How to cure exudative pleurisy. Effective alternative treatment of pleurisy of the lungs Exudative pleurisy syndromes
Treatment of pleurisy with folk methods
Greetings, dear readers of the blog Narmedblog.ru. Autumn is upon us, winter is coming. The cold season contributes to the emergence of massive colds, ranging from the common cold to the dangerous flu and pneumonia. The topic of today's article is the treatment of pleurisy with folk methods.
Causes of pleurisy and its symptoms
● On all sides, our lungs are covered with a special membrane called the pleura. This shell protects them: they slide freely along the chest when breathing. In inflammatory processes, the pleura thickens and swells, becomes uneven - thus pleurisy occurs.
● By itself, pleurisy, as a rule, is recorded very rarely: with massive hypothermia or trauma in the chest area. In most cases, pleurisy is a companion of some other pulmonary disease: tuberculosis, pneumonia, bronchitis. Somewhat less often, it develops as a complication of diseases of the abdominal organs: pancreatitis or hepatitis.
● In medicine, two types of pleurisy are distinguished: dry and effusion (or exudative) - with the release of fluid into the pleural cavity.
● With dry pleurisy, there is no fluid in the pleural cavity, the pleural sheets rub against each other during breathing, causing acute pain in the chest, especially when coughing. You can often hear from a patient with pleurisy: "I have so much pain in my chest, as if someone were stabbing with an awl." He has to take a forced position in order to at least a little soothe the pain: he lies on the healthy side of the chest or leans against some object.
● With dry pleurisy, body temperature rises, it often reaches 38−38.5 degrees. Appetite decreases, the patient loses weight.
● When fluid accumulates in the pleural cavity, the volume of which can reach up to five liters, the pain subsides, instead of a dry cough, a wet one appears, and noticeable shortness of breath begins. Bubbling breathing - heard at a distance, it is superficial, irregular, often whistling. This condition is accompanied by weakness, chills and profuse sweat.
How to differentiate pleurisy from other pulmonary diseases
● To make a diagnosis, clinical observations alone are not enough - the results of laboratory blood tests, X-ray examination of the chest organs are needed. The presence of a serious inflammatory process in the body is indicated by anemia (anemia), leukocytosis (increased number of leukocytes), an increase in ESR (erythrocyte sedimentation rate) up to 70-80 units.
● A fairly reliable method for diagnosing pleurisy is chest X-ray, but it has such a minus: it can fix blackout in the pleural cavity only when the volume of pleural fluid in the pleural cavity is at least 300−500 ml. That is, the x-ray will not show the presence of dry pleurisy.
● There is another way to clarify the diagnosis - puncture of the pleural cavity. Using this method, the doctor directs the pleural fluid for laboratory testing and subsequently, by its quantity, color, consistency, and the presence of microbial flora, determines both the degree of the inflammatory process and the cause of the disease.
“Attention: only a certified doctor can establish an accurate diagnosis and prescribe treatment for you, so I strongly recommend that you coordinate with your doctor all the recommendations below”
Treatment of pleurisy - the first stage
● Do not delay with the disease, contact your local doctor. Self-medication can cause the compressed lung to completely stop functioning. Treatment of pleurisy should be comprehensive. First of all, you need to stop the main process that led to the occurrence of pleurisy.
● In the future, antibiotics and anti-inflammatory drugs are prescribed. Of the antibiotics, clindamycin, fortum, cefobid, cefatoxime are the most effective. The course of treatment lasts 2-3 weeks, after which, if necessary, you can replace antibiotics with - sumamed, augmentin, amoxil.
● Depending on the severity of the disease, the treatment of pleurisy lasts up to two months, and strictly individually for each patient. Together with antibiotics, the doctor prescribes non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs: voltaren or ibuprofen; in especially severe cases, persons with a weakened immune system are prescribed a hormonal drug - prednisone.
● With dry pleurisy, if there is no high temperature (fever), the patient is prescribed distractions: alcohol warming wraps (compresses), mustard plasters, cans on the chest area.
Treatment of pleurisy with folk methods
● Many collections of medicinal herbs effectively affect the inflammatory process in the lungs, however, in the treatment of pleurisy, they are prescribed in combination with pharmaceutical drugs, and during the period of convalescence (recovery). In diseases of the upper respiratory tract, licorice root, white willow bark, fennel fruit, lime blossom, plantain herb, hyssop, knotweed, coltsfoot leaves have proven themselves as an expectorant and anti-inflammatory agent.
● Recipe #1. Pour two tablespoons of chopped fennel fruits with a glass of boiling water and put in a water bath for 15-20 minutes. Let it brew for one hour. Take ⅓ cup of decoction three times a day for dry pleurisy.
● Recipe number 2 - with exudative (effusion) pleurisy. Pour two glasses of boiled water with 50 grams of lime blossom and two tablespoons of birch buds; heat the treatment mixture in a water bath for 15 minutes and leave after that for one hour. Strain the broth and add one glass of linden honey and aloe juice to it, put it back in a water bath for five minutes. Stir and add one glass of vegetable oil (preferably olive oil). Take one tablespoon before meals three times a day for one month.
● Recipe number 3 - for the treatment of dry and exudative pleurisy. Grind and mix equal proportions of coltsfoot leaves, black elderberry flowers and knotweed herb. One tablespoon of the collection pour 200 ml. boiling water and insist in a thermos for half an hour. Drink ¼ cup of infusion half an hour before meals three times or four times a day.
General therapeutic and preventive measures for pleurisy
● A patient with pleurisy after prolonged use of antibiotics becomes weak, his immune activity decreases. He needs to urgently restore his lost strength. Nutrition should be high-calorie, balanced, rich in vitamins and minerals. In order not to provoke a cough, it is better to refuse spicy food.
● With exudative pleurisy, water-salt metabolism in the body is disturbed, therefore it is recommended to limit salt intake to 5 grams, as well as liquids to 1 liter per day.
● During the period of convalescence, you should walk more often in the fresh air, do morning exercises and feasible physical activity. This significantly improves blood circulation, prevents the formation of adhesions in the pleural region, relieves excruciating shortness of breath, that is, gradually returns you to your previous normal active and fulfilling life.
Stay healthy and God bless you!!!
Sometimes dry pleurisy, with improper treatment, flows into exudative. This form of the disease is characterized by the fact that fluid accumulates in the pleural cavity. And the disease manifests itself with the following symptoms:
Depending on the form of the disease, the causes of its occurrence are different. Pleurisy develops in such situations:
Treatment of pleurisy must be comprehensive. It should be carried out in the direction of identifying and eliminating the main causes of the disease. Of course, not all forms of pleurisy can be cured on their own at home, but if the disease is not started, even representatives of official medicine recommend effective folk remedies.
Treatment of pleurisy at the initial stage of development can be carried out with the help of warming and analgesic compresses.
An excellent effect is given by a compress from a sponge, which must be moistened in hot water and applied to the site of pain localization.
To reduce pain in case of illness at home, you can use essential oils - lavender, fir, pine. It is necessary to take 10 drops of any oil mixed with olive oil, and gently rub the sternum area. You can also mix 2.5 g of lavender and eucalyptus oils, add 30 g of camphor and rub this mixture into the sore spot 2-3 times a day. After rubbing in the oils, apply a warming compress from above and bandage it tightly.
