What the human body is capable of. How a person works: the structure of the body and its functions. Females are much more sensitive to odors than males
The human body is a mysterious, complex mechanism that is capable of not only performing physical actions, but also feeling and thinking. A general overview of the human body shows that out of the seven billion people living on Earth, no people are absolutely similar in appearance, but the structure of the body is 99% the same for everyone. Nature has arranged it in such a way that with clear, coordinated work of all organs, the mechanisms of vital activity ensure the long existence of our body.
General overview of the human body
The human body is a single organism, where the action of all organs and systems is closely interconnected. The basic unit is the cell. By the time we reach adulthood, the human body consists of an average of three billion cells. All of them are formed into systems, each of which plays an important role in life. Human body systems:
- The cardiovascular system. It includes capillaries, arteries, veins, and the heart. The main thing is pumping blood, delivering it to all organs. The left side of the heart is a “pump” for the whole body, the right side of the heart muscle delivers blood to the lungs to enrich it with oxygen. The heart has three layers (myocardium, epicardium, endocardium). Each of them has a different density and functionality.
- The digestive system satisfies the need for food and converts nutrients into necessary energy. Consists of the digestive tract: oral cavity, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, colon, ending in the rectum.
- Skin covering. The life activity of the human body is constantly associated with various risks. The skin protects the body from environmental influences and external irritants. The cutaneous system consists of the skin (including sebaceous and sweat glands), hair, nails and micromuscles that hold the hair.
- Lymphatic system. The main function is the extraction and transportation of lymph throughout the body.
- Musculoskeletal system. It consists of the human skeleton, in which all the bones are combined with each other by joints, supported by muscles, attached to the skeleton by tendons. The study of the human body often begins with studying the structure of the skeleton. In total, the skeleton consists of 206 bones.
- Nervous system. The nervous system is responsible in the body for information about the body and the environment. Divided into peripheral and central.
- Reproductive system. The most complex system of the body, the female one is completely different from the male one. Responsible for sexual function and, in general, for procreation of the human race.
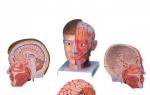
How a person works: arrangement of organs. Head

Each human organ is individual, located in a specific place and performs its own function. When making a general overview of the human body, it is important to understand where each organ is located. This will help to avoid any injuries, as well as determine which specialist to contact for a particular disease.
The brain, perhaps, remains the most mysterious and unsolved element of the body. All parts of the body are subordinate to this center. The brain is located in the cranium, protected by strong bones of the skull. Nerves run from the brain throughout the body, carrying impulse signals for one or another action. Thanks to the commands of the brain, we see, hear, feel, move, generally live and exist.
Rib cage

Everyone should know how a person works, in what places the main organs are located. Let's look at the chest. On the front, cervical side, under the Adam's apple, it is located and can be called the “battery” of our body. It is responsible for the production of the main hormones that ensure all the coordinated functioning of the organs of our body. With age, the thyroid gland can descend and even end up in the chest cavity.
The thoracic cavity is separated from the abdominal cavity by the muscular organ diaphragm. The heart is shifted to the left, located between the right and left lungs, behind the sternum. The lungs occupy most of the chest space. They run from the heart to the ribs, are dome-shaped, and are located at the back towards the spine. The bases of the lungs rest against the muscular diaphragm. Protected by ribs.
Abdomen

The main reservoir for receiving and storing food is the stomach. It is located under the diaphragm, on the left side of the peritoneum. At the back, just below the stomach, is the pancreas. It breaks down fats, carbohydrates, proteins and produces glucagon and insulin - the most important hormones.
On the right, under the diaphragm, is the liver. The coordinated functioning of the human body largely depends on this organ. The liver is our main filter. At the bottom of the liver, in a recess, is the gallbladder, which plays an important role in processing food. The spleen lies on the left side of the hypochondrium; it protects our body from various infections, as well as from blood loss.
Intestines
Below the stomach, the peritoneal space is occupied by the small intestine, which is a long, tangled tube. The beginning of the large intestine is on the right side. The colon then flows around the top of the peritoneum and down the left side. The cecum is called the appendix. The large intestine passes into the rectum and ends with the anus, the outlet through which feces are removed.
Genitourinary organs
Considering the systems of the human body, you understand that each of them is important and necessary in its own way. The kidneys belong to the paired organs of the genitourinary system. The left kidney is located slightly higher due to the increased size of the liver located on the right. At the top of each kidney are the adrenal glands. Their role is enormous; they release more than thirty hormones directly into the bloodstream. Below, in the pelvis, is the bladder. In men, behind it are the seminal vesicles and intestines. In women - the vagina, from below - the pelvic floor muscles. Two tiny glands - the ovaries - lie in the pelvic cavity, on opposite sides of the uterus, attached to it by ligaments. In men, the testes (testicles) are located in the scrotum, which is brought out. Below the bladder is the prostate gland.
Cell

Carrying out a general overview of the human body, we put the cell first. It is the smallest functional and structural unit. There are more than two hundred types of cells in the human body, each of them has its own composition, functionality, and structure. If we look at the general plan of the building, it is the same. The membrane, cytoplasm and nucleus are the main components of any cell. The membrane is formed by the glycocalyx and plasmalemma. The cytoplasm distinguishes between organelle and hyaloplasm.
The cell membrane provides receptor function, selective permeability, transmission of electrical and chemical signals, and separates it from the protoplast.
The main ones in life are irritability, metabolism, reproduction, aging, death.
Metabolism occurs continuously. Various substances that take part in energy and plastic metabolism constantly enter the cell, used components are removed, and thermal energy is released.
The cell is capable of responding to various internal and external stimuli. The form of the response is excitability, it is associated with the charge of the cell membrane.
Each cell has its own life cycle. Every day in the human body, about 1-2% of cells die as a result of aging and new ones are born; this process is continuous.
Fabrics

A tissue is a collection of cells and intercellular substance that have a common structure, function, and origin. There are four types of tissues in the human body:
- Based on ectodermal origin, quickly regenerates, has a minimum of intercellular substance, no vessels, and is located on the basement membrane. There are several types of epithelium: single-layer - flat, cylindrical, cubic, ciliated epithelium, multilayer - keratinizing, non-keratinizing, glandular epithelium.
- Connective tissue. Originates from mesoderm. The shape of the cells is varied, the intercellular substance is developed. There are fibrous - loose tissue, dense tissue, cartilage, bone, fat, lymph, blood. Hematopoietic tissues also belong to connective tissues.
- Muscle. Has the properties to contract and excite. There are skeletal striated, cardiac striated, and smooth.
- The most important properties are excitability and conductivity. Tissue of ectodermal origin, represented by neuroglia and neurons.

