Online maps with monitoring of seismic activity of the earth. Geography of earthquakes
An earthquake is a violent shaking of the Earth's surface resulting from a sudden release of energy in the earth's crust, which creates seismic waves. It is one of the deadliest natural disasters and often results in ground breaking, earth trembling and liquefaction, landslides, tremors or tsunamis.
If we look at the structure of the earthquakes that occur around the world, it becomes clear that most of the seismic activity is concentrated in a number of different earthquake belts. Earthquakes are unpredictable in terms of when they strike, but certain areas are the most likely to hit.
The world map of earthquakes shows that most of them lie in precise zones, often along the edges of the continents or in the middle of the ocean. The world is divided into seismic zones based on tectonic plates and earthquake magnitude. Here list of the most earthquake-prone countries in the world:

Several cities are also vulnerable to earthquake damage in Indonesia. Indonesia's capital, Jakarta, is in a difficult position. Not only is it located on top of the Pacific Ring of Fire, but, a little less than half the city is below sea level, it sits on soft ground that has the potential to liquefy if struck by an earthquake of sufficient magnitude.
But the complications don't end there. The height of Jakarta also puts the city at risk of flooding. On December 26, 2004, an earthquake occurred in the Indian Ocean with its epicenter on the west coast of the island of Sumatra, Indonesia.
A mega-strength underwater earthquake occurred when the Indian Plate subducted under the Burmese Plate and triggered a series of devastating tsunamis along the coastline of much of the Indian Ocean coastline, killing 230,000 people in 14 countries and flooding coastal areas with waves up to 30 meters high.
Indonesia was the most affected area, with the most deaths estimated at around 170,000. This is the third largest earthquake ever recorded on seismographs.

Turkey is located in the seismic zone between the Arabian, Eurasian and African plates. This geographic location suggests that an earthquake can occur in the country at any given time. Turkey has a long history of large earthquakes, which often occur in progressive contiguous earthquakes.
The magnitude 7.6 earthquake that struck western Turkey on August 17, 1999 is one of the world's longest and most well-studied strike-slip (horizontal) faults: the East-West strike of the North Anatolian Fault.
The incident lasted only 37 seconds, killing about 17,000 people. Over 50,000 people were injured and over 5,000,000 people were left homeless, making it one of the most devastating earthquakes of the 20th century.

Mexico is another earthquake prone country and has experienced several high magnitude earthquakes in the past. Situated on three large tectonic plates namely the Cocos Plate, the Pacific Plate and the North American Plate that make up the earth's surface, Mexico is one of the most seismically active areas on earth.
The movement of these plates causes earthquakes and volcanic activity. Mexico has an extensive history of devastating earthquakes and volcanic eruptions. In September 1985, an earthquake measuring 8.1 on the Richter scale was concentrated in the 300-kilometer subduction zone off Acapulco, killing 4,000 people in Mexico City.
One of the recent earthquakes occurred in 2014 in the state of Guerrero with a magnitude of 7.2, the impact caused numerous casualties in the region.

El Salvador is another dangerous seismically active country where massive damage was done due to the earthquake. The small Central American Republic of El Salvador has experienced, on average, one devastating earthquake per decade over the past hundred years. There were two large earthquakes on January 13 and February 13, 2001, with magnitudes of 7.7 and 6.6, respectively.
These two events, which have different tectonic origins, show patterns in the region's seismicity, although neither of these events had known precedents in the earthquake catalog in terms of size and location. Earthquakes damaged thousands of traditionally built houses and caused hundreds of landslides, which are the main causes of deaths.
Earthquakes have clearly demonstrated increasing seismic risk trends in El Salvador due to rapid population growth in areas of high quake and landslide risk, exacerbated by deforestation and uncontrolled urbanization. The institutional arrangements needed to control land use and building practices are very weak and represent a major barrier to risk reduction.

Another earthquake-prone country is Pakistan, which is geologically and chemically located in the Indus-Tsangpo suture zone, which is about 200 km north of the front Himalayas and is defined by an ophiolite chain along the southern margin. This region has the highest rates of seismic activity and the largest earthquakes in the Himalaya region, caused mainly by fault movement.
A 7.6 magnitude earthquake hit Pakistan's Kashmir in October 2005, killing more than 73,000 people, many in remote parts of the country, in sparsely populated urban centers such as Islamabad. Most recently, in September 2013, a powerful earthquake measuring 7.7 on the Richter scale occurred, causing enormous damage to people's lives and property, killing at least 825 people and injuring hundreds of people.

The Philippines lies on the edge of the Pacific Plate, which has traditionally been considered a seismically hot zone that surrounds the state. The danger of earthquakes in Manila is created three times more often. The city comfortably adjoins the Pacific Ring of Fire, which, of course, makes it especially sensitive not only to earthquakes, but also to volcanic eruptions.
The threat to Manila is aggravated by soft soil, which poses a risk of soil liquefaction. On October 15, 2013, an earthquake measuring 7.1 on the Richter scale hit the central Philippines. According to official statistics from the National Disaster Reduction and Management Council (NDRRMC), 222 people died, 8 were missing, and 976 people were injured.
Overall, more than 73,000 buildings and structures were damaged, of which more than 14,500 were completely destroyed. It was the deadliest earthquake in the Philippines in 23 years. The power released by the earthquake was equivalent to 32 Hiroshima bombs.

