform proper breathing to lose belly fat. The technique is not that complicated if you understand it step by step. You can master it using the following instructions:
- Position. The specific position must be taken depending on the exercise being performed. In general, for convenience, you can simply stand up straight, place your feet shoulder-width apart, and ideally, rest your palms on your knees.
- Exhale slowly. It is necessary to purse your lips into a tube, and then smoothly exhale all the air in your lungs.
- Intense deep breath. After exhaling completely, you need to inhale sharply through your nose to take in as much air as possible.
- Exhale quickly. Next, you need to fold your lips into a tight line and forcefully exhale air through your mouth, making a sound similar to “groin.” In this case, the stomach should be pulled in and practically pressed against the spine.
- Holding your breath. At this stage, you need to take the position of the exercise being performed or remain in the same position if you are just training the bodyflex technique. Next comes holding your breath for 8-10 counts, and for beginners - for 5.
- Relaxation. After holding your breath, you can return to normal breathing and relax.
Breathing exercises
Bodyflex for the abdomen and sides is an easy way for men and women to reduce their waist and get rid of excess fat deposits on it.
To achieve a more effective result, not just correct breathing using the technique described above, but also several exercises will help. By doing them daily, you will be able to notice a decrease in your waist size within a week.
Each exercise helps develop one or another part of the abs, so it’s better to do them in combination, one after the other.
Side stretch
The first exercise to create a flat stomach is stretching. It will help tighten up this problem area. The algorithm for performing the exercise is very simple:
- Take a breathing position - spread your legs shoulder-width apart, bend them slightly, push your buttocks back, and place your palms just above your knees.
- Perform the breathing technique itself described above.
- At the delay stage, do the following - rest your left elbow on your left knee, transfer your body weight to the same leg, and stretch the other back. Next, raise your right hand and stretch it upward so that you feel the stretching of the muscles from the armpit to the waist.
- Count to 8, then take the starting position.
- Repeat 3 times on each side.
Another necessary exercise for working out the waist muscles is the abdominal press. It is already performed in a lying position, but breathing for losing belly fat remains the same. The sequence of actions is as follows:
- Lie on your back, bend your legs, but leave your feet on the floor.
- Without raising your head, perform a breathing exercise, then, at the stage of holding your breath, stretch your arms up, lifting your shoulders off the floor. At the same time, tilt your head back.
- Next, gradually take the initial pose and immediately repeat the exercise 2 more times.
Exercise scissors
Although it is incorrect to divide the abs into upper and lower, these parts are actually worked out differently. The latter is more difficult to train, which is why it is often hidden under a thicker layer of fat. The “scissors” exercise will help you reduce it. This is also belly breathing for weight loss in a special position. The execution algorithm is as follows:
- Again, lie on the floor, place your hands under your buttocks.
- Next, do the bodyflex breathing exercise again and, during the delay stage, raise your legs about 10 cm from the floor.
- Perform swings with a wide amplitude, crossing your legs alternately. Count to 8-10.
The ability to hold your breath is the basis for this and, in general, a useful skill for life.
Below we will look at examples of exercises and tips that will help you learn how to learn to hold your breath for a long time.
Dry training is safer than activities in the water. If you do the exercises incorrectly, you can bring yourself to a state of fainting, which under water is life-threatening, but on land, in most cases, does not pose a life-threatening threat.
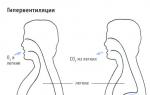
Hyperventilation
This exercise teaches you how to draw the maximum amount of oxygen into the blood, more than with normal inhalation. It consists of a series of frequent, deep, slow breaths and short, quick exhalations.
It is performed as training before a dive or immersion.
Number of inhalations/exhalations – from 4 to 6.
Movement of the chest while holding your breath
This exercise allows you to get additional oxygen by expanding the lungs and increasing the area of the alveoli.
- At first - hyperventilation(several frequent deep breaths and exhalations).
- After - take a full deep breath and stop breathing.