Systems, functions of organs
So, we looked at the structure and functions of the human body. Let us summarize the results obtained and present all the functions of individual systems in the form of a table.
System parts | ||
Musculoskeletal | Skeleton, muscles | Protection and support of the body. Movement |
Blood | Vessels, heart | Metabolism. Supplying organs with oxygen and nutrients, removing harmful substances |
Respiratory | Airways. Lungs | Gas exchange, breathing |
Digestive | Digestive tract, digestive glands | Food processing, nutrient absorption, removal of residues |
Pokrovnaya | Protection. Removal of harmful substances, temperature regulation, touch |
|
Urinary | Salt metabolism, removal of harmful substances |
|
Genitals | Reproduction |
|
Brain, spinal cord | Connects systems throughout the body |
|
Endocrine | Coordinates the activities of the entire body |
As you can see, the human body is an integral dynamic system with a special structure.
Content
The study of the complex structure of the human body and the arrangement of internal organs is the subject of human anatomy. Discipline helps us understand the structure of our body, which is one of the most complex on the planet. All its parts perform strictly defined functions and they are all interconnected. Modern anatomy is a science that distinguishes both what we observe visually and the structure of the human body hidden from the eyes.
What is human anatomy
This is the name of one of the sections of biology and morphology (along with cytology and histology), which studies the structure of the human body, its origin, formation, evolutionary development at a level above the cellular level. Anatomy (from the Greek Anatomia - cut, opening, dissection) studies what the external parts of the body look like. It also describes the internal environment and microscopic structure of organs.
The separation of human anatomy from the comparative anatomies of all living organisms is due to the presence of thinking. There are several main forms of this science:
- Normal or systematic. This section studies the body of the “normal”, i.e. a healthy person by tissues, organs, and their systems.
- Pathological. This is a scientific and applied discipline that studies diseases.
- Topographical or surgical. It is called this because it has practical significance for surgery. Complements descriptive human anatomy.
Normal anatomy
Extensive material has led to the complexity of studying the anatomy of the human body. For this reason, it became necessary to artificially divide it into parts - organ systems. They are considered normal, or systematic, anatomy. She breaks down the complex into simpler ones. Normal human anatomy studies the body in a healthy state. This is its difference from pathological. Plastic anatomy studies appearance. It is used to depict a human figure.
- topographical;
- typical;
- comparative;
- theoretical;
- age;
- X-ray anatomy.
Pathological human anatomy
This type of science, along with physiology, studies the changes that occur in the human body during certain diseases. Anatomical studies are carried out microscopically, which helps to identify pathological physiological factors in tissues, organs, and their combinations. The object in this case is the corpses of people who died from various diseases.
The study of the anatomy of a living person is carried out using harmless methods. This discipline is mandatory in medical universities. Anatomical knowledge here is divided into:
- general, reflecting methods of anatomical studies of pathological processes;
- particular ones, describing the morphological manifestations of individual diseases, for example, tuberculosis, cirrhosis, rheumatism.
Topographic (surgical)
This type of science developed as a result of the need for practical medicine. The doctor N.I. is considered its creator. Pirogov. Scientific human anatomy studies the arrangement of elements relative to each other, layer-by-layer structure, the process of lymph flow, and blood supply in a healthy body. This takes into account gender characteristics and changes associated with age-related anatomy.
Human anatomical structure
The functional elements of the human body are cells. Their accumulation forms the tissue from which all parts of the body are composed. The latter are combined in the body into systems:
- Digestive. It is considered the most difficult. The organs of the digestive system are responsible for the process of digesting food.
- Cardiovascular. The function of the circulatory system is to supply blood to all parts of the human body. This includes lymphatic vessels.
- Endocrine. Its function is to regulate nervous and biological processes in the body.
- Genitourinary. It differs in men and women and provides reproductive and excretory functions.
- Intercession. Protects the insides from external influences.
- Respiratory. Saturates blood with oxygen and converts it into carbon dioxide.
- Musculoskeletal. Responsible for moving a person and maintaining the body in a certain position.
- Nervous. Includes the spinal cord and brain, which regulate all body functions.
The structure of human internal organs
The branch of anatomy that studies the internal systems of humans is called splanchnology. These include respiratory, genitourinary and digestive. Each has characteristic anatomical and functional connections. They can be united by the common property of metabolism between the external environment and humans. In the evolution of the organism, it is believed that the respiratory system buds off from certain parts of the digestive tract.
Organs of the respiratory system
They ensure a continuous supply of oxygen to all organs and remove carbon dioxide from them. This system is divided into the upper and lower respiratory tract. The list of the first includes:
- Nose. Produces mucus, which traps foreign particles when breathing.
- Sinuses. Air-filled cavities in the lower jaw, sphenoid, ethmoid, frontal bones.
- Throat. It is divided into the nasopharynx (provides air flow), the oropharynx (contains tonsils that have a protective function), and the hypopharynx (serves as a passage for food).
- Larynx. Prevents food from entering the respiratory tract.
Another part of this system is the lower respiratory tract. They include the organs of the thoracic cavity, presented in the following short list:
- Trachea. It starts after the larynx and extends down to the chest. Responsible for air filtration.
- Bronchi. Similar in structure to the trachea, they continue to purify the air.
- Lungs. Located on either side of the heart in the chest. Each lung is responsible for the vital process of exchanging oxygen with carbon dioxide.