Ecuador has several active volcanoes, making the country extremely prone to high magnitude earthquakes and tremors. The country is located in a seismic zone between the South American Plate and the Nazca Plate. Earthquakes that affect Ecuador can be divided into those that are the result of movement along the subduction junction along the plate boundary, those that are the result of deformation within the S American and Nazca Plates, and those associated with active volcanoes.
On August 12, 2014, an earthquake of magnitude 5.1 on the Richter scale struck Quito, followed by an aftershock of magnitude 4.3. 2 people died and 8 were injured.

India has also experienced a series of several deadly earthquakes due to the movement of the Indian tectonic plate at a rate of 47mm each year. Due to the movement of tectonic plates, India is prone to earthquakes. India has been divided into five zones based on peak ground acceleration.
On December 26, 2004, an earthquake generated the third deadliest tsunami in the history of the world, killing 15,000 people in India. The earthquake in the state of Gujarat occurred on January 26, 2001, on the celebration of the 52nd day of the Republic of India.
It lasted more than 2 minutes and amounted to 7.7 points on the kanamori scale, according to statistics, from 13,805 to 20,023 people died, another 167,000 people were injured and about 400,000 houses were destroyed.

If the calculations are correct, then a citizen in Nepal is more likely to die in an earthquake than any citizen in the world. Nepal is a country prone to natural disasters. Floods, landslides, epidemics and fires cause significant property damage in Nepal every year. It is one of the most seismically active regions in the world.
Mountains are built as a result of the movement of Indian tectonic plates under Central Asia. These two large plates of the earth's crust are approaching at a relative rate of 4-5 cm per year. The peaks on Everest and its sister mountains are subject to numerous aftershocks. In addition, the remains of a prehistoric lake, in a 300-meter deep layer of black clay, lie in the lowlands of the Kathmandu valley. This increases the damage from strong earthquakes.
Thus, the region becomes susceptible to soil liquefaction. During strong earthquakes, solid ground turns into something like quicksand, swallowing everything above the ground. In April 2015, an earthquake in Nepal killed over 8,000 people and injured more than 21,000. The earthquake triggered an avalanche on Everest where 21 people died, making 25 April 2015 the deadliest day on the mountain in history.

Japan tops the list of earthquake-prone areas. Japan's physical geographic location along the Pacific Ring of Fire makes the country very sensitive to earthquakes and tsunamis. Ring of Fire - The tectonic plates in the Pacific Basin are responsible for 90% of the world's earthquakes and 81% of the world's strongest earthquakes.
At the pinnacle of its prolific tectonic activity, Japan is also home to 452 volcanoes, making it the most destructive geographic location in terms of natural disasters. The powerful earthquake that hit Japan on March 11, 2011 struck hard and became one of the five largest earthquakes in the world since the beginning of seismological records.
It was followed by a tsunami with waves up to 10 m high. The disaster killed thousands of people and caused extensive damage to buildings and infrastructure, which led to significant accidents at four large nuclear power plants.
You will see the effects of the most powerful earthquakes in the world and understand why this phenomenon is considered so dangerous.
The destructive power of an earthquake depends on its magnitude (in the hypocenter, i.e. in the source), the depth of the earthquake source and the distance from the epicenter (the projection point of the source on the earth's surface).
Examples of media reports and explanations of terms:
"According to ***, there, at so much Moscow time, an earthquake occurred magnitude in the source M=4.3 points on the nine-point Richter scale, at a depth of 15 km from sea level.
The epicenter of the earthquake was located 100 kilometers southeast of the city ***. Tremors were felt in the village *** force up to four points, and in the city of *** - three points (on a 12-point scale). According to the latest data, there are no casualties and serious damage. During the week, 4 earthquakes with a magnitude of 2.3 to 4.3 on the Richter scale were recorded in this area, which were also felt in neighboring regions. According to statistics provided by seismologists, the average interval between series of earthquakes of magnitude up to four points in this area is approximately *** years.
Or
"An earthquake with a magnitude, in the source, 4.3 happened there. Its epicenter was one hundred kilometers southeast of the city ***. The depth of the focus was 15 km" from sea level.
Or
A four-point earth happened somewhere today.
Magnitude earthquake (not to be confused with "strength", and leave points alone) - quantitatively characterizes its energy, at the source, on a nine-point Richter scale (0-9). It is calculated based on the results of measurements by instruments (seismographs) at the nearest, to the epicenter, seismic stations of different countries. An earthquake of magnitude 6 or more, with a nearby epicenter and a shallow source, is considered strong and can cause significant damage and casualties among the population, especially if buildings and residential structures are not designed for proper seismic resistance or are built by low-skilled guest workers, with rude violations of building codes and regulations.
Strength earthquake shocks (intensity) - a qualitative (felt, visible) characteristic of the degree of destruction and other manifestations on the earth's surface, at a specific point on the earth's surface. For this, a twelve-point scale (1-12) or a modified Mercalli scale is used. They differ little. The real danger is tremors with a force of four points or more.
Forecast. Before a strong earthquake, in a few minutes or even hours, domestic animals and birds begin to scream and rush about, tend to run away from the house to the street, to hide. Dogs try to lead their owners, children to a safe place. Cats take away kittens. Aquarium fish - worried, trying to jump out of the aquarium water. Rats and mice run out of the basements of houses. Wild animals, in advance - a few hours or days before the earthquake, flocks leave the dangerous area. Snakes and lizards crawl out of their holes (even in winter, and at night and in bad weather), Birds constantly scream, fly in circles for a long time and randomly. Animals and birds lose their appetite, their behavior changes greatly - they, without attacking each other, move away from danger together.
Those who were born, grew up and lived (under natural conditions) in earthquake-prone areas have the best sensitivity. The skill is retained for a long time. Their reaction is more often selective, only to close (local earthquakes) and dangerous in strength (more than two to four points).
Seismologists and volcanologists use scientific, instrumental methods of forecasting and early warning methods: constant monitoring of seismic activity with a network of sensitive sensors, regular measurements and detection of increases in the concentration of helium and radon in the surface air and at depth, etc.
The dependence of the intensity of the earth from distance to epicenter. From closely located epicenters of earthquakes of great strength (if the "seven" of magnitude or higher strikes) - very sharp shocks and shocks are felt, intense shaking, glows, sparks are visible, an underground rumble, crackling and roar of collapsing buildings and falling, broken trees is heard, there is a sharp wind amplification. At distances of hundreds of kilometers, from the epicenter, the echoes of an earthquake reach - low-frequency, relatively slow oscillations, undulating swaying of the daytime surface of the earth. The farther away, the smaller their vertical amplitude and longer period (up to a minute or more, with a distance to the epicenter of several thousand kilometers), with the exception of anomalously intense and resonant manifestations at certain distances from the epicenter and along large, deep tectonic faults.
Influence of tidal (gravitational) effects. Seismicity increases - on the new moon and, especially, on the full moon, as well as when the Moon is in perigee (closer to the Earth). There is also a seasonal dependence: in autumn and, especially, in winter, it shakes harder and more often than in spring and summer.
Geological factor. The greatest damage from an earthquake occurs at the outcrops of rocky rocks and if they are covered with loose deposits of small thickness, which are thrown up on their base. Safer soil conditions are territories with thick strata of loose forges. rocks in which the seismic wave weakens, is extinguished until it reaches the earth's surface.
Tsunami occur if the epicenter of the earth is near the sea coast. Water, at the first blow, first leaves the coast, and then, accelerating, in the form of a large wave, it falls on the coast. The brightness of the glow of marine organisms also rises sharply two or three minutes before the tsunami.
The seismic activity map is updated every 20 minutes.
To take a closer look at the area and scores, click on the source of the earthquake with the cursor, you will be taken to an enlarged area of the mapAutomatic GEOFON Global Seismic Moniton Map
red - last 24 hours
orange - last 1-4 days
yellow - last 4-14 days
Earthquakes in the last 30 days with a magnitude of 4 or more
EMSC+Google Map
Earthquakes in the World
red - last 24 hours
orange - from 24 to 48 hours
yellow - for the last 3-17 days
purple- from 2 weeks to 5 years
Seismic of the Atlantic Ocean

