Shoulder dislocation treatment after medication reduction. What is a dislocation of the shoulder joint (shoulder) and what procedures are used to treat it. Joint reduction methods in the hospital
Shoulder dislocation is a fairly serious, and usually reversible, joint injury. An injury requires urgent and qualified medical assistance. Depending on the type of pathology, the cause and prescription of the displacement, as well as the presence or absence of complications, the tactics of medical care and further treatment at home are built. Delay in the provision of qualified assistance can lead to the development of chronic or habitual dislocation of the shoulder joint, which will require surgery.
According to medical statistics, dislocation of the head of the shoulder is quite common. This is due to the anatomical structure of the joint. Being spherical in its configuration, the joint is designed to perform movements in various planes, which is the reason for its instability.
Initially, shoulder dislocations are divided into congenital and acquired.
Congenital misalignments of the shoulder joint are uncommon and are usually associated with hip dysplasia in infants. During birth, the child receives a birth injury, in which the head of the humerus falls out of the articular bag. Identification and therapy of congenital displacements usually occurs in the delivery room immediately after the baby is born.
Acquired dislocation of the shoulder is much more common. It accounts for 80-85% of all damage to this joint. Pathology is divided into two types:
- Traumatic dislocation.
- Non-traumatic (habitual) dislocation.
In the direction of the shift of the head of the shoulder, there are:
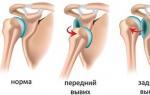
- anterior dislocation, in which the head of the humerus protrudes forward (most common);
- posterior dislocation is formed when the head goes back;
- lower dislocation, when the head moves down.

In addition, there is a division of injuries by statute of limitations:
- acute (3 days from the moment of damage);
- subacute (4 weeks from the date of dislocation);
- chronic (more than a month after the injury).
In children, subluxation of the shoulder joint is most often recorded when the ligaments are stretched, but the joint remains fixed in the articular bag. Such a displacement is usually easily reduced, so there are usually no negative consequences.
Any injury to the shoulder, accompanied by pain, swelling and changes in the configuration of the joint, requires urgent medical attention.
Subluxation and habitual dislocation
In medical practice, in addition to dislocation, two more types of joint displacement are often encountered:
- subluxation;
- habitual dislocation.
Subluxation
Subluxation is characterized not by the complete exit of the head from the articular bag, but only by a slight shift to the side. Such a pathology is not accompanied by rupture of ligaments and tendons or fracture of bones. The performance of the joint is partially preserved and quickly restored after reduction.
If the head of the bone periodically comes out of the joint capsule without visible traumatic damage, this condition is called habitual dislocation of the shoulder. Displacement can occur with a circular rotation of the arms or a simple raising of the limb up.
As a rule, this pathology occurs against the background of untimely or incorrect treatment of various kinds of injuries that lead to weakening of the ligaments and instability of the joint. In addition, structural features can become the cause of joint prolapse: a mismatch in the size of the articular bag and the head of the humerus, an overly stretched capsule, or weakness of the periarticular muscles. 
Often, slipping of the head of the shoulder is observed in athletes or in people performing monotonous, monotonous hand movements. In such patients, damage to the right shoulder joint is diagnosed much more often than the left one. A person can adjust the joint on their own by pulling the hand down or moving the hand to the side. However, without adequate therapy, the displacement of the joints occurs more and more often, acquiring a pathological character.
Delaying the treatment of habitual dislocation is very dangerous. With each prolapse of the head and subsequent reduction, the cartilage tissue is damaged, which leads to the formation of arthrosis.
As a rule, habitual dislocation is not amenable to conservative treatment. Therefore, the patient is offered a surgical operation.
Shoulder dislocation symptoms
Despite the variety of displacements of the shoulder joint, their symptoms are practically the same. Some difference in symptoms is observed only in acute and chronic forms of dislocation.
Acute injury is characterized by the following clinical picture:

Chronic (chronic) dislocations are characterized by intracavitary proliferation of connective tissue that fills the joint bag and nearby areas. Shoulder muscles atrophy and cease to perform their function. The primary displacement of the joint is always very painful, because the ligaments and the articular bag are torn. With repeated injuries, there is slight discomfort in the shoulder area, external deformation and limited movement in the damaged joint.
An old dislocation is very difficult to correct, since the connective tissue that has grown inside the articular cavity prevents the free return of the humeral head to its normal position. In this case, surgical intervention is necessary.
Diagnosis and first aid for shoulder dislocation
Diagnostic measures begin with the collection of an anamnesis, then an examination of the victim is carried out and a medical history is compiled. Then the patient is assigned an x-ray in two projections to clarify the diagnosis and exclude fractures. To determine the degree of damage to the ligaments and tendons, computed or magnetic resonance imaging is performed.
First aid
To provide first aid, it is necessary to immediately fix the injured arm by bending it at the elbow and securing it with a bandage. The victim should be taken to a medical facility as soon as possible for specialized care. It is strictly forbidden to adjust the shoulder on your own. 
Before being transported to the hospital, the patient should be given an anesthetic and immediately applied to the injury site with cold (stick ice, a cold compress, or a heating pad with ice water).
Methods for the treatment of dislocation of the shoulder joint, rehabilitation at home
The main goal of therapeutic measures is to restore the structure and performance of the joints. This is achieved through the following activities:
- joint fixation;
- reduction of dislocation, including with the help of a surgical operation;
- complete rehabilitation.
Reduction is carried out only by a qualified specialist in a hospital, after diagnostic measures and the use of local or general anesthesia.
Conservative treatment
Conservative therapy includes several types of reduction. In addition to the procedure are:

All these activities are carried out at home after the reduction procedure.
Today there are several types of closed joint reduction. Like any minor surgery, it should be performed by a traumatologist or a team of specialists. The following methods are the most effective and less traumatic:
- Kocher method;
- reduction according to the Dzhanilidze method;
- Hippocratic method;
- Mukhin-Mota technique (used for all types of displacement).
The traumatologist makes a reduction until a click is heard. This suggests that the head of the shoulder entered the glenoid cavity. The reduced joint must be immobilized with a tight bandage or orthosis. 
The intervention is carried out under the mandatory supervision of an anesthesiologist. The simplest and most effective way of anesthesia is the technique proposed by V.A. Meshkov.
If the patient is diagnosed with a habitual dislocation or there is an associated fracture, a surgical operation is prescribed. In case of traumatic displacement of the humerus, the intervention involves the elimination of dislocation, stitching together damaged tissues and combining bones. Then a plaster cast is applied to the affected joint, a plan of therapeutic measures is drawn up for the rehabilitation period.
To restore the structure and stability of the joints when diagnosing a habitual dislocation, the Bankart operation is used. The procedure is performed using an atroscope. During the intervention, the surgeon removes damaged tissues, if necessary, sutures the joint capsule. 
Extra-articular plastic surgery and strengthening of ligaments and tendons of periarticular muscles are very popular among specialists. In the course of treatment, the head of the shoulder is strengthened in a physiological position in order to prevent its subsequent displacement.
Another common method of surgical intervention is the Eden method or its variant proposed by Andina. During the procedure, the head of the shoulder is given a new shape, which maximizes its fixation in the articular bag.
All considered types of operations and their modifications give the least number of complications.
Treatment at home
When talking about therapy at home, this means a set of measures carried out at home after reduction, aimed at restoring the efficiency of the joint. All activities are carried out only on the prescription of the attending physician and under his supervision. Not bad conservative treatment to supplement.
