What does physiotherapy mean? Indications, reviews and side effects of SMT physiotherapy. Laser therapy for spinal hernia
This is treatment using physical factors: electric current, light, ultrasound, radiation, as well as everything that nature has given us: sun, air, water and dirt. Physiotherapy also includes massage, that is, mechanical influence.This was how they treated when medicine was in its infancy, and even then it helped. Now physiotherapy has many opportunities and few contraindications, so it is one of the most interesting branches in medicine.
Why is it needed?
Physiotherapy is needed for quick recovery and recovery from illness. When the disease is chronic, physiotherapy helps to keep fit and live without exacerbations.Physiotherapy is needed when medications and surgeries do not bring the desired effect or do not help completely. Some diseases, especially injuries, are generally difficult to treat. But gradual rehabilitation gives results.
If you want to quickly forget about the consequences of the disease, go to the physical therapy room.
How do the procedures work?
Physical therapy is a large industry, so each type of treatment affects the body differently.The procedures improve blood circulation and enhance metabolic processes. Along with them, regeneration also increases, that is, independent tissue restoration, so physiotherapy helps with ulcers, skin diseases, and so on. These are galvanization methods, pulsed currents, high frequency currents, ultrasound.
With the help of popular electrophoresis, it is possible to drive the medicine into the tissues next to the sore spot, so that the drugs enter exactly the source of pain and do not pass through the stomach and intestines.
The current stimulates the nervous system, helps muscles relax and contract (electrical stimulation method).
The effects of heat and light work in a similar way: they make the blood move faster and speed up recovery from injury or illness. This is laser therapy, ultra-high frequency electromagnetic oscillations.
The procedures increase phagocytic activity - when the body's cells themselves destroy bacteria, viruses and other infections. We can say that their appetite increases, so this is useful after an infection. For this purpose, infrared rays and ultraviolet are used.
Physiotherapy relaxes the smooth muscles that make up internal organs and blood vessels and improves tissue nutrition. Therefore, it is used for cardiovascular diseases and any problems with internal organs.
When is physical therapy prescribed?
The decision is made by the attending physician. He also chooses the necessary procedure and its duration.Physiotherapy can be prescribed in almost all cases when the illness suffered is more serious than a common ARVI, after injuries, or when the disease has become chronic. Restoring and strengthening the body is never unnecessary.
Who should not undergo the procedure?
Physiotherapy is not prescribed in the acute stage if the disease has recently appeared or is out of control. Also, physical therapy cannot be performed if you have:- oncological diseases;
- blood diseases;
- heat;
- severe pain;
- bleeding.
There are contraindications to certain procedures; they are associated with intolerance to a certain type of treatment.
Are there any side effects?
Yes, like any method. Problems are identified immediately during the procedure: discomfort, redness, swelling, pain, burns. Serious damage is very rare because the impact on the body is minimal.Is it possible somehow without procedures?
You can, if you already feel good. Physiotherapy is a substitute for a healthy lifestyle when the patient is unable to engage in rehabilitation (due to severe weakness) or simply does not want to do so. Then you have to stimulate the body additionally.And if you are in pain and unwell, then follow all the doctor’s orders and get to the physiotherapist’s office.
It hurts?
Typically, there is minimal discomfort during physical therapy. A tingling or burning sensation appears from current or heat, but it should not be strong.Most of the procedures are even pleasant. For example, breathing in the humid sea air is also physiotherapy. Long walks in the mountains and running are physiotherapy. Regular exercise, exercise and warm-up, baths, electric sleep and massage are physiotherapy.
Is it true that some devices help with everything?
Of course not. Physiotherapy has a non-specific effect. That is, it does not eliminate the cause of the disease, it helps the body work better and recover faster. That is why the same procedures are prescribed for completely different diseases.No one method can fight all diseases. Physiotherapy only helps you feel better.
One device can be used for different diseases. But one device cannot cure them.
Is all physical therapy effective?
No. We are all different. The same procedure will help someone more, someone less. This depends on the form of the underlying disease and on the condition as a whole.There are also clearly anti-scientific methods that have nothing to do with physiotherapy and medicine in general, for example
Physiotherapy is a branch of medicine that studies the effects of natural and artificially created physical factors on the human body. Many of these factors are used by doctors to prevent and treat pathologies of various organs and systems. Physiotherapy, keeping pace with medicine, has already undergone many historical stages, and continues to develop rapidly to this day.