Human abdominal organs
The abdominal cavity has a complex structure. Its elements are located in the center, left and right. According to human anatomy, the main organs in the abdominal cavity are as follows:
- Stomach. Located on the left under the diaphragm. Responsible for the primary digestion of food and signals satiety.
- The kidneys are located symmetrically at the bottom of the peritoneum. They perform the urinary function. The substance of the kidney consists of nephrons.
- Pancreas. Located just below the stomach. Produces enzymes for digestion.
- Liver. It is located on the right under the diaphragm. Removes poisons, toxins, removes unnecessary elements.
- Spleen. Located behind the stomach, it is responsible for the immune system and ensures hematopoiesis.
- Intestines. Located in the lower abdomen, it absorbs all useful substances.
- Appendix. It is an appendage of the cecum. Its function is protective.
- Gallbladder. Located below the liver. Accumulates incoming bile.
Genitourinary system
This includes the organs of the human pelvic cavity. There are significant differences in the structure of this part between men and women. They are located in organs that provide reproductive function. In general, the description of the structure of the pelvis includes information about:
- Bladder. Collects urine before urination. Located below in front of the pubic bone.
- Female genital organs. The uterus is located below the bladder, and the ovaries are slightly higher above it. They produce eggs responsible for reproduction.
- Male genital organs. The prostate gland is also located under the bladder and is responsible for the production of secretory fluid. The testicles are located in the scrotum; they produce sex cells and hormones.
Human endocrine organs
The system responsible for regulating the activities of the human body through hormones is endocrine. Science distinguishes two devices in it:
- Diffuse. Endocrine cells here are not concentrated in one place. Some functions are performed by the liver, kidneys, stomach, intestines and spleen.
- Glandular. Includes the thyroid, parathyroid glands, thymus, pituitary gland, adrenal glands.
Thyroid and parathyroid glands
The largest endocrine gland is the thyroid. It is located on the neck in front of the trachea, on its lateral walls. The gland is partially adjacent to the thyroid cartilage and consists of two lobes and an isthmus necessary for their connection. The function of the thyroid gland is to produce hormones that promote growth, development, and regulate metabolism. Not far from it are the parathyroid glands, which have the following structural features:
- Quantity. There are 4 of them in the body - 2 upper, 2 lower.
- Place. Located on the posterior surface of the lateral lobes of the thyroid gland.
- Function. Responsible for the exchange of calcium and phosphorus (parathyroid hormone).
Anatomy of the thymus
The thymus, or thymus gland, is located behind the manubrium and part of the body of the sternum in the upper anterior region of the chest cavity. It consists of two lobes connected by loose connective tissue. The upper ends of the thymus are narrower, so they extend beyond the chest cavity and reach the thyroid gland. In this organ, lymphocytes acquire properties that provide protective functions against cells foreign to the body.
Structure and functions of the pituitary gland
A small spherical or oval gland with a reddish tint is the pituitary gland. It is connected directly to the brain. The pituitary gland has two lobes:
- Front. It affects the growth and development of the entire body as a whole, stimulates the activity of the thyroid gland, adrenal cortex, and gonads.
- Rear. Responsible for enhancing the work of vascular smooth muscles, increases blood pressure, and affects the reabsorption of water in the kidneys.

Adrenal glands, gonads and endocrine pancreas
The paired organ located above the upper end of the kidney in the retroperitoneal tissue is the adrenal gland. On the anterior surface it has one or more grooves that act as gates for outgoing veins and incoming arteries. Functions of the adrenal glands: production of adrenaline in the blood, neutralization of toxins in muscle cells. Other elements of the endocrine system:
- Sex glands. The testes contain interstitial cells responsible for the development of secondary sexual characteristics. The ovaries secrete folliculin, which regulates menstruation and affects the nervous state.
- Endocrine part of the pancreas. It contains pancreatic islets that secrete insulin and glucagon into the blood. This ensures regulation of carbohydrate metabolism.
Musculoskeletal system
This system is a set of structures that provide support to parts of the body and help a person move in space. The entire apparatus is divided into two parts:
- Osteoarticular. From a mechanical point of view, it is a system of levers that, as a result of muscle contraction, transmit forces. This part is considered passive.
- Muscular. The active part of the musculoskeletal system is muscles, ligaments, tendons, cartilaginous structures, and synovial bursae.
Anatomy of bones and joints
The skeleton consists of bones and joints. Its functions are the perception of loads, the protection of soft tissues, and the implementation of movements. Bone marrow cells produce new blood cells. Joints are the points of contact between bones, between bones and cartilage. The most common type is synovial. Bones develop as a child grows, providing support for the entire body. They make up the skeleton. It contains 206 individual bones, made up of bone tissue and bone cells. All of them are located in the axial (80 pieces) and appendicular (126 pieces) skeleton.
The weight of bones in an adult is about 17-18% of body weight. According to the description of the structures of the skeletal system, its main elements are:
- Scull. Consists of 22 connected bones, excluding only the lower jaw. Functions of the skeleton in this part: protecting the brain from damage, supporting the nose, eyes, mouth.
- Spine. Formed by 26 vertebrae. The main functions of the spine: protective, shock-absorbing, motor, supporting.
- Rib cage. Includes the sternum, 12 pairs of ribs. They protect the chest cavity.
- Limbs. This includes the shoulders, hands, forearms, hip bones, feet and legs. Provide basic motor activity.
The structure of the muscular skeleton
The human anatomy also studies the muscle apparatus. There is even a special section - myology. The main function of muscles is to provide a person with the ability to move. About 700 muscles are attached to the bones of the skeletal system. They make up about 50% of a person’s body weight. The main types of muscles are as follows:
- Visceral. They are located inside organs and ensure the movement of substances.
- Heart. Located only in the heart, it is necessary for pumping blood throughout the human body.
- Skeletal. This type of muscle tissue is controlled by a person consciously.