The recovery period is divided into several stages, for each of which appropriate therapeutic measures have been developed.
First stage
The period begins 21 days after reduction and lasts no more than three months. During this time, damaged tissues heal and scars form in the area of the articular capsule and cartilaginous lip.
At the first stage of rehabilitation, the patient is prescribed simple warm-up movements in the wrist joint and joints of the hand of the affected limb, cold compresses on the affected area, taking painkillers and anti-inflammatory drugs, electrophoresis sessions with novocaine on the affected shoulder area.
Second stage of recovery
This period lasts 1-1.5 months and includes light warm-up movements of the shoulder in different directions. If pain occurs, all exercises must be stopped and rest for 2-3 days. After gymnastics, a cold compress is applied to the articulation area.
For a faster recovery of working capacity, the patient is prescribed physiotherapy sessions: magnetotherapy, UHF, electrophoresis with analgesics and anti-inflammatory drugs.
The third stage starts from 4–5 months after conservative or surgical intervention. At this time, the patient is allowed to increase the load on the arm. You can perform smooth abduction of the limb to the side, careful circular rotation of the shoulder. 
At a later stage of rehabilitation, it should include a variety of hand movements in all planes. Exercise is best done for 10-15 minutes several times a day. As the muscles and tendons strengthen, the patient is allowed to use dumbbells to increase the load. Sports equipment will help restore muscle strength and ligament elasticity.
Therapeutic gymnastics is a necessary measure during the rehabilitation period. It will help restore blood circulation and nutrition of cartilage and muscle tissues.
Careful adherence to the doctor's recommendations will allow the patient to fully recover no later than six months after the injury and not be afraid of re-dislocation of the shoulder joint. Competent treatment at home is designed to prevent such serious complications as arthrosis, arthritis, and also to eliminate possible joint contracture.
It just so happens that the most common dislocation faced by a person is a shoulder dislocation. And on the eve of summer holidays and active fun in nature, it is worth remembering what you need to do in case of shoulder dislocation, and what you should not do in any case.
How to build shoulders at home
Why does the shoulder "fly out"? Because nature, providing the mobility of the shoulder joint, sacrificed its strength. The large head of the humerus is placed in a very shallow cavity (capsule) of the joint, and the ligaments that hold them there are few and weak. Therefore, when falling on an arm extended to the side (football, volleyball, excessive alcohol addiction - there are a lot of reasons), the head of the shoulder simply pops out of the articular cavity.
If this happened, then the fate of your hand now depends on what kind of first aid you were given. If, after watching movies, someone tries to jerk your hand, trying to return the joint to its place, drive it away from you with all the remaining limbs, as a last resort - run away. Otherwise, you risk getting an injury worse than the one that has already happened - not only ligaments, tendons, but also nerves and blood vessels will be torn.
So it's better to follow the rules.
Rule one (providing assistance on the spot)
Fix the joint with a bandage or splint, and immediately go to the emergency room or hospital. There, an x-ray should be taken to rule out or confirm bone damage. Then, under local anesthesia, a gentle reduction of the dislocation will be performed and a plaster splint will be applied for 3 weeks. This is necessary to heal soft tissue ruptures.
It is impossible to remove the splint ahead of time on your own, even if nothing hurts, and even more so, you can’t start slowly “working out” the joint. As a result, the fragile capsule and ligaments do not withstand the load and you get a second dislocation. Over time, the joint becomes so loose that the dislocation turns from primary to habitual. The shoulder will fly out when putting on a coat and even when turning from side to side in bed. And it is possible to treat habitual dislocation only surgically.
Rule two (immobility 3 weeks)
When your joint has been immobilized (immobilized) with a splint, immediately start doing isometric exercises (without moving the joint) for the muscles surrounding the shoulder joint. Press the elbow bend of the splint against the wall or on the wrist of the other hand. Each tension lasts at first 1-2 seconds, but gradually this time increases to 6-8 seconds. Repeat until tired 2-3 times a day.
After the splint is removed, it is best to take a course of complex rehabilitation - electrical stimulation of the muscles of the hand, massage, therapeutic exercises, exercises in the water). If this is not done, then a repeated dislocation, and after it the usual one, will not keep you waiting.
Rule three (comprehensive rehabilitation)
The purpose of rehabilitation is not only to restore joint mobility, but also to prevent re-dislocations. Strengthen with the help of special exercises you need the whole complex of muscles of the hand. It is generally pointless to limit yourself to strengthening only the biceps, triceps and deltoid muscles known to everyone, it will tear where it is thin.
After all, the main role in stabilizing the shoulder joint belongs not to large muscles, but to small rotator muscles that turn the shoulder in and out. Their tendons braid the shoulder joint around the perimeter. So, it is best to spend money on a good rehabilitation doctor in a good center and then not know how to save money and periodically visit the trauma department of the clinic.
Thank you for your help in preparing the material. Department of Rehabilitation Therapy of the Moscow Scientific and Practical Center for Sports Medicine Mark Gershburg.
With a dislocation of the shoulder joint, the doctor may order a CT scan in the following cases:
- if radiography does not accurately determine the extent of joint damage;
- if a fracture of the humerus or scapula is suspected, which are not displayed on a conventional radiograph;
- with suspicion of damage to the vessels of the shoulder ( CT with contrast);
- when planning shoulder surgery.
Magnetic resonance imaging ( MRI)
Magnetic resonance imaging is a modern high-precision method for studying the internal organs and tissues of the body, which is considered absolutely safe and harmless to humans. The procedure itself is identical to computed tomography, but unlike CT, where X-rays are used to obtain an image, MRI uses the effect of nuclear magnetic resonance, which allows you to get more accurate images of soft tissues, ligaments, cartilage surfaces, joint capsules, blood vessels. The main advantage over CT is the complete absence of radiation, so the only contraindication for MRI is the presence of metal parts in the patient's body ( implants, metal fragments after injuries).Indications for MRI with dislocation of the shoulder joint:
- clarification of the results of conventional radiography in the presence of contraindications to CT;
- doubtful data obtained from CT;
- determination of the volume of damage to periarticular tissues ( rupture of the joint capsule, ligaments, muscles);
- for the diagnosis of compression of the vessels of the shoulder ( no contrast needed).
Ultrasonography ( ultrasound) shoulder joint
Ultrasound is a modern, safe examination method based on the use of ultrasonic waves. This study is usually ordered when fluid accumulation is suspected ( blood) in the cavity of the shoulder joint. However, according to ultrasound data, the nature of the lesion of periarticular tissues can also be determined ( ruptures of the capsule, ligaments, muscles), and when using ultrasound in Doppler mode ( a mode that allows you to judge the speed and quality of blood flow) the presence and degree of compression of the shoulder vessels can be determined.First aid for suspected shoulder dislocation
 First aid for suspected dislocation of the shoulder should be to limit movements in the area of the damaged joint, eliminate the traumatic factor, and seek medical help in a timely manner.
First aid for suspected dislocation of the shoulder should be to limit movements in the area of the damaged joint, eliminate the traumatic factor, and seek medical help in a timely manner. If a shoulder dislocation is suspected, the following steps should be taken:
- ensure complete rest of the joint ( stop all movement);
- apply ice or any other cold ( reduces inflammation and tissue swelling);
- call an ambulance.
Do I need to call an ambulance?
