After mirena spotting. Brown discharge - Mirena. Uterine bleeding - causes and symptoms, how to stop. Dicynon for uterine bleeding
One of the most popular types of contraception is the Mirena intrauterine device. It has a number of advantages: it is established for a long time, unlike tablets, which must be taken daily. In addition, it is often prescribed for therapeutic and prophylactic purposes. However, there are also inconveniences associated with this type of contraception. How the Mirena spiral and menstruation interact with each other, whether it is worth worrying if a failure occurs, will be discussed below.
How does it affect the body
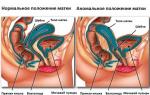
An intrauterine device is a T-shaped device that is inserted into the uterus as a form of contraception to prevent unwanted pregnancy.
The Mirena coil contains the hormone levonorgestrel, which is released into the uterus. It blocks the growth and rejection of the endometrium and works only inside the uterine cavity, which reduces the risk of hormonal side effects.
Due to the reaction to the agent, the secretion of cervical mucus increases, which creates an obstacle to the movement of spermatozoa into the uterine cavity. The spiral contributes to the suppression of sperm motility inside the uterus and fallopian tubes. Sometimes a contraceptive blocks ovulation, which creates the maximum contraceptive effect.
Only a doctor can install Mirena after a thorough examination:
- It is necessary to pass a smear on the flora in order to exclude, and in another case, to treat existing inflammations.
- Blood test for hCG.
- Cytological studies are necessary in order to exclude precancerous and cancerous formations.
- An ultrasound is prescribed to make sure that the uterus and ovaries are normal.
Prolonged spotting may be present for six months after the installation of the spiral. This is a normal reaction of the reproductive system to the installation of foreign material. If the discharge does not stop after six months, you should voice the problem to the doctor.
The installation of an intrauterine device can sometimes be accompanied by unwanted side effects, among which the most common are:
- migraine;
- acne rashes;
- irregular menstruation;
- depressive states;
- heart pain;
- jumps in blood pressure.
Indications for use
The main indication for the use of an intrauterine device is, directly, the prevention of pregnancy. However, it should be borne in mind that during sexual contact it does not protect against STDs, so this type of contraception is not suitable for women who are prone to casual sex and chronic infectious pathologies.
Read also 🗓 Will there be periods after removal of the uterus

Often, the intrauterine device is used for intense menstrual flow for unknown reasons, having previously excluded possible malignant tumors in the organs of the reproductive system. Due to its action, Mirena is prescribed as a prophylaxis for endometrial hyperplasia, fibroids, with severe menopause.
The nature of menstruation when using the IUD
After installing the Mirena contraceptive, ideally, menstruation should begin at the right time. But it should be taken into account that the body has undergone a certain stress, so at first a slight delay is allowed, which should not exceed three weeks. If after three weeks there is no menstruation, you need to urgently go to the hospital. This may be a signal that, despite the installation of the spiral, conception did occur.
Short delays can be for six months after installation, and they are dangerous for the body.
The first menstruation after the installation of the spiral, as a rule, is characterized by increased intensity. Why is this happening? Firstly, stress after installation is accompanied by hormonal failure, and secondly, the contraceptive changes the composition of cervical mucus and the nature of the endometrium, which directly affects the amount of menstrual fluid. During this period, a woman may use more than one pad every 3 hours and pain medication to relieve menstrual cramps.
At first, it is advisable not to use sanitary tampons, as they can interfere with the adaptation of the system and increase the risk of infection.
After a few cycles, menstrual flow returns to its normal appearance. For six months, bleeding can turn into spotting, which is not dangerous. They testify to the habituation of the body to a foreign adaptation. There should be no accompanying pain.

If, after several cycles, menstruation remains as heavy as the first time after the installation of a contraceptive, you should consult a doctor. A similar phenomenon may indicate the side effects of Mirena, which indicates that the body does not accept this contraceptive.
Often women complain about the cessation of menstruation, six months after the installation of a contraceptive. If the delay has been going on for more than two weeks, the first thing you need to do is a pregnancy test or a blood test for hCG. The intrauterine device reliably prevents unwanted pregnancy, but all possible options should be considered, in addition, there have been cases when the device imperceptibly fell out. If the reason for the absence of menstruation is not pregnancy, then there is no reason to worry. Mirena's hormones block the growth of the endometrium, which is why there is nothing to go out during the expected period. It is not dangerous for the woman's body. After removing the spiral, menstruation will be restored within a couple of months.
Modern contraception is an extensive range of devices and medicines. Someone prefers hormonal drugs, but they have a large number of contraindications and side effects. Nowadays, the intrauterine device is very popular. With its correct installation and compliance with all the rules of use, the contraceptive effect reaches 99%. In most cases, female representatives using this device talk about unusual discharge after installing the spiral. How safe they are, what is considered the norm, and when to sound the alarm - we'll talk in this article.
Spiral installation features
The intrauterine device has proven itself for many years as a means of protection. It is a T-shaped gynecological device made of plastic or metal. Some IUDs contain progestogen hormone or copper. These include the levonorgestrel-releasing system Mirena.
The action of the spiral is due to the stopping of the penetration of spermatozoa into the upper parts of the female reproductive system, egg transport and fertilization. With the Mirena spiral, the cervical mucus also thickens, which blocks the proliferation of the endometrium. Due to this root effect, the action of the contraceptive is quite long, sometimes even reaching several years.
