Prostate adenoma by ultrasound. Ultrasound of the prostate: procedure technique, interpretation, reviews. Ultrasound of the prostate gland. Methodology and indications for examination
Statistics show that ultrasound for prostate adenoma helps make a diagnosis in approximately 15-20% of cases, in patients who are not even aware of the presence of this disease. Ultrasound examination helps to identify pathological changes in the early stages, which has a beneficial effect on the prognosis of the prescribed therapy.
Is it possible to detect prostate adenoma using ultrasound?
Ultrasound examination is carried out in two ways. The accuracy of the diagnosis depends on the chosen method.Diagnosis is carried out transabdominally and transrectally. Each method has its own advantages:

Ultrasound signs of prostate adenoma can only be detected by a competent specialist. The reliability of the results is influenced by the professionalism of the doctor.
How to prepare for an ultrasound of prostate adenoma
Preparation for an ultrasound takes place in several stages:- The doctor tells the patient the essence of the diagnostic procedure.
- On the day before the diagnostic study, a cleansing enema is performed. Removing fecal matter from the rectum contributes to better visualization of the ultrasound picture.
- During transabdominal diagnostics, the patient is recommended to drink 2 liters of water approximately 3 hours before the examination.
How to do an ultrasound of prostate adenoma
Ultrasound scanning, as described above, is carried out in two different ways:- With the transabdominal method, the abdominal cavity is scanned with a sensor. In addition to the presence of prostate adenoma, the method allows you to see related pathologies, but does not provide an accurate result.
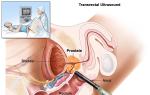
- Transrectal ultrasound is performed after inserting the sensor into the rectum. For TRUS, the patient is placed on a couch with his legs bent with his knees to his chin. The sensor is inserted through the anus, leading to the place where the rectum comes into contact with the prostate gland.
What does BPH look like on an ultrasound?
At first glance, the results of ultrasound diagnostics are so complex and confusing that it seems impossible to understand them on your own. In fact, everything is much simpler. If you understand the basic diagnostic criteria, you can decipher the test results yourself:- Shape and contour of the prostate – the prostate gland when scanned resembles a chestnut. If there are violations, the volume of the adenoma increases and changes. The interlobar track is smoothed out. The gland becomes like a ball.
The dimensions of the prostate with hyperplasia on ultrasound will be outside the normal range: upper-inferior section 2.4-4.1 cm; transverse 2.7-4.3 cm; anteroposterior 1.6-2.3 cm; volume 16-18 cm³. - Echogenicity is the most important research parameter. In case of acute prostatitis, the results will indicate: hypoechogenicity, low echogenicity, etc. In case of a chronic disease, the protocol will indicate a hyperechoic area.
- Echostructure is an indicator indicating the stage of prostate adenoma and the nature of the formation. Normally, the echostructure is homogeneous. Diffuse compactions and heterogeneity indicate cystic formations, adhesions, benign and malignant neoplasms.
- Vascularization - provides information about the blood flow of the prostate gland, more precisely about disturbances in the supply of blood to individual areas and the presence of congestion.

The results of the study indicate several more diagnostic criteria, but shape, echogenicity, echostructure and vascularization are the four most important and informative parameters necessary for an accurate diagnosis.
After receiving the tests, the urologist will calculate the total volume of prostatic hyperplasia on an ultrasound scan. Each age category has its own rate of prostate growth. The calculation is performed using the Gromov or ellipsoid formula.
According to ultrasound data, the degree of increase in hyperplasia is determined. Results are divided into three categories based on severity: simple, moderate and complex.
Ultrasound diagnostics has no side effects, does not require special training, and is informative and accurate. The frequency of ultrasound examination is not limited.
A patient suffering from prostate diseases is recommended to undergo the procedure every six months. Thus, the attending physician will be able to see the effectiveness of the prescribed therapy and adjust the treatment.
For patients, this is a simple painless procedure, and for a urologist, it is an informative and indicative method of clinical examination. Moreover, unlike other methods, ultrasound can be performed as needed at short intervals without side effects on a man’s health.
Indications for testing
- If you experience discomfort when urinating or pain in the lower abdomen, it is recommended to undergo an ultrasound
Pathologies and neoplasms identified during a rectal digital examination in a urologist’s office, for example, a noticeable increase in the size of the prostate, its hardening, etc.
Methodology
Ultrasound is often performed using the transrectal method (through the rectum). A transrectal examination allows the doctor to examine the structure of the prostate in detail, as well as carefully examine the seminal vesicles.
The sensor of the high-frequency ultrasound device for this type of examination is small in size (no more than 2 cm in diameter), so discomfort during the procedure is minimized. During the procedure, the sensor is located near the prostate gland. During the procedure, the patient lies on his left side with his legs bent towards his stomach.
Ultrasound examination of the prostate gland can also be performed transabdominally (through the skin of the anterior abdominal wall). This method is indicative, because it cannot give a clear picture, unlike the transrectal one.
Preliminary preparation
To perform an ultrasound using the transabdominal method, the patient must come to the procedure with a full bladder.
To carry out the procedure using the transrectal method, preliminary preparation of the patient is required. The procedure itself is usually scheduled for the morning, and the evening before it is recommended to do a rectal enema.
What diseases can be detected
Using an ultrasound examination, a specialist evaluates the structure of the gland, its density, size, homogeneity, and the presence of any neoplasms. Normally, the size of the prostate should not exceed 3*3*5 cm, and the volume should not exceed 25 ml.
Depending on the results, the following diseases may be identified:
Ultrasound can reveal: prostatitis, adenoma, prostate cancer and prostate cyst
Prostatitis
Inflammatory disease of the prostate gland. The main symptoms of the disease are burning and discomfort during ejaculation and urination, frequent urination, and erectile dysfunction.
An ultrasound examination of prostatitis shows an enlarged prostate.
Prostate adenoma (benign hyperplasia)
A disease that is accompanied by a significant increase in the size of the prostate, which over time leads to disturbances in the outflow of urine and the inability to empty the bladder.