Some collections of plants are effective in treating the disease. Traditional healers recommend using the following medicines before meals:
A very effective remedy for pleurisy is the following recipe: squeeze the juice from 4 lemons and chop 200 g of horseradish, mix everything. Take 0.5 tsp before meals. in the morning and in the evening. This tool contributes to the rapid resorption of fluid in the pleural cavity and does not adversely affect the digestive tract. In parallel with this recipe, you should drink 3 times a day 1/3 cup of the infusion of the medicinal collection, which includes cudweed, coltsfoot, mint, licorice, elecampane.
In addition to home treatment, a person is prescribed therapeutic exercises and special massage. They also recommend proper nutrition, which is aimed at quickly eliminating the inflammatory process and improving immunity.
- Cover 61
- Respiratory 53
- Digestive 48
- Blood 45
- Reproductive 37
- Nervous 34
- Musculoskeletal 25
- excretory 21
Honey to maintain immunity is simply irreplaceable. It contains a huge amount of useful elements, so it successfully fights even the most serious diseases, and also blocks inflammatory processes in the early stages.
Random video release about traditional medicine
When reprinting and copying texts, an active indexed link to the source is required. Photo and video materials are not the property of the site
Ask your question to our experts and
site visitors. All consultations are free
Treatment of pleurisy with folk remedies and the best recipes
In order not to worsen the state of your own health or your loved ones, you should contact a narrow-profile pulmonologist at the first manifestations of the disease. Only a specialist will be able to make a correct diagnosis and prescribe an effective drug therapy, individually selected for each patient. If the stage of the disease has not yet acquired a complex form of development, the treatment of pleurisy with folk remedies can show itself no less effectively in practice. For the treatment of an advanced stage of pleurisy, unfortunately, folk methods alone will not be enough, therefore, antibiotics are included in the treatment therapy, which effectively stop the inflammatory process.
Symptoms and causes of the disease
In the human body, pleurisy can develop for the following reasons:
- as a complication after previous tuberculosis or pneumonia;
- against the background of allergic diseases;
- due to severe damage to the chest.
Sometimes the disease develops in people who suffer from rheumatism.
The symptoms by which it is realistic to determine the development of pleurisy are as follows:
- stabbing pain under the ribs, which can only appear when inhaling;
- brief fever;
- rapid and shallow breathing;
- troublesome dry cough.
In medicine, there are several types of pleurisy:
- fibrinous-exudative;
- diffusely encysted;
- aseptic-infectious.
If the lesions are not treated, the disease can take on a purulent form, which will be much more difficult to get rid of.
Therapeutic technique
- if the lesion manifested itself as a complication, Gentamicin or Amoxiclav is most often prescribed;
- if pleurisy has developed against the background of rheumatism, the attending physician may prescribe Diclofenac or Ketan;
- with the development of pleurisy on the background of tuberculosis, Tubazid is prescribed for treatment.
As you can see, several types of antibiotics are used to treat pleurisy. And since each drug has a certain effect, only a qualified doctor is ready to choose the most suitable and effective one.
In addition to antibiotics, the following procedures can be included in therapeutic therapy:
It will be necessary and daily to perform special exercises that the doctor will develop and introduce into physiotherapy exercises.
Folk compositions for the treatment of pleurisy
- The composition used for the treatment technique, exudative lesions.
To prepare the composition, you will need the following ingredients:
- 150 ml of ordinary aloe juice;
- natural honey, it is advisable to use linden or May - 120 ml;
- olive oil - 75 ml;
- dried birch buds - 75 g;
- dried linden flowers - 75 g.
You need to take the composition for 20 days, 2 tablespoons 10-15 minutes before meals.
- Dry pleurisy is effectively treated with a composition based on freshly squeezed beetroot juice. To prepare it you will need:
- 150 ml freshly squeezed beetroot juice;
- 1 glass of natural liquid honey.
- Encapsulated pleurisy is effectively treated with a composition based on ordinary onions and high-quality white wine. For cooking you will need:
- 350 g finely chopped onion;
- 550 ml of high-quality white wine;
- 150 ml of honey, preferably May or lime.
All components are thoroughly mixed, infused in a glass opaque container for 7-9 days. The strained composition is taken 10-15 minutes before meals, 2 tablespoons for 20 days.
Grind all the ingredients in a coffee grinder, mix. 3 art. spoons of the resulting mixture are poured into a thermos, the herbs are poured with boiling water, taking 3 cups of settled boiled water for this. In the morning, the composition is filtered through gauze. It is recommended to take an infusion of 0.5 cups 3 times a day (15-20 minutes before meals).
Pleurisy
Pleurisy can be caused by infection, tumor development, or traumatic injury to the chest.
Pleurisy symptoms.
Inflammation of the pleura causes pain with deep inhalation, as well as with movements of the chest.
Traditional methods of treatment of pleurisy.
The specific cause of pleurisy determines the nature of the treatment, which may include antimicrobial and anti-inflammatory agents.
Treatment of pleurisy with folk remedies
home remedies for pleurisy
Mix the juice of 1 onion with honey in a ratio of 1:1. Take 1 tablespoon 2 times a day after meals. It is a good anti-infective agent.
Mix black radish juice with honey in a ratio of 1:1. Take 1 tablespoon 3 times a day for pleurisy.
Juice and pulp of common cherries take 0.25 cups 3 times a day after meals with pleurisy.
Mix 30 g of camphor oil, 2.5 g of lavender oil and eucalyptus oil. Rub into the affected side 2-3 times a day. After that, apply a warm compress or bandage tightly.
Heat olive oil in a water bath and rub into a sore side with pleurisy, then make a compress and wrap yourself warmly.
At the beginning of the disease, a compress from a sponge dipped in hot water helps. Salt or sea water is especially effective for pleurisy.
See also recipes in the topic bronchitis, pneumonia
Herbs and fees for the treatment of pleurisy
Take 2 parts of anise fruits, marshmallow root, licorice root, 1 part of pine buds and sage leaf. Brew 1 tablespoon of the mixture in 1 cup of boiling water, close tightly and leave for 5 hours, strain and take 1 tablespoon 4-5 times a day for pleurisy.
Take 2 parts of a coltsfoot leaf, 1 part of elecampane root, peppermint leaf, licorice root, marsh cudweed herb. Prepare an infusion (1 tablespoon of the mixture per 1 cup of boiling water) and take 0.5 cup 3 times a day before meals with pleurisy.
Pour 1 tablespoon of horsetail 0.5 liters of boiling water and leave for 3 hours. Drink 0.5 cup 4 times a day for pleurisy.
See also recipes in topic Bronchitis and Pneumonia.
Doctor's comments on folk remedies for pleurisy
You can use folk remedies in addition to the treatment prescribed by your doctor. For example, you can use the following from the article: onion, garlic, radish - they have antibacterial properties (if the cause of pleurisy is infectious), and you can also use fees consisting of the following components: horsetail, aloe, birch buds, mother-and- stepmothers, mint, elecampane, licorice, pine buds, sage (in addition to antimicrobial, they also have a tonic, antipyretic, analgesic and other beneficial effects).
There must also be local treatment in the form of: evacuation of the contents with the help of repeated thoracocentesis, with the introduction of a drainage tube, sanitation of the pleural cavity and the introduction of antiseptic and antibacterial, as well as fibrinolytic drugs, therapeutic thoracoscopy, thoracotomy, resection of the rib and subsequent drainage of the purulent cavity and others methods depending on the severity, up to the removal of the lung. As you can see, this is a very serious pathology that requires mandatory medical treatment, which must be prescribed, controlled and monitored by the doctor.
During the period of remission, therapeutic exercises are prescribed.
