Is there endometriosis? Video - Endometriosis: causes, symptoms, treatment. Fallopian tube endometriosis
Not all women know what endometriosis of the uterine body is, and meanwhile, the disease can occur without pronounced symptoms, and it is very difficult to detect it during a routine gynecological examination.
Endometriosis of the uterus is a disease that is characterized by the growth of the endometrium in atypical places for it. The endometrium is the mucous layer of the uterus, in its structure there are many glands and blood vessels. The endometrium is made up of:
- outer layer - it changes depending on the phase of the menstrual cycle;
- deep layer - it is not subject to changes due to hormonal surges.
In the first menstrual phase, the outer layer actively grows, and in the second, if fertilization has not occurred, it is rejected. If we translate the name endometriosis into an accessible language, then it will mean the appearance of tissues similar in structure to the endometrium outside the uterus.
The exact causes of endometriosis have not yet been established. There are several theories about the origin of the disease:
- Implantation version - with hormonal disorders, endometrial cells increase the ability to adhere (stick) in various places. If there is a high uterine pressure, then the cells can migrate to other tissues and continue their active growth there. Migration to neighboring organs (ovaries, tubes) can also occur during menstruation;
- genetic theory. The occurrence of endometriosis in women can occur in several generations of the same family. Scientists identify a specific genetic marker that indicates a predisposition to the disease;
- immune theory. The body's defense systems remove any tissues and neoplasms that have appeared in the wrong place. With a decrease in immunity, endometrial cells outside the uterus do not die, but take root and function normally;
- The theory of metaplasia. Many scientists suggest that some tissues can turn into endometrioid under the influence of various causes.
Most Common Causes
There are several causes of endometriosis:
- after incorrect gynecological instrumental manipulations on the genitals, for example, cauterization of cervical erosion, endometrial cells can migrate into the vagina and take root there, or endometrioid tissue can enter the peritoneum during cesarean section;
- frequent abortions and other mechanical damage to the inner layer of the mucosa make its structure loose, thanks to which the cells penetrate deep into the muscle tissue and continue to actively grow and change in the phases of the cycle;

- intake can also cause endometriosis. All women with such a disease have a low level, but an increased content of estrogen, and;
- with various diseases of the liver, which is involved in the regulation of estrogen levels, their excess in the body can be observed, which provokes hormonal dysfunction;
- the intrauterine device can also cause the development of endometriosis. In the place of its attachment in the mucosa, an inflammatory process is formed. The tissues of the mucosa become loose and through the pores, during menstruation, the endometrium penetrates beyond the uterus.

Disease classification
Having found out what endometriosis is, you can consider its varieties. The disease is classified according to the location of the endometrium:
- genital;
- extragenital;
- combined form.

The most common form is genital, when tissues are localized on the tubes, the outer side of the uterus, and the ovaries. Most often, lesions of the muscular walls of the uterus are noted, and manifests itself in the form of strong menstrual bleeding with different intensity and duration.
Extragenital endometriosis is characterized by damage to the abdominal organs, urinary canals, and lungs. This kind of disease is much rarer and very difficult to diagnose.
The combined form is diagnosed when the genitals and internal organs are simultaneously affected.
Endometriosis of the uterus manifests itself in three forms:
- focal, when small islands form in muscle tissues;
- nodular, when the tissue takes the form of a knot similar to a fibroid;
- diffuse, when the endometrioid tissue is located in a chaotic manner, there are no clearly defined boundaries.

Often, diffuse endometriosis of the body of the uterus is combined with other forms, for example, nodular.
Prevalence and development of endometriosis
In gynecology, endometriosis of the uterus is divided according to the degree of development and prevalence:
- the first degree includes the disease if the foci of occurrence are found at a depth of less than one centimeter;
- if the foci are localized in the muscle tissue by about half of its thickness, then the second degree is assigned;
- when endometriosis has spread to the entire muscle wall, the third degree is ascertained;
- if the foci have spread through the entire muscle, go outside and are localized on the abdominal organs - this is the fourth degree.

If endometriosis is extragenital in nature, then it is classified according to the degree of prevalence:
- small forms - when the foci are single, shallow, and affect the small surface of the ovaries and the abdominal cavity;
- moderate, when the foci spread to both ovaries, form adhesive processes in the retrouterine space;
- severe form - with it, endometrioid tissue is localized on all internal organs of the abdominal cavity, including the rectum.

If endometriosis spreads only to the ovaries, doctors distinguish three stages of its development:
- the first - several small dot foci on one ovary, which do not contain cystic cavities;
- the second - cystic cavities are formed from several foci, but they do not exceed 6 cm;
- the third - cysts appear on both ovaries, up to 6 cm in size;
- fourth - cysts exceed 6 cm in volume and spread not only to the ovaries, but also to neighboring tissues.
From the second stage, adhesive processes begin to develop and gradually spread to the pelvic region.
Symptoms of endometriosis
The very first signs of endometriosis of the uterus are a change in the menstrual cycle and the intensity of bleeding, accompanied by severe pain. Depending on the stage of development of the disease, the following symptoms may occur:
- heaviness in the lower abdomen;
- the occurrence of a feeling of fullness;
- nausea;
- vomit;
- painful intercourse;
- in the first days of menstruation, body temperature may rise.

The course of the disease is accompanied by heavy bleeding, which can lead to anemia. In this case, the following will be added to the symptoms of endometriosis of the uterus:
- weakness;
- drowsiness;
- fast fatiguability;
- fainting states;
- dizziness.

The main thing that endometriosis is dangerous for is that its symptoms coincide with many other diseases, so women often attribute such manifestations to painful menstruation and do not attach much importance to them.
Diagnostics
Endometriosis of the uterus is very difficult to detect during a routine examination, often the disease is asymptomatic, it is detected by chance, during routine or comprehensive examinations.
Diagnosis of endometriosis can be carried out in various ways:
- hysteroscopy;
- lab tests;
- gynecological examination.

One of the most effective diagnostic methods is transvaginal ultrasound. With this examination, the doctor can diagnose endometriosis by the following signs:
- heterogeneous thickness of the uterine walls;
- the uterus is changed in size, it becomes like a ball, enlarged as at 5–8 weeks of pregnancy;
- heterogeneous myometrium containing cystic cavities.