The main signs of the disease are a feeling of incomplete emptying of the bladder, frequent urination, a weak stream of urine, and in an advanced stage, a delay in the outflow of urine.
It is believed that adenoma occurs in every second man over 60 years of age. Timely treatment often leads to good results. In the later stages of the disease, the only treatment method is surgery.
During an ultrasound examination of the prostate gland, the patient experiences an increase in the size of the prostate and adenomatous nodes.
A malignant formation that most often develops in men after 60 years of age. The disease can occur for a long time without the manifestation of any symptoms, which leads to late detection and treatment of prostate cancer.
In order to timely detect the disease, all men over 50 years of age are recommended to undergo an ultrasound examination of the prostate gland every year.
Cyst
A disease characterized by the formation of a small cavity filled with fluid in the gland. Typically, a prostate cyst develops against the background of a chronic form of prostatitis. Using an ultrasound examination of the prostate gland, it is possible to determine the position of the cyst and its size.
TRUS and ultrasound for prostate adenoma
Statistics show that ultrasound for prostate adenoma helps make a diagnosis in approximately 15-20% of cases, in patients who are not even aware of the presence of this disease. Ultrasound examination helps to identify pathological changes in the early stages, which has a beneficial effect on the prognosis of the prescribed therapy.
Is it possible to detect prostate adenoma using ultrasound?
Ultrasound examination is carried out in two ways. The accuracy of the diagnosis depends on the chosen method.
Diagnosis is carried out transabdominally and transrectally. Each method has its own advantages:
- Transabdominal method – causes less discomfort for the patient. Considered less informative. It is extremely difficult to diagnose prostate adenoma by transabdominal ultrasound, but it is possible to examine and accurately determine the stage of the disease.
Transbdominal ultrasound diagnostics is required in the presence of hemorrhoids, diseases of the rectum, and inflammation of the skin around the anus.
The reliability of TRUS for diagnosing BPH during rectal examination is quite high. Transrectal examination helps to identify the disease at an early stage. You can distinguish prostate adenoma from chronic prostatitis by ultrasound.
How to prepare for an ultrasound of prostate adenoma
Preparation for an ultrasound takes place in several stages:
- The doctor tells the patient the essence of the diagnostic procedure.
Preparing a patient for an ultrasound does not require much time and, if necessary, is prescribed immediately after visiting a urologist to clarify the diagnosis and carry out differential diagnostics.
How to do an ultrasound of prostate adenoma
Ultrasound scanning, as described above, is carried out in two different ways:
- With the transabdominal method, the abdominal cavity is scanned with a sensor. In addition to the presence of prostate adenoma, the method allows you to see related pathologies, but does not provide an accurate result.
The doctor conducting the diagnostic procedure draws up a protocol describing the ultrasound of the prostate adenoma. Based on the results of the study, drug therapy is prescribed.
What does BPH look like on an ultrasound?
At first glance, the results of ultrasound diagnostics are so complex and confusing that it seems impossible to understand them on your own. In fact, everything is much simpler. If you understand the basic diagnostic criteria, you can decipher the test results yourself:
- Shape and contour of the prostate – the prostate gland when scanned resembles a chestnut. If there are violations, the volume of the adenoma increases and changes. The interlobar track is smoothed out. The gland becomes like a ball.
The dimensions of the prostate with hyperplasia on ultrasound will be outside the normal range: upper-inferior section 2.4-4.1 cm; transverse 2.7-4.3 cm; anteroposterior 1.6-2.3 cm; volume cm³.
Urinalysis for prostate adenoma (BPH)
What not to eat if you have prostate adenoma
Is there a relationship between adenoma and prostate cancer?
Is there a temperature with prostate adenoma?
Is it possible to have sex with prostate adenoma?
What is the difference between prostate adenoma and prostatitis?
Features of ultrasound examination for prostate adenoma
Ultrasound examination of the prostate gland is often used to diagnose diseases and for preventive purposes, so every man should know the specifics of this procedure. We will focus on the methods of performing ultrasound, the specifics of preparation and interpretation of the results.
In what cases can a man be prescribed an ultrasound scan?
An ultrasound is necessary to clarify the diagnosis if the patient has the following symptoms:
- pain during urination and ejaculation;
- increase in the number of urges;
- urination disorders;
- reproductive dysfunction;
- deviation from the norm in blood, urine or seminal fluid.
A referral for echography is also issued if structural irregularities are detected during a digital rectal examination. In men over 50 years of age, the likelihood of developing prostatic hyperplasia increases, therefore, to prevent the disease at an early stage, you should undergo a preventive examination, including an ultrasound scan, at least once a year.
Research methods
Of all the possible methods of ultrasound scanning, transabdominal and transrectal ultrasound are widely used. In the first case, the study is performed through the abdominal wall, in the second, the emitter is inserted through the anus into the rectal cavity.
The most informative is a transrectal examination, since the sensor is as close to the prostate as possible. However, this method has certain contraindications: exacerbation of hemorrhoids, cracks in the walls of the rectum, or recent surgery.
If there are contraindications, echography is performed through the abdominal wall. At the same time, the image quality does not allow a detailed examination of the prostate tissue, but only gives a general idea of the state of the organ.
Sequence of actions during ultrasound examination
Preparation for an ultrasound begins 2-3 days in advance. The patient is advised to follow a diet to prevent increased gas formation. If the scan will be performed abdominally, 2 hours before the procedure you need to fill your bladder (drink a liter of still water).
The research is carried out as follows:
- the man lies on his back and exposes the lower abdomen;
- the surface of the skin at the point of contact with the sensor is lubricated with gel to create a transition environment and improve scanning quality;
- By directing the sensor in different directions, the doctor examines the prostate in different planes.
For transrectal ultrasound, preparation includes thorough bowel cleansing. To do this, you can use a laxative (8-10 hours before the procedure) or a cleansing enema (2-3 hours before the procedure).
The sequence of actions of the patient and the doctor is as follows:
- the patient lies on the couch on his left side, slightly pulling his legs towards his body;
- Before insertion, a condom is placed on the ultrasound sensor and lubricated with gel for more free penetration into the rectal cavity;
- the examination is carried out at a depth of 4-5 cm; if it is necessary to examine the seminal vesicles, a deeper insertion of the device will be required.