The spiral is installed quickly and painlessly. However, some contraindications for IUDs should be considered. These include:
- various types of neoplasms of the genital organs,
- inflammatory processes in the components of the genitourinary system,
- various injuries of the uterus, including postoperative,
- bleeding of unclear etymology,
- cardiovascular diseases,
- diabetes.
In addition to a small number of contraindications, this contraceptive has no disadvantages. The benefits also include the fact that it can be used at any age, even in teenagers. For example, often at an early stage, when menstruation still sometimes makes itself felt. The tool helps to avoid pregnancy and smooth out hormonal changes.
The spiral does not affect other systems and organs of the female body, it can be used up to 10 years, and the price is affordable for any category of the population. But with Mirena, given its hormonal components, side effects may occur. Whichever spiral you choose, it should only be installed by a competent specialist on the preliminary appointment of your doctor.
As a rule, the spiral should be placed at the end of menstruation. This procedure lasts about 15 minutes. Fixing it in the uterine cavity is painless, local anesthesia is most often used.

What discharge during the IUD is considered the norm
Discharge after coil placement is a common occurrence that causes concern for first-time coil users. Do not worry, because in most cases - this is the norm. Experts say that such symptoms after installing an intrauterine device are a common side effect, which rather means a normal reaction of the body than a pathological one.
Basically, these are brown discharges that can begin a few days after the insertion of the IUD, and they can go from several days to several months.
It is worth considering that this device is introduced shortly before the end of the menstrual period, respectively, spotting after installation may be the planned end of menstruation. This may be copious discharge of bloody mucus or a slight daub. Also, such manifestations between menstruation can also be the norm.
After the introduction of the IUD, discharge may also occur due to the fact that the small vessels of the endometrium (internal tissue of the uterus) were affected. Such bleeding is insignificant, but may be accompanied by pulling pains.
Brown discharge with a spiral may be a natural reaction of the body to a foreign object. This phenomenon can be delayed even for six months. It is also not a violation of the change in the nature of menstruation: bleeding can become much stronger, or vice versa, the amount of blood will decrease.
After installing Mirena, the body may react to hormones introduced from the outside with brown discharge. After a while, the hormonal balance will resume, and these phenomena will disappear.
If the bleeding does not go away for a long time, and the pain does not leave you, you should consult a doctor, because this is already a deviation from the norm.
Pathological discharge when using a spiral
Infection
This contraceptive is designed to protect a woman from unwanted pregnancy, but it does not perform a barrier function from various infections, viruses and fungi. Moreover, it is a kind of conductor for them and in some situations can even be the root cause of inflammation of the pelvic organs. This may be indicated by excessive bleeding with uncomfortable sensations, or by the presence of an unpleasant odor or greenish or yellowish mucus secreted.
Fixture offset
One of the complications that can provoke spotting during an established spiral is its loss or displacement. This includes both spontaneous violation of the position, and rejection by her body. A foreign body is a rather large load on a well-functioning reproductive system, so it can take this device for an excessively long time, letting it know with bloody daubs, or not accept it at all.
To avoid displacement of this tool, it is not recommended to lift heavy objects, apply loads or have sex in the first 2 weeks after implantation. It is recommended to regularly check that the helix is in place to avoid misalignment. This can lead to injury to the organs of the genitourinary system, as well as unwanted pregnancy.
In 0.02% of cases of the installation of this contraceptive, bleeding can be caused by damage or puncture of the uterus. This is due to improper insertion or placement of the device. The phenomenon is very rare, but it has a place to be. In this situation, the main thing is to consult a doctor in time to avoid inflammatory processes and pathological trauma.
Ectopic pregnancy
Since no contraceptive can guarantee a 100% result, conception can still occur with a spiral. But if this happens, then most likely in the form of an ectopic pregnancy. A sure sign of this is brown and bloody discharge with increasing and prolonged pain. Follow the link to see pregnancies may appear.
The spiral has "antennae" that expand the walls of the uterus. In rare cases, this is precisely what can be indicated by an increased amount of blood released during menstruation.
Whatever the reason, you need to contact a specialist to determine the cause of the discharge. It is worth remembering that the problem does not go away on its own, and a large blood loss can lead to anemia and other serious consequences.
Many women are interested in the technical issues of implantation. For many, reliability in methods of diagnosis and identification of contraindications for this species is important. Important, as well, information about the possible side effects of this type of contraception, issues of restoring fertility. We will try to provide you with the most complete and reliable information.
What examinations need to be done before inserting the uterine coil?
A conversation with the patient allows the doctor to identify her chronic gynecological diseases.
Bacteriological analysis of smears from the vagina and cervix.
Careful screening for sexually transmitted infections: A, B, and C.
Colposcopy (instrumental examination of the vaginal cavity and cervical mucosa).
Pelvic organs.
When and how is the spiral inserted?
The introduction of the spiral is unlimited by a strictly defined period of the cycle. However, it is recommended to introduce on the 4-8th day of the menstrual cycle, during this period the uterine mucosa is less vulnerable, the cervical canal is ajar - all this makes the introduction of the spiral less traumatic and safe. Also, menstrual flow is a reliable sign of absence. Bloody discharge, characteristic of the early period after the implantation of an intrauterine contraceptive (IUD) does not cause psychological discomfort in a woman, since menstruation is still ongoing.