- During a stop - arm movements to move the chest and lungs. The arms are extended forward, pulled back in an extended position, and brought together in front. The fingers are clenched into a fist while performing movements.
Relaxation

The ability to relax is necessary to take a full deep breath and saturate the blood with plenty of oxygen. Constriction reduces the volume of the lungs and does not allow you to breathe deeply.
In this regard, it is important to learn to control your condition and, if necessary, to breathe in as deeply as possible.
Breath holding training underwater
In order to learn to hold your breath for a long time, exercises in water are first of all important, which are aimed at training the lungs and accustoming the body to a small amount of oxygen. They can be static and dynamic.
Among static exercises– many of those that are performed on land.
Among the dynamic– a series of dives and dives at various distances and periods of time.
For training on the water, the presence of a partner, assistant or coach is required.
Interval exercises: static and dynamic
First series of approaches consists of performing breath holds of equal duration, with the rest time between them being reduced. Namely:
- Diving for 1 minute (or diving with fins 20-25 m). Free breathing for 1 minute 30 seconds.
During rest, you need to breathe calmly, without deep breaths and hyperventilation.
- Diving 1 minute (or diving 20-25 m). Rest for a minute and 15 seconds.
- Dive for 1 minute or 20-25 m and normal breathing for 1 minute.
- Diving – 1 min. or 20-25 m and breathing for 45 seconds.
- Diving or 20-25 m, breathing 30 seconds.
- Dive for 1 min. (diving 20-25 m), breathing 15 seconds.

Since this series of approaches is difficult for a beginner, at the initial stage, you can hold your breath for less than 1 minute, or dive less than 20 m.
For example, start training with a delay of 20 seconds (or 10 m). Next, if possible, increase the distance and time of inhalation holding.
Second series of approaches differs in that the rest time remains constant, the time you hold your breath changes.
The exercise will also have a dynamic and static option. In the static version, they hold their breath while lying on the water, and rest with their feet resting on the bottom of a pool or river (in shallow water). In dynamics, they hold their breath while swimming underwater with fins for several tens of meters, and during rest they swim on the surface and breathe freely, or stand in the water.
- Dive 40 m (or hold for 2 minutes), breathe for 2 minutes.
- Diving 35 m (or holding for 1 minute and 45 seconds), breathing for the same 2 minutes.
- Dive 30 m (or hold for 1 minute 30 seconds), breathe for 2 minutes.
- Diving 25 m (or 1 minute and 15 seconds), breathing - the same 2 minutes.
- Dive 20 m (1 minute), breathe 2 minutes.
Note: the rest time between dives can be measured not in minutes, but in the number of breaths. For example – 10 or 20 breaths. Then, during training, the number of breaths is gradually reduced - 10, 8, 6, 4.
When performing the listed exercises, acid accumulates in a person’s blood and acidosis develops. Periodically performing these exercises trains the body to work in conditions of increased blood acidity, as well as to quickly recover from acidosis.
Intermittent exercise
This - frequent short breath delays with short rest periods.
They aimed at accelerating heart rate, which allows you to pump blood faster and saturate it more fully with oxygen when you inhale.
It is useful to perform these exercises before a deep, long dive in order to accommodate more oxygen in the blood during the subsequent inhalation.
There are a lot of options for performing intermittent exercises, we will give one of them.
You should perform 10 breath holds for 30 seconds with rest periods separating them (also 30 seconds). Repeat the series of exercises 2 or 3 times.
In the static version, intermittent exercises are performed while standing in the water. In dynamic mode, they swim on the surface of the water, periodically diving to a shallow depth.
Intermittent exercise can also be done on land.
Holding your breath in static
You can also train holding your breath under water in a static state - by immersing your face in the water and keeping your body still.
This exercise can be performed at different depths, namely:
- On the surface of the water - lying face down on the water.
- Sitting at the bottom of the pool.
- Standing at the bottom of the pool.
- At the bottom of the pool - lying face down.