In cases where a patient is diagnosed with prostate adenoma, as a rule, a parallel examination of the condition of the bladder and urinary tract is carried out. In later stages of hyperplasia, it may be necessary to determine residual urine volumes. To obtain the most reliable information, it is necessary to fill the bladder in a slightly different way than during a routine examination of the prostate gland.
You must take a container with liquid (1-1.5 liters) with you and start drinking it in the clinic half an hour before the ultrasound. Scanning begins after the patient feels the urge to urinate. After a complete examination of the organ in a full state, the patient will be asked to empty the bladder and continue the examination. This method allows you to see changes after emptying, determine the condition of the bladder walls and the presence of residual urine.
What indicators are determined during the study?
During the scanning of the prostate gland, all data is entered into a protocol, on the basis of which the doctor gives a final conclusion.
The following data is set:
What data may indicate prostate hyperplasia
The use of a diagnostic method such as ultrasound allows us to identify various pathologies of the prostate gland. In older patients, dysfunction of the genitourinary system is in most cases associated with the development of hyperplasia - a benign neoplasm that forms in glandular, connective or muscle tissues. When scanning, the tumor appears as a capsule-enclosed formation with clear contours. Ultrasound allows you to determine the presence of an adenoma, the size of which is at least 7 mm in diameter. The form of pathology is also determined: diffuse or nodular.
If a tumor is present, the doctor assesses how much the enlarged prostate is compressing the urethra and determines the presence of structural changes in the bladder. To confirm the diagnosis, the patient may be prescribed an additional ultrasound - Doppler ultrasound. With its help, it is possible to establish how blood flows in the prostate.
With hyperplasia, the following changes are noted in the circulatory system of the prostate gland:
- in the peripheral parts of the organ the number of blood vessels decreases, while in the central part their number increases;
- the speed of blood flow in the vessels of the urethra increases;
- the peak velocity in the capsule vessels also increases.
If prostate adenoma is detected, the specialist determines the degree of development of the disease and determines possible deviations in the functioning and structure of the organs of the urinary system. Based on the results of echography, a diagnosis is made and the most appropriate methods of treating the pathology in each specific situation are determined. Among other diagnostic techniques, ultrasound scanning is one of the most informative and accurate.
Add a comment Cancel reply
You must consult your doctor before using any treatments or medications.
Copying site materials is prohibited. All texts on our website are original and protected by the Russian Copyright Law.
How to correctly decipher a prostate ultrasound?
Ultrasound of the prostate is an informative and accessible research method that allows you to obtain comprehensive information about the condition of this gland. When receiving ultrasound results, most patients find it difficult to evaluate them, since the form contains numerical parameters and unclear descriptions. Decoding or correct interpretation of the obtained data is within the competence of the doctor. However, nothing prevents you from lifting the veil of secrecy and learning to distinguish normal indicators from pathological ones.
How does the prostate gland work?
The shape of the gland resembles a chestnut; it can be conditionally divided into two lobes along the groove on the posterior surface of the prostate. The body of the organ contains up to 50 small glands, each of which has a duct. Merging, the ducts form an outlet into the urethra. In addition, in medical practice it is customary to distinguish zones in the gland, each of which has its own characteristic features.
The location of the prostate gland is the pelvis, below the bladder. The prostate covers the urethra (urethra), its back part is adjacent to the rectum, and the top is connected to the pelvic floor muscles (diaphragm).
There are inferolateral, upper and lower surfaces. In the posterior surface of the prostatic urethra there is a seminal tubercle, which has a prostatic utricle in its upper part, through the openings of which seminal fluid enters the urethra. The ejaculatory ducts connect to it, passing through the body of the prostate from behind.
In addition to the glandular layers, the prostate gland also has fibromuscular tissue. When performing an ultrasound, it becomes possible to study the condition of the tissues and ducts of the gland, which makes it possible to accurately determine the location of the inflammatory or other pathological process.
Indications for prostate examination
Indications for an ultrasound scan are any data indicating disturbances in the functioning of the prostate gland, obtained through laboratory tests, examination of the patient, and collection of anamnesis.
Let us note the main symptoms indicating the need for an ultrasound examination:
- pain in the lower abdomen;
- urination disorders (the stream becomes weak, the urge appears at night, the process itself becomes painful);
- deterioration of potency;
- age after forty years.
Types of ultrasound examination of the prostate
The following methods are used to examine the prostate using ultrasound:
- Transabdominal ultrasound (TAUS) is the most common method of primary diagnosis of prostate diseases. This method is completely painless and harmless, has no contraindications, but does not allow obtaining high-resolution images. It is carried out by moving the sensor along the abdominal wall of the lower abdomen.
- Transperinial examination is carried out similarly to transabdominal, only the area of examination is the surface of the perineum. Allows you to obtain an image of the apex of the prostate, but the resolution is also low and detailed data cannot be obtained.
- The transurethral method makes it possible to obtain high-quality images thanks to high-frequency ultrasound radiation. This method is very traumatic and requires preparation. Due to the serious complications that it can entail (acute urinary retention due to adenoma, infection of the urinary tract and trauma), the bottom method is used in exceptional cases when the transrectal method is contraindicated due to diseases of the rectum.
- Transrectal ultrasound examination – TRUS – is currently the most universal method of examination, providing a complete picture of the condition of the prostate gland with high-quality images. During the procedure, the sensor is inserted into the rectum 6-7 cm. This unpleasant method of examination is unacceptable only for diseases and injuries of the rectum, when the likelihood of intestinal bleeding from such an intervention is high.
Summarizing all of the above, it should be noted that transabdominal ultrasound is always the first step before TRUS. This is due to the fact that carrying out this procedure (inserting a sensor into the rectum) is associated with some inconveniences of a physical and psychological nature.
Preparation for ultrasound examination
The positive features of examination using TRUS and transabdominal examination include minimal preparation. So, for ultrasound performed on the surface of the abdominal wall, it is necessary to have a slightly full bladder (about 150 ml of urine). This effect can be achieved by drinking 1.5 liters of liquid an hour before the procedure.