Organs of the human cardiovascular system
The cardiovascular system includes the heart, blood vessels and about 5 liters of transported blood. Their main function is to transport oxygen, hormones, nutrients and cellular waste. This system works only due to the heart, which, while remaining at rest, pumps about 5 liters of blood throughout the body every minute. It continues to work even at night, when most of the rest of the body is resting.
Anatomy of the heart
This organ has a muscular hollow structure. The blood in it flows into the venous trunks and is then driven into the arterial system. The heart consists of 4 chambers: 2 ventricles, 2 atria. The left parts act as the arterial heart, and the right parts act as the venous heart. This division is based on the blood in the chambers. In human anatomy, the heart is a pumping organ, since its function is to pump blood. There are only 2 circles of blood circulation in the body:
- small, or pulmonary, transporting venous blood;
- large, carrying oxygenated blood.
Vessels of the pulmonary circle
The pulmonary circulation moves blood from the right side of the heart towards the lungs. There it is filled with oxygen. This is the main function of the vessels of the pulmonary circle. Then the blood returns back, but to the left half of the heart. The pulmonary circuit is supported by the right atrium and right ventricle - for it they are pumping chambers. This circulation includes:
- right and left pulmonary arteries;
- their branches are arterioles, capillaries and precapillaries;
- venules and veins that merge into 4 pulmonary veins, which flow into the left atrium.
Arteries and veins of the systemic circulation
The bodily, or systemic, circulation in human anatomy is designed to deliver oxygen and nutrients to all tissues. Its function is the subsequent removal of carbon dioxide from them with metabolic products. The circle begins in the left ventricle - from the aorta, which carries arterial blood. Next comes the division into:
- Arteries. They go to all the insides except the lungs and heart. Contains nutrients.
- Arterioles. These are small arteries that carry blood to the capillaries.
- Capillaries. In them, the blood releases nutrients with oxygen, and in return takes in carbon dioxide and metabolic products.
- Venules. These are return vessels that ensure the return of blood. Similar to arterioles.
- Vienna. They merge into two large trunks - the superior and inferior vena cava, which flow into the right atrium.
Anatomy of the structure of the nervous system
Sense organs, nervous tissue and cells, spinal cord and brain - this is what the nervous system consists of. Their combination provides control of the body and the interconnection of its parts. The central nervous system is the control center consisting of the brain and spinal cord. It is responsible for evaluating information coming from outside and making certain decisions by a person.
Location of human organs CNS
Human anatomy says that the main function of the central nervous system is to carry out simple and complex reflexes. The following important bodies are responsible for them:
- Brain. Located in the brain part of the skull. It consists of several sections and 4 communicating cavities - the cerebral ventricles. performs higher mental functions: consciousness, voluntary actions, memory, planning. It also supports breathing, heart rate, digestion and blood pressure.
- Spinal cord. Located in the spinal canal, it is a white cord. It has longitudinal grooves on the anterior and posterior surfaces, and the spinal canal in the center. The spinal cord consists of white (conducting nerve signals from the brain) and gray (creating reflexes to stimuli) matter.

Functioning of the peripheral nervous system
This includes elements of the nervous system located outside the spinal cord and brain. This part stands out conditionally. It includes the following:
- Spinal nerves. Each person has 31 pairs. The posterior branches of the spinal nerves run between the transverse processes of the vertebrae. They innervate the back of the head and deep back muscles.
- Cranial nerves. There are 12 pairs. Innervates the organs of vision, hearing, smell, glands of the oral cavity, teeth and facial skin.
- Sensory receptors. These are specific cells that perceive irritation from the external environment and convert it into nerve impulses.
Human anatomical atlas
The structure of the human body is described in detail in the anatomical atlas. The material in it shows the body as a whole, consisting of individual elements. Many encyclopedias were written by various medical scientists who studied human anatomy. These collections contain visual diagrams of the placement of organs of each system. This makes it easier to see the relationship between them. In general, an anatomical atlas is a detailed description of the internal structure of a person.
Every organism living on our planet has limits to its capabilities. What can a person withstand?
How long can we survive in space without a spacesuit?

There are many misconceptions on this topic. In fact, we can live there for a few minutes.
Let's comment on a few myths that some people still believe:
A person will burst due to zero pressure.
Our skin is too elastic to rip. Instead, our body will only swell slightly.
A person's blood will boil.
In a vacuum, the boiling point of liquids is indeed lower than on Earth, but the blood will be inside the body, where the pressure will still remain.
A person will freeze due to low temperatures.
There is practically nothing in outer space, so we will simply give up our heat to nothing. But we will still feel cool, since all the moisture will evaporate from the skin.
But lack of oxygen can kill a person in the first place. Even if we try to hold our breath, the air will still rush out of our lungs with enormous force and speed. As a result, after 10-20 seconds the person will lose consciousness. Then, within one or two minutes, it will still be possible to save him by picking him up in time and providing the necessary medical assistance, but later it will not be possible.
How much electric shock can we withstand?

Electric current passing through the human body can cause two types of injuries - electric shock and electrical injury.
An electric shock is more dangerous, since it affects the entire body. Death occurs from paralysis of the heart or breathing, and sometimes from both at the same time.
Electrical injuries refer to shock to external parts of the body; these are burns, metallization of the skin, etc. Electrical injuries are, as a rule, of a mixed nature and depend on the magnitude and type of current flowing through the human body, the duration of its exposure, the paths along which the current passes, as well as on the physical and mental state of the person in moment of defeat.
A person begins to feel alternating current of industrial frequency at 0.6 - 15 mA. A current of 12 - 15 mA causes severe pain in the fingers and hands. A person can withstand this state for 5-10 seconds and can independently tear his hands away from the electrodes. A current of 20 - 25 mA causes very severe pain, the arms become paralyzed, breathing becomes difficult, and the person cannot free himself from the electrodes. At a current of 50-80 mA, respiratory paralysis occurs, and at 90-100 mA, cardiac paralysis and death occur.
How much can we eat?

