Diarrhea in an elderly person for a long time. Water diarrhea in an adult: treatment. Tablets for diarrhea in adults. Rice cereal decoction
Diarrhea in older people is a dangerous condition because in old age a person acquires many chronic diseases, and the immune system is no longer as strong as in younger patients.
Diarrhea in the elderly: causes, treatment and prevention. This will be discussed in the article.
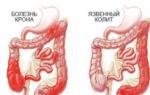
Crohn's disease
This is an inflammatory pathology that affects the lower part of the small intestine, but can spread its negative effect to almost any part of the digestive tract.
Clinical picture
Crohn's disease can be severe, but in older people it is mainly localized near the anus. The patient complains of fever, chills, and fatigue. With purulent complications, the temperature rises to 40 degrees. A person suddenly loses weight because the intestines do not absorb nutrients in full.
There is constant diarrhea in old age, sometimes with rotting processes of undigested food residues in the intestines. There may be blood in the stool. The stomach hurts, the pain is similar to acute appendicitis. Intestinal obstruction, abscesses develop, and the intestinal walls become ulcerated. Internal bleeding due to ulcers and fistulas is possible.
A person's large joints are affected and vision decreases.
A rash often appears on the skin.
When it becomes chronic, anal fissures, ulcers, fistulas, internal bleeding appear, sepsis and the development of tumors are possible.
Ulcerative and infectious colitis
 The appearance of colitis in the intestines in elderly patients is associated with damage to the arteries by atherosclerosis. When they become blocked, tissue necrosis begins. Another cause of colitis is protrusion of the intestinal walls due to weakened muscular apparatus and impaired functioning of the intestine (diverticulosis). Infection with pathogenic bacteria and viruses, leading to infectious colitis, also has a negative impact.
The appearance of colitis in the intestines in elderly patients is associated with damage to the arteries by atherosclerosis. When they become blocked, tissue necrosis begins. Another cause of colitis is protrusion of the intestinal walls due to weakened muscular apparatus and impaired functioning of the intestine (diverticulosis). Infection with pathogenic bacteria and viruses, leading to infectious colitis, also has a negative impact.
Clinical picture
- Severe pain, sometimes developing into intestinal obstruction.
- Possible peritonitis.
- Abnormal stool (diarrhea).
- Development of perforations and abscesses.
- The stool is watery and does not stop with regular medications.
- With infectious colitis, there is blood in the stool.
Endocrine system diseases
These pathologies appear more often in older people than in younger patients. Every tenth elderly patient hospitalized with prolonged diarrhea has symptoms of thyroid pathology. The symptoms are not so pronounced. This complicates the diagnosis of endocrine diseases.
Age-related nodular changes in the thyroid gland often force doctors to use additional methods for diagnosing diseases.
Clinical picture
Long-term diarrhea occurs in older people. They quickly lose body weight and have a rapid heartbeat. With hypothyroidism, on the contrary, a person sharply gains weight and experiences constipation for a long time.
Diabetes
Diabetes mellitus, according to statistics, is observed in every 10 people over 65 years of age, and by the age of 75 this figure rises to 23%. This is associated with age-related increases in blood sugar, decreased insulin production, and insulin resistance.
Most often it affects people who are overweight.
Clinical picture
Patients experience itching and dry skin. They complain of frequent urination and frequent thirst. Their vision deteriorates and their legs swell. There may be cramps of the lower extremities. A person loses weight and any wounds on his body do not heal well. From the gastrointestinal tract, there is prolonged diarrhea, a feeling of constant fullness of the stomach, and the patient feels nauseous. There may be a splashing sound in the stomach.
Addison's disease
 This is a rare disease that affects the adrenal cortex. Typically, this pathology develops in people between 20 and 40 years old, but it can also occur at a later age. The disease is presumably provoked by severe viral diseases, oncology, and renal failure.
This is a rare disease that affects the adrenal cortex. Typically, this pathology develops in people between 20 and 40 years old, but it can also occur at a later age. The disease is presumably provoked by severe viral diseases, oncology, and renal failure.
The exact cause of the disease has not been identified.
Clinical picture
Symptoms are varied, making diagnosis difficult. At the onset of the disease, the skin becomes pale and dry. The skin on the palms is less elastic. The patient's blood pressure decreases and heart failure occurs. Neurological disorders are possible. Diarrhea often occurs and a person feels nauseous. As the disease progresses, peptic ulcer disease begins and gastritis develops.
Malignant tumor
This is the proliferation of epithelial tissue with the formation of a tumor. As the tumor develops, it affects other organs and systems of the body.
Clinical picture
Symptoms can be different and depend on the location of the tumor and the period of development of the disease. Most often, diarrhea begins with stomach cancer. The patient's appetite worsens and he quickly becomes full. There is discomfort and a feeling of heaviness in the stomach. A person suffers from attacks of nausea and vomiting. The stool is disrupted (constipation or diarrhea), the person is weakened and irritated.
There is blood in the stool and vomit.
Oncological disease is often disguised as other diseases or is asymptomatic.
It is difficult for a person to hold feces with the sphincter, the stool is watery, and the stomach hurts. Diarrhea worsens when special diets for cancer patients are not followed.
Defecation can be:
- Up to 4 times a day.
- From 4 to 6 times a day.
- From 7 times a day or more. In this case, the patient is recommended to be hospitalized.
Intolerance to certain foods
From time to time they may disappear, then return again.
Clinical picture
- Migraine.
- Swelling
- Constant depression and fatigue.
- Asthma.
- Colic.
- Skin rash and hives.
- Drowsiness.
- Colitis.
From the intestines, bloating, increased gas formation, abdominal pain, diarrhea or constipation are observed.
Allergic reaction
This is a disruption of the immune system that provokes special reactions to irritants.
May be caused by food (raspberries, strawberries, citrus fruits, chocolate, eggs); on plants (pollen); on medications (intolerance to chemicals, dyes, antibiotics).
Clinical picture
Allergies can have many manifestations.
- From the respiratory organs. Sneezing, allergic rhinitis, cough with sore throat, choking.
- The skin begins to peel, hives, blisters, rashes, and swelling.
- The eyes are affected by conjunctivitis, a burning sensation appears, and the eyes water.
- Gastrointestinal tract. The patient begins to have diarrhea, attacks of nausea or vomiting. Colic in the intestines is observed.
- State of shock. The person loses consciousness and a rash appears on the skin. There is severe shortness of breath and suffocation.
Pancreatitis
 Pancreatitis in older people is most often caused by age-related changes. The first changes begin at the age of 40–45: the number of acini and cells decreases. In an eighty-year-old man, the pancreas shrinks by half. It is often provoked by stones in the pancreas, frequent alcohol consumption, and organ injuries. Another reason is cystic degeneration and deterioration in secretion activity due to the proliferation of the epithelium and aging sclerosis of duct cells. Exacerbations are also caused by blood clotting disorders. Because of this, blood clots form and an exacerbation begins.
Pancreatitis in older people is most often caused by age-related changes. The first changes begin at the age of 40–45: the number of acini and cells decreases. In an eighty-year-old man, the pancreas shrinks by half. It is often provoked by stones in the pancreas, frequent alcohol consumption, and organ injuries. Another reason is cystic degeneration and deterioration in secretion activity due to the proliferation of the epithelium and aging sclerosis of duct cells. Exacerbations are also caused by blood clotting disorders. Because of this, blood clots form and an exacerbation begins.
In older people, the hemorrhagic form more often develops, which leads not only to swelling of the organ tissue, but also to death.
Clinical picture
- Pain in the upper peritoneum, radiating to the sternum or back.
- Vomiting, shortness of breath.
- The sclera of the eyes turn yellow.
- Cardiopalmus.
- Development of anemia.
- Sudden weight loss.
The patient develops diarrhea with changes in the composition of stool. It contains a lot of undigested food particles. The feces are gray-green, oily, with a fetid odor, and are difficult to wash off the walls of the toilet.
Diarrhea can be dangerous due to severe dehydration, which can even lead to death.
Dehydration can be identified by a decrease in the elasticity of skin folds.
Previous operations on the intestines
This is a surgical intervention in the gastrointestinal tract. The operation may have a different focus and method of implementation, depending on the treatment of the disease.
Laparoscopy. Several punctures in the abdominal cavity through which the operation is performed. Reduces the risk of complications, the patient recovers in 3-5 days.
Laparotomy surgery. Open abdominal surgery with cutting into the abdominal cavity. It requires stitches. Recovery takes 1 to 2 weeks. It should not be used by pregnant women, obese people or people with diabetes.
An operation to remove one section can be performed with partial excision, otherwise the digestion process is disrupted.
If half of the small intestine is removed, the patient is fed only through an IV.
Clinical symptoms
Diarrhea is a common complication after intestinal surgery when part of the small intestine is removed. This is called short bowel syndrome, when food is not fully digested. This process provokes diarrhea.
But it cannot be ruled out that diarrhea could have started due to colitis, dysentery, dysbiosis or other diseases that were not treated before surgery. The cause may also be antibiotic treatment after surgery or the effects of anesthesia.
If diarrhea accompanies fever.
Attacks of nausea and vomiting are most likely a complication after surgery associated with infection.
Stress, nervous system disorders
Nervous diarrhea is a disorder of the intestinal motility system with abdominal pain and liquid stool. Causes: nervous shock.
Typically, nervous diarrhea has a genetic predisposition.
Clinical picture
- The stool is mushy or semi-liquid and may become runny.