Some features of preparation for TRUS
Transrectal ultrasound examinations should be approached with clean bowel to avoid surprises during transducer insertion. For effective emptying, you can use a ready-made microenema or carry out the traditional procedure yourself.
TRUS is preceded by sigmoidoscopy or sigmoidoscopy if rectal disease is suspected to prevent bleeding and mechanical damage.
How the research is carried out
A transabdominal prostate scan is always performed first. If deviations from the norm are detected at this stage of the examination, TRUS is indicated.
During a transabdominal ultrasound examination, the patient lies on his back on a couch. The sensor is placed in the area of the pubic symphysis (above the pubis) and from there it is passed upward with a slight tilt forward to obtain a better image. Then the direction of movement is changed perpendicular to the original one and, thus, the gland is examined in transverse and longitudinal sections.
When performing TRUS, a urological chair is used, but in practice, more often than not, a regular couch is used instead. The patient lies on his left side, tucking his knees to his stomach. A rubber balloon is put on the sensor, lubricated with gel or Vaseline, and inserted into the anus to a depth of about seven or six centimeters. To improve visibility, the balloon can be filled with water.
What is measured on an ultrasound
During an ultrasound examination, the size of the prostate gland itself, the clarity of its contours, the uniformity of the tissue and its echogenicity are determined. The following parameters are measured in the prostate:
- transverse size (width);
- top-bottom size (length);
- anterior-posterior size (thickness).
The volume of the gland is calculated using the formula for the volume of an ellipsoid or simply by multiplying the product of all three sizes by a factor of 0.52.
How to decipher ultrasound data
Each study is accompanied by a form describing the characteristics and parameters of the prostate gland. In order to make their decoding more understandable, let’s consider what indicators are determined by ultrasound and TRUS. They are:
- dimensions;
- echogenicity;
- homogeneity of structure;
- the presence of stones, calcifications or cysts;
- condition of the ejaculatory ducts.
Let's look at each of these parameters separately.
Prostate sizes
With age, the male body experiences changes in the size of the prostate. Over the years, this gland reaches its constant size, then, in a normal state of male health, its growth stops and no increase occurs. In pathological conditions, the prostate gland grows, its structure changes, not only the functioning of the reproductive system is disrupted, but a malignant neoplasm can also develop.
Given the fact that the urethra passes through the prostate, acute urinary retention may occur. Impaired urine outflow contributes to the development of inflammatory diseases in the bladder and kidneys and disrupts the normal functioning of the excretory system. Let's look at what tests look like for various diseases and normally.
To accurately determine the correspondence of the size of the prostate obtained by ultrasound with the patient’s age, you can use the formula of Doctor of Medical Sciences A.I. Gromova:
Ultrasound picture for prostate diseases
Deciphering ultrasound for various diseases is not difficult. Thus, the main sign of adenoma is a significant change in size and the appearance of inclusions in the body of the gland (in the nodular form). They are formations with increased echogenicity, measuring about 7 mm. Cysts or calcifications may be detected on the surface of the nodes. The diffuse form has a pronounced heterogeneous structure and the absence of nodes.
In case of prostatitis, the interpretation of ultrasound is quite simple: increased echogenicity indicates a chronic, and decreased echogenicity indicates an acute inflammatory process. The contours lose clarity, differentiation of the glandular tissue from the fibromuscular tissue is difficult, and the presence of hyper- and hypoechoic areas is characteristic. If an abscess develops, ultrasound reveals an anechoic or hypoechoic formation.
Cysts on ultrasound are identified as areas with hypo or anechoicity. Small formations (up to 5 mm) may be present in healthy men.
Deciphering stones in iron has its own characteristics. Stones are small areas of hyperechogenicity, which can have different sizes and be present in the singular or plural.
The appearance of nodular formations with varying echogenicity is characteristic. Enlargement of the lymph nodes to two or more centimeters should be the reason for further examination of the patient to determine the oncological nature of the pathology using other methods.
Conclusion
Diseases affecting the prostate are mostly detected by ultrasound. The results of this diagnostic method have a reliability of slightly less than 80%. Therefore, the very first study, if genitourinary diseases are suspected, will be an ultrasound. The use of Dopplerometry allows one to assess the intensity of blood circulation in the gland, which is also important information in a comprehensive examination of a urological patient.
Ultrasound of the prostate gland: preparation, how it is performed, interpretation of the results
Types of ultrasound examination of the prostate gland and preparation
Transrectal ultrasound of the prostate gland is performed by inserting a sensor into the rectum; with this method of examination, the prostate is visualized much better.
Performing an enema before a transabdominal ultrasound is desirable, but not required.
Inflammatory process in the pelvis in a man.
To clarify the causes of infertility.
To assess the effectiveness of the therapy.
To exclude or confirm a tumor process in the prostate.
When blood appears in semen.
Pain in the lower abdomen.
Enlarged inguinal lymph nodes.
For symptoms of urinary dysfunction.
For the purpose of dynamic observation.
With a history of bladder tumors, during observation.
Elevated levels of prostate-specific antigen (PSA) in the blood.
Normal prostate parameters on ultrasound or interpretation of results
An ultrasound photo of the prostate gland is called a “sonogram” or “echogram”
Therefore, each age group has its own normal limits.
Antero-posterior 1.6–2.3 cm
Upper–lower 2.4–4.1 cm
Note that if the volume of the prostate is greater than the age norm, this does not necessarily indicate a pathological process, but further observation should not be refused.
Structure of gland tissue.
Volume of hyperplastic prostate tissue.
Condition of surrounding tissues.
Pathological formations, their location and size.
Growth of adenomatous nodes in BPH.
Doppler ultrasound evaluates the blood flow of the organ and the pathological tumor. And the arteries and veins in the body can be represented on the screen, like on a geographical map.
The echographic picture of prostate cancer differs from that of a cyst, but it is not possible to verify the diagnosis using ultrasound diagnostics.
To confirm or refute a malignant tumor of the prostate gland, a transrectal biopsy of organ tissue is performed, followed by histological examination.