Useful tips for practicing holding your breath are outlined in these two videos:
How to increase lung capacity
The time for which a person can hold his breath depends on the volume of the lungs and the efficiency of oxygen consumption within the body. An increase in lung size does not mean physical stretching or expansion of the lungs. This is understood as an increase in their ability to accommodate a large volume of air and saturate a large amount of blood with oxygen.
The volume of air that can fit in the lung cavity with one breath depends on the development of the pulmonary muscles. And the amount of oxygen that enters the blood with each breath depends on the surface area of the pulmonary alveoli. The larger it is, the more oxygen the blood will saturate with each breath. The greater the amount of oxygen in the blood, the longer the diving time you can expect.
Do cardio exercises to increase lung capacity. They are performed on land and in water, and also transfer part of the training to high mountains, or imitate work in conditions of lack of oxygen (imitate high altitudes by slightly squeezing the nose).
Playing wind instruments can also increase lung capacity.
Cardio exercises
 Options for cardio exercises on machines
Options for cardio exercises on machines Cardio exercises teach the body to work in conditions of oxygen deficiency, which is formed during prolonged physical activity, which develops the lungs and improves the body’s ability to efficiently consume oxygen.
Examples of cardio exercises:
- Long distance running. For training purposes, while running, concentrate on the number of inhalations and exits.
They determine how many breaths there are for a certain number of steps (for example, 10 steps) and try to reduce their number by at least 1 or 2 breaths.
- Swimming in fins with a snorkel and mask.
- Intense swimming, And .
- A ride on the bicycle.
The duration of cardio exercises ranges from 20 to 50 minutes (daily or every other day).
Exercise to develop the lower part of the lungs
Typically, most people have little use of the lower region during daily breathing. Therefore it is less developed. If you fully include the lower sections in the breathing process, this will increase the volume of your lungs.
To do this, perform an exercise in which it is necessary to breathe only in the lower part for 1-2 minutes:
- To control body movements hands are placed: one on the stomach and the other on the chest.
- Next, while inhaling, make sure that the hand on the chest did not move(air did not fill the middle and upper parts of the lungs), and hand on stomach raised and sank (air fills the lower part of the lungs).
Aperture control
 The diaphragm plays a huge role in breathing
The diaphragm plays a huge role in breathing Inhaling with slow exhalation teaches you to control the movement of the diaphragm and thereby completely fill the lower section of the lungs with air. It also teaches you how to properly recover from prolonged breath holding.
This is done as follows:
- Deep breath.
- Stop breathing for 1 minute.
- Exhalation slows down and is done through pursed lips.
Note: according to freedivers, a deep breath should take up to 20 seconds.
Breathing while walking
During slow breathing, you need to count the number of steps that occur for each exhalation/inhalation. Afterwards, they try to increase the number of steps (by one, two or three) that occur per inhalation and exhalation.
Additional Methods
Additional options for increasing lung capacity are discussed in this video:
Training Basics
The success of learning to hold your breath depends on a properly structured complex and regimen of stress and training.
Training mode
The training regimen is prescribed based on general recommendations (1 or 2 times a day, possibly every other day), a general set of exercises, taking into account your own individual characteristics.
The frequency of training is selected in such a way that they weren't too frequent(the body must recover) and too rare(the body will have time to relax more than necessary).
Training effect
 The training effect can be achieved by freediving
The training effect can be achieved by freediving The purpose of the classes is to learn to hold your breath for a long time, to accustom the body to work in conditions of a lack of oxygen and an increased amount of carbon dioxide, and also to teach it to store a large amount of oxygen in one breath.
This goal is achieved in the process of performing various exercises thanks to the body's adaptive reactions. Eg, Holding your breath decreases your heart rate. This is a natural reaction to a lack of oxygen in the blood. When you surface, your heart rate is restored. This adaptation reaction is called temporary.
For divers, underwater athletes, hunters and fishermen, and people who often hold their breath, temporary adaptation turns into long-term adaptation. That is, even after surfacing, the pulse continues to remain reduced. This phenomenon is called sports bradycardia. Athletes need it for efficient use of oxygen and high-quality diving.
