Adhesions of the intestine and small pelvis after surgery: what they appear from and how to treat. Adhesion medication after surgery
What happens to our body during operations? First, the tissues are cut, then connected, and they are forced to grow together again. It is believed that laparoscopic surgery, which is performed through several small incisions (“punctures”), is much less traumatic, since the surface of the surgical field is significantly smaller than with a conventional band “open” operation.
During laparoscopy, on a thin membrane covering the inner surface of the abdominal wall, damage is formed at the points of passage of instruments, incisions or clips. After the instrument is removed, this section of the damaged membrane (called the serous membrane) heals on its own.
How do adhesions and scars form?
However, our tissues have one natural property that cannot be canceled - they seek to protect our body. And sometimes the development of so-called protective factors after damage occurs intensely - with a margin.
What is the treatment of adhesions after surgery?
In practice, it looks like this: in places of damage to the serous membrane, collagen and elastic fibers and connective tissue cells are intensively produced. If at this time some internal organ (for example, a loop of the intestine) touches the site of the damaged serosa, it is involuntarily involved in this process. A cord is formed from the connective tissue, which leads from the wall of the internal organs to the inner surface of the abdominal wall. This is called soldering.
Adhesions can also connect internal organs to each other. Each of them also covers the serous membrane. During the operation, its micro-tears are not excluded. And these places of microtrauma can also subsequently become a source of formation of adhesions between this organ and the organs adjacent to it.
Also, at the site of contact and healing of tissues after their dissection or rupture, a scar may form, in which ordinary tissue is replaced by a more rigid and inelastic connective tissue. Scars can be on the skin, and may be on the internal organs.
Why are sleepers bad?
Nature took care that in our harmonious body the organs were completed and laid out clearly and correctly, as in Tetris. They occupy the entire interior space and touch each other with suitable sides, like a carefully fitted puzzle. If we consider all the organs separately from the body, one can be amazed at how much space they occupy and how they fit inside us! Precisely because postoperative scars and adhesions violate this original harmony, they affect our body.
What is the negative effect of adhesions. They:
- disrupt the mobility of the organ, which affects its function. Moreover, both external mobility, which depends on the movements of the diaphragm, and internal mobility, which is active and does not depend on the movement of the diaphragm, suffer;
- disrupt blood circulation in the affected organ;
- violate the innervation of the body;
- contribute to the occurrence of pain and spasms in the organ.
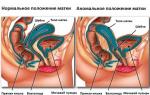
Sometimes the adhesion is so powerful that it can disrupt the anatomically correct position of the organ. All of these causes lead to other disorders in the body. Moreover, which at first glance are not connected with the affected area. Adhesions and scars that have arisen after abdominal surgery can “radiate” with pain in various parts of the spine, joints, lead to a change in posture and a violation of the position of the body in space, etc.
How are adhesions treated?
According to the timing of the formation of adhesions, there are:
- 7-14 days after the operation - the phase of young adhesions, when adhesions are still very loose and easily torn;
- 14-30 days after the operation - the phase of mature adhesions, when the adhesions are compacted and become strong.
Starting from the 30th day after the operation and further, for several years, there is a process of restructuring and the formation of scars and adhesions. The process is individual, much depends on the properties of the organism itself, its anatomical structure, the functioning of internal organs.
The doctor may suspect the presence of an adhesive process in the abdominal cavity according to clinical data, the collection of anamnesis and the results of such studies as ultrasound, CT, colonoscopy. The adhesive process in the abdominal cavity and the pelvic cavity can be treated medically or surgically. During the operation, adhesions are separated, but this method should be resorted to only in extreme cases, if the strands are so thick and coarse that they greatly impair the function of the organ, and a more loyal and sparing treatment does not help.
How osteopathy affects adhesions
The osteopathic doctor is able to feel with his hands where the adhesions are located and where they lead, where they are attached and what they pinch. He is also able to loosen their tension in a few sessions, can restore, balance and balance damaged organs, and therefore restore their function to the fullest extent possible.
It is also in the power of the osteopathic doctor to interrupt the chains of damage and pain in the parts of the body that seem to be unrelated to the operated area. After all, our body is a holistic system where everything is interconnected. The osteopath directly affects the adhesion, without violating the integrity of body tissues, and therefore without an additional factor stimulating the formation of connective tissue. By restoring and harmonizing the function of the suffering organ, the body releases energy to launch a complete recovery in possible individual conditions for the whole organism.