Our stomach can hold 3-4 liters of food and drink. But what if you try to eat more? In practice this is impossible, because in this case everything will start to come out.
However, it is quite possible to die from overeating.
To do this, you need to fill yourself with products that can enter into chemical reactions with each other, and the gas formed in this case can lead to rupture of the stomach.
How long can we stay awake?

It is known that Air Force pilots, after three or four days of being awake, fell into such an uncontrollable state that they crashed their planes (falling asleep at the controls). Even one night without sleep affects a driver's ability in the same way as intoxication. The absolute limit of voluntary sleep resistance is 264 hours (about 11 days). This record was set by 17-year-old Randy Gardner for a high school science fair in 1965. Before he fell asleep on the 11th day, he was actually a plant with his eyes open.
In June this year, a 26-year-old Chinese man died after 11 days spent without sleep trying to watch all the games of the European Championship. At the same time, he consumed alcohol and smoked, which makes it difficult to accurately establish the cause of death. But definitely not a single person died due to lack of sleep. And for obvious ethical reasons, scientists cannot determine this period in laboratory conditions.
But they were able to do it in rats. In 1999, sleep researchers at the University of Chicago placed rats on a spinning disk placed over a pool of water. They continuously recorded the rats' behavior using a computer program that could detect the onset of sleep. When the rat began to fall asleep, the disc would suddenly turn, waking it up, throwing it against the wall and threatening to throw it into the water. The rats typically died after two weeks of this treatment. Before death, the rodents showed symptoms of hypermetabolism, a condition in which the body's resting metabolic rate increases so much that all excess calories are burned, even when the body is completely immobile.
Hypermetabolism is associated with lack of sleep.
How much radiation can we withstand?

Radiation is a long-term danger because it causes DNA mutations, changing the genetic code in a way that leads to cancerous cell growth. But what dose of radiation will kill you immediately? According to Peter Caracappa, a nuclear engineer and radiation safety specialist at Rensler Polytechnic Institute, a dose of 5-6 sieverts (Sv) within a few minutes will destroy too many cells for the body to cope with. “The longer the dose accumulation period, the higher the chances of survival, as the body tries to repair itself during this time,” Caracappa explained.
By comparison, some workers at Japan's Fukushima nuclear power plant received between 0.4 and 1.5 sieverts of radiation in an hour while confronting the accident last March. Although they survived, their risk of cancer was significantly increased, scientists say.
Even if nuclear accidents and supernova explosions are avoided, natural background radiation on Earth (from sources such as uranium in the soil, cosmic rays and medical devices) increases our chances of getting cancer in any year by 0.025 percent, Caracappa says. This sets a somewhat strange limit on human lifespan.
"The average person... exposed to an average dose of background radiation every year for 4,000 years, in the absence of other factors, will inevitably develop radiation-induced cancer," Caracappa says. In other words, even if we could defeat all diseases and turn off the genetic commands that control the aging process, we still would not live more than 4,000 years.
How much acceleration can we handle?
The ribcage protects our heart from strong impacts, but it is not a reliable protection against the jerks that have become possible today thanks to the development of technology. What acceleration can this organ of ours withstand?
NASA and military researchers have conducted a series of tests in an attempt to answer this question. The purpose of these tests was the safety of space and aircraft structures. (We don't want astronauts to lose consciousness when the rocket takes off.) Horizontal acceleration - a jerk to the side - has a negative effect on our insides, due to the asymmetry of the acting forces. According to a recent article published in the journal Popular Science, horizontal acceleration of 14 g can tear our organs apart from each other. Acceleration along the body towards the head can shift all the blood to the legs. Such a vertical acceleration of 4 to 8 g will render you unconscious. (1 g is the force of gravity that we feel on the earth's surface; 14 g is the force of gravity on a planet 14 times more massive than ours.)
Acceleration directed forward or backward is most beneficial for the body, since it accelerates the head and heart equally. The military's "human braking" experiments in the 1940s and 1950s (which essentially involved a rocket sled moving around Edwards Air Force Base in California) showed that we could brake at an acceleration of 45 g, and still be alive to tell the tale. With this kind of braking, when traveling at speeds above 600 mph, you can stop in a split second after traveling a few hundred feet. At 50 g of braking, experts estimate that we will probably turn into a bag of separate organs.
How long can we live without oxygen?

An ordinary person can be without air for a maximum of 5 minutes, a trained person - up to 9 minutes. Then the person begins to convulse, and death occurs. The main danger that awaits a person in the absence of air for a long time is oxygen starvation of the brain, which very quickly leads to loss of consciousness and death.
Freedivers are lovers of diving to depths without any equipment. They use various techniques that allow them to train their body and do without air for a long time without harmful consequences. From such training, changes occur in the body that adapt a person to oxygen starvation - a slowdown in heart rate, an increase in hemoglobin levels, and blood flow from the extremities to vital organs. At a depth of more than 50 m, the alveoli* are filled with plasma, this maintains the required volume of the lungs and protects them from compression and destruction. Researchers have found similar changes in the body in pearl divers, who are able to dive to great depths and stay there for 2 to 6 minutes.
On June 3, 2012, German diver Tom Sitas spent more than two dozen minutes underwater live in front of an astonished crowd. The record is 22 minutes 22 seconds.
* Alveolus - the end part of the respiratory apparatus in the lung, having the shape of a bubble open into the lumen of the alveolar duct. The alveoli participate in the act of breathing, carrying out gas exchange with the pulmonary capillaries.
What is the lethal dose of apples?