The spiral can be administered immediately after or within 4 days after or (spontaneous abortion) provided there are no signs of inflammation or. If during this period the implantation of the IUD is not performed, then its introduction must be carried out at the onset of the next menstruation.
One-stage termination of pregnancy and implantation of the IUD into the uterine cavity is practiced. The introduction of the IUD immediately after or in the postpartum period (within 48 hours after birth) greatly increases the risk of expulsion (loss) of the contraceptive. If the IUD is not inserted during the specified period, then the procedure can be performed 4-6 weeks after childbirth.

Stages of introducing an intrauterine contraceptive
Before the introduction is mandatory vaginal examination and probing of the uterine cavity.
The IUD is installed in a special room under aseptic conditions. As a rule, the insertion of an IUD is painless and does not require anesthesia.
The introduction of a spiral is possible only with I and II degrees of purity of the vagina. In the event that an infectious-inflammatory disease of the internal genital organs is detected or the purity of the vagina corresponds to the III or IV degree, then an in-depth gynecological examination is necessary, followed by antimicrobial treatment. Upon completion of treatment, a control examination of its effectiveness is necessary. After an effective antimicrobial treatment of an infectious and inflammatory disease of the pelvic organs, subject to complete recovery, a 6-10-month break is necessary for complete recovery and to exclude the transition of the disease to a chronic form, before the introduction of the IUD.
Is it necessary to monitor patients using intrauterine contraceptives?
During the first week after the introduction of the IUD, it is recommended to refrain from sexual activity and intense physical activity.
The first control examination should be carried out by a gynecologist in 7-10 days. When examining a doctor, they are interested in the presence of threads in the vaginal cavity - this is necessary to make sure that the IUD is installed correctly. Now - after the first gynecological examination, sexual life is allowed without the use of an additional method of contraception. An ultrasound of the pelvic organs is also performed in order to clarify the location of the IUD in the uterine cavity.
The next examination is carried out after one month, during the first year - at least once every 6 months, then - annually with a bacterioscopic examination of the discharge of the cervix. Ultrasound is recommended to produce according to indications.
It is necessary to train a woman after each menstruation to palpate the presence of spiral threads in order to detect the prolapse of the spiral in time. In the absence of threads in the vaginal cavity, a gynecological examination and ultrasound of the pelvic organs are necessary to clarify the location of the spiral. 
Possible adverse reactions and complications when using intrauterine contraceptives
Complications associated with IUD implantation are more often observed in patients with menstrual irregularities in the past, chronic pelvic inflammatory diseases (PID) in remission and when the doctor ignores contraindications to IUD insertion. Complications arising from intrauterine contraception are usually divided into 3 groups: complications caused by the introduction of the IUD, in the process of finding the spiral in the uterine cavity and arising during or after the extraction of the contraceptive. The most common complications are: pain syndrome, prolapse of the IUD, inflammatory diseases of the pelvic organs and bleeding.
Complications arising at the time of the introduction of an intrauterine contraceptive:
Cervical injury
Uterine bleeding
Damage to the uterus. This complication occurs rarely, as a rule, due to incorrect technique for inserting the IUD or insertion contrary to contraindications.
Complications arising in the process of contraception:
Pain syndrome - more often expressed in minor pains in the lower abdomen, which may appear immediately after the introduction of the IUD, but they stop after a few hours or after treatment. Pain during the period during menstruation is observed in 9.6-11% of cases.
IUD prolapse more often observed in young nulliparous women - this is due to increased contractility and excitability of the uterus. The frequency of loss depends on the type of IUD and is 3-16%. With age, an increase in the number of births and abortions, their frequency of this phenomenon decreases. Expulsion (falling out) often occurs during the first days or 1-3 months after the introduction of the IUD.
In identifying the causes of pain, the main role is played by such studies as ultrasound and hysteroscopy, which allow you to accurately determine the position of the IUD in the uterine cavity or outside it.
Pelvic inflammatory disease (PID)
. Against the background of copper-containing IUDs, inflammatory reactions occur in 3.8-14.3% of cases and can manifest as cervicitis (inflammation of the cervix), endometritis (inflammation of the uterine mucosa), pelvic peritonitis (inflammation of the mucosa covering the pelvic organs) or pelvic (limited to the capsule accumulation of purulent exudate). As a rule, the inflammatory process is associated with an exacerbation of an existing chronic infectious and inflammatory disease of the genital organs. In the event that the inflammatory process occurs within 20 days after the introduction of the spiral, then it can be associated with the introduction of a contraceptive. The question of removing the coil and conducting antibiotic therapy is decided by the doctor individually for each woman.
Menometrorrhagia (uterine bleeding) . After the introduction of the IUD, the first 5-10 days in women, as a rule, there are slight or moderate bleeding or clear discharge that does not require treatment; only in some cases (2.1-3.8%) there is a need for drug treatment. Perhaps the appearance of intermenstrual spotting (in 1.5-24% of cases), which often occur in women with menstrual irregularities, as well as in the presence of induced abortions in the past. The issue of prescribing treatment is decided by the gynecologist individually. In the event that heavy bleeding during menstruation is accompanied by pain and does not stop on the background of drug treatment, this is an indication for the removal of the spiral.