Prostate cancer
Prostate cancer (arrow)
If the tumor is located on the surface, or the process has gone too far, then the fatty tissue is modified. At stage T4, the process may involve vesicles, bladder, urethra, and regional lymph nodes.
And this sonogram shows prostate cancer in a more advanced stage, arrow 1 – germination into the seminal vesicles and arrow 2 – into the wall of the bladder
Prostate adenoma
Transabdominal sonogram of the prostate, a – frontal projection, b sagittal projection, arrow – BPH with intravesical growth
Transrectal sonogram of the prostate
(hyperechoic foci without acoustic effect).
Short time after surgery for removal of hemorrhoids, excision of rectal fissures.
Acute inflammatory conditions of the rectum.
Latest articles in the section:
In modern urology, the treatment procedure using the Intramag device with the Intraterm attachment is successfully used. This type of physiotherapeutic effect has a pronounced therapeutic effect.
The device "Urologist Adept Optima" was used to treat background infertility in patients after suffering from inflammation of the prostate. Main actions: laser and electrical stimulation. Laser
Therapy of the inflammatory process in the prostate gland implies an integrated approach, an important step in which will be physical therapy using the Matrix hardware complex
Treatment of infectious prostatitis involves the use of complex therapy, which includes antibiotics, anti-inflammatory drugs, and herbal remedies. One of the points in general
Clinics and doctors
Everything about the health of the genital organs and genitourinary system,
All articles located on the site are for informational purposes only. Only a doctor can prescribe specific treatment!
Diagnosis of prostate adenoma: methods and preparation
Adenoma of the prostate (prostate gland) is one of the most well-known problems in men after 40 years of age, but the initial manifestations of this disease occur even in middle-aged people.
Most men are afraid of it, but you just need to recognize it in time and start fighting.
Symptoms and signs
How to determine prostate adenoma? Every body always gives a timely alarm signal, if something is wrong with it, some organ fails. There are a number of signs that require you to undergo a full examination in order to protect yourself from the development of prostate adenoma. Among them, the most common are lower back pain, an increased feeling of dryness and an irresistible desire to drink more water, and painful ejaculation.
The symptoms of adenoma, following from the testimony of patients, are defined as:
- frequent desire to urinate, especially at night;
- delayed onset of urination;
- very quarrelsome stream of urine;
- Rarely does bleeding occur.
The presence of the symptoms described above depends on the level of neglect of this disease. There are three stages of the disease. At the first stage of BPH, the bladder is still fully emptied; no noticeable changes occur in the upper parts of the urinary tract.
At the second stage of prostate adenoma, the increasing difficulty in the outflow of urine from the bladder systematically increases, a compensatory thickening of its muscle wall is formed, which is illustrated by urine residues during the process of natural relief.
The patient has a certain feeling of incomplete emptying; he urinates several times in a row in a small stream. Cases of urinary retention due to the intake of various alcoholic beverages are also quite possible.
For the last stage, a typical sign was loss of bladder muscle tone.
This manifests itself as hesitation or unexpected incontinence, which results in the involuntary release of small amounts of urine, even when the bladder is actually completely full of fluid.
Prostate adenoma - diagnosis in men
The presence of prostate adenoma is possible only after a thorough collection of anamnesis and client complaints. Only a specialist in the field of medicine - a urologist - can conduct a full examination and prescribe the correct treatment and prevention. There are several options for correctly diagnosing BPH (benign prostatic hyperplasia).
The methodology for identifying prostate adenoma includes a number of procedures:
- Rectal examination - the doctor inserts a finger into the opening of the rectum to check the prostate for enlargement.
- Blood test - determines the presence or absence of a kidney problem. For uncomplicated prostate adenoma, blood tests should be normal.
- Urinalysis – checks the body for infections.
- Ultrasound examination – diagnostics of the functional state of the entire bladder, determination of the amount of residual fluid in it.
- Biopsy - taking samples of prostate tissue to rule out prostate cancer.
- Examination of the bladder using a special endoscope.
The combination of all of the above examination methods guarantees accuracy in diagnosing the disease and choosing the most effective treatment for prostate adenoma: medication or surgery.
Prostate ultrasound differs from other ultrasound examinations due to the fact that in most cases it is performed transrectally (through the rectum).
Ultrasound shows the most accurate signs of BPH; they serve as the basis for prescribing the correct treatment. This examination is carried out with a special small sensor to minimize the patient’s discomfort. At the same time, during the procedure itself, the latter is forced to lie on his left side, with his legs tucked towards the abdominal area.
In medical practice, there is another method of performing ultrasound - transabdominal, when the sensor is located on the skin of the anterior abdominal wall. This option has a significant drawback in that such a study can only provide a general idea of the clinical picture of the disease.
- When it is carried out in the first way, the patient, a couple of hours before the procedure itself, is organized to cleanse the rectum with an enema or by introducing a glycerin suppository into it. All this is done to ensure that feces do not become an obstacle when viewing the gland and also do not serve as a source of inconvenience for the patient and the doctor, respectively.
- Another condition for complying with all the rules for ultrasound is the filling of the bladder. For this purpose, you need to drink at least a liter of liquid (this can be compote, still water, fruit juice, or even just tea).
- You should see a doctor if you feel the urge to urinate. Then you can begin ultrasound examination of prostate adenoma.
Echosigns of BPH: what is it?
By the concept of echo signs of benign prostatic hyperplasia, doctors mean what the machine examines during ultrasound.
In our case, these include:
- Prostate enlargement up to 20 cubic centimeters.
- Changes in prostate tissue, which manifests itself in scarring of the affected cells and heterogeneity of the organ itself.
- The formation of calcifications, edema, fibrosis as a result of a long-term inflammatory process in the prostate area.
Conclusion
The key to success in any treatment is timely and accurate diagnosis of the problem area. Prostate adenoma is not a detriment to a man’s health, but just an ailment that can be easily cured if, at the very beginning, when identifying any of the symptoms and signs inherent in it, you contact a qualified specialist.