- Defecation 3–4 times a day (can reach 7–9 times a day).
- False urge to defecate.
- There may be mucus in the stool.
- Defecation begins immediately after eating.
- Bloating.
- Pain on palpation of the abdominal wall.
Uremia
Uremia is a disease caused by impaired kidney function. With it, the kidneys poorly filter decay products, accumulating urea and nitrogen. May be one of the stages of renal failure. Urgent treatment is necessary, otherwise intoxication of the body will occur, leading to death.
Clinical picture
- Darkening of urine, presence of pus, sediment or blood in it.
- Frequent urination.
- Pain in the sides, lower abdomen and lumbar region.
- Aversion to food.
- Weight loss.
- Nausea and vomiting.
- Belching and heartburn.
- Abnormal bowel movements (constipation, diarrhea).
- The amount of urine decreases as the disease progresses.
- Loss of strength, drowsiness.
Blood often appears in stool and vomit.
The patient feels nauseous even when there is no food in the stomach.
Lack of essential substances and microelements in the body
This condition leads to most diseases in the body. It disrupts the functioning of the spleen, stomach, kidneys, and intestines.
Most often, diarrhea occurs due to a lack of zinc in the body.
Clinical picture
- Noise in ears.
- White spots appear on the nail plates.
- Scaly rashes on the skin.
- Diarrhea.
- Partial loss of taste.
- The patient does not recognize some odors.
- Wounds on the skin do not heal well.
Other reasons
- Dental problems.
- Poor chewing of food.
- Dry mouth and poor saliva processing of food.
- Diseases of the nervous system.
- Taking certain groups of medications.
Treatment
Before treatment, the patient needs a comprehensive examination to identify the causes of the disease.
- Standard treatment regimen:
- Restoring water-salt balance (drink plenty of fluids, Regidron).
- Taking activated carbon or other sorbents.
- Taking medications as prescribed by a doctor (antispasmodics, antibiotics, antidiarrheal medications, etc.).
- Diet.
- Traditional medicine.
First aid
- Complete refusal of food for a day.
- Gastric lavage.
- At high temperatures, give Nurofen.
- After each bowel movement you should drink Regidron solution.
- On the second day, split meals with steamed dishes. Complete rejection of the daily diet.
- Call a doctor at home or consult a doctor.
When should I see a doctor?
- Fever for 1–2 days.
- Stool with blood, mucus, pus.
- Severe pain in the peritoneum.
- Uncontrollable vomiting.
- Severe uncontrolled dehydration.
How to determine and what to do if you are dehydrated?
To monitor the loss of water in an elderly patient's body, a pinch test is performed. To do this, use your fingers to fix a fold of skin on the back of the patient’s hand for a few seconds. The fold is released and monitored to see how quickly the skin regains its elasticity. If it does not take its natural form for a long time, then there is little water in the body and it needs to be replenished.
When a patient is dehydrated, he or she experiences a migraine, loss of appetite, decreased blood pressure, and rapid heartbeat. An elderly patient's mouth becomes dry, and pain begins in the sternum area. Shortness of breath occurs, the person does not sweat.
To avoid dehydration, you should adhere to a drinking regime of 30–40 grams of water per 1 kg of person’s weight.
The amount of fluid lost should be equal to the amount of fluid drunk.
Medicines

Loperamide
Release form: tablets. The medicine makes the movement of stool through the intestines slower. After consumption, nutrients from the food consumed are better absorbed. Not recommended for constipation. Not suitable for pregnant women and nursing mothers. Not for children under 5 years old.
Price: 20–30 rubles per package.

Ciprofloxacin
Release form: tablets. This is an antibiotic that eliminates pathogenic flora in infectious diseases. Contraindications: Not recommended for pregnant women and nursing mothers.
Cost of medicine: from 40 to 50 rubles.

Intetrix
Release form: tablets. It is an antiseptic for the gastrointestinal tract. Effective against salmonellosis, infection with E. coli, and staphylococci. Contraindications: pregnant and nursing mothers. Should not be taken by people with hypersensitivity to the components of the medication. Prohibited for children.
Cost: 400–500 rubles per package.

Activated carbon
Release form: tablets. Sorbent that absorbs toxins and harmful substances. Children are given crushed tablets that are mixed in water. Contraindicated for stomach ulcers.
Prohibited for ulcerative colitis.
ethnoscience
Congee
Take 3 teaspoons of rice and pour 0.5 liters of water. Boil the mixture over low heat for 30–40 minutes. Dosage: ¼ cup in 3-4 doses per day.
Vodka with salt
For one-time use of the medicine you will need 60 grams of vodka and a pinch of salt. Salt is mixed with vodka. The patient can choose the amount of salt as desired. Wash down vodka with water or fruit drink.
Oak bark decoction
Take a teaspoon of oak bark and pour a glass of boiling water. Leave for an hour and strain through cheesecloth. The medicine should be taken 2 teaspoons every few hours.
Daily dosage: a glass of decoction.
Pomegranate peel
We clean the pomegranates, peel them and dry them. You can supplement the crusts with partitions. It is recommended to chew the dried peels. They have a strong antiseptic and astringent effect.
Black tea
Take 4 teaspoons of black tea and pour a glass of vodka. The resulting mixture is heated in a water bath. You cannot bring it to a boil. After foam appears, the medicine is removed from the stove. After this, the mixture is wrapped in a warm blanket and continues to infuse until it cools.
You should drink it 2 teaspoons every 2 hours.
Nutrition and drinking regimen
Authorized products
- Puree porridges.
- Crackers.
- Baked apples.
- The meat is introduced on the second day. Boiled or steamed meat is recommended.
- Vegetarian soups.
- Compote, tea, jelly.
- Yogurts with beneficial bifidobacteria.
Prohibited Products
- Raw vegetables and fruits.
- Fatty dishes.
- Roast.
- Canned food, marinades.
- Spices.
- Milk.
You should drink every 2-3 hours.
Menu for every day
First day
- Rice based broth. Blueberry jelly.
- Tea with biscuits.
- Vegetable broth soup with rice and meatballs. Tea with crackers.
- Berry compote. Oven baked apple.
- Mashed potatoes, fish fillet. Mineral water without gas.
Second day
- Oatmeal cooked in water.
- Green tea with biscuits.
- Kissel.
- Rice, a piece of boiled chicken. Berry jelly.
- Banana.
- A couple of potatoes, boiled in their skins. Steamed cutlet.
The third day
- Rice and boiled egg.
- Steamed omelette. Green tea with biscuits.
- Kissel with breadcrumbs.
- A piece of boiled fish. Buckwheat. Green tea.
- Kissel with biscuits.
Prevention of the condition
- Eating probiotics and enzymes.
- It is recommended to include onions and garlic, mustard, radish, horseradish, and tarragon into the diet.
- You should drink freshly squeezed juices (dogwood, black currant, strawberry).
- Taking herbal infusions.
- Fortifying teas.
Diarrhea in older people is a rather complex condition, which is aggravated by dehydration.
It can be caused not only by food intolerance or stress, but also by serious diseases, for example, diabetes, Crohn's disease, and cancer. Particular attention should be paid to bloody stools or prolonged diarrhea. In these cases, you cannot self-medicate; you must consult a doctor.
In particularly difficult cases, hospitalization and long-term treatment may be required.
Be sure to watch the following video, it may be very helpful
Diarrhea is a painful condition of the body in which frequent defecation of liquid stool occurs. Diarrhea is usually not a big concern in younger generations, but diarrhea can be a serious problem in older people.
With age, significant changes occur in the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract.
Starting from the oral cavity and ending with the large intestine, all organs undergo various types of transformations.
Features of the gastrointestinal tract system in older people:
- Oral cavity. Depletion of facial and chewing muscles occurs. The process of digesting and chewing food is disrupted.
- Esophagus. The organ itself and all its layers, incl. muscle layer. All this leads to difficulty swallowing and a high risk of hernia formation.
- Stomach. It is significantly reduced in size and is no longer located vertically, but horizontally. At the same time, less and less enzymes, hydrochloric acid and gastric juice are produced. The blood supply to the walls of the stomach, motor function and metabolic processes are disrupted.
- Small intestine. The completeness of food processing is impaired.
- Colon. The formation of fecal stones, a tendency to “senile constipation” develops. In the intestinal microflora, the number of harmful bacteria increases, and the presence of lactic acids decreases, as a result of which endotoxins increase and the synthesis of vitamins B and K is disrupted.
- Liver. The weight of the liver decreases, as does its functionality. All this leads to disruption of the metabolism of proteins, fats, carbohydrates, pigments, and a decrease in the neutralizing function of the liver. The excretory function of the organ is also impaired, as a result of which medications are eliminated more and more slowly and can become heated in the body.
- Gallbladder. This organ, unlike the liver, on the contrary, increases in size, but is also a bad sign. In the gallbladder, with age, there is a disruption in the timely flow of bile into the intestines, thereby increasing the possibility of stone formation.
- Pancreas. Due to a decrease in blood supply and the number of glandular and islet cells, external and internal secretory functions decrease.
During the aging process the body not only loses its former youth, but also a violation of all functions in vital organs occurs, in particular, the organs of the gastrointestinal tract. As a result, a person begins to get sick often, and defecation is accompanied not only by “senile constipation,” but also by frequent diarrhea and diarrhea, which causes a lot of inconvenience and discomfort. In this regard, there is an urgent need to select proper nutrition and a balanced diet. Not only health, but also life expectancy depends on the diet of older people.