The onset of pregnancy
. Intrauterine contraceptives are recognized as highly effective contraceptives, but in 0.5-2% of cases an unwanted pregnancy can still occur. At the same time, the frequency of spontaneous abortions increases significantly, even if the woman wants to keep the pregnancy and medication is used to maintain the pregnancy. Approximately in 1/3 of cases, the onset of pregnancy is associated with complete or partial prolapse of the IUD.
Complications arising after the removal of an intrauterine contraceptive.
Chronic inflammation of the pelvic organs
Ectopic pregnancy 
Indications for removal of intrauterine contraceptives
The desire of a woman.
Expiration date.
(one year after the last menstruation).
Medical indications:
Pregnancy.
Pain.
Bleeding that threatens the woman's life.
PID, acute or exacerbation of chronic.
body of the uterus or cervix. 
Method for removing intrauterine contraceptives
The IUD is removed by a gynecologist in a special room using medical instruments and in compliance with all the rules of asepsis and antisepsis.
Before removing the spiral, the gynecologist performs a vaginal examination.
After a gynecological examination, an antiseptic treatment of the cervix is performed. The removal of the spiral is carried out for the control threads.
The site provides reference information for informational purposes only. Diagnosis and treatment of diseases should be carried out under the supervision of a specialist. All drugs have contraindications. Expert advice is required!
General characteristics
Therapeutic intrauterine system Mirena as an intrauterine contraceptive (IUD)
Therapeutic intrauterine system (hormonal intrauterine system, hormonal intrauterine device, Navy) Mirena refers to intrauterine hormonal contraceptives.In the 1960s and 1970s, copper-containing IUDs appeared, the efficiency of which was even higher. However, the problem of metrorrhagia (uterine bleeding) was not solved by the second generation of intrauterine contraceptives.
And finally, in the second half of the 70s, the first hormone-containing intrauterine contraceptives appeared - a new, third generation of IUDs. These medical devices combine the positive aspects of the IUD and hormonal oral contraceptives.
Hormone-containing intrauterine contraceptives are more effective than others contraceptives this group. In addition, they do not lead to uterine bleeding. Against the background of the use of hormone-containing intrauterine contraceptives, menstrual bleeding becomes less abundant.
Description of the dosage form
The Mirena intrauterine hormonal system has a T-shaped body that provides a stable location in the uterine cavity. At one end, the body has a loop to which threads are attached to remove the system. On the body there is a hormonal-elastomer core, which is a substance of white or almost white color. The core is covered with a translucent membrane that regulates the flow of the active substance into the uterine cavity.The active hormonal substance of the system - the progestogen drug levonorgestrel - is presented in an amount of 52 mg. Auxiliary substance - polydimethylsiloxane elastomer.
The Mirena intrauterine hormonal system is located in the cavity of the conductor tube. The conductor and body of the drug do not have impurities.
Each package of Mirena contains one intrauterine hormonal system, placed in a vacuum plastic-paper shell.
The acquired dosage form of Mirena before use should be kept in a place protected from sunlight, at room temperature (15-30 degrees). The shelf life is three years.
Metabolism of the active substance in the body
The hormonal IUD Mirena begins to secrete levonorgestrel immediately after being placed in the uterine cavity. The release rate of the active substance after administration is 20 µg/day, by the end of the fifth year it decreases to 10 µg/day.The distribution of levonorgestrol characterizes Mirena as a drug of predominantly local action. The highest concentration of the substance is stored in the endometrium (the lining of the uterus). In the myometrium (in the muscular membrane), the concentration of levonorgestrel barely reaches 1% of the concentration in the endometrium. The concentration of levonorgestrel in blood plasma is 1000 times less than in the endometrium.
The active substance enters the bloodstream approximately one hour after the introduction of the system. The maximum concentration of levonorgestrel in the blood serum is reached after two weeks.
Body weight significantly affects the concentration of the active substance in the blood plasma. In women with reduced weight (37-54 kg), the concentration of levonorgestrol in the blood is on average one and a half times higher.
The active substance is almost completely metabolized (broken down) in the liver, and excreted through the kidneys and intestines.
Operating principle
The most important contraceptive effects of the Mirena intrauterine hormonal system are due to a weak local reaction to a foreign body in the uterine cavity, and mainly to the local influence of the progestogen drug levonorgestrol.There is a suppression of the functional activity of the epithelium of the uterine cavity: the normal growth of the endometrium is inhibited, the activity of its glands decreases, transformations occur in the submucosa - all these changes ultimately prevent the implantation of a fertilized egg.
Another important contraceptive effect is the increase in the viscosity of the mucus secreted by the glands of the cervix, and the thickening of the mucous membrane of the cervical canal, which prevents the penetration of spermatozoa into the uterine cavity.
In addition, the Mirena drug inhibits sperm motility in the uterine cavity and in the fallopian tubes.
In the first months of use, due to the restructuring of the uterine mucosa, irregular spotting is possible. But in the future, inhibition of the proliferation of the endometrial epithelium leads to a pronounced decrease in the volume and duration of menstrual bleeding, up to amenorrhea (cessation of menstruation).