About 1.5 mg of hydrogen cyanide per kilogram of the human body.
We all know that apples are healthy and tasty. However, their seeds contain small amounts of a compound that turns into the dangerous toxin hydrogen cyanide or hydrocyanic acid when digested.
It is estimated that an apple contains about 700 mg of hydrogen cyanide per kilogram of dry weight, and about 1.5 mg of cyanide per kilogram of the human body can kill. This means you need to chew and swallow half a cup of apple seeds in one sitting.
Symptoms of mild cyanide poisoning include confusion, dizziness, headache and vomiting. Large doses can lead to breathing problems, kidney failure and, in rare cases, death.
But none of this will happen if you do not chew or grind the apple seeds, but swallow them whole. This will allow them to pass through the digestive system without causing harm.
The human body is unique. And most people know about the structure of the human body only the information that was obtained during their school years. In this article we will tell you information about the human body that amazes and surprises and which you most likely have never heard or even suspected.
The human body has not yet been fully studied, but even what is already known for certain is simply amazing. And we are not talking about some supernatural possibilities, but about quite ordinary facts and figures.
So, everyone knows that the human body mainly consists of water. More precisely, by 60%. Yes, more than half of us are water - blood, lymph, intercellular fluid. With age, the percentage of water in the body decreases by 15-20% - this is one of the reasons for aging
1. A feeling of fatigue appears at loads of 35-65% of absolute capabilities.
2. The activity of the cardiovascular system is maximum at 18 hours, minimum at 3-4 hours.
3. The biological qualities of the offspring increase from the 1st to the 4th child, then decrease.
4. During normal breathing, a person inhales 500 cubic centimeters of air, when playing a wind instrument - 3500 cubic centimeters.
5. The surface of the lungs is about 100 square meters.
6. The right lung of a person holds more air than the left.
7. An adult takes approximately 23,000 breaths (and exhalations) per day.
8. The composition of blood plasma in the human body resembles the composition of the water of the prehistoric seas in which life originated.
9. In one contraction, the heart pumps 200 ml. blood.
10. Complete circulation of the blood of an adult is completed in 20-28 seconds, in a child - in 15 seconds, in a teenager - in 18 seconds. During the day, blood circulates through the body 1.5-2 thousand times.
11. There are 40 capillaries in 1 cubic millimeter of skin, 2500 capillaries in muscles, 4000 capillaries in cardiac muscle.
12. Three strength training sessions per week give the greatest effect.
13. The norm of physical activity is 7-10 km (10,000-14,000 steps).
14. The strongest muscle in the human body is the tongue, not the heart. The heart is the most resilient muscle.
15. For a young man, the norm of energy consumption is 3000 kcal. Of these, 1700 are for basic metabolism, 170 are for digestion, and 130 are for muscle work.
16. The total length of hair on the head grown by the average person during a lifetime is 725 kilometers.
17. Fingernails grow about 4 times faster than toenails.+
18. In one day, a person generates so much heat that it is enough to bring 33 liters of ice water to a boil.
9. It is estimated that a person consumes 2.5 tons of protein, 1.3 tons of fat, 17.5 tons of carbohydrates and 75 tons of water over a lifetime.
20. It is impossible to sneeze with your eyes open.
21. A person who smokes a pack of cigarettes a day drinks half a cup of tar a year.
22. Each human finger bends approximately 25 million times during a lifetime.
23. Women blink about 2 times more often than men.
24. In terms of hardness, tooth enamel can be compared to quartz. It is known that even the tip of a saber becomes dull when it hits the enamel.
25. On 1 square centimeter of skin there are 100 pain points, and in total there are about a million of them on the surface.
26. Scientifically, the navel is called “umbilicus”.
27. Man is the only representative of the animal world who is able to draw straight lines.
28. Men with blond hair grow a beard faster than men with dark hair.
29. When a person smiles, he uses 17 muscles.
30. Human DNA contains about 80,000 genes.
31. Men are classified as dwarfs if their height is less than 130 cm, and women – 120 cm.
32. The lifespan of leukocytes in the human body is 2-4 days, and erythrocytes – from 3 to 4 months.+
33. The names of the fingers of the hand in the French are: pous, index, major, anulaire, oriculaire.
34. The size of a person’s heart is equal to the size of his fist, and its weight in an adult will be 220-260 grams.
35. There are only 4 minerals in the human body: apatite, aragonite, calcite and cristobalite.
36. In one day, the human brain generates more electrical impulses than all the phones in the world combined.
37. “Snow blindness” - the effect of blinding a person from a strong direct beam.
38. Bacteria living in the human body total 2 kilograms.
39. 100,000 chemical reactions occur per second in the human brain.
40. Babies are born without kneecaps. They are formed only at the age of 2-6 years.
41. The surface area of human lungs is approximately equal to the area of a tennis court.
42. At the moment of birth, there are already 14 billion cells in the child’s brain, and this number no longer increases, but even vice versa. After reaching the age of 25, this number decreases by 100 thousand per day. For example, in a minute spent reading the text, about 70 cells die. At the age of 40, the process of brain degradation accelerates sharply, and after the age of 50, neurons (nerve cells) dry out and the volume of the brain decreases.
43. In psychiatry, a syndrome accompanied by depersonalization, impaired perception of time and space, one’s own body and the environment, is officially called “Alice in Wonderland.”
44. The length of the human small intestine during life is 2.5 meters. After death, the muscles of the intestinal wall relax, and its length becomes 6 meters.
45. A person has about 2 million sweat glands on his body. The average adult loses 540 calories with every liter of sweat. Men produce 40% more sweat than women.
46. During the entire life cycle, the female body reproduces 7 million eggs.
47. The human eye can distinguish 10 million different color shades.
48. About 40,000 bacteria “live” in the human mouth.
49. Papaphobia is the fear of the Pope (Roman). I'm not kidding.
50. The human spine consists of 33 or 34 vertebrae.
51. Sperm cells are the smallest in a man's body.
52. There are about 2000 taste buds on the human tongue.
53. In Mesopotamia there was a strict law for doctors. If the patient died, the doctor was executed. If the patient was blind, the doctor was also blinded.
54. There are about 300 bones in the body of a newborn, but only 206 remain in an adult.