See inaccuracies, incomplete or incorrect information? Do you know how to make an article better?
Would you like to suggest photos on the topic for publication?
Please help us make the site better! Leave a message and your contacts in the comments - we will contact you and together we will make the publication better!
Many symptoms characteristic of prostate adenoma are not unique to it - they can also occur with other urological diseases. So in any case, a consultation with a urologist is necessary.
And of course, the sooner they contact the better, it is better to treat in the initial stages with medications than later with surgery.
The prostate gland, also called the prostate, is an important organ of the male genitourinary system. The general well-being of a person and his sexual life depend on its functioning. Unfortunately, the prostate is susceptible to various pathologies. Ultrasound of the prostate gland is the most informative diagnostic method. Deciphering the results may indicate the presence of various serious diseases.
-
Structure and role of the prostate
The prostate gland is an unpaired male glandular-muscular organ. It is located in the retroperitoneum under the bladder and surrounds the opening of the urethra. The prostate gland is small in size. Its normal length is from 4 to 4.5 cm, its thickness is from 1.4 to 2 cm, and its width is from 2.5 to 3 cm. The approximate weight of the prostate is 20 g.
Experts conventionally divide the prostate gland into lobes. They are not clearly defined. Most of the prostate consists of the lateral lobes. They are located on both sides of the urethra. The anterior lobe is located in front of the urethra, the posterior lobe is behind it, and the middle lobe is between the urethra and the ejaculatory ducts.
The prostate gland is surrounded on all sides by a connective tissue capsule. On the outside, it is still covered with a layer of fibrous connective tissue, forming a fascial sheath.
In the male body, the prostate performs several important functions. Firstly, it produces a special secretion that enters the seminal fluid and is released at the time of ejaculation through the excretory ducts into the urethra. Secondly, the prostate serves as a special valve. During an erection, this glandular-muscular organ closes the exit from the bladder.
Types of research and features of implementation
How a prostate ultrasound is done is a pressing question for most men. The examination of the gland is carried out in two ways: transabdominal and rectal. In the first case, the ultrasound sensor is placed on the stomach. With the rectal method, the device is inserted through the anus.
Transabdominal ultrasound prostate gland gives an idea of the condition of the kidneys, bladder, and the amount of fluid remaining in it. This study is also carried out to evaluate the shape and volume of the glandular-muscular organ.
You can more clearly examine the prostate and study its structure using a prostate ultrasound performed rectally. Before the procedure, the person takes the desired position: lies on his left side. In this case, the patient bends his legs and presses them to his stomach. A specialist for examining the prostate inserts a probe into the anus 5-6 cm or deeper if it is necessary to evaluate the seminal vesicles. First, a transverse and then a longitudinal scan is done.
Preparatory process
A specialist can tell you how to prepare for a prostate ultrasound. You should definitely consult him about this before doing anything. A prerequisite for performing a prostate ultrasound is the non-emptying of the bladder. Patients are advised not to urinate for 1.5-2 hours. If you are unable to follow this rule, you can drink 400 ml of liquid 90-120 minutes before the test. With a full bladder, it will be easier for specialists to assess the condition of the kidneys and examine the bladder and prostate gland.
After a transabdominal examination, doctors direct patients to have a bowel movement. Then another scan of the bladder is done to detect any remaining urine in the bladder. Next, a rectal examination begins. A cleansing enema is required so that the rectum is empty.
Normal echographic picture
In order for the interpretation of ultrasound results to be correct, you need to know the normal echo picture of the prostate. When a transverse scan is performed at the level of the seminal vesicles, these paired organs of the male reproductive system are identified as semilunar formations. Sizes and their volume vary. They are individual for each patient. The structure of organs is normally homogeneous, and echogenicity is low.
Normally, the contours of the prostate are smooth. Its structure is homogeneous, fine-grained. Ultrasound of the prostate gland reveals two zones distinguished by echogenicity. The first of these is a small hypoechoic central area of the prostate. Normally, it looks like a cone, with the base facing the bladder. The second zone is the peripheral part. Its echogenicity is much higher. This part covers the central area from the sides and from the bottom.
When examination is carried out at the level of the seminal tubercle, the prostate takes the form of a triangle. The base of the gland is directed towards the sensor. A hypoechoic central area is noticeable in the center of the organ. Above it, the anterior fibromuscular zone is revealed in the form of a strip, the echogenicity of which is more intense.
In a longitudinal study performed at the level of midline sections of the urethra, the prostate appears as an ovoid. All parts of the glandular-muscular organ are clearly visualized. Closer to the ultrasonic sensor is the peripheral part. Above it, a central hypoechoic zone is visible. Above these areas, the urethra is visualized.
Study results: main pathologies
Ultrasound of the prostate gland with detected changes
Acute prostatitis
An ultrasound scan is necessary if acute prostatitis is suspected. This disease refers to inflammation of the prostate gland in men, which develops due to the ingress of various microorganisms into it. In acute prostatitis, body temperature rises, chills occur, and pain appears in the perineal area.
If the inflammatory process covers the posterior urethra and the neck of the bladder, then patients begin to complain of frequent urge to go to the toilet and a burning sensation in the urethra. The disease may also cause delays in urination. This occurs because the size and volume of the prostate increases.
In case of acute inflammation, the following echographic signs can be detected at the time of ultrasound of the prostate gland:
- increased volume and size of the organ;
- variegated echostructure;
- reduced echogenicity of the parenchyma;
- broken contours;
- reduced degree of vascularization.
Chronic prostatitis
Interpretation of ultrasound results may indicate the presence of chronic prostatitis. Approximately 35−45% of men aged 20−40 years experience this prolonged inflammation of the glandular-muscular organ. The clinical picture of this disease is quite varied. Some complain of difficulty urinating and pain, while others do not experience any symptoms at all.
In most cases, the size and volume of the gland remain the same. Ultrasound of the prostate reveals areas of increased echogenicity with unclear edges. If stagnation prevails, then the volume and size of the gland increase, and the organ acquires a spherical shape. The echostructure turns out to be heterogeneous or variegated. The seminal vesicles and vas deferens dilate.