Pacific Ocean. Far East. Kuriles. Fault lines of the Pacific Ridge

Russia and Central Asia

Europe

Indonesian region

EMSC
Table data for the selected period:
http://www.emsc-csem.org/index.php?page=current&sub=list
Live Earthquake Mashup
Excellent map, direct analogue of Google planet with attached KML files
http://www.oe-files.de/gmaps/eqmashup.html
Earthquakes Canada
Map of seismic activity in Canada. All earthquakes in the last 30 days.
To view the area and scores, click on the source of the earthquake with the cursor, you will be taken to the information of the map areaThe updated list of earthquakes is online.
Geophysical Survey RAS
Shows the last 15 earthquakes
Map of tectonic plates of the world

Scientists have compiled a map of the largest tectonic plates:
- Australian;
- Arabian subcontinent;
- Antarctic;
- African;
- Hindustan;
- Eurasian;
- Nazca plate;
- Cooker Coconut;
- Pacific;
- North and South American platforms;
- Scotia plate;
- Philippine plate.
From theory, we know that the solid shell of the earth (lithosphere) consists not only of the plates that form the relief of the surface of the planet, but also of the deep part - the mantle. Continental platforms have a thickness of 35 km (in the flat areas) to 70 km (in the zone of mountain ranges). Scientists have proven that the plate in the Himalayas has the greatest thickness. Here the thickness of the platform reaches 90 km. The thinnest lithosphere is found in the ocean zone. Its thickness does not exceed 10 km, and in some areas this figure is 5 km. Based on the information about the depth at which the epicenter of the earthquake is located and what is the speed of propagation of seismic waves, calculations are made of the thickness of the sections of the earth's crust.
Map of faults and seismically dangerous places
The map shows the places of seismically dangerous zones. The zones are highlighted in color from green to red. The closer the color is to red, the more likely strong and destructive earthquakes are. The map was created on the data of earthquakes that have occurred since 1973.
Nuclear power plants are marked on the map. The location of a nuclear power plant in a seismically hazardous area increases the danger to the population.
Hazard grade. Switch on switch off
Seismic activity scale. Richter scale. Earthquake by type of activity.
| Mercalli scale | Richter scale | Visible action |
|
1 |
0 -4.3 |
Vibration from an earthquake is recorded only by instruments |
|
2 |
Earthquake vibrations are felt when standing on stairs | |
|
3 |
Earthquake shocks are felt indoors, light vibrations of objects | |
|
4 |
4.3-4.8 |
The clinking of dishes, the swaying of trees, the tremors of an earthquake are felt in parked cars. |
|
5 |
The creaking of doors, the awakening of the sleeping, the transfusion of liquid from the vessels | |
|
6 |
4.8-6.2 |
During an earthquake, unsteady walking of people, damage to windows, falling pictures from the walls |
|
7 |
It is difficult to stand, the tiles on the houses are crumbling, large bells are ringing from the earthquake | |
|
8 |
6.2-7.3 |
Damage to chimneys, damage to sewer networks during such an earthquake |
|
9 |
General panic from the earthquake, damage to foundations | |
|
10 |
Most buildings damaged*, major landslides, rivers bursting their banks | |
|
11 |
7.3-8.9 |
Bent railway tracks, road damage, large cracks in the ground, falling rocks |
|
12 |
Complete destruction, waves on the surface of the earth, changes in the course of rivers, poor visibility | |
| * Specially designed buildings with earthquake protection are able to withstand shocks up to 8.5 on the Richter scale | ||
The amount of energy released during an earthquake
| The strength of the earthquake on the Richter scale | The amount of energy in an earthquake (equivalent to trinitrotoluene), t |
| 4 | 6 |
| 5 | 199 |
| 6 | 6270 |
| 7 | 199’000 |
| 8 | 6’270’000 |
| 9 | 99’000’000 |
Map of earthquakes in Europe for the last 24 hours