Comments
You might be interested in articles:
New video on our YouTube channel:
New articles on traditional medicine:
Do not miss new information about your disease on the pages of our group!
- You are here: #160;
- home
- Folk recipes for diseases
- Respiratory diseases
- Pleurisy
2018 Symptoms and treatment of folk remedies at home
No comments yet!
sovet-medika.ru
Treatment of pleurisy with folk remedies can significantly improve the patient's well-being and speed up his recovery. At the same time, they should not be used instead of medicines - this is fraught with the most sad consequences.
See also: Symptoms and treatment of dry pleurisy of the lungs
Causes and symptoms
By itself, pleurisy is not considered as a separate disease. It always develops against the background of another pathology and, in fact, is its complication. As a rule, provocateurs are infections that invade the lungs.
The most common ailments that contribute to the development of pleurisy:
- pneumonia;
- tuberculosis;
- rheumatism;
- pancreatitis.
Sometimes the problem appears as a result of trauma to the chest or as a postoperative complication.
The following signs indicate the development of pleurisy:
- persistent dry cough;
- pain that occurs during a deep breath or in a certain position (usually lying on your side);
- shallow breathing;
- asymmetry in filling the lungs with air (the affected part works more slowly);
- the presence of subfebrile temperature for a long time;
- general malaise;
- high sweating;
- weakness;
- frequent hiccups;
- pain when swallowing.
Treatment
In acute pleurisy, the patient requires bed rest and inpatient treatment. To relieve pain appoint:
- compresses;
- banks;
- mustard plasters.
They also prescribe:
- anesthetics;
- antitussives;
- desensitizing drugs;
- anti-inflammatory.
In the recovery stage, physiotherapy and exercise therapy are of great benefit.
Folk remedies
By themselves, the recipes below are not able to save a person from pleurisy. However, they can significantly speed up recovery and provide complete rehabilitation. It is only necessary to remember - before using any folk remedy, it is recommended to consult a doctor.
The most popular recipe, judging by the reviews, is as follows:
- rub a large onion;
- squeeze juice out of it;
- mixed 1 to 1 with liquid honey.
Take the drug twice a day and only after meals (preferably in the afternoon). Single dose - 2 tablespoons.
Honey is also often mixed in equal parts with black radish juice. This remedy is recommended to be taken at least 3 times a day.
Here is another very useful tool:
- cherries are freed from stones;
- knead with a fork or grind in a blender;
- eat after each meal, in the amount of a quarter cup.
When the acute phase of pleurisy is left behind, you can increase the effectiveness of medications with homemade lozenges. They are prepared from taken in equal proportions:
- butter;
- almonds;
- nettle seed;
- honey.
All ingredients are ground and slightly cooled. Then small balls are made from the mass.
They have high efficiency and various herbal preparations. The next one is very good:
- anise;
- marshmallow;
- licorice;
- pine buds;
- sage.
All components are taken in the same amount. A spoonful of the mixture is brewed in 200 milligrams of boiling water and kept warm for 5 hours. The finished product is filtered and consumed up to 5 times a day for a tablespoon.
Encapsulated pleurisy helps to cure the following remedy:
- ground fresh onion - 350 grams;
- good dry wine - 550 milliliters;
- lime (acacia) honey - 150.
The medicine is kept in the refrigerator for a day and then consumed in a tablespoon at least three times a day.
The following collection will also be useful here:
- peppermint;
- elecampane (root);
- cottonweed;
- licorice;
- coltsfoot.
The infusion is prepared from a glass of boiling water and a tablespoon of dry composition. The resulting volume is drunk in three doses.
Treatment of exudative pleurisy provides another drug. The days of it are taken:
- aloe juice (200 ml);
- linden honey (200 ml);
- vegetable unrefined oil (100 ml).
To this are added birch buds (half a glass), lime blossom (the same amount). The last two ingredients are poured with half a liter of boiling water and boiled for an additional quarter of an hour in a water bath. After cooling, the drug is filtered, honey and aloe are added to it and again heated a little. At the end put vegetable oil. This medicine is recommended to drink 2 tablespoons up to three times a day. It will allow you to quickly get rid of the temperature.
Horsetail cones are also very effective for pleurisy. To stock up on infusion for the whole day, you need to take 2 tablespoons of dry raw materials per liter of boiling water and leave for at least 3 hours. The medicine is filtered and divided into 4 portions.
Folk remedies for external use
For grinding, a good ointment is prepared from:
- badger fat (300 g);
- a similar amount of aloe leaves ground in a meat grinder;
- cups of honey.
The ingredients are mixed and put in a non-hot oven for 15 minutes. Then the drug is cooled and used to rub the back and chest. If desired, it is permissible to use it inside. This should be done before meals and at least 3 times a day.
Another composition for rubbing:
- camphor - 30 grams;
- eucalyptus and lavender oils in a teaspoon.
The resulting balm is used in the morning and evening.
Also useful for patients with pleurisy and rubbing with olive oil. Only the Extra Virgin variety is allowed to be used. Before the procedure, it must be slightly warmed up in a water bath. Enhances the effect of such an application installed on top of mustard plasters.
For any pulmonary ailments, the essential oil of fir or cedar is extremely useful. It can be used in two ways:
- in the form of inhalations;
- for rubbing.
To reduce the intensity of pain, it is necessary to apply a gauze bag filled with dry mustard.
Also relieves the condition of the ointment from:
- 30 milliliters of purified kerosene;
- 50 g of sea salt;
- the same amount of mustard.
Here is a great compress recipe:
- 2 glasses of water;
- a teaspoon of honey;
- dining room - mustard powder.
In the resulting solution, a towel is moistened, which is then applied to the patient's chest. The top is covered with a warm blanket. After half an hour, the compress is removed, and the patient continues to warm himself in bed for another hour.
legkievnorme.ru
Treatment of pleurisy with folk methods
How to treat pleurisy at home
Greetings, dear readers of the Narmedblog.ru blog. Autumn is upon us, winter is coming. The cold season contributes to the emergence of massive colds, ranging from the common cold to the dangerous flu and pneumonia.
The topic of today's article is pleurisy treatment folk methods.
Causes of pleurisy and its symptoms
● On all sides, our lungs are covered with a special membrane called the pleura. This shell protects them: they slide freely along the chest when breathing.
In inflammatory processes, the pleura thickens and swells, becomes uneven - thus pleurisy occurs.
● By itself, pleurisy, as a rule, is recorded very rarely: with massive hypothermia or trauma in the chest area. In most cases, pleurisy is a companion of some other pulmonary disease: tuberculosis, pneumonia, bronchitis.
Somewhat less often, it develops as a complication of diseases of the abdominal organs: pancreatitis or hepatitis.
● In medicine, two types of pleurisy are distinguished: dry and effusion (or exudative) - with the release of fluid into the pleural cavity.
● With dry pleurisy, there is no fluid in the pleural cavity, the pleural sheets rub against each other during breathing, causing acute pain in the chest, especially when coughing.
You can often hear from a patient with pleurisy: "I have so much pain in my chest, as if someone were stabbing with an awl." He has to take a forced position in order to at least a little soothe the pain: he lies on the healthy side of the chest or leans against some object.
● With dry pleurisy, body temperature rises, it often reaches 38-38.5 degrees. Appetite decreases, the patient loses weight.
● When fluid accumulates in the pleural cavity, the volume of which can reach up to five liters, the pain subsides, instead of a dry cough, a wet one appears, and noticeable shortness of breath begins.