Indications for use
 The Mirena intrauterine hormonal system is intended, first of all, to prevent unwanted pregnancy.
The Mirena intrauterine hormonal system is intended, first of all, to prevent unwanted pregnancy. In addition, the drug is used for excessively heavy menstrual bleeding of unknown etiology (in cases where the possibility of oncological diseases of the female genital area is excluded).
As a local progestogen drug, the Mirena intrauterine device is used to prevent endometrial hyperplasia (growth) during estrogen replacement therapy (this kind of treatment is indicated after surgery to remove both ovaries, as well as with severe menopause).
Contraindications
Mirena is an intrauterine contraceptive, so it is categorically contraindicated in inflammatory diseases of the female genital area, such as:- acute and chronic inflammatory diseases of the pelvic organs;
- infectious lesions of the lower urinary tract;
- postpartum endometritis;
- septic abortion that took place less than three months prior to insertion.
As an intrauterine contraceptive, Mirena is also contraindicated in cervical dysplasia, malignant neoplasms of the body and cervix, congenital or acquired changes in the configuration of the uterine cavity (including fibromyomas).
Since the active substance of the drug is metabolized in the liver, the Mirena intrauterine hormonal system is contraindicated in oncological pathology of this organ, as well as in acute hepatitis and cirrhosis. If jaundice of unknown origin has previously occurred, the drug should be used with great caution.
Since levonorgestrol is a gestagenic drug, Mirena is contraindicated in all gestagen-dependent oncological diseases (primarily in breast cancer).
The systemic effect of levonorgestrol on a woman's body is weak. Nevertheless, the Mirena intrauterine hormonal system should be used with extreme caution in cases where progestin preparations are contraindicated. This is especially true for severe circulatory disorders (heart attacks, strokes), severe migraine attacks in history (including those that may indicate severe disorders of cerebral circulation), arterial hypertension, severe forms of diabetes mellitus, thrombophlebitis and a tendency to thromboembolic complications.
In such cases, the degree of risk (the severity of the symptoms of the disease, which is a relative contraindication to prescribing the drug) and the benefits of its use should be correlated. The issue of using Mirena is decided in consultation with a professional, and during the application of the spiral, constant medical supervision and laboratory control are necessary.
Mirena is contraindicated in pregnancy (diagnosed or suspected) and in case of hypersensitivity to the components of the drug.
Side effects
Common Side Effects
 Common side effects are commonly referred to as concomitant symptoms that appear at least in every hundredth, and no more than in every tenth patient using the spiral.
Common side effects are commonly referred to as concomitant symptoms that appear at least in every hundredth, and no more than in every tenth patient using the spiral. Women using Mirena most often experience unpleasant symptoms from the central nervous system, such as: nervousness, irritability, bad mood, decreased libido, headache.
On the part of the gastrointestinal tract, patients are often concerned about pain in the abdomen, nausea, and vomiting.
Among the adverse effects on appearance, acne and weight gain are most commonly observed.
Often, patients make many complaints about the state of the reproductive system and mammary glands: pain in the pelvic area, spotting, vulvovaginitis, tension and soreness of the mammary glands.
Back pain resembling sciatica is relatively common.
All the symptoms described above are most pronounced in the first months of using the Mirena IUD, then their intensity decreases, and in the vast majority of cases, unpleasant symptoms disappear completely.
Rare side effects
Rare side effects include concomitant signs of drug use that appear no more often than every hundredth patient, and no less than every thousandth.Rare adverse side effects of Mirena include the following:
- emotional lability (frequent mood swings);
- the appearance of edema;
- alopecia (baldness);
- hirsutism (increased hairiness);
- skin itching;
Very rare side effects
Very rare effects of the drug Mirena (less than one in a thousand) include allergic reactions in the form of a rash and urticaria. When such signs appear, other possible causes of skin allergies should be excluded and, if necessary, the use of the IUD should be discontinued.Instructions for use
Insertion of the intrauterine device Mirena
 Sterile vacuum packaging is opened immediately before the installation of the system. A prematurely opened system must be disposed of as medical waste.
Sterile vacuum packaging is opened immediately before the installation of the system. A prematurely opened system must be disposed of as medical waste. Only a doctor with sufficient experience in carrying out such manipulations can install the Mirena intrauterine system.
Before installing the Mirena coil, it is necessary to consult a gynecologist and get information about all the risks and possible adverse side effects.
Having decided on the installation of the Mirena IUD, a woman must undergo an examination of the mammary glands and mammography, as well as a gynecological examination, including a study of the pelvic organs and colposcopy (or at least a cervical smear analysis).
It is necessary to exclude oncological pathology of the female genital organs, pregnancy and sexually transmitted infections. All inflammatory gynecological diseases should be completely cured by the time of installation.
It is extremely important before installing the Mirena coil to determine the location of the uterus in the small pelvis, as well as the size and configuration of the uterine cavity. The correct placement of the IUD in the uterine cavity guarantees the effectiveness of the Mirena system, and prevents its expulsion (expulsion).
For women of childbearing age, Mirena is installed in the first seven days of the menstrual cycle.
If there are no medical contraindications, the Mirena IUD can be installed immediately after an artificial or spontaneous abortion in the first trimester of pregnancy.
Surgical intervention is extremely rare.