If you suspect a dislocation of the shoulder joint, it is recommended to call an ambulance, since, firstly, the ambulance doctor can relieve the pain of the victim, and secondly, it can eliminate some serious complications. However, provided there are no signs of damage to the nerves or blood vessels, you can do without calling an ambulance. However, it should be understood that the treatment of dislocation can only be carried out in a medical institution and only by qualified personnel. Thus, if after an injury that caused a dislocation of the joint, the patient's condition is stable and an ambulance was not called, you should contact the local trauma center as soon as possible. It should be borne in mind that the sooner the dislocation is reduced, the higher the chances of a full restoration of joint function.What is the best position for the patient?
The victim must provide maximum rest to the damaged joint. This is achieved by positioning the free upper limb in the abduction position ( posterior dislocation adduction). At the same time, the forearm is bent at the level of the elbow and rests on a roller pressed against the side of the body. In this case, to ensure complete immobility, it is recommended to use a bandage that supports the arm ( a triangular kerchief into which the forearm is placed and which is tied around the neck).It is not recommended to lean or rest on the injured shoulder or free upper limb, as this can provoke even greater displacement of the articular surfaces, rupture of the ligamentous apparatus and damage to the vascular bundle.
Is it necessary to give pain medication?
Self-administration of medications is not recommended, however, if it is impossible to get prompt medical care, the victim can take some painkillers, thereby reducing negative experiences from pain. In most cases, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs should be used, which, due to their effect on the synthesis of certain biologically active substances, can reduce the intensity of pain.You can take the following drugs:
- paracetamol at a dose of 500 - 1000 mg ( one or two tablets);
- diclofenac in a daily dose of 75 - 150 mg;
- ketorolac at a dose of 10 - 30 mg;
- ibuprofen in a daily dose of up to 1200 - 2400 mg.
Shoulder dislocation treatment

How is a dislocation reduced?
There are more than 50 ways to reduce a dislocated shoulder. Regardless of the chosen reduction technique, the patient needs sedation ( drug sedation) and anesthesia, which are achieved by introducing 1-2 ml of a 2% solution of promedol intramuscularly and intra-articular injection of 20-50 ml of a 1% solution of novocaine. Thanks to the action of these drugs, partial muscle relaxation is achieved, which facilitates reduction and eliminates the risk of damage to tendons and muscles.In trauma practice, the following methods of reduction of shoulder dislocation are used:
- Reduction according to Dzhanelidze. The classical method of Janelidze is based on the gradual relaxation of the muscles. It is the least traumatic and therefore the most preferred in modern traumatology. The patient is placed in the supine position on a flat horizontal surface ( couch, table), so that the dislocated limb hangs down from the edge of the table. A sandbag or towel is placed under the shoulder blade to ensure its tighter fit to the surface. The patient’s head is held by an assistant, but you can do without him by placing the victim’s head on a small table, bedside table or a special Trubnikov tripod. After about 15-25 minutes, novocaine blockade relaxes the muscles of the shoulder girdle and, under the influence of gravity, the head of the humerus approaches the glenoid cavity of the scapula. In some cases, reduction may occur on its own. If this does not happen, the traumatologist takes a position in front of the patient, bends his hanging arm in the elbow joint at an angle of 90 degrees, with one hand presses down on the forearm in the area of the elbow bend, while with the other hand, covering the patient’s forearm at the hand, rotates in the shoulder joint outward and then inward. The moment of reduction is accompanied by a characteristic click.
- Reduction according to Kocher. This method is more traumatic than the previous one and is used for anterior dislocations of the shoulder in physically strong individuals, with stale dislocations. The patient is in the supine position. The traumatologist grabs the limb by the lower third of the shoulder at the wrist joint, bends it at the elbow joint to an angle of 90 degrees, and carries out traction along the axis of the shoulder, bringing the limb to the body. The assistant at this time fixes the patient's shoulder girdle. While maintaining traction along the axis of the shoulder, the traumatologist brings the elbow as far forward and medially as possible, and then, without changing the position of the limb, rotates the shoulder inward, while the hand of the injured limb moves to a healthy shoulder joint, and the forearm lies on the chest. When the dislocation is reduced, a characteristic click is felt. After that, a plaster splint is applied with a hanging bandage and a gauze roller. After removing the splint, the patient is prescribed a physiotherapy complex of exercises in order to restore the tone of the muscles that fix the articular bag.
- Reduction according to Hippocrates. This method is considered the most ancient and simple, along with the Cooper method. The patient is in the supine position. The traumatologist sits or stands facing the patient from the side of the dislocation and grabs the forearm in the area of the wrist joint with both hands. The doctor places the heel of his open leg, the same name as the victim's dislocated arm, in his armpit and presses on the head of the humerus that has shifted into it, simultaneously stretching the arm along the axis. The displaced head of the humerus is reduced into the articular cavity. Traction ( tension) is made along the body.
- Cooper method. The patient is in a sitting position on a stool or a low chair. Putting his foot on the same stool or chair, the traumatologist puts his knee into the armpit, the dislocated arm is captured with both hands in the wrist area, the shoulder is simultaneously traction down and the dislocated head of the humerus is pushed up with the knee.
- Chaklin method. The patient is in the supine position, the traumatologist grabs the outer third of the pre-bent forearm with one hand and abducts and tractions the limb along its axis, with the other hand, pressure is applied to the head of the humerus in the axillary fossa.
- Shulyak method. Produced by two traumatologists. The patient is in the supine position. The first of them rests his forearm against the lateral surface of the chest so that his fist looks into the axillary region and comes into contact with the dislocated head of the humerus, and the second traumatologist performs traction while bringing the arm to the body. The emphasis of the head in the fist and the adduction of the limb creates a lever that promotes reduction.
Do I need to immobilize the hand after reduction?
After reduction for 3 weeks, immobilization is necessary ( immobilization) of the injured limb, in order to minimize movement in the affected joint and thus provide complete rest and optimal conditions for healing and recovery. Without proper immobilization, the healing process of the joint capsule and ligamentous apparatus can be disrupted, which is fraught with the development of habitual dislocations.In the presence of associated fractures of the humerus, clavicle, or scapula, much longer immobilization may be required ( from 2 - 3 weeks to several months), which will depend on the type of fracture, the degree of displacement of bone fragments, and also on the way these fragments are compared ( surgical or conservative).
Surgical treatment of dislocation of the shoulder joint
The main indication for surgical intervention is the formation of habitual dislocation or chronic instability of the head of the humerus. In connection with repeated and habitual dislocations, the joint capsule is stretched, hypermobility and instability appear. The pockets formed in the capsule become habitual places for the head of the shoulder to slip off.Surgical treatment has the following goals:
- restoration and strengthening of the ligamentous apparatus;
- comparison of the articular cavity of the scapula with the head of the humerus;
- elimination of the habitual dislocation of the shoulder.
- Operation Turner. The Turner operation is a minimally invasive operation, that is, it is performed by introducing a special optical instrument and a number of small manipulators into the joint area through several small skin incisions. The meaning of the operation is to excise the elliptical flap of the capsule in the region of the lower pole, followed by tight suturing of the articular capsule. The operation is complicated by the proximity of the neurovascular bundle. The main advantage of this operation is minimal injury to soft tissues, a relatively small cosmetic defect ( a small, barely noticeable scar forms in the incision area) and rapid recovery after the intervention.
- Operation Putti. The Putti operation is more traumatic than the Turner operation, but it is used in the absence of the necessary equipment, as well as in the need for wider access in the presence of associated injuries. With this intervention, a T-shaped incision is made to access the shoulder joint, followed by dissection of a number of muscles. During the operation, the capsule is sutured, which significantly strengthens it. The operation is extremely traumatic and requires a long recovery period.