Bubbling breathing - heard at a distance, it is superficial, non-rhythmic, often whistling. This condition is accompanied by weakness, chills and profuse sweat.
How to differentiate pleurisy from other pulmonary diseases
● Clinical observations alone are not enough to make a diagnosis - the results of laboratory blood tests, X-ray examination of the chest organs are needed.
The presence of a serious inflammatory process in the body is indicated by anemia (anemia), leukocytosis (increased number of leukocytes), an increase in ESR (erythrocyte sedimentation rate) up to 70-80 units.
● A fairly reliable method for diagnosing pleurisy is chest X-ray, but it has such a minus: it can fix darkening in the pleural cavity only when the volume of pleural fluid in the pleural cavity is at least 300-500 ml. That is, the x-ray will not show the presence of dry pleurisy.
● There is another way to clarify the diagnosis - puncture of the pleural cavity. Using this method, the doctor directs the pleural fluid for laboratory testing and subsequently, by its quantity, color, consistency, and the presence of microbial flora, determines both the degree of the inflammatory process and the cause of the disease.
“Attention: only a certified doctor can establish an accurate diagnosis and prescribe treatment for you, so I strongly recommend that you coordinate with your doctor all the recommendations below”
Treatment of pleurisy - the first stage
● Do not delay with the disease, contact your local doctor. Self-medication can cause the compressed lung to completely stop functioning. Pleurisy treatment should be complex.
First of all, you need to stop the main process that led to the occurrence of pleurisy.
● In the future, antibiotics and anti-inflammatory drugs are prescribed. Of the antibiotics, clindamycin, fortum, cefobid, cefatoxime are the most effective.
The course of treatment lasts 2-3 weeks, after which, if necessary, you can replace antibiotics with - sumamed, augmentin, amoxil.
● Depending on the severity of the disease, the treatment of pleurisy lasts up to two months, and strictly individually for each patient. Together with antibiotics, the doctor prescribes non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs: voltaren or ibuprofen; in especially severe cases, people with weakened immunity are prescribed a hormonal medicine - prednisolone.
● With dry pleurisy, if there is no high temperature (fever), the patient is prescribed distractions: alcohol warming wraps (compresses), mustard plasters, cans on the chest area.
Treatment of pleurisy with folk methods
● Many collections of medicinal herbs effectively affect the inflammatory process in the lungs, however, in the treatment of pleurisy, they are prescribed in combination with pharmaceutical drugs, and during the period of convalescence (recovery).
In diseases of the upper respiratory tract, licorice root, white willow bark, fennel fruit, lime blossom, plantain herb, hyssop, knotweed, coltsfoot leaves have proven themselves as an expectorant and anti-inflammatory agent.
● Recipe #1. Pour two tablespoons of crushed fennel fruits with a glass of boiling water and put in a water bath for 15-20 minutes. Let it brew for one hour. Take ⅓ cup of decoction three times a day for dry pleurisy.
● Recipe #2- with exudative (effusion) pleurisy. Pour two glasses of boiled water with 50 grams of lime blossom and two tablespoons of birch buds; heat the treatment mixture in a water bath for 15 minutes and leave after that for one hour.
Strain the broth and add one glass of linden honey and aloe juice to it, put it back in a water bath for five minutes. Stir and add one glass of vegetable oil (preferably olive oil).
Take one tablespoon before meals three times a day for one month.
● Recipe #3- for the treatment of dry and exudative pleurisy. Grind and mix equal proportions of coltsfoot leaves, black elderberry flowers and knotweed herb.
One tablespoon of the collection pour 200 ml. boiling water and insist in a thermos for half an hour. Drink ¼ cup of infusion half an hour before meals three times or four times a day.
General therapeutic and preventive measures for pleurisy
● A patient with pleurisy after prolonged use of antibiotics becomes weak, his immune activity decreases. He needs to urgently restore his lost strength.
Nutrition should be high-calorie, balanced, rich in vitamins and minerals. In order not to provoke a cough, it is better to refuse spicy food.
● With exudative pleurisy, water-salt metabolism in the body is disturbed, therefore it is recommended to limit salt intake to 5 grams, as well as liquids to 1 liter per day.
● During the period of convalescence, you should walk more often in the fresh air, do morning exercises and feasible physical activity.
This significantly improves blood circulation, prevents the formation of adhesions in the pleural region, relieves excruciating shortness of breath, that is, gradually returns you to your previous normal active and fulfilling life. Treat colds promptly.
Stay healthy and God bless you!!!
narmedblog.ru
- Treatment with medicinal plants
- Treatment of disease with juices
- Treatment of pleurisy with oils
- Other folk recipes
With pleurisy of the lungs, treatment with alternative methods should be carried out only after consulting a doctor. The disease is an inflammation of the petals of the pleura. It should be noted that pleurisy does not act as an independent disease, but is a secondary ailment that complicates the course of diseases of the organs of the diaphragm, mediastinum, chest wall and subphrenic space. With this disease, a person experiences pain during breathing. The feeling of discomfort arises from the friction of the rough sheets of the pleura against each other. Fever, shortness of breath, general weakness and cough may appear.
Currently, doctors can offer many medical treatments for pleurisy of the lungs. But, despite this, a huge number of patients refuse them, preferring not to poison their body with potent drugs, but to deal with unpleasant symptoms with the help of traditional medicine.
Treatment with medicinal plants
Treatment of pleurisy with folk remedies involves the use of mixtures, which include medicinal plants containing a huge amount of useful trace elements. It is thanks to such a rich composition that folk remedies based on components of plant origin can help cure pleurisy of the lungs in the shortest possible time:
150 g of chopped horseradish root must be mixed with juice squeezed from 3 lemons. The resulting consistency should be consumed twice a day for half a spoon. The first dose of the medicine should be in the early morning (on an empty stomach), and the second - just before going to bed. This remedy also has excellent diuretic properties.
At home, you can make very effective compresses from the root of Caucasian ginseng. The root of the plant should be washed, cleaned and chopped on a fine grater. The root must be at least 3 years old.
After that, the resulting slurry should be laid out on compress paper, covered with a gauze bandage on top and applied to the stomach area. First, several small holes should be made on the paper. After that, put cotton wool on the compress and wrap it with a warm scarf. Such a compress should be done twice a day (until the symptoms disappear completely).
2 tablespoons of marshmallow roots should be mixed with the same amount of anise fruits and licorice root, with 1 spoon of sage leaves and 1 spoon of pine buds.
1 spoon of the resulting raw material must be poured with 250 ml of boiling water. After that, the resulting liquid must be poured into a jar, close it with a lid and insist in a dark place for at least 5 days. Ready tincture should be filtered and consumed 5 times a day, 1 spoonful. Positive results will not be long in coming.
Pleurisy can be treated with the following tincture. 1 tablespoon of elecampane root should be mixed with the same amount of licorice root, chopped peppermint leaves and marsh cudweed grass. The resulting mixture must be mixed with 2 tablespoons of crushed coltsfoot leaves. 1 spoon of the resulting mass should be poured with 1 cup of boiling water. Take this remedy should be three times a day for 150 ml.
- This is a disease of the respiratory system, which is characterized by damage to the pleura of an infectious, tumoral or other nature.
The defeat of the pleural cavity is accompanied by the accumulation of an excess amount of exudate (effusion), which leads to a feeling of heaviness in the patient, reflex cough, increasing shortness of breath and fever.
The main treatment of exudative pleurisy is to remove the accumulated fluid from the pleural cavity, as well as to carry out pathogenetic and symptomatic therapy.