Amenorrhea Amenorrhea is a common complication of the Mirena IUD. As a rule, it develops gradually during the first six months of using a contraceptive.
Amenorrhea is a common complication of the Mirena IUD. As a rule, it develops gradually during the first six months of using a contraceptive.
With the disappearance of menstrual bleeding, pregnancy should be excluded (conduct a routine test). If the test is negative, you can not repeat it in the future. The normal menstrual cycle will resume after the removal of Mirena.
Spiral Removal
After 5 years of use, the Mirena coil should be removed. In cases where, after removing the IUD, a woman is going to continue contraceptive measures, the Mirena coil should be removed at the beginning of the menstrual cycle. If the IUD is removed in the middle of the cycle, and before that unprotected sexual intercourse took place, then the woman is at real risk of becoming pregnant.If a woman wishes to continue using the IUD, a new IUD can be inserted immediately after removal. In cases where, after removing the IUD, a new intrauterine contraceptive is immediately installed, manipulations can be performed at any period of the cycle.
After removal of the Mirena IUD, the integrity of the spiral should be checked, since if it is difficult to remove the product, the substance sometimes slips into the uterine cavity.
Installation and removal of the Mirena coil may be accompanied by pain and bleeding of varying severity. In some cases, fainting is possible. In women with epilepsy, insertion or removal of a coil may cause a seizure.
Mirena intrauterine device and pregnancy
The drug has a very high efficiency. In cases where an unwanted pregnancy does occur, an ectopic pregnancy should be ruled out first. In uterine pregnancy, the question of its interruption is raised.If the woman decides to keep the child, then the spiral is carefully removed from the uterine cavity. In cases where it is not possible to remove the intrauterine system, the woman is warned about the possible risks of pregnancy with an IUD in the uterine cavity (spontaneous premature termination of pregnancy).
The possible adverse effect of the drug on the development of the fetus should be taken into account. There are very few cases of bearing a child with the Mirena intrauterine system due to the high contraceptive properties of the drug. However, a woman is advised to report that there are no clinical data on the occurrence of fetal pathology under the influence of this drug.
Application for lactation
 The active substance of the Navy Mirena in small concentrations penetrates the blood plasma, and can be excreted during lactation, so that the content of levonorgestrel in breast milk is about 0.1% of the daily dose of the substance secreted by the system.
The active substance of the Navy Mirena in small concentrations penetrates the blood plasma, and can be excreted during lactation, so that the content of levonorgestrel in breast milk is about 0.1% of the daily dose of the substance secreted by the system. It is unlikely that such a dose could affect the general condition of the infant. Experts say that the use of Mirena during lactation six weeks after birth is quite safe for a breastfed baby.
FAQ
The cost of Mirena is quite high. I have heard that the use of the helix comes with a lot of unpleasant side effects. Is there any positive effect of the drug on the body?
The Mirena intrauterine hormonal system has the following therapeutic (not contraceptive) effects:- a decrease in the volume and duration of uterine bleeding (idiopathic - that is, not caused by any concomitant pathology);
- increased hemoglobin levels;
- normalization of iron metabolism in the body;
- general strengthening action);
- reduction of pain syndrome during painful menstruation;
- prevention of endometriosis and uterine fibroids;
- prevention of hyperplasia and endometrial cancer.
Is it possible to use the Mirena coil for myoma to treat a tumor?
The Mirena therapeutic system inhibits the growth of the fibroid tumor node. However, additional examination and consultation with a doctor is necessary. Much depends on the size of the nodes and their location. For example, submucosal fibroid nodes that change the configuration of the uterine cavity are an absolute contraindication for the use of the Mirena IUD.Does Mirena help with endometriosis?
The intrauterine system releases a hormone into the uterine cavity that inhibits endometrial proliferation - this is the basis for the ability of the Mirena spiral to prevent the development of endometriosis.In recent years, works have appeared that testify to the therapeutic effect of the Mirena spiral in endometriosis. Clinical data are rather contradictory. In addition, it should be noted that the treatment of endometriosis with hormonal IUDs is not used in all countries.
From the standpoint of evidence-based medicine, the Mirena spiral for endometriosis, like any other hormonal therapy, can only give a temporary result. The National Guidelines of the Russian Federation on gynecology recommends starting with surgical treatment, as the most radical one.
However, in each case, a thorough examination and consultation of doctors is necessary - a gynecologist, surgeon and endocrinologist.
My periods completely stopped six months after the installation of the Mirena spiral. This is fine? Will I be able to get pregnant after the coil is removed?
Amenorrhea (cessation of menstruation) is a normal reaction of the body to the action of the Mirena hormonal system, which occurs in every fifth woman using the spiral. As a rule, this condition develops gradually.At the first disappearance of menstrual bleeding, pregnancy should be excluded. The effectiveness of the drug is very high, but experts still recommend taking the test. If the test result is negative, then you don't have to worry. After the removal of the Mirena spiral, menstruation will be restored, and a normal pregnancy can be expected.
Is there any pain, discharge or uterine bleeding after the installation of the Mirena coil?