Causes and signs of diarrhea in the elderly
In old age, the duration of diarrhea can reach several days, and loose stools themselves occur about 4–6 times a day.
In this case, the causes of diarrhea can be any.
Causes of diarrhea:
- Crohn's disease;
- ulcerative colitis, incl. infectious;
- pathologies of the endocrine system;
- diabetes;
- Addison's disease;
- malignant tumors;
- food intolerance or allergies to some of them;
- chronic pancreatitis;
- various operations on the intestines;
- lack of zinc in the body;
- uremia;
- nervous system disorders;
- taking certain medications.
It can be quite difficult to prevent diarrhea in older people, but there are some signs that signal the possibility of diarrhea.
Signs of diarrhea:
- bloating, rumbling in the stomach;
- moderate or severe pain in the stomach;
- stool becomes thinner;
- nausea;
- feeling of dry mouth, constant desire to drink water;
- fatigue;
- urine changes color to darker;
- appetite is lost.
In most cases, diarrhea goes away on its own, but if diarrhea is accompanied by vomiting, high fever, there is blood in the stool, deterioration in general condition, dehydration, then in such cases you should immediately consult a doctor or call an ambulance.
What should the diet be like?
 In old age it is extremely important to eat right, since not every food is suitable, and many foods are not worth eating at all. In some cases, a diet is even required. A diet is understood as a specially designed diet not for the purpose of losing weight, but with the goal of eliminating from the diet foods that are harmful to the “elderly” body. Properly selected products will help avoid serious illnesses, as well as the possible occurrence of diarrhea and its complications.
In old age it is extremely important to eat right, since not every food is suitable, and many foods are not worth eating at all. In some cases, a diet is even required. A diet is understood as a specially designed diet not for the purpose of losing weight, but with the goal of eliminating from the diet foods that are harmful to the “elderly” body. Properly selected products will help avoid serious illnesses, as well as the possible occurrence of diarrhea and its complications.
Food products for older people should be varied, easily perceived and digestible, biologically valuable, but compared to what the younger generation consumes, food should be less energetically valuable. At the same time, the food must contain enough proteins, vitamins, minerals, salts, in particular iron, potassium and calcium.
Authorized Products:
- corn, sunflower, soybean oils;
- lean meat (chicken, turkey);
- low-fat cottage cheese, cheese, fermented milk products, milk;
- egg whites;
- vegetable, fish and lean meat (chicken) soups;
- low-fat fish;
- seafood;
- vegetables, berries, fruits;
- porridge (preferably whole grain cereals, such as pearl barley);
- vegetable salads (preferably with vegetable oil);
- meat by-products, in particular liver (for example, beef);
- bread made from wholemeal flour or bran;
- fruit drinks, decoctions (for example, from rose hips), juices;
- weak tea and coffee (it is better to replace coffee with chicory), etc.
- fatty cheese, cottage cheese;
- sour cream, cream (possible in limited quantities);
- fatty meat (pork);
- fried food;
- egg yolks;
- sugar;
- sweet flour dishes (cakes);
- various confectionery products (sweets, chocolate, cream products);
- sweet, carbonated drinks, kvass;
- pasta;
- rice (causes constipation);
- legumes (peas, beans);
- smoked, salted, spicy foods;
- mustard, mayonnaise, horseradish%
- margarine, etc.
Menu options for the day
It is worth eating frequently, about 4–6 times a day, but in small portions.
Food should be easy to chew. It is forbidden to overeat, as too much stress on the gastrointestinal tract can cause consequences.
1 menu option
 1 meal (breakfast): omelet, oatmeal porridge with milk, weak tea with milk.
1 meal (breakfast): omelet, oatmeal porridge with milk, weak tea with milk.
Meal 2 (second breakfast): 1 – 2 fruits (baked apple, banana or pear).
Meal 3 (lunch): vegetable soup, chicken cutlets with mashed potatoes, dried apricots and raisins compote.
Meal 5 (dinner): boiled fish with stewed cabbage, vinaigrette, tea.
Meal 6 (at night): yogurt.
2 menu option
 1 meal (breakfast): buckwheat porridge, cottage cheese with low-fat sour cream and sugar, tea with milk.
1 meal (breakfast): buckwheat porridge, cottage cheese with low-fat sour cream and sugar, tea with milk.
Meal 2 (second breakfast): salad of cucumbers and tomatoes with vegetable oil.
3rd meal (lunch): chicken soup, pilaf with boiled meat and vegetables, compote.
Meal 4 (afternoon snack): rosehip decoction, any juice.
Meal 5 (dinner): boiled meat with vegetables, apple soufflé, tea.
Meal 6 (at night): kefir.
During the day, in addition to the main menu, you can have bread (250 - 300 g), sugar (20 - 30 g), butter (10 g).
The menu is approximate. Everyone must independently or with the help of doctors determine their daily diet, diet. It is important to monitor your weight - do not overeat or deplete your body, and take all measures to normalize your weight.
Treatment methods
In addition to proper nutrition, diarrhea can be cured with the help of medications or traditional recipes.
Among the medications, the following medications effectively treat diarrhea:
- Smecta;
- Activated carbon;
- Enterosgel;
- Phthalazol;
- Neosmectin, etc.
Medicines act quickly and effectively, most of them help eliminate diarrhea in the first hours of use, in addition, medicines normalize the process of digestion, stomach and intestines.
Traditional medicine effectively fights diarrhea. Decoctions and infusions are prepared from plants and herbs, which normalize the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract and help eliminate diarrhea. Actively used plants include rowan, marshmallow, plantain, St. John's wort, bird cherry, oak bark and many others.
Rowan decoction, St. John's wort and marshmallow
Ingredients:
- marshmallow root (part 2);
- St. John's wort (part 3);
- rowan berries (part 4);
- boiling water (0.5 l.).
 Method of preparation and use:
Method of preparation and use:
Mix all parts of the herbs. Take 1 tablespoon of the resulting mixture and pour boiling water. Let it sit for 40 – 60 minutes and strain. We take the decoction during the day 4 times, 0.5 cups each.
In old age, it is especially important to pay attention to your health. It is important not only to constantly visit medical institutions, but also to regularly breathe fresh air, lead an active lifestyle, walk a lot, if possible, play sports or do light exercise, and most importantly, eat right.
Diarrhea is a painful condition of the body in which frequent defecation of liquid stool occurs. Diarrhea is usually not a big concern in younger generations, but diarrhea can be a serious problem in older people.
Features of the gastrointestinal tract system in old age
With age, significant changes occur in the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract.
Starting from the oral cavity and ending with the large intestine, all organs undergo various types of transformations.
Features of the gastrointestinal tract system in older people:
Oral cavity. Depletion of facial and chewing muscles occurs. The process of digesting and chewing food is disrupted. Esophagus. The organ itself and all its layers, incl. muscle layer. All this leads to difficulty swallowing and a high risk of hernia formation. Stomach. It is significantly reduced in size and is no longer located vertically, but horizontally. At the same time, less and less enzymes, hydrochloric acid and gastric juice are produced. The blood supply to the walls of the stomach, motor function and metabolic processes are disrupted. Small intestine. The completeness of food processing is impaired. Colon. The formation of fecal stones, a tendency to “senile constipation” develops. In the intestinal microflora, the number of harmful bacteria increases, and the presence of lactic acids decreases, as a result of which endotoxins increase and the synthesis of vitamins B and K is disrupted. Liver. The weight of the liver decreases, as does its functionality. All this leads to disruption of the metabolism of proteins, fats, carbohydrates, pigments, and a decrease in the neutralizing function of the liver. The excretory function of the organ is also impaired, as a result of which medications are eliminated more and more slowly and can become heated in the body. Gallbladder. This organ, unlike the liver, on the contrary, increases in size, but is also a bad sign. In the gallbladder, with age, there is a disruption in the timely flow of bile into the intestines, thereby increasing the possibility of stone formation. Pancreas. Due to a decrease in blood supply and the number of glandular and islet cells, external and internal secretory functions decrease.
In the process of aging, the body not only loses its former youth, but also a disruption of all functions in vital organs occurs, in particular, the organs of the gastrointestinal tract. As a result, a person begins to get sick often, and defecation is accompanied not only by “senile constipation,” but also by frequent diarrhea and diarrhea, which causes a lot of inconvenience and discomfort. In this regard, there is an urgent need to select proper nutrition and a balanced diet. Not only health, but also life expectancy depends on the diet of older people.
Causes and signs of diarrhea in the elderly
In old age, the duration of diarrhea can reach several days, and loose stools themselves occur about 4–6 times a day.
In this case, the causes of diarrhea can be any.
Causes of diarrhea:
Crohn's disease; ulcerative colitis, incl. infectious; pathologies of the endocrine system; diabetes; Addison's disease; malignant tumors; food intolerance or allergies to some of them; chronic pancreatitis; various operations on the intestines; lack of zinc in the body; uremia; nervous system disorders; taking certain medications.
It can be quite difficult to prevent diarrhea in older people, but there are some signs that signal the possibility of diarrhea.
Signs of diarrhea:
bloating, rumbling in the stomach; moderate or severe pain in the stomach; stool becomes thinner; nausea; feeling of dry mouth, constant desire to drink water; fatigue; urine changes color to darker; appetite is lost.