Any surgical intervention, no matter how minimally sparing it may be, leaves behind a lot of negative changes, injuries and stress that the body has to deal with alone. What the body will undertake for its treatment, what it will sacrifice, how it will limit itself is always individual. But within the framework of self-preservation, this is always expressed in the loss of function to one degree or another, and hence the subsequent suffering of the whole organism with loss of compensation and the expenditure of much greater forces for normal functioning throughout life.
Therefore, if in your life you have had surgical interventions on the abdominal organs, consult an osteopath. It does not matter whether the operation was conventional or performed using a gentle laparoscopic method. Any discomfort has a reason, which means there is an opportunity to solve it.
An osteopath can use pulse diagnostics to determine the significance of adhesions or scars on the body. This means that if the properties of your pulse change when you press on the postoperative scar, then this zone is important and significant for the whole body, and you need to work with this adhesion or scar.
Adhesions and scars have the following significance and prevalence of influence:
- local (influence is limited to the area of the scar or adhesions);
- regional (the influence extends to the entire chest or abdominal region where the spike is located);
- global (affects the entire organism, up to a violation of its position in space).
How long does osteopathic treatment last?
If the patient has undergone surgery, then tactically the osteopath will act as follows. 10 days after the operation, when the sutures are removed, the doctor will work with the scar itself in layers, work with the tissues directly around the scar itself and restore that independent mobility of the organ, which does not depend on the movement of the diaphragm. This period of work is within 10 days to 3 months after the operation.
If the duration after the operation is 3 or more months, then the doctor will pay attention to all surrounding organs and tissues in the operation area, influence the mobility of all internal organs in general and directly to the localization sites of the adhesions themselves.
The information was prepared by the leading specialist of the clinic of osteopathy and family medicine Osteo Poly Clinic, osteopathic doctor, chiropractor, endoscopist surgeon.
The site is a medical portal for online consultations of pediatric and adult doctors of all specialties. You can ask a question about "adhesions after hysterectomy" and get a free online consultation with a doctor.
Ask your questionQuestions and answers on: adhesions after hysterectomy
2012-04-26 05:55:29
Ludmila asks:
After the removal of the uterus and appendages on the right, 3 years have passed, during intercourse, severe pain in the abdomen and gives in all directions and into the anus, when ultrasound was done a year ago - adhesions, how can I alleviate my condition and are adhesions curable?
Responsible Kravchenko Elena Anatolievna:
Good afternoon, Lyudmila. Adhesive disease is treated surgically. To alleviate your condition, visit a gynecologist, he will examine you and prescribe a treatment and a consultation with a surgeon.
2014-07-10 12:35:49
Carey asks:
I have adhesions after the operation to remove the ovarian cyst, and there was also inflammation of the appendages, The gynecologist prescribed vitamins B1, B6 and aloe intramuscularly, the inflammation went away, but colposcopy showed erosion of the cervix, Yesterday I was cauterized with erosion of the cervix, I also continue to take injections intramuscularly Vitamins B1, B6 and aloe, tk. the course is not over yet, is it harmful after cauterization of erosion?
2013-11-08 19:12:13
Margaret asks:
Hello November 5 this year was a milk surgery in gynecology. Dissection of adhesions after 2 cesarean; How to behave after the operation I have 2 children 3 and 5 years old
I am alone with them. what is needed and how long does the recovery process take, what is impossible?
Responsible Serpeninova Irina Viktorovna:
The recovery period, which requires restriction of physical activity, usually lasts six months, but in each case, recommendations are given by the operating doctor.
2012-01-04 14:09:56
Ludmila asks:
Hello. In August 2011, I had an operation to remove the uterus (myoma). In December, signs of adhesions-pain began to appear, there was even an attack. I want to ask if I can take the drug Longidase in suppositories rectally. I myself am a pharmacist, I know about this drug, I want to consult with you. an assumption about them. After the operation, a histology of the tissues was done - there was a leomyoma of the uterus, leukoplasia of the cervix with stromal fibrosis. Thank you in advance for your answer.
Responsible Serpeninova Irina Viktorovna:
Longidaza is a powder for preparing a solution for intramuscular or s / c injections in ampoules or vials. It is not produced in suppositories and there is no evidence whether its properties will be preserved when preparing suppositories from it on its own. Use it in the way recommended by the manufacturer.
2011-03-06 18:36:34
Ramsia asks:
Hello dear doctors!
07/01/2009 at the age of 47, I underwent surgery for cervical dysplasia of the 3rd degree. (The focus was in the neck measuring 05. * 1 cm) - cervical extrusion with appendages. There was no menopause and the ovaries were healthy, but the gynecologist-oncologist advised me to urgently remove the ovaries before the operation, as well. taking into account their experience and my pathology, I can get to them again on the operating table with such a pathology or even worse. They did not leave me other options and I agreed.