Seismic activity on the planet over the past day

Seismic activity on the planet over the past week

| >>> Seismomonitor (overlaid on the map) | >>> USGS Seismomonitor (mapped) | >>>Seismomonitor (clickable map) | >>>Seismic monitor EUROPE |
Earthquake map according to Google service
Seismic activity map online, updated every 20 minutes. In addition, you can always find out whether there was an earthquake today or not. This allows you to more visually evaluate the information provided.
Seismic activity map of the EMSC service and Google Map
The map of seismic activity of the world allows you to select a section of the earth's surface by pressing the mouse button. In this case, the selected area will be displayed separately in the window, on which earthquake epicenters are indicated in detail. The online seismic monitor allows you to get comprehensive data when choosing any of the sources. The table shows the coordinates of the epicenters and the power of tremors, ranging from 24 hours to 30 days. Also, on the map of the region, seismic fixation stations located in the selected area are displayed.
Earthquake map from quakes.globalincidentmap.com
Earthquake map from emsc-csem.org
Behavior before, during and after an earthquake
|
The vast majority of earthquakes have a duration of about one, rarely more than one minute. However, the intensity of oscillations during this time is not the same. As a rule, an earthquake begins with relatively weak vibrations (sometimes imperceptible), which last 10-20 seconds, then the main phase of the earthquake occurs, at which the vibrations reach their greatest intensity, followed by a gradual decline. Qualitatively erected and well-maintained buildings that do not have special anti-seismic measures are able to withstand earthquakes of up to six points without much damage. Buildings that are in an unsatisfactory technical condition and dilapidated, under the threat of strong earthquakes, are doubly dangerous. Before the earthquake Inside the house, securely attach cabinets, shelves, and furniture walls to the walls and floor. Furniture, standing and hanging objects in living quarters are placed so that if they fall, sleeping people are not injured and passages and exits from the apartment remain free. All heavy objects should be moved to the lower shelves and places. Shelves with utensils must be closed. Fix chandeliers and overhead lights securely, do not use glass lampshades. Do not clutter up the aisles and exits from rooms and apartments with things. Flammable, caustic, poisonous liquids and powders must be securely sealed, closed in strong, fixed containers and boxes. All family members should be well aware of the safest places in residential premises: in the openings of the internal main walls near these walls, at the supporting columns and under the frame beams, in the corners of the internal main walls and under solid furniture (tables, beds). And dangerous places too: near large glazed openings and partitions, corner rooms of buildings, especially the last floors. During an earthquake Don't panic! Quickly focus on the implementation of previously thought out actions, but be ready to act according to circumstances. In the house/apartment: If you are in a low, up to 2-3 floors building, then it is better to leave it quickly. This is especially true if the building is not earthquake resistant. Run out quickly, but carefully, beware of falling objects, broken wires and other sources of danger, and immediately move away from the building, away from the open area. When on the upper floors of a multi-story building, do not rush to the stairs and elevators. Most likely, they will be overcrowded with people, and the elevators are disabled. Therefore, it is better to stay in the building and, having previously opened the front door, which in the future may turn out to be jammed from distortions, quickly take the safest place in the room: under solid furniture, at the wall of the supporting column closest to the center of the building, in the doorway of the main walls, in the corner rooms. And always away from windows, heavy objects and equipment that could tip over. Help the disabled and the elderly. Do not enter buildings or run around them. Once next to a tall building, stand in the doorway, this will protect you from falling pieces of glass, balconies, cornices and parapets. It is best to be in an open area, away from buildings and power lines. In transport Any transport must be calmly and quickly stopped, as far as possible from tall buildings, overpasses, bridges, power lines or anything that can collapse from strong shocks. Drivers of buses and trams, having stopped the transport, must open all the doors. After the earthquake While in the building, remain calm, assess the situation. Examine yourself and those around you, if necessary, provide medical assistance to those in need. Wear sturdy shoes to protect your feet from splinters and debris. Going down the stairs, check the reliability of its structures. Check for a fire hazard. The resulting flame must be extinguished immediately. If you notice damage to the wiring, turn off the power, if it has not already been done. According to the materials of the State Committee of the Republic of Buryatia
|
As earthquake statistics show, seismological disasters account for 13% of the total number of natural disasters. Over the past hundred years, about 2,000 aftershocks with a magnitude of 7 or more have occurred in the world. Of these, 65 cases exceeded the 8 mark.
The situation in the world
If you look at the world map, on which seismological activity is displayed with dots, you can notice one pattern. These are some characteristic lines along which tremors are intensely recorded. The tectonic boundaries of the earth's crust are located in these zones. As statistics have established, strong catastrophic earthquakes, entailing the most devastating consequences, occur due to stress in the focus of "grinding" of tectonic plates. 
Earthquake statistics for 100 years show that only on continental tectonic plates (not oceanic) about a hundred seismic catastrophes occurred, in which 1.4 million people died. In total, 130 strong earthquakes were recorded during this period.
The table shows the largest known seismic catastrophes since the 16th century:
| Year | Location of the incident | Destruction and casualties |
| 1556 | China | 830 thousand people became victims. According to current estimates, the earthquake can be assigned the highest score - 12 points. |
| 1755 | Lisbon (Portugal) | The city was completely destroyed, 100 thousand inhabitants died |
| 1906 | San Francisco (USA) | Most of the city was destroyed, 1,500 people became victims (7.8 points) |
| 1908 | Messina (Italy) | The destruction claimed 87 thousand human lives (magnitude 7.5) |
| 1948 | Ashgabat (Turkmenistan) | 175 thousand people died |
| 1960 | Chile | The largest earthquake recorded in the last century. He was rated 9.5 points. Three cities were destroyed. About 10 thousand inhabitants became victims |
| 1976 | Tien Shan (China) | Magnitude 8.2. 242 thousand people died |