This article talks about what physiotherapy is in medicine, what place it occupies, how it appeared and developed. It contains data on the proposed mechanism of therapeutic effects, as well as the main modern methods of physiotherapy that are currently popular.
Brief historical background
Even at the beginning of its development, humanity realized that it was possible to extract positive health effects from such natural factors as sunlight, water, heat, steam, earth, etc. Ancient doctors, based on their experience, advised the use of one or another natural a phenomenon in various ailments of the body. For example, it was recommended to treat pain in the joints with sand heated in the sun. Some doctors paid attention to the healing effect of natural mineral waters and prescribed a certain type of water for various ailments. In China, physical treatments have taken the form of acupressure.
As science developed, a detailed study of physical phenomena and numerous experiments in this area, certain physical phenomena were discovered, which people immediately tried to find application in medicine. Since the 19th century, sciences such as physics and chemistry began to develop particularly rapidly, which gave impetus to the emergence of new opportunities in physiotherapeutic treatment. Thus, a source of direct electric current was created, the features of the therapeutic effect from the use of galvanization were studied, and the first methods of electrical stimulation were developed.
In the 20th century, all physical treatment methods known at that time were combined into a separate scientific discipline - physiotherapy.
At the present stage of development of this area of medical science, a more detailed study of physical treatment methods was carried out, which led to the emergence of methods such as medicinal electrophoresis, magnetophoresis, and ultraphonophoresis. Later, techniques were developed based on a combination of several methods of physical influence ─ vacuum-darsonvalization, etc.
Types of physiotherapy
There are many classifications of physiotherapeutic treatment methods. Depending on the effect on different organ systems, the following are distinguished:
- Acting primarily on the central nervous system: sedative, tonic, psychostimulant.
- With an effect on the peripheral nervous system: anesthetic, stimulating free nerve endings, trophostimulating, neurostimulating.
- Acting on the muscular system: aimed at muscle relaxation or myostimulation.
- Affecting the cardiovascular system: lowering blood pressure, dilating blood vessels and relieving spasms, vasoconstrictor, cardiotonic and lymphatic drainage (with a decongestant effect).
- With an effect on the blood system: decreasing and increasing blood clotting, hemostimulating and hemodestructive.
- Affecting the respiratory system: mucokinetic, bronchodilator.
- Having an effect on the digestive organs: increasing gastric secretion, decreasing gastric secretion, increasing or weakening intestinal motor activity, promoting bile secretion.
- Affecting the skin and connective tissues: astringent, antipruritic, enveloping, stimulating the release of melanin, keratolytic, diaphoretic, changing the metabolism of connective tissue, promoting the resorption of scar tissue and smoothing the skin.
- Having an effect on the urinary system: diuretics, improving erectile function, stimulating reproductive abilities.
- Acting on the hormonal system: stimulating the hypothalamus, pituitary gland, thyroid gland, pancreas, adrenal glands.
- Correcting general metabolism: vitamin-stimulating, plastic, stimulating the work of enzymes.
- Changing the body's immunity: immunostimulating, immunosuppressive.
- Affecting various pathogens: antiviral, mycocidal and bactericidal.
- Healing wounds and burns: stimulating recovery processes after various wounds and injuries, anti-burn.
- Influencing the course of oncological diseases: oncodestructive, cytolytic.

Physiotherapy methods are also divided into types depending on the nature of the physical factor used in the technique:
- Methods based on the use of the properties of electric current of various parameters (galvanization, darsonvalization, medicinal electrophoresis, electrosleep).
- Techniques based on the use of the properties of a magnetic field (magnetotherapy).
- Using the therapeutic properties of the electric field (Franklinization).
- Methods based on the use of electromagnetic waves of different frequencies for therapeutic purposes: ultra-high frequency (microwave) and with different wavelengths ─ centimeter wave (SMV), decimeter wave (UHF).
- The use of electromagnetic oscillations in the optical range: infrared therapy, ultraviolet therapy (DUV, SUV, KUV), laser therapy.
- Targeted application of acoustic waves of a certain frequency (shock wave therapy (SWT)).