After the operation, she felt more or less satisfactory.
But after 8 months there was pain in the lower abdomen, a feeling of heaviness. The pain radiates to the sacrum, rectum. I stopped feeling the urge to defecate. I feel some kind of unpleasant sensation, and with a digital examination I feel that the rectal ampulla is full of feces and I feel the bulging of the vaginal stump into the rectum. Weakness, fatigue. These pains have been tormenting me for a year now. She became nervous and irritable. I’m already thinking about suicide (I wish I could take sleeping pills and fall asleep, forget about this pain). I have been taking Angelique for 7 months, because. there were hot flashes and increased glucose, cholesterol and bladder problems. It got a little better.
On CT scan of the small pelvis - Condition after extirpation of the uterus with appendages. The stump of the vagina with clear uneven contours, the surrounding tissue with fibrous changes and "small" calcifications. The bladder is significantly filled, of the usual form with clear, even contours, the contents are homogeneous.
Ultrasound of the pelvic organs: In the small pelvis, there is an adhesive process, no visible formations have been identified. The bladder has clear, even contours, the walls are compacted, without visible additional formations.
Volume of initial urine:-350 ml.
The volume of residual urine is 55 ml.
Irriography - With the retrograde introduction of a liquid barium suspension, all sections of the large intestine were performed up to the dome of the blind. The localization of the loops of the sigma and the descending colon is disturbed. The descending colon is displaced medially, binds the knee bend, the sigma forms multiple loopy bends and kinks against the background of its lengthening, the displacement of the loops is sharply limited and painful. In the descending colon, in the sigma, the haustration is smoothed, uneven, the mucosal folds are moderately thickened. Symmetrical haustration is preserved throughout the rest of the colon. No organic constrictions or filling defects were found.
conclusion: R signs of violation of the anatomical localization of the distal colon as an indirect sign of adhesive disease, signs of chronic colitis.
EGDS-Esophagus is freely passable. The mucosa is pink. Gastric mucosa, pink, edematous. Pyloric sphincter concentric. Bulb 12 of the duodenum is not deformed, the mucosa is pink, it looks like “mannoly cereals!” The onion part is pink.
Conclusion - superficial gastritis. Moderate inflammation. Indirect signs of pancreatitis.
Colonoscopy - perianal area is clean. Colonoscopy was performed up to the splenic angle of the colon. The mucosa is pink throughout, the vascular pattern is not changed. The peristalsis is uniform. The conclusion is that there were no signs of inflammation.
A few days ago, I went for a consultation with a surgeon and a gynecologist about adhesive disease. The gynecologist prescribed electrophoresis on the lower abdomen with lidase (1.5 years have passed since the operation), will lidase help now? I heard about longidase. What is it? Does it help?
The surgeon looked at my examination results and sent me to an oncologist: let them figure out what kind of "small" calcifications on the peritoneum! If the adhesive process
then we will wait for the OKN. Then, according to emergency indications, we will operate.
IN HOW! So you have to wait for OKN or peritonitis or intestinal necrosis! And if the ambulance does not arrive on time or will bring to a drunken surgeon for the holidays! What then! Die!
2 days ago I went to another surgeon, because. no strength to endure the pain. The female surgeon looked at all the examinations and my stomach and diagnosed it as an adhesive disease of the abdominal cavity. Dolichosigma. Colonoptosis. Coccygodenia.
She prescribed Movalis, candles. Milgama No. 10 Magnetotherapy on the cross. Electrophoresis with novocaine No. 10.
She advised me to go for a consultation with a proctologist - maybe she says prolapse of the small intestine?
I'm tired of doctors, drugs and pain. I don't want to live! But it seems like she’s not old yet, and I need to work a lot, I have a loan in a bank. But I can’t work.
Tell or Say please, it is possible to remove commissures by a laparoscope. I heard it's done. We do not have it in Astrakhan, and our surgeons are against this method of removing adhesions. They say how you inflate your stomach with carbon gas, when you have it all in adhesions, Even the normal anatomical position of the intestine is disturbed! Yes, and you can die during this operation. In general, they consoled me.
And further. Please tell me what research method and which doctor can diagnose prolapse of the small intestine?
If in my situation it is possible to dissect the adhesions with a laparoscope, then where is it done well (so as not to earn even more problems and die) After the hysterectomy with appendages, for cervical dysplasia 3 tbsp. In the histological response after the operation, the endometrium is in the proliferation phase. In the neck of the gland of the endocervix. In the area of the external pharynx, a squamous epithelium with parakeratosis, hyperkeratosis. In the ovaries, theca tissue, white bodies. Given the results of this histological picture, did I have endometriosis? if so, can there be pain in the abdomen due to this or is it adhesions? If you have endometriosis, how can you treat it?