The nodular form of the disease is very similar to fibroids, so the doctor should prescribe an additional examination.
Hysteroscopy is the best way to diagnose diffuse endometriosis. During the procedure, it is possible to detect the localization of endometrioid cells. With the help of ultrasound examination, endometriosis of the ovaries is clearly visible.
Laparoscopy is the most reliable way to detect external endometriosis. It allows you to establish an accurate diagnosis with almost 100% probability. Laboratory diagnostics can indicate a change in the hormonal background in a woman, reveal the presence of inflammatory processes, the development of anemia. But this is only an intermediate stage of diagnosis.

Treatment
Like all women's diseases, vaginal endometriosis must be treated. But it's unlikely to get rid of the problem completely. When diagnosing the first and second stages of endometriosis, treatment is not prescribed, but it is necessary to undergo regular examinations and control the degree of prevalence of tissues. Modern diagnostic methods make it possible to determine the development of the disease in the early stages, so the number of patients with such a diagnosis has sharply increased.
If local endometriosis is detected, intrauterine devices are not recommended for patients, but it is worth taking a responsible approach to the issue of preventing unwanted pregnancy, since abortion can give a big impetus to the development of the disease.
Endometriosis most often occurs in women of reproductive age. If the disease is detected in the premenopausal period and is asymptomatic, then drug treatment is not prescribed, but constant monitoring is necessary.
There are two ways to treat diffuse and nodular endometriosis:
- conservative - taking medication;
- surgical - removal of neoplasms.

Medication involves taking hormonal drugs, their action is aimed at reducing the secretion of estrogens. Simultaneously with hormonal treatment, symptomatic therapy is carried out to reduce pain. Can be used:
- antispasmodic tablets;
- anti-inflammatory drugs;
- vaginal suppositories;
- anal candles.

Surgical intervention is indicated when diagnosing the following forms of the disease:
- Endometrioid cysts on the ovaries;
- Endometriosis of the uterus 3 and 4 degrees;
- Extragenital endometriosis, when large areas of internal organs are affected, as a result of which their normal functioning is disrupted.
If drug treatment has not brought positive changes or it is contraindicated for the patient, then they also resort to the surgical method. Laparoscopy is most commonly used for surgical removal of tissue. When symptoms are identified and treatment is prescribed in a timely manner, it is possible to achieve a long-term remission, return the patient to her usual way of life.

Prevention of endometriosis should be aimed at timely elimination of menstrual irregularities, regulation of hormone production, and prevention of invasive procedures in the uterus. The probability of occurrence of the disease with the extinction of reproductive function in women is sharply reduced.
What could be the consequences?
If you do not pay due attention to the disease, then its development can lead to such consequences:
- infertility;
- increased risk of miscarriage during pregnancy;
- development of anemia;
- develop chronic diseases of the affected internal organs;
- endometrioid tissues can compress nerve endings, which will provoke neurological problems.

Advanced stages of the disease can lead to the removal of the ovaries and uterus, which will mean a complete loss of reproductive function.
Planning for pregnancy with endometriosis
Endometriosis significantly reduces the reproductive function, because there are:
- structural changes in the uterine walls;
- the ovaries are damaged, which leads to hormonal imbalance;
- adhesive processes develop in the genitals.