Depending on the etiology of the disease, exudative pleurisy is divided into two types: infectious and non-infectious.
Most infectious exudative pleurisy occurs as a result of complications of pathologies of the lungs, nearby organs and tissues, as well as severe systemic ailments.
The infectious form of pleurisy appears against the background of the following processes in the lungs:
lung abscess;
In this case, the cause of the disease is the ingress of infectious irritants from the listed diseases into the pleural cavity.
In addition, microorganisms from the focus of inflammation can circulate through the lymphatic and circulatory systems.
In the case of a disease of tuberculous etiology, an increased reactivity of the body to the effects of a tubercle bacillus is observed, as a result of which the fluid begins to accumulate even with the penetration of a small amount of pathogens.

This type of exudative pleurisy occurs mainly in adult patients.
Causes of aseptic (non-infectious) effusion pleurisy:
Trauma, wound of the chest, as a result of which there was a hemorrhage in the pleural region;
Pulmonary infarction due to pulmonary embolism;
Malignant neoplasms in the pleura and lungs;
Systemic connective tissue diseases (rheumatoid arthritis, collagenosis);
kidney failure;
Diseases of the circulatory and lymphatic systems;
Cirrhosis of the liver (provokes right-sided pleurisy);
Inflammatory process in the pancreas.
Often, exudative pleurisy has a unilateral form, with the exception of metastatic processes, systemic lupus erythematosus and lymphoma, on the basis of which bilateral pleural exudate can develop.
Symptoms of the disease
Symptoms of exudative pleurisy depend on the volume, nature and intensity of fluid accumulation:
Chest pain
At an early stage, when the fluid is just beginning to accumulate, the patient is tormented by increasing pain in the chest. With the development of the disease, the pleural layers begin to separate from each other, which reduces the excitation of the intercostal nerve fibers and relieves pain.
The pain syndrome is replaced by other symptoms: a feeling of heaviness in the affected side of the chest, reflex cough and shortness of breath, which forces the patient to take a position on the affected side.

Cough and shortness of breath
These symptoms depend on the amount of accumulated effusion, impaired ventilation of the diseased lung due to pressure and displacement of the mediastinal organs. Cough at the initial stage is dry, with the progression of the disease becomes wet.
Symptoms of respiratory failure
Characterized by pale or cyanotic skin, the appearance of cyanosis and acrocyanosis. If the fluid has accumulated not only in the pleural region, but also in the mediastinum, there are swelling in the neck and face, swelling of the veins, and a change in voice.

Other signs
Tachycardia, lowering blood pressure.
Convexity of the chest in the area of accumulated exudate.
Auxiliary symptoms: febrile temperature, sweating, drowsiness.
Fever, chills, signs of intoxication, headaches, loss of appetite.
These symptoms can occur with an infectious form of effusion pleurisy.
Pleural empyema. It develops with suppuration of accumulated exudate.
Examination of the chest, as a rule, determines superficial frequent breathing, asymmetry of the chest, lagging behind the diseased side in the process of respiratory movements.

Palpation gives the patient pain, weakened voice sounds are noted on the affected half of the chest.
There are three phases of the course of the disease:
Exudation lasts up to three weeks, during which time up to 10 liters of exudate can accumulate.
Stabilization, with the onset of which the formation of the effusion stops, but the process of its absorption does not yet occur.
Resorption, which is characterized by resorption of exudate. In most debilitated patients, this stage lasts up to two to three weeks.
Diagnosis of the disease
Before prescribing treatment for effusion pleurisy, the doctor conducts a comprehensive diagnosis that establishes the causes of the disease and determines the main pathology.
Percussion of the lungs
Defines dull sounds over the effusion. Topographic percussion notes the displacement of the lower edge of the lungs, as well as a decrease in respiratory mobility.
Auscultation
At an early stage, it marks a place with weak vesicular breathing, as well as noises resulting from friction of the pleura.
It can and determines the main pathology, which has become a focal point for a complex diagnosis of the disease, which, after pleural friction, can be established the presence of leukocytosis, neutrophilia, shift of leukocytes and the formula to the left, as well as increased ESR.

Pleural effusion analysis
Serous fluid is characteristic of tuberculous pleurisy, purulent exudate is formed during lung gangrene with entry into the pleural space.
Fluid of a serous-purulent nature and containing fibrin protein is characteristic of the rheumatoid and tuberculous nature of pleurisy. Microscopic examination reveals the presence of leukocytes, neutrophils, lymphocytes and eosinophils.
Radiography
It reveals the darkening and shift of the organs of the mediastinal system in a healthy direction.
Therapy of the disease
The main treatment of exudative pleurisy is the evacuation of fluid from the pleural space, as well as the impact on the main pathology, which provoked the consequences.
Most often, pleural exudate is observed on the right, but a more severe variant of development is also possible - bilateral exudative pleurisy.
With an excessive volume of effusion, a puncture or drainage of the pleural cavity is performed, allowing the evacuation of fluid, straightening the deformed lung, reducing shortness of breath, lowering body temperature, etc.
Surgical removal of the fluid is performed if the following symptoms are observed:
A large volume of pleural fluid, reaching up to 2 ribs;
The exudate presses on the surrounding organs;
There is a risk of suppuration of the pleura.
Taking into account the cause of pleurisy, medication is prescribed:
Tubersculostatic drugs (with tuberculous form of exudative pleurisy);
Antibacterial agents (with pneumatic pleurisy);
Cytostatic agents (for tumors and metestases);
Glucocorticoid drugs (for lupus erythematosus and rheumatoid arthritis)
Diuretic treatment for pleurisy caused by cirrhosis of the liver (usually affecting the lung located on the right).
Regardless of the etiology of the disease, analgesics, anti-inflammatory, antitussive, desensitizing agents are prescribed.

At the stage when the effusion is resorbed, auxiliary treatment is added to the main therapy:
Halotherapy (oxygen therapy);
Transfusion of plasma-substituting compounds;
Treatment based on chest massage, vibration massage;
Physiotherapeutic treatment, for example, compresses based on paraffin applications (in the absence of contraindications);
Complications against the background of empyema are treated with the introduction of antiseptic drugs and antibiotics into the pleural cavity.
Chronic suppuration of the exudate is eliminated by surgical intervention through thoracostomy, pleurectomy, in which decortication of the lung is carried out.
Exudative pleurisy, provoked by malignant neoplasms, provides for treatment based on chemotherapy, chemical pleurodesis.

Prevention of exudative pleurisy is aimed primarily at the timely diagnosis and proper treatment of pathologies that cause the formation of exudate in the pleural cavity.
Lung diseases, despite the achievements of modern medicine, are still very common. The reason is the deterioration of the environmental situation. Pollution of the atmosphere with waste from hazardous industries, vehicle exhaust gases leads to breathing problems. An important role is played by smoking, bacteria, viruses and malignant tumors. All these heterogeneous harmful factors can lead to a special lung disease - exudative pleurisy.
The role of the lungs in the development of exudative pleurisy
All the work of providing the body with oxygen is carried out by the lungs. For greater reliability, nature has created two identical organs, each of which is able to cope with its duties alone. The lungs consist of two fundamentally different parts - the bronchial and alveolar tree. The bronchi are a system of tubes of different diameters through which air enters the lungs. There is no gas exchange between air and blood in this area. For this purpose, oxygen needs to get into the alveoli. These are small spherical structures that connect with the smallest bronchus into an integral system. The alveoli are densely entangled on all sides with a network of small vessels - pulmonary capillaries. It is here at the border of the alveoli and vascular walls that oxygen enters the systemic circulation.