Help me please. Thank you.
Responsible Tovstolytkina Natalia Petrovna:
Hello Ramsia. Let's start with the last question. The data of your histological conclusion do not give any reason to suspect you have endometriosis. Regarding the adhesive process, it is very doubtful that it began 8 months after the operation. Rather, it could have been earlier, but it is necessary to look for another cause of the pain that has appeared. You need to start with a consultation with a neurologist, perhaps an MRI scan to rule out diseases of the spine that can give similar pain. Hormone replacement therapy is also mandatory - then thoughts of suicide will pass by themselves. With regard to enzyme preparations, it is very doubtful their effect in a year or two after the operation. After another operation to cut the adhesions, you may develop new ones, because. This is how your body reacts to surgical interventions. And do not forget about a healthy lifestyle - a diet that does not constipate, exercise therapy, swimming pool, etc. 80% of health is you yourself, without doctors and medicines. Good luck.
2008-10-19 01:43:38
Anna asks:
Hello! Please advise how should I proceed. In 2005, I had a cyst removed from my left ovary (laparoscopy). She was then treated with danazol for 5 months. X-ray tubes showed complete obstruction of the left and partial right. Now they put (ultrasound) adenomyosis of the uterus, the initial stage. Symptoms of endometriosis appeared 4 months ago (discharge 2 days before menstruation and heavy clots on day 2). I was scheduled for an operation to dissect adhesions and remove foci of endometriosis and HSG. Should I undergo hormonal treatment before surgery.
Responsible Bystrov Leonid Alexandrovich:
Hello Anna! Usually, endometriosis undergoes hormone therapy after laparoscopy, because. laparoscopy can also reveal other forms of endometriosis. If there is a laparoscopy, then the HSG is no longer needed.
2016-03-30 15:58:25
Christina asks:
Hello!
I am 34 years old, married for 4 years, I can not get pregnant, myoma or polyp on the leg inside the uterus. After MRI and ultrasound, the doctors did not determine.
I am going to have an operation to remove this disease and at the same time check the patency of the fallopian tubes.
The doctor said about postoperative adhesions, so he warned that he would use Intercoat gel.
What do you think: is it harmful to use this gel?
And after this surgical intervention, will I be able to carry a child after artificial insemination?
Thank you in advance,
Christina
Responsible Palyga Igor Evgenievich:
Hello Christina! Are you planning a laparoscopy? Or a hysteroscopy? In any case, after these two interventions, postoperative adhesions are not formed. If the fallopian tubes turn out to be impassable, then not a single gel will help. If the gel is injected into the uterine cavity, it will not adversely affect the implantation of the embryo during IVF, as well as the carrying of the pregnancy.
2014-10-03 17:08:27
Natalia asks:
Tell me, please, is it possible to engage in masturbation and oral sex after laparoscopy of uterine fibroids (5 subserous nodes) and removal of adhesions. The mother was left. The operation was 24 days ago. The doctor said sexual rest for 2 months.
2013-08-07 11:41:27
Elena asks:
Hello, I am 35 years old, 5 pregnancies 1995 - abortion, 1997 abortion, 1999 - pregnancy, ended with the birth of a healthy child (rupture of the cervix during childbirth), 2010 - missed pregnancy (no one saw the fetus on ultrasound, ended in miscarriage, pregnancy diagnosed posthumously by hCG, 2013 - pregnancy after IUI, froze for a period of 6 weeks 4 days.
Over the past year I have experienced the following:
1. August 2012 - cyst rupture, resulting in an attack of appendicitis, abdominal surgery, 2 courses of antibiotics.
2. October 2012 - hospitalization in an ambulance, pain syndrome, endometrioma + terrible endometriosis + adhesive process was diagnosed, no surgery, a course of antibiotics. Appointed Visan, did not take it, decided to consult with other specialists.
3. It turns out that every 2 months (when the left ovary is working) a pain syndrome occurs, literally the whole body hurts, the temperature is up to 38.
December 2012 - planned laparoscopy to remove the endometrioma (3.7 cm), dissection of adhesions. Before operation again a pain syndrome. Terrible endometriosis was not confirmed by laparoscopy. No hormonal support after the operation was prescribed, they said to become pregnant.
4. May 2013 - IUI (in addition to all of the above, there is also a male factor. Before IUI, an endometrioid cyst of 3.5 cm was visible on ultrasound. Pregnancy occurred on the first attempt. After ultrasound at 6 weeks, the doctor canceled utrozhestan. Pregnancy froze for 6 weeks 4 days.