But if this diagnosis is established in time, and all necessary treatment measures are taken, then pregnancy can occur within the first year after the course of therapy.
Endometriosis does not have any effect on the development of the fetus, but there are high risks of premature birth, spontaneous miscarriage, uterine rupture during childbirth. A pregnant woman with such a disease should always be under the supervision of an experienced gynecologist. And after childbirth, treatment should be continued.
Bibliography
- Gestagens in obstetric and gynecological practice. Korkhov VV, Tapilskaya NI 2005 Publisher: Special Literature.
- Intrauterine infection: Management of pregnancy, childbirth and the postpartum period. UMO certification for medical education. Sidorova I.S., Makarov I.O., Matvienko N.A. 2008 Publisher: MEDpress.
- Miscarriage, infection, innate immunity. O.V.Makarov, L.V.Kovalchuk, L.V.Gankovskaya, I.V.Bakhareva, O.A.Gankovskaya. Moscow, GEOTAR-Media, 2007
- Atlas of ultrasound diagnostics in obstetrics and gynecology. Dubile P., Benson K.B. 2009 Publisher: MEDpress-inform.
Endometrioid disease (endometriosis) is a pathological benign process of growth of endometrial-like tissue outside the cavity.
Endometriosis of the uterus or adenomyosis is the germination and reproduction of endometrial-like tissue in various parts of the muscular layer of the uterine wall.
In adenomyosis, endometrioid "implants", similar to the glandular and stromal components of the basal mucosal layer, are introduced into the myometrium at different depths, causing deformation and inflammation of the surrounding tissues.
 Internal endometriosis
Internal endometriosis Endometriosis of the body of the uterus - what is it?
Endometriosis of the body of the uterus, adenomyosis, internal endometriosis, endometriosis of the uterus - all this is the same disease.
Recently, endometriosis of the body of the uterus is considered as a special, independent variant of endometrioid disease.
Endometriosis of the uterus in the structure of endometriosis. Adenomyosis in the classification of endometriosis
Adenomyosis in the classification of endometriosis Endometriosis of the uterus: ICD-10 code
N80.0 Endometriosis of uterus (adenomyosis)
Causes of the disease
There is still no single point of view on the causes of endometriosis of the uterus. Since the end of the twentieth century, a significant role has been assigned to genetic factors, i.e. congenital predisposition to the development of the disease.
The key link and trigger mechanism of adenomyosis today is considered mechanical damage to the transition zone of the myometrium(Junctional Zone, JZ).
The transitional zone (JZ) or subendometrial myometrium is the border layer of myometrium located directly under the uterine mucosa. Normally, the JZ thickness in women of childbearing age does not exceed 2-8 mm.
It has been proven that during abortions, especially those performed with the help of curettage (curettage), when taking a biopsy of the endometrium or other gynecological, surgical manipulations, the border between the endo- and myometrium can be destroyed. This makes it easier for endometrial components to enter and survive in the new environment.
However, further formation and progressive growth of endometrioid foci in the muscular layer of the uterus is possible only against the background of a weakening of immune control and a violation of the hormonal status of a woman. Endometriosis of the uterus is a complex, multifactorial pathological process.
The mechanism of development of endometriosis of the uterus Pathological circle of adenomyosis Risk factors for uterine endometriosis
Pathological circle of adenomyosis Risk factors for uterine endometriosis
- Genetic predisposition ("familial" form of endometriosis).
- Curettage of the uterus.
- Prolonged use of a contraceptive intrauterine device (IUD).
- Inflammatory processes of the mucous membrane of the uterus.
- Violation of immunity: local and / or general.
- Local hormonal imbalance: increased regional estrogen synthesis (local hyperestrogenism), reduced sensitivity to progesterone in the focus of endometriosis.
- Adverse environmental and social factors.
- chronic stress.
There are several types (forms) of adenomyosis:
- Diffuse (up to 80% of cases).
- Diffuse-nodular (approximately 10%).
- Focal (up to 7%).
- (until 3%).
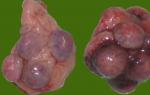
With the formation of endometrial cavities in the myomertium, they speak of cystic endometriosis.
 Types of adenomyosis
Types of adenomyosis
According to the modern classification (L. V. Adamyan), internal diffuse endometriosis, depending on the depth of the lesion, is divided into 4 degrees (stages):
- Ι degree (stage) of adenomyosis - the pathological process is limited to the submucosa and transition zone.
- ΙΙ degree (stage) - the process extends to the myometrium, but does not reach the outer (serous) membrane of the uterus.
- ΙΙΙ degree (stage) - the entire myometrium is involved in the disease process, up to the serous membrane of the uterus.
- ΙV degree (stage) - the pathological process goes beyond the uterus, affecting other organs and tissues.
The combination of adenomyosis with external genital endometriosis is observed in 70% of cases.
 Stages of adenomyosis
Stages of adenomyosis What is dangerous endometriosis of the uterus:
- Decreased quality of life and work capacity.
- Development of severe, life-threatening secondary anemia.
- Infertility.
- Malignancy (malignancy).
The ability of endometrioid foci to "filter" (infiltrate) into the surrounding tissues, the tendency of their growth in distant organs, the absence of a connective tissue capsule around the pathological areas - all this brings endometriosis of the uterus closer to the tumor process.
The disease is distinguished from a true tumor by the absence of pronounced cellular atypia and the dependence of the clinical manifestations of the disease on menstrual function. Wherein the possibility of malignant degeneration of endometriosis is undeniable.
- Pain in the pelvic area and lower back. In most cases, the intensity of pain is associated with the menstrual cycle: during the period of menstruation, it is maximum.
- Painful menstruation (algomenorrhea).
- Painful intercourse (dyspareunia).
- Scanty, chocolate-brown bloody discharge from uterus a few days before and after menstruation.
- Prolonged heavy menstruation, up to cyclic uterine bleeding (hyperpolymenorrhea) with the occurrence of secondary anemia.
- Miscarriages in early pregnancy.
- Infertility (primary and/or secondary).
- PMS: nervousness, headaches, fever, sleep disturbance, vegetative-vascular disorders.
Unlike sometimes occurring (periodic) "monthly" pain, pain with endometriosis of the uterus during menstruation always occurs and is observed regularly for 6 or more months in a row.
The nature of the pain:
- pulling, stabbing, cutting ... variable; in the lower abdomen, in the lower back;
- constant: from mild to moderate to intense.
- increases on the eve of menstruation;
- pain during menstruation may resemble a picture of an acute abdomen, accompanied by bloating, flatulence.
 Clinical symptoms of uterine endometriosis
Clinical symptoms of uterine endometriosis One of the frequent signs of the disease and the only reason for the patient to see a doctor is infertility. Miscarriage (spontaneous abortion, miscarriage) often precedes the development of typical (pain, "chocolate daub", heavy periods) clinical symptoms of endometriosis.
Pain, although a frequent, but subjective sign of the disease - each woman evaluates the intensity and / or significance of the pain syndrome in different ways.
Sometimes the first sign by which adenomyosis can be suspected is heavy and prolonged periods(hyperpolymenorrhea).
 Signs of internal endometriosis
Signs of internal endometriosis Diagnosis of endometriosis of the uterus
1. Gynecological examinationWith a bimanual gynecological examination, a clinical sign of adenomyosis may be an increase in the size of the uterus, especially pronounced on the eve of menstruation.
A spherical uterus is a sign of diffuse adenomyosis.
A tuberous uterus is a sign of the nodular form of adenomyosis.
Small forms of adenomyosis (endometrioid lesions
Complaints of the patient and a routine gynecological examination can only suggest the presence of uterine endometriosis. Instrumental studies are needed to make an accurate diagnosis.
2. Transvaginal ultrasoundSonography (ultrasound) remains the most accessible and fairly informative method for diagnosing adenomyosis today.
When conducting ultrasound using a vaginal sensor in the second half of the menstrual cycle, uterine endometriosis is detected
in 90-95% of cases
Optimal timing of ultrasound if adenomyosis is suspected:
- in the second phase of the menstrual cycle, preferably on the eve of menstruation.
- control ultrasound is performed immediately after the end of menstruation.
Clinical ultrasound signs of uterine endometriosis:
Adenomyosis Ι degree(small forms of endometriosis):
- Anechogenic tubular zones, up to 1.0 cm in size, located from the endometrium to the myometrium.
- Small, up to 0.2 cm, hypo- and anechogenic oval-shaped structures in the basal layer of the endometrium.
- Unevenness, serration, indentation of the basal layer of the endometrium; other endometrial defects.
- Small (up to 0.3 cm) areas of increased echogenicity in the transition zone of the myometrium.
- The thickness of the wall of the uterus: normal, close to normal.
Adenomyosis ΙΙ degree:
- In the subendometrial layer of the myometrium, there are zones of increased heterogeneous echogenicity of various sizes with the content of rounded anechoic inclusions, 0.2-0.5 cm in diameter.
- The thickness of the uterine wall slightly exceeds the upper limit of normal.
- The walls of the uterus are thickened unevenly, with a difference of up to 0.4 cm or more in relation to each other.
Adenomyosis ΙΙΙ degree:
- The uterus is enlarged.
- The walls of the uterus are thickened unevenly.
- In the myometrium: a zone of increased heterogeneous echogenicity, occupying more than half the thickness of the uterine wall. Bands of increased and medium echogenicity.
- In areas of increased echogenicity, there are many anechoic inclusions and cavities of various shapes, 2.0–4.0 cm in diameter.
- A significant decrease in the thickness of the endometrium.
Nodular, focal adenomyosis:
- In the wall of the uterus, a rounded zone of increased echogenicity with small (0.2-0.4 cm) anechoic inclusions or cavities is determined.
- M-echo deformity (with submucosal location of endometrioid nodes).
- The change in the size of the uterus and the thickness of the uterine wall depends on the size and number of nodular formations.
Additional methods for diagnosing uterine endometriosis
CT, hysterosalpingoscopy (-graphy) and laparoscopy are not methods of choice for the diagnosis of adeomyosis. These studies are carried out on an individual basis.
1. Magnetic resonance imagingMRI is the most accurate method for diagnosing endometrioid disease. But in the case of adenomyosis, the significance of MRI is comparable to a transvaginal ultrasound performed on the eve of menstruation.
MRI is prescribed according to individual indications, to exclude / confirm the combination of adenomyosis with various forms of external genital and / or extragenital endometriosis, other types of benign and / or malignant proliferative diseases. With the help of MRI, it determines the exact localization of endometriotic lesions.
2.CFM - color Doppler mapping.This is a study of the rate of blood flow in the uterus.
Endometrioid heterotopias are avascular formations, they do not reveal growth zones of new vessels. The resistance index in the foci of endometriosis increases with the severity of the pathological process.
Allows you to visualize the signs of adenomyosis, to make a targeted biopsy of suspicious areas.
Hysteroscopic signs of uterine endometriosis:- The uterine cavity is deformed.
- On the pale pink mucosa, dark red crypts are visible - the mouths of endometrioid "moves" of various sizes. They may ooze dark red blood.
Separate diagnostic curettage of the endometrium with further histological examination of the removed tissue to determine the endometriosis of the uterus does not have great diagnostic value (after all, endometrioid foci are located in the thickness of the myometrium). Curettage under the control of hysteroscopy is done to identify / exclude the combination of adenomyosis with cancer of the uterine body,. This is important for choosing the right tactics for further treatment.
 Instrumental diagnosis of uterine endometriosis 4. Surgical hysteroscopy and histology.
Instrumental diagnosis of uterine endometriosis 4. Surgical hysteroscopy and histology.
Histological verification of adenomyosis is carried out after hysteroresectoscopy. During a minimally invasive endoscopic operation performed by vaginal access, endometrial tissue is taken along with a portion of the myometrium. Then the removed tissue is examined under a microscope (histological examination) and an accurate diagnosis is made.
5.Laparoscopy.The "gold standard" for diagnosing external forms of endometriosis
at stage 4 of adenomyosis, laparoscopy remains. This therapeutic and diagnostic operation is carried out by introducing endoscopic equipment into the abdominal cavity through punctures of the abdominal wall.
How to treat endometriosis of the uterus
The treatment of adenomyosis remains a complex and ambiguous problem, purely individual for each patient, for each specific case of the disease.
 Treatment of internal endometriosis
Treatment of internal endometriosis Hormonal treatment of uterine endometriosis
Speaking about the effectiveness of hormonal treatment, you need to know that none of the drug therapy regimens leads to a complete cure and does not eliminate the possibility of recurrence of endometriosis.
The effect of hormonal treatment is temporary - after discontinuation of drugs, the disease may gradually return.
In cases of asymptomatic course of uterine endometriosis, ultrasound signs of the disease are not an indication for hormone therapy.
With asymptomatic adenomyosis of 1-2 degrees, “waiting tactics” is advisable, i.e. the patient does not receive hormonal treatment, but is under close dynamic observation. According to the indications, restorative and physiotherapy, immunocorrection, antioxidant and anti-inflammatory therapy can be prescribed (see below).
Goals of hormone therapy:
- Reducing the size of endometriosis foci.
- Reducing the severity of symptoms of the disease.
- Reducing the risk of surgical and / or repeated surgical intervention.
- Fight against hyperestrogenism, stabilization of hormonal levels.
- Prevention of progression and recurrence of the disease.
- Preservation of fertility (childbearing function).
Drug therapy of endometriosis of the uterus is primarily focused on patients interested in future pregnancy.
Hormone therapy is based on the significant role of endocrine factors in the development of endometrioid disease. It is carried out in the absence of contraindications and side effects. Initially, treatment is prescribed for 3 months. Then evaluate its effectiveness and, if successful, extend it for 6-9 months. In case of an unsatisfactory result, a replacement of the drug or surgical treatment is indicated.
Hormonal preparations of the first stage for endometriosis of the uterus1. Oral progestogens.
Monotherapy with progesterone-like drugs is considered quite effective with adenomyosis. Progestogens are prescribed continuously, in sufficiently high doses for 3-6 months or more. The frequency of side effects they have is significantly lower than that of A-GnRH (see below).
Pills for endometriosis of the uterus
2. COC - combined oral contraceptives.
They are used to reduce pain (pelvic pain relief) associated with uterine endometriosis in women who are not interested in pregnancy. With dysmenorrhea (hyperpolymenorrhea), COCs are prescribed continuously. The effectiveness of these drugs in the treatment of endometriosis is low. More often they are prescribed as maintenance postoperative therapy, to prevent the recurrence of the disease.
The drug of choice for the treatment of endometriosis is considered a remedy.
COC preparations are contraindicated in women with adenomyosis suffering from migraine.
Hormonal preparations of the second stage for endometriosis of the uterus1. Gonadotropin-releasing hormone (A-GnRH) agonists
/doctor's consultation required/
| Name A-GnRH | Reception scheme (a course of treatment up to 6 months) | Possible side effects |
| Goserelin (Zoladex) | 3.6 mg subcutaneously 1 time in 28 days | Hot flashes, sweating, vaginal dryness, headache, mood lability, osteoporosis, negative effects on the cardiovascular system, liver. |
| Leuprorelin (Lyukrin depot) | 3.75 mg each intramuscularly 1 time in 28 days |
Same |
| Buserelin | 3.75 mg each intramuscularly 1 time in 28 days. Or 150 mcg each squirting in every nostril 3 times a day. |
Same |
| Triptorelin (Diferelin, Decapeptyl depot) | 3.75 mg each intramuscularly 1 time in 28 days. |
Same |
Treatment with A-GnRH drugs is considered the "gold standard" of drug therapy for endometriosis.
A-GnRH is used to treat severe forms of uterine endometriosis. Against the background of taking these drugs, menstruation stops in women (a "medicated pseudomenopause" occurs). After discontinuation of the drug, the menstrual cycle is restored independently. The frequency of recurrence of endometriosis 5 years after the end of the course of A-GnRH reaches approximately 50%.
Long-term (more than 6 months) A-GnRH therapy is possible, but always under the guise of "return" hormone replacement therapy (HRT) with estrogen and progesterone. This method of treatment of endometriosis is considered efficient enough.
2. Parenteral progestogens.
- Depot medroxyprogesterone acetate (Depo-Provera) - injected under the skin at 104 mg every 12 weeks.
The effectiveness of parenteral progestogens is comparable to A-GnRH. But the long-term use of both is undesirable due to the negative impact on bone mineral density (risk of osteoporosis).
A significant disadvantage of progestogen treatment is breakthrough bleeding (dysfunctional uterine bleeding that occurs in response to progesterone stimulation of the endometrium). Therefore, it is more expedient to inject therapeutic agents directly into the uterus, in the form of an IUD.
3. Hormonal intrauterine device LNG-IUD Mirena:
A levonorgestrel-releasing intrauterine system is recommended for the treatment of adenomyosis in women uninterested in pregnancy.
High performance Mirena proven by the agency of the Ministry of Health and Social. USFDA services.
Duration of application is 5 years.
4. Antigonadotropins for the treatment of endometriosis:
- Gestrinone (Nemestran)
- Danazol (Danol, Danoval)
These drugs are currently rarely used due to frequent side effects due to androgenic influence (acne, seborrhea, male pattern hair growth, weight gain, voice change, reduction of mammary glands, etc.)
A woman's health depends on many factors. What is endometriosis? What are the symptoms and treatment of the disease? What are the main signs of pathology? What are the causes of the disease, and what first aid is needed? In this article, you will learn all about endometriosis.
What kind of disease
Endometriosis is a gynecological disease characterized by the growth of the glandular tissue of the uterus beyond this organ. The epithelium can grow in the peritoneum, intestines, ovaries and other, even more distant systems.
Regardless of in which part of the body the endometrium has grown, it undergoes the same changes as the epithelium in the uterus.
This female disease is very common. In adult women, it occurs more often in reproductive age, only in 2% of cases among the elderly. In girls, endometriosis is possible during the formation of the reproductive system. The highest prevalence of the disease is observed in women after 40 years to 44. In women after 50 years, the disease occurs less frequently. It is not easy to determine the disease, since often the pathology occurs in an asymptomatic or latent form.
It is possible to single out the classification of endometriosis both according to the etiology of the pathology and the place of localization of the process. There are two types of the disease:
- genital;
- extragenital form.
With genital endometriosis, the process of endometrial growth extends exclusively to the genitals. The extragenital type of the disease implies that organs located outside the reproductive system are involved in the process.