Gland abscess
Ultrasound results may contain this diagnosis. Late detection and improper treatment of acute prostatitis often leads to the development of complications such as prostate abscess. The patient's body temperature rises and his general condition worsens. On palpation, a symptom of fluctuation is noticed (i.e., the presence of fluid, pus is felt).
In the initial stages, prostate abscess is difficult to detect rectally. It is often detected after a breakthrough, when serious complications arise (for example, paraprostatitis - an inflammatory process that affects the tissues surrounding the prostate gland).
The echographic picture of this pathology varies. If the abscess is just beginning to form, then an ultrasound of the prostate reveals the following signs:
- asymmetry of one of the lobes of the prostate gland;
- variegated echostructure;
- the appearance of a hypoechoic area;
- the appearance of zones of reduced vascularization (vessels are identified along the periphery of abscesses, and in the center there is an avascular zone).

A 60-year-old patient has problems urinating. Ultrasound revealed prostate abscess
Benign hyperplasia (adenoma) of the prostate
Men over 50 years of age often develop benign hyperplasia of the gland. Due to an adenoma, a small nodule (or nodules) forms in a person’s prostate. It grows slowly and begins to put pressure on the urethra. This negatively affects excretory function. Urination is impaired.
The presence of benign prostatic hyperplasia (adenoma) in men is indicated by the following ultrasound signs:
- increased size and volume of the prostate;
- violation of the ratio of the peripheral and central parts of the gland;
- changing its shape;
- change in echostructure and increased echogenicity of the central part of the gland.
Prostate cancer
In addition to adenoma, another common disease is gland cancer. This is a common form of malignant tumor. There are no special symptoms indicating the development of the disease in men. The clinical picture is the same as for benign formations:
- frequent or difficult urination;
- pain in the perineum, kidneys;
- feeling of incomplete emptying of the bladder.
A malignant neoplasm on a prostate ultrasound performed rectally can be detected as a hypoechoic node (dark element). It is easily detected against the background of the more echogenic parenchyma of the glandular-muscular organ. This echographic picture is most common.
Prostate cancer may have another echographic variant. Interpreting ultrasound results will be difficult if a person has an isoechoic formation. The tumor in such cases has the same density as that of the surrounding healthy tissue.
Sometimes the interpretation of an ultrasound scan of the prostate gland indicates that the malignant neoplasm has spread to the central parts of the gland. The results show that asymmetry of the organ has arisen. There is no clear visualization of the capsule on the affected side. With invasion into the capsule, its thickening above the tumor, bulging, and intermittent contours are revealed. If the entire gland is affected, then blurred edges and a sharp deformation of the structure are noted.
Comprehensive ultrasound: why is it performed?
During an ultrasound of the prostate gland, specialists must evaluate the condition of the kidneys and bladder. This comprehensive procedure is a good way to obtain the information needed to assess a man’s health.
Often the signs of diseases of the genitourinary system and its organs (including the kidneys) may be similar. That is why during an ultrasound of the prostate, specialists evaluate not only it, but also other structures. Indications for the study are:
- pain in the perineum;
- discomfort at the time of emptying the bladder;
- pain in the lower abdomen;
- deviations from the norm in the results of urine analysis, spermogram.
Ultrasound of the prostate is the leading way to identify various pathologies of the prostate gland in men. The use of this diagnostic method transabdominally or rectally is indicated in the presence of laboratory or clinical data indicating the presence of an adenoma or other disease in a particular person. Ultrasound of the prostate gland is still performed during preventive examinations of people over 50 years of age and during interventional procedures.
Thyroid adenoma is a benign tumor that develops more often in women aged 40–50 years. The disease has a long and chronic course. The main danger is the degeneration of the tumor into a malignant process. Therefore, regular monitoring of the tumor is necessary.
The most accessible method of observation is ultrasound diagnostics. Read on to find out how a thyroid adenoma is detected by ultrasound.
Anatomy of the thyroid gland
The thyroid gland is one of the largest endocrine glands in the human body. Its weight is 30–40 g, width 4–6 cm in diameter. Normally, it is located in the cervical region in front of the trachea, adjacent to the upper part of the larynx and thyroid cartilage.
 The organ consists of two lobes - right and left, connected by an isthmus. The area connecting the lobes can be detected independently by placing your fingers on the front surface of the neck, approximately 4–6 cm below the chin. When swallowing, a small cushion will be felt under your fingers - this is the isthmus. The lobes of the gland are not normally palpable
The organ consists of two lobes - right and left, connected by an isthmus. The area connecting the lobes can be detected independently by placing your fingers on the front surface of the neck, approximately 4–6 cm below the chin. When swallowing, a small cushion will be felt under your fingers - this is the isthmus. The lobes of the gland are not normally palpable
The posterior surface of the thyroid gland is adjacent to the larynx, the anterior part of the organ is covered with connective tissue fascia and neck muscles. The gland capsule not only surrounds the organ from the outside, but also forms internal partitions that divide it into follicles containing colloid, the main structural substance of the parenchyma.
Causes of development of thyroid adenoma
Thyroid hormones affect all body functions. Therefore, its work is regulated by thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) of the anterior pituitary gland. When the concentration of triiodothyronines in the blood drops, TSH is released, stimulating the functioning of the organ. In turn, high levels of thyroxine inhibit TSH synthesis. This mechanism is called negative feedback and prevents excessive stimulation of the gland.
The exact mechanisms of development of tumor processes are unknown. Possible causes of the disease are the following:
- Failure in the regulation of thyroid hormone synthesis. If regulatory processes are disrupted, excessive proliferation of the follicle epithelium and the formation of cysts are possible.
- Iodine deficiency. For the formation of thyroxine, iodine is necessary, which enters the body from the external environment. Insufficient intake of this microelement leads to disruption of the thyroid gland and the development of tumor processes.
- Unfavorable environmental conditions. The thyroid gland is exposed to the influence of the external environment: increased radiation, high concentrations of heavy metals, etc. these factors lead to disruption of the regulation and functioning of the organ, which is manifested by the development of adenoma.
- Hereditary predisposition. Having close relatives with similar diseases.