5. July 2013 - vacuum regulation, on the 4th day after it, pain syndrome.
What could be the most likely cause of the fading?
1. The presence of an endometrioid cyst.
2. Cancel Utrozhestan
3. Genetic abnormalities (analysis for karyotypes is not yet ready)
4. Long flight by plane (at 4 and 6 weeks)
And the most important question: is it possible to attempt IUI again and when, and how it can end. 2 missed pregnancies - a trend, the 3rd time is scary.
From this article you will learn what causes adhesions after removal of the uterus.Adhesions after hysterectomy
Adhesions are seals from the connective tissue that appear after inflammation or surgical interventions drag from organ to organ. Adhesions may occur after surgery. This is a compaction of connective tissue that passes from one organ to another.
Adhesions can form after surgery if hypoxia or ischemia of tissues occurs, rough manipulation of the tissue, drying of tissues during surgery, the presence of blood, separation of former adhesions, the presence of foreign bodies.
The fallopian tubes, uterus and ovaries can be involved in the adhesive process that occurs with inflammation of neighboring organs (appendicitis - inflammation of the appendix), as well as with lesions of the small and large intestines. In this case, the genital organs themselves suffer little: the adhesive process almost does not violate their internal structure. If inflammation occurs inside the genital organs, not only the formation of adhesions occurs, but also damage to the genital organs themselves. The most unprotected in this regard is the fallopian tube - one of the most delicate and finely arranged smooth muscle organs.
Adhesions after hysterectomy
Foreign bodies may remain after the operation, for example, particles of talc from the surgeon's gloves, or fibers from tampons, gauze, have entered the body cavity. Adhesions can also occur with endometriosis. This is the entry of some menstrual blood into the abdominal cavity through the fallopian tubes. If a woman has a good immune system, then the cells of the uterine lining that are in the menstrual blood are removed by themselves. And if the immune system is impaired, then adhesions can form.
If it is too late to see a doctor, then after the treatment of adhesions, the fallopian tube will no longer be able to promote a fertilized egg. Then fertilization will be practically impossible, even artificially. Sometimes after a disease, in order to enable a woman to become pregnant, IVF is done, and the fallopian tube will have to be removed completely. After inflammation, the walls of the fallopian tube can stick together and grow together, which means that the egg cannot pass. And it will be necessary to remove the adhesions and the pipe.
Once in the fallopian tubes, the infection first affects the mucous membrane of the fallopian tube (endosalpinx), then the muscle layer (myosalpinx), and only at the last stage, the outermost layer of the fallopian tube (perisalpinx) is involved in the inflammatory process and conditions arise for the formation of adhesions. If the treatment of adhesions is late or not effective enough, after recovery, not only adhesions remain, but also irreversible damage to the mucous membrane of the tube and its muscular layer. Cilia disappear, and scar tissue forms in place of smooth muscle fibers.
Adhesions after hysterectomy
The fallopian tube can turn into a connective tissue sac (sactosalpinx), i.e. she loses the ability to promote a fertilized egg. With such disorders, the elimination of adhesions cannot restore the function of the fallopian tube, and the presence of a focus of the inflammatory process leads to a decrease in the likelihood of pregnancy even in the tube from the opposite side or with the help of in vitro fertilization. In such cases, in order to increase the chances of pregnancy with IVF, which can be carried out after recovery, it is necessary to remove the entire tube. As a result of inflammation, gluing and fusion of the walls of the fallopian tube can occur, which leads to obstruction of the tube for the egg and is also an indication for separation of adhesions or removal of the tube.
With the help of special tools, dissection and removal of adhesions are performed. This can be done with laser therapy, electrosurgery and aquadissection.
Laparoscopy is considered a low-traumatic surgical intervention, which is performed according to various indications. Complications after it are extremely rare, and the recovery period does not last long. But can adhesions form after laparoscopy? This operation is the safest way to treat gynecological diseases. It is often used to eliminate adhesions, but it can also be the cause of their formation.
- These are seals made of connective tissue, with which the internal organs are interconnected. This is contrary to human anatomy. Adhesions after laparoscopy look like transparent or whitish stripes. They lead to deviations in the work of the body. That is why the adhesive process refers to pathological phenomena and needs treatment.
Adhesions after laparoscopy of the ovary are rare, but extremely darken the life of a woman. They do not always make themselves felt, but sometimes they lead to the development of complications. In addition, the cause of the pathology may be inflammatory processes in the pelvic area. It is noteworthy that adhesions form at almost any age.