The genital type of pathology can be divided into the following subspecies:
- peritoneal;
- extraperitoneal (retrocervical);
- interior.
In peritoneal endometriosis, the following organs are involved in the process of epithelial growth:
- ovaries;
- pelvic peritoneum;
- the fallopian tubes.
With retrocervical endometriosis, the lower layers of the genital tract are affected - the vagina, cervix, rectovaginal septum.
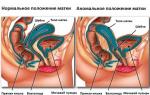
When internal endometriosis develops, a significant increase in the uterus occurs, since the organ itself is involved in the process. Tissue growth occurs within the muscle layer. The body of the uterus acquires a spherical shape and in size it can reach the volumes that are observed in the second month of pregnancy.
Localization sites for external endometriosis largely depend on the stage of the disease. Possible focal endometriosis of the bladder, endometriosis of the ovary and other organs. Even the lungs and kidneys can be affected.
Depending on the stage of the disease, the following features can be distinguished:
- disease of the 1st degree - foci of endometriosis of the cervix are superficial and single;
- with endometriosis of the 2nd degree, the lesions are larger and deeper;
- grade 3 is characterized by the appearance of many foci, cysts on the ovaries, adhesions in the peritoneum;
- Grade 4 is difficult to cure, there are many foci, cysts are large, bilateral, the epithelium grows into the vagina and intestines.