In most cases, diarrhea goes away on its own, but if diarrhea is accompanied by vomiting, high fever, there is blood in the stool, deterioration in general condition, dehydration, then in such cases you should immediately consult a doctor or call an ambulance.
What should the diet be like?
In old age, it is extremely important to eat properly, since not every food is suitable, and many foods are not worth eating at all. In some cases, a diet is even required. A diet is understood as a specially designed diet not for the purpose of losing weight, but with the goal of eliminating from the diet foods that are harmful to the “elderly” body. Properly selected products will help avoid serious illnesses, as well as the possible occurrence of diarrhea and its complications.
Food products for older people should be varied, easily perceived and digestible, biologically valuable, but compared to what the younger generation consumes, food should be less energetically valuable. At the same time, the food must contain enough proteins, vitamins, minerals, salts, in particular iron, potassium and calcium.
Authorized products:
corn, sunflower, soybean oils; lean meat (chicken, turkey); low-fat cottage cheese, cheese, fermented milk products, milk; egg whites; vegetable, fish and lean meat (chicken) soups; low-fat fish; seafood; vegetables, berries, fruits; porridge (preferably whole grain cereals, such as pearl barley); vegetable salads (preferably with vegetable oil); meat by-products, in particular liver (for example, beef); bread made from wholemeal flour or bran; fruit drinks, decoctions (for example, from rose hips), juices; weak tea and coffee (it is better to replace coffee with chicory), etc.
fatty cheese, cottage cheese; sour cream, cream (possible in limited quantities); fatty meat (pork); fried food; egg yolks; sugar; sweet flour dishes (cakes); various confectionery products (sweets, chocolate, cream products); sweet, carbonated drinks, kvass; pasta; rice (causes constipation); legumes (peas, beans); smoked, salted, spicy foods; mustard, mayonnaise, horseradish% margarine, etc.
Menu options for the day
It is worth eating frequently, about 4–6 times a day, but in small portions.
Food should be easy to chew. It is forbidden to overeat, as too much stress on the gastrointestinal tract can cause consequences.
1 menu option
1 meal (breakfast): omelet, oatmeal porridge with milk, weak tea with milk.
Meal 2 (second breakfast): 1 – 2 fruits (baked apple, banana or pear).
Meal 3 (lunch): vegetable soup, chicken cutlets with mashed potatoes, dried apricots and raisins compote.
Meal 5 (dinner): boiled fish with stewed cabbage, vinaigrette, tea.
Meal 6 (at night): yogurt.
2 menu option
1 meal (breakfast): buckwheat porridge, cottage cheese with low-fat sour cream and sugar, tea with milk.
Meal 2 (second breakfast): salad of cucumbers and tomatoes with vegetable oil.
3rd meal (lunch): chicken soup, pilaf with boiled meat and vegetables, compote.
Meal 4 (afternoon snack): rosehip decoction, any juice.
Meal 5 (dinner): boiled meat with vegetables, apple soufflé, tea.
Meal 6 (at night): kefir.
During the day, in addition to the main menu, you can have bread (250 - 300 g), sugar (20 - 30 g), butter (10 g).
The menu is approximate. Everyone must independently or with the help of doctors determine their daily diet, diet. It is important to monitor your weight - do not overeat or deplete your body, and take all measures to normalize your weight.
Treatment methods
In addition to proper nutrition, diarrhea can be cured with the help of medications or traditional recipes.
Among the medications, the following medications effectively treat diarrhea:
Smecta; Activated carbon; Enterosgel; Phthalazol; Neosmectin, etc.
Medicines act quickly and effectively, most of them help eliminate diarrhea in the first hours of use, in addition, medicines normalize the process of digestion, stomach and intestines.
Traditional medicine effectively fights diarrhea. Decoctions and infusions are prepared from plants and herbs, which normalize the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract and help eliminate diarrhea. Actively used plants include rowan, marshmallow, plantain, St. John's wort, bird cherry, oak bark and many others.
Rowan decoction, St. John's wort and marshmallow
marshmallow root (part 2); St. John's wort (part 3); rowan berries (part 4); boiling water (0.5 l.).
Method of preparation and use:
Mix all parts of the herbs. Take 1 tablespoon of the resulting mixture and pour boiling water. Let it sit for 40 – 60 minutes and strain. We take the decoction during the day 4 times, 0.5 cups each.
In old age, it is especially important to pay attention to your health. It is important not only to constantly visit medical institutions, but also to regularly breathe fresh air, lead an active lifestyle, walk a lot, if possible, play sports or do light exercise, and most importantly, eat right.
Do you still think that healing your stomach and intestines is difficult?
Judging by the fact that you are now reading these lines, victory in the fight against diseases of the gastrointestinal tract is not yet on your side...
Have you already thought about surgery? This is understandable, because the stomach is a very important organ, and its proper functioning is the key to health and well-being. Frequent abdominal pain, heartburn, bloating, belching, nausea, bowel dysfunction... All these symptoms are familiar to you firsthand.
But perhaps it would be more correct to treat not the effect, but the cause? Here is the story of Galina Savina, about how she got rid of all these unpleasant symptoms... Read the article >>>
Discomfort in the intestines has at least once disrupted the usual course of life for any person.
If the functioning of the colon is disrupted, the liquid is not absorbed into the blood, but leaves the body with feces. The frequency of bowel movements more than 3 times per day allows us to talk about such a disorder in the gastrointestinal tract as diarrhea.
Diarrhea- This is a symptom that indicates problems in the functioning of the body. The danger of diarrhea is its consequences.
What are the dangers of diarrhea?
The main danger of diarrhea (diarrhea) is dehydration, which leads to serious complications.
The painful condition of diarrhea is characterized by symptoms such as:
dry mucous membranes in the mouth; white coating on the tongue and palate; constant feeling of thirst; lack of urination; dehydration and weight loss; decreased temperature and blood pressure, rapid heartbeat.
A very dangerous consequence of prolonged diarrhea is liver dysfunction. A decrease or absence of urination indicates a disruption in the functioning of the kidneys to eliminate waste products. Decay products that are not removed from the body accumulate, and this leads to poisoning of the body, damage to all its organs.
Prevention of dehydration should begin as soon as it becomes clear that liquid bowel movements are not isolated. Take Regidron solution, salted water, and chamomile decoction.
Basics of proper nutrition for diarrhea
In the acute period, on the first day, food is completely excluded, and large fluid intake is indicated. From day 2, or if your condition is stable, you can start eating only recommended foods.
Products are used in processed form, boiled or steamed. Frying is excluded.
It is necessary to eat frequently (every 3 hours) in small portions and mainly with strengthening foods. Drink plenty of fluids. Salt all food to reduce dehydration of the body (salt tends to retain water in the body). It is recommended to eat warm food, similar to a body temperature of 36 C.
Forbidden foods for diarrhea
All foods that cause fermentation and irritate the mucous membranes of the stomach and intestines are prohibited.
fresh and raw vegetables (white cabbage, tomatoes, cucumbers, radishes, radishes); fresh fruits (apples, green bananas, all citrus fruits, etc.); high-calorie foods (fatty fish, meat, lard, butter and vegetable oil) ;canned, pickled products, including home canned food; nuts and legumes; mushrooms; sweets, confectionery, gray and brown bread; dairy and fermented milk products (whole milk, kefir, cottage cheese); various sauces (ketchup, mayonnaise), spices and other condiments; all alcoholic drinks, carbonated drinks, coffee.
What can you eat if you have diarrhea?
The list of foods consumed for diarrhea is small. You can diversify the table with different variations of their preparation.
 What to eat if you have diarrhea:
What to eat if you have diarrhea:
all types of porridges (preference is given to rice and oatmeal), boiled in water without oil and milk; rice broth; boiled eggs and steamed omelettes; chicken broth; steamed meat and fish dishes (in the form of cutlets and meatballs); vegetable puree (boiled, grated vegetables); white bread croutons, yesterday's bread.
What drinks can you drink if you have diarrhea?
It is necessary to constantly replenish water losses by drinking 2-3 liters of fluid per day.
What to drink if you have diarrhea:
clean water in sufficient quantities; rice broth; various jelly; dried fruit compote; infusion of pomegranate peels gives a good fixing effect; chamomile infusion; black tea.
Diet No. 4
Diet (table) No. 4 was developed by nutritionist M.I. Pevzner. This is one of the 15 diets he developed, recommended for dietary nutrition in the treatment of dysfunctions of the gastrointestinal tract. Table No. 4 helps reduce painful symptoms of intestinal diseases and inflammatory processes, eliminates rotting and fermentation in the intestines.
Main nutrition rules for diet No. 4:
6 meals a day, consisting of mucous, liquid, puree-shaped dishes; “boiled” and steam cooking methods; solid, thick, as well as cold and hot foods are excluded.
Dietary table No. 4 includes:
Cereals - buckwheat, oatmeal, rice, semolina, cooked in water; Vegetables - beets, potatoes, pumpkin, carrots in grated form as an additive to soups; Berries and fruits - grated into puree, as well as in the form of compote, jelly and jelly; Meat -beef, veal chopped in the form of meatballs and cutlets; Chicken egg as an addition to soups; Fish - low-fat varieties in the form of meatballs and cutlets; Soups made from lean fish or chicken broth with the addition of slimy rice; Rusks from white bread; Drinks made from dried berries Juices diluted with water. Tea and cocoa brewed with water.
Also excluded:
carbonated and cold drinks; alcohol; grape and plum juices; milk and kvass.