- Operation Boychev. Boychev's operation is in many ways similar to Putti's operation. It also involves a wide T-shaped incision of the skin, followed by dissection of the underlying muscles. However, with this intervention, the joint capsule is sutured after the preliminary removal of a small triangular fragment - this allows not to increase the thickness of the capsule.
- Operation Bankart. The Bankart operation is a minimally invasive operation during which a special instrument is inserted into the joint cavity ( arthroscope), which stabilizes the shoulder joint. Thanks to this intervention, it is possible to achieve a comprehensive elimination of several factors that implement dislocation of the head of the humerus and recovery in the shortest possible time. However, due to the lack of necessary equipment and sufficient qualifications of doctors, this operation is not widely used in modern traumatology.
Therapeutic exercises after reduction of dislocation
Immediately after reduction of the dislocation for 4-6 weeks, immobilization of the shoulder joint is indicated using a special bandage ( Deso bandage). During this time, movements in the shoulder joint should be avoided, however, in order to prevent atrophy of the muscles of the arm and to improve blood circulation in the relevant area, some light exercises with movement in the wrist are recommended.Within a month after the reduction of the dislocation, it is recommended to practice the following exercises:
- brush rotation;
- clenching fingers into a fist without load ( exercises with a carpal expander can provoke muscle contractions in the shoulder area with a violation of the immobilization regimen);
- static contraction of the shoulder muscles ( a short tension of the biceps, triceps muscles of the shoulder, as well as the deltoid muscle, improves blood circulation and maintains tone).
4 to 6 weeks after the reduction of the dislocation, the following exercises are recommended:
- joint flexion ( forward shoulder movement);
- joint extension ( back shoulder movement).
These gymnastic exercises should be repeated 5-6 times a day for half an hour at a slow pace. This allows you to restore the function of the joint in the most sparing and optimal mode and ensure the most complete restoration of the ligamentous apparatus.
5-7 weeks after the reduction of the dislocation, the immobilizing bandage is removed completely. At this stage, the importance of therapeutic exercises is extremely high, since properly selected exercises allow you to restore joint mobility without the risk of damage to the joint capsule, muscles and ligaments.
The task of therapeutic exercises in the period of joint recovery is:
- restoration of range of motion in the shoulder joint;
- strengthening of muscle structures;
- elimination of adhesions;
- joint stabilization;
- restoration of the elasticity of the joint capsule.
- active abduction and adduction of the shoulder;
- external and internal rotation of the shoulder.
Physiotherapy after reduction of dislocation
Physiotherapy is a set of measures aimed at restoring the structure and function of the joint and its stabilization, which are based on various methods of physical impact.Through the influence of physical factors ( heat, direct or alternating electric current, ultrasound, magnetic field, etc.) achieve various therapeutic effects, which, to one degree or another, contribute to the acceleration of healing and recovery.
Physiotherapy has the following effects:
- eliminate tissue edema;
- reduce the intensity of pain;
- promote the resorption of blood clots;
- improve local blood circulation;
- improve tissue oxygen saturation;
- activate the protective reserves of the body;
- accelerate recovery and healing;
- facilitate the delivery of drugs to the affected area.
Physiotherapy used to treat shoulder dislocation
| Type of procedure | Mechanism of therapeutic action | Contraindications | Duration of treatment |
| High Intensity Pulsed Magnetic Therapy | The impact is based on the occurrence of a torque for biological molecules under the influence of a magnetic field. This leads to a change in the permeability of cell membranes, to an increase in a number of anabolic and catabolic reactions, to an intensification of the oxidation of free radicals. The result is a significant anti-inflammatory effect. It should be noted that this type of physiotherapy has the most pronounced analgesic effect, which is established after the first session ( or during the first two or three procedures). In addition, magnetotherapy stimulates the regeneration of damaged tissues, providing a pronounced healing effect. | With low blood pressure, with blood pathologies, with a tendency to form blood clots, with bone fractures until the fragments are stabilized. | 6 - 10 procedures for 10 - 15 minutes each. |
| Low intensity pulsed magnetotherapy | It is based on a change in the electronic potential of biological molecules, which leads to an increase in metabolism, an acceleration of redox reactions, and an increase in the permeability of biological membranes. The local and general protective potential increases due to the stimulation of antibody production, the activity of the autonomic nervous system stabilizes. An anti-inflammatory effect develops. The swelling of tissues in the affected area decreases, the growth and regeneration of damaged areas improves. | During bleeding, with low blood pressure, in the presence of metal implants and a pacemaker. | 10 - 15 procedures for half an hour daily. |
| diadynamic therapy | It is based on the impact on the body of pulsed currents with a frequency of 50 - 100 Hz. These currents irritate the peripheral nerve endings, which leads to disruption of the conduction of pain signals. Impact on the vegetative ( autonomous) the nervous system leads to the expansion of peripheral capillaries with improved blood circulation at the level of peripheral tissues. An analgesic effect develops, local blood circulation improves significantly, the processes of nutrition and respiration of tissues are normalized. During exposure to currents, muscle contraction of the skeletal muscles occurs, which maintains its tone. | In the presence of purulent diseases of the skin and subcutaneous fatty tissue, with bleeding, epilepsy, in the presence of pacemakers. | 9 - 10 daily sessions. |
| inductothermy | It is a method of influencing tissues using a high-frequency magnetic field. Under the action of the eddy currents formed in this field, tissues are heated to a depth of about 5–10 cm. This leads to the fact that blood circulation improves in the corresponding area, tissue respiration and nutrition increase, and the immune system normalizes. An analgesic, anti-inflammatory effect develops. With repeated exposure, muscle spasm is eliminated, the function of skeletal muscles improves. | With malignant tumors, inflammatory diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, during pregnancy, as well as with tuberculosis and during myocardial infarction. | 10 procedures for 10 - 20 minutes each. |
| Applications with paraffin | They allow you to evenly and for a long time warm up the damaged areas of the body. This improves tissue nutrition, normalizes blood circulation, reduces swelling and inflammation. | In acute infectious and inflammatory diseases, diseases of the kidneys and blood, as well as in malignant tumors. | 10 procedures for 25 - 30 minutes each. |
| Local cryotherapy | It is based on short-term exposure to cold air ( temperature down to minus 30 degrees) on the injured part of the body. As a result, local metabolism slows down, oxygen consumption decreases. In deeper tissues, a reflex reaction occurs, which is aimed at normalizing the work of the corresponding area and protecting against possible damage. Thus, under the influence of low temperature, the healing process is accelerated, immunity function is normalized, and blood circulation improves. | In diseases of the peripheral vessels, as under the influence of cold, a spasm may occur with impaired blood circulation in the peripheral tissues. In addition, this physiotherapy is contraindicated for children under five years of age. | 10 daily treatments, each taking five to ten minutes. |
Physiotherapy procedures are a fairly effective method of additional treatment, which allows you to speed up the recovery process and is able to eliminate some unwanted symptoms without the use of pharmacological drugs. However, it should be understood that, like any other medical procedures and means, physiotherapy has a number of side effects and contraindications. For this reason, all of them must be agreed with the attending physician.
It should be noted that physiotherapy cannot cure a dislocated joint without appropriate reduction or surgery. The combination of various physiotherapy procedures with therapeutic exercises allows you to achieve a speedy recovery and return to normal daily activities.