Internal endometriosis (in which the uterus itself is affected) is also called adenomyosis. It is divided into several stages depending on the degree of damage to the organ:
Endometriosis lesions can vary in size and shape. In diameter, they can reach from a few millimeters to 2-4 cm. As menstruation approaches, they become more pronounced.

Among other things, endometriosis is classified into:
- diffuse;
- nodal;
- focal.
With a diffuse type of pathology, the endometrium grows over the entire surface of the mucous membrane. With nodular foci distributed locally. For focal lesions, only some parts of the uterine wall are involved in the process. All this can be seen in the photographs taken during the examination.
Note! If the disease is not treated, a complication develops in the form of chronic endometriosis.
Causes of endometriosis
The reasons why endometriosis of the vagina, uterus or bladder develops are not known for certain. Long research has helped to compile a list of assumptions, but there is still no exact answer.
There are several versions:
- endometrial cells enter the abdominal cavity during menstruation, which take root and begin to grow;
- a jump in hormones leads to the development of the disease - the growth of follicle-stimulating hormone against the background of a decrease in progesterone;
- hereditary disposition to pathology;
- a decrease in immune defense, since, with normal indicators, the endometrium cannot take root outside the uterus;
- the degeneration of one tissue into another is called metaplasia.
Regardless of which organ undergoes pathology, whether it is endometriosis of the intestine or ovary, the causes of the development of the disease are the same.
Risk group
To notice the first signs of the disease, women at risk should be especially attentive to their feelings and well-being. If unusual phenomena appear, you should consult a doctor. If endometriosis is not treated with effective methods, it leads to unpleasant consequences, including infertility.

There is a risk of problems in such situations:
To get rid of the disease, it is important to recognize the signs of the disease in time. This will help knowledge of the symptoms of pathology.
Symptoms of endometriosis
The doctor can diagnose the pathology and prescribe treatment. However, only the woman herself can note the main complaints that are worth paying attention to. The main symptoms include the following:
- dysmenorrhea;
- discharge before menstruation;
- infertility;
- signs of intoxication.
Much depends on the stage of pathology and the location of endometriosis. So, dysmenorrhea occurs in almost all forms of the disease. Women experience severe pain, both before menstruation, during bleeding, and for several days after its completion. Attacks of pain are cramping, sharp, radiating to the lower back and pelvic area.
Note! In patients with endometriosis, signs of premenstrual syndrome are very pronounced.
A few days before the expected start of menstruation, women may experience spotting brown discharge. The duration of bleeding increases, and the menstrual cycle itself becomes shorter. When the pathology is complicated by fibroids, the release of blood is possible at any time of the cycle, including during ovulation.
With endometriosis, sexual intercourse becomes painful, regardless of the day of the cycle. The pain is acute, gives to the perineum, peritoneum and rectum.