| 1988 | Armenia | Several cities and towns were destroyed. More than 25 thousand victims recorded (7.3 points) |
| 1990 | Iran | About 50 thousand inhabitants died (magnitude 7.4) |
| 2004 | Indian Ocean | The epicenter of the earthquake 9.3 points was at the bottom of the ocean, formed claimed the lives of 250 thousand inhabitants |
| 2011 | Japan | An earthquake with a magnitude of 9.1 caused the death of more than 15 thousand people and caused enormous economic and environmental consequences not only for Japan, but for the whole world. |
Over 30 years of the end of the 20th century, about 1 million people died in seismic catastrophes. This is about 33 thousand per year. Over the past 10 years, earthquake statistics show an increase in the average annual figure to 45 thousand victims.  Hundreds of imperceptible oscillations of the earth's surface occur every day on the planet. This is not always associated with the movement of the earth's crust. Human actions: construction, mining, blasting - they all entail fluctuations recorded by modern seismographs every second. However, since 2009, the USGS Geological Survey, which collects data on earthquake statistics in the world, has ceased to take into account shocks below 4.5.
Hundreds of imperceptible oscillations of the earth's surface occur every day on the planet. This is not always associated with the movement of the earth's crust. Human actions: construction, mining, blasting - they all entail fluctuations recorded by modern seismographs every second. However, since 2009, the USGS Geological Survey, which collects data on earthquake statistics in the world, has ceased to take into account shocks below 4.5.
The island of Crete
The island is located in a tectonic fault zone, so increased seismological activity there is a frequent phenomenon. Earthquakes in Crete, according to statistics, do not exceed 5 points. With such a force, there are no devastating consequences, and the locals do not pay attention to this shaking at all. On the graph, you can see the number of registered seismic shocks by month with a magnitude above 1 point. It can be seen that in recent years their intensity has increased somewhat. 
Earthquakes in Italy
The country is located in a zone of seismic activity on the territory of the same tectonic fault as Greece. Earthquake statistics in Italy over the past 5 years show an increase in the number of monthly shocks from 700 to 2000. In August 2016, a strong earthquake of magnitude 6.2 occurred. That day claimed the lives of 295 people, more than 400 were injured.
In January 2017, another earthquake of magnitude less than 6 took place in Italy, and there were almost no victims of the destruction. However, a push has caused in the province of Pescara. The hotel Rigopiano was buried under it, killing 30 people.
There are resources where earthquake statistics are displayed online. For example, the organization IRIS (USA), engaged in the collection, systematization, study and distribution of seismological data, presents a monitor of this type: 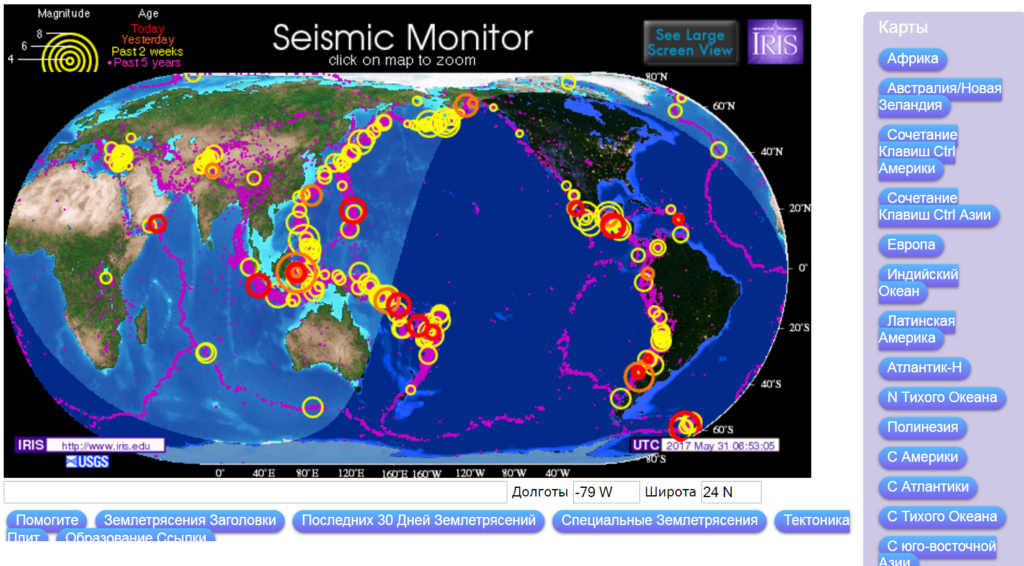 Information is available on the site that displays the presence of earthquakes on the planet at the moment. Here their magnitude is shown, there is information for yesterday, as well as events 2 weeks or 5 years ago. You can consider in more detail the parts of the planet of interest by selecting the appropriate map from the list.
Information is available on the site that displays the presence of earthquakes on the planet at the moment. Here their magnitude is shown, there is information for yesterday, as well as events 2 weeks or 5 years ago. You can consider in more detail the parts of the planet of interest by selecting the appropriate map from the list.
The situation in Russia
According to the statistics of earthquakes in Russia and the OSR (General Seismic Zoning) map, more than 26% of the area in the country is located in seismically hazardous zones. There may be shocks from 7 points. This includes Kamchatka, the Baikal region, the Kuriles, Altai, the North Caucasus and the Sayan Mountains. There are about 3,000 villages, about 100 thermal power plants and hydroelectric power stations, 5 nuclear power plants and enterprises of increased environmental danger.
Krasnodar region
There are about 28 districts of the region in the zone, of which there are approximately 4 million people. Among them is the large resort city of Sochi - according to earthquake statistics, the last seismic activity above 4 points was recorded in the fall of 2016. The Kuban is mostly located in the zone of 8–10 magnitude earthquakes (MSK-64 scale). This is the highest seismic hazard index throughout the Russian Federation.
The reason is the resumption of tectonic processes in 1980. Earthquake statistics in the Krasnodar Territory annually record about 250 seismic shocks of more than 2 points. Since 1973, 130 of them have been a strength of 4 points. Tremors with a magnitude of more than 6 points are recorded once every 5 years, and above 7 - once every 11 years. 
Irkutsk
Due to its location near the Baikal Rift, Irkutsk's earthquake statistics record up to 40 minor shocks every month. In August 2008, seismic activity with a magnitude of 6.2 was recorded. The epicenter was in Lake Baikal, where the indicator reached 7 points. Some buildings cracked, but no significant damage or casualties were recorded. In February 2016, another earthquake of magnitude 5.5 occurred.
Yekaterinburg
Despite the fact that the growth of the Ural Mountains has long ceased, the statistics of earthquakes in Yekaterinburg continues to be replenished with new data. In 2015, a 4.2 magnitude shock was recorded there, no one was injured.
Conclusion
Between the end of 2008 and 2011, there was a decrease in seismic activity on the planet, to a level of less than 2,500 cases per month and a magnitude above 4.5. However, after the earthquake in Japan in 2011, in the period from 2011 to 2016, there is a tendency to increase the activity of tremors around the world by almost 2 times. Earthquake statistics for recent years are as follows:
- tremors from 8 points and above - 1 time / year;
- from 7 to 7.9 points - 17 times / year;
- from 6 to 6.9 - 134 times / year;
- from 5 to 5.9 - 1319 times / year.
 Predicting earthquakes is very difficult. Often you can say with certainty where it will happen, but when exactly it will happen is impossible to determine. However, there are biological precursors. On the eve of a strong earthquake, other representatives of the fauna living in this area begin to behave abnormally.
Predicting earthquakes is very difficult. Often you can say with certainty where it will happen, but when exactly it will happen is impossible to determine. However, there are biological precursors. On the eve of a strong earthquake, other representatives of the fauna living in this area begin to behave abnormally.
Most of the largest earthquakes follow the same scenario: rigid plate structures, consisting of the earth's crust and mantle, move by colliding with each other. In total, there are 7 largest plates in the world: Antarctic, Eurasian, Indo-Australian, North American, Pacific and South American.