- Use of ultrasonic vibrations (UT).

About theories regarding the mechanism of action
Throughout the history of the development of physiotherapeutic science, there have been several theories about the mechanism of action of physical factors on the body. At the beginning of the 20th century, the thermal theory was considered the main one, and the effect of all existing methods was considered completely nonspecific, rather having a positive psychotherapeutic effect. Doctors used such procedures rather to calm the nerves and after-treatment of already recovering patients, and rarely as the main treatment.
With the advent of new research in the field of physiology (thanks to I.P. Pavlov, I.M. Sechenov and others), when it became known about the enormous importance of the activity of the nervous system in the development of various pathological conditions, the idea of the neurogenic effect of physical methods was developed. With the study of the reflex mechanism of the therapeutic effect of physiotherapy methods, they have received greater recognition and widespread and conscious use in medicine.
At the end of the 20th century, after the discovery of the molecular mechanisms of physiotherapeutic effects, some theories, for example, free radical, ionic, thermal and conformational, received experimental confirmation. At this time, new methods of physical treatment arose, such as ultrasound therapy, pulsed and high-frequency electrotherapy, and magnetic therapy.
Goals of physiotherapy

The main areas of application of physiotherapeutic methods include:
- Medicinal. Most techniques are used after the acute phase of any disease has disappeared. Physiotherapy shows good results precisely at the stage of recovery, recovery and rehabilitation. The choice of a specific method of physiotherapy, dosage and duration of the course is made by the attending physician, taking into account the age and condition of the patient.
- Rehabilitation. Some physical therapy methods are used at all stages of treatment and subsequent recovery. In patients with neurological pathologies, as well as diseases of the musculoskeletal system, the use of physical factors is the main one in the rehabilitation system.
- Preventive. Methods for healing the body and increasing resistance to various infectious and other diseases are based on physiotherapy.
- Diagnostic. Techniques that were used only as treatment also formed the basis for such diagnostic methods as X-ray diagnostics, ultrasound diagnostics, etc.
Indications

Physiotherapy methods help in the treatment of the following pathologies:
- From the heart and blood vessels: vegetative-vascular dystonia, obliterating diseases of the arteries of the upper and lower extremities, heart attack during the rehabilitation period.
- Digestive organs: stomach and duodenal ulcers, gastritis and colitis.
- Respiratory system: chronic bronchitis, bronchial asthma.
- Diseases of the ENT organs: otitis media, sinusitis, rhinitis, etc.
- Diseases of the nervous system: osteochondrosis, radiculitis, plexitis of the brachial and other nerve plexuses.
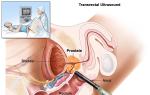
- Diseases of the urinary and reproductive systems: cystitis, prostatitis, prostate adenoma, etc.
- Gynecological diseases: adnexitis, ovarian cyst, uterine fibroids.
- Endocrine pathologies: thyroid diseases, obesity.
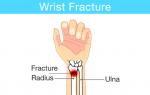
- Diseases of the musculoskeletal system: osteochondrosis, scoliosis, hernia of the lumbar spine, arthrosis, bursitis, tendovaginitis.
- Various injuries and sprains of ligaments in the knee, ankle, etc.
- Dental diseases: stomatitis, gingivitis, periodontal disease.
- Skin diseases: dermatitis, eczema.
The prescription of one or another method of physiotherapy is always individual. Only the attending physician can correctly choose the right technique, dosage and duration of the course; there should be no place for self-medication.
Contraindications

The main contraindication to physiotherapy sessions is the presence of:
- Cancer, cancer cachexia.
- Diseases of the blood system.
- Decompensated diseases of the cardiovascular system.
- Bleeding or increased risk of bleeding.
- Increased body temperature.
- Acute phase of bacterial, viral or fungal infection.
- Mental illnesses in which the patient does not control his actions.
For all these diseases, some methods of private physiotherapy can be used, but there are absolute contraindications even to some types of physiotherapy. These include:
- Individual intolerance to a certain physical factor.
- Location of metal structures in the area of expected impact.
- Implanted pacemaker or artificial pacemaker.