Infertility is usually the main sign of the "asymptomatic" course of the disease. Due to endometriosis, adhesions are formed in the fallopian tubes and ovaries. All this makes the paths impassable and the mature egg does not have time to get into the uterine cavity for fertilization.
Intoxication occurs infrequently, but the following manifestations are possible:
- nausea;
- vomit;
- temperature increase;
- itching on the skin and in the vagina;
- fever.
During the diagnosis, altered indicators of the erythrocyte sedimentation rate and the level of leukocytes can be detected.
Symptoms may appear from the organs in which the epithelium has sprouted. So, with an exacerbation of endometriosis of the intestine, increased peristalsis is observed. If the bladder is involved in the process, there will be problems with urination and pain of this nature.
Diagnostic measures
In order for the doctor to make a diagnosis and write an effective prescription, it is necessary to undergo some examinations.
First, the doctor will examine the patient. In some forms of endometriosis, a pelvic exam can be painful. The uterus can be enlarged up to 6-8 weeks, depending on the stage of the disease. Shortly before the onset of menstruation, the organ becomes especially dense and enlarged.
With endometriosis, the following instrumental studies are carried out:
- Ultrasound of the uterus and genital tract;
- blood analysis;
- laparoscopy;
- hysteroscopy;
MRI is extremely rare, although this technique is very accurate. The point is the high cost and the availability of other alternative methods. During laparoscopy, altered foci can be seen. On examination, you can see that the affected areas are brown.
The doctor will carefully examine not only the uterus, but also the adjacent organs in order to identify the growth of the endometrium there. The necessary diagnostic methods are determined by the doctor after a visual examination and collection of symptoms.
Important! When going to a gynecologist's appointment, a woman should carry a menstrual calendar with her, which will help the doctor get an idea of her cycle.
Endometriosis can be treated conservatively at home, or surgery can be used. Unfortunately, even surgical removal of formations does not always guarantee a favorable prognosis.

Which therapy will be chosen depends largely on the patient's condition and on her desire to have children in the future. Medical treatment does not increase the likelihood of fertility restoration. After the examination, the doctor may recommend both hormonal and non-hormonal treatment.
However, just taking the medication prescribed by the doctor is not enough. It is important to follow a diet. Food should be high in calories, but not contain a lot of salt and pepper. Physical exercise, daily walks at an average pace are also important. It is important to create a balance between existing loads and rest.
The entire treatment regimen is aimed at:
- elimination of psychological causes with the use of sedatives;
- strengthening immune defenses to prevent the formation of new foci of endometriosis (for example, with the help of "Genferon");
- anesthesia;
- maintaining the functioning of the liver and pancreas.
At the recovery stage after endometriosis, the doctor decides whether physical therapy is needed or not. In practice, this technique is rarely used.
Treatment for menopause and in cases where a woman no longer plans to have children consists in removing the uterus along with endometrial foci. In more than half of the cases, this gives a long-term remission.
With endometriosis, hormone therapy can be prescribed by an experienced doctor. It is forbidden to do this on your own, since it is possible to clearly determine the dosage only after studying the results of the tests. The use of such drugs without the appointment of a specialist can be dangerous.
Hormone therapy for endometriosis includes:

Surgery is performed in the following cases:
If it is decided to perform the operation, then the patient is prepared. She takes a course of some hormonal drugs. Then, after excision, electrophoresis with iodine and zinc is performed, and a course of antibiotics can be prescribed to prevent the addition of a secondary bacterial infection.
Treatment with folk remedies is not prohibited, but it can be carried out along with drug therapy. Otherwise, the effectiveness of folk methods will be minimal. In addition, some methods can harm the body.
What are the consequences
When endometriosis is diagnosed in women of childbearing age, pregnancy is ruled out in most cases. It is usually not possible to completely cure the pathology. Even with a combination of surgical and medical treatment, the periods of remission are not too long and sooner or later an exacerbation occurs.
A more successful prognosis for the course of the disease is made in cases where a woman is in. Then, as the production of sex hormones decreases, endometriosis gradually fades away.
After prolonged clinical treatment (at least three years), some women were able to conceive. However, during pregnancy against the background of remission of endometriosis, the risk of miscarriage is high, especially in the first weeks.
Preventive measures
Every woman should take preventive measures. This also applies to those who have achieved some success in the treatment of the disease. Preventive measures include the following:
- abstaining from sexual intercourse during menstruation;
- maintaining an active lifestyle;
- regular visits to the gynecologist;
- immediate treatment of all inflammatory diseases of the genital area;
- refusal to conduct abortions, including medical ones;
- minimizing emotional experiences and stress;
- maintaining normal body weight.

If a woman carefully follows these recommendations, the risk of suffering from endometriosis is significantly reduced.
When the first unpleasant signs of the disease appear, you should consult a doctor as soon as possible. An ultrasound examination will allow diagnosing pathology at the initial stage and applying only drug therapy without surgical intervention.
Watch the video:
Endometriosis of the uterus is a disease characterized by the growth of cells of the uterine layer of the endometrium outside the uterine cavity. If it is not treated in a timely manner, the pathology will gradually affect the internal organs of the genitourinary system and peritoneum. considered: hormonal failure, menstrual irregularities, pain in the lower abdomen, intoxication. The disease provokes a number of complications, for example, endometriosis of the fallopian tubes leads to female infertility.
Such a gynecological disease as endometriosis occupies the 3rd place in terms of prevalence after infectious and inflammatory diseases of the genitourinary system. The exact causes of the sudden growth of the endometrium are unknown.