55. In one year, a person’s heart beats 36,800,000 times.
56. Colorblindness is 10 times more common among men than among women.
57. About half of the human bones are in the feet and wrists.
58. During the Middle Ages, doctors, when in doubt about the diagnosis, diagnosed “syphilis”.
59. The total length of blood vessels in the human body is approximately 100,000 km.
60. The bone marrow of an adult, a loose mass that fills the internal cavities of some bones, weighs on average 2600 grams.
Over 70 years of life it gives 650 kg. red blood cells and a ton of white blood cells.
61. In a calm state, lying down, a person consumes 400-500 liters of oxygen per day, making 12-20 inhalations and exhalations per minute.
For comparison: the respiratory rate of a horse is 12 respiratory movements per minute, rats are 60, canaries are 108. In spring, the respiratory rate is on average one third higher than in autumn
62. The normal pulse in a calm state is 60-80 beats per minute, and in women the heart beats at 6-8 beats per minute. more often than in men. During heavy physical activity, the heart rate can accelerate to 200 or more beats per minute.+
63. The total area of the cerebral cortex varies from 1468 to 1670 square centimeters.
64. Starting from the thirtieth year of life, 30-50 thousand nerve cells die every day in a person. The main dimensions of the brain decrease. With age, the brain not only loses weight, but also changes shape - it becomes flattened. In men, brain weight is maximum at 20-29 years old, in women - at 15-19.
65. The mass of the human brain is 1/46 of the total body mass, the mass of the elephant’s brain is only 1/560 of the body mass.
66. Even stern men shed 1-3 milliliters of tears every day. Tears are constantly produced by the lacrimal glands and moisturize the cornea of the eye, protecting it from exposure to air and dust.
67. The total weight of muscles in a man is about 40% of his body weight, and in a woman it is about 30%.
68. A hole with a diameter of 3-4 thousandths of a millimeter, pierced in a sheet of tin, behind which a light bulb is lit, is clearly visible to the normal eye.
69. The eye is capable of distinguishing 130-250 pure color tones and 5-10 million mixed shades.
70. Complete adaptation of the eye to darkness takes 60-80 minutes.
71. The finger is capable of feeling vibrations with an amplitude of two ten-thousandths of a millimeter.
72. The average surface area of human skin is about 2 square meters.
73. The skin contains 250 thousand cold receptors, 30 thousand heat receptors, a million pain endings, half a million touch receptors and three million sweat glands.
74. Average number of hairs on head:
for blondes - 140,000, for brunettes - 102,000
for brown-haired people - 109,000, for red-haired ones - 88,000.
The total number of hairs on the body, except the head, is about 20 thousand.
75. Hair grows at a rate of 0.35-0.40 mm per day.
76. Fingernails grow at a rate of 0.086 millimeters per day, and toenails grow at a rate of 0.05 millimeters. Over the course of a year, about two grams of nails grow on the fingers.
77. There are about 25,000 cells in the inner ear that respond to sound. The range of frequencies perceived by hearing lies between 16 and 20,000 hertz. By the age of 35, the upper limit of hearing drops to 15,000 hertz.
78. The ear is most sensitive to the range of 2000-2300 hertz. The best ear for music (the ability to distinguish pitch) falls in the region of 80-600 hertz. Here our ear is able to distinguish, for example, two sounds with a frequency of 100 hertz and 100.1 hertz. In total, a person distinguishes between 3-4 thousand sounds of different pitches.
79. We become aware of sound 35-175 milliseconds after it reaches the ear. It takes another 180-500 milliseconds for the ear to achieve the best sensitivity - to “tune in”.
80. The area of the olfactory zone of the nose is 5 sq. cm. There are about a million olfactory nerve endings located here.
81. When chewing food, the jaw muscles develop a force of up to 72 kilograms on the molars, and up to 20 kilograms on the incisors. Chewing bread requires an effort of 25 kg, and fried veal requires 15 kg.
82. The feeling of thirst appears with a loss of water equal to one percent of body weight. A loss of more than 5% can lead to fainting, and more than 10% can lead to death.
83. A sip of water - is it a lot or a little? Numerous measurements have shown that a man swallows an average of 21 milliliters of liquid in one gulp, and a woman swallows 14 milliliters.
84. Lucia Zarate (1864-1890) is considered the smallest woman in the world. At birth, the child's height was 17 centimeters. Lucia grew to 43 centimeters and weighed 2.2 kilograms.
85. Ventilation of the lungs (the number of breaths multiplied by the volume of inhaled air) in a healthy person reaches 5-9 liters per minute.
86. A person can live without food for a week, but without water - only three days (during this period a person loses 10% of water, which leads to death
87. Nails on the toes grow more slowly than on the hands - due to less intense blood circulation, shoes, daily microtraumas
88. Different people have different sensitivity to tastes - some do not feel sour, others salty. The fewer receptors “working”, the worse the sensitivity
89. Many women stubbornly struggle with excessive hair growth (hirsutism), but not everyone knows that this phenomenon has a reason: increased levels of male sex hormones.+
90. Blondes have the thinnest, but also the thickest hair. And the thickest and rarest are among redheads. Brown-haired and brunettes are the “golden mean”.
These are the facts about the human body. Indeed, man is a unique creature.
Guys, we put our soul into the site. Thank you for that
that you are discovering this beauty. Thanks for the inspiration and goosebumps.
Join us on Facebook And In contact with
Man is very intelligent. But evolution doesn't create perfection, it only produces function, says Princeton University anthropologist Alan Mann. Despite the huge number of coordinatedly working organs in our body, there are also shortcomings. However, most of them are associated with the difficult process of evolution.
We are in website collected 10 of the most obvious errors in the structure of the human body and, having read the research of gerontologists from the USA, as well as Chip Rowe’s “Defective Statement of the Human Body,” presented how the situation could be corrected.
1. We can't breathe and swallow at the same time
The food we swallow and the air we breathe enter our bodies through the same pathway. The trachea and esophagus are divided. To prevent food from entering the trachea, a special organ - the epiglottis - reflexively closes the opening of the larynx when you swallow. But sometimes it doesn't work fast enough. If you talk and laugh while eating, food may slip and enter your respiratory tract. Sometimes this leads to death.
By the way, babies can swallow and breathe at the same time, but over time they lose this amazing ability.