Answers to frequently asked questions
What is a habitual shoulder dislocation?
A habitual dislocation of the shoulder is a pathological situation in which, under the influence of a traumatic factor of low intensity or as a result of contraction of the own muscles of the shoulder girdle, repeated dislocations occur in the shoulder joint. In other words, a habitual dislocation is such a dislocation of the shoulder, which subsequently occurs again.The shoulder joint is the most mobile joint in the human body. This articulation allows movement in three mutually perpendicular planes with a fairly large amplitude, and due to the non-rigid connection of the upper limb belt with the body, the free limb can perform even more movements than the joint provides.
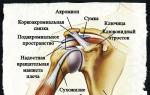
It is the shoulder joint that is the key element in the movement of the free upper limb. This structure is formed by two bones and a number of connective tissue ligaments, which, due to their tension, stabilize and strengthen the joint.
The shoulder joint is formed by the following anatomical structures:
- Shoulder blade. On the lateral surface of the scapula there is an articular notch, along the perimeter of which there is an articular lip, which is involved in the formation of the shoulder joint. Due to the presence of a cartilaginous articular lip, the area of the articular surface slightly increases without loss of possible movements. The labrum helps stabilize the joint by preventing the head of the humerus from sliding back and forth.
- Brachial bone. The head of the humerus is spherical, due to which it is able to rotate in all planes. Normally, it is in contact with the articular notch of the scapula. The area of the head of the humerus is much larger than the area of the articular notch, which allows to increase the range of motion in the joint, but which reduces the strength of the joint itself.
- Articular bag. The joint bag is a connective tissue capsule stretched between the lateral surfaces of the articular notch of the scapula and the anatomical neck of the shoulder, which closes the joint space. It maintains the anatomical integrity of the joint by providing some tension to the elastic fibers, as well as by maintaining negative pressure within the joint.
- Shoulder ligaments. The shoulder joint strengthens a relatively small number of ligaments, which allows it to maintain a large degree of mobility.
Habitual dislocation is accompanied by a slightly poorer clinical picture than the first one. However, in most cases there is a deformity of the shoulder with displacement of the head of the humerus anteriorly or posteriorly. The pain syndrome may initially be severe, but over time, its intensity decreases.
Treatment of habitual dislocation of the shoulder is exclusively surgical. This is due to the fact that conservative methods cannot restore the structural integrity of the articular lip and articular capsule. Modern traumatological operations allow this surgical intervention to be performed with minimal damage to surrounding tissues. However, in some cases, a wide incision of the joint area is required for adequate suturing of the capsule. The choice of the type of surgical intervention largely depends on the type of human activity, since after some of the operations the range of motion in the shoulder joint may be somewhat reduced.
Can you fix a dislocated shoulder on your own?
It is categorically not recommended to correct a dislocated shoulder on your own, because without proper equipment, preparation of the victim and the necessary qualifications, a number of large vessels and nerves can be damaged, as well as provoke irreversible deformation of the articular surfaces with subsequent disability.Correct reduction of the dislocation of the shoulder joint requires compliance with the following rules:
- Examination of the joint for fractures. Often a dislocation in the shoulder joint is accompanied by a fracture of the humerus, scapula or collarbone. The presence of these fractures requires a completely different approach and in many cases involves surgery. To check the integrity of the bone skeleton of the upper limb, X-rays in two projections, computed tomography, and magnetic resonance imaging are used. Magnetic resonance imaging also allows you to identify the degree of damage to the joint capsule, nerves and blood vessels, as well as muscles.
- Examination of the upper limb for damage to the nerves and blood vessels. It is carried out during a clinical examination, by identifying areas with lost sensitivity, as well as by comparing the pulse on the radial artery of both hands. Also, the examination of blood vessels is carried out by introducing a contrast agent during radiography.
- Adequate anesthesia. The pain syndrome provokes a reflex muscle spasm, which does not allow the joint to be repositioned. In addition, pain causes discomfort and significant suffering to the victim.
- Muscle relaxation. Muscle relaxation is achieved by injecting a local anesthetic into the brachial plexus ( the place of passage of large nerve trunks that give motor and sensory impulses to the muscles of the shoulder girdle) or by intravenous administration of drugs that cause muscle relaxation during general anesthesia.
- Joint control. After repositioning the joint, it is necessary to perform X-ray control of the correctness of the comparison of the articular surfaces.
Reduction of the shoulder joint at home is associated with a high risk of damage to the joint capsule, stretching and rupture of muscles, nerves and blood vessels. It is necessary to carry out this procedure only in a medical institution. It should be understood that the reduction of a dislocated joint must be carried out within the first few days, otherwise the articular surfaces begin to atrophy and the joint loses its original function.
What is a dislocation? This is the impossibility of implementing the full range of motion in the shoulder joint due to the lack of contact of the articular surfaces of the bones included in it. In cases where there is at least some minimal area of contact of the bones, this injury is called a subluxation.
Anatomy of the shoulder joint: why does dislocation occur?
A feature of the shoulder joint is considered to be the most complete of all human bone joints, the range of motion in all possible planes, which occurs due to:
- a relatively flat and wide surface of the articular cavity of the scapula, limited only by a special protruding cartilage (articular lip) along its edges;
- a clear rounded shape of the head of the humerus;
- elasticity of the joint capsule, hermetically limiting the joint cavity from the surrounding tissues.
This makes it possible:
- carry out rotation in the joint in various axes and volumes;
- adduct and abduct the humerus in relation to the body;
- perform flexion and extension.
However, the reverse side of the ability to make such movements was the great instability of the shoulder joint, which, under certain conditions, leads to separation of the communicating surfaces of the bones, followed by dislocation.
The clavicle (not directly included in the shoulder joint, but located in close proximity to the articulation capsule from above), as well as the ligamentous and muscular apparatus covering the shoulder joint from the front, top and back sides, sharply reduce instability and serve as a powerful protection against dislocation with minor and normal loads or movements.
Causes of dislocation in the shoulder joint
- Out-of-bounds movement in a rotational type joint (around an axis)
Most often, they occur under the action of external forces, for example, when a heavy object is held by the hand or when the hand is twisted, which is carried out by an outside force.

Most often occurs when falling on an outstretched arm or with a direct blow directly to the shoulder joint.
- Routine, repetitive, repeated over a long period of time from day to day within the limits of the joint, accompanied by stretching of the capsule.
They are found in some professions that require significant physical exertion in the shoulder girdle. In addition, it is a common sports injury in athletes using throwing movements, swimmers and tennis players.
- Congenital anatomical features of the joint, providing excessive mobility
- Changes in the glenoid cavity of the scapula in the form of a flatter surface without the presence of restrictions on the periphery in the form of an articular lip (scapular dysplasia).
- Underdevelopment (hypoplasia) of the lower third of the glenoid fossa of the scapula, combined with underdevelopment (immaturity) of the capsule of the shoulder joint.
- Changed position of the scapula in the form of deviation back or forward.
- Underdevelopment and weakness of the rotator cuff muscle.
- Severe pain in the joint immediately after the traumatic impact
It is due to:
- damage to the tendon capsule, along the entire diameter of the head of the humerus;
- rupture of the ligaments surrounding the joint;
- damage to the muscular apparatus;
- squeezing or rupture of blood vessels;
- infringement of large nerves and its sensitive endings.
When a dislocation occurs for the first time, the pain is so intense that the victim may faint with nausea and vomiting, he may also lose consciousness.