The lung consists of the bronchial and alveolar treeEach lung contains ten full-fledged segments containing a large bronchus, a network of smaller ones and many alveoli. Gas exchange takes place in each segment. Twenty virtually identical structural units determine the fantastic tensile strength of the entire respiratory system. The failure of even half of the segments will not allow the body to suffer significant losses in oxygen supply. The main protector of the lungs is a frame of twelve pairs of ribs and a strong outer shell - the pleura. It covers the lungs from the outside (visceral pleura) and the chest from the inside (parietal pleura). Between these layers there is a small free space - the pleural cavity. Normally, there is a small amount of fluid present. It helps the lungs to move inside the pleural cavity to ensure inhalation and exhalation.
 Pleural cavity - a small space between the visceral and parietal pleura
Pleural cavity - a small space between the visceral and parietal pleura Exudative - inflammation of the visceral and parietal pleura, which leads to excessive accumulation of fluid. This disease is by no means extremely rare. In the world, one million cases of this disease are registered annually among adults and children. As a rule, pleurisy is not a completely independent diagnosis. In conjunction with it, other pathologies are necessarily present.
 With exudative pleurisy, fluid accumulates in the pleural cavity
With exudative pleurisy, fluid accumulates in the pleural cavity Pleurisy - video
Classification
Exudative pleurisy is a heterogeneous disease. According to a number of signs, several forms of this pathology can be distinguished.
- According to the cause that caused inflammation, the disease is divided into two types:
- infectious pleurisy. The starting point of the disease is the entry of microbes into the pleural cavity;
- aseptic pleurisy. In this case, the cause of inflammation is your own immune system, which aggressively affects the alveoli, bronchi and pleura.
- Microbes that most often cause pleurisy:

- According to the nature of inflammation of the pleura, there are:

- According to the type of course, the forms of the disease are distinguished:
- acute pleurisy is characterized by vivid symptoms and rapid accumulation of fluid;
- chronic pleurisy has a long course, the fluid may periodically disappear under the influence of treatment and then accumulate again.
Causes and development factors
Common to any type of exudative pleurisy is inflammation of the pleura, which consists of connective tissue. The trigger is most often an infection. Microbes appear in the pleural cavity with blood flow or penetrate there directly from the lungs. The body's immune system sends white blood cells to fight infection. They populate the pleura in large numbers and slow down the blood flow in it. Gradually, the liquid part of the blood begins to seep out of the vessels and fill a small slit-like space between the parietal and visceral pleura. Most often, inflammation in this scenario is caused by a tuberculosis bacillus. As a habitat, she chooses areas of the lung that are directly adjacent to the pleura.
 Tuberculosis of the lungs in the later stages is characterized by pleurisy and the formation of cavities (caverns)
Tuberculosis of the lungs in the later stages is characterized by pleurisy and the formation of cavities (caverns) Tuberculosis - video
The lungs are often affected by immune diseases. For some unknown reason, white blood cells tend to the areas of the lung that lie between the bronchi and alveoli. Here there is a special connective tissue, which becomes a target for the aggression of the immune system. Along with these areas, the pleura also suffers - a large array of connective tissue.
 Immune disease often affects the pleura and connective tissue of the lungs
Immune disease often affects the pleura and connective tissue of the lungs Any pathological area in the lung quickly becomes the cause of inflammation of the pleura and accumulation of fluid. In this way, the body tries to stop the spread of the disease. The pathological site can be a focus of inflammation or a malignant tumor from the bronchi and alveoli. The tumor can grow in another organ - the ovary, kidney, stomach. The cause of pleurisy is metastasis - a secondary focus of a malignant neoplasm.
 Metastasis is a secondary focus of malignant tumor growth.
Metastasis is a secondary focus of malignant tumor growth. Lung cancer - video
Symptoms and signs
Exudative pleurisy can be asymptomatic for a long time. The slow accumulation of fluid makes the disease invisible. Signs of pleurisy are often masked by symptoms of the underlying disease.
Symptoms of exudative pleurisy - table
Methods for diagnosing pleurisy
Diagnosis of exudative pleurisy is a task for an experienced specialist. To determine the nature of the disease and the amount of accumulated fluid, a qualitative versatile examination is necessary. An important role is played by laboratory tests and instrumental methods:
- an external examination will help the doctor identify some indirect signs of pleurisy - a change in the shape of the chest, cyanosis of the skin and mucous membranes. Auscultation of the lungs (listening) is a method that has been used since time immemorial. Under normal conditions, with a simple phonendoscope device above the lungs, one can hear a clearly distinguishable noise of the alveoli expanding on inspiration. The fluid in the pleural cavity greatly muffles this sound. This feature is easily captured by a specialist;
- a blood test is a standard diagnostic method that must be performed regardless of the alleged diagnosis. Inflammation changes the composition of the blood in a characteristic way: the number of white blood cells and leukocytes increases (the rate of sedimentation of red blood cells of erythrocytes to the bottom of the test tube);
- the lungs and pleura are the most suitable objects in the body for examination by radiography. Dense ribs and air in the lungs create excellent light contrast. Against this background, inflammatory foci and tumors are well diagnosed. The accumulation of liquid in the picture looks dense and completely obscures other details. The level of fluid in the pleural cavity, due to its anatomical features, does not look horizontal in the picture, but oblique. By the location of this line, you can approximately estimate the amount of fluid in the pleural cavity.