Endometriosis of the uterus has its own classification, based on which organs of the reproductive system are affected by the pathological process:
- peritoneal type- the endometrium affects the ovaries, fallopian tubes and penetrates into the abdominal cavity; It also occurs among this pathology,
- extraperitoneal view- endometriosis of the vagina, the spread of the endometrium to the external genital organs, the cervix;
- internal type- endometrial cells grow into a layer of myometrium. When an internal type of pathology develops, the uterus looks like a pear, it is enlarged, in appearance it corresponds to the 6th week of pregnancy.
There is a mixed form of uterine endometriosis, when endometrial cells simultaneously affect both the vagina and the muscular layer of the uterine cavity. This pathological condition is observed in extremely rare cases, with a protracted and aggravated course of the disease, the treatment of which was not carried out in a timely manner.
The classification of endometriosis in women is based on the severity of the clinical case (how deeply pathogenic cells have penetrated):
- endometriosis of the 1st degree - 1-2 foci of the disease, which are located on the surface of the soft structures of the genital organs;
- endometriosis of the 2nd degree - there are many pathological foci, they penetrate deeper into the structure of organs;
- 3 degree of the disease - a large number of foci, there are complications, adhesions appear in the fallopian tubes, multiple cysts form on the ovaries;
- Grade 4 - multiple foci penetrate deep into the structure of organs, lead to the development of cysts on the ovaries, there is a total lesion of the organs of the genitourinary system. Treatment of this stage of development of the pathology is extremely difficult and rarely gives a positive result.
Endometriosis of the uterus of the internal type is also divided into stages, based on how deeply the cells have penetrated into the soft structure:
- stage 1 - the initial degree of the disease;
- stage two - the spread of multiple foci, penetrating deep into the myometrium;
- the third stage - the entire muscle layer is affected by endometrial cells;
- stage 4 - the uterus grows into the peritoneum.

Endometrial foci can be large and small, they are often round in shape, but there are also shapeless ones. Sizes range from a few millimeters to centimeters. An increase in foci in volume is noted before menstruation. This is due to the fact that the blood vessels expand, blood circulation is accelerated.
Reasons for the appearance
What symptoms occur with endometriosis of the uterus, and what it is, gynecology knows, but why it occurs is still unknown. There are several theories describing the possible causes of endometriosis:
- retrograde theory, according to which, during menstruation, endometrial cells with blood penetrate into the peritoneum, where they begin to actively grow into soft structures;
- genetic heritage - many women's diseases have a hereditary predisposition, and endometriosis is no exception. If close blood relatives had this disease, the risks of its occurrence increase significantly;

- distribution of endometrial cells to neighboring internal organs of the genitourinary system through the lymph;
- pathology of the development of the female reproductive system during the period of intrauterine formation of internal organs.
It should be understood that endometriosis will not occur in a woman just because such a pathological process was present in the mother or grandmother. For the development of the disease, certain provoking factors are needed:
- inflammatory diseases of the genitourinary system; sexually transmitted infections;
- natural childbirth that took place with a complication or led to trauma to the mucous membrane of the cervix;
- the presence of bad habits (smoking, excessive drinking of alcohol, coffee);
- transferred surgical interventions on the organs of the reproductive system, in particular, operations in the uterine cavity, abortions;
- disorders of the thyroid gland;

- hormonal failure is a common cause that provokes the development of the disease;
- depressed immune system;
- overweight, obesity;
- insufficient amount of iron in the body.
There are psychological reasons for the development of endometriosis. This is due to the fact that a woman denies and suppresses her feminine in every possible way. Psychology calls this condition a violation of gender self-identification. A woman does not want to know and reveal her beauty, sexuality, destiny, while she will identify and behave like a girl, an old woman or a man. Such conditions are treated by a psychologist. Endometriosis of the uterus of a psychological nature occurs in young, successful women who want to pursue only their careers, deny the desire to have a family and children.

In addition to the fact that the causes of endometriosis remain unknown, and the disease itself can occur without a pronounced symptomatic picture, it is important to undergo a preventive examination by a gynecologist at least 2 times a year. Early diagnosis contributes to the timely detection of pathology, and the treatment itself will be much easier, it will be possible to prevent serious complications.
Clinical picture
It is not always possible to recognize endometriosis in the early stages of the development of the pathological process. Symptoms of a pathological condition can be very different, depending on the individual characteristics of the organism, the presence or absence of concomitant diseases. Signs of the disease may appear immediately and be pronounced, or absent altogether.
How to recognize the disease? There are a number of the most common signs, the presence of which is a reason for an immediate appeal to a gynecologist:
- Pain in the lower abdomen. The nature and intensity of pain can be very diverse, from acute to aching. The intensity is moderate or mild. There is an increase in the pain symptom during menstruation and sex, after sexual intimacy, physical activity;
- Allocations. On this basis, endometriosis can be determined - menstruation becomes abundant, there is a slight bleeding of a smearing nature in the middle of the cycle, after intimacy.

Why is endometriosis dangerous? In addition to violations of the organs of the genitourinary system, heavy bleeding during menstruation and discharge in the middle of the cycle lead to the development of iron deficiency anemia. With this disease, the following symptoms occur:
- weak, constantly breaking nail plate;
- sudden onset of shortness of breath, at first only after physical activity, later on even with minor exertion;
- constant feeling of drowsiness;
- rapid fatigue;
- skin and mucous membranes become pale.
Women who are sick with endometriosis may for a long period of time not be aware of what pathological process is taking place in their reproductive system. Often, in the absence of any signs of the disease, a woman who dreams of becoming a mother is faced with the problem of conception. When diagnosing the causes of infertility, in many cases, a neglected form of this pathology is detected.

Methods of diagnosis and therapy
Despite the fact that the causes of uterine endometriosis are unknown, the treatment of the disease is scheduled to the smallest detail. Depending on the severity of the clinical case, conservative methods of treatment are used or an operation is performed. Before treating a pathology, it is necessary to determine the stage of development and identify the presence of complications.
How to identify endometriosis? To begin with, a gynecological examination is performed, during which foci are identified. They look like sores of blue or burgundy color, from which ichor oozes. To clarify the primary diagnosis, an ultrasound with a photo is performed. The pictures will show the exact location of the foci. Given the danger of endometriosis, its treatment must be carried out in a timely manner.

Medical therapy includes:
- taking hormonal drugs;
- the use of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs;
- the appointment of drugs from the group of immunomodulators aimed at restoring the protective functions of the immune system.
Treatment includes symptomatic therapy aimed at suppressing the main signs of the disease. To stop pain in the lower abdomen, prevent bleeding in the middle of the cycle and normalize menstruation, analgesics, sedatives, and antispasmodics are prescribed. Vitamin complexes are prescribed without fail, in particular, the emphasis is on vitamin C and A. If anemia begins to develop against the background of constant bleeding, iron preparations are prescribed.