- Traumatic injuries, hypothermia.
- Chronic infections, frequent colds.

Methods for diagnosing thyroid adenoma
An accurate diagnosis is made using various examination methods. Laboratory tests show the level of TSH and thyroxine in the blood and allow us to conclude whether there is increased or decreased organ function. With hormonally intact formation, the concentration of hormones remains normal.
To assess the hormonal activity of the adenoma, a radiodiagnostic method is used - isotope scanning. The patient is injected with a radioactive isotope of iodine and its accumulation in the thyroid gland is studied. Depending on the level of absorption of the isotope, they are distinguished:
- « cold» nodes – do not capture iodine and do not synthesize hormones;
- « hot» nodes - absorb iodine isotope and synthesize thyroxine.
Ultrasound diagnostic methods are used to determine the size, number and precise location of tumor formations. In addition, ultrasound is used to control manipulations during fine-needle biopsy of the thyroid gland.

Diagnosis of thyroid adenoma by ultrasound - principle and types of research
Ultrasound of the thyroid gland is the most widely used method for diagnosing tumor formations of the organ. Ultrasound waves penetrate the coda and reflect from the parenchyma of the gland, making it possible to visualize the size and location of tumors. Indications for ultrasound are:
- suspected thyroid tumor;
- monitoring the growth of an adenoma or node if the diagnosis has already been made;
- the need for a tumor biopsy;
- carrying out differential diagnosis between cystic tumors and thyroid adenoma.
No special preparation for ultrasound is required. During the procedure, the patient lies on a couch with his head thrown back. To obtain the clearest possible picture directly during the examination, the doctor asks the patient not to move his head or swallow.
Ultrasound-guided fine-needle tumor biopsy
A simple ultrasound examination does not give an accurate answer to the question of the benign or malignant nature of the formation. For this purpose, aspiration biopsy of the thyroid gland is used. Under ultrasound control, a thin needle is used to puncture the adenoma and collect biological material, which is then studied by a morphologist.

Color Doppler mapping of the thyroid gland
To study blood flow in an organ, ultrasound diagnostics is used in a special Doppler mode, which allows one to visualize blood flows both in healthy parenchyma and in tumor formations.
The undoubted advantages of ultrasound diagnostics are the availability of the method, ease of examination, quick results, and low cost. This makes ultrasound the most preferred diagnostic method for thyroid pathologies. Computed tomography and MRI are also highly accurate research methods, but have a much higher cost; in the case of CT, they are associated with radioactive radiation. These methods are used in diagnosing oncological processes to identify metastases in regional tissues.
There are practically no contraindications to the study. A possible obstacle is damage to the skin in the area where the organ is located. In this case, performing an ultrasound is difficult, so a special gel is applied to the skin before the procedure to remove the layer of air.
Useful video
The doctor explains what is important to know about this nodular formation in this video.
What does a thyroid adenoma look like on ultrasound?
It is impossible to accurately determine the nature of the process using ultrasound examination. This will require sampling of the internal contents - an aspiration biopsy. However, adenoma has its own characteristic ultrasound signs:

Thyroid cancer is characterized by an invasive growth pattern; as a rule, the tumor grows into the connective tissue capsule. Ultrasound signs of potential malignancy of the process:
- hypoechogenicity of formations;
- fuzzy and uneven contour of nodes;
- size more than 1 cm;
- heterogeneous structure of the tumor parenchyma with foci of necrosis or fibrosis;
- Doppler scanning reveals increased blood flow;
- the presence of metastases in regional lymph nodes.
What to do next
If an ultrasound examination of the thyroid gland shows the presence of an adenoma, the following must be done:

The danger of thyroid adenoma is its possible degeneration into a malignant tumor. Therefore, when making this diagnosis, regular medical supervision is important and the preferred method of examination in this case is ultrasound diagnostics.
Prostate is an important element of the male reproductive system. It is located in close proximity to the bladder, closely adjacent to the urethra. A feature of the prostate is the production of a specific secretion that is included in the components of seminal fluid. The secretion helps give sperm the necessary mobility; it is not directly involved in fertilization, but if it is absent from the seminal fluid, fertilization is impossible. The seminal vesicles are located slightly behind the prostate; they are responsible for the production of seminal fluid. However, inflammation of the prostate gland can affect the quality of sperm, which often causes complete infertility.
BPH
Prostate adenoma usually referred to as an increase in organ volume due to benign neoplasms. And since the adenoma covers the urethra, the organ enlarged as a result of the tumor blocks the canal, which leads to difficulties during emptying the bladder. This is one of the most common male ailments; almost half of the male population over the age of 60 suffers from this disease. Therefore, the sooner prostate disease is diagnosed, the more effective the treatment will be, since with advanced forms of this disease, only one treatment option is possible - surgery. Today there is no other diagnostic method that can be used to determine the initial stage of the disease other than ultrasound. And even at the first signs of prostate dysfunction, you should immediately consult a doctor; timely treatment will help you not only maintain your health, but also save money on treatment.
Methods for diagnosing prostate diseases
Ultrasound of prostate adenoma is considered the main method for diagnosing diseases of the genitourinary system in men. Indications for an ultrasound examination may include frequent urge or, on the contrary, difficulty and pain when urinating, problems with potency, a feeling of heaviness in the lower abdomen after bowel movement, pain in the groin area. An ultrasound procedure is often prescribed by the attending physician if, as a result of a rectal examination, he detects changes in the condition of the prostate.
In order to get the most accurate picture of the condition of the prostate gland, Ultrasound of prostate adenoma usually performed transrectally. This method involves inserting an ultrasound transducer into the rectum. The patient is usually on his right side with his legs tightly pressed to his chest.
During diagnostics, patients do not feel much discomfort, since the sensor inserted into the rectum has a very modest size. In cases where the transrectal method is impossible for medical reasons, for example, with hemorrhoids, the procedure is performed transabdominally, that is, through the wall of the abdominal cavity. However, this method can only be used as an auxiliary method, because with its help it is possible to obtain very approximate results. You can undergo this type of examination in our clinic!