Over the past two billion years, the movement of the plates has accelerated significantly, which, accordingly, increased the chances of such a catastrophe. On the other hand, based on studies of the movement of tectonic plates, scientists can, albeit approximately, predict the appearance of the next major earthquake. Based on publicly available data, we have estimated a list of cities where the likelihood of such an event is very high right now.
San Francisco
A powerful earthquake with an epicenter in the Santa Cruz Mountains, about a hundred kilometers from the city of San Francisco, is just around the corner. More specifically, over the next couple of years. However, most of the inhabitants of the City by the Bay prepared for the catastrophe, having stocked up for the future with medicines, drinking water and food. In turn, the city authorities are busy with the fact that they urgently carry out work to strengthen buildings.
Fremantle
Fremantle is a port city located on the west coast of Australia. According to seismological research by specialists from the University of Sydney, from the end of 2016 to 2024, a strong earthquake of about 6 on the Richter scale is expected there. However, the main danger is that the shock could occur at the bottom of the ocean near the city, causing a tsunami.
Tokyo
According to experts, a major earthquake with an epicenter in the Japanese capital with a probability of 75% can occur at any time within the next 30 years. According to the model created by scientists, about 23 thousand people will become a victim of the disaster and over 600 thousand buildings will be destroyed. In addition to improving the seismic resistance of buildings and demolishing old structures, the Tokyo administration will introduce non-combustible building materials. The 1995 Kobe earthquake showed the Japanese that people are more likely to fall victim not to collapsed buildings, but to post-disaster fires.
Los Angeles
Earthquakes in the City of Angels happen quite often, but there have been no truly large ones for more than a century. The more gloomy is the forecast presented by seismologists and geologists from the US Geological Society. Based on the analysis of soils and tectonic plates under central California, scientists concluded that before 2037 an earthquake of magnitude 6.7 could occur here. A push of such force, under certain circumstances, can turn a city into ruins.
Panama
Over the next few years, a powerful earthquake, with a power of more than 8.5 on the Richter scale, will occur in the area of the Isthmus of Panama. These conclusions were made by specialists from the University of San Diego, after they conducted seismological studies of faults adjacent to the Panama Canal. The action of an earthquake of truly catastrophic proportions will be felt by the inhabitants of both Americas. And most of all, of course, the capital of the republic, Panama, where about 1.5 million people live, will suffer.
Petropavlovsk-Kamchatsky
A strong earthquake in the medium term, that is, in the next 4-5 years, will occur in the area of Petropavlovsk-Kamchatsky. Such data were reported in the seismology department of the Schmidt Institute of Physics of the Earth. In connection with this forecast, work is underway to strengthen buildings in Kamchatka, and the Ministry of Emergency Situations checks the seismic resistance of buildings. In addition, a network of stations was organized to monitor the symptoms of an approaching earthquake: high-frequency fluctuations in the earth's crust, water levels in wells, fluctuations in magnetic fields.
Grozny
According to the same department of seismology, a major earthquake in the period from 2017 to 2036. may occur in the North Caucasus, on the border of Chechnya and Dagestan. In contrast to the situation in Kamchatka, no work is being carried out to reduce the possible damage from earthquakes, which can lead to a greater number of human casualties than if such work were carried out.
New York
New research results by American seismologists from Columbia University indicate a high seismic hazard at the present time in the vicinity of New York. The magnitude of the earthquake could reach five points, which could lead to the complete destruction of old buildings in the city. Another cause for concern was the nuclear power plant, located right at the intersection of two faults, ie. in an extremely dangerous region. Its destruction could make New York a second Chernobyl.
Banda Aceh
Indonesia is located in the most seismically active zone of the planet, and therefore you will not surprise anyone here with earthquakes. In particular, the island of Sumatra, constantly turns out to be almost right at the epicenter of tremors. An exception will not be a new earthquake predicted by seismologists, with an epicenter 28 km from the city of Banda Aceh, which will occur in the next six months.
Bucharest
The strongest earthquake in Romania can be provoked by blasting in shale rocks carried out in the Carpathian Mountains. Geophysicists from the Romanian National Institute report that the epicenter of the future earthquake will be in the same place, at a depth of 40 kilometers. The fact is that work to search for shale gas in these layers of the earth can cause displacements of the earth's crust and, as a result, earthquakes.
The strongest earthquakes throughout the history of mankind caused enormous material damage and caused a huge number of casualties among the population. The first mention of tremors date back to 2000 BC.
And despite the achievements of modern science and the development of technology, no one still can predict the exact time when the elements will strike, so it often becomes impossible to quickly and timely evacuate people.
Earthquakes are natural disasters that kill the most people, much more than, for example, hurricanes or typhoons.
In this rating, we will talk about the 12 most powerful and destructive earthquakes in the history of mankind.
12. Lisbon
November 1, 1755, in the capital of Portugal, the city of Lisbon, there was a strong earthquake, later called the Great Lisbon Earthquake. It was a terrible coincidence that on November 1, All Saints Day, thousands of residents gathered for mass in the churches of Lisbon. These churches, like other buildings throughout the city, could not withstand the powerful shocks and collapsed, burying thousands of unfortunate people under their rubble.
Then a 6-meter tsunami wave poured into the city, covering the survivors, rushing in panic along the streets of the destroyed Lisbon. The destruction and loss of life was enormous! As a result of the earthquake, which lasted no more than 6 minutes, caused by a tsunami and numerous fires that engulfed the city, at least 80,000 residents of the capital of Portugal died.
Many famous figures and philosophers dealt with this deadly earthquake in their works, for example, Immanuel Kant, who tried to find a scientific explanation for such a large-scale tragedy.
11. San Francisco