About unwanted effects
Since physical factors are used in minimal doses during physical therapy sessions, the likelihood of side effects and allergic reactions is low. This is the main advantage of physical therapy over treatment using pharmaceutical drugs.
Purpose principles

When turning to various methods of physiotherapy, the doctor is guided by the following principles:
- The physical factors that are supposed to influence the patient’s body must be optimally selected, that is, most suitable for solving specific health problems.
- The approach to each patient must be individual. Gender, age, constitutional features, and severity of the condition are taken into account. The more subtle the approach, the better.
- If the patient has pain, it must be eliminated during the first few sessions.
- Physiotherapy is almost never used in the acute and subacute periods of diseases, however, some of its techniques can be used to influence the very cause of the disease, and also act as symptomatic treatment. If physiotherapy procedures are prescribed in the acute phase of the disease, then the physical factors selected for influence must be of low intensity, in order to act locally, they must be aimed directly at the cause of the pathology. During recovery, as well as during chronic disease, it is permissible to increase the intensity of the physical factors used for treatment.
- Treatment using physiotherapeutic methods must necessarily be a course course; the lack of effect after the first few procedures does not become a basis for discontinuing therapy.
- An integrated approach to treatment. In addition to the instructions of the physical therapist, the patient may be prescribed medication therapy. When used together, physiotherapy and pharmacotherapy provide optimal results.
Features of application

With the help of physiotherapeutic methods, the doctor can enhance the effect of certain medications, promote their accelerated elimination from the body, or reduce their side effects. In addition, when using most physical treatment methods, the therapeutic effect persists for some time due to the formation of a kind of “depot” in the body.
Despite the fact that the effect after a single session may be insignificant, after a whole course the therapeutic effect will last from several weeks to several months. Subsequently, if necessary, the doctor may prescribe a repeat course or change the method of physical treatment.
An important feature is also that almost all physiotherapeutic methods are well compatible with other therapeutic agents, and can and even should be used in combination to obtain an optimal result.
How and where it is carried out
Physiotherapeutic treatment courses are provided free of charge in specialized departments at outpatient and inpatient state medical institutions. Physiotherapists and nurses of the relevant departments have the right to perform certain procedures. In order to receive one or another course of physiotherapy for free, you must have a referral from a doctor. If desired, all procedures can be performed in a private medical center (the cost of their services varies).
If necessary, you can purchase the necessary equipment and medications and undergo physical therapy at home. To do this, you will need to invite a nurse from the physiotherapy department, she will conduct a trial session and teach you how to use the device correctly, so that you can then cope on your own.
In children

Physiotherapy is widely used in childhood, including infants. Due to the small number of contraindications and the low likelihood of side effects, physiotherapy occupies an important place in pediatrics. Listed here are a number of pathologies that occur more often in children than in adults and lead to the need for physiotherapy. These primarily include:
- Diseases of the musculoskeletal system, including congenital ones, such as hip dysplasia, etc.
- Diseases of the ENT organs: rhinitis, otitis media, sinusitis, various diseases of the throat and larynx. Irradiation with a Minin lamp, UHF therapy, and ultraviolet irradiation techniques, including ultraviolet radiation, are used.
- Diseases of the respiratory system.
- Birth injuries and associated neurological diseases of the baby (cerebral palsy, increased intracranial pressure). In this case, electrophoresis using the Ratner method is considered effective.
- Hemolytic disease. Phototherapy is used to relieve it.
During pregnancy
The following reasons may be indications for physiotherapy during pregnancy:
- Toxicosis of the first half of pregnancy.
- Preeclampsia.
- Symphysiopathy ─ divergence of the pelvic bones.
- Intrauterine growth retardation.
- Threat of miscarriage, possibility of premature birth.
- Acute respiratory diseases.

All information about which methods are safe to use during pregnancy can be obtained from your doctor. He will select an individual course of physical treatment and determine its optimal duration.
Physiotherapy is needed to prepare for the onset of labor in the later stages, as well as for a speedy recovery after childbirth. Physiotherapy methods accelerate the healing of almost any postoperative wounds (if a cesarean section was performed or incisions were required during childbirth), stimulate uterine contractions when it is incompletely involuted after childbirth, and contribute to the normalization of intestinal motility. In the postpartum period, physiotherapy helps in the prevention and treatment of lactostasis.