Nutrition in accordance with diet No. 4 lasts one and a half weeks. By adhering to diet No. 4, already in the first week the signs of inflammation of the intestinal walls decrease and fermentation in the intestines decreases.
You should exit diet No. 4 gradually.
Approximate menu for diarrhea for one day
 So, an approximate menu for diarrhea for one day:
So, an approximate menu for diarrhea for one day:
Breakfast: rice porridge or steamed omelet, tea. Snack: ripe banana or baked apple, tea or infusion of chamomile, rose hips. Lunch: soup with meatballs or steamed cutlets, compote or tea. Snack: jelly or compote, white bread or croutons. Dinner : buckwheat porridge with steamed fish, chamomile infusion or tea.
Diarrhea in women who are breastfeeding
Sometimes young mothers experience diarrhea during lactation.
There are several reasons:
often irritable bowel syndrome (associated with stress after childbirth, lack of sleep); excessive consumption of foods that tend to loosen stools (prunes, beets, kefir); allergic reactions; infection.
It is important to remember that diarrhea leads to dehydration, and a lack of fluid negatively affects lactation, reducing the quantity and quality of breast milk.
What should breastfeeding women eat if they have diarrhea?
decoction of rice; any well-cooked porridge in water without oil; white bread croutons; vegetable soups; boiled eggs, steamed omelet; low-fat steamed fish and meat.
Be sure to drink 2-3 liters of fluid per day. This could be water, tea, dried fruit compote, berry jelly (taking into account the likelihood of an allergic reaction of the baby).
Infusions of chamomile, fennel seeds and dill water help fight diarrhea, but also additionally stimulate lactation and improve the taste of breast milk.
Diarrhea in the elderly
Abnormal bowel movements (diarrhea or constipation) are common in older people.
As a result of natural aging, many changes occur in the body:
disruption of the chewing process and, as a result, assimilation of food; the stomach becomes smaller in volume, the production of gastric juice is reduced; the functionality of the liver and pancreas is reduced; the intestinal microflora is disrupted.
To reduce digestive problems, older people are advised to:
Eat often (about 6 times a day) and in small portions. Do not overeat. Give preference to recommended products.
What can you drink if you have an intestinal disorder:
various jelly (have a good ability to coat the walls of the stomach and intestines); compotes and infusions of dried fruits and rose hips; tea and infusions of medicinal plants (chamomile, oak bark, sage).
It is important for older people to undergo examinations on time, exercise whenever possible, walk a lot and lead an active lifestyle.
Irritable bowel syndrome
Irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) characterized by impaired intestinal motor functions.
This violation is expressed by such phenomena as:
diarrhea; bloating; intestinal colic without infectious or immune damage in the intestines; constipation or a combination of diarrhea and constipation.
Causes of irritable bowel syndrome:
stress, most often IBS manifests itself in young people and women of different ages; unhealthy eating behavior, an abundance of fatty, high-calorie foods, insufficient dietary fiber in food; hormonal levels in women (diarrhea is observed at the beginning or end of menstruation); abuse of alcohol, coffee and carbonated drinks drinks; intestinal dysbiosis.
To get rid of IBS, it is necessary to analyze the factors that cause it and take measures to eliminate them.
What to eat for diarrhea in adults with irritable bowel syndrome:
All types of porridges cooked in water. Boiled or steamed vegetables. The exceptions are irritating intestines, cabbage, cucumbers, tomatoes. Fruits in the form of puree or baked (apples, pears). Boiled, baked or steamed meat and fish in the form of cutlets or meatballs. Fermented milk products.
Until the consequences of IBS are eliminated, the following are excluded from the diet:
fresh vegetables and fruits; nuts, mushrooms; any pastries; carbonated and alcoholic drinks, coffee.
Diet after diarrhea
Features of nutrition after diarrhea:
You can return to your normal diet no earlier than 1.5-2 weeks after diarrhea. Add foods carefully so as not to provoke a new digestive breakdown. Gradually you can add pasta, milk to dishes (milk half with water), potatoes, cottage cheese, pumpkin , zucchini.
The right diet is half the battle against diarrhea. Basically, diarrhea, if you follow nutritional recommendations, goes away on its own, but if it is accompanied by high fever, vomiting, blood in the stool, or your general physical condition worsens, you should consult a doctor or call an ambulance.
Usually, such a frequent bowel disorder as diarrhea does not cause serious concern for young children and the elderly, but diarrhea can cause severe dehydration with all the ensuing consequences. The danger of diarrhea in older people, regardless of the reasons that caused this phenomenon, is that chronic diseases accumulate with age, and the body’s defenses, on the contrary, weaken.
If for middle and younger ages the main reasons for which digestive disorders are noted are poor-quality products, poor personal hygiene, and the use of medications, then for older people the situation is somewhat different. Of course, the causes of diarrhea in the elderly may be the same factors that are characteristic of younger people, but they are mainly associated with weakened performance and a slowdown of all basic functional processes. Among them are:
- Reduced fermentation levels, impairing nutrient hydrolysis and leading to diarrhea.
- A decrease in the number of taste buds when a person skews the consumption of sweet, spicy or salty foods, which negatively affects the performance of the gastrointestinal tract.
- Use of antibiotics.
In addition, in older people, the level of saliva secretion, which plays an important role in the process of digesting food and the absorption of nutrients by the body, decreases. In this case, the oral cavity dries out, and weakened masticatory muscles do not provide normal chewing, disrupting the swallowing process. Diarrhea in the elderly, which does not go away for a long time, can be caused by the consequences of certain diseases. In an elderly person, loose stools can occur due to a disease of the endocrine system (diabetes mellitus, Addison's disease).
Diarrhea in older people can be functional and serves as the body’s reaction to a stressful situation, fear or nervous overstrain. At the same time, intestinal activity is activated, accelerating the movement of food through the esophagus. As a result, beneficial substances do not have time to be absorbed, and undigested food remains, along with the liquid accumulated in the esophagus, fly out of the body in transit, that is, diarrhea occurs in the elderly. The danger of diarrhea in the elderly is that the already weakened body loses the water necessary for normal functioning and severe dehydration is possible. In addition, chronic diarrhea can cause exacerbation of existing diseases.
Contents [Show]
Treatment of diarrhea in the elderly
Considering that the body of an elderly person does not have sufficient resistance to factors that cause stomach upset, diarrhea in the elderly requires an immediate response. Dehydration due to diarrhea in an old person, even if it lasts only one day, is extremely dangerous. The difficulty of treating diarrhea in older people is that in diseases of the digestive system, the symptoms are unclear, and it is very difficult to determine the cause of diarrhea, especially in the early stages.
In some cases, the type and nature of diarrhea can determine the cause of indigestion. For example, with irritable bowel syndrome, diarrhea with mucus will only occur during the daytime. If there is mucus and pus in the diarrhea, this indicates infectious colitis. In any case, research is necessary to confirm or refute the infectious origin of the pathology. If you contact a medical facility in a timely manner, the prognosis is usually favorable. Delayed treatment and inappropriate treatment creates additional difficulties and worsens the chances of a successful recovery for an old person.
After contacting a doctor who will prescribe the necessary laboratory and instrumental tests, it is necessary to take measures to restore lost fluid to prevent dehydration. Special solutions are recommended, such as Regidron, Citroglucosolan, which allow you to simultaneously replenish the amount of microelements (potassium, sodium, chlorine) that are excreted during diarrhea. To reduce the number of bowel movements, codeine phosphate and adsorbent drugs (Smecta, activated carbon and others) are prescribed. Medicinal saline solutions are taken at intervals of two hours. It is recommended to take adsorbents with plenty of water.
The next step in the treatment of diarrhea in older people is dietary nutrition. In case of very severe stool upset, rice water has an excellent consolidating effect. It is advisable to abstain from any food at all on the first day, limiting yourself to drinking plenty of fluids. In the future, the menu should include quickly digestible products that do not have a fermentation effect and do not irritate the mucous membrane. It is recommended to give preference in the diet to vegetable soups or soups prepared with lean meat broth. The diet for this category of people is determined by the doctor individually, taking into account all the features.
Elderly people should take medications only after consulting a doctor and based on his prescription. You need to be especially careful with antibiotics, which are widely used to fight infections. Often, loose stools can be caused by antibiotics, which were used, for example, to fight infections associated with the respiratory system. In this case, it is recommended to include yoghurts enriched with bifidobacteria additives in the diet.
The presence of bananas, boiled potatoes, rice porridge cooked in water in the diet, and buckwheat porridge for IBS is very useful for consolidating stool. Due to the fact that the use of medications to treat diarrhea in older people for one reason or another is sometimes impossible, traditional medicine, along with diet, is of great importance. There are a huge number of recipes offered by traditional medicine, but they can only be used after visiting a medical facility and consulting with a doctor.
Diarrhea in the elderly: causes
Diarrhea is a pathological condition of the body in which frequent bowel movements with loose stools occur, accompanied by pain and cramps.
In old age, many processes occurring in the body slow down. From the gastrointestinal tract, this is expressed by a decrease in the level of enzymes and a deterioration in the hydrolysis of nutrients. Changes in the oral cavity, when not all teeth are preserved, lead to the fact that food is not chewed sufficiently. The number of taste buds decreases, which leads to a weakening of taste sensitivity, especially for sweets. The secretion of saliva decreases and this is the cause of dry mouth. The swallowing process is impaired due to muscle weakness and strength. Changes also occur in the pancreas. Its secretory function decreases. The liver decreases in size and the amount of bile produced decreases. The mucous membrane of the small intestine becomes thinner, which disrupts the secretion of enzymes necessary for the absorption of fats and milk.