As a manifestation of the severity of the pain syndrome, hemodynamic parameters may change (fall or increase in blood pressure, changes in the nature of the pulse).
With repeated (habitual) dislocations, which occur, as a rule, due to insufficient treatment of the first, the pain syndrome is already less pronounced, if not completely absent.
- Limitation of movement in the joint
 Most often observed when the head of the humerus falls below the articular surface of the scapula (lower dislocation).
Most often observed when the head of the humerus falls below the articular surface of the scapula (lower dislocation).
The patient at the same time cannot lower the hand laid aside due to the occurrence of springy movements and sharp pain. The second, healthy hand, he supports it in the allotted position.
With posterior and anterior dislocation, movement restrictions occur in other planes, and in various variations.
- Changing the appearance of the shoulder joint
The rounded shape of the shoulder is lost, in its place a small fossa appears with a protrusion of the coracoid process of the scapula above it. The head of the humerus is determined in an atypical place for it, for example, in the armpit.
The soft tissues surrounding the joint become edematous, their hemorrhagic impregnation is possible (bruises appear).
In cases where the head of the humerus infringes on the trunk of a large nerve, some disorders develop sensitivity of the upper limb.
- Paresthesia (sensations of "crawling").
- Severe pain along the entire nerve from the shoulder to the hand.
- Complete lack of sensitivity of the hand to various stimuli.
These symptoms make it possible to diagnose shoulder dislocation with a high degree of certainty.
However, it should be remembered that dislocations can often be accompanied by fractures. And, if a fracture of the humerus is easy to establish by a kind of “grinding” of the fragments that the victim complains about, then damage to the scapula (the most common) cannot be detected without additional research methods.
Therefore, before providing medical care (especially in cases where the dislocation happened for the first time), radiation confirmation of the diagnosis is required.
- Banal x-ray examination is sufficient in most cases.
- If damage to large vessels and nerves is suspected, CT and MRI are used.
First aid for dislocation
At the stage before hospitalization, it is important to properly provide first aid to the victim. This will allow him to more easily endure transportation and protect him from possible additional damage to the joint and surrounding tissues.
- You should not forcefully change the forced position of the limb.
- If the dislocation allows, then, having previously inserted a cotton-gauze roller into the armpit, the limb is fixed to the body with bandaging. This is done to immobilize the joint.
How to treat?
The decision on the method of treatment is made by a specialist, a traumatologist, to whom it is necessary to deliver the victim.
Shoulder dislocation treatment includes a number of steps.
1 . Reduction of dislocation
It is carried out both conservatively and with the help of surgical intervention.
Conservative treatment consists in manual reduction of the dislocation.

During the operation, the fixation of the joint in the physiological position is carried out instrumentally (using special needles).
Indications for surgical treatment are:
- repeated re-dislocations;
- complex dislocations, accompanied by fractures of the head of the humerus and scapula;
- chronic dislocations (when there was no manual treatment within 2-3 weeks after the injury).
2. Immobilization
It is performed after the reduction of the dislocation by additional fixation of the joint with special bandages or plaster bandages.
The average duration of immobilization will be 3-6 weeks.
3. Drug therapy
It consists in taking anti-inflammatory and analgesic drugs (otrofen, ibuprofen, pentalgin, etc.), as well as drugs that improve local blood circulation and relieve swelling.
Medication is limited to three to four days after the reduction of the dislocation.
4. Restoration (rehabilitation) and preservation of the health of the damaged shoulder joint
This is carried out by methods of physical therapy, physiotherapy and massage in combination, taking into account the individual characteristics of the injury.
Rehabilitation begins already in the first days of immobilization by activating the muscles of the injured arm so that they retain their functionality until the bandage is removed.
- The first exercises are prescribed for the fingers of the hand and the wrist joint.
- The next step is the impact on the joint itself, the articular bag and the muscles covering it. The purpose of these actions is to relax the muscles that were spasmodic for the first time after removing the bandage and improve mobility in the joint with the help of a gentle load and massage according to a special program.
In the exercises, additional objects are used - a ball, a stick, dumbbells. This period lasts up to three months from the moment of injury.
Full restoration of the joint with the possibility of obtaining the previous loads is quite feasible six months after the reduction of the dislocation.
 Independent (or with the help of outsiders) reduction of a dislocation of the shoulder joint is possible only in cases where such a dislocation in a patient has previously occurred repeatedly, and seeking professional help is currently impossible.
Independent (or with the help of outsiders) reduction of a dislocation of the shoulder joint is possible only in cases where such a dislocation in a patient has previously occurred repeatedly, and seeking professional help is currently impossible.
Most often, such (habitual) dislocations occur already with a slight load on the joint. Their frequency, occurring six months after the reduction of the previous one, increases to a dozen per year, reaching in some situations (washing, scratching) up to several times a day.
This condition requires mandatory surgical correction of the defect to prevent dislocations in the future.
Self-reduction is feasible in various ways, and each patient chooses for himself his own
- Clutching the wrist of the injured hand between the knees, he leans the torso back.
- A healthy hand pulls a dislocated arm.
- Independently rotates and abducts the arm in the required (opposite in the location of the dislocated head of the humerus) direction.
With outside help, it is possible to correct a dislocation if a certain procedure is followed (Hypocrates' method).
- The patient lies on his back, preferably on a hill (bench, table).
- The caregiver comes up from the side of the injury and firmly grasps the victim’s hand with his own hands, pulling on the injured limb.
- At the same time, he sets the heel of his foot into the armpit of the patient and presses on the head of the humerus that has shifted down.
This is enough for reduction, which is characterized by a “click” sensation.
Movements should be smooth, and in no case should unexpected jerks be allowed, which will only aggravate the dislocation.
Exercise therapy or therapeutic exercises
In the period of immobilization, a set of exercises includes:
- passive (with the help of a healthy hand) and active finger movements with subsequent transfer of load to the wrist joint4
- sequential, following one after another, tension of the muscles of the hand in the first days after the injury, supplemented by tension in the muscles of the forearm at the end of the first week after the injury and the muscles of the shoulder in the next two to three weeks.
The transition to the load on the next joint of the dislocated arm or muscle group does not at all cancel the set of exercises started earlier, but only complements them.
In the post-immobilization period, after the removal of the cast, certain exercises are included in the rehabilitation of the joint.

- Light rocking movements of the limb back and forth.
- Abduction of the arm bent at the elbow to the side.
- Lifting first with the help of a healthy, and then without it, the injured arm forward.
- Dosed pressure with the fingertips of a straightened arm on the horizontal (table) and side (wall) surfaces.
- Rotation with the palm of a free-hanging arm.
- Bringing together and breeding both shoulder blades.
- Raising the arm up (or putting the arm behind the back).
General principles of physiotherapy exercises for shoulder dislocation
- Paired and simultaneous execution of exercises with a healthy hand.
- A gradual increase in the pace and number of exercises and approaches to them.
- The presence of visual control over the joint and movements with the help of a large mirror.
- After 4 weeks after the injury, it is necessary to include additional sports equipment in classes: gymnastic stick, mace, ball, dumbbells, expander.
In addition to physical exercises, self-service skills are practiced at each stage.
As the patient recovers, the patient should be included in homework.
Massage and physiotherapeutic procedures (hydrotherapy, UHF, magnetotherapy) are also considered important components of rehabilitation. They are prescribed in the first days after conservative or surgical treatment. Their goal is to relieve pain and improve blood supply in the area of dislocation.