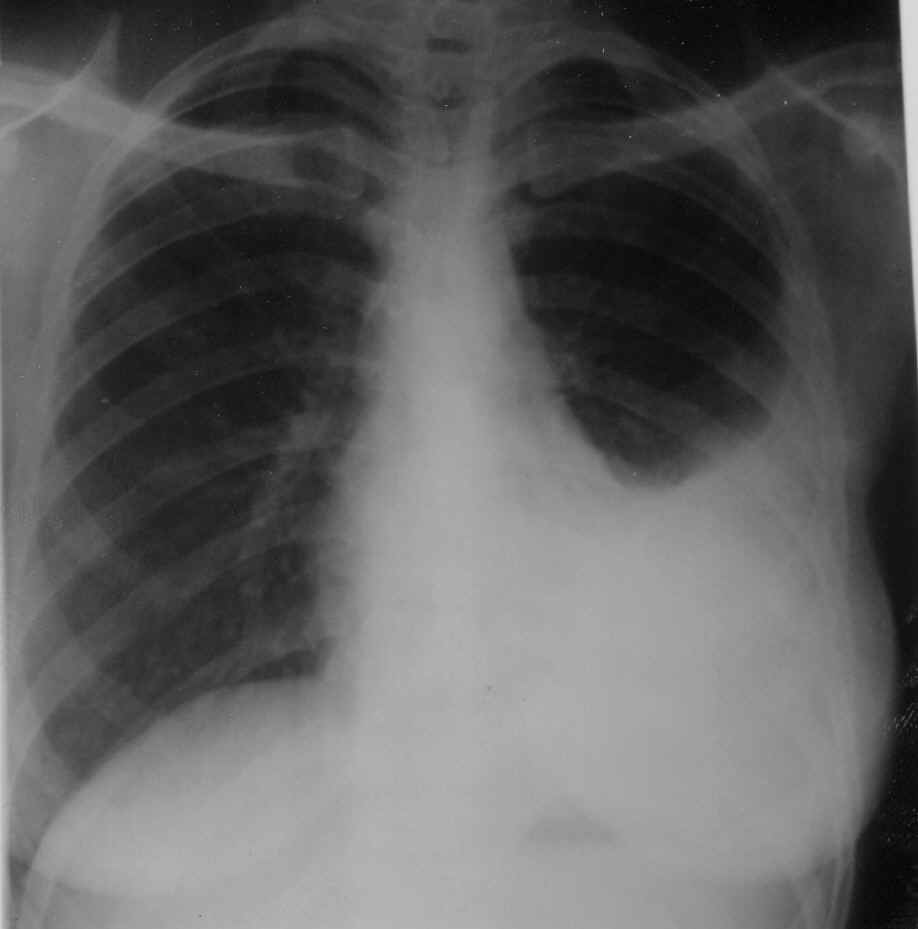 Radiography is the main method for diagnosing exudative pleurisy
Radiography is the main method for diagnosing exudative pleurisy - tomography is a method for a more detailed diagnosis of the anatomy of the lungs. CT uses X-rays to build images, MRI uses nuclear magnetic resonance. Pictures taken at different levels make it possible to identify foci of pneumonia, tumors, and tuberculous changes. In addition, CT and MRI can accurately assess the amount of fluid accumulated in the pleural cavity;
 Tomography - a method of detailed diagnosis of pleurisy
Tomography - a method of detailed diagnosis of pleurisy - to diagnose the nature of pleurisy, a fluid taken with a syringe through a puncture of the chest wall (pleural puncture) is examined. The study of the material is carried out in several ways. The detection of protein and leukocytes proves the inflammatory nature of the fluid. Under a microscope, a specialist will detect microbes and cells of a malignant tumor. To determine a specific type of pathogenic bacterium, the liquid is placed on a nutrient medium and kept at body temperature. Grown bacteria are studied under a microscope and with the help of biochemical analyzes, which makes it possible to establish their specific species;
 Puncture of the pleura - a diagnostic measure for exudative pleurisy
Puncture of the pleura - a diagnostic measure for exudative pleurisy - thoracoscopy is a modern method for diagnosing pulmonary diseases. Through a puncture, a miniature video camera is inserted into the pleural cavity, which allows you to examine the visceral and parietal pleura. During the procedure, a section of the pleura and lung is taken with a special tool. The resulting material after preparation and staining is studied under a microscope. It is histology that often puts an end to the final diagnosis;
 Thoracoscopy - a modern low-traumatic research method
Thoracoscopy - a modern low-traumatic research method - if the infectious nature of pleurisy is suspected, the blood is examined for the presence of specific antibody proteins by enzyme immunoassay and polymerase chain reaction.
Polymerase chain reaction - video
Treatment Methods
Therapy of exudative pleurisy is carried out by an experienced specialist. Establishing an accurate diagnosis and selecting drugs requires hospitalization. After discharge, therapy continues, in some cases for life. Treatment of exudative pleurisy is usually complex, aimed at eliminating the cause of the disease, inflammation of the pleura and accumulated fluid.
Medicines for the treatment of pleurisy
Pleurisy is a reason for prescribing drugs. Currently, there is a large selection of tools that can effectively fight infection, inflammation, malignant tumors, and immune responses.
Preparations for the treatment of pleurisy - table
| Pharmacological group | Examples of drugs | Diseases in which drugs are used |
| Antibiotics |
|
|
| Anti-inflammatory drugs |
|
|
| Steroid hormones |
|
|
| Cytostatics |
|
|
| Diuretics |
| Heart failure |
Preparations for the treatment of exudative pleurisy - photo gallery
 Rifampicin - a drug for the treatment of tuberculosis
Rifampicin - a drug for the treatment of tuberculosis  Clarithromycin is prescribed for nonspecific exudative pleurisy
Clarithromycin is prescribed for nonspecific exudative pleurisy  Meloxicam belongs to the group of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs.
Meloxicam belongs to the group of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs.  Prednisolone has a powerful anti-inflammatory effect
Prednisolone has a powerful anti-inflammatory effect  Methotrexate is an anticancer drug
Methotrexate is an anticancer drug  Lasix is an effective diuretic
Lasix is an effective diuretic
Surgical treatment of exudative pleurisy
In some cases, drug treatment of pleurisy must be combined with surgery. The help of a surgeon is necessary in the following cases:

Physiotherapy
Physiotherapy successfully complements the complex treatment of exudative pleurisy. To eliminate the liquid, the following types of procedures are prescribed:

Diet
With exudative pleurisy, it is recommended to adjust the diet. The increase in protein and vitamins allows the body to cope with the disease faster and increase the overall resistance to infections and other harmful factors. It is advisable to take food in several doses (5-6 times a day). All cooking methods are acceptable. It is recommended to use the following products:
- bread made from wheat and rye flour;
- meat of various varieties;
- sea and river fish;
- dairy and dairy products;
- vegetable and meat soups;
- garnish of rice and buckwheat;
- berry desserts;
- fresh juices;
- cottage cheese and cheese.
 Wheat bread contains B vitamins
Wheat bread contains B vitamins  Meat is a source of protein
Meat is a source of protein  Dairy products contain calcium
Dairy products contain calcium  Vegetable soup is the perfect first course
Vegetable soup is the perfect first course  Freshly squeezed juice contains vitamin C
Freshly squeezed juice contains vitamin C
If possible, the following foods should be excluded from the diet:
- cream confectionery;
- cooking oil;
- fatty varieties of pork and lamb;
- carbonated drinks;
- alcohol;
- strong coffee and tea.
 Confectionery with cream is not recommended.
Confectionery with cream is not recommended.  Fatty meats are not recommended.
Fatty meats are not recommended.  Alcohol affects the lungs
Alcohol affects the lungs  Strong tea contains a lot of caffeine
Strong tea contains a lot of caffeine  Strong coffee causes heart palpitations and high blood pressure
Strong coffee causes heart palpitations and high blood pressure
Exudative pleurisy is a serious disease, so treatment with folk remedies is not recommended.
Complications and prognosis
The prognosis of therapy for exudative pleurisy is extremely individual and depends on the nature of the disease. Pneumonia is treatable with antibiotics. With a successful combination of circumstances, it is possible to nullify the manifestations of tuberculosis. The tumor in the initial stages is amenable to surgical treatment. Chronic diseases cannot be completely eliminated, however, timely treatment allows the disease to be transferred to the stage of inactive manifestations. The most serious complication of exudative pleurisy is respiratory failure.
Prevention
Prevention of pleurisy includes the following measures:

Exudative pleurisy is a serious disease. Finding a definitive diagnosis can take time. Treatment of the disease is often lifelong. However, timely access to a specialist will significantly increase the chances of a favorable outcome.
Exudative or effusion pleurisy is a pathology of the respiratory system, in which a large amount of fluid (exudate) accumulates in the pleural cavity, the symptoms are distinct, the treatment is conservative and surgical (puncture and drainage). Normally, the space between the two layers of the pleura contains only a few milliliters of fluid, which ensures the sliding of the pleura. The fluid is produced and absorbed at a certain rate, but under the influence of pathologies, the production of exudate increases, and its removal from the pleural cavity slows down.
In the vast majority of cases, effusion pleurisy is not an independent disease, but a symptom of another pathology. But occasionally primary pleurisy is also diagnosed.
Classification of exudative pleurisy
Effusion can be classified according to various criteria:
- According to the etiology of the disease: infectious, aseptic.