Older people love sweets, and the process of absorption of carbohydrates is already impaired, so digestive upset occurs - diarrhea. Diarrhea is often caused by the use of antibiotics.
Diarrhea in an elderly person for a long time
When an elderly person has prolonged diarrhea, first of all, it is necessary to exclude fecal impaction and pseudomembranous colitis. It is possible that this is a symptom of Crohn's disease or ulcerative colitis. They are characterized by profuse diarrhea and weight loss.
Diseases of the endocrine system can also manifest as diarrhea that lasts a long time. Similar symptoms are observed in diabetes mellitus and Addison's disease. Bloody diarrhea may indicate infectious colitis or a malignant tumor. These diseases can only be diagnosed by undergoing a special medical examination.
Diarrhea in the elderly: treatment
Prescribing treatment for diarrhea in an elderly person requires a very thorough medical examination and an individual approach to each patient. The main danger lies in dehydration of the body, so the fluid deficiency must be replenished as soon as possible. Drinking plenty of Regidron solution helps, which should be drunk every two hours throughout the day.
Many medications can have serious side effects, so your doctor will prescribe activated charcoal with plenty of liquid.
Rice water helps a lot. Add one and a half teaspoons of rice to half a liter of boiling water and cook over low heat for forty minutes. Then you need to cool and strain. Take one quadruple glass during the day at intervals of two to three hours.
Diet for diarrhea in the elderly
During the first day of diarrhea, you should refrain from eating. Then they use only easily digestible food, which will not cause fermentation and will not give a laxative effect. These can be purees and mashed porridges. Instead of bread, eat crackers and biscuits. Baked apples have a good effect on digestion. After a couple of days, you can move on to meat dishes, but only steamed ones. These can be meatballs, chicken cutlets, meatballs. Soups should be either vegetable or low-fat meat broth. Raw vegetables, fruits and milk should be excluded for a while, as well as spices, fried and fatty foods. Cottage cheese and kefir can be introduced into the diet gradually and in small portions. Drink compotes, jelly and weak tea. Include natural-based yoghurts containing bifidobacteria in your diet.
Similar articles:
Traveler's diarrhea
Diarrhea in homosexual men
Diarrhea in a nursing mother
Diarrhea in an adult
With age, lost youth is visible not only in the mirror. In an elderly person, all organs and systems begin to malfunction, which is noticeable to a person even without medical education. One of these striking symptoms is diarrhea. What are the most common causes of diarrhea in older people and what measures need to be taken to normalize stool? We will try to answer all these questions.
Causes of diarrhea
In old age, loose stools can be caused by a variety of reasons, ranging from a harmless disorder to serious pathologies of the gastrointestinal tract. And, the older the patient’s age, the longer the list of probable diseases. This is due to changes occurring in various parts of the digestive tract:
- depletion of facial muscles and disorders of the masticatory apparatus, preventing high-quality chewing of food;
- elongation of the esophagus with subsequent deformation of all its tissues and, as a result, difficulty swallowing;
- change in the size of the stomach and insufficient production of gastric juice;
- decrease in the completeness of processing of consumed food in the small intestine;
- the formation of fecal stones in the large intestine, which leads to the growth of pathogenic microflora and disruption of the synthesis of vitamin K and B;
- changes in the specific gravity of the liver and a decrease in the quality of its functions (regulation of protein and carbohydrate metabolism, detoxification);
- an increase in the size of the gallbladder and disruptions in the production of bile;
- dystrophic or pathological changes in the pancreas, lack of enzymes produced to digest food.
The causes of diarrhea can also be classic, for example, eating low-quality food, intestinal infections, sudden climate change, antibacterial therapy or stress.
But, as practice shows, all these diseases are typical for younger patients. But grandparents feel the symptoms of diarrhea due to more serious changes occurring in their body. In addition to the above, if a patient complains of diarrhea for a long time, this may indicate the development of the following diseases:
- chronic inflammation in the small or large intestine (Crohn's disease);
- damage to the mucous membrane of the large intestine of various types (ulcerative colitis);
- endocrinological diseases;
- diabetes;
- chronic insufficiency of the adrenal cortex (Addison's disease);
- chronic inflammation of the pancreas (pancreatitis);
- malignant neoplasms;
- previous operations;
- intoxication with protein breakdown products due to impaired renal function (uremia);
- lack of zinc in the body.
A decrease in the sensitivity of taste buds leads to the consumption of overly spicy, sweet or salty foods. This negatively affects the functioning of not only the digestive tract, but also all other organs.
Features of treatment
Diarrhea in the elderly requires immediate treatment. After all, at this age, the immune system, like the entire body as a whole, is not able to fully resist infections. Therefore, even one-day diarrhea can provoke dehydration and rapid deterioration of the patient’s condition.
But treating diarrhea without an established cause is not easy. Moreover, in old people the general clinical picture of diseases of the digestive organs is poorly expressed, and often diarrhea is the only symptom indicating ongoing pathological processes. Therefore, the first thing you need to pay attention to is the nature of the bowel movements. For example, liquid stool mixed with mucous contents that is disturbing only during the daytime may indicate irritable bowel syndrome. But the cause of round-the-clock diarrhea with mucus and pus is most likely infectious colitis.
Based on the diagnostic results and after the cause of diarrhea in older people has been established, treatment is selected on an individual basis. And a favorable prognosis can only be guaranteed if you consult a doctor in a timely manner. At the same time, the lack of qualified help significantly reduces the chances of a full recovery.
Rehydration and detoxification
The processes of restoring lost fluids and minerals must begin before going to the doctor, continuing until diarrhea in older people completely stops. The classic version, water or compotes, are ineffective in this regard. After all, with their help, only water reserves in the body are replenished, and the electrolyte balance remains disturbed. Therefore, the best remedy in this situation is pharmaceutical drugs, for example, Regidron or Citroglucosolan.
But in the question of how to stop diarrhea, sorbents come to the rescue, binding toxic substances and preventing their further penetration into the blood. This can be activated carbon, Smecta, Polysorb and others. But it should be understood that taking these drugs is a temporary measure that does not exclude a full examination. After all, if a patient is constantly bothered by diarrhea due to oncology, then the likelihood of recovery on sorbents is zero.
Diet
The next stage is diet. Following a diet for diarrhea in older people is a mandatory component of treatment, regardless of the cause of the disorder. Basic rules on how and what to feed a patient with diarrhea:
- Complete refusal to eat on the first day after signs of diarrhea appear. During this time, you can “eat” with water, jelly, tea, fresh compote and pharmaceutical solutions for rehydration.
- From the second day, meals for diarrhea consist of easily digestible dishes and foods that do not cause gas formation or fermentation in the intestines. This could be oatmeal or rice porridge, mashed potatoes, homemade crackers, baked apples and boiled vegetables.
- Meat is introduced into the diet only on the fourth or fifth day. These can be low-fat varieties such as rabbit or chicken fillet, boiled or steamed.
- At the same time, soups were introduced into the diet. It is recommended to cook them in vegetable broth. If meat is used, only skinless chicken or turkey is acceptable. The meat broth must be secondary, that is, after the first boil, it is drained.
- Gradually, natural-based fermented milk products are being added to the menu. Use starter cultures for homemade yoghurt, cottage cheese and kefir, as this is where live bacteria are contained.
Old people who suffer from diarrhea for a long time should not be fed raw fruits and vegetables, fresh milk, fried and fatty foods. The ban is also imposed on all kinds of spices and spices that have an irritating effect on the stomach and intestines.
Folk remedies
Treatment with folk remedies in people over 50 years of age can only be carried out in combination with drug therapy and strictly under the supervision of a doctor. Popular recipes:
Rice cereal decoction
To prepare it, add 1.5 teaspoons of rice with water (0.5 l). Cook the porridge over low heat for 30–40 minutes. Strain the finished broth and take 50 ml every 2-3 hours. A bedridden patient must be fed with a teaspoon. Read more about the benefits and uses of rice water here.
Oak bark infusion
Pour 200 ml of boiling water over one tablespoon of dry raw material and leave to steep for a while. Strain the finished product and take 5-10 ml every 2-3 hours. The daily dose of oak infusion is up to 250 ml. We wrote other recipes with oak bark for diarrhea here.
Video: How to treat diarrhea at home?
Some extreme patients believe that they know on their own how to treat diarrhea, and use very specific traditional medicine recipes for this. For example, a glass of vodka with added salt. But you should understand that at this age, alcohol and salt can seriously harm your health. Therefore, when making decisions on your own, do not forget to assess the risks. Better yet, don’t experiment!
Diarrhea in older people: why does it appear and how to deal with it?
Diarrhea is the result of pathological processes in the body, manifested through disorders of the gastrointestinal tract. Avoiding various medical terms, it is popularly called diarrhea. Disturbances in the functioning of the stomach are characterized by severe spasmodic pain in it and the appearance of loose stools. The most suitable treatment for severe diarrhea in older people is a strict diet. A failure of the digestive system can affect a person of any age. At the same time, young patients are more likely than older patients to suffer from diarrhea as a result of eating poor quality foods, deliberate or unintentional violation of personal hygiene rules, and the use of medications with a side effect in the form of indigestion.
Other common causes of diarrhea attacks among older people include the ones listed above that can also occur, but this is much less common.