On April 18, 1906, at 5:12 am, powerful tremors shook the sleeping San Francisco. The force of the shocks was 7.9 points and as a result of a strong earthquake in the city, 80% of the buildings were destroyed.
After the first count of the dead, the authorities reported 400 victims, but later their number increased to 3,000 people. However, the main damage to the city was caused not by the earthquake itself, but by the monstrous fire caused by it. As a result, more than 28,000 buildings were destroyed throughout San Francisco, and property damage amounted to more than $ 400 million at the rate of that time.
Many residents themselves set fire to their dilapidated houses, which were insured against fire, but not against earthquakes.
10. Messina

The largest earthquake in Europe was the earthquake in Sicily and Southern Italy, when on December 28, 1908, as a result of the most powerful tremors with a force of 7.5 on the Richter scale, according to various experts, from 120 to 200,000 people died.
The epicenter of the disaster was the Strait of Messina, located between the Apennine Peninsula and Sicily, the city of Messina suffered the most, where there was practically not a single surviving building left. A huge tsunami wave, caused by tremors and reinforced by an underwater landslide, also brought a lot of destruction.
Documented fact: rescuers were able to pull two malnourished, dehydrated, but alive children from the rubble, 18 days after the disaster! Numerous and extensive destruction was caused primarily by the poor quality of buildings in Messina and other parts of Sicily.
Russian sailors of the imperial fleet provided invaluable assistance to the inhabitants of Messina. The ships as part of the training group sailed the Mediterranean and on the day of the tragedy ended up in the port of Augusta in Sicily. Immediately after the tremors, the sailors organized a rescue operation and thanks to their courageous actions, thousands of residents were saved.
9. Haiyuan

One of the deadliest earthquakes in human history was the devastating earthquake that hit Haiyuan County in Gansu Province on December 16, 1920.
Historians estimate that at least 230,000 people died that day. The strength of the tremors was such that entire villages disappeared in the faults of the earth's crust, such large cities as Xi'an, Taiyuan and Lanzhou were very badly damaged. Incredibly, but strong waves formed after the impact of the elements were recorded even in Norway.
Modern researchers believe that the death toll was much higher and totals at least 270,000 people. At that time, it was 59% of the population of Haiyuan County. Several tens of thousands of people died from the cold after their homes were destroyed by the elements.
8. Chile