Immediately after the installation of Mirena, a slight pain syndrome and spotting are possible. Severe pain and bleeding may indicate that the IUD has not been inserted correctly. In this case, the Mirena coil must be removed.Pain, discharge or uterine bleeding a considerable time after the installation of the Mirena coil may indicate the onset of expulsion (expulsion of the drug from the uterine cavity) or an ectopic pregnancy. Therefore, if such symptoms appear, you should immediately consult a doctor.
Does Mirena affect weight? I really want to buy the Mirena intrauterine device, but I'm afraid to lose shape (there is a tendency to be overweight).
Weight gain is a fairly common unpleasant side effect of the Mirena spiral. However, it should be noted that not everyone is getting fat. According to clinical data, at least nine out of ten women do not even notice a slight increase in weight after the insertion of an IUD.In addition, weight gain is one of the side effects of Mirena, most pronounced in the first months after installation. As a rule, in the future, the tendency to be overweight, caused by a hormonal drug, disappears.
According to the existing tendency to be overweight, it is impossible to judge the possibility of weight gain after installing the Mirena spiral, since the appearance of this side effect and the degree of its severity depends on the individual response to the hormonal drug.
I was protected by hormonal preparations. There are no side effects, but I often forget to take pills. What is the best way for me to switch from pills to Mirena?
If you took the pills irregularly, then there is a risk of pregnancy, which should be excluded when prescribing the Mirena spiral.In addition, it is necessary to undergo a complete gynecological examination (examination of the pelvic organs, colposcopy) and check the condition of the mammary glands.
If there are no contraindications to the use of the IUD, it is best to insert the spiral on the fourth or sixth day of the menstrual cycle. On the day of installation of the Mirena spiral, contraceptive pills are canceled.
When does pregnancy occur after Mirena removal?
Clinical data indicate that 80% of women who want to have a baby become pregnant in the first year after the removal of the Mirena coil. This is even slightly above the usual level of fertility (fertility).Of course, it takes some time to restore the normal state of the reproductive system, which is individual for each woman.
For patients for whom pregnancy is undesirable, doctors advise immediately after removing the Mirena coil to take measures to prevent conception, since in many women the likelihood of pregnancy appears immediately after the system is terminated.
Where to buy a Mirena coil?
The Mirena intrauterine device can be bought at a pharmacy. The drug is dispensed by prescription.An intrauterine device (IUD) is a T-shaped device that is inserted into the uterine cavity to achieve a contraceptive effect.
There are 2 types of spirals: spirals containing copper or silver, and spirals containing hormones. Spirals containing hormones are recognized as more effective, therefore, they are now more often used in gynecological practice.
What is the Mirena intrauterine device?
The Mirena IUD is a coil containing the hormone levonorgestrel. Every day, Mirena releases a certain small dose of a hormone into the uterine cavity, which acts only within the uterus and is practically not absorbed into the blood. Due to this, the risk of side effects of hormonal effects is significantly reduced, there is no suppression of the ovaries and there is a therapeutic effect, which we will discuss below.
How effective is the Mirena IUD?
More than 20 years have passed since the advent of the Mirena Navy. During this time, Mirena has shown high efficacy in preventing unwanted pregnancy.
According to statistics, within one year of using Mirena, pregnancy occurs in one woman out of 500. Compared to birth control pills, the Mirena spiral is a more reliable contraceptive.
What are the pros and cons of the Mirena IUD compared to other contraceptive methods?
Mirena has its advantages and disadvantages, so it is not suitable for all women. After learning about the pros and cons of Mirena, you can decide if this method of protection against pregnancy is right for you.
Mirena Pros:
- Having installed a spiral once, you no longer need to worry about contraception. While birth control pills need to be taken every day in order for the contraceptive effect to remain reliable.
- The coil does not need to be changed often: you can walk with one coil for up to 5 years in a row. Whereas birth control pills or condoms need to be replenished monthly.
- Unlike condoms, during intercourse, the coil is not felt by you or your sexual partner.
- Unlike birth control pills, the spiral does not increase appetite and does not cause water retention in the body, which means it will not cause weight gain.
- It can be used as a treatment for adenomyosis (endometriosis of the uterus) and for.
- Reduces blood loss during menstruation and.
Cons of Mirena:
- It is impossible to install a spiral on your own: for this you need to visit a gynecologist.
- Unlike, it does not protect against sexually transmitted diseases (including HIV infection, herpes, etc.), therefore it is not suitable for women who have sex with unfamiliar partners.
- In the first 4 months after the installation of the spiral, a woman has an increased risk of inflammation of the fallopian tubes ().
- May cause long-term appearance in the first months after installation.
- May cause irregular periods in the first months after insertion.
- It can cause a temporary cessation of menstruation, but after the removal of the spiral, menstruation returns within 1-3 months.
- May cause . These cysts are not dangerous to health and rarely require any treatment. Usually, they resolve themselves within a few months after the appearance.
- There is a risk of unnoticeable loss of the spiral, which can lead to an unwanted pregnancy.
- If pregnancy occurs while wearing the spiral, then there is a risk of an early miscarriage.
At what age can Mirena be installed?
Among gynecologists, there is an unspoken rule that intrauterine devices can only be installed in women who have given birth. However, there are studies in which the spirals were installed in nulliparous women, and even girls under 18 years old, and at the same time, the spirals were effective and safe.
And yet, most gynecologists will not undertake to put a spiral if you are under 25 years old and you have not yet given birth.