Causes of diarrhea in older people, why does diarrhea occur in older people?
With age, a person experiences a natural weakening of the body and a decrease in the productivity of all basic processes. Therefore, you can support the functioning of vital systems, reducing the load on them, by following a diet.
Complications that affect the functioning of the digestive system are expressed through a decline in enzyme levels and failures in the hydrolysis of nutrients, which directly affects the frequency of loose stools. One of the reasons for this situation, when severe diarrhea appears, is the deterioration of the health of the teeth and their loss, leading to careless chewing of food, which enters the stomach in large pieces and complicates the functioning of the digestive organs in the process of digesting and assimilating what is eaten.
Also an important factor influencing the condition and functioning of the digestive system and the appearance of diarrhea in older people is the age-related reduction in the number of taste buds. Because of this, a person, without feeling the full taste of the food he eats, eats too much salty, sweet, spicy or sour food, excessively irritating the walls of the esophagus, stomach and intestines.
Another age-related change in the digestion of an elderly person, which can also affect the appearance of diarrhea, is a decrease in the secretion of the salivary glands, as a result of which the oral cavity often dries out, which entails weakening of the masticatory muscles and instability of the swallowing process. These changes themselves may not be noticeable, but their result - loss of control over the amount eaten - has a serious impact on the functioning of the body. Therefore, for elderly people, following a diet becomes necessary.
What other causes of diarrhea in older people, causes of diarrhea, and frequent loose stools in older people could be. Transformations also occur in the pancreas, in particular, by reducing secretory function. The liver loses its previous size, becoming significantly smaller. At the same time, the volume of bile secreted becomes scanty.
Due to the thinning of the intestinal mucous layer, a disrupted fermentation process starts. This change can be felt when consuming dairy products and fats. They are absorbed worse than before, which causes diarrhea. Its onset can also be triggered by eating sweets in large quantities. An elderly body digests carbohydrates less well, so if you eat a large amount of sweets, digestive processes are disrupted, leading to diarrhea and diarrhea.
It is important to know that antibiotics can cause diarrhea. In case of prolonged diarrhea in an elderly person, you should get rid of the fecal impaction and check for the presence of pseudomembranous colitis. If you lose sight of them, you can allow the development of serious complications - the formation of ulcerative colitis or Crohn's disease. With these diseases, the patient begins to rapidly lose weight during loose stools.
Diarrhea that does not stop for a long time is also caused by diseases of the endocrine system. If the cause is one or more of these, treating diarrhea will take a lot of effort and time. Diarrhea is accompanied by disorders such as diabetes mellitus and Addison's disease, which require the use of a special diet.
Observation is very important when dealing with diarrhea in older people. It is necessary to monitor not only the patient’s sensations, but also the color, consistency and composition of stool. In particular, if they contain blood impurities, there is a high probability of developing infectious colitis or the presence of a malignant neoplasm. If blood appears in liquid stool, you should immediately contact a medical facility for examination.
Treatment of diarrhea, diarrhea in the elderly, how to treat diarrhea in old age?
Treatment of diarrhea in an elderly person should be preceded by a general medical examination. With its help, it becomes possible to detect a disease that entails such an unpleasant symptom as intestinal disorder. Both examination and treatment are individual and depend on many factors. In this case, one thing remains common to any patient - ensuring a sufficient level of fluid in the body, since loose stools lead to severe and rapid dehydration.
Maintaining water-salt balance is especially important in old age. Regidron is recognized as one of the best means for replenishing fluid in the body. Even taking into account all the advantages of Regidron, before using it you should definitely read the instructions in order to check for contraindications and avoid side effects. How to treat diarrhea for older people? In addition to the prescribed medications, the attending physician may recommend that the patient use activated charcoal and follow a diet for several days. Rice water is considered a non-medicinal remedy for getting rid of profuse diarrhea. To prepare it, you need to boil 1.5 tsp for 40 minutes. rice in 0.5 l. boiled water. After this, the broth is cooled, filtered through a sieve and taken during the day, a quarter glass every 2-3 hours.
It is noteworthy that most diseases that manifest as diarrhea begin the same in people of any age. Typically symptoms of illness are abdominal pain and loose stools. At the same time, a number of diseases provoke diarrhea at fairly late stages, as a result of which diagnosis based only on such a sign as diarrhea leads to the loss of precious time. Some diseases require a full examination and a careful approach to the selection of tests and other studies. Therefore, it is very important to pay attention to any deterioration in the well-being of an elderly person. You should not put off visiting a doctor for a long time if you have severe diarrhea. Timely diagnosis and initiation of treatment can help eliminate the disease at its inception.
Treatment of diarrhea in the elderly with folk remedies at home
Typically, diarrhea is treated with medication. However, due to age characteristics, it is not always possible for older people to use it. The knowledge of traditional medicine comes to the rescue, but the use of its remedies must be agreed upon with the attending physician. The best remedy for treating diarrhea, including the presence of blood in the stool, is chicken stomach membranes, dried and ground to a powder. For medicinal purposes, take 1 tsp. powder 2-3 times a day. Drinking a decoction of rice and an infusion of medicinal chamomile flowers is also considered effective. All these remedies can be used only with the approval of the attending physician and following a diet.
Diet for an elderly person with diarrhea, what can and cannot be eaten with diarrhea?
The greatest threat for older people with loose stools is dehydration. In this regard, treatment and diet are needed when the first signs of illness are detected. The diet should be followed starting from the first day of the disease. Initially, you need to refuse food altogether, drinking only plenty of liquid. The food that the patient eats should be easily digestible, not have a weakening effect and not cause fermentation.
It is allowed to eat crackers and biscuits, mashed porridges, mashed potatoes, and baked apples. The introduction of meat products into the diet is carried out no earlier than 3-5 days, depending on the patient’s condition. Meat should be cooked exclusively by steaming. The most recommended during such a diet are vegetable soups or soups made with lean meat. The consumption of dairy products, raw vegetables and fruits, sweets, fried and fatty foods is prohibited. You can drink weak tea, as well as unsweetened compotes and jelly.
Digestion of food occurs much more slowly with aging than with young people, so exiting the diet should be done very carefully and gradually. It should be noted that the definition of diseases in older people is quite complex, and therefore, actions regarding any treatment must be agreed upon with a qualified specialist. It is also important to know that an elderly person during illness, unfortunately, may be unable to control the occurrence of bowel movements, which leads to the need for his relatives or guardians to monitor this. When leaving your place of residence, you need to ensure that your time away from home is as short as possible or make sure that there is a restroom at the place of your visit. Diarrhea in older people in more than 70% of cases is evidence of illness, and therefore requires diagnosis and consultation with a doctor.
Complications, what could be the consequences?
As noted above, a person’s main enemy in case of bowel dysfunction is dehydration. To support the normal functioning of the body, you should drink more fluids. Lack of water increases the risk of hypertension or heart attack. To prevent diarrhea, older people need to carefully monitor their diet, drink 2-3 liters of water a day and spend time in the fresh air.
Everyone, even healthy people, has experienced diarrhea, or diarrhea. There are a huge number of reasons for its appearance, starting with food products that are incompatible with each other and ending with very severe infections.
In this article, we will not consider severe infections accompanied by painful diarrhea, such as cholera and others. This is a separate topic.
Watery diarrhea
Watery diarrhea occurs when the small intestine is involved in the pathological process. This may be a situation where poisoning has occurred with poor-quality food products or during acute intestinal infections.
Sometimes the number of pathogenic bacteria present in the intestines can be very small. It is not the bacteria themselves that are dangerous, but their metabolic products, the toxins they release.
In the cold season, watery stools sometimes occur due to a number of viruses that are active in winter. These are so-called rotavirus infections, which are very easy to catch.
Why is water diarrhea dangerous?
Diarrhea can be roughly divided into watery stools without pathological impurities, such as blood, and diarrhea streaked with blood. If blood appears in the intestinal discharge, this is a signal to seek medical help, because... The causes of this symptom can be very serious: intestinal bleeding, hemorrhoidal bleeding or a serious bacterial infection. All these conditions can threaten the patient's life. But this also needs to be discussed separately.
So, if water diarrhea occurs in an adult, treatment should be immediate. It should be noted that with watery stools there is a large loss of water, and if this process is also accompanied by vomiting, then we can talk about dehydration, and it can occur very quickly if emergency measures are not taken.
The human body normally contains about 85-90% water. More precisely, the brain, muscles and heart contain approximately 76% fluid, blood - 84%, and only the human skeleton consists of 15-20% water. From this you can understand how important water is for humans. Every cell of our body consists of water, and if there is a lack of fluid, all systems and organs will suffer. In addition, during diarrhea, along with water, a huge amount of minerals that the body needs is released.
For a small child, a loss of 10% of body weight due to watery diarrhea is fatal. If a child weighs 5 kg, then a loss of 500 ml of fluid will be fatal for him. For adults, losing 10% of their body weight in a short period of time is more problematic, because... their weight is much greater, so they have time to make a decision. Dehydration (dehydration) is most dangerous for children and the elderly. Diarrhea in an adult - what to do? Of course, treat.
Diarrhea is not a diagnosis, but a symptom. To choose the right treatment tactics, it is necessary to establish the true cause of loose stools. Even if an adult has loose stools 2-3 times a day, which does not pose a threat to his life, over time (if this lasts for several days), the body will be severely depleted and the water-salt balance will be disrupted. Recovery will take much longer than the duration of the illness. If an adult has water diarrhea, treatment is necessary, especially if an elderly person suffers from this symptom.