Basic principles of massaging the affected limb

Features of the habitual dislocation of the shoulder joint and its surgical treatment
The main feature of the habitual dislocation of the shoulder joint, which develops due to incorrect manual reduction of the previous one or inferiority of the articular surfaces, is an increasing increase in its instability after each episode of repeated prolapse of the humeral head.
In cases where the dislocation has already occurred repeatedly, only surgical intervention can stop this chain of injuries. Physical exercises that the patient begins to perform to strengthen the joint after repeated dislocations will no longer increase the stability of the operation and, on the contrary, may cause subsequent dislocations with further destruction of the joint.
There are numerous surgical options. However, with the widespread introduction of endoscopic, minimally invasive technologies into practice, the most common manipulation has become Bankart operation.
- Under the control of optical (arthroscope) instruments, surgical instruments are inserted through holes pierced in the joint wall.
- With its help, plastic methods create a new articular lip along the periphery of the articular surface of the scapula to replace the one lost after numerous injuries or completely absent.
- For the reconstruction of the lips, special screw-in small needles (fixators) are used, which can be metal, remaining forever, or from a material that dissolves over time.
 For the use of each type of fixatives, there are indications, and their choice is made by a trauma surgeon.
For the use of each type of fixatives, there are indications, and their choice is made by a trauma surgeon.
In addition to using an arthroscope, operations can be performed in an open way when the articular bag is opened and all manipulations are carried out under the direct visual control of the doctor.
The final stage of both types of operations on the joint are actions to directly strengthen the tendons and muscles that cover it.
Positive results of surgical treatment with a complete absence of re-dislocations after it can be achieved in 85-92% of cases.
Life after surgery: rehabilitation and recovery
According to the methods and terms of rehabilitation after surgical correction of the habitual dislocation of the shoulder, the management of the patient after the operation completely coincides with the periods described above after manual reduction of the shoulder.
The peculiarity, perhaps, is only the special care for postoperative sutures and intra-articular drainage, which can be left for some time after the operation for additional control and administration of drugs that accelerate reparative processes.
The sutures are removed 7-9 days after the operation.
Article content: classList.toggle()">expand
Dislocation of the shoulder joint is a very common injury, especially among people involved in various sports.
Most often, when this joint is injured, the head of the shoulder bone falls forward, while the injured arm, as it were, turns outwards and is retracted to the side.
This condition is called an anterior dislocation or its anterior form, and it is this type of shoulder dislocation that occurs most often, in almost 96% of cases.
In the article, you will learn everything about rehabilitation after a dislocation of the shoulder joint, as well as what exercises should be performed for treatment during the recovery period.
Shoulder dislocation treatment
When you receive an injury accompanied by a dislocation of the shoulder, it is important to quickly provide (receive) first aid, since further treatment, its complexity, effectiveness and the appearance of possible consequences depend on this. It is important to immediately call a doctor or an ambulance, but if possible, it is better to take the person to the nearest clinic on your own.
Before the arrival of the doctor, as first aid to the victim, certain measures can be taken, in particular:
- Apply a kerchief fixing bandage, which will relieve the load from the damaged joint and ease the pain.
- Apply ice to the injury site to prevent swelling that will make reduction difficult.
- Try to keep the injured arm still.
Treatment for a dislocation is always based on the severity of the injury and the type of injury sustained, which is usually determined by x-rays. As a rule, treatment always begins with the reduction of the injury, which can be carried out in several ways under anesthesia or local anesthesia.
The choice of reduction method depends mainly on the characteristics of the injury., the location of the dislocated joint, as well as the physique of the victim. It is important to exclude the presence of possible and damage to the bones.
After that, a bandage is applied to the patient for a certain time, after which a course of rehabilitation measures begins, the duration of which in most cases depends on the correctness of first aid and the speed of reduction.
Why is rehabilitation needed?
After reduction, the next step in therapy is correct and adequate rehabilitation. It is important to take into account the fact that after the reduction, especially if it required surgical intervention by the surgeon, the shoulder should be at rest for a certain period of time, which is always set by the doctor, based on the patient's condition and the characteristics of the corrected injury.
In older people, this period can be quite long, and sometimes it reaches 1.5 - 2 months.. In younger people, immobilization time may be shorter, depending on the nature of the injury and how it is reduced.
After that, measures begin aimed at rehabilitation, the goal of which is always to fully restore the functions of the joint lost due to injury. That is why, after the end of the period of immobility, it is so important to properly knead the joint, develop it and strengthen the muscles, primarily those that are responsible for the ability to rotate the shoulder.
For rehabilitation, the doctor prescribes to the patient a number of exercises after a dislocation of the shoulder joint for the entire course of rehabilitation, while it starts with easier exercises, gradually moving on to more complex ones. But it is important to start such a course only after being prescribed by a doctor, and strictly follow all the instructions.
Initial recovery after shoulder dislocation
The initial recovery is the period of time that begins immediately after the reduction of the dislocation of the shoulder joint and continues until the appointment of physical exercises aimed at restoring mobility and strengthening the muscles.
- Immobilization of the reduced joint for about a week, which is achieved by applying a special bandage that fixes the shoulder in the required correct position. In addition, splints can be used for fixation, as well as gypsum, if necessary. It is important that the injured arm is at rest for a week.
- If there are complications in the form of damage to muscles, soft tissues or bones (including their fractures), fixation of the reduced shoulder may be required for a longer time.
- In some cases, the doctor may also prescribe the use of special anti-inflammatory drugs belonging to the nonsteroidal group, in particular Ibuprofen, which not only eliminate the inflammatory process, but also relieve pain.
- At the end of the period of immobility, the joint should be gradually included in the work, starting with a small load and exercises prescribed by the doctor. It is important that the load increases gradually and evenly.
- To prevent re-dislocation, one should not forget about strengthening the ligaments.
- It is also recommended to use special preparations and supplements designed to strengthen the ligaments and restore the structure of the joints, containing the necessary vitamins. You can use some types of ointments.
- In the early stages of rehabilitation, light exercises are most often prescribed, for example, with a soft expander, as well as lightweight dumbbells.
Rehabilitation activities
As a rule, after the reduction of a dislocated shoulder, rehabilitation measures are carried out in 4 successive stages, and it is very important that the patient goes through all of them.

At the second stage(from the 2nd to the 4th week) rehabilitation measures are considered to be:
- The appointment of light movements in the shoulder joint, which should not cause severe pain.
- If there is no pain, the doctor prescribes more serious warm-up exercises that restore the mobility of the damaged joint.
- It is allowed to remove the bandage.
- After training, it is important to apply cold to the joint so that swelling does not occur.
- In no case should any combined movements be performed at this stage, such as turning the shoulder, especially outward, as well as spreading the arms to the sides. Such actions can lead to re-dislocation and many complications.
Similar articles 
At the third stage(from the 4th to the 6th week) rehabilitation procedures include:
- In ensuring full mobility of the damaged joint, regular exercise.
- At the beginning of the abduction of the arm to the side, but only if the damaged joint does not hurt and the exercise does not cause suffering.
- Carrying out regular classes with exercises to restore the previous mobility.
- It is important to try to achieve the full value of the movements performed.
The fourth stage of rehabilitation after shoulder dislocation and recovery is the return of the patient to his usual activities and lifestyle, to the possibility of lifting small weights. If a person was involved in power sports before the injury, then at this stage he can return to training, starting work with low loads and gradually increasing them.