The earthquake in Chile on May 22, 1960, is considered the strongest earthquake in the history of seismology, the magnitude of the tremors was 9.5 on the Richter scale. The earthquake was so powerful that it caused tsunami waves over 10 meters high, covering not only the coast of Chile, but also causing great damage to the city of Hilo in Hawaii, and some of the waves reached the coast of Japan and the Philippines.
More than 6,000 people died, most of them hit by the tsunami, the destruction was unimaginable. 2 million people were left without housing and shelter, and the amount of damage amounted to more than 500 million dollars. In some areas of Chile, the impact of the tsunami wave was so strong that many houses were blown 3 km inland.
7. Alaska

On March 27, 1964, the most powerful earthquake in American history hit Alaska. The strength of the rumors was 9.2 on the Richter scale and this earthquake became the strongest since the elements struck in Chile in 1960.
129 people died, of which 6 were unfortunate victims of the tremors, the rest were washed away by a huge tsunami wave. The elements caused the greatest destruction in Anchorage, and tremors were registered in 47 US states.
6. Kobe

The earthquake in Kobe, Japan on January 16, 1995 was one of the most devastating in history. Tremors with a force of 7.3 began at 05:46 am local time and continued for several days. As a result, more than 6,000 people died, 26,000 were injured.
The damage done to the infrastructure of the city was simply enormous. More than 200,000 buildings were destroyed, 120 out of 150 berths were destroyed in the port of Kobe, and there was no power supply for several days. The total damage from the impact of the elements amounted to about 200 billion dollars, which at that time was 2.5% of Japan's total GDP.
Not only government services rushed to help the affected residents, but also the Japanese mafia - the yakuza, whose members delivered water and food to the victims of the disaster.
5. Sumatra

On December 26, 2004, the strongest tsunami that hit the coasts of Thailand, Indonesia, Sri Lanka and other countries was caused by a devastating earthquake measuring 9.1 on the Richter scale. The epicenter of the tremors was in the Indian Ocean, near the island of Simeulue, off the northwestern coast of Sumatra. The earthquake was unusually large, there was a shift of the earth's crust at a distance of 1200 km.
The height of the tsunami waves reached 15-30 meters and according to various estimates, from 230 to 300,000 people became victims of the disaster, although it is impossible to calculate the exact number of deaths. Many people were simply washed away into the ocean.
One of the reasons for this number of victims was the lack of an early warning system in the Indian Ocean, with which it was possible to inform the local population about the approaching tsunami.
4. Kashmir

On October 8, 2005, in the Kashmir region, which is under the control of Pakistan, there was the strongest earthquake in South Asia in the last hundred years. The force of the tremors was 7.6 on the Richter scale, which is comparable to the San Francisco earthquake in 1906.
According to official data, 84,000 people died as a result of the disaster, according to unofficial data, more than 200,000. Rescue work was hampered by the military conflict between Pakistan and India in the region. Many villages and villages were completely wiped off the face of the earth, and the city of Balakot in Pakistan was also completely destroyed. In India, 1300 people became victims of the earthquake.
3. Haiti

On January 12, 2010, an earthquake measuring 7 on the Richter scale hit Haiti. The main blow fell on the capital of the state - the city of Port-au-Prince. The consequences were terrible: almost 3 million people were left homeless, all hospitals and thousands of residential buildings were destroyed. The number of victims was simply enormous, according to various estimates from 160 to 230,000 people.
Criminals who escaped from the prison destroyed by the elements poured into the city, cases of looting, robberies and robberies became frequent on the streets. The material damage from the earthquake is estimated at 5.6 billion dollars.
Despite the fact that many states - Russia, France, Spain, Ukraine, the USA, Canada and dozens of others - provided all possible assistance in eliminating the consequences of the elements of Haiti, more than five years after the earthquake, more than 80,000 people still live in makeshift camps for refugees.
Haiti is the poorest country in the western hemisphere and this natural disaster dealt an irreparable blow to the economy and the standard of living of citizens.
2. Earthquake in Japan

On March 11, 2011, the strongest earthquake in Japanese history struck the Tohoku region. The epicenter was located east of the island of Honshu and the strength of the tremors was 9.1 on the Richter scale.
As a result of the disaster, the nuclear power plant in the city of Fukushima was badly damaged and power units at reactors 1, 2, and 3 were destroyed. Many areas became uninhabitable as a result of radioactive radiation.
After underwater tremors, a huge tsunami wave covered the coast and destroyed thousands of administrative and residential buildings. More than 16,000 people died, 2,500 are still considered missing.
The material damage also turned out to be colossal - more than 100 billion dollars. And given that it may take years to completely restore the destroyed infrastructure, the amount of damage can increase several times.
1. Spitak and Leninakan

There are many tragic dates in the history of the USSR, and one of the most famous is the earthquake that shook the Armenian SSR on December 7, 1988. The most powerful tremors in just half a minute almost completely destroyed the northern part of the republic, capturing the territory where more than 1 million inhabitants lived.
The consequences of the disaster were monstrous: the city of Spitak was almost completely wiped off the face of the Earth, Leninakan was badly damaged, more than 300 villages were destroyed and 40% of the industrial capacities of the republic were destroyed. More than 500 thousand Armenians were left homeless, according to various estimates, from 25,000 to 170,000 people died, 17,000 citizens were left disabled.
111 states and all the republics of the USSR provided assistance in the restoration of destroyed Armenia.