Physiotherapy is also relevant not only during pregnancy, but also in gynecology. Diseases for which one or another method of physical treatment is used are indicated in the indications for physical therapy.
Thus, physiotherapy is a field of medicine that, both independently and in combination with other treatment methods (for example, pharmacotherapy), allows you to treat a huge range of different diseases. This part of medical science will never stop developing. The emergence of more and more new discoveries in the field of physics, chemistry and medicine will lead to the emergence of new, more advanced methods of physiotherapy.
Physiotherapy is a set of methods for treating various diseases using physical factors such as electric current, magnetic radiation, heat, air, light and many others.
Physiotherapy– this is an integral part of the rehabilitation period after severe injuries, as well as a lifesaver for chronic diseases of various organs.
Physiotherapy is actively developing. Today, there are a lot of different methods that can have a beneficial effect both on the body as a whole and on local problem areas.
Qualified Physiotherapist using special equipment, selects treatment procedures, taking into account the characteristics of the patient, his age and stage of development of the disease.
The most common physiotherapeutic methods are:
- SMT physiotherapy,
- UHF physiotherapy (exposure to high-frequency magnetic field),
- magnet physiotherapy,
- phototherapy,
- electrophoresis,
- heat therapy (paraffin) and others.
As a rule, they are painless and do not cause allergic reactions or other side effects. However, most of them have contraindications, so it is very important to consult a physical therapist before starting physical therapy.
Among the simplest methods physiotherapy highlight the familiar cups, compresses, applying a heating pad or, conversely, an ice pack. These seemingly elementary procedures can have an amazing effect on the state of the body.
Physiotherapy in gynecology
Physiotherapy used in the treatment of diseases of the female genitourinary system. Among the most common intimate problems that it helps to eliminate physiotherapy, we can highlight:
- chronic diseases of the uterus,
- heavy and painful periods,
- menopause period,
- rehabilitation after genital surgery,
- amenorrhea and others.
Physiotherapy is popular during pregnancy. This is an alternative method to drug treatment, which can easily harm the unborn baby.
They can be especially effective when there is a threat of miscarriage or a threat of premature birth.
Also, such treatment can have a beneficial effect on the general condition of the expectant mother, preventing or eliminating toxicosis.
Physiotherapy for osteochondrosis
Physiotherapy for osteochondrosis has become popular due to its ability to affect certain joints and bones without affecting surrounding tissues and organs.
This treatment method causes virtually no side effects. Physiotherapeutic procedures can be used both during an exacerbation of the disease and at all stages of its development.
Among such procedures, shock wave therapy, laser therapy, detensor therapy, ultrasound and ultraviolet exposure should be noted. Magnetic physiotherapy is also widely used in the treatment of osteochondrosis.
Physiotherapy in dentistry
In dentistry physiotherapeutic procedures began to be used relatively recently. As a rule, they are aimed at speeding up the rehabilitation period after jaw surgery.
Such procedures are also used in the treatment of periodontitis, which can occur as a result of tooth filling with phosphate cement.
Physiotherapy in dentistry consists of procedures such as phonophoresis, laser and magnetic therapy, as well as SMT procedures and exposure to infrared radiation.
Physiotherapy is a branch of medicine that definitely has a future, since physiotherapeutic methods are safe and effective in treating a wide variety of diseases of the human body.
Physiotherapy is a field of medicine that studies the effects of natural factors on the body. Treatment using natural factors allows you to reduce the amount of pharmacological drugs used by the patient, and in some cases, completely abandon them. Medicines have many side effects and can cause adverse symptoms and reactions. Physical factors, as a rule, are perceived favorably by the body and make it possible to achieve significant success in the treatment of many diseases.
History of the development of physiotherapy
Scientists of antiquity wrote about the usefulness of using natural factors to treat diseases: Hippocrates, Asclepiades, Galen, Pliny successfully used massage techniques, healing mud, and also fish that generate an electric charge. Scientists in Ancient China developed techniques for acupuncture and acupressure. The works of these great scientists laid the foundations of physiotherapy.
In the Middle Ages, doctors of the East, Byzantium and Ancient Rus' generalized the knowledge of the ancestors of science, formulated its main postulates, determined methods for treating certain diseases, as well as indications and contraindications for the use of certain natural factors in medical practice.