Causes of diarrhea
Diarrhea is a kind of defensive reaction to the introduction of pathogenic microorganisms, viruses and bacteria. In this way, the body itself is protected from the harmful effects of pathogenic microflora and carries out its detoxification. But if this condition does not go away within a few hours, help is needed. Especially if there is a temperature and in this case it is necessary. Hyperthermia (increased temperature) may indicate general intoxication of the body. This condition requires an appropriate attitude. You can't leave everything to chance. Some people believe that diarrhea is not really a disease. Diarrhea still needs to be treated if it lasts more than one day. This way you can save your body from serious consequences.

If the patient complains of diarrhea, abdominal pain, treatment is also necessary. Pain is a serious symptom that may indicate a serious illness such as pancreatitis, hepatitis, gallstones or appendicitis. If you experience pain with diarrhea, you should see a doctor. In some of these situations, surgical treatment is necessary.
There are other causes of diarrhea:
- dyspeptic - this is the most common cause of diarrhea; it can occur due to insufficient secretion of the stomach, improper functioning of the glands and, as a result, improper digestion of ingested food;
- infectious - can be caused by dysentery bacillus, various intestinal viruses, amoebas and food toxins;
- nutritional is an allergic reaction to food;
- toxic - poisoning with poisons and toxic substances, such as arsenic or mercury;
- medicinal - caused by side effects of medications, for example, some antibiotics in the intestines kill not only pathogenic flora, but also beneficial ones, thereby causing diarrhea;
- neurogenic - can be caused by strong emotions or fear; such diarrhea is also called “bear disease”.
Patients experience diarrhea differently, depending on the individual characteristics of the body. For example, loose stools 2-3 times a day in some people cause weakness and poor health, while in others diarrhea 5-6 times a day does not cause negative consequences.

If diarrhea lasts a short time, it usually does not cause negative consequences and passes without much harm to health. If diarrhea continues for a long time and is accompanied by bloating, rumbling, false urge to defecate (tenesmus), nausea, vomiting, heartburn and causes severe weakness (depletion of the body), then this condition requires emergency medical care. Often patients with such symptoms are hospitalized.
For any type of diarrhea, it is necessary to drink enough fluid. Compliance with the drinking regime can protect against negative consequences and keep the patient’s body in good shape.
It is better to drink mineral water without gas content, it will help maintain the water-salt balance. If prolonged water diarrhea occurs in an adult, treatment is necessary. If home treatment does not help, and diarrhea does not go away within a few days, this is a serious reason to seek help from a medical facility. If severe diarrhea develops, a doctor will determine the cause and treatment.
Diet for diarrhea
Gentle, regardless of the reasons that caused it, is necessary. Until the condition improves and the symptoms of intoxication disappear, you need to follow a diet.
The following products are allowed:
- porridge with water;
- jelly;
- lean boiled or steamed meat;
- steam cutlets;
- boiled or steamed fish.
Prohibited products:
- fatty foods;
- fried foods;
- sweets;
- spicy dishes;
- pickled products;
- any canned food;
- carbonated drinks;
- coffee;
- tea is too strong;
- any alcohol.
After the diarrhea disappears and the diet improves, you need to stick to it for a few more days, at least for a week. By gradually adding other previously prohibited foods to the diet, the weakened body is prepared for the usual diet. You cannot immediately return to your usual diet. A sudden return of the wrong dish to the menu can upset the fragile and unstable balance after illness.
Diarrhea: causes and treatment
Treatment of diarrhea directly depends on the cause that caused it. What medications for diarrhea are most effective? We'll talk about this in this section.

First of all, any diarrhea should not be treated with antibiotics. This is done only in severe cases, for example, if the cause of the pathological process really poses a serious danger. This applies to diseases such as salmonellosis or cholera. In this case, the patient must be hospitalized, and further treatment will be carried out under the strict supervision of doctors. If water diarrhea is observed in an adult, treatment should be aimed at preventing dehydration and restoring water-salt balance. For these purposes, solutions such as “Regidron” or “Oralit” are suitable; you can also drink mineral water without gas.
Solutions are taken after each stool, half a glass. In addition, you should drink at least 4 glasses of one of these medications within 12 hours.
Medicines for diarrhea
Medicines for diarrhea are not a panacea at all. A range of interventions should be considered when treating diarrhea. The most important of which, as already mentioned, is the fight against Let's look at medications for diarrhea in adults, which are used most often.
All of them are divided into several pharmacological groups:
- sulfonamide drugs ("Fthalazol");
- antibiotics (Levomycetin, Tetracycline tablets);
- nitrofurans (drug "Furazolidone");
- antimicrobial drugs ("Enterofuril", "Sulgin");
- antifungal (Intetrix) - used for;
- enterosorbents (activated carbon);
- antiviral drugs.
Let's look at the most famous ones among adults. In what case is it advisable to take this or that drug?

Activated charcoal for diarrhea
What to give for diarrhea to an adult? Enterosorbents are a group of drugs that have an adsorbing and enveloping effect. Treatment should begin with activated carbon. Sometimes this is enough. These tablets for diarrhea in adults (and children) are not absorbed in the intestines.
Activated carbon is taken at the rate of one tablet per 10 kg of patient weight. So, if the patient weighs 60 kg, then, accordingly, he should take 6 tablets and drink plenty of water.
Activated carbon absorbs all harmful toxins, bacteria and viruses, and also binds water and covers the intestinal wall with a protective layer. After this, it is excreted naturally. It should be noted that after taking tablets of this drug, the stool will be black. There is no need to be afraid of this. If diarrhea occurs due to poor-quality products, then activated carbon in most cases is sufficient for treatment.
The drug "Fthalazol" for diarrhea
This group is most appropriate to take for infectious types of diarrhea (dysentery, enterocolitis and colitis of an infectious nature). Taking the medicine "Fthalazol" for allergic types of diarrhea and ordinary indigestion will be ineffective. Its effect is noticeable only on day 2-3, when the growth of pathogenic microflora under the influence of the drug is stopped.
Imodium for diarrhea
The drug "Imodium" (its other name is "Suprelol", "Lopedium" and "Loperamide") begins to act within the first 40-60 minutes. This drug is effective for diarrhea caused by poor-quality foods, as well as irritable bowel syndrome and in the initial stages of infectious diarrhea. It helps well with frequent vomiting. This drug is convenient to take with you on the road. Diarrhea is a common companion for travelers.
Treatment with Loperamide and Simethicone
This is a new generation drug, it is a combined remedy for diarrhea “Imodium Plus” and includes the so-called antifoam agent - simethicone. This substance eliminates bloating and adsorbs unnecessary intestinal gases. Thanks to it, spastic pain and the feeling of intestinal distension disappear. These are chewable tablets for diarrhea in adults. It is not recommended to give them to children under 12 years of age.
Natural Remedies for Diarrhea
This includes drugs such as Smecta and Kaopectate. These drugs are used for rotavirus infections. It should be noted that the drug "Kaopectate" is contraindicated in childhood.
These drugs belong to the group of enterosorbents; they gradually reduce the frequency of trips to the toilet, and also relieve bloating and rumbling in the abdomen.
Tablets "Linex" for diarrhea
This product contains beneficial microflora and has a positive effect on the entire gastrointestinal tract. It includes 3 types of positive microflora:
- lactobacilli - have a positive effect on the functioning of the small intestine;
- enterococci - have a similar effect and help the small intestine function properly;
- bifidobacteria - actively work in the large intestine.
Folk remedies for diarrhea

Traditional medicine knows many ways to treat such ailments as diarrhea. Folk remedies for treating diarrhea have been proven for centuries.
- A decoction of pomegranate peels is considered an effective remedy for intestinal disorders. To prepare the medicine, you need to take a well-washed peel of one fruit and pour a glass of cold water. Boil over low heat for 10 minutes, cool and strain. Take this remedy every two hours, 2 tbsp. spoons.
- Traditional treatment for diarrhea involves the use of rice water. Taking this remedy every 20-30 minutes for 3-4 hours will relieve bloating and stop diarrhea.
- Wormwood will help cope with diarrhea. But you need to be careful with this product: do not exceed the dosage and do not use it for too long. To prepare the medicine, add 1 teaspoon of dry herb to one glass of boiling water and leave for half an hour. Take the medicine 30 minutes before meals, 1 tbsp. spoon.
- A very strong folk remedy for diarrhea using an alcoholic infusion of walnut partitions has been known for a long time. It must be taken without exceeding the permissible dose (5-6 drops), otherwise it may provoke a reverse reaction - constipation. As soon as the number of trips to the toilet decreases, you need to reduce the dosage to 2-3 drops. It is clear that alcohol tinctures can only be used internally for treatment by adults. To prepare the drug, take 1 tbsp. spoon of ground walnut partitions and pour one glass of vodka. Leave in darkness for 5-7 days. This product is prepared for future use and stored in the refrigerator. It is recommended to always have this medicine on hand for those who are prone to frequent intestinal disorders.
Conclusion
For ailments such as diarrhea, folk remedies can be very effective. Whatever the nature of the origin of diarrhea, this fact must be taken seriously. If you cannot cope with an intestinal disorder on your own, and pain or fever also occurs, in this case you need to seek medical help. This is especially true for elderly citizens, because... They become dehydrated much earlier than young people in full bloom.