Factors contributing to the development of adhesions after laparoscopy:
- diabetes;
- damage to the sheets of the peritoneum or their "overdrying" due to filling the abdominal cavity with carbon dioxide at the wrong temperature;
- the movement of bacteria to the area of surgical intervention from other parts of the body (this prevents normal tissue repair);
- advanced age;
- burn damage to tissues with a radio wave knife, plasma scalpel or other device in the process of coagulation;
- use that resolves for too long;
- oxygen starvation of tissues and improper metabolism in them;
- leaving cotton balls, suture material, etc. in the area of manipulation;
- the development of a postoperative infectious process (rare).

Symptoms of adhesions in the pelvis
Signs of adhesions may be absent. As the postoperative scar thickens, the appearance of pulling pains in the operated area, aggravated by active movements, as well as pain during intimacy, is not excluded.
The following manifestations of pathology are possible:
- development of intestinal obstruction;
- improper functioning of internal organs;
- pain in the pelvic region (abdominal or chronic);
- menstrual irregularities;
- infertility;
- the presence of uterine bleeding with an unpleasant odor, not caused by menstruation.
What to do if adhesions form after laparoscopy
Change in diet
In the presence of an adhesive process after surgery, the laparoscopic method shows a change in the diet, which contributes to the speedy elimination of the pathology. Spicy, fried and fatty foods are excluded from the diet, as well as:
- products that increase gas formation in the intestines;
- alcohol;
- spicy and fatty sauces;
- pickled and smoked dishes;
- canned food.
The menu for spikes should consist of sour-milk products, lean soups, low-fat meat and fish dishes, chicken eggs, fruits and vegetables, and various cereals. It is optimal to eat small meals five to six times a day.
To avoid the development of the adhesive process, it is recommended to use an anti-adhesion gel, for example, Mesogel. It is rubbed into the skin in a thin layer. You can perform special exercises aimed at eliminating the pathology. You can learn more about anti-adhesion exercises HERE.

Adhesion therapy
In the asymptomatic course of the pathology, conservative therapy is indicated, involving the use of drugs and the passage of physiotherapeutic procedures. If these methods are ineffective, then at the request of the patient, relaparoscopy is performed.
The chronic pain form is usually treated conservatively, including by local action on the affected tissues. Physiotherapy and electrophoresis procedures are practiced using absorbable agents (iodides and lidases). Drugs are prescribed to relieve pain and other symptoms of pathology.
A patient who developed intestinal obstruction as a result of the adhesive process is hospitalized in a hospital. Next, an analysis of the viability of the intestine is carried out and the issue of the need to capture healthy tissue is decided.
Laparoscopic removal of adhesions
 Dissection of adhesions is carried out by laparoscopic access. At the same time, three incisions are made on the woman's stomach (no more than a few millimeters in size). In the process of manipulation, the normal ratio of the organs of the reproductive system is restored, adhesions are removed, and a new hole is formed in the fallopian tube instead of the sealed one.
Dissection of adhesions is carried out by laparoscopic access. At the same time, three incisions are made on the woman's stomach (no more than a few millimeters in size). In the process of manipulation, the normal ratio of the organs of the reproductive system is restored, adhesions are removed, and a new hole is formed in the fallopian tube instead of the sealed one.
Ways to remove adhesions:
- laser therapy, in which adhesions after removal of the uterus and ovaries or other surgery are dissected with a laser;
- aquadissection - problematic tissues are removed with the help of water, which is supplied under pressure;
- electrosurgery, in which an electric knife is used to eliminate adhesions in the pelvis.
Laparoscopy of the resulting adhesions rarely leads to complications. After it, the patient is in the hospital for no more than two days. They let her go home on the third day, and from that moment she is under the supervision of a gynecologist at her place of residence.
Prevention of adhesion formation after laparoscopy
To prevent adhesions after laparoscopic surgery, it is necessary to focus not only on drug treatment. The patient needs to move carefully after the operation, temporarily giving up active sports. Below are other measures to prevent the development of pathology.
- Drug therapy, consisting of antibacterial and anti-inflammatory drugs, as well as anticoagulants and fibrinolytic agents, will help to avoid the formation of adhesions. The action of the latter is aimed at preventing the growth of fibrin - the main component of adhesions. Longidaza, Wobenzym, Askorutin are often prescribed. Collection No. 59 normalizes female reproductive function, eliminates the inflammatory process in the ovaries, reduces the likelihood of adhesion formation.
Drug therapy lasts 2-4 weeks. As practice shows, in women who undergo it, the adhesive process develops less frequently than in those who neglect the doctor's prescriptions.
Another way to prevent pathology is the introduction of a barrier fluid into the abdominal cavity, which prevents the connection of tissues with fibrin threads. Due to a special solution, the organs stop touching and “sticking together” with each other.