Now you know how to strengthen the shoulder joint after dislocation and do it right.
Physiotherapy
You will be interested... This method of treatment for dislocation of the shoulder joint has a special advantage, because it is not only effective, but also safe, because no drugs are required for medical procedures. To influence the damaged joint, various methods of physiotherapy treatment can be used to help strengthen muscles and internal tissues, as well as eliminate inflammation.
This method of treatment for dislocation of the shoulder joint has a special advantage, because it is not only effective, but also safe, because no drugs are required for medical procedures. To influence the damaged joint, various methods of physiotherapy treatment can be used to help strengthen muscles and internal tissues, as well as eliminate inflammation. Physiotherapy procedures are an excellent means of not only rehabilitation after injuries, but also a preventive measure to strengthen the shoulder joint. When they are used in the human body, all natural biological processes are activated, recovery from the disease is accelerated, the injured joint is restored, but, in addition, the overall immune system is strengthened, as well as the activation of natural defenses.
Today, for the treatment of injured joints in physiotherapy, a number of methods are used that show excellent results in terms of efficiency, in particular:

exercise therapy
Consider how to develop a shoulder joint after a dislocation with the help of physiotherapy exercises.
Exercise therapy after a dislocation of the shoulder joint is usually represented by a whole complex of elementary exercises, due to which a person gradually restores the lost motor activity of the damaged joint.
During the exercises, the strength of the deltoid muscle, as well as the biceps and triceps, is replenished, which gradually leads the injured joint itself to a stable state. The correct implementation of the exercises recommended by the doctor for shoulder dislocation is not only the key to a complete recovery, but also the prevention of a possible relapse (re-dislocation).
Treatment and training begin after the reduction of the dislocation of the shoulder and the end of the rest period of the joint. The first lessons in this case always consist of light and very simple exercises, the purpose of which is to generally increase the muscle tone of the injured arm and ensure sufficient blood flow. Gradually, on the recommendation of the doctor, the load on the arm and the joint itself should be increased, and the range of exercises performed should be expanded.
It is important to remember that even simple exercises after an injury, performed incorrectly, can lead to complications and an increase in the recovery period.
Extreme caution should be exercised when performing power loads after reduction of the dislocation, since such exercises, if performed incorrectly or in an inadequate state of the load, can lead not only to stretching of the weakened ligaments, but also to their rupture. Therefore, for a successful and complete recovery, you should fully follow the recommendations of the doctor and not self-medicate.
During the rehabilitation period after reduction of a dislocated shoulder, the focus is on restoring lost muscle strength, since it is thanks to strong muscles that the joint is stabilized, while the head of the bone is set in the correct position. Stabilization of the head also occurs in the anteroposterior direction, which further prevents it from slipping and leaving the articular region.
Rehabilitation measures of physiotherapy exercises for shoulder dislocation are usually carried out in 3 stages:
- Initial recovery is the period during the first 3 weeks after reduction.
- Recovery of working capacity - the period of the first 3 months after the injury.
- The period of full recovery, which can take up to 6 months (depending on the complexity of the injury and its characteristics).
Such a classification is usually conditional, since the periods of each stage can be increased or decreased by the doctor on an individual basis, based on the patient's condition and the characteristics of the injury.
Thishealthy
know!
In the initial stage, which begins almost immediately after the injury is reduced and the joint is fixed and lasts about 3 weeks, it is allowed and recommended to perform exercises that will prepare the damaged joint and muscles for more complex loads in the future. Also, exercises in this period are also performed to stabilize metabolic processes, normalize blood circulation in the arm and joint. As a rule, during this period, the doctor recommends performing:
- Gentle and very careful movements with the fingers of the injured hand and the entire hand, including the wrist joint.
- Light exercises aimed at periodic tension of muscle blocks of all parts of the arm.
With the beginning of the second stage, the exercises become more difficult, while the load gradually increases, which is necessary to eliminate muscle contracture, strengthen them, and increase endurance:
- You can not only freely move your fingers and hand, clench your hand into a fist, but also carry out flexion actions at the elbow.
- It is recommended to carefully lift the injured hand while holding it with a healthy hand.
- You can make accurate and slow abduction of the injured arm to the side.
- Careful abduction of the injured arm behind the back, gradually this exercise is performed without support, synchronously, with both hands.
- Smooth hand swing.
- After the doctor allows, you can also carry out rotational movements with both hands.
It is important that the recommended exercises are performed simultaneously with both hands to ensure an even load. Of course, at first, the exercises are difficult and require the support of a healthy hand, but gradually it is necessary to move on to performing the complex with both hands.
As a rule, exercises to restore the shoulder joint after a dislocation with some kind of load, for example, light weight dumbbells, can be performed within 4-5 weeks after the injury has been reduced. For classes, you can use other devices, in particular, a special gymnastic stick, small balls, expanders, gradually moving on to simulators. With the correct implementation of all the recommendations, the complete restoration of the former mobility occurs after 5-6 months.
Features of rehabilitation after surgery
As a rule, surgical intervention is not often required for a dislocated shoulder, but in some cases there is no other way to prevent the possibility of subsequent injury. Most often, an operation is required in cases where the main vessels, tendons, bones, muscles or nerve endings were damaged during an injury. The operation is performed if necessary as soon as possible after the injury.
Sometimes doctors suggest surgery for a normal primary dislocation in order to optimally stabilize the joint by strengthening the ligaments. There are many methods for carrying out such an operation, and the choice of a particular one usually depends on the patient's physique, characteristics of his activity and lifestyle.
Rehabilitation after surgery mainly depends on the choicemethod and the patient's condition. As a rule, the stages of recovery are practically the same as for non-surgical reduction of an injury, but their general period, like each of them, can be significantly delayed, and the procedures and exercises themselves will require more accuracy and caution when performed.
An important point here is the restoration of muscles damaged during surgery, for which special drugs of the enzyme category can be prescribed, especially if a person went in for sports before the injury. An obligatory moment after such an operation is cryotherapy procedures, carried out 5 to 7 times a day for 15 minutes in the first phase of rehabilitation when the joint is immobilized.
It is important that rehabilitation procedures begin immediately after such an operation and are carried out along with the main treatment. The first exercises in the initial stage of recovery should be performed for several seconds with obligatory relaxation and a gradual increase in time, under the strict supervision of a doctor or exercise therapy instructor. An increase in the load occurs only with the permission of the controlling specialist.
The final recovery period in this case begins in the interval of 12-15 weeks after the operation, in some cases, the complete recovery of the joint and return to normal activities, as well as sports, occurs after about 6-9 months.
What not to do during the recovery period
Of course, the first thing that is not recommended when receiving such an injury is to try to set the joint on your own without having the necessary qualifications for this, especially if you can get adequate medical care. A dislocated shoulder can only be corrected in an emergency.
After the reduction of the dislocation, you can not self-medicate. It is very important to strictly follow the recommendations and prescriptions of the doctor. It is impossible to neglect the performance of elementary exercises in the initial stage of rehabilitation, since this period is very important.
You should not arbitrarily increase the load, trying to speed up recovery, because in this case, instead of benefit, you can harm yourself and provoke not only the occurrence of many complications, but also re-dislocation of the joint.
It is impossible to perform strength exercises at the first and second stages of rehabilitation without prior preparation, even if a person has previously been involved in such a sport. Such actions can lead to severe stretching of weakened ligaments and even their rupture, which will significantly complicate the condition and may provoke further limitation of mobility.