What tests should be taken before putting the Mirena coil?
Before installing the coil, your doctor will prescribe:
- to make sure there is no inflammation. If the smear detects inflammation, then you will need to be treated first and only after recovery, the doctor will install the spiral.
- to make sure your cervix is healthy and you don't have any precancerous or cancerous changes.
- to make sure that the uterus has a normal shape and the installation of the spiral will be safe. You will not be able to put a spiral with a bicornuate uterus, the presence of partitions in the uterus or other abnormalities in the development of the uterus.
- or to make sure you are not pregnant.
For whom is the Mirena IUD contraindicated?
There are not so many contraindications for installing Mirena. This:
- Pregnancy or suspected pregnancy
- Inflammation of the vagina or cervix
- Chronic genital tract infections that often get worse
- Inflammation of the urethra or bladder
- Precancerous or cancerous changes in the cervix
- Cancer or suspected breast cancer
- Inflammation of the uterus (endometritis) after childbirth or abortion within the last 3 months
- Anomalies in the development of the uterus: bicornuate uterus, septa in the uterus, etc.
To make sure that the spiral is in place, you can try to feel its "antennae" yourself. To do this, wash your hands thoroughly and insert the fingers of one hand deep into the vagina to reach the cervix. "Antennae" to the touch resemble the threads of fishing line. The length of the "antennae" can vary: you can only feel the tips, or feel 2-3 cm. If the threads are longer than 2-3 cm, or if you have not felt them, then you need to contact a gynecologist.
How often do I need to visit a gynecologist if there is a Mirena spiral?
If nothing bothers you, then the first visit to the gynecologist should be done a month after the installation of the spiral. Then visit your doctor in another 2 months. If the doctor confirms that Mirena is in place, then further visits should be done once a year.
Smearing discharge after installing the Mirena coil
In the first months after the installation of Mirena, prolonged spotting bloody (dark brown, brown, black) discharge may appear. This is a normal phenomenon associated with the installation of the spiral. Such discharge can be observed during the first 3-6 months after the installation of Mirena. If spotting persists for more than 6 months, then you need to visit a gynecologist.
Irregular periods after Mirena
Some women who use the Mirena intrauterine device may experience irregular periods. This not connected with hormonal disorders or ovarian dysfunction. The cause of the failure of the menstrual cycle is the local effect of the spiral on the endometrium of the uterus. It is not dangerous to health and does not lead to any negative consequences.
Consult your gynecologist if irregular periods persist for 6 months or more after coil insertion.
No period after Mirena coil
Approximately 20% of women who use the Mirena coil for a year or more, menstruation stops altogether.
If the next menstruation has not come, and more than 6 weeks have passed since the last menstruation, pregnancy must first be excluded. To do this, you can either pass.
If pregnancy is excluded, then the absence of menstruation is caused by a spiral. The hormones that the intrauterine device releases affect the endometrium, inhibiting its growth. The endometrium remains thin and therefore menstruation does not occur. The absence of menstruation does not adversely affect the body and does not cause any consequences in the future.
Menstruation recovers on its own within 1-3 months after the removal of the spiral.
What should I do if I become pregnant while wearing Mirena?
The likelihood of pregnancy while wearing Mirena is quite small, and yet, such cases are described.
If the pregnancy test showed a positive result, then you need to visit a gynecologist as soon as possible. The gynecologist will examine you and send you for an ultrasound. Ultrasound will help determine where the fetus is located: in the uterus or is it an ectopic pregnancy. If the fetus is located in the uterus, then there is a chance to keep the pregnancy.
Do I need to remove the coil if pregnancy occurs?
In order to reduce the risk of early miscarriage and, doctors recommend removing the intrauterine device. In the first hours and days after the removal of the spiral, the risk of miscarriage will be quite high, but if the pregnancy can be maintained, then nothing will threaten the unborn child.
If you decide not to remove the spiral, or if its removal is impossible for other reasons, then during pregnancy you will need more careful monitoring by doctors in order to prevent or identify possible complications (miscarriage, inflammation, premature birth) in time.
Can Mirena cause developmental anomalies in an unborn child?
Unfortunately, this is not yet known, since there were not so many cases of pregnancy, and it is impossible to compile any reliable statistics.
Cases of the birth of healthy children after pregnancy with a helix are described. Cases of birth of children with developmental anomalies also exist, but so far it has not been possible to establish whether there is a connection between these anomalies and the fact that the coil was not removed during pregnancy.
How is Mirena coil replaced or removed?
Mirena coil works for 5 years. After this period, the spiral should be removed (if you are planning a pregnancy or want to switch to another method of contraception), or replaced with another spiral (if you are not planning a pregnancy and do not want to switch to other methods of contraception).
You can remove the coil earlier if you are planning a pregnancy. To do this, it is not necessary to wait until the five-year term of the Mirena expires.
It is best to remove the Mirena coil during the next menstruation. If your periods stop while wearing Mirena, or if you want to remove the coil outside of your period, then you need to start using condoms 7 days before removing the coil.
If you want to replace the coil, you do not need to use condoms, and the replacement can be done on any day of the cycle.
When can I get pregnant after Mirena removal?
The Mirena spiral does not affect the functioning of the ovaries, so you can become pregnant in the next cycle after Mirena removal.