- softening of the connective tissue. As a result, it becomes more elastic, which reduces the severity of the pain syndrome, contributes to the prevention and treatment of the adhesive process.
- improvement of tissue metabolism. Adhesions often lead to squeezing of the organs, which is the cause of chronic constipation and menstrual irregularities. Physiotherapy normalizes metabolism and blood circulation in tissues, stimulating the regeneration of the latter.
- Therapeutic massage is usually used in conjunction with physiotherapy. For some patients, it is contraindicated. The obstacles to its implementation are:
- any oncological;
- the presence of an infectious disease due to the laparoscopy performed;
- violations of the integrity of the skin in the pelvic or abdominal cavity.
Moderate physical activity and the implementation of special exercises will help prevent the appearance of adhesions. Before you start them, you should consult with your doctor.
To avoid adhesions, you need to adhere to a certain diet. In addition, infection should not be allowed to enter the seam, and it is also forbidden to play sports for some time. Proper lifestyle significantly reduces the likelihood of developing pathology.
It is desirable that the specialist explain to the patient all the measures to prevent the adhesive process. This is important to do before a hysterectomy or any other surgery. A woman is unlikely to have to do a second laparoscopy of the appendages if she is attentive to her health, avoids strong physical exertion and follows all the doctor's instructions in the postoperative period.
Adhesions after removal of the uterus are a common complication and occur in 90% of operated women. This is a dangerous consequence of surgical intervention, since as a result various functional disorders in the functioning of internal organs can occur, up to symptoms of intestinal obstruction.
What are spikes
Extensive adhesions of internal organs are also called adhesive disease by doctors. However, it is important to distinguish the physiological process of adhesion formation from the pathological one.
Removal of the uterus (hysterectomy) is always accompanied by the formation of connective tissue scars at the sites of scars and incisions. The resulting scars are physiological adhesions. The scarring of the wound gradually stops, due to which the normal functioning of the organs is restored, and the symptoms of inflammation disappear.
Important! The process of formation of adhesions (or scarring) after removal of the uterus is a normal physiological condition that has nothing to do with pathology. If the formation of connective tissue does not stop, and fibrous cords grow and grow into other internal organs, this is a pathology called adhesive disease. It has its own symptoms and requires serious medical intervention.
These pathological fibrous bands have a whitish tint. They look like fibrous formations that connect the internal organs. The strength of the strands is high, which is why it is necessary to resort to a second operation to remove them.

Reasons for the formation of adhesions after removal of the uterus
In the body, adhesions occur mainly only after extensive operations that require the removal of one or two organs at once. The reasons for their occurrence are diverse and depend on a number of factors:
- How long was the operation.
- The amount of surgery.
- The volume of blood loss.
- Internal bleeding in the postoperative period. In this case, there is an active resorption of blood accumulated in the abdominal cavity, and this predisposes to the occurrence of adhesions.
- Infection of wounds in the postoperative period.
- genetic predisposition. This is due to the fact that a special enzyme is not formed in a genetically predisposed organism that can dissolve fibrin overlays, which ultimately leads to symptoms of adhesive disease.
- People of asthenic physique.
- In addition, the occurrence of adhesions depends on the actions of the surgeon himself. What is important here is how correctly the incision was made, what suture materials were used, how professionally the suture itself was applied.
- There are cases when surgeons left foreign objects in the abdominal cavity. It also predisposes to the development of adhesions after hysterectomy and the onset of symptoms of adhesive disease.
Symptoms of adhesions after surgery
You can suspect adhesive disease in a woman who has recently had a uterus removed by the following symptoms:
- Aching or pulling pains in the lower abdomen, forcing to take an antalgic (forced) position. Pain can be permanent or intermittent, reaching a high intensity.
- Delay and other disorders of urination and defecation, up to the absence of urine and feces.
- Symptoms of dyspeptic disorders: pain throughout the abdomen, flatulence and gas formation, "sheep feces", a feeling of increased intestinal motility and others.
- Subfebrile or febrile body temperature (increase to 38-40 C).
- Feeling of severe pain when probing the postoperative scar, its redness and swelling.
- Pain during intercourse. Discharge from the vagina is bloody.
- If several weeks have passed since the removal of the uterus, then when these symptoms appear, you should immediately contact your doctor (gynecologist).
Important! Symptoms of adhesive disease are nonspecific. This means that if a woman makes such complaints, then no qualified doctor can say with full confidence that she has formed adhesions in the small pelvis. To confirm the diagnosis, instrumental and laboratory methods of examination are necessary.