Surgical intervention is prescribed in cases where drug therapy does not give a positive result, or the woman has already passed her reproductive age and will no longer have children. The operation involves the removal of endometriosis foci with a radioknife or laser. So, the consequences of endometriosis, untreated on time, can be the most severe. Sometimes the only treatment is the removal of the uterus and appendages, if the development of this disease has led to their total dysfunction.
Possible Complications
Every woman should know what endometriosis is and why it is dangerous in order to prevent the consequences in time. This disease leads to a failure of the hormonal background, disruption of the internal organs of the genitourinary system. In addition, it can provoke the formation of multiple cysts in the ovaries, the development of an oncological neoplasm. As a result of a long absence of treatment, the fallopian tubes overlap with adhesions, which makes it impossible to conceive a child.
Possibility of conception
in the early stages of the disease. 2nd and 3rd degree of the pathological process must be cured before conception. In a pregnant woman, endometrial pathology can provoke severe complications, cause miscarriage in the early stages or premature birth in the 3rd trimester. If the disease has passed into the 4th, most severe stage, pregnancy is naturally excluded, IVF attempts may also lead to nothing.
If a woman who has undergone conservative treatment or removal of foci wants to become a mother in the future, it is recommended to plan a pregnancy immediately after the menstrual cycle normalizes. The risks of recurrence remain after surgery, and the natural change in hormonal levels during pregnancy will help prevent the recurrence of the disease.
Signs of endometriosis occur in women with pathological growth of tissue lining the inner cavity of the uterus. The endometrium passes to other organs, the abdominal wall, intestinal tissues.
Common symptoms that occur in a woman are manifested in the form of heavy menstruation, spotting in the middle of the cycle, pain in the lower abdomen.
No doctor can name the exact causes of the pathology. However, among the likely factors that cause signs of endometriosis in a woman are the following:
- Retrograde menses. At the onset of menstruation, the discharge does not completely go out through the genital tract, but is partially thrown into the abdominal cavity through the fallopian tubes. This phenomenon is not uncommon in completely healthy women. However, with good immunity, endometrioid tissue cells are rejected and are not able to take root in an atypical place.
- genetic factor. The disease can be inherited through the female line. If mother, grandmother, aunts had a problem, there is nothing to be surprised at.
- Weak immune defense of the body. Normally, endometrioid tissue cells are destroyed and excreted from the body. Poor immunity can cause the growth of the endometrium outside the uterine cavity.
- Hormonal imbalance. Endometrial tissue cells are sensitive to the effects of female sex hormones - estrogen and progesterone. An increase in the concentration, for example, of estrogen, in the body can cause the appearance of endometrioid lesions.
- Surgical intervention., curettage can injure the tissue lining the uterine cavity, resulting in endometriosis.
Other causes of endometriosis:
- genital infections;
- the use of contraceptives in the form of an IUD (intrauterine device);
- excess body weight;
- bad ecology;
- insufficient amount of iron in the body;
- problems with the liver.
Signs of endometriosis in women
All the symptoms that cause endometriosis can be conditionally divided into groups:
- Pain syndrome.
- Cycle problems.
- Inability to conceive a child.
- Psycho-emotional problems.
- Other nonspecific manifestations.
Pain syndrome
Women with endometriosis may experience the following symptoms:
- depending on the days of the menstrual cycle.
- Pain syndrome that occurs due to sexual intercourse.
- Pain not associated with either the first or the second.
The nature of the pain can also be different, and its intensity is directly dependent on the following reasons:
- the location of the lesions (the most severe pain occurs if endometriosis has affected the cervix);
- the extent of endometriosis lesions (when lesions occur in the abdominal cavity, affect the bladder);
- the formation of adhesions in the pelvic organs;
- the duration of the disease;
- high or low pain threshold in a woman.
Cycle problems
Almost always accompanies endometrioid pathology.
A woman may observe the following symptoms:
- a few days before the expected date of menstruation, accompanied by a strong pain effect;
On the video about the signs of endometriosis and its treatment:
Impossibility of conception
Infertility is diagnosed in most women who are faced with the problem of endometriosis.
The following reasons interfere with natural conception:
- hormonal imbalance in the body, which leads to the absence of a mature egg;
- adhesions in the fallopian tubes due to the inflammatory process;
- the impossibility of implantation of a fertilized egg due to a violation of the normal properties of the endometrium.
Psycho-emotional problems
Infertility, a constant feeling of pain, hormonal failure, cycle disturbance, frequent and heavy periods - all this seriously affects the psycho-emotional state of the patient.
As a result, the following manifestations are possible:
- imbalance;
- excessive irritability;
- insomnia;
- anxiety;
- depressive mood.
Other non-specific manifestations
In addition to the specific symptoms of endometriosis listed above, women can also be diagnosed with general signs, which include:
- poor general health;
- constant weakness and fatigue;
- frequent headaches;
- reduced performance.
Carrying out diagnostics

 If you find signs of endometriosis, deterioration of health, a woman needs to make a visit to the doctor.
If you find signs of endometriosis, deterioration of health, a woman needs to make a visit to the doctor.
A physical examination will be carried out in the gynecological office, then the following procedures will be prescribed (which ones, the attending doctor decides):
- Ultrasound of the pelvic organs - conventional or transvaginal.
- Laparoscopy - is used both for examination in case of suspected endometriosis, and for the treatment of this pathology.
Is not always easy. The fact is that pain in the lower abdomen and other symptoms often merge with, which is a common occurrence in a number of women.
Treatment Methods
The goal of treatment is the elimination of endometrioid lesions, pain syndrome and the fight against infertility. The choice of methods of therapy is influenced by the symptoms of the disease, the desire of a woman to become a mother or lack of it, planning a pregnancy now or the possibility of postponing this issue until a later time.
Can be assigned to:
- hormone therapy;
- anti-inflammatory drugs.
In the most difficult cases, surgical treatment is indicated.
Duphaston
One of the commonly prescribed drugs is. This is a hormonal agent, which is based on progestogen or synthetic progesterone.
The action of Duphaston is aimed at eliminating pathological endometrial foci, while the drug does not affect ovulation and the menstrual cycle. The dosage is prescribed by the doctor.
Prevention measures
The sooner a woman visits a gynecologist when she feels unwell, the greater the likelihood of a complete cure in the future. Self-treatment or waiting tactics are not acceptable, since in this case the disease further develops, which is fraught with the formation of adhesive processes, new lesions and an increase in their area.
Basic preventive measures:
- immediate medical attention for painful or abnormal periods;
- timely treatment of genital infections and inflammatory diseases;
- examination by a doctor after artificial termination of pregnancy or other surgical interventions;
- observance of intimate hygiene;
- use of hormonal contraception.
Endometriosis is a disease that affects the pelvic organs of a woman. This is a pathological growth of the internal tissue of the uterus. Treatment is medical or surgical. But the best therapy is still active prevention, which means being attentive to your health and visiting a doctor in a timely manner.