With the subsequent development of science and scientific thinking, the empirical approach to understanding the impact of natural factors on the body was replaced by an evidence-based one. The descriptive basis of treatment began to lay the foundation of scientific discoveries in physics, chemistry, medicine, mathematics, etc. These data helped to substantiate and experimentally confirm the positive effect of the use of therapeutic factors to treat a particular disease.
In addition, in the 19th century, the possibilities for using physical factors expanded significantly due to the emergence of methods for obtaining various types of healing energy artificially, in other words, hardware physiotherapy. It was at this time that scientific works appeared on the therapeutic effects of galvanization and electrophoresis (treatment of syphilis with mercury), and somewhat later - scientific developments of stimulation of certain points of muscles and nerves. In 1807, the book of Tsion I.F. was published. “Fundamentals of Electrotherapy,” for which the author was awarded the Gold Medal of the Paris Academy of Sciences. In the same millennium, the first franklinization apparatus appeared (1882) thanks to the successful study of the characteristics of the electromagnetic field (1865), and the invention of a high-frequency oscillation generator by Nikola Tesla (1891) allowed D'Arsonval J.A. (1891) to propose a method of high-frequency electrotherapy, now known by the name of its “master” - darsonvalization. In 1903, N. Finsen was awarded the Nobel Prize for developing the fundamentals of phototherapy.
In parallel with the development of hardware physiotherapy, balneology and balneology were actively developing, resorts were opened in Russia and Europe, offering to use the healing properties of mineral waters and medicinal mud to treat various pathologies, scientific works devoted to balneology appeared, and the first departments of hydrotherapy were opened.
By the beginning of the 20th century, the difficult path of collecting data, scientifically substantiating the impact of natural factors on body functions, monitoring the effectiveness and safety of physiotherapy procedures had been passed, which made it possible in 1905, in the Belgian city of Liege, at the first congress of physiotherapists to combine all the knowledge and works related to the use of therapeutic factors in medicine into a single clinical and scientific discipline - physiotherapy.
Further developments and research dealt with many issues and problems related to physiotherapy, which were carried out on a large scale in Russia and Western Europe, where treatment with natural factors remains at its best to this day.
Today, the scientific minds of physiotherapy and related sciences are working on research related to the study of the effects of physical factors at the subcellular and molecular levels, which allows us to supplement, clarify, and even, in some cases, change ideas about the interaction of a natural factor with living tissues. And also make adjustments to indications, contraindications to procedures, dosing, combination with other types of treatment, exposure time and other important indicators in the use of physiotherapeutic procedures.
Goals of physiotherapy:
The use of natural factors makes it possible to achieve maximum effect in the treatment of diseases, reduce the risk of developing adverse reactions, get rid of pathologies or increase the time of remission between exacerbations, and also physiotherapeutic methods are used for preventive purposes.
Therapeutic effects:
- Improving blood and lymph circulation;
- Anesthesia;
- Stimulation of immunity;
- Improved joint and muscle sensation;
- Improved feedback;
- Stimulation of metabolic processes;
- Acceleration of tissue repair and regeneration processes;
- Resorption of edema;
- Myostimulation;
- Muscle relaxation;
- General relaxation;
- Increased compensatory capabilities of the body;
- Restoration of normal function of organs and tissues;
- Increased performance;
- Fighting depression;
- Reducing the rehabilitation period;
- Preparation for surgical interventions.
Application in medical fields
Physiotherapeutic treatment is actively and successfully used in many medical areas: gynecology, urology, venereology, sexopathology, surgery, dentistry, ophthalmology, neurology, pediatrics, cardiology, pulmonology, gastroenterology, psychology, rehabilitation, orthopedics, rheumatology, cosmetology, trichology, dermatology, endocrinology, traumatology and even oncology.
Methods of carrying out procedures:
The following types of physiotherapeutic effects are distinguished: general, local, on metameric zones (i.e. on certain segmental reflex zones), on biologically active points and Zakharyin-Ged zones.
Features of the application of procedures:
- Only one general procedure can be performed on one day; the total number of exposure methods should not exceed three. Local procedures are carried out before general ones.