Diagnosis of adhesive process in the postoperative period
A preliminary diagnosis is made after a thorough history taking, patient complaints and symptoms of the disease. To confirm the presence of adhesions, the doctor prescribes an additional examination:
- General blood analysis. Needed to check if you have inflammation in the body. Also evaluate the activity of the fibrinolytic system of the blood.
- Ultrasound of the abdominal cavity and the pelvic cavity. The visual method of examination helps with a 100% guarantee to say whether there is an adhesive process in the small pelvis after the operation of removing the uterus.
- X-ray examination of the intestines with the help of contrast (coloring) substances. An auxiliary method that allows you to judge the patency of the intestine and the degree of narrowing of its lumen.
- Laparoscopic diagnostics is also used, during which individual adhesive formations are dissected and removed, and the issue of repeated surgical intervention is also resolved.

Surgical treatment of adhesions
Mostly adhesive disease is treated surgically. This is due to the fact that conservative treatment is not effective, it is used only as a prophylaxis in the postoperative period and to relieve the symptoms of the disease.
There are 2 types of operation:
- Laparoscopic surgery. It is carried out using special fiber optic equipment. At the same time, 2-3 small incisions are made on the skin of the anterior abdominal wall, and then the abdominal wall is pierced in these places. These incisions provide access to the abdominal cavity. The advantage of this operation is that the dissection of adhesions is carried out under the control of the optical system, with minimal trauma to internal organs. With the help of special laparoscopic instruments, fibrous cords are cut, followed by hemostasis. Pain and complications after such surgery are extremely rare. The recovery period takes several days, the symptoms of the adhesive process disappear almost immediately, physical activity is possible the very next day after the operation.
- Laparotomy. Shown in two situations:
- There is no possibility of laparoscopic surgery.
- The presence of symptoms of an extensive adhesive process in the abdominal cavity.
In this case, the lower middle access is used first, and then it is expanded upwards to 15-20 cm. This is done in order to carefully examine all organs and remove overgrown adhesions. Such an operation is highly traumatic, has a risk of postoperative complications or recurrence of the disease. The recovery period takes about two weeks.
After the operation of dissection of adhesions, it is necessary to constantly visit the attending physician in order to observe the processes occurring in the small pelvis

Important! No doctor can give a full guarantee that adhesive disease will not return to you again. Removal of adhesions is the same operation as removal of the uterus, which means that fibrous bands between organs can form again. To prevent this from happening, follow the doctor's recommendations in the postoperative period and prevent the recurrence of the disease.
Prevention of adhesion formation
If you are scheduled for surgery to remove the uterus, carefully approach the choice of a surgeon. The course of the postoperative period largely depends on it.
What will the doctor do
Only absorbable surgical suture material is used to suture the wound. This is necessary as a hysterectomy is an extensive and highly traumatic operation. Threads are a foreign body that will become overgrown with connective tissue and subsequently form adhesions.
Professionally sutures when the edges of the wound are in contact throughout with each other.
Drug prevention of adhesive disease in the postoperative period. The doctor prescribes broad-spectrum antibiotics (to prevent infection, suppress inflammation), anticoagulants.
Early appointment of physiotherapy with electrophoresis of enzymes that destroy fibrin (lidase, hyaluronidase and others). They destroy dense adhesive formations, which contributes to the rapid extinction of the symptoms of the disease.
Dynamic observation after surgery, careful monitoring of the state of the pelvic organs using ultrasound.

What should you do
Early physical activity after hysterectomy is important for the prevention of adhesions. The fact is that while walking improves intestinal motility, which prevents the development of adhesions.
The second point is diet. Eliminate salty, spicy, fried, alcohol, carbonated drinks. They disrupt digestion, and intestinal motility weakens. It is necessary to eat up to 6-8 times a day in fractional small portions. This will not overload the intestines, which means it will not be constricted by fibrous overlays.
With regards to folk methods of treatment, they can be used as an addition to drug therapy and only after consulting the attending physician. For the prevention and treatment of adhesions in folk medicine, infusions and decoctions of plantain, dill, flax seeds, St. John's wort, aloe leaves are used.
Summing up
Adhesive disease disrupts the physiological functioning of all organs of the abdominal cavity. It is a consequence of highly traumatic operations. Advanced forms of adhesive disease can only be treated by surgery, but this also harms the body. To prevent this from happening, it is necessary to follow the recommendations of the attending physician in the postoperative period and to prevent the recurrence of the disease. When the first symptoms appear, indicating the presence of adhesions in the body, you should immediately consult a doctor for consultation and subsequent diagnosis.
Video: When to be afraid of adhesions? The main symptoms of impending problems