- According to the course of the pathological process: acute, subacute, chronic.
- According to the composition of the effusion: serous, hemorrhagic, serous-fibrinous, eosinophilic, purulent, putrefactive, cholesterol, chylous, mixed.
- According to the localization of the effusion: free, encysted (limited by adhesions between the pleura).
At the same time, encysted forms can be subdivided depending on where exactly the localization of the accumulation of exudate is located: apical, parietal, diaphragmatic, osteodiaphragmatic, paramediastinal, interlobar.
Also, pleurisy can affect the pleura of both lungs (bilateral) or only one (right-sided, left-sided).
Development mechanism
Normally, between the sheets of the pleura there is no more than 10 ml of fluid, but during effusion, its amount can reach 4 liters, and even exceed this figure.
This is due to the following pathological processes:
- increase in the permeability of the vascular walls;
- increased intravascular pressure;
- reduction of the barrier function of the visceral pleura;
- a decrease in the resolving effusion of the function of the parietal pleura.
As a result, fluid accumulates in the pleural cavity, and its excretion through the capillaries and lymphatic vessels does not occur. Filling the pleural cavity with fluid leads to squeezing of the lungs (or one lung, if the pleurisy is unilateral) and disruption of the respiratory process.
The reasons
The etiology of exudative pleurisy can be different. More often, the cause of the syndrome is the ingestion of infectious agents (bacteria, viruses, fungi) into the pleural cavity. Tuberculosis (up to 80% of all cases), pneumonia, lung abscess can also act as a cause of infectious pleurisy.
Aseptic pleurisy develops against the background of various diseases, both of the lungs and other body systems, which include allergic reactions and autoimmune systemic diseases. There is a category of post-traumatic effusion pleurisy, as well as pneumothorax against the background of oncological tumors.
infectious causes
Infectious exudative pleurisy complicates inflammatory processes:
- pneumonia - microbial inflammation of the respiratory tissue of the lungs;
- abscess - a focus of suppuration of the lung;
- gangrene - infectious destruction of the lung;
- tuberculosis of the lungs.
The cause of infectious exudative pleurisy is the penetration of pathogens of the underlying disease into the pleural cavity. Microbes get there from the focus of decay or inflammation, located close to the outer shell of the organ. Also, the infection can travel through the lymphatic capillaries and blood vessels.
The cause of exudative pleurisy of tuberculous etiology is an avalanche-like increase in the sensitivity of the patient's body to tubercle bacillus (sensitization). The result of sensitization is the rapid accumulation of reactive effusion when even single microbes enter the pleura. Tuberculous exudative pleurisy affects mainly adult patients.
The accumulation of effusion in the chest cavity for non-inflammatory or unknown reasons is termed "hydrothorax" or non-infectious (aseptic) effusion pleurisy.
Non-infectious causes
- chest injury with hemorrhage in the pleural cavity;
- pulmonary infarction due to blockage of the pulmonary artery by a thrombus - a blood clot;
- malignant tumors of the pleura and lungs (carcinomatosis, mesothelioma, cancer);
- chronic circulatory failure;
- chronic renal failure;
- autoimmune connective tissue diseases (rheumatism, collagenoses);
- malignant tumors of the blood;
- cirrhosis of the liver provokes right-sided exudative pleurisy;
- inflammation of the pancreas causes reactive left-sided effusion pleurisy.
Symptoms of exudative pleurisy
The clinical picture of the disease depends on its severity, the type of exudate, the amount of accumulated effusion.
The more common symptoms include:
- shortness of breath
- chest pain;
- inability to take a deep breath;
- cough;
- general weakness, loss of appetite;
- periodically rising temperature.
With purulent effusion, the disease is more severe, with fever and symptoms of intoxication. The clinical picture is also influenced by the fact which lung is affected: left-sided pleural effusion provokes symptoms from the heart muscle, for example, arrhythmia, an increase in heart rate up to 120 beats per minute.
Phases of the development of the disease
Pathology progresses through three stages:
- accumulation of exudate in the pleural cavity;
- stabilization of the state, when the amount of effusion does not increase or decrease;
- resorption of exudate.
Each stage can last up to 3 weeks.
X-ray signs
The radiological symptom of exudative pleurisy is a massive shading of the lung field in the lower sections. In contrast to pneumonic blackout, the x-ray shadow of the pleural effusion has an oblique ascending border.
Diagnostics
Diagnosis begins with an examination of the patient, taking an anamnesis. Among the characteristic signs, one can note the pallor of the skin, shallow breathing, the desire to lie on one side in a certain position, if the pleurisy is one-sided. During the act of breathing, the affected part of the chest lags behind, with percussion (tapping) the sound is dulled, bursts are heard when listening to the lungs with a stethoscope.
After that, the patient is sent for functional and laboratory diagnostics:
- X-rays of light;
- thoracocentesis - taking part of the pleural effusion for research;
- Ultrasound of the pleural cavity;
- CT scan of the lungs;
- thoracoscopy - endoscopic examination of the pleural cavity through a puncture of the chest;
- biochemical and general blood test.
The most accurate and therefore mandatory research methods are X-ray and thoracocentesis.
Treatment of exudative pleurisy
Treatment of exudative pleurisy is carried out in accordance with the underlying disease, usually includes the evacuation of the effusion and the elimination of the cause of the pathology with the help of medications.
Infectious processes complicated by pleural effusion are treated with antibiotics.
With a significant accumulation of fluid in the chest cavity, it is removed through a puncture in the chest wall (and the pleural cavity). The resulting effusion is sent to the laboratory. The results of the tests help to find out the cause of pleurisy and choose the necessary treatment.
A modern way of diagnosing and treating exudative pleurisy is videothoracoscopy. The endoscopic apparatus is inserted into the pleural cavity through a small puncture in the chest wall. The surgeon examines the chest cavity from the inside, takes samples of the effusion and pieces of the pleura for analysis, and performs therapeutic measures.
Pleural puncture
Pleural puncture is a method of removing exudate from the pleural cavity with a puncture. When excess fluid is removed, the lung expands, and the person instantly feels relieved. The procedure is performed under local anesthesia, the effusion is removed slowly, and the resulting fluid is sent to the laboratory for analysis.
Through a needle after drainage of the pleural cavity, drugs can be injected into the pleural cavity: antiseptics, antibiotics, hormonal and antitumor agents, depending on the diagnosis.
Medical therapy
Medications are prescribed depending on the diagnosis:
- in tuberculosis - tuberculostatic drugs;
- with pneumonia - antibiotics;
- in oncology - cytostatics;
- with autoimmune pathologies, allergies - glucocorticoids, etc.
It can also be prescribed funds for symptomatic treatment, to quickly alleviate the patient's well-being: antitussive drugs, analgesics, antispasmodics, diuretics.
Physiotherapy
Physiotherapy helps speed up the healing process, so it is used in conjunction with drug treatment and drainage of the pleural cavity. With effusion, chest massage, electrophoresis, paraffin therapy, and breathing exercises are effective.
Physiotherapy, like other methods of therapy, is prescribed by the attending physician.
Prevention
Prevention of exudative pleurisy is a set of recommendations for a healthy lifestyle and timely access to a doctor:
- to give up smoking;
- climatotherapy with sea air;
- hardening of the body;
- proper treatment of any infections, refusal of self-medication;
- regular fluorography (1 time per year).
If the disease has already been transferred, an x-ray should be performed 6 months after recovery.