- You cannot take procedures with the opposite effect on the same day: for example, after heat treatment - ice baths.
- You cannot prescribe more than one procedure per projection or reflexogenic zone.
- It is impossible to combine the influence of physiotherapeutic factors with acupuncture.
- It must be taken into account that physical factors can enhance the effect of some medications; therefore, it is necessary to adjust the dose of the medication taken.
- It is necessary to observe the compatibility of physical factors.
- Repeated courses are prescribed 2-6 months after the end of the previous course, depending on the specific method.
Features of the use of physical factors in children:
- Physiotherapy should be taken no later than 40 minutes before meals and no earlier than 1 hour after meals.
- The child should be rested and calm.
- It is recommended to prescribe one general procedure on one day; if necessary, one local procedure can be performed after 2 hours.
- A child’s body differs from an adult in the longer retention of the effect of physiotherapeutic influence, therefore the same therapeutic factor can be repeated only after several months, and if it becomes necessary to use treatment at an earlier date, the physiotherapeutic method should be changed to one with a similar effect.
- Treatment with any natural factor should begin with minimal dosages, gradually increasing the intensity to the required value.
- Constant monitoring of the little patient’s condition is mandatory, and it is necessary to monitor not only local reactions, but also changes in the person’s general well-being: sleep, appetite, physical activity, mood, weight gain, etc. During the first procedures, a doctor must be present next to the child, and not just the nurse who performs the procedure.
- The duration of the procedure, quantity per course, intensity, concentration and other indicators of the procedures should be significantly lower than for an adult patient. On average, all indicators of procedures for children are reduced in relation to “adults” by 1/3-1/5.
- If possible, you should avoid using general procedures and limit yourself to local ones, and local treatment is recommended only using portable equipment, since its power is lower than stationary equipment.
Physiotherapy sections:
Electrotherapy:
- Galvanization;
- Electrophoresis;
- Amplipulse therapy;
- Electrical stimulation;
- Darsonvalization;
- Electrosleep;
- Diadynamic therapy;
- Interference therapy;
- Inductotherapy;
- Fluctuarization;
- Electronarcosis;
- Ultratonotherapy.
- Franklinization;
- Microwave (SMV and UHF therapy);
- Infit therapy;
Phototherapy:
- Ultraviolet;
- Infrared radiation;
- Visible radiation.
Heat therapy:
- Paraffin;
- Ozokerite;
- Psammotherapy (sand);
- Clay therapy;
- Mud therapy;
- Baths and saunas.
Hydrotherapy:
- Baths;
- Souls;
- Pouring;
- Rubdowns;
- Underwater massage.
Physical impact:
- Massage;
- Mechanotherapy;
- Manual therapy;
- Physiotherapy;
- Vibration therapy;
Climatotherapy:
- Heliotherapy;
- Aerotherapy;
- Speleotherapy;
- Thalassotherapy.
Physiopharmacological treatment:
- Electrophoresis;
- Electroaerosol therapy;
- Ultraphonophoresis.
Contraindications for the use of physiotherapy:
Absolute contraindications
- Acute febrile conditions;
- Less than 3 months after acute myocardial infarction;
- Tendency to bleeding;
- Blood diseases;
- Decompensation of chronic diseases;
- General serious condition of the patient;
- Cachexia;
- Mental illnesses that do not allow the patient to control the procedure;
- Presence of a pacemaker;
- Individual intolerance to a certain therapeutic factor;
In pediatrics:
The following areas cannot be affected:
- Bone growth zones;
- Heart area;
- Areas of impaired blood supply;
- Parenchymal organs;
- Endocrine organs.
Relative contraindications:
If the patient has the following conditions and diseases, physiotherapy can be carried out by choosing a specific method of influence, setting an individual treatment time and area of the procedure, as well as manipulation techniques.
- Neoplastic processes;
- Violation of the integrity of the skin at the site of the procedure;
- Pregnancy and lactation;
- Gallstones and urolithiasis;
- Severe hypotension;
- Thrombophlebitis;
- Osteoporosis.
With a professional approach, correct prescription and following the doctor’s recommendations by the patient, the use of physiotherapeutic treatment methods is absolutely safe. Exposure to natural factors is physiological, practically does not cause negative effects, it is pleasant and effective.