- How would it be better? Take whales, for example. Their larynx is located in the breathing hole at the very top of the head. If we move the larynx into the nose, we can have two independent tubes. The fly in the ointment: we will forget how to speak.
2. We only have one row of teeth, and even then we have a few extra ones.
You only have one set of teeth that should last you a lifetime. But, according to statistics, few people can maintain it in full force until old age. But the teeth are not renewed.
Moreover, wisdom teeth are generally useless. Our ancestors needed them with their longer jawbone and fit in the mouth without any problems. Now these teeth do not help us in any way in the process of chewing food - they are the same rudiment as the tailbone.
- How would it be better? Depending on the species, a shark can have from 4 to 28 rows of teeth in its mouth, and the loss of a few of them is not at all critical. But to accommodate more teeth, a person's mouth must also be larger.
3. The retina in our eyes is located inside out
The photoreceptor cells in the retina are like microphones facing backwards. This placement causes light to travel the entire length of each cell and through the blood and tissue to reach the lens.
Due to the imperfection of this design, the retina is prone to detachment from its supporting tissues - this is one of the main causes of blindness. For the same reason, we have a blind spot - an area insensitive to light.
- How would it be better? In many representatives of the animal world, the structure of the eye is arranged differently. For example, in the retina of squids and octopuses, photoreceptor cells are turned towards the light source, which makes the structure of their eyes much more “logical” than those of humans. So it’s worth taking an example from them - just turn your retina over.
4. Unprotected stomach
The entire body, even the face and hands, can withstand heavy loads and withstand serious impacts. For example, the brain is protected by a strong skull. And only the abdominal cavity, filled with vital organs, is covered only by a thin layer of muscles. Therefore, it only takes an unfortunate fall for a person to damage internal organs.
- How would it be better? Our body can be compared to a castle, which is surrounded by thick walls, but in the middle there is a bridge covered with a fence made of boards. To prevent hernias and improve protection of the abdominal organs, it would be a good idea to increase the number of ribs.
5. Our spine should not be straight
Anything that people wear above the waist creates pressure on the spine, causing it to bend and creating additional stress on all internal organs. Hence - chronic fatigue and back pain. Even with an active lifestyle, the spine “wears out” over time from stress.
To keep the body and head in a straight position, the spine should not be straight, but curved forward, that is, have a pronounced S-shape. But the problem is that there are many side effects from such curvatures, for example, increased pressure on internal organs and blood vessels, their compression and displacement.
- How would it be better? Bruce Latimer of Case University in Cleveland believes that the ideal spine in dogs is one continuous arc from the sacrum to the neck. There is only one catch: in order to support the weight of our heads and not fall forward, we would have to get back onto all fours.
6. And the legs are too complicated
There are as many as 26 bones in the human leg (30 if you count from the hip). This was necessary for our ancestors, who moved through the trees. A person began to walk on the ground, but in his legs there were still moving parts and ligaments that practically did not participate in the walking process. As a result, we have such troubles as sprains, dislocations and fractures.
- How would it be better? The ostrich’s leg is more convenient and “efficient”: its ankles and shin bones are connected, there are only two toes, and they also participate in the process of movement. You can also turn the kneecap back, because it very often suffers from falls or impacts.
7. Our regeneration is not well developed
If a person loses the first phalanx of the fingertip to a certain level, the missing part will be restored within 3 months. Initially it was believed that this was possible only in children, but scientist R.B. Borgens believed that this phenomenon is also observed in adults. However, we cannot grow an entire organ or limb due to the increasing complexity of our organisms.
- How would it be better? Newts are best able to regenerate damaged limbs. They are able to restore the lens of the eye, limbs, tail and even part of the lower jaw with new teeth. Such an ability would definitely not hurt us.
8. Scientists still haven’t fully decided why we need an appendix.
Many people ask “Why does a person need an appendix?” causes confusion. And at the same time, from 5 to 10% of people have experienced inflammation of the appendix - appendicitis, when urgent surgical intervention is needed.
Charles Darwin considered the appendix to be a vestige inherited from our ancestors. They used it for certain processes that facilitate the absorption of food.
- How would it be better? At first glance, it seems that it would be better for a person to be born without an appendix at all. But it is an immune and protective organ (even if not the most obvious one) and proves that there are no unnecessary “spare parts” in the human body.
believes that the Y chromosomes, which determine the male sex, will disappear in 125 thousand years. The fact is that, unlike other chromosomes, they cannot repair themselves. “In each new generation, 1% of men will have a mutation that will reduce their ability to fertilize by 10%,” the scientist believes.
It is worth keeping in mind the fact that with increasing alcohol consumption, environmental pollution and constant stress, the disappearance of Y chromosomes may accelerate.
How would it be better? Save men. We really hope that the development of science will not allow such a sad course of events. The task of saving the Y chromosome should become a priority for scientists.
Researchers add to this list the multifunctionality of the genitals, the inability to biosynthesize vitamin C, and even the fact that the vital male reproductive organs are located outside and are therefore very vulnerable.
Bonus: this is what scientists think a person of the future should look like
As you can see, this man looks very unusual, but it is precisely this complexion, according to gerontologists, that would help him avoid many health problems. However, each change has its own side effects: for example, extra ribs will deprive us of flexibility and mobility, and the connection of the bones in the legs will make it impossible to play football.
Do you think a person of the future will be able to look the way scientists imagine? And if you could change something in the structure of your own body, what would you like to change?