The long-term fitness effect explains why training needs to be stable and last for a fairly long period of time.
Freediving trainer - diving without scuba gear. Freediver athletes dive in a pool or in the sea. At competitions, holding their breath, they lie quietly, swim as far as possible or dive as deep as possible.
“The world records are fantastic - holding your breath for more than 11 minutes at rest, 200 meters long in a pool and 217 meters deep. But what happens in the body at this time is not yet fully understood, and the long-term effects are also unclear,” said Irina.
Stefan Mifsud sets world record for breath-holding: 11 minutes 35 seconds
The longer the delay lasts, the more carbon dioxide accumulates in the blood, and the oxygen content decreases. Researchers have suggested that under such conditions, the functioning of the brain may change: the speed of reactions and thought processes will decrease, and attention will deteriorate.
How long can you not breathe?
The study compared the results of two groups of subjects: 13 professional freedivers and nine people without special training. One of the professional freedrivers held his breath the longest - for 5 minutes 45 seconds.
It is believed that an ordinary person can go without breathing for about a minute, but during the study it turned out that this is not so. If you explain to the participant in advance what awaits him and what sensations he will experience, then the time of holding his breath can be increased, removing the psychological barrier. Thanks to this, the best result in the control group was 4 minutes 23 seconds.
Freediver training in the pool. Photo: Elina Manninen/Shutterstock
“If you know what happens to the body during breath-holding, what you should be afraid of and what not, you can calmly accept unpleasant sensations and increase the breath-hold to 2-3 minutes. Until involuntary contractions of the diaphragm begin—a reflex urge to inhale—there is nothing to fear,” said Patricia Ratmanova.
What happens when you hold your breath for a long time
In order to assess brain function and the state of the body during breath holding, the researchers recorded an electroencephalogram, cardiogram, blood pressure, oxygen levels in the blood and brain tissue, and other indicators. Immediately after holding their breath, the subjects were given a test of attention and hand-eye coordination—a proofreading test. Volunteers received a sheet with rows of letters printed in random order. Their task was to look through the letters and look for those that were named by the researchers. They had to underline one of the given letters and cross out the other.
“We expected brain function to deteriorate, but this turned out to be completely wrong. Brain activity did not change, attention did not decrease - we did not find any negative changes, even with long breath holds,” said Patricia.
Scientists have suggested that in humans, as in marine mammals (whales, dolphins, seals), the so-called “diving reflex” is triggered. It aims to protect the brain and heart from lack of oxygen.

A subject in the control group during a study in the laboratory of the physiology of muscle activity of the Institute of Medical and Biological Problems of the Russian Academy of Sciences. Photo courtesy of Patricia Ratmanova
During the “dive reflex,” blood vessels in the periphery of the body constrict, which reduces blood flow to the muscles and oxygen consumption, blood pressure increases and the heart rate slows down. As a result, blood flows primarily to the heart and brain. In the brain, on the contrary, blood vessels dilate, increasing blood flow and oxygen supply to brain cells. As a result, brain function does not suffer when holding your breath.
Meditation and Holotropic Breathwork
However, breathing exercises can affect brain function, sometimes this effect is positive, sometimes it is dangerous.
“Techniques used in meditation typically involve slowing down the breathing rhythm or holding the breath for short periods of time. Their main task is to help a person concentrate on the sensations of his own body and distract from external stimuli. There is no harm from such breathing exercises,” Patricia explained.
Hyperventilation, which, for example, underlies holotropic breathing, can be dangerous.
“When we breathe deeply and rhythmically, carbon dioxide is washed out of our blood. The body reacts to this by reflexively constricting blood vessels. As a result, despite deep breathing, so-called cerebral hypoxia occurs - a lack of oxygen in the brain,” the researcher said.
This may trigger an epileptic attack in some people. “There are those who are predisposed to epilepsy and don’t even know it. Such people can live their entire lives without a single attack if they are not provoked by hyperventilation. And after epilepsy manifests itself for the first time, attacks may recur,